Cramping ovaries early pregnancy
Ovary Pain in Early Pregnancy: Causes, Management, and More
Pregnancy causes a lot of changes to the body. Some of those changes can cause mild discomfort or light cramping in the area around your ovaries. Ovary pain may cause pain on one side of your lower abdominal or pelvic area. It can also sometimes cause pain in the back or thigh.
Ovary pain may be a sign that implantation is occurring, or it could be a response to the change in hormones that you’ll experience in early pregnancy.
Any serious ovary pain should be reported to your doctor. Seek immediate medical attention if you’re pregnant and experience sharp or long-lasting pain accompanied by:
- nausea
- vaginal bleeding
- fever
- feeling faint
- vomiting
Read on to learn more about causes for ovary pain in early pregnancy and when to seek medical help.
The following may cause pain in the area of your ovaries in early pregnancy.
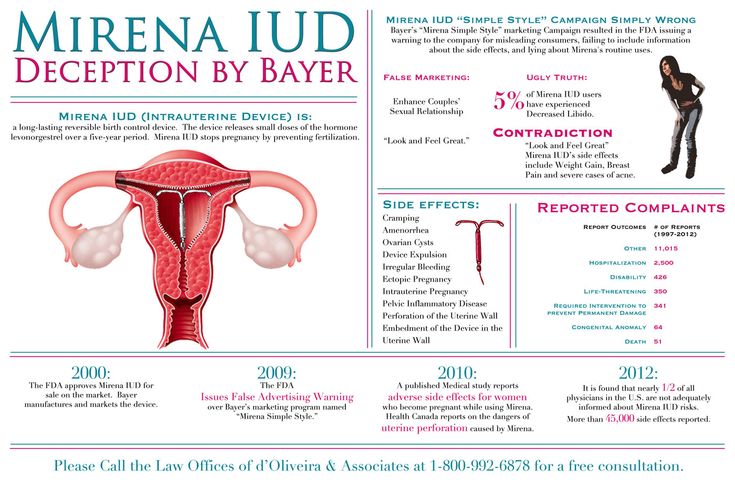
Ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg attaches itself in a place other than the inside of the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes.
Symptoms include:
- sharp or stabbing pain, usually on one side of the pelvis or abdomen
- vaginal bleeding that’s heavier or lighter than your normal period
- weakness, dizziness, or fainting
- gastrointestinal or stomach discomfort
Seek medical help right away if you think you’re experiencing an ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancies are not viable, and, left untreated, may result in a ruptured fallopian tube or other serious complications.
Miscarriage
A miscarriage is the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks.
Possible symptoms include:
- vaginal bleeding
- pelvic pain, low back pain, or abdominal pain
- passing tissue or discharge through the vagina
Let your doctor know if you’re experiencing miscarriage symptoms. There’s no way to stop a miscarriage, but in some cases, medication or surgery is needed to prevent complications.
Ovarian cyst
Most ovarian cysts are asymptomatic and harmless. But cysts that continue to grow can rupture or twist, or cause complications during pregnancy and delivery.
But cysts that continue to grow can rupture or twist, or cause complications during pregnancy and delivery.
Symptoms may include:
- pelvic pain, which may be isolated to one side
- abdominal fullness, heaviness, or bloating
- pain with fever or vomiting
Seek medical help if you have sharp or stabbing pain, especially with fever or vomiting. You should also let your OB-GYN know if you have a known ovarian cyst. They may want to monitor the cyst throughout your pregnancy.
Ovarian rupture and torsion
An ovarian rupture is a medical emergency. It can cause internal bleeding.
Ovarian torsion is also a medical emergency where a large cyst causes an ovary to twist or move from its original position. This can cut off blood supply to the ovary.
Symptoms of a rupture or torsion may include:
- severe or sharp pelvic pain, sometimes isolated to one side
- fever
- dizziness
- rapid breathing
Always let the hospital staff know if you’re pregnant and all your symptoms. You may need an ultrasound or MRI. Your doctor can then determine if surgery is necessary or recommend alternative treatment options.
You may need an ultrasound or MRI. Your doctor can then determine if surgery is necessary or recommend alternative treatment options.
Other possible causes
Other causes of pain near your ovaries during early pregnancy may include:
- gastrointestinal or stomach issues
- stretching of the uterus
- fibroids
Let your doctor know about your symptoms at your first pregnancy appointment.
Is it a sign of implantation?
Implantation occurs when a fertilized egg attaches to the interior lining of the uterus. It typically occurs 6 to 12 days after conception. Implantation occurs before you are far enough along to have a positive pregnancy test.
Cramps around the time when implantation would occur could be an early sign of pregnancy, but until you’ve had a positive pregnancy test, it’s impossible to know if the cramps are a sign of pregnancy or an impending menstrual period.
If your period doesn’t start when expected, take a pregnancy test three days to one week later to confirm pregnancy.
Let your doctor know if you have sharp or chronic ovarian pain on one or both sides that doesn’t go away on its own. You may need emergency medical care, especially if you have sharp or chronic pain along with one or more of the following symptoms:
- nausea
- vaginal bleeding
- high fever
- feeling faint
- vomiting
Ovarian pain during pregnancy that doesn’t go away on its own may need to be treated by a doctor.
But if your doctor does not recommend any medical treatment for your pain, you may be able to manage mild discomfort at home.
- Change positions slowly, especially when going from sitting to standing. That can help reduce incidence of pain.
- Get plenty of rest, and change or reduce your workout routine if you experience discomfort related to exercise.
- Soak in a warm (not hot) bath.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Apply gentle pressure to the sore area.
Many pain relievers aren’t safe to take during early pregnancy. Talk to your doctor before taking medication to manage pain.
Talk to your doctor before taking medication to manage pain.
You should also talk to you doctor before applying heat, such as from a hot compress. Too much heat could cause serious birth defects.
Treatment will depending on the underlying cause. In some cases, you may not need treatment.
For treatment of an ovarian cyst, your doctor will take into account factors like the size of the cyst, whether or not it has ruptured or twisted, and how far along you are in your pregnancy. They will make a treatment recommendation that will give you and your baby the healthiest outcome possible.
In some cases, surgery can be safely performed during pregnancy. Your healthcare team will tell you about the risks and possible outcomes based on your circumstances.
If your pain is caused by an ectopic pregnancy, your doctor will likely prescribe the medication methotrexate. This drug can stop the growth of rapidly dividing cells, such as the cells of the ectopic mass. If medication doesn’t work, surgery may be necessary.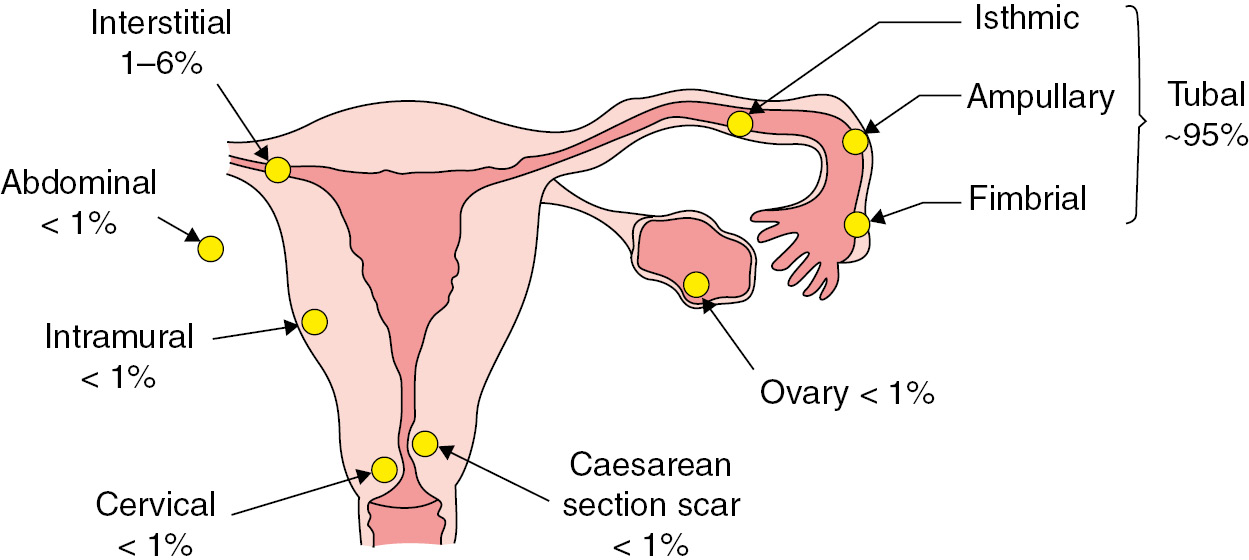
If you are having a miscarriage, you may be able to pass the pregnancy at home. In other cases, you may need medication to help you pass the tissue from the pregnancy loss or you may need a procedure known as dilation and curettage (D and C). D and C is a minor surgery that can be used to remove the tissue from the lost pregnancy.
Always let your doctor know if you are experiencing ovarian pain during pregnancy.
Seek emergency medical care for sharp or stabbing pain that doesn’t go away on its own, and let the hospital staff know you are pregnant. Your doctor and healthcare team can come up with a treatment plan for the healthiest outcome.
Ovary Pain During Pregnancy: What Does It Mean?
Causes of ovary pain during pregnancy
The reasons behind ovary pain during pregnancy range from relatively harmless to more serious conditions that require immediate attention. A sharp, stabbing pain in your left or right side or a dull, throbbing pain that doesn’t go away should be discussed with your ob-gyn.
Take a quiz
Find out what you can do with our Health Assistant
Ovary pain during pregnancy can be attributed to a number of things:
Expanding uterus
As your uterus expands to accommodate your baby, it presses against your ovaries. Hormonal changes also cause pain in the round ligaments along either side of your abdomen. This, in turn, puts a dull sensation of pressure on your ovaries.
