Down syndrome can have babies
Down Syndrome Misconceptions vs. Reality
There are many misconceptions about people with Down syndrome. These misconceptions are largely a result of two contributing factors:
(1) the syndrome itself has changed so fundamentally (for the better) with the dismantling of the inhumane institutions where people with Down syndrome were previously forced to live, and
(2) the lack of medical and basic scientific research makes it difficult to get accurate, updated information about people with Down syndrome.
The Global Down Syndrome Foundation (GLOBAL) is dedicated to correcting misconceptions and over time providing funding for research that will better address medical and cognitive issues associated with the condition.
Misconception: Only older parents have children with Down syndrome.
Reality: According to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention research, about 80% of children who have Down syndrome are born to women younger than 35. The CDC research shows that the chances of having a baby with Down syndrome does increase with age. However, younger women have more babies, so more children with Down syndrome are born to younger mothers.
Misconception: A child with Down syndrome will ruin a marriage.
Reality: A recent Vanderbilt Kennedy Center study published in the American Association of Intellectual Disabilities indicates that divorce rates are lower in families of children with Down syndrome. The study was one of the largest to date and included 647 families who have children with Down syndrome.
Misconception: A child with Down syndrome negatively impacts their siblings.
Reality: Studies do not support that a child with Down syndrome will have a negative impact on siblings. For example, a recent study published in the Journal of Intellectual Disability Research found no long-term detrimental effects to siblings. In fact, some mental health professionals point to the psychological advantages of such a child cared for within the family circle. They have documented siblings who have increased tolerance, compassion and awareness, in contrast to all typical siblings.
They have documented siblings who have increased tolerance, compassion and awareness, in contrast to all typical siblings.
The average life expectancy for a person with Down syndrome is nearly 60 years old. Some people with Down syndrome have lived into their 80s.
Misconception: People who have Down syndrome die young.
Reality: The average life expectancy for a person with Down syndrome is nearly 60 years old. Some people with Down syndrome have lived into their 80s. It is true that people with Down syndrome on average don’t live as long as their typical counterparts. Unfortunately, the average life expectancy for an African-American in the U.S. with Down syndrome is just 35 years old. This appalling statistic deserves the full attention of our government and scientific community.
Misconception: People who have Down syndrome cannot walk or play sports.Reality: An inability to walk is not a characteristic of Down syndrome. However, getting early physical therapy to ensure proper walking is important and builds the foundation for sports aptitude. GLOBAL provides sports opportunities through the “Dare to Play” camps. Individuals with Down syndrome have a variety of athletic abilities and levels of agility, in the same way that typical people do. All over the world, there are sports teams that include people with Down syndrome including through Special Olympics.
However, getting early physical therapy to ensure proper walking is important and builds the foundation for sports aptitude. GLOBAL provides sports opportunities through the “Dare to Play” camps. Individuals with Down syndrome have a variety of athletic abilities and levels of agility, in the same way that typical people do. All over the world, there are sports teams that include people with Down syndrome including through Special Olympics.
Misconception: People with Down syndrome can’t read or write.
Reality: The majority of children with Down syndrome can learn to read and write. Research shows that teaching reading to children with disabilities, including those with Down syndrome, is most effective when teachers are well trained, have high expectations of their students, and students’ progress is formally evaluated. More research is needed to determine how to most effectively teach children with Down syndrome to read and write.
Misconception: People with Down syndrome can’t go to regular public schools.
Reality: It is not only advisable that children with Down syndrome attend their public schools, in the U.S. it is required by law that public schools accept and provide an appropriate education to them. This requirement is outlined in the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). IDEA stipulates that all children with disabilities must have available to them a free, appropriate public education that meets their unique needs and prepares them for further education, employment, and independent living.
Further, studies show that including students with disabilities in the classroom improves the academic progress of students without disabilities.
Misconception: People who have Down syndrome don’t feel pain.
Reality: People with Down syndrome absolutely feel pain. Reaction to pain is not always apparent; for example, a 2000 study published in the medical journal, Lancet, suggests that such individuals express pain more slowly and less precisely than the rest of us. Parents and guardians need to be firm with the medical community and insist that people with Down syndrome be given the same types of pain-control procedures as a typical person, even in the absence of obvious signs of pain.
Parents and guardians need to be firm with the medical community and insist that people with Down syndrome be given the same types of pain-control procedures as a typical person, even in the absence of obvious signs of pain.
Misconception: People with Down syndrome all look alike.
Reality: Many but not all people with Down syndrome share common features. For example, many but not all people with Down syndrome have almond-shaped eyes and a short stature. However, like typical people who share similar features, they look more like their families than each other.
Misconception: All people with Down syndrome are overweight.
Reality: Not all people with Down syndrome are overweight. However, there is a relationship between Down syndrome and obesity, although the actual degree of obesity relative to the typical population needs further study. According to one study of 247 people with Down syndrome published in the Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, women and men with Down syndrome more likely to overweight or obese than compared to the typical population.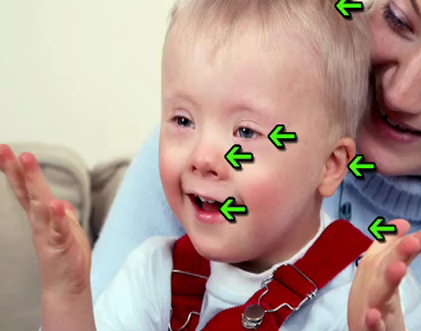
Research suggests that both the thyroid and a lower metabolic rate contribute to people with Down syndrome being overweight. This lower metabolic rate means that children with Down syndrome burn fewer calories overall compared to a typical child and need to need to exercise more to burn off the same number of calories. It is important for everyone to eat right and exercise.
Misconception: All people who have Down syndrome will develop Alzheimer’s disease.
Reality: Numerous studies have shown that virtually 100% of people with Down syndrome will have the plaques and tangles in the brain associated with Alzheimer’s disease (e.g. Zigman et al., 1993, 19, 41-70) but not necessarily the actual symptomatic disease. How many people with Down syndrome will develop the symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease needs additional research. One study from 1989 indicates that between 20-55% of people with Down syndrome will develop symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease before the age of 50 (i.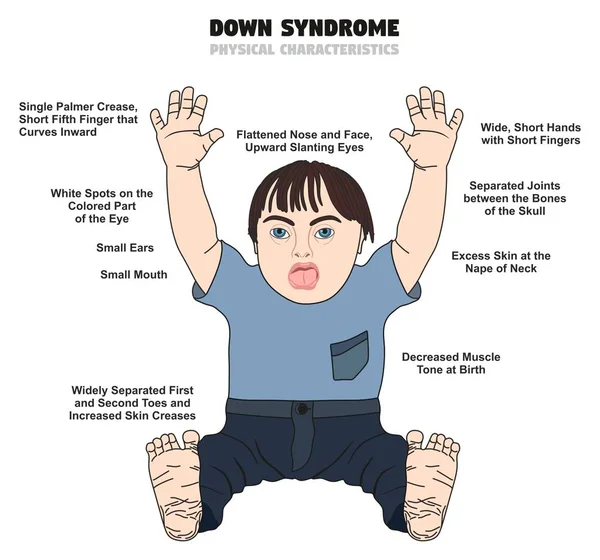 e. Australia and New Zealand Journal of Developmental Disabilities, Haveman et al.,15, 241-255).
e. Australia and New Zealand Journal of Developmental Disabilities, Haveman et al.,15, 241-255).
Clearly, this is an important area of research for people with Down syndrome and Alzheimer’s and the Global Down Syndrome Foundation is committed to ensuring such research happens.
Misconception: People who have Down syndrome cannot have children.
Reality: It’s true that a person with Down syndrome may have significant challenges in rearing a child. But women who have Down syndrome are fertile and can give birth to children. According to older studies, that are being reinvestigated, men with Down syndrome are infertile. However, it is important to note, there have been a handful of documented instances (see American Society of Reproductive Medicine and Journal of Medical Genetics) of men with Down syndrome who have fathered children.
An increasing number of adults with Down syndrome in the U.S. are living independently with limited assistance from family members or the state.
 A small percentage are able to live entirely independently.
A small percentage are able to live entirely independently.Misconception: Adults who have Down syndrome cannot live independently or get jobs.
Reality: An increasing number of adults with Down syndrome in the U.S. are living independently with limited assistance from family members or the state. A small percentage are able to live entirely independently. In the U.S. some students who have Down syndrome graduate from high school, and some go on to attend post-secondary education.
More opportunities are available for education and employment today than ever before. Anecdotally, we know that people with Down syndrome can be excellent employees and some employers have reported a higher satisfaction level among ALL workers when they have co-workers who have Down syndrome.
Misconception: People who have Down syndrome are always happy.
Reality: People with Down syndrome are more like typical people than they are different. Everyone has feelings and moods. One recent literature review of previous studies found that people with Down syndrome are at a higher risk for depression. And there is evidence that it is under-treated. Just as in the typical population, it is important that adults with Down syndrome have educational, work and social opportunities, as well as adaptive life-skills.
One recent literature review of previous studies found that people with Down syndrome are at a higher risk for depression. And there is evidence that it is under-treated. Just as in the typical population, it is important that adults with Down syndrome have educational, work and social opportunities, as well as adaptive life-skills.
Misconception: People who have Down syndrome have no memory.
Reality: As any related parent or professional will attest, people with Down syndrome absolutely have memory, and like typical individuals, their ability to remember varies from person to person.
Misconception: Babies who have Down syndrome are a result of incest.
Reality: There is absolutely no relationship between incest and Down syndrome.
Facts about Down Syndrome | CDC
Down syndrome is a condition in which a person has an extra chromosome.
What is Down Syndrome?
Down syndrome is a condition in which a person has an extra chromosome. Chromosomes are small “packages” of genes in the body. They determine how a baby’s body forms and functions as it grows during pregnancy and after birth. Typically, a baby is born with 46 chromosomes. Babies with Down syndrome have an extra copy of one of these chromosomes, chromosome 21. A medical term for having an extra copy of a chromosome is ‘trisomy.’ Down syndrome is also referred to as Trisomy 21. This extra copy changes how the baby’s body and brain develop, which can cause both mental and physical challenges for the baby.
Chromosomes are small “packages” of genes in the body. They determine how a baby’s body forms and functions as it grows during pregnancy and after birth. Typically, a baby is born with 46 chromosomes. Babies with Down syndrome have an extra copy of one of these chromosomes, chromosome 21. A medical term for having an extra copy of a chromosome is ‘trisomy.’ Down syndrome is also referred to as Trisomy 21. This extra copy changes how the baby’s body and brain develop, which can cause both mental and physical challenges for the baby.
Even though people with Down syndrome might act and look similar, each person has different abilities. People with Down syndrome usually have an IQ (a measure of intelligence) in the mildly-to-moderately low range and are slower to speak than other children.
Some common physical features of Down syndrome include:
- A flattened face, especially the bridge of the nose
- Almond-shaped eyes that slant up
- A short neck
- Small ears
- A tongue that tends to stick out of the mouth
- Tiny white spots on the iris (colored part) of the eye
- Small hands and feet
- A single line across the palm of the hand (palmar crease)
- Small pinky fingers that sometimes curve toward the thumb
- Poor muscle tone or loose joints
- Shorter in height as children and adults
How Many Babies are Born with Down Syndrome?
Down syndrome remains the most common chromosomal condition diagnosed in the United States. Each year, about 6,000 babies born in the United States have Down syndrome. This means that Down syndrome occurs in about 1 in every 700 babies.1
Each year, about 6,000 babies born in the United States have Down syndrome. This means that Down syndrome occurs in about 1 in every 700 babies.1
Types of Down Syndrome
There are three types of Down syndrome. People often can’t tell the difference between each type without looking at the chromosomes because the physical features and behaviors are similar.
- Trisomy 21: About 95% of people with Down syndrome have Trisomy 21.2 With this type of Down syndrome, each cell in the body has 3 separate copies of chromosome 21 instead of the usual 2 copies.
- Translocation Down syndrome: This type accounts for a small percentage of people with Down syndrome (about 3%).2 This occurs when an extra part or a whole extra chromosome 21 is present, but it is attached or “trans-located” to a different chromosome rather than being a separate chromosome 21.
- Mosaic Down syndrome: This type affects about 2% of the people with Down syndrome.
 2 Mosaic means mixture or combination. For children with mosaic Down syndrome, some of their cells have 3 copies of chromosome 21, but other cells have the typical two copies of chromosome 21. Children with mosaic Down syndrome may have the same features as other children with Down syndrome. However, they may have fewer features of the condition due to the presence of some (or many) cells with a typical number of chromosomes.
2 Mosaic means mixture or combination. For children with mosaic Down syndrome, some of their cells have 3 copies of chromosome 21, but other cells have the typical two copies of chromosome 21. Children with mosaic Down syndrome may have the same features as other children with Down syndrome. However, they may have fewer features of the condition due to the presence of some (or many) cells with a typical number of chromosomes.
Causes and Risk Factors
- The extra chromosome 21 leads to the physical features and developmental challenges that can occur among people with Down syndrome. Researchers know that Down syndrome is caused by an extra chromosome, but no one knows for sure why Down syndrome occurs or how many different factors play a role.
- One factor that increases the risk for having a baby with Down syndrome is the mother’s age. Women who are 35 years or older when they become pregnant are more likely to have a pregnancy affected by Down syndrome than women who become pregnant at a younger age.
 3-5However, the majority of babies with Down syndrome are born to mothers less than 35 years old, because there are many more births among younger women.6,7
3-5However, the majority of babies with Down syndrome are born to mothers less than 35 years old, because there are many more births among younger women.6,7
Diagnosis
There are two basic types of tests available to detect Down syndrome during pregnancy: screening tests and diagnostic tests. A screening test can tell a woman and her healthcare provider whether her pregnancy has a lower or higher chance of having Down syndrome. Screening tests do not provide an absolute diagnosis, but they are safer for the mother and the developing baby. Diagnostic tests can typically detect whether or not a baby will have Down syndrome, but they can be more risky for the mother and developing baby. Neither screening nor diagnostic tests can predict the full impact of Down syndrome on a baby; no one can predict this.
Screening Tests
Screening tests often include a combination of a blood test, which measures the amount of various substances in the mother’s blood (e. g., MS-AFP, Triple Screen, Quad-screen), and an ultrasound, which creates a picture of the baby. During an ultrasound, one of the things the technician looks at is the fluid behind the baby’s neck. Extra fluid in this region could indicate a genetic problem. These screening tests can help determine the baby’s risk of Down syndrome. Rarely, screening tests can give an abnormal result even when there is nothing wrong with the baby. Sometimes, the test results are normal and yet they miss a problem that does exist.
g., MS-AFP, Triple Screen, Quad-screen), and an ultrasound, which creates a picture of the baby. During an ultrasound, one of the things the technician looks at is the fluid behind the baby’s neck. Extra fluid in this region could indicate a genetic problem. These screening tests can help determine the baby’s risk of Down syndrome. Rarely, screening tests can give an abnormal result even when there is nothing wrong with the baby. Sometimes, the test results are normal and yet they miss a problem that does exist.
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnostic tests are usually performed after a positive screening test in order to confirm a Down syndrome diagnosis. Types of diagnostic tests include:
- Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)—examines material from the placenta
- Amniocentesis—examines the amniotic fluid (the fluid from the sac surrounding the baby)
- Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PUBS)—examines blood from the umbilical cord
These tests look for changes in the chromosomes that would indicate a Down syndrome diagnosis.
Other Health Problems
Many people with Down syndrome have the common facial features and no other major birth defects. However, some people with Down syndrome might have one or more major birth defects or other medical problems. Some of the more common health problems among children with Down syndrome are listed below.8
- Hearing loss
- Obstructive sleep apnea, which is a condition where the person’s breathing temporarily stops while asleep
- Ear infections
- Eye diseases
- Heart defects present at birth
Health care providers routinely monitor children with Down syndrome for these conditions.
Treatments
Down syndrome is a lifelong condition. Services early in life will often help babies and children with Down syndrome to improve their physical and intellectual abilities. Most of these services focus on helping children with Down syndrome develop to their full potential. These services include speech, occupational, and physical therapy, and they are typically offered through early intervention programs in each state. Children with Down syndrome may also need extra help or attention in school, although many children are included in regular classes.
Children with Down syndrome may also need extra help or attention in school, although many children are included in regular classes.
Other Resources
The views of these organizations are their own and do not reflect the official position of CDC.
- Down Syndrome Research Foundation (DSRF)external icon
DSRF initiates research studies to better understand the learning styles of those with Down syndrome. - Global Down Syndrome Foundationexternal icon
This foundation is dedicated to significantly improving the lives of people with Down syndrome through research, medical care, education and advocacy. - National Association for Down Syndromeexternal icon
The National Association for Down Syndrome supports all persons with Down syndrome in achieving their full potential. They seek to help families, educate the public, address social issues and challenges, and facilitate active participation. - National Down Syndrome Society (NDSS)external icon
NDSS seeks to increase awareness and acceptance of those with Down syndrome.
References
- Mai CT, Isenburg JL, Canfield MA, Meyer RE, Correa A, Alverson CJ, Lupo PJ, Riehle‐Colarusso T, Cho SJ, Aggarwal D, Kirby RS. National population‐based estimates for major birth defects, 2010–2014. Birth Defects Research. 2019; 111(18): 1420-1435.
- Shin M, Siffel C, Correa A. Survival of children with mosaic Down syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2010;152A:800-1.
- Allen EG, Freeman SB, Druschel C, et al. Maternal age and risk for trisomy 21 assessed by the origin of chromosome nondisjunction: a report from the Atlanta and National Down Syndrome Projects. Hum Genet. 2009 Feb;125(1):41-52.
- Ghosh S, Feingold E, Dey SK. Etiology of Down syndrome: Evidence for consistent association among altered meiotic recombination, nondisjunction, and maternal age across populations. Am J Med Genet A. 2009 Jul;149A(7):1415-20.
- Sherman SL, Allen EG, Bean LH, Freeman SB. Epidemiology of Down syndrome. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev.
 2007;13(3):221-7.
2007;13(3):221-7. - Adams MM, Erickson JD, Layde PM, Oakley GP. Down’s syndrome. Recent trends in the United States. JAMA. 1981 Aug 14;246(7):758-60.
- Olsen CL, Cross PK, Gensburg LJ, Hughes JP. The effects of prenatal diagnosis, population ageing, and changing fertility rates on the live birth prevalence of Down syndrome in New York State, 1983-1992. Prenat Diagn. 1996 Nov;16(11):991-1002.