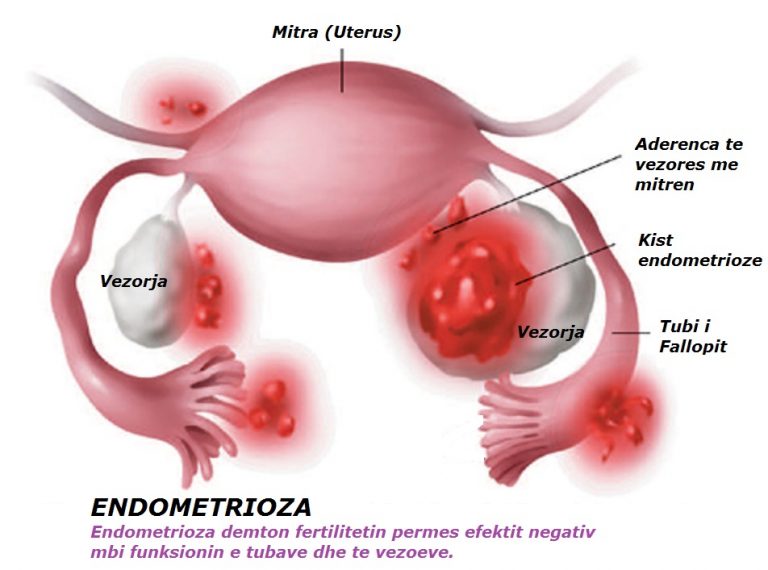
Endometriosis
Ordinarily, your uterus produces a lining of blood and mucus for a fertilized egg to implant itself. For those with endometriosis, however, this lining grows outside the uterus. It’s a painful condition that occurs monthly.
Painful periods or intercourse, heavy flow, and infertility are all symptoms of endometriosis. To diagnose this condition, your doctor will need to conduct an MRI or laparoscopic examination.
While periods are an opportunity for unused uterine tissues to exit the body through the vagina, endometrial buildup (foci) can’t leave the body.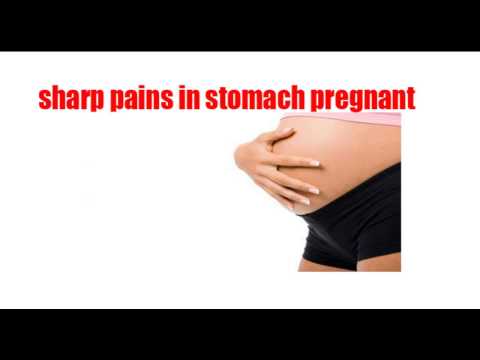 Scar tissue accumulates, leading to pain and swelling, especially around your ovaries.
Scar tissue accumulates, leading to pain and swelling, especially around your ovaries.
Painful periods or intercourse, heavy flow, and infertility are all symptoms of endometriosis. To diagnose this condition, your doctor will need to conduct an MRI or laparoscopic examination.
Ovarian cyst
Cysts are small, fluid-filled sacs on the surface of your ovaries. They’re pretty common, particularly during your childbearing years. When an egg isn’t fully released, it doesn’t leave the sac and instead develops into a cyst.
Single cysts tend to go away on their own, without any noticeable pain. Occasionally, though, they’ll rupture and cause a mild, dull pain.
Cysts are pretty common, particularly during your childbearing years. When an egg isn’t fully released, it doesn’t leave the sac and instead develops into a cyst.
Discomfort due to intercourse or a bowel movement often indicates ovarian cysts. Nausea or vomiting, bloating, and a feeling of fullness after a light meal are further warning signs. If this happens, see your doctor for an ultrasound or pelvic exam.
If this happens, see your doctor for an ultrasound or pelvic exam.
A serious condition, known as polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), disproportionately affects overweight or obese women. It’s a hormonal disorder which causes multiple ovarian cysts, excess testosterone production, possible infertility, and ovary pain.
Ovarian torsion or rupture
In rare instances, your ovaries may wrap themselves around your uterine tubes or blood vessels. This restricts blood flow and can rupture the ovaries or kill the eggs inside them.
Ovarian torsion often occurs during in vitro fertilization. Fertility drugs increase the number of eggs you have, which makes the ovaries heavy and swollen. Additionally, strenuous exercise such as heavy cardio, weight lifting, and abdominal crunches put you at greater risk for ovarian torsion.
Ovarian torsion often occurs during in vitro fertilization. Fertility drugs increase the number of eggs you have, which makes the ovaries heavy and swollen.
If left untreated, ovarian torsion may lead to ovarian rupture, which is extremely serious. Other triggers include a large ruptured cyst that damaged the ovaries (due to vigorous sexual activity, for example) or an ectopic pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg implants anywhere besides the uterus. If conception occurs early in your cycle and the egg hasn’t reached your uterus, the sperm fertilizes it farther up the uterine tubes. The egg then attaches inside the uterine tube, which is not equipped to accommodate a growing embryo.
Sometimes, ectopic pregnancies rupture the uterine tube, resulting in pain and vaginal bleeding. Bleeding is either lighter or heavier than typical menstrual flow, and has a different consistency. Ectopic pregnancy also causes lightheadedness, nausea, or dizziness. If you observe these symptoms, consult your doctor.
Early pregnancy loss
Early pregnancy loss is particularly common in the first trimester. You may feel ovary pain and notice severe cramping and bleeding during a miscarriage. Cramping indicates that your uterus is attempting to expel the miscarriage, and it places pressure on your ovaries in the process.
You may feel ovary pain and notice severe cramping and bleeding during a miscarriage. Cramping indicates that your uterus is attempting to expel the miscarriage, and it places pressure on your ovaries in the process.
Fibroids
Fibroids are noncancerous growths in or around your uterus. These small, abnormal groups of cells aren’t life-threatening, but they can produce heavy, prolonged periods and lower back and ovary pain.
They also make it harder to conceive and trigger frequent urination (due to increased pressure on your bladder or pelvic floor).
Fibroids are noncancerous growths in or around your uterus. These small, abnormal groups of cells aren’t life-threatening, but they can produce heavy, prolonged periods and lower back and ovary pain.
Fibroids can be so small they’re only detectable with an ultrasound, or so large that they expand into your abdomen and create a distended belly. Larger masses often produce constant, dull ovary pain and might require surgery.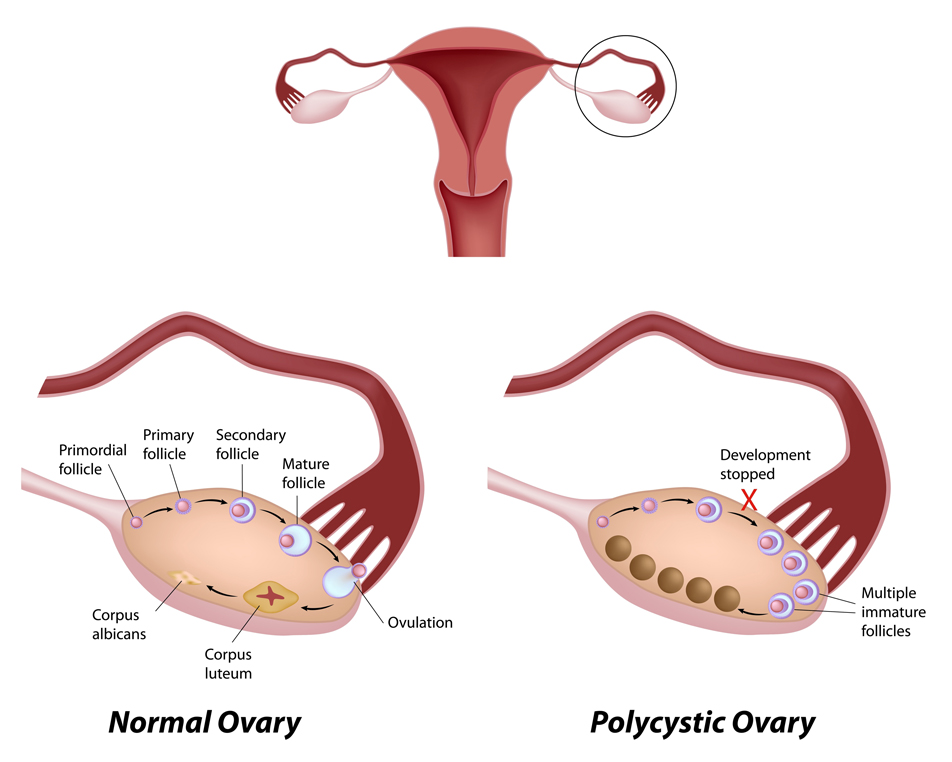
Placental abruption
The risk of placental abruption is highest towards the end of your pregnancy. This is when the placenta partially or fully separates from the uterine wall. This often causes sudden spotting or vaginal bleeding, depending on where the separation occurred and the severity of tearing. The pressure this puts on your ovaries also results in a sharp pain.
The risk of placental abruption is highest towards the end of your pregnancy. This is when the placenta partially or fully separates from the uterine wall.
Without the placenta intact, your baby won’t receive vital oxygen-rich blood and nutrients. Instead, blood pools inside your uterus, and unless it’s released through the vagina, it builds up a dangerous amount of pressure.
Seek immediate medical attention if you feel a pulling sensation, suddenly begin bleeding, or observe a swollen area on your baby bump.
Safe ways to treat ovary pain during pregnancy
Depending on the underlying cause, you might be able to treat ovary pain at home. Place a heating pad over the area where you’re feeling pain or soreness. Try to rest by sitting in a partially elevated position. Lying completely flat may actually pull or stretch your ovaries and other affected areas.
Place a heating pad over the area where you’re feeling pain or soreness. Try to rest by sitting in a partially elevated position. Lying completely flat may actually pull or stretch your ovaries and other affected areas.
A warm (but not hot) shower or bath is another effective remedy. Consider wearing a pelvic support garment to hold your uterus in place, alleviating pressure on your abdominal wall and ovaries. Lastly, remember to check with your doctor before taking any OTC pain medications.
Does ovary pain signal implantation?
Once pregnant, you could notice cramping or dull pain in your uterus, breast soreness, and lightheadedness. However, some women say they actually experience ovary pain during the implantation process. If this is the case, see your doctor right away as it’s a possible indication of ectopic pregnancy.
When to see a doctor
If you’re pregnant or sexually active, you should never ignore a sharp, stabbing pain in either side of your abdomen. Ovary pain during pregnancy accompanied by cramps, bleeding, or dizziness requires immediate medical attention.