- Bull MJ, the Committee on Genetics. Health supervision for children with Down syndrome. Pediatrics. 2011;128:393-406.
myths and facts – nakedheart.online
in the photo Nika Kirillova
Texts
Tatyana Morozova
clinical psychologistSvyatoslav Dovbnya
pediatric neurologist21 prevention March 2020
9000 in one in 700 children, it is one of the most common and well-studied chromosomal disorders. The Naked Heart Foundation has prepared a material about the main myths around Down syndrome, which it is high time to debunk. Access to verified, up-to-date information helps fight prejudices and overcome unfounded fears, contributing to the formation of an inclusive society.
Access to verified, up-to-date information helps fight prejudices and overcome unfounded fears, contributing to the formation of an inclusive society. Myth 1. Children with Down syndrome are born to parents who lead an unhealthy lifestyle, for example, abuse alcohol and drugs
A child with Down syndrome can be born in any family. The exact cause of this disorder is unknown. Numerous studies conducted to date find no relationship between the birth of a child with Down syndrome and exposure to external factors, such as maternal abuse during pregnancy or the socioeconomic status of the family. Research also refutes early misconceptions about the impact of incest.
It is absolutely known and proven that the probability of having a child with Down syndrome is slightly increased in mothers over 35 years old, especially if this is the first pregnancy. However, almost 80% of children with Down syndrome are born to mothers younger than this age, because young women give birth more often.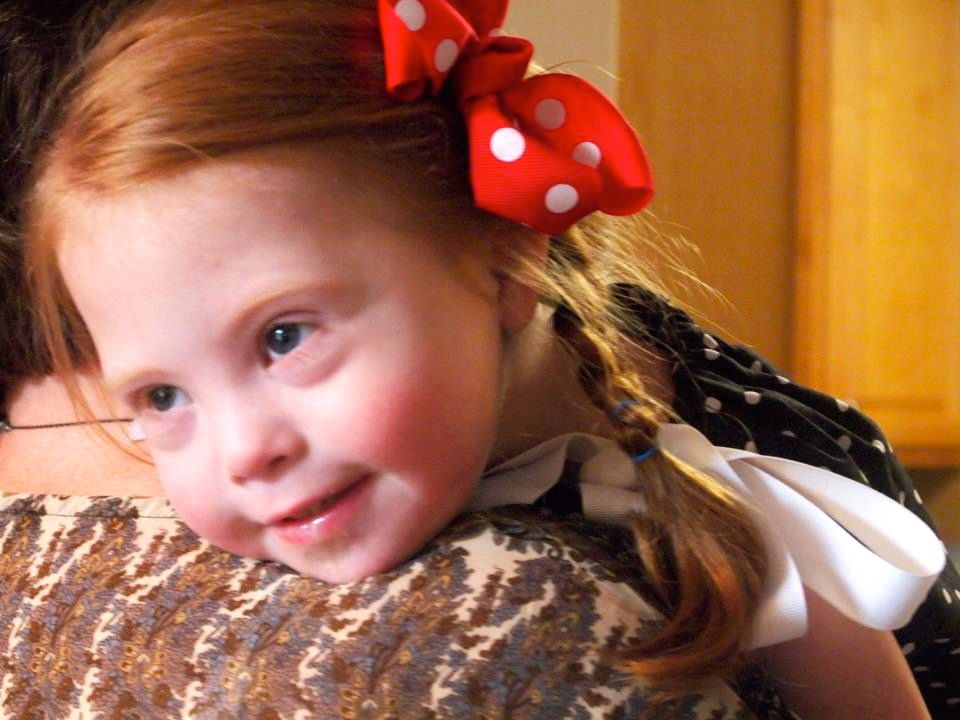
Mai C.T., Isenburg J.L., Canfield M.A., Meyer R.E., Correa A., Alverson C.J., Lupo P.J., Riehle-Colarusso T., Cho S.J., Aggarwal D., Kirby R.S. National population-based estimates for major birth defects, 2010–2014. Birth Defects Research. 2019; 111(18): 1420 – 1435.
Sherman S.L., Allen E.G., Bean L.H., Freeman S.B. Epidemiology of Down Syndrome. MentRetardDevDisabilResRev. 2007;13(3):221 – 7.
The state of the body resulting from the prolonged absence of one or another reinforcement; a procedure for increasing the effectiveness of reinforcement (for example, stopping access to reinforcement for some time before the study). The opposite of saturation.
The degree of satisfaction of the material, social and spiritual needs of a person. The quality of life is influenced by many factors: self-care skills, health status, the ability to communicate, study, work, spend leisure time, the level of independence and independence from caregivers, etc.
From lat. communicato - "message", "transmission"; communico - "I make common, I connect." This is the exchange of signs, messages and information between two or more individuals.
Early intervention is a system of care for young children with or at risk of developmental disabilities and their families. In the Russian Federation, the synonym "early assistance" is also common. In the RR program, an interdisciplinary team of specialists helps the family create optimal conditions for the development of the child, supports parents or other adults raising the child, helps them overcome difficulties in raising a child with special needs. With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
A form of communication through language constructs. This is the main way of self-expression and interaction between people.
Ability to manage your relationships with other people. They allow you to communicate competently, affect the quality of communication and the effectiveness of contact with others, and help control emotions and behavior. These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
A group of methods used to convey messages to people with no or severe limitations in spoken language. The ADC is based on the idea that sign activity, which manifests itself in the process of communication, is diverse, that is, information can be transmitted and received through various channels of human perception.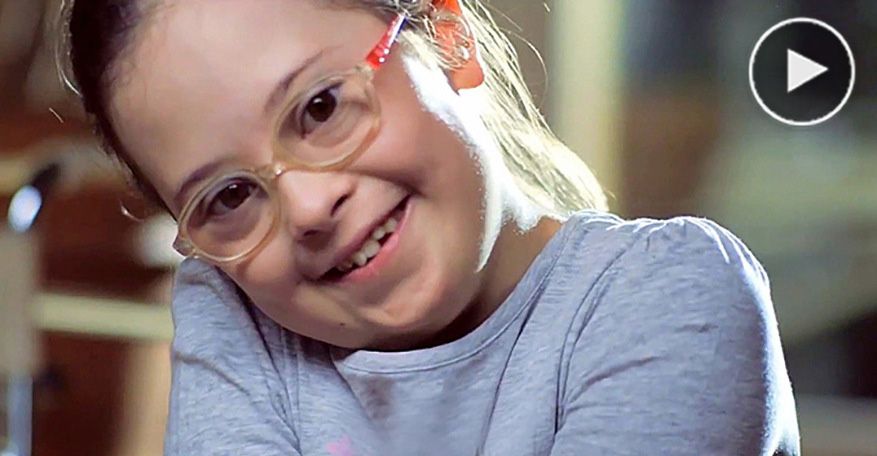
pattern - "sample", "template", "system". This is a set of stereotypical behavioral responses or sequences of actions.
Myth 2. Down's disease needs to be treated
In the modern world, it is customary to talk about a syndrome, not a disease. Down syndrome is a congenital and incurable chromosomal disorder (people with this syndrome have an extra copy - trisomy - of the 21st chromosome). Down's disease is an obsolete name for this condition that has been out of use for a long time.
Although there is no cure, early intervention programs, alternative and complementary communication technologies, and inclusive education can significantly improve the quality of life of people with this developmental disability.
The state of the body resulting from a prolonged absence of one or another reinforcement; a procedure for increasing the effectiveness of reinforcement (for example, stopping access to reinforcement for some time before the study). The opposite of saturation.
Degree of satisfaction of the material, social and spiritual needs of a person. The quality of life is influenced by many factors: self-care skills, health status, the ability to communicate, study, work, spend leisure time, the level of independence and independence from caregivers, etc.
From lat. communicato - "message", "transmission"; communico - "I make common, I connect." This is the exchange of signs, messages and information between two or more individuals.
Early intervention is a system of care for young children with or at risk of developmental disabilities and their families. In the Russian Federation, the synonym "early assistance" is also common. In the RR program, an interdisciplinary team of specialists helps the family create optimal conditions for the development of the child, supports parents or other adults raising the child, helps them overcome difficulties in raising a child with special needs. With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
A form of communication through language constructs. This is the main way of self-expression and interaction between people.
Ability to manage your relationships with other people. They allow you to communicate competently, affect the quality of communication and the effectiveness of contact with others, and help control emotions and behavior. These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
A group of methods used to convey messages to people with no or severe limitations in spoken language. The ADC is based on the idea that sign activity, which manifests itself in the process of communication, is diverse, that is, information can be transmitted and received through various channels of human perception.
pattern - "sample", "template", "system". This is a set of stereotypical behavioral responses or sequences of actions.
Myth 3. People with Down syndrome are always "sunny", cheerful and sociable, they like to sing and dance
People with Down syndrome are very different. Some like to sing, others like to draw, someone is attracted to cars, and someone is attracted to nature. Communication and social life are important for all people, people with Down syndrome are no exception. They have all the same emotions as the rest. They, like everyone else, are not only happy, but also sad, offended and upset. Sometimes people with disabilities, including people with Down syndrome, are even more vulnerable and less protected. For example, studies show that depression occurs in adolescents with Down syndrome even more often than in their peers.
They have all the same emotions as the rest. They, like everyone else, are not only happy, but also sad, offended and upset. Sometimes people with disabilities, including people with Down syndrome, are even more vulnerable and less protected. For example, studies show that depression occurs in adolescents with Down syndrome even more often than in their peers.
Here on you can hear a Canadian woman with Down Syndrome talk about whether she is always happy.
Dykens E.M., Shah B., Davis B. et al. Psychiatric disorders in adolescents and young adults with Down syndrome and other intellectual disabilities. J Neurodevelop Disord 7, 9 (2015).
The state of the body resulting from a prolonged absence of one or another reinforcement; a procedure for increasing the effectiveness of reinforcement (for example, stopping access to reinforcement for some time before the study). The opposite of saturation.
Degree of satisfaction of material, social and spiritual needs of a person. The quality of life is influenced by many factors: self-care skills, health status, the ability to communicate, study, work, spend leisure time, the level of independence and independence from caregivers, etc.
The quality of life is influenced by many factors: self-care skills, health status, the ability to communicate, study, work, spend leisure time, the level of independence and independence from caregivers, etc.
From lat. communicato - "message", "transmission"; communico - "I make common, I connect." This is the exchange of signs, messages and information between two or more individuals.
Early intervention is a system of care for young children with or at risk of developmental disabilities and their families. In the Russian Federation, the synonym "early assistance" is also common. In the RR program, an interdisciplinary team of specialists helps the family create optimal conditions for the development of the child, supports parents or other adults raising the child, helps them overcome difficulties in raising a child with special needs. With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
A form of communication through language constructs. This is the main way of self-expression and interaction between people.
Ability to manage your relationships with other people. They allow you to communicate competently, affect the quality of communication and the effectiveness of contact with others, and help control emotions and behavior. These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
A group of methods used to convey messages to people with no or severe limitations in spoken language. The ADC is based on the idea that sign activity, which manifests itself in the process of communication, is diverse, that is, information can be transmitted and received through various channels of human perception.
The ADC is based on the idea that sign activity, which manifests itself in the process of communication, is diverse, that is, information can be transmitted and received through various channels of human perception.
pattern - "sample", "template", "system". This is a set of stereotypical behavioral responses or sequences of actions.
Myth 4: People with Down syndrome have a very short life expectancy
This is not true. As for all of us, the life expectancy of a person with Down syndrome depends largely on the quality of life and medical care. These components of life have changed dramatically in most countries over the past decades, and the life expectancy of people has changed, especially for those for whom medical support is critical, which also applies to people with Down syndrome.
For example, according to the CDC, in the United States in the 1960s, the average life expectancy for a person with Down syndrome was 10 years, and now it is over 60 years.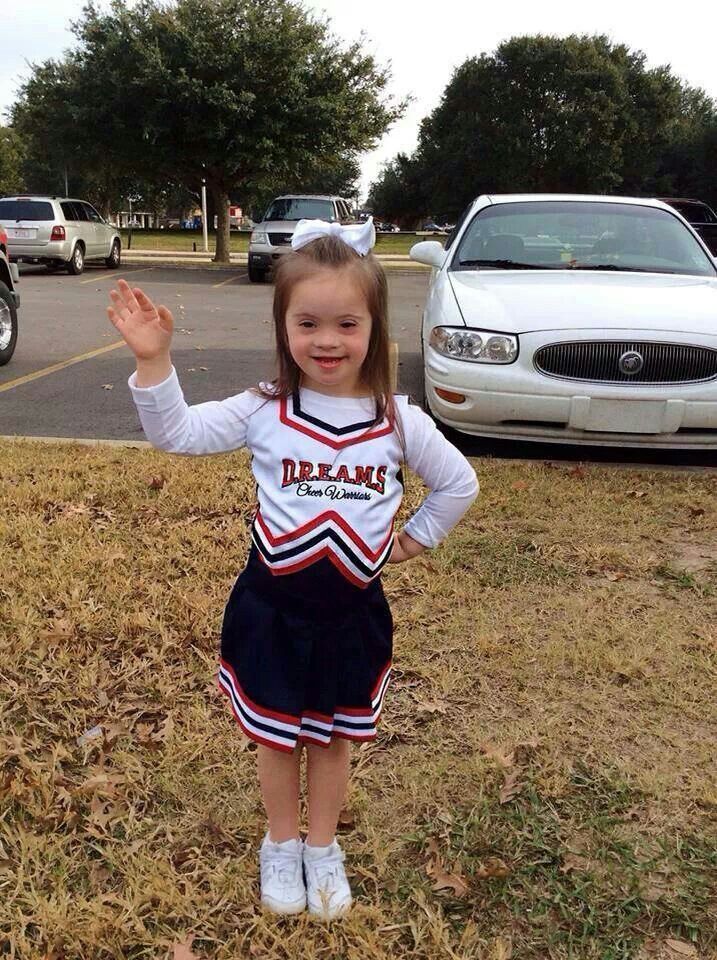
The same trend of a significant increase in life expectancy is observed throughout the rest of the world, however, according to Downside Up experts, reliable Russian statistics do not yet exist.
The life expectancy of a person with Down syndrome largely depends not only on the availability of medical care, but also on where he lives - in a family or in a closed institution (boarding school). Before start 9In the 0s of the last century in the USSR, most children with Down syndrome were taken to children's homes immediately after birth. Living in such institutions for children with Down syndrome is a disaster. Their quality of life there is very low due to deprivation and inadequate care.
In addition, children with Down's syndrome were often considered unpromising and did not receive the necessary medical care (for example, they were denied cardiac surgery for congenital heart defects). This led to the fact that many of them simply did not have a chance to survive. Suffice it to recall foreign statistics 1960s and denial of treatment during the Soviet era: then children with Down syndrome simply died due to lack of help and the hardships of life in boarding schools - hence the myth that people with this disorder do not live long.
Suffice it to recall foreign statistics 1960s and denial of treatment during the Soviet era: then children with Down syndrome simply died due to lack of help and the hardships of life in boarding schools - hence the myth that people with this disorder do not live long.
Since the mid-1990s, work has begun in Russia aimed at supporting families and preventing the placement of children with Down syndrome in orphanages and neuropsychiatric boarding schools, which is still ongoing. The first support programs for families who raised a child at home appeared.
There have been major changes in legislation. There are no more "diagnoses" like "unteachable" or "unpromising". It is impossible to imagine that a person with developmental disabilities can be officially denied medical care, not having a child undergo a cardiac operation, or not taking a child to kindergarten and school, etc. New effective services for children with Down syndrome and their families began to develop. Such programs help these children to develop and learn new things better, improve the quality of life of the children themselves and their families, and help young people learn the skills of supported employment. All this helps a person with Down syndrome to live a long and fulfilling life.
All this helps a person with Down syndrome to live a long and fulfilling life.
Elizabeth Head, Wayne P. Silverman, David Patterson, Ira T. Lott. Aging and Down Syndrome, - Current Gerontology and Geriatrics Research. 2012
Tsao R., Kindelberger C., Fréminville B., Touraine R., Gerald Bussy. Am. Variability of the aging process in dementia-free adults with Down syndrome. Journal Intellect Dev Disabil. Jan 2015; 120(1):3 – 15.
The life cycle of a person with Down syndrome in the 21st century: the connection between science and practice
The state of the body resulting from a prolonged absence of one or another reinforcement; a procedure for increasing the effectiveness of reinforcement (for example, stopping access to reinforcement for some time before the study). The opposite of saturation.
Degree of satisfaction of the material, social and spiritual needs of a person. The quality of life is influenced by many factors: self-care skills, health status, the ability to communicate, study, work, spend leisure time, the level of independence and independence from caregivers, etc.
From lat. communicato - "message", "transmission"; communico - "I make common, I connect." This is the exchange of signs, messages and information between two or more individuals.
Early intervention is a system of care for young children with or at risk of developmental disabilities and their families. In the Russian Federation, the synonym "early assistance" is also common. In the RR program, an interdisciplinary team of specialists helps the family create optimal conditions for the development of the child, supports parents or other adults raising the child, helps them overcome difficulties in raising a child with special needs. With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
A form of communication through language constructs. This is the main way of self-expression and interaction between people.
Ability to manage your relationships with other people. They allow you to communicate competently, affect the quality of communication and the effectiveness of contact with others, and help control emotions and behavior. These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
A group of methods used to convey messages to people with no or severe limitations in spoken language. The ADC is based on the idea that sign activity, which manifests itself in the process of communication, is diverse, that is, information can be transmitted and received through various channels of human perception.
pattern - "sample", "template", "system". This is a set of stereotypical behavioral responses or sequences of actions.
Myth 5. A child with Down syndrome is always a burden on the family
There are many happy families raising children with Down syndrome. For them, this is primarily a beloved child. Interestingly, the divorce rate in families raising a child with Down syndrome is even lower than the average for the population.
Society creates many difficulties for families if it is not ready to accept people with disabilities and provide services that meet their needs.
There are no medicines in the world that improve the development of a child, but this does not mean that a child with Down syndrome cannot be helped. There are successful methods of teaching new skills and support programs for families with proven effectiveness.
Urbano, Richard & Hodapp, Robert. (2007). Divorce in Families of Children With Down Syndrome: A Population-Based Study. American journal of mental retardation : AJMR. 112. 261-74. 10.1352/0895-8017(2007)112[261:DIFOCW]2.0.CO;2.
American journal of mental retardation : AJMR. 112. 261-74. 10.1352/0895-8017(2007)112[261:DIFOCW]2.0.CO;2.
Mohammed Nawi A, Ismail A, Abdullah S. The Impact on Family among Down syndrome Children with Early Intervention. IranJPublicHealth. 2013Sep;42(9):996-1006. PMID: 26060660; PMCID: PMC4453896
The state of the body resulting from the prolonged absence of a particular reinforcement; a procedure for increasing the effectiveness of reinforcement (for example, stopping access to reinforcement for some time before the study). The opposite of saturation.