Ovary pain during pregnancy accompanied by cramps, bleeding, or dizziness requires immediate medical attention.
Ovaries hurt during pregnancy: the main causes of pain in the early stages
Pregnancy is a special state of the body in which any habitual phenomena can be interpreted ambiguously. For example, pain or other unpleasant sensations do not always indicate the presence of an ailment, sometimes they are the result of normal processes occurring in a woman's body. In this article, we will tell you why the ovaries can hurt during early pregnancy.
Non-dangerous ovarian pain in the first weeks of term
Fortunately, in many cases, the unpleasant pain experienced by pregnant women does not pose any threat and is part of the physiological changes in the body. Let's take a closer look at what pains in the ovarian region can be considered harmless:
- Many future mothers begin to feel discomfort in the abdomen literally from the first days after conception.
 It is at this time that the fetal egg descends into the uterus and is introduced into its mucous membrane, which causes periodic pain.
It is at this time that the fetal egg descends into the uterus and is introduced into its mucous membrane, which causes periodic pain. - Over time, the uterus begins to grow and increase, this puts a load on the ligaments that support it. Many women during early pregnancy think that they have an ovary, in fact, this stretching of the ligaments and skin leads to pain in the lower and sides of the abdomen. Most often, discomfort occurs due to physical exertion, sudden movements, but sometimes pain is felt even when the body is relaxed. If, for example, you lie on one side for a long time, the lateral ligament is stretched and is in constant tension.
- Pregnant women tend to constantly worry about their health, which is why they mistake bowel disorders for ovarian pain. It is known that progesterone disrupts normal intestinal motility and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, so digestive problems during this period of a woman's life are common.
- It is believed that the age of the expectant mother and the number of pregnancies also play a role.
 For example, with complaints that the ovary is pulled during early pregnancy, patients aged 18-25 who are carrying a child for the first time most often turn to doctors. With subsequent conceptions, many of them no longer feel such discomfort.
For example, with complaints that the ovary is pulled during early pregnancy, patients aged 18-25 who are carrying a child for the first time most often turn to doctors. With subsequent conceptions, many of them no longer feel such discomfort. - The causes of pain in the organs of the reproductive system are also hormonal changes that inevitably occur in the body with the onset of conception.
A common cause of ovarian pain is a corpus luteum cyst. This term itself sounds intimidating, but in fact, a corpus luteum cyst of the ovary is a completely normal phenomenon in the initial stages of pregnancy. Such a formation occurs at the site of the follicle, from which the egg had previously left.
If the egg has been fertilized, the cyst significantly increases in size and begins to produce progesterone, the main pregnancy hormone responsible for the normal bearing of the child. In the event that the cyst grows too large, it stretches the ovarian capsule, which leads to pain.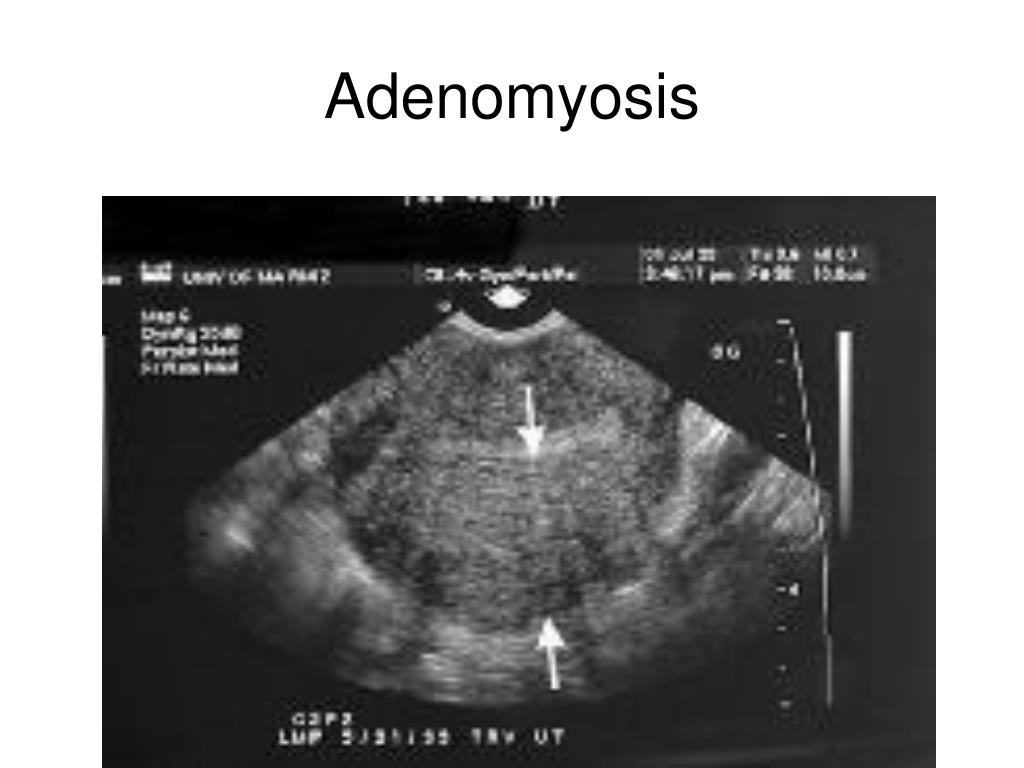
Such pains do not pose any threat, and the corpus luteum cyst itself disappears no later than 12-13 weeks.
Ovarian tingling during early pregnancy is often the result of artificial stimulation during in vitro fertilization. This phenomenon is also considered normal.
For women whose ovaries are prone to polycystic disease, the likelihood of such sensations is markedly increased.
In order not to torment yourself with unnecessary doubts and fears, in case of any unusual and unusual manifestations, it is better to contact your doctor.
Pathological pain in the ovaries in the early stages of pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy
Pain in the abdomen, unfortunately, is not always harmless. Sometimes they can be the result of a dangerous pathology. For example, this common symptom is observed in ectopic pregnancy.
Cutting, sharp or severe pulling pain, often accompanied by bloody discharge, and sometimes full-fledged profuse bleeding, is definitely an indication to call an ambulance. An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fetal egg attaches not to the endometrium of the uterus, but to the cavity of another organ, most often, to the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube.
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fetal egg attaches not to the endometrium of the uterus, but to the cavity of another organ, most often, to the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube.
As the embryo grows, it ruptures the tube, causing bleeding and pain. An ectopic pregnancy can be detected at an early stage, then health risks will be minimized.
Pain due to inflammation
Inflammation of the ovaries is one of the likely causes of pain in the right, left side, lower abdomen or in the lumbar region. Unfortunately, such a disease occupies one of the leading places among all gynecological pathologies.
Inflammation can be either acute or chronic, with the latter being considered the most dangerous. A timely untreated ailment often makes itself felt during pregnancy, when a woman is most vulnerable. It is extremely difficult to treat the disease during the period of bearing a child, since antibiotics and many other medicines cannot be used.
That is why it is so important to have regular check-ups with a gynecologist and solve health problems in time.
Inflammation of the ovaries can be the result of a common cold, or it can be caused by various unpleasant pathogens: chlamydia, candida fungi, cytomegalovirus, mycoplasmas and others.
Most of these infections are sexually transmitted, and some viruses and germs are very difficult to detect. For example, chlamydia can be detected only by a special method, and the symptoms are often similar to other diseases.
The above pathogens cause inflammation of the organs of the reproductive system: oophoritis, adnexitis, etc.
If, with the onset of pregnancy, pain in the ovaries appears, this may also indicate that some chronic diseases have passed into an acute phase.
The body of the expectant mother is vulnerable to any disease due to a decrease in immunity, which always occurs with the onset of conception.
It is best to plan pregnancy in advance in order to have time to undergo all the necessary examinations and cure chronic diseases.
Inflammation of the kidneys or bladder is a common cause of abdominal pain. Depending on the complexity of the condition, such a patient can be placed in a hospital for constant supervision, adequate treatment or some kind of preventive measures can be prescribed.
Causes of pain in the ovaries of a non-inflammatory nature
Discomfort or sharp discomfort in the abdomen can occur not only due to inflammation, but also as a result of other diseases:
- polycystic;
- apoplexy;
- tumor formations;
- cysts.
An ovarian cyst in early pregnancy often causes severe pain of considerable duration. If the cyst is solid, the pain may not be very intense, pulling, dull. Sharp sensations most often occur when the cyst bursts and fluid from it enters the abdominal cavity.
In addition to pain, this condition is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, nausea, vomiting, and the appearance of an unhealthy blush on the cheeks. If you do not call an ambulance in time and do not operate on the patient, a dangerous complication may develop - peritonitis.
If you do not call an ambulance in time and do not operate on the patient, a dangerous complication may develop - peritonitis.
Inflammation of the abdominal cavity can lead to the worst consequences, including death.
Torsion of the cyst stem is also accompanied by intense pain. Feeling something like this, a pregnant woman should immediately consult a doctor. If the cyst has retained its integrity, it can be cured with medication using hormonal drugs, without resorting to surgical intervention.
One of the most unpleasant causes of abdominal pain is an ovarian tumor. Tumors, which can be both benign and malignant, reaching a significant size, compress other organs and lead to pain.
Psychogenic causes of abdominal pain
Some psychogenic factors can be attributed to the causes of pain in the ovaries during early pregnancy. It makes sense to be examined by a psychiatrist when all other possible causes of discomfort have been excluded.
Pregnancy is a complex condition that affects not only the physical sense of self, but also the psyche. Sometimes during the period of bearing a child, his mother may manifest diseases such as hypochondria, hysteria, depression.
The mental state often affects the well-being, leading to the appearance of pain in various organs.
What should a pregnant woman do in case of abdominal pain
Only a qualified doctor can reliably find out the cause of discomfort, so in no case should you self-medicate or let everything take its course. The following symptoms are considered reasons for urgent treatment to the hospital:
- increased pain, change from dull pulling pain to cutting and sharp;
- prolonged period of pain symptoms;
- appearance of pink, brown, red spotting;
- bleeding from the genitals;
- fever;
- the appearance of profuse secretions of white, yellow, green color with an unpleasant odor;
- "petrification" of the abdomen;
- heaviness in the lower abdomen.