The degree of satisfaction of the material, social and spiritual needs of a person. The quality of life is influenced by many factors: self-care skills, health status, the ability to communicate, study, work, spend leisure time, the level of independence and independence from caregivers, etc.
From lat. communicato - "message", "transmission"; communico - "I make common, I connect. " This is the exchange of signs, messages and information between two or more individuals.
" This is the exchange of signs, messages and information between two or more individuals.
Early intervention is a system of care for young children with or at risk of developmental disabilities and their families. In the Russian Federation, the synonym "early assistance" is also common. In the RR program, an interdisciplinary team of specialists helps the family create optimal conditions for the development of the child, supports parents or other adults raising the child, helps them overcome difficulties in raising a child with special needs. With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
A form of communication through language constructs. This is the main way of self-expression and interaction between people.
Ability to manage your relationships with other people. They allow you to communicate competently, affect the quality of communication and the effectiveness of contact with others, and help control emotions and behavior. These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
A group of methods used to convey messages to people with no or severe limitations in spoken language. The ADC is based on the idea that sign activity, which manifests itself in the process of communication, is diverse, that is, information can be transmitted and received through various channels of human perception.
pattern - "sample", "template", "system". This is a set of stereotypical behavioral responses or sequences of actions.
Myth 6. A child with Down syndrome is unlikely to become a productive member of society
It must be understood that knowledge about Down syndrome has changed dramatically over the past decades, high-quality research and new proven knowledge have appeared. This condition is no longer considered a disease throughout the civilized world, and many people with Down syndrome can live independently and participate fully in society. So, according to the Global Down Syndrome Foundation, with adequate support and the opportunity to live in a family, the life expectancy of a person with the syndrome increases, as does his average IQ. More and more people with Down syndrome are graduating from high school, some are studying at universities, many are getting jobs, starting families, and so on.
The opportunity to have friends, communicate and learn new things, make choices and do things you love increases self-esteem and the chances of success in anyone's life. People with Down syndrome are no exception.
People with Down syndrome are no exception.
The state of the body resulting from the prolonged absence of one or another reinforcement; a procedure for increasing the effectiveness of reinforcement (for example, stopping access to reinforcement for some time before the study). The opposite of saturation.
The degree of satisfaction of the material, social and spiritual needs of a person. The quality of life is influenced by many factors: self-care skills, health status, the ability to communicate, study, work, spend leisure time, the level of independence and independence from caregivers, etc.
From lat. communicato - "message", "transmission"; communico - "I make common, I connect." This is the exchange of signs, messages and information between two or more individuals.
Early intervention is a system of care for young children with or at risk of developmental disabilities and their families. In the Russian Federation, the synonym "early assistance" is also common. In the RR program, an interdisciplinary team of specialists helps the family create optimal conditions for the development of the child, supports parents or other adults raising the child, helps them overcome difficulties in raising a child with special needs. With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
In the Russian Federation, the synonym "early assistance" is also common. In the RR program, an interdisciplinary team of specialists helps the family create optimal conditions for the development of the child, supports parents or other adults raising the child, helps them overcome difficulties in raising a child with special needs. With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
A form of communication through language constructs. This is the main way of self-expression and interaction between people.
This is the main way of self-expression and interaction between people.
Ability to manage your relationships with other people. They allow you to communicate competently, affect the quality of communication and the effectiveness of contact with others, and help control emotions and behavior. These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
A group of methods used to convey messages to people with no or severe limitations in spoken language. The ADC is based on the idea that sign activity, which manifests itself in the process of communication, is diverse, that is, information can be transmitted and received through various channels of human perception.
pattern - "sample", "template", "system". This is a set of stereotypical behavioral responses or sequences of actions.
Myth 7.
 If a child with Down syndrome does not use speech, it means that he does not understand what others are saying. Features of the structure of the speech apparatus and muscle tone can impede the development of speech. In order for a person with Down syndrome, who does not yet use speech, to express his desires, comment, ask questions and express his opinion, it is customary to use methods of alternative or additional communication (ADC). Such methods include pictures, gestures, special programs for communication on a tablet, etc. This improves opportunities for communication and accelerates the development of speech.
If a child with Down syndrome does not use speech, it means that he does not understand what others are saying. Features of the structure of the speech apparatus and muscle tone can impede the development of speech. In order for a person with Down syndrome, who does not yet use speech, to express his desires, comment, ask questions and express his opinion, it is customary to use methods of alternative or additional communication (ADC). Such methods include pictures, gestures, special programs for communication on a tablet, etc. This improves opportunities for communication and accelerates the development of speech. Barbosa RTA, de Oliveira ASB, de Lima Antão JYF, et al. Augmentative and alternative communication in children with Down's syndrome: a systematic review. BMCpediatr. 2018;18(1):160. Published2018 May11. doi:10.1186/s12887-018-1144-5
The state of the body resulting from the prolonged absence of one or another reinforcement; a procedure for increasing the effectiveness of reinforcement (for example, stopping access to reinforcement for some time before the study).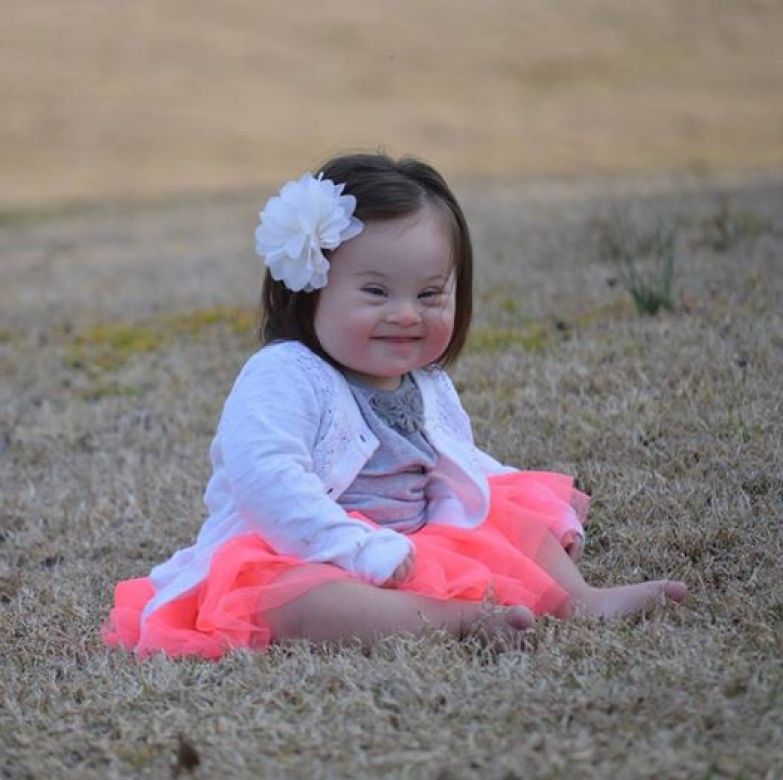 The opposite of saturation.
The opposite of saturation.
Degree of satisfaction of material, social and spiritual needs of a person. The quality of life is influenced by many factors: self-care skills, health status, the ability to communicate, study, work, spend leisure time, the level of independence and independence from caregivers, etc.
From lat. communicato - "message", "transmission"; communico - "I make common, I connect." This is the exchange of signs, messages and information between two or more individuals.
Early intervention is a system of care for young children with or at risk of developmental disabilities and their families. In the Russian Federation, the synonym "early assistance" is also common. In the RR program, an interdisciplinary team of specialists helps the family create optimal conditions for the development of the child, supports parents or other adults raising the child, helps them overcome difficulties in raising a child with special needs.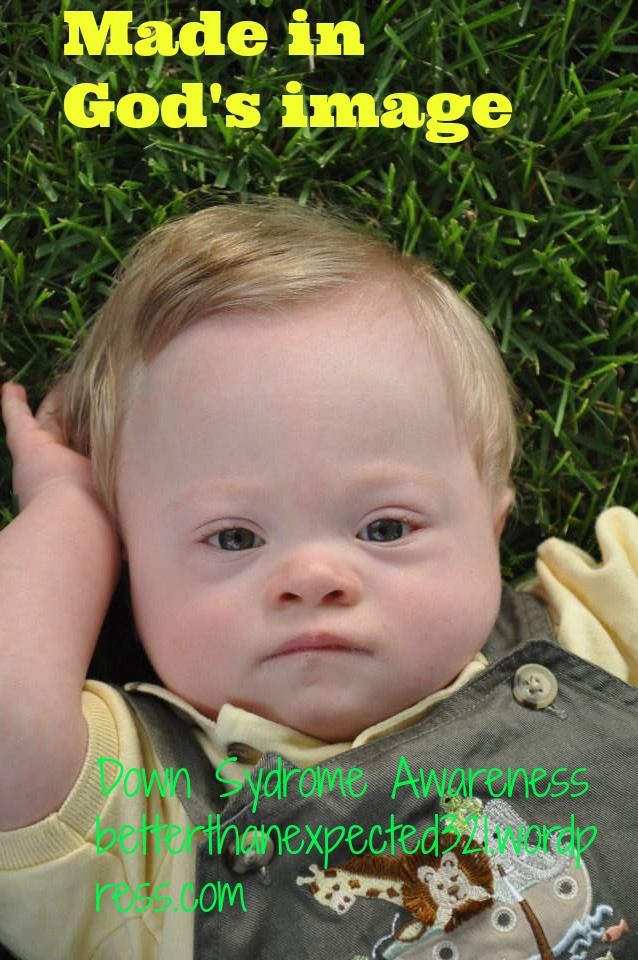 With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
A form of communication through language constructs. This is the main way of self-expression and interaction between people.
Ability to manage your relationships with other people. They allow you to communicate competently, affect the quality of communication and the effectiveness of contact with others, and help control emotions and behavior. These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
A group of methods used to convey messages to people with no or severe limitations in spoken language. The ADC is based on the idea that sign activity, which manifests itself in the process of communication, is diverse, that is, information can be transmitted and received through various channels of human perception.
pattern - "sample", "template", "system". This is a set of stereotypical behavioral responses or sequences of actions.
Myth 8. People with Down syndrome can be dangerous to others
Aggressive behavior is not characteristic of people with Down syndrome. And if they have difficulties with behavior, they are most likely due to peculiarities in the development of communication and speech. Until the child is able to express his desires or protests in words, he can scream, push, stomp his feet. Learning acceptable ways to communicate leads to a reduction in unwanted behavior. Consistency and clear expectations, reinforcing positive behaviors, help children with Down syndrome develop social skills, independence, and behave in the same way as other children.
Learning acceptable ways to communicate leads to a reduction in unwanted behavior. Consistency and clear expectations, reinforcing positive behaviors, help children with Down syndrome develop social skills, independence, and behave in the same way as other children.
Barbosa, R.T.d., de Oliveira, A.S.B., de Lima Antão, J.Y.F. et al. Augmentative and alternative communication in children with Down's syndrome: a systematic review. BMC Pediatr 18, 160 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-018-1144-5
The state of the body resulting from the prolonged absence of one or another reinforcement; a procedure for increasing the effectiveness of reinforcement (for example, stopping access to reinforcement for some time before the study). The opposite of saturation.
Degree of satisfaction of material, social and spiritual needs of a person. The quality of life is influenced by many factors: self-care skills, health status, the ability to communicate, study, work, spend leisure time, the level of independence and independence from caregivers, etc.
From lat. communicato - "message", "transmission"; communico - "I make common, I connect." This is the exchange of signs, messages and information between two or more individuals.
Early intervention is a system of care for young children with or at risk of developmental disabilities and their families. In the Russian Federation, the synonym "early assistance" is also common. In the RR program, an interdisciplinary team of specialists helps the family create optimal conditions for the development of the child, supports parents or other adults raising the child, helps them overcome difficulties in raising a child with special needs. With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
A form of communication through language constructs. This is the main way of self-expression and interaction between people.
Ability to manage your relationships with other people. They allow you to communicate competently, affect the quality of communication and the effectiveness of contact with others, and help control emotions and behavior. These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
A group of methods used to convey messages to people with no or severe limitations in spoken language. The ADC is based on the idea that sign activity, which manifests itself in the process of communication, is diverse, that is, information can be transmitted and received through various channels of human perception.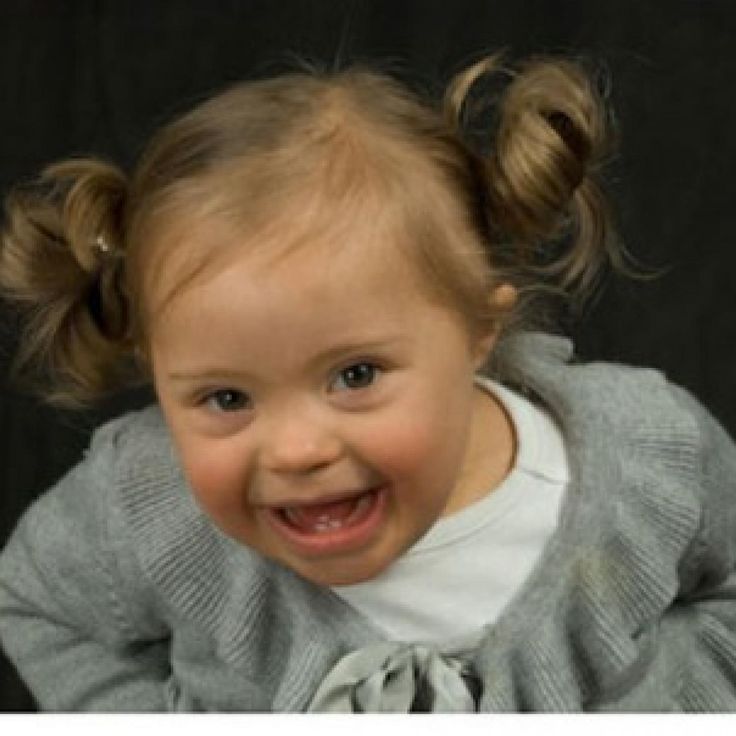
pattern - "sample", "template", "system". This is a set of stereotypical behavioral responses or sequences of actions.
Myth 9. Typically developing children should not play with children with Down syndrome - they can pick up "bad behavior" from them
Most children with Down syndrome behave in the same way as other children. In addition, the main mechanism for learning new skills and patterns of behavior is the reactions of others. Children learn what the environment reinforces: if you want children to behave in a certain way, reinforce their good behavior with your attention and praise. In addition, social skills are difficult to develop when there are no other people around. From early childhood, for successful development, it is important for a child to be surrounded by typically developing peers. It helps in developing social skills. A child with Down syndrome can successfully socialize and make friends. Scientific evidence confirms that inclusive education has a positive impact on both children with Down syndrome and their typically developing peers.
De Graaf, Gert & Van Hove, Geert & Haveman, Meindert. (2012). Effects of regular versus special school placement on students with Down syndrome: A systematic review of studies.
The state of the body resulting from a prolonged absence of one or another reinforcement; a procedure for increasing the effectiveness of reinforcement (for example, stopping access to reinforcement for some time before the study). The opposite of saturation.
The degree of satisfaction of the material, social and spiritual needs of a person. The quality of life is influenced by many factors: self-care skills, health status, the ability to communicate, study, work, spend leisure time, the level of independence and independence from caregivers, etc.
From lat. communicato - "message", "transmission"; communico - "I make common, I connect." This is the exchange of signs, messages and information between two or more individuals.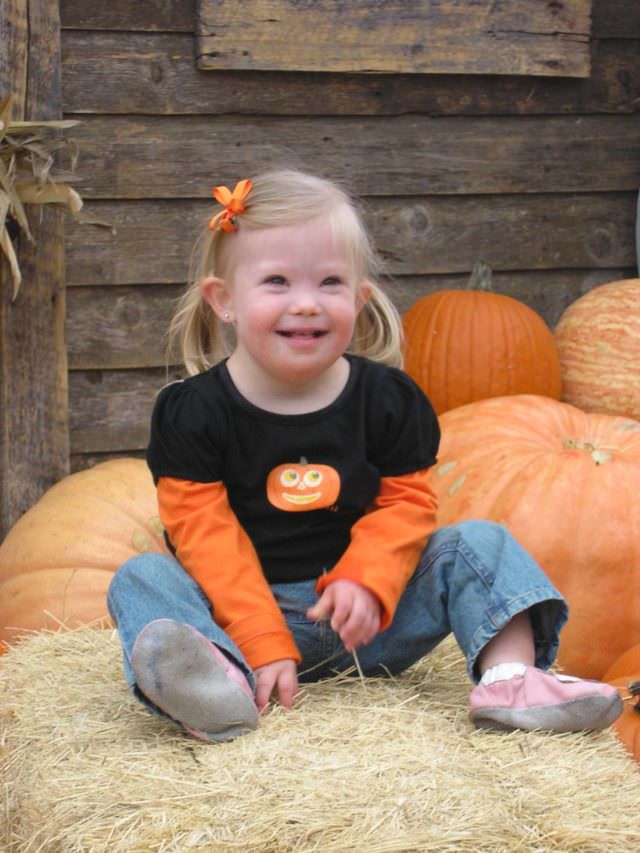
Early intervention is a system of care for young children with or at risk of developmental disabilities and their families. In the Russian Federation, the synonym "early assistance" is also common. In the RR program, an interdisciplinary team of specialists helps the family create optimal conditions for the development of the child, supports parents or other adults raising the child, helps them overcome difficulties in raising a child with special needs. With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.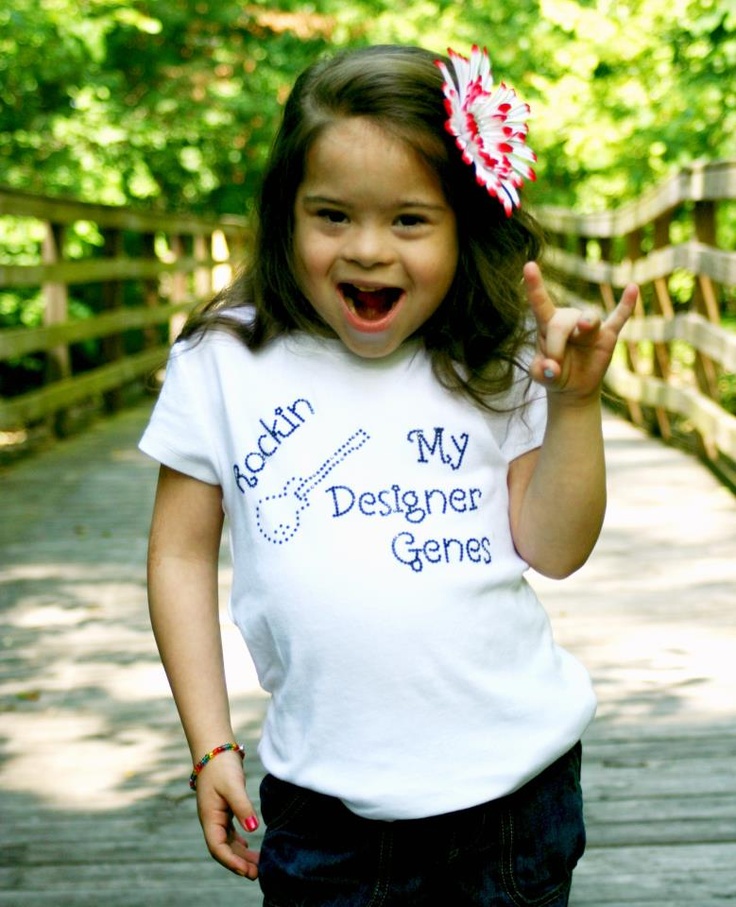
A form of communication through language constructs. This is the main way of self-expression and interaction between people.