Women who went to the doctor with pain in the ovaries, underwent all the necessary examinations, and who did not have dangerous pathologies, are recommended to deal with the malaise in the following ways:
- Try to lie in a comfortable position, relax completely, breathe deeply, dream about something joyful. If fatigue or nervous tension is the cause of discomfort, a good rest will help eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
- A warm compress will help relieve tension in the ligaments that support the uterus. Place something warm on your stomach, at a pleasant temperature, but never hot.
- Your doctor can give you advice on light exercise. Moderate exercise will not hurt even during pregnancy, on the contrary, such physical education will have a restorative and tonic effect on the body.
- Since the cause of abdominal pain may not be the ovaries, but a malfunctioning intestine, carefully think about how you eat, review your diet, eliminate harmful foods from it.
 Avoid foods that cause gas.
Avoid foods that cause gas. - Eliminate annoying factors from your life, or at least try to minimize them. This will help you avoid nervous tension, unnecessary frustration, depression or bad mood.
Pain in the ovaries during pregnancy. Video
Ovaries hurt during pregnancy - causes at different periods
While carrying a child, a woman carefully listens to her own feelings in order to recognize possible health problems in a timely manner. Ovaries often hurt during pregnancy , discomfort worries at different times. Why unpleasant sensations arise, how dangerous they are, how to deal with them - we will talk about all this with you today.
Can the ovaries hurt during pregnancy
After conception, there is a restructuring in the work of almost all organs and systems, the work of the whole organism is aimed at ensuring that the fetus can grow and develop normally.
When pregnancy occurs, the gonads "fall asleep" - this prevents the maturation of a new egg and the onset of ovulation. After conception, the level of progesterone, estrogen, hCG increases, blood circulation accelerates in the pelvic organs. All this leads to the fact that the size of the ovaries increases, the glands are slightly displaced, they begin to ache.
After conception, the level of progesterone, estrogen, hCG increases, blood circulation accelerates in the pelvic organs. All this leads to the fact that the size of the ovaries increases, the glands are slightly displaced, they begin to ache.
Therefore, slight pain in the ovaries in future mothers is a normal phenomenon, provided that there are no other dangerous manifestations of pathologies, the general condition of the woman does not worsen.
The main causes of pain in the ovaries in the early stages
During pregnancy, pain in the ovaries occurs on one or both sides, develops under the influence of physiological or pathological factors.
Can the ovary hurt at the beginning of pregnancy?
Yes, it is in the early stages that discomfort in the lower abdomen occurs most often. Often, the problem is diagnosed in women under the age of 25 who are preparing to become a mother for the first time.
Why the ovaries hurt in the first trimester:
- Fixation of the fertilized egg in the epithelium of the uterus - discomfort occurs about a week after conception, accompanied by a pain syndrome of a pulling nature.

- Enlargement of the uterus - during pregnancy, the main reproductive organ is constantly growing, the load on the muscles increases. Discomfort in the lower abdomen is not caused by problems with the ovaries - it is the ligaments of the uterus that hurt. Unpleasant sensations are aggravated during physical exertion, with a sharp change in body position, they are disturbed in the morning if during sleep the expectant mother slept on her side for a long time.
- Hormonal changes.
- Corpus luteum cyst - occurs in the follicle at the site of the release of the egg. During pregnancy, the neoplasm actively synthesizes progesterone, increases in size, and begins to stretch the walls of the ovary. Usually the cyst resolves simultaneously with the corpus luteum, this happens by the end of the 11th week.
Almost always, tingling, pulling pain in the gonads occurs if conception occurred with the help of IVF - this is how the body reacts to active stimulation of the ovaries.
Pain in the ovaries in the later stages
In the later stages, the woman's body begins to actively prepare for the upcoming birth, the hormonal background changes.
From the 14th week of pregnancy, relaxin begins to be actively produced - this hormone helps to soften the cartilage tissue, ligaments, which allows the pelvic bones to diverge during childbirth.
A high level of relaxin softens the cervix, which causes pain in the lower abdomen. Doctors recommend women not to be nervous in such a situation, the problem does not require special drug therapy.
Pain in the ovaries as a sign of serious illness
Typically, ovarian pain in expectant mothers is of a short-term nature, while the general state of health remains within the normal range. But if discomfort appears often, accompanied by weakness, deterioration of health, this may be a sign of the development of serious diseases of the reproductive or digestive system.
What pathologies cause pain in the ovaries:
- Ectopic pregnancy - at 5-6 weeks of gestation, there is a sharp cutting pain that covers the entire lower abdomen, uterine bleeding opens.
- Miscarriage - accompanied by severe sharp pain in the lower abdomen, which radiates to the lumbar region, spotting spotting appears.
- Adnexitis, oophoritis - inflammation of the ovaries is accompanied by unilateral pain in the lower abdomen, in the lumbar region, the pathology develops in the I, II trimester of pregnancy. Colds, chlamydia, candidiasis, and other sexually transmitted infections can provoke the development of the disease.
- Rupture of the ovary - the problem often affects the right gonad. The reasons are weight lifting, excessive physical activity, too active friction during sex, vascular pathologies of the appendages.
- Rupture or torsion of an ovarian cyst - the pathology is accompanied by bouts of nausea, vomiting, severe pain, and an increase in temperature.
Pain in the ovarian region can be caused by prolonged constipation, disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract, often occurs with cystitis and pyelonephritis, with an attack of appendicitis.
When do you need to see a doctor urgently?
Pain in the lower abdomen is sharp, stabbing, acute, covers the lower back, legs, discomfort does not subside all day. Dangerous symptoms are fever, the appearance of bloody, atypical vaginal discharge with unpleasant odors, frequent bouts of vomiting and nausea, an acute and hard abdomen.
What to do if the ovaries hurt during pregnancy
To eliminate the pulling pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes just rest is enough - take a comfortable position, dim the light, try to relax as much as possible, breathe slowly.
In the later stages, a warm, but not hot compress will help to cope with discomfort. Well eliminates pain and spasms, special yoga for pregnant women, and traditional medicine will help.
A few simple recipes:
- Pour 1 tbsp. l. dried blueberries 200 ml of water, leave in a sealed container for 30 minutes. Drink 100 ml of the drink in the morning and evening.
- Mix equal proportions of blackcurrant and rose hips, pour 2 tbsp.
 l collecting 300 ml of boiling water, let it brew for a quarter of an hour. Drink a healthy drink throughout the day instead of tea.
l collecting 300 ml of boiling water, let it brew for a quarter of an hour. Drink a healthy drink throughout the day instead of tea. - Brew 1 liter of boiling water 3 tbsp. l. linden, leave in a sealed container for 20 minutes, strain. Take 5 ml of infusion three times a day.
Ovaries hurt a lot - what to do?
Expectant mother should not take strong painkillers, relatively safe drugs for pain relief during pregnancy - No-shpa, Paracetamol.
Prevention
To avoid health problems during pregnancy, plan conception in advance, undergo examinations in advance, take tests, give up addictions, identify and eliminate all diseases.
During pregnancy, follow the daily routine, eat right and balanced, do not forget about moderate physical activity and daily walks in the fresh air, do not be nervous. Pain in the lower abdomen often occurs due to digestive problems, to avoid this, remove from the diet all foods that can provoke constipation and flatulence.
Conclusion
Discomfort in the ovaries is a common occurrence during pregnancy, most often discomfort occurs against the background of hormonal and physiological changes in the body.
Tell me if you had a similar problem, what remedies helped you get rid of ovarian pain. And do not forget to share the article with your friends on social networks - every expectant mother needs to know what health problems can arise during childbearing, and how to deal with them.
Ovaries hurt during pregnancy - what to do?
Pain in the ovaries is a fairly common, although not entirely characteristic, symptom in the early stages of pregnancy. Why do such manifestations occur, how dangerous are they, and what to do if they occur? You will find answers to these questions in the article.
What happens to the ovaries during pregnancy
When a woman is not pregnant, the ovaries are needed for the production of sex hormones and the maturation of eggs.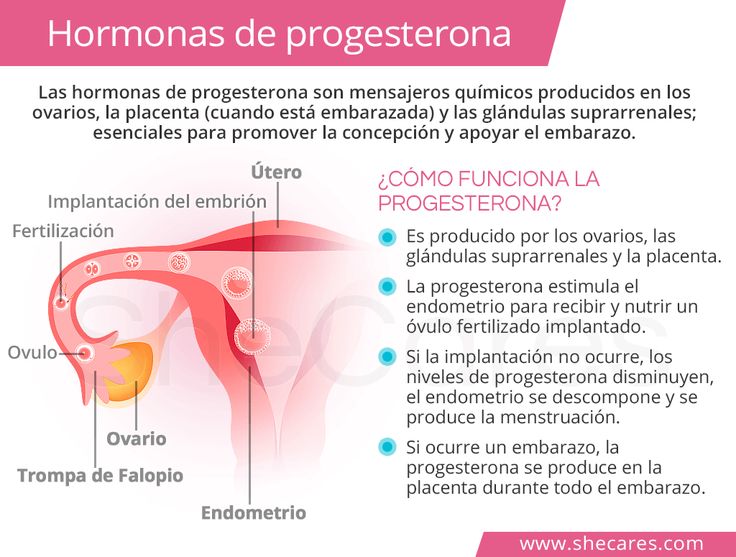
What happens to them during gestation? The organ "falls asleep" so that a new ovulation does not occur, and the eggs do not mature. corpus luteum appears, producing 2 types of hormones - estrogens and progesterone.
After 12 weeks of existence, the corpus luteum disappears and the placenta is formed. During pregnancy, blood circulation in the genitals increases. Due to this, the ovaries become larger, somewhat change their localization.
Can they get sick, and if so, why? The answer is in the next section.
Why the ovaries hurt - possible causes
When pain appears in the lower abdomen on the left or right, you need to understand what caused it. The reasons may be varied.
Physiological
- The introduction of the embryo into the uterine mucosa. From the very beginning of pregnancy on the 7th day of fertilization, unpleasant sensations appear in the lower abdomen, resembling pain before menstruation, due to the lowering of the fetal egg into the uterus with subsequent implantation.
 This is absolutely normal.
This is absolutely normal. - The appearance of stress on the ligaments of the uterus. Over time, as the size of the fetus increases, the uterus also grows, causing the tissues that support it to become tense. Pregnant women think that the ovaries hurt, although in fact, discomfort in the lower and sides of the abdomen is formed due to sprains. Pain occurs during physical exertion, sudden movements, or even in a relaxed state, when a girl spends a long time on her side.
- Number of pregnancies, age of the future mother. Most often, pain in the lower abdomen occurs in patients under the age of 25, and bearing a child for the first time. During the next pregnancies, expectant mothers almost do not complain about discomfort in this area.
- Hormonal changes. Under the influence of restructuring, discomfort similar to pain in the ovarian region may appear.
- Yellow body cyst. The condition is not considered a pathology: it occurs in the early stages up to 11 weeks.
 Education appears in the place where the female germ cell came out of the follicle. During gestation, the cyst enlarges, producing progesterone. When it reaches a large size, the formation stretches the ovarian capsule, forming discomfort and pain. Do not be afraid of this condition: it does not affect the course of pregnancy. The cyst disappears along with the corpus luteum at the onset of 12 weeks.
Education appears in the place where the female germ cell came out of the follicle. During gestation, the cyst enlarges, producing progesterone. When it reaches a large size, the formation stretches the ovarian capsule, forming discomfort and pain. Do not be afraid of this condition: it does not affect the course of pregnancy. The cyst disappears along with the corpus luteum at the onset of 12 weeks. - Artificial stimulation in IVF. After in vitro fertilization, the expectant mother complains of tingling sensations, pulling pain in the lower abdomen in the area of the ovaries.
- Relaxin production. From the 14th to the 39th week of the term, the body of the expectant mother produces a hormone. It helps to facilitate the passage of the child through the birth canal, the divergence of the pelvic bones. There may be pulling pains on the sides of the abdomen, in the lower back.
Pathological
During gestation, discomfort can be a manifestation of dangerous diseases in the expectant mother:
- Ectopic pregnancy.
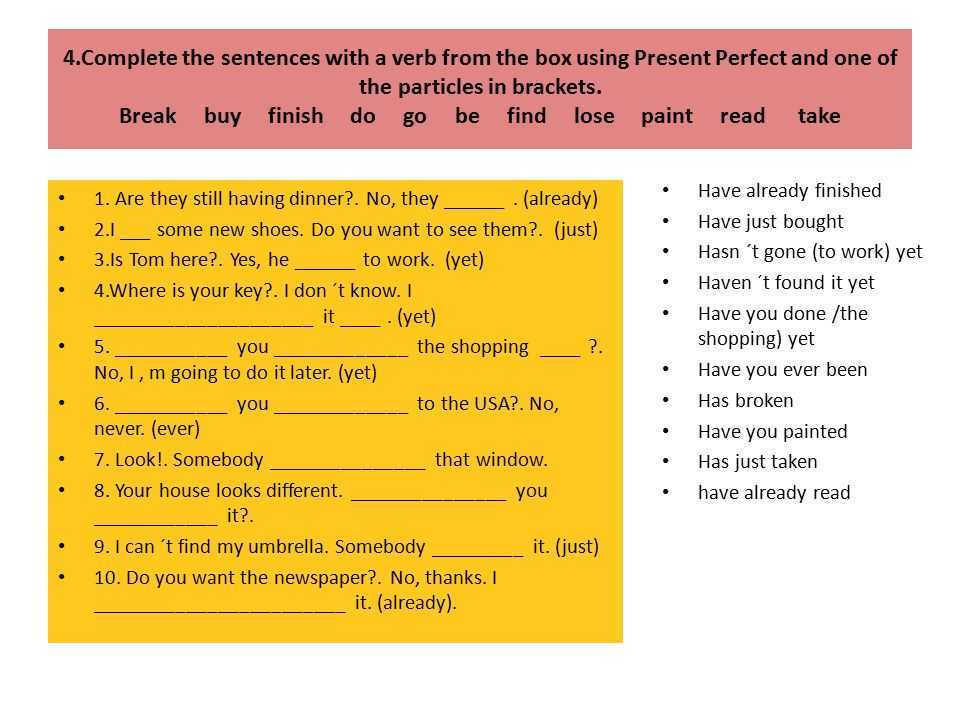
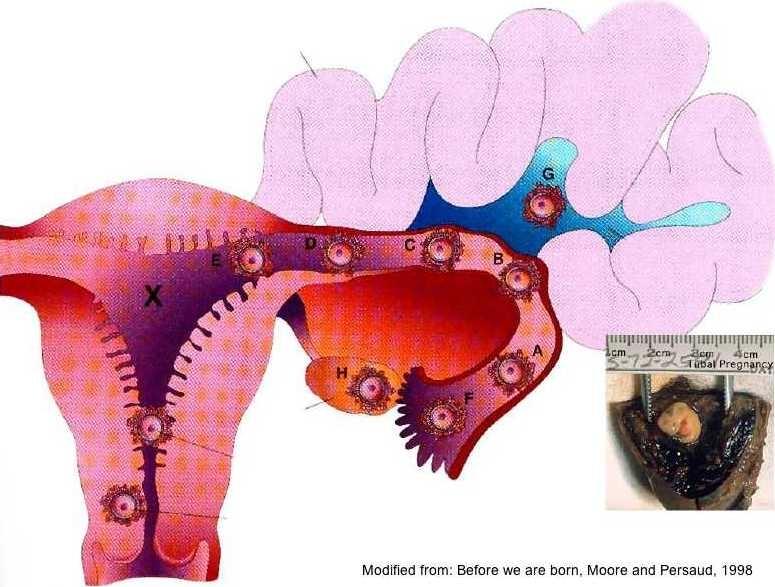
 This is an emergency condition that develops due to the attachment of the fetal egg not to the uterine mucosa, but to another organ. The most common ectopic pregnancy is the fallopian tube. All signs of normal gestation appear. If a woman has done a test, it shows a weak line, which, when the fertilization has occurred, may disappear when it is re-determined. The disease is characterized by a delay in menstruation, the appearance of cutting, acute pain in the abdomen at 5-6 weeks of gestation and is accompanied by red discharge or heavy bleeding. The embryo grows and may subsequently burst the tube.
This is an emergency condition that develops due to the attachment of the fetal egg not to the uterine mucosa, but to another organ. The most common ectopic pregnancy is the fallopian tube. All signs of normal gestation appear. If a woman has done a test, it shows a weak line, which, when the fertilization has occurred, may disappear when it is re-determined. The disease is characterized by a delay in menstruation, the appearance of cutting, acute pain in the abdomen at 5-6 weeks of gestation and is accompanied by red discharge or heavy bleeding. The embryo grows and may subsequently burst the tube. - Inflammatory processes of the ovary - adnexitis, oophoritis. Unpleasant sensations occur in the left or right side, lower abdomen or lumbar region, most often in the first or second trimester. Inflammation can be acute or chronic, the latter being considered more dangerous. During pregnancy, the disease makes itself felt, since the woman is most vulnerable during gestation.
 The development of the disease occurs as a result of a common cold, as well as when affected by sexual infections - chlamydia, mycoplasmas, cytomegalovirus, a fungus of the genus Candida.
The development of the disease occurs as a result of a common cold, as well as when affected by sexual infections - chlamydia, mycoplasmas, cytomegalovirus, a fungus of the genus Candida. - Apoplexy. During pregnancy, ovarian rupture occurs at the stage of formation of the corpus luteum. It is easily injured, sprouting new vessels. When a vessel is damaged, the blood forms a hematoma, which, increasing, breaks the organ. The most common rupture of the right appendage, as it is better supplied with blood compared to the left. Apoplexy occurs due to weight lifting, excessive physical activity, violent sexual contact, trauma, pathology of the vessels of the appendage.
- Rupture of an ovarian cyst. At an early stage, the formation is characterized by a pulling dull pain in the right or left side. When it bursts, fluid escapes into the abdominal cavity. There are strong, sharp pains, nausea and vomiting, body temperature rises. An equally dangerous condition is the torsion of the cyst leg, in which severe pain in the lower abdomen also appears.

Watch a video about ovarian cysts during pregnancy:
Non-obstetric
Sometimes discomfort in the area of the appendages is not associated with any disease in them.
Pathology of other organs occurs, and the pregnant woman believes that abdominal pain is associated with the ovaries:
- Digestion disorders. During gestation, constipation occurs due to malnutrition and non-compliance with the drinking regimen. Also, the problem with digestion is provoked by toxicosis: an aversion to many products with a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract is caused. After 30 weeks, the body of the expectant mother prepares for childbirth: progesterone is actively produced, which relaxes the smooth muscles of the organs.
 Along with this, the hormone acts on the smooth muscle fibers of the gastrointestinal tract - the walls of the intestine, the gallbladder. A woman is worried about belching, flatulence, a feeling of heaviness and discomfort in the abdomen.
Along with this, the hormone acts on the smooth muscle fibers of the gastrointestinal tract - the walls of the intestine, the gallbladder. A woman is worried about belching, flatulence, a feeling of heaviness and discomfort in the abdomen. - Inflammatory diseases of the kidneys, bladder. Pyelonephritis and cystitis are common causes of pain in the lower abdomen.
- Acute appendicitis. With pain in the right side, the pregnant woman may think that her right appendage hurts. In fact, the appendix has become inflamed, and the woman needs urgent medical attention. If a pregnant woman has a sore right side, she must be examined by a surgeon with a gynecologist.
How to deal with pain
What can be done to prevent ovarian pain? To begin with, understand why the symptoms arose. Only a doctor can accurately determine the cause of discomfort.
That's why a consultation with a gynecologist is a must. Even if a woman feels only pulling, unsharp pains, a visit to a specialist is necessary.
Ignoring the symptoms increases the risk to the health of the mother and baby.
In the early stages
If the discomfort in the abdomen is mild, you can try to eliminate them yourself.
Doctors recommend doing the following:
- Get into a comfortable lying position, try to relax completely until you feel better. If the cause of pain is nervous strain or fatigue, the symptoms disappear at rest.