Ability to manage your relationships with other people. They allow you to communicate competently, affect the quality of communication and the effectiveness of contact with others, and help control emotions and behavior. These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
A group of methods used to convey messages to people with no or severe limitations in spoken language. The ADC is based on the idea that sign activity, which manifests itself in the process of communication, is diverse, that is, information can be transmitted and received through various channels of human perception.
pattern - "sample", "template", "system". This is a set of stereotypical behavioral responses or sequences of actions.
Myth 10. People with Down syndrome are not sexual and do not have sex / all people with Down syndrome are hypersexual
Sexuality is inherent in all people, and people with Down syndrome are no exception. They can love, have sex and build partnerships. Studies refute increased aggressiveness, including of a sexual nature, on the part of people with Down syndrome. So, for example, they are much less likely than other people with disabilities to exhibit this kind of behavior.
Sexuality includes having sex, but the concept of sexuality is much broader. Sexuality has many manifestations - this is the acceptance of one's body, and the corresponding sex-role behavior that is safe for a person, and the ability to establish close relationships. Violation of the boundaries of private and public (lack of understanding of social distance, acceptable topics for conversation, acceptable social behavior) is sometimes mistaken for hypersexuality. This is fundamentally wrong. It is very important for people with intellectual disabilities to learn safe behavior, to understand the relevant rules, the difference between public and private.
It is very important for people with intellectual disabilities to learn safe behavior, to understand the relevant rules, the difference between public and private.
There are special sex education programs for people with Down syndrome and their families. Such programs should be an integral part of a comprehensive support program that includes assistance in developing communication and behavioral management. This is especially important as studies show that such people are statistically more likely to be victims of sexual abuse or exploitation. To reiterate, people with Down syndrome can have intimate lives, love, have sex, and form close partnerships. And the question of whether to have sex or not and with whom to do it, each adult decides for himself.
Murphy N. Sexuality in children and adolescents with disabilities. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2005 Sep;47(9):640-4. review. PubMed PMID: 16138674.
Holland-Hall C, Quint EH. Sexuality and Disability in Adolescents. Pediatric Clin North Am. 2017 Apr;64(2):435-449. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2016.11.011. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Review. PubMed PMID: 28292457.
Pediatric Clin North Am. 2017 Apr;64(2):435-449. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2016.11.011. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Review. PubMed PMID: 28292457.
Sexuality and persons with Down syndrome.
Sexuality and persons with Down syndrome. A study from Brazil.
Bononi B.M., Sant; Anna M.J., de Oliveira A.C., Renattini T.S., Pinto C.F., Passarelli M.L., Coates V., Omar H.A.., - J Adolesc Med Health. 2009 Jul-Sep;21(3):319-26.
The state of the body resulting from a prolonged absence of one or another reinforcement; a procedure for increasing the effectiveness of reinforcement (for example, stopping access to reinforcement for some time before the study). The opposite of saturation.
The degree of satisfaction of the material, social and spiritual needs of a person. The quality of life is influenced by many factors: self-care skills, health status, the ability to communicate, study, work, spend leisure time, the level of independence and independence from caregivers, etc.
From lat. communicato - "message", "transmission"; communico - "I make common, I connect." This is the exchange of signs, messages and information between two or more individuals.
Early intervention is a system of care for young children with or at risk of developmental disabilities and their families. In the Russian Federation, the synonym "early assistance" is also common. In the RR program, an interdisciplinary team of specialists helps the family create optimal conditions for the development of the child, supports parents or other adults raising the child, helps them overcome difficulties in raising a child with special needs. With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team.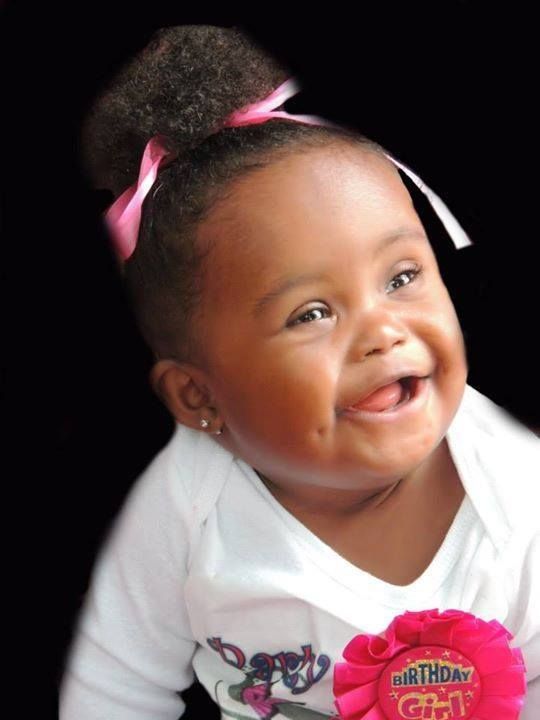 Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
A form of communication through language constructs. This is the main way of self-expression and interaction between people.
Ability to manage your relationships with other people. They allow you to communicate competently, affect the quality of communication and the effectiveness of contact with others, and help control emotions and behavior. These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
A group of methods used to convey messages to people with no or severe limitations in spoken language. The ADC is based on the idea that sign activity, which manifests itself in the process of communication, is diverse, that is, information can be transmitted and received through various channels of human perception.
pattern - "sample", "template", "system". This is a set of stereotypical behavioral responses or sequences of actions.
Egor Sapychev is on the photo
Maxim Shcherbatykh is on the photo
This area began to appear only in recent decades, because in a situation where the life expectancy of people with Down syndrome was extremely low, they lived in social isolation, often in boarding schools, they had practically no opportunity to enter into close relationships, start a family and children.
Current research indicates that up to 50% of women with Down syndrome may have children. According to various sources, from 35 to 50% of children born to mothers with Down syndrome will also have Down syndrome or other developmental disorders. Data on fathers with Down syndrome are still very limited. In most cases, men with Down syndrome cannot have children, and there are only a few scientific publications on individual cases of children born to fathers with Down syndrome.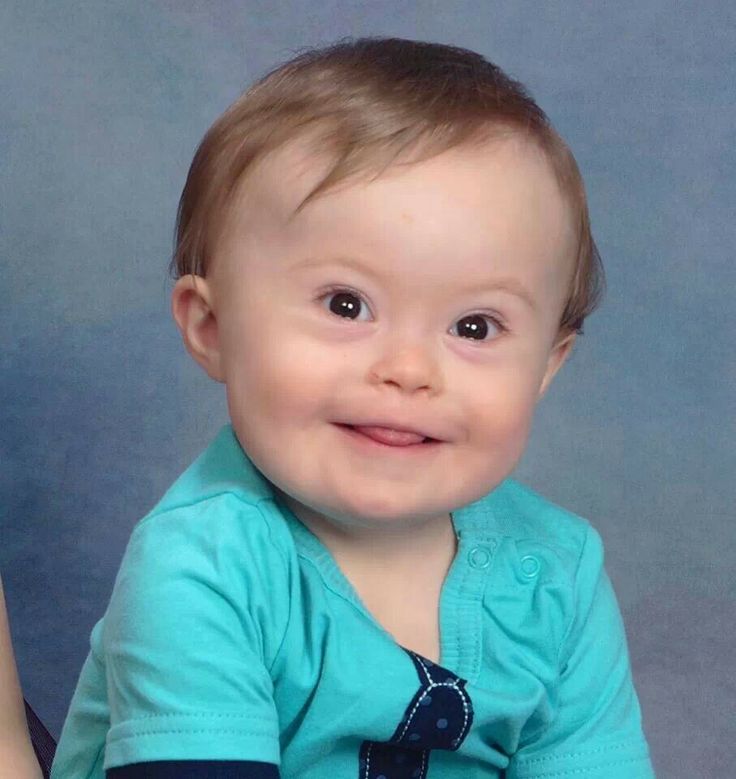
Down syndrome and infertility: what support should we provide? Parizot E., Dard R., Janel N., Vialard F. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2019Jun; 36(6):1063-1067. Epub 2019 May 9.
Fertility in men with Down syndrome: a case report. Fertil Steril. 2006 Dec;86(6):1765.e1-3. Epub 2006 Nov 13.