- Cease any physical activity, especially that which involves heavy lifting.
- Try to avoid stressful situations, do not be nervous.
- If the pain in the abdomen increases or bleeding occurs, do not tolerate it and call an ambulance immediately.
In the later stages
If you feel discomfort in the genital area in the later stages, do not panic.
After consulting with a doctor, you will receive valuable recommendations that will be followed:
- If discomfort is associated with tension in the uterine ligaments, the expectant mother should apply a warm compress or something warm at a comfortable temperature, but not hot.
- Do moderate physical activity. It has a tonic and restorative effect on the female body.
- When the cause of pulling pains in the abdomen is indigestion, the first thing a pregnant woman should do is to review her diet, eliminating harmful foods that cause gas formation and constipation.
When to see a doctor
There are reasons for urgent medical attention:
- Increased pain: change from dull, pulling discomfort to cutting and sharp.
- The symptom does not subside for a long time.
- Spotting brown, red or pinkish discharge from the genital tract.
- Occurrence of bleeding from the organs of the reproductive system.
- High body temperature.
- Discharge from the genital tract whitish, yellow or green discharge with a foul odor.
- Sensation of "petrification" of the abdomen.
Treatment with folk remedies
During gestation, the expectant mother is forbidden to take many pharmaceuticals. Traditional medicine comes to the aid of a pregnant woman.
Traditional medicine comes to the aid of a pregnant woman.
According to women on the forums, "grandma's recipes" not only cope with painful sensations, but also do not harm the embryo. Nevertheless, alternative medicine should be used only after consulting a doctor. Some seemingly harmless herbal preparations can provoke contractions and miscarriage.
Proven recipes:
- Blueberry infusion. To prepare, take 1 tbsp. l. raw materials, pour a glass of boiling water and leave for about half an hour. The resulting drink drink ½ cup in the morning and evening.
- Infusion of wild rose berries with blackcurrant. Take the fruits in the same proportion, pour boiling water over them. Infuse the drink for about an hour, then strain it and drink instead of tea. Add some sugar if desired.
- Linden infusion. Prepare a small handful of tree fruit. Pour 1 liter of boiling water over them, leave for about 15-20 minutes. Strain the product and take 1 tsp.
 3 times a day.
3 times a day. - Melissa infusion . 4 tbsp. l. Pour raw materials with a glass of boiling water. Then leave the medicine to infuse for 1 hour. Strain and drink half a glass three times a day.
Before using them, be sure to consult your doctor in order to avoid negative effects on the mother's body and fetus.
Disease prevention
Doctors say that the main measure to prevent any painful manifestations during gestation is pregnancy planning.
It is necessary to give up bad habits, timely identify and cure diseases that, during gestation, can harm the health of the baby. This is especially true of sexual infections.
If the fallopian tubes have adhesions or synechiae, surgery will be required to cut them in order to prevent an ectopic pregnancy.
It is necessary to observe the regime of work with rest, avoiding overwork and fatigue.
Experts allow moderate physical activity, but heavy lifting, heavy exercise, violent sexual contact should be completely excluded.
It is recommended to spend more time outdoors, to eliminate any stressful situations. The expectant mother should eat right, making up a balanced diet.
Conclusion
Pain in the ovaries during pregnancy is quite common. This is not surprising, since the woman's body begins to rebuild, and the ovaries also undergo changes. To determine the diagnosis, the expectant mother must visit a doctor in order to exclude serious diseases and bear a healthy child.
Ovaries hurt during pregnancy: what does it mean
Diseases of the genital organs lie in wait for a woman at any age. Pain in the ovaries during pregnancy is dangerous, because the appendages play an important role in this process.
The appearance of discomfort in the lower abdomen requires an immediate consultation with a doctor in order to find out the cause of the pain and provide timely assistance to a pregnant woman.
In most cases, with a prompt visit to the clinic, expectant mothers manage to save the fetus and give birth to a healthy baby.
What happens to the ovaries during pregnancy?
In the female body, the ovaries play an extremely important role - it is thanks to this paired organ that the eggs are formed, and the general hormonal background is maintained.
When the egg successfully meets the sperm and attaches itself in the uterus, pregnancy occurs.
This becomes a signal for the cessation of the production of female germ cells for the near future, and the ovaries are now mastering a new function - in one of them a corpus luteum is formed, which is, in fact, a temporary endocrine gland.
The corpus luteum has a very important function during pregnancy - during the first trimester it produces the level of progesterone necessary for normal gestation.
In addition to qualitative changes in the ovaries, quantitative changes can also be noted. First of all, we note that the ovaries vary somewhat in size. With the intensification of blood circulation, they become a little larger, and also move from their usual position, leaning forward and shifting upward.
Causes of pain
During pregnancy, the ovaries continue to function, supporting the activity of the corpus luteum. Such a load on the appendages can provoke pain. Causes of pain can be grouped into three categories: physiological, pathological, and non-obstetric.
Physiological pain in the ovaries
Is a normal process. This is the body's response to some inconvenience that it begins to experience after the onset of pregnancy, however, such sensations are in no way connected with the development of a serious pathology.
Causes of pain can be as follows:
- Sprains of ligaments and muscles, which are provoked by displacement of internal organs due to the growth of the uterus. The ovaries during pregnancy do not hurt much, such pain is tolerable, aching in nature, not accompanied by other alarming symptoms.
- Awkward movements can also provoke discomfort in the ovarian region, but such pain is almost always understandable - women feel that it hurts due to a sharp turn, tilt, or other actions.
Pathological pains
Indicate that something is wrong with the ovary.
The causes of pathological sensations can be as follows:
- The presence of an inflammatory process is almost always accompanied by painful sensations. With mild or chronic inflammation, aching pain can radiate to the sacral spine, spread to the entire lower abdomen and intensify with urination.
- Ovarian cyst may be affected by pregnancy. Usually the pain is of a pulling nature and appears on the side where the affected organ is located.
- Ovarian apoplexy - rupture of the appendage, most often accompanied by increased pressure in it.
Non-obstetric pains
Discomfort in the appendages, which are associated with pathologies of other organs, but are manifested by the localization of the appendages. When such pain occurs during pregnancy, women may quite reasonably think that the ovary hurts.
In fact, the causes of non-obstetrical pain are as follows:
- Kidney problems, most often an exacerbation of a chronic pathology that existed before pregnancy.

- Exacerbation of cholecystitis.
- Bladder inflammation.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Appendicitis.
In any case, no matter what pain a pregnant woman has, she must be examined by a gynecologist. For example, if the right ovary hurts during pregnancy, this may indicate appendicitis, for which assistance should be provided on the first day of the development of the disease, or even earlier. Only with early diagnosis and timely treatment is a favorable outcome possible.
Pain in the early stages
If a woman has pain in her ovaries during early pregnancy, this can be due to several reasons:
- Cyst of the corpus luteum. Usually it does not pose a serious danger and develops along with the development of this gland. In most cases, in pregnant women, a cyst appears in one ovary, so pain is observed in one side. More about the cyst →
- Spontaneous abortion is an alarming cause of pain in the ovaries. The onset of a miscarriage is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the sacrum.
 More about spontaneous abortion →
More about spontaneous abortion →
Pain after IVF
In vitro fertilization is accompanied by a superovulation procedure, when the ovary must produce several eggs, as well as an increase in the size of the ovaries. This is necessary for a successful fertilization process.
Due to their growth, the ovaries become more mobile, which threatens them with involuntary twisting - one of the most common pathologies in IVF. If the ovary turns very strongly on its leg, this can lead to a cessation of blood supply, and then to necrosis of the appendage. Usually the pain is acute, the ovary can get sick suddenly.
Late pregnancy pain
In the last trimester, a pregnant woman's body prepares for childbirth. It would seem, why do the ovaries hurt during late pregnancy, if all nine months have passed without complications? Preparing for childbirth also provokes serious changes in the hormonal background of the expectant mother.
For example, the hormone relaxin, which is responsible for softening the cartilaginous and ligamentous tissues of the mother, and the divergence of the pelvic bones, exhibits increased activity. This hormone softens the cervix. All these changes also contribute to the appearance of discomfort in the ovaries, but doctors call such pains false and, in the absence of other indications, no treatment is prescribed.
This hormone softens the cervix. All these changes also contribute to the appearance of discomfort in the ovaries, but doctors call such pains false and, in the absence of other indications, no treatment is prescribed.
When should you see a doctor?
If pain of any nature occurs at any time, the woman must inform the doctor about it.
Sharp discomfort for several hours, as well as bleeding from the genitals, should cause an ambulance call.
Do not ignore the appearance of pain - if it does not pose a threat to the life and health of the child, the doctor will report this, and in the future such sensations will not cause panic for the pregnant woman.
If discomfort has become a symptom of a serious pathology, it must be immediately eliminated. A pregnant woman cannot and should not make diagnoses on her own or ignore alarming symptoms - each case is individual, and therefore requires the consultation of a narrow specialist.
What to do when pain occurs?
Tell your doctor if you experience any pain. Only a doctor will be able to find out the cause of the pain and prescribe the necessary drugs to eliminate them. For more serious pathologies, the doctor may decide on an operation.
At the initial stage, if the pain is not severe, the pregnant woman should go to bed, calm down, and rest until the discomfort disappears completely.
It is very important to stop any physical activity, especially associated with lifting weights, to eliminate all stress factors.
What to do if the pain is severe?
In the event of severe pain and bloody discharge from the genital organs, an ambulance should be called, as these symptoms indicate that a spontaneous abortion has begun. If severe pain is not accompanied by bleeding, you can drink a No-shpa tablet.
As soon as the pain subsides a little, the pregnant woman should visit a doctor. It is better to do this in the near future, since certain situations require urgent treatment.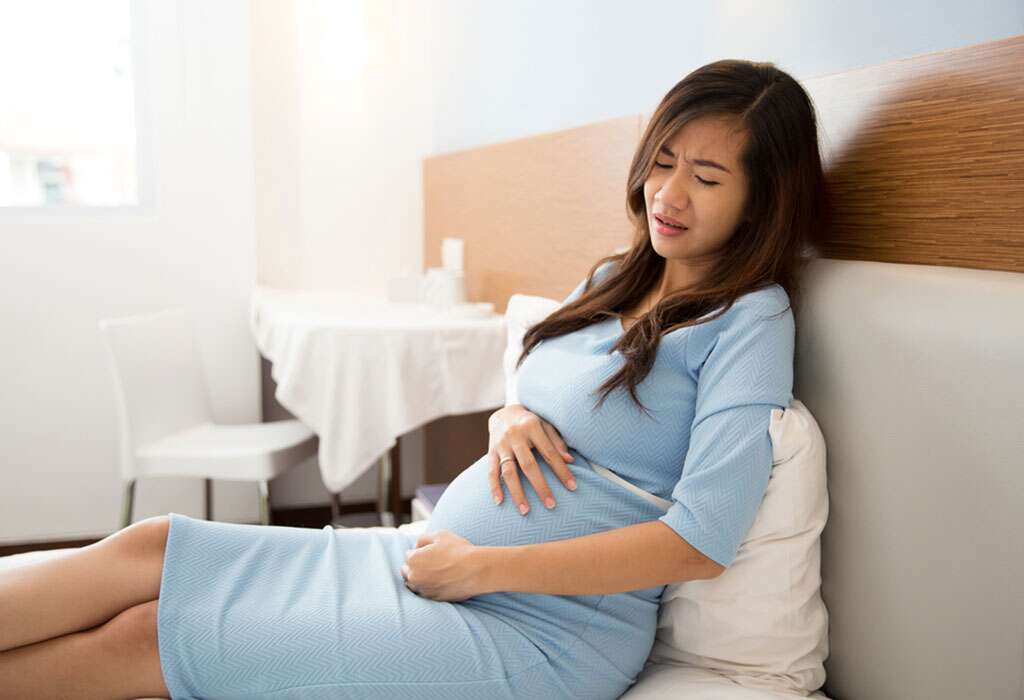
Particular attention should be paid if the left ovary hurts during pregnancy or the right one - such a one-sided character may indicate a serious pathology (adnexitis or cyst).
Preventive measures
The best measures to prevent such pains can be considered the good health of the woman before the onset of fertilization. That is why it is recommended to plan pregnancy in advance - get rid of bad habits, treat all diseases, especially the genital area, inform the doctor about chronic or hereditary pathologies, for example, allergic reactions.
When pregnancy occurs, it is very important to observe the regime of work and rest, to follow the doctor's recommendations at all stages of fetal development. A pregnant woman is recommended to regularly visit the fresh air, eliminate all stress factors, eat right and not overwork the body.
Anna Vishnyakova, doctor,
especially for Mama66.ru
Why does the stomach pull in the early stages of pregnancy?
Why does the stomach pull in the early stages of pregnancy? This question often worries expectant mothers, and at times leads to panic. When is discomfort pathology, and when is it normal?
When is discomfort pathology, and when is it normal?
Pregnancy is a special time for a mother and her baby. After all, the connection between them is inextricable, and every negative influence or stress affects both of them.
Possible causes of pain
Every woman dreams of an easy pregnancy and no cause for alarm. However, a very common complaint among pregnant women is pain in the lower abdomen of a pulling or aching nature.
Complaints are so common that it is necessary to clearly understand when pulling sensations during pregnancy are pathological and require immediate medical attention, and when they are completely physiological and require only general recommendations.
Of course, pain in the lower abdomen can appear at any stage of pregnancy, however, most often women notice their appearance in the early stages of pregnancy.
Painful sensations in the abdomen during pregnancy are very diverse both in subjective sensations and in their localization, in intensity of occurrence. Pain can appear both at rest and after any physical activity. Unpleasant sensations can manifest themselves in one place, or radiate to other areas.
Pain can appear both at rest and after any physical activity. Unpleasant sensations can manifest themselves in one place, or radiate to other areas.
Unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen are rarely avoided during pregnancy. These sensations can occur not only in pathology. During pregnancy, the uterus increases in size, there is a tension in its ligaments and muscles. In addition, there is a displacement of the pelvic organs. All this leads to the appearance of pulling or aching sensations in the abdomen. All these phenomena are manifestations of physiological changes that occur to a woman during pregnancy.
Of course, this state of fear does not cause and does not require any intervention on the part of the doctor. However, pulling pains in the lower abdomen are not always a physiological process. It happens that this indicates that the pregnancy proceeds with pathology and requires medical adjustment.
That is why, if there are pulling or aching pains in the lower abdomen, it is necessary to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist in order to accurately determine the cause of the pain.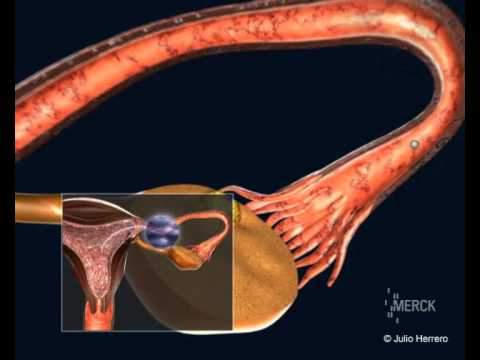
Never self-medicate. Remember that you are responsible not only for yourself, but also for the little man that you carry under your heart.
Abdominal pain during pregnancy can be:
- "obstetric";
- "non-obstetric".
Pain associated with pregnancy may be developmental:
- physiological changes during pregnancy;
- threatened miscarriage;
- missed pregnancy;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Pain not associated with pregnancy may occur with:
- inflammatory processes;
- pathologies of the digestive system;
- surgical diseases;
- diseases of other organs or systems.
Pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy as a variant of the norm
Not all pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy is a manifestation of pathology. Sometimes they can occur during the normal course of pregnancy.
As a physiological process, pain in the lower abdomen can occur in the following situations:
- sign of pregnancy;
- displacement of the pelvic organs by the growing uterus;
- stretching of the ligaments and muscles associated with the growth of the uterus.

Abdominal pain is a sign of pregnancy
Finding out that you are pregnant is now not a big deal, because there are pregnancy tests. In addition, a delay in menstruation can serve as evidence of pregnancy.
All this is good when menstruation is regular and delayed by at least 14 days. In this case, the pregnancy test may be positive. However, do not forget that not all tests are highly accurate, so it can show two cherished strips much later than we would like.
Therefore, it is necessary to pay close attention to the sensations of your body, because it signals the onset of pregnancy long before the manifestation of a delay in menstruation.
If you assume that pregnancy is possible, then listen carefully to your body: it can send you a signal in the form of pulling pains in the lower abdomen. At the same time, the pains will differ in their intensity: one woman will say that the pains are unbearable, the other will not notice them at all. Each woman is individual.
Each woman is individual.
If each menstruation is preceded by unpleasant pain in the lower abdomen or lower back, you may not understand that once again they are associated with the onset of pregnancy.
Pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy may be associated with the implantation process. To do this, you need to remember the process of fertilization of the egg by the sperm. After their fusion in the fallopian tubes, the fertilized egg enters the uterus under the action of the movement of cilia in the fallopian tubes. The uterine endometrium is a loose mass where a fertilized egg is implanted.
The process of implantation is the insertion of a fertilized egg into the endometrium of the uterus. At this time, there is a violation of the integrity of the endometrium, which may be accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen. In addition, sometimes slight dark bloody discharge may appear from the genital tract, which can be perceived as the beginning of another menstruation.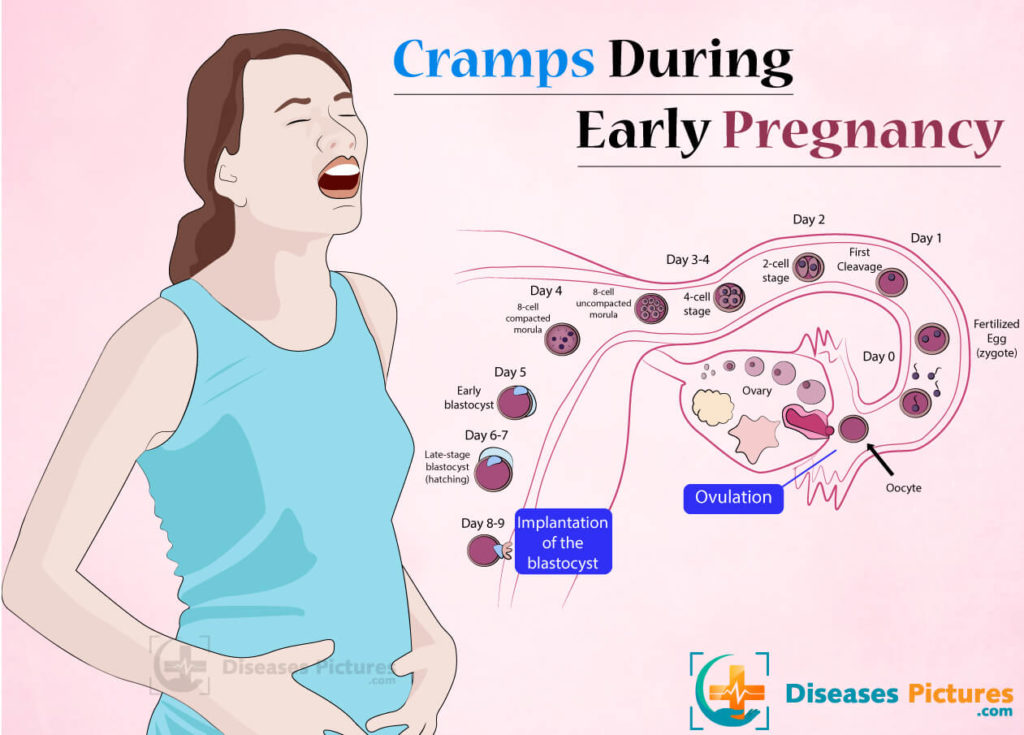
Threatened miscarriage
A fairly common cause of pain in the lower abdomen is a threatened miscarriage. This condition is individual and does not depend on physical exertion or complete rest, but on the condition of the woman and her unborn child.
Among the reasons that can cause a miscarriage are:
- severe physical exertion;
- sexual contact;
- malnutrition of the ovum;
- genetic disorders and other causes.