The Guide to Good Health for Teens and Adults with Down Syndrome. woodbine house. Chicoine, Brian and McGuire, Dennis. Bethesda, MD: Woodbine House. (2010)
Sexuality: Your Sons and Daughters with Intellectual Disabilities. Melberg, Schwier and Hingsburger, Eds. Baltimore, MD: Brookes Publishing. (2000)
Teaching Children with Down Syndrome About Their Bodies, Boundaries, and Sexuality: A Guide for Parents and Professionals. Bethesda, MD: Woodbine House. (2005)
The state of the body resulting from a prolonged absence of one or another reinforcement; a procedure for increasing the effectiveness of reinforcement (for example, stopping access to reinforcement for some time before the study).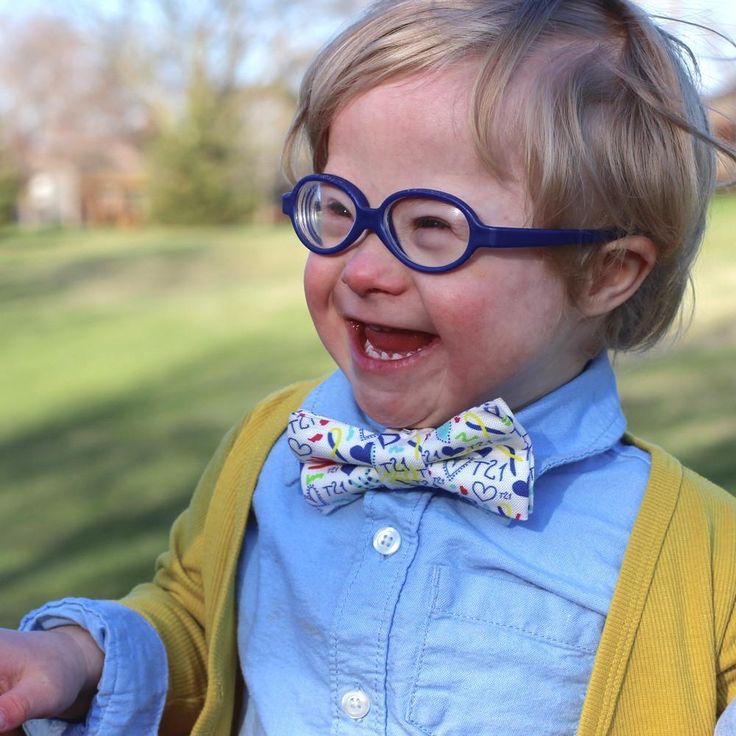 The opposite of saturation.
The opposite of saturation.
The degree of satisfaction of the material, social and spiritual needs of a person. The quality of life is influenced by many factors: self-care skills, health status, the ability to communicate, study, work, spend leisure time, the level of independence and independence from caregivers, etc.
From lat. communicato - "message", "transmission"; communico - "I make common, I connect." This is the exchange of signs, messages and information between two or more individuals.
Early intervention is a system of care for young children with or at risk of developmental disabilities and their families. In the Russian Federation, the synonym "early assistance" is also common. In the RR program, an interdisciplinary team of specialists helps the family create optimal conditions for the development of the child, supports parents or other adults raising the child, helps them overcome difficulties in raising a child with special needs. With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
A form of communication through language constructs. This is the main way of self-expression and interaction between people.
Ability to manage your relationships with other people. They allow you to communicate competently, affect the quality of communication and the effectiveness of contact with others, and help control emotions and behavior.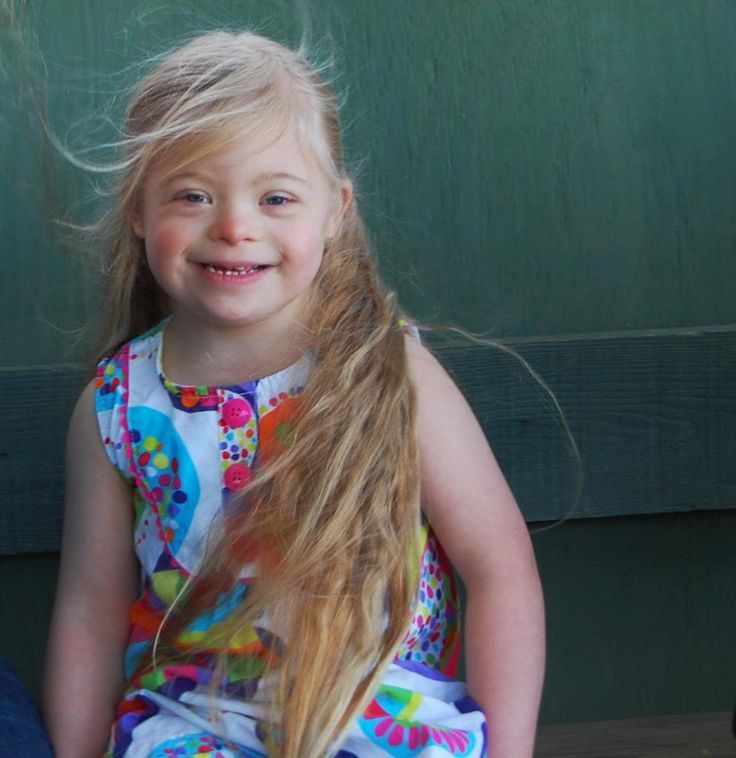 These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
A group of methods used to convey messages to people with no or severe limitations in spoken language. The ADC is based on the idea that sign activity, which manifests itself in the process of communication, is diverse, that is, information can be transmitted and received through various channels of human perception.
pattern - "sample", "template", "system". This is a set of stereotypical behavioral responses or sequences of actions.
Myth 12. For children with Down syndrome, it is better to be in institutions where there are trained specialists and medical care
Living in a closed institution (children's home or boarding school) seriously harms the development of any child. Children with Down syndrome and other developmental disabilities are even more vulnerable to these negative influences than typically developing children. The family is a critically important component of the development of the child and his formation as a full and productive person participating in the life of society.
The family is a critically important component of the development of the child and his formation as a full and productive person participating in the life of society.
Life in a caring family, the opportunity to study in kindergarten and school, communicate with typical peers help a child with Down syndrome to develop better. And placement in a children's home or a psycho-neurological boarding school negatively affects the physical and cognitive development of children with Down syndrome. A lot of research has been devoted to this issue, and in 2019 the Naked Heart Foundation published the book "Abandoned Children", detailing one of the most significant international studies in this area.
The state of the body resulting from a prolonged absence of one or another reinforcement; a procedure for increasing the effectiveness of reinforcement (for example, stopping access to reinforcement for some time before the study). The opposite of saturation.
Degree of satisfaction of the material, social and spiritual needs of a person. The quality of life is influenced by many factors: self-care skills, health status, the ability to communicate, study, work, spend leisure time, the level of independence and independence from caregivers, etc.
The quality of life is influenced by many factors: self-care skills, health status, the ability to communicate, study, work, spend leisure time, the level of independence and independence from caregivers, etc.
From lat. communicato - "message", "transmission"; communico - "I make common, I connect." This is the exchange of signs, messages and information between two or more individuals.
Early intervention is a system of care for young children with or at risk of developmental disabilities and their families. In the Russian Federation, the synonym "early assistance" is also common. In the RR program, an interdisciplinary team of specialists helps the family create optimal conditions for the development of the child, supports parents or other adults raising the child, helps them overcome difficulties in raising a child with special needs. With such support, parents have a real opportunity to leave the child in the family, providing him with optimal conditions for growth and development, and not send him to a closed institution, depriving him of the main thing - parental love and care. Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
Parents (carers of the child) are an integral part of the team. Educators, speech therapists, pediatricians, neurologists, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, as well as social educators and social workers work in early intervention programs. Early intervention programs are based on an assessment of the needs of the child and his family.
A form of communication through language constructs. This is the main way of self-expression and interaction between people.
Ability to manage your relationships with other people. They allow you to communicate competently, affect the quality of communication and the effectiveness of contact with others, and help control emotions and behavior. These are all abilities that are used to communicate and interact with other people both with the help of speech and without words, through gestures, body language.
A group of methods used to convey messages to people with no or severe limitations in spoken language.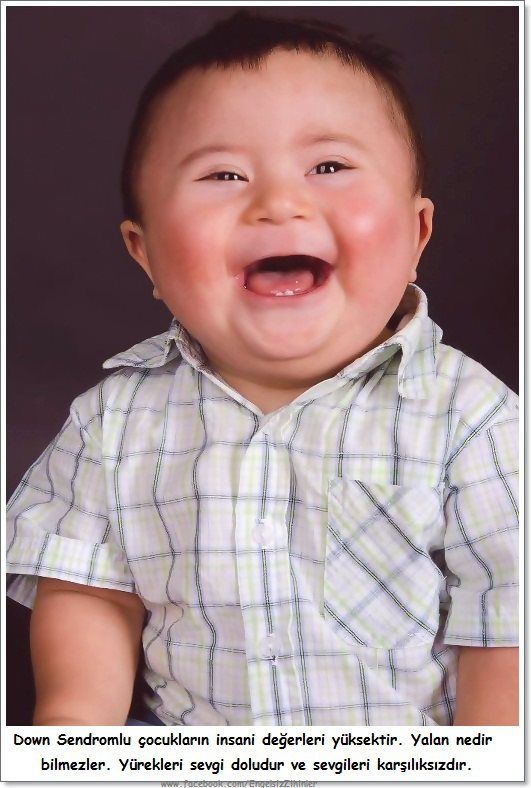 The ADC is based on the idea that sign activity, which manifests itself in the process of communication, is diverse, that is, information can be transmitted and received through various channels of human perception.
The ADC is based on the idea that sign activity, which manifests itself in the process of communication, is diverse, that is, information can be transmitted and received through various channels of human perception.
pattern - "sample", "template", "system". This is a set of stereotypical behavioral responses or sequences of actions.
Share:
Related tags: Down syndrome
TextsParents are not to blame: about the real causes of disability
Complete employment: Myths and facts