Of course, this is not evidence that a miscarriage will not occur with complete rest. Miscarriage can occur due to genetic abnormalities, and due to stress. No woman is immune from the threat of pregnancy loss.
That is why attention and sensitivity to the state of your body is so necessary, which will in every possible way send signals that the pregnancy is not going the way you want.
Threatened miscarriage is accompanied by:
- aching or pulling pains in the lower abdomen;
- aching or drawing pains in the small of the back or sacrum.

- bloody discharge from the genital tract.
If you have pain in the lower abdomen, you should consult a doctor, as a threatened miscarriage, if medical assistance is not provided, can turn into an abortion that has begun, the treatment of which is much more difficult, if not completely useless.
An ambulance should be called if:
- pain in the lower abdomen gets worse;
- pains begin to radiate to other areas;
- painful sensations do not go away for a long time;
- bloody discharge from the genital tract appeared.
Increased pain
If the pulling pains in the lower abdomen are weak, do not increase and do not radiate to other areas, then you can come to the antenatal clinic in the daytime on your own. This will not threaten serious complications of your condition.
If the pain becomes more intense, does not go away at rest, you should not self-medicate, take drugs without a doctor's prescription.
Do not put anything on the stomach. Both hot and cold application can contribute to the onset of a miscarriage. In addition, with the threat of termination of pregnancy, this manipulation will not remove the pain.
Localized pain
When a threatened miscarriage occurs, pain of a pulling or aching nature disturbs the pregnant woman in the lower abdomen.
If the pains have a clear localization in a certain place, most often on the right or left, then a mandatory consultation with a specialist is necessary, since an ectopic pregnancy or surgical pathology, such as appendicitis, may develop.
Bloody discharge from the genital tract
If bloody discharge from the genital tract has joined the pulling pain in the lower abdomen, urgent medical attention is needed. This phenomenon may indicate a miscarriage that has begun.
The discharge may be scanty, spotting or copious, dark or bright. In any case, you can not do without consulting an obstetrician-gynecologist.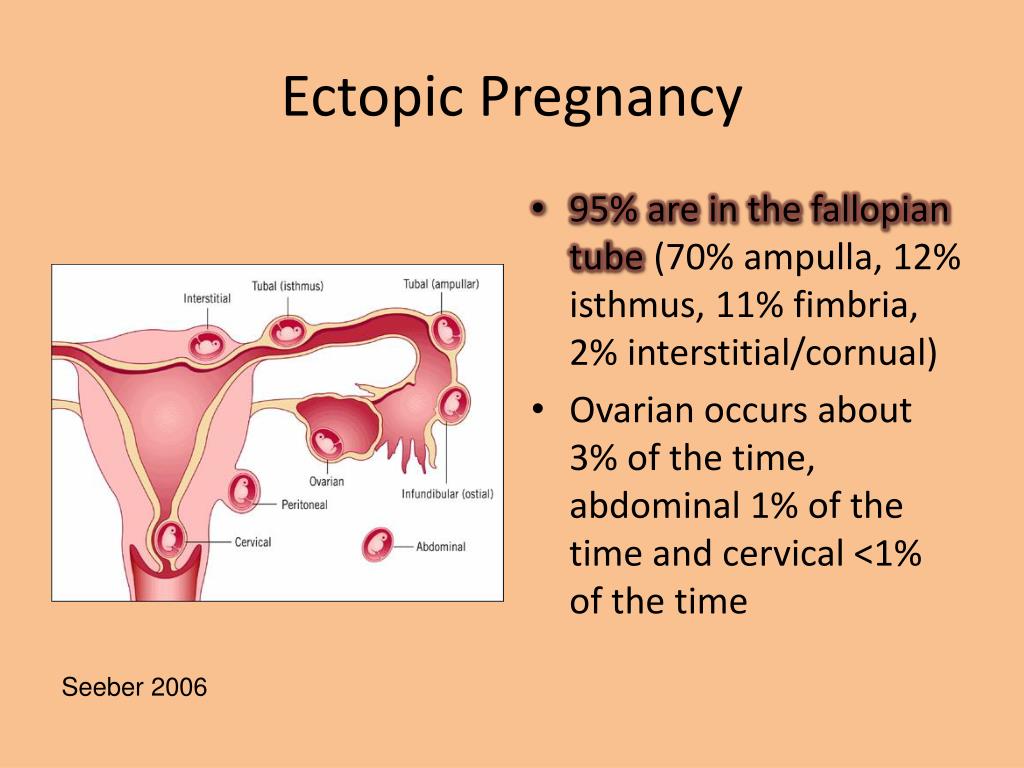
There are situations when there is no pain, but there is bloody discharge from the genital tract. This case also requires specialist advice.
Any bloody discharge from the genital tract may indicate a miscarriage. Only timely treatment can contribute to the preservation and prolongation of pregnancy.
In some cases, the appearance of bloody discharge from the genital tract may be a manifestation of a miscarriage, which requires immediate medical attention.
Miscarriage
The fertilized egg does not always develop correctly. In some cases, there is a cessation of its division and death. Most often, miscarriage occurs due to any mutations. At the same time, the woman does not suspect that the pregnancy has stopped.
However, the dead fetal egg begins to be rejected on its own. At the same time, there are pulling pains in the lower abdomen, which are soon joined by bloody discharge from the genital tract.
When a miscarriage is diagnosed, curettage of the uterine cavity may be indicated. Conservative management is also possible, but this can only be determined by a specialist after consultation.
Conservative management is also possible, but this can only be determined by a specialist after consultation.
Ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy most often occurs as a tubal pregnancy, when the fertilized egg does not reach the uterus, and the implantation process occurs in the fallopian tube. At the same time, the development of the fetal egg can continue for a long time without any manifestations, up to 12 weeks of pregnancy. However, most often such a pregnancy is interrupted at 6 to 8 weeks.
The fertilized egg develops and grows, which causes pain in the right or left side of the lower abdomen. The pains are unilateral, are obsessive, tend to increase.
In addition to pain in the lower abdomen, bloody discharge from the genital tract appears, and the pain begins to radiate to the leg from the side of the pain. There may be unpleasant sensations of pressure on the rectum. Medical surgery is the only way to save a woman's life. Preservation of pregnancy is impossible.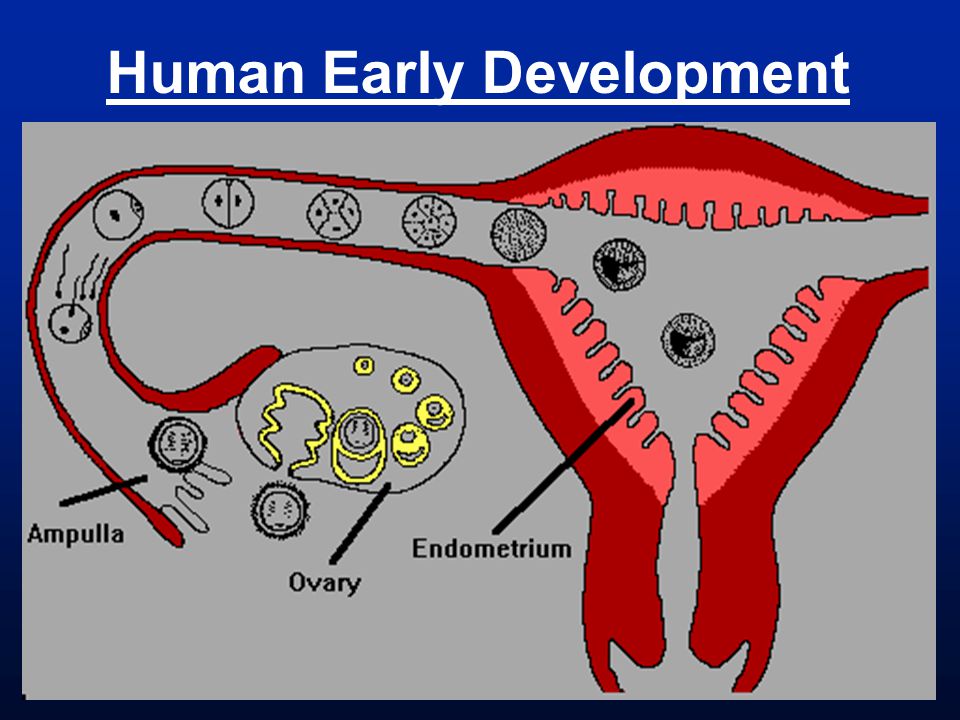
"Non-obstetric" causes of pain in the lower abdomen
Inflammatory processes
Among the "non-obstetric" causes of pain in the lower abdomen, the most common are inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs. If earlier it was believed that there could be no inflammation in pregnant women, now it has been proven that a decrease in the immunity of a pregnant woman awakens all pathological processes in her body.
Pain in inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs differ in their intensity. At the same time, they occur in the lower abdomen and most often have a pulling or aching character.
Pathology of the digestive system
Very often, pulling pains in the lower abdomen can occur in a pregnant woman due to problems with the digestive tract. During pregnancy, there is a decrease in intestinal contractility. In addition, there are significant changes in the hormonal background of a woman. Therefore, very often pregnancy is accompanied by constipation and bloating. To normalize digestion, a change in diet is recommended and mild laxatives can be taken.
To normalize digestion, a change in diet is recommended and mild laxatives can be taken.
Surgical pathology
Of the surgical pathologies that may be accompanied by pulling pains in the lower abdomen during pregnancy, acute appendicitis is the most common.
In the early stages of pregnancy, it is obligatory to differentiate obstetric and gynecological diseases from appendicitis, since it has similar symptoms. There are pains in the lower abdomen, which most often occur in the navel or stomach, and then descend to the right iliac region. Nausea, vomiting, fever joins. The only treatment is surgery. In this case, the pregnancy is preserved.
Diseases of other organs or systems
In addition to obstetric and surgical causes that can cause pulling pains in the lower abdomen in early pregnancy, other body systems may also be involved in the pathological process. The most common lesion is the urinary tract.
Cystitis
Cystitis due to the anatomical features of a woman can occur at any time and in any condition, so pregnant women are just as susceptible to it as non-pregnant women.