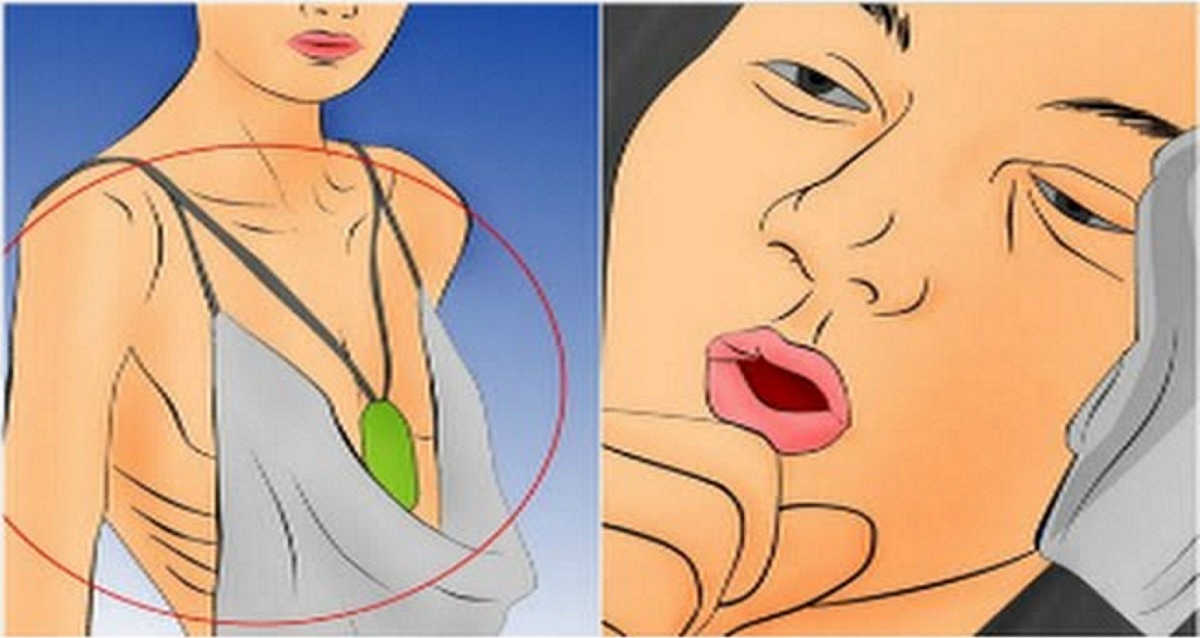
Skin is hot no fever
My Skin Feels Hot to Touch
Have you ever touched your skin and thought that it felt hotter than normal? There are a few possible reasons that this could be occurring.
When skin feels hot to the touch, it often means that the body’s temperature is hotter than normal. This can happen due to an infection or an illness, but it can also be caused by an environmental situation that increases body temperature.
Additionally, a specific area of skin may feel hot to the touch due to an increase in blood flow near the surface. This happens when the body is trying to address something like an infection, irritant, or insect sting. In this case, hot skin may also be accompanied by redness or swelling.
It’s important to determine what’s causing your skin to feel hot so that you can receive the appropriate treatment. Below, we’ll explore the common causes of why your skin may feel hot to the touch, some potential treatments, and when you should seek help.
There are several reasons why your skin could feel hot to the touch. Many of them are related to health conditions, while others can be associated with the environment. The common causes of hot skin include:
- fever
- heat-related illness
- high environmental temperature
- exercise or physical exertion
- wearing heavy clothes
- drinking alcoholic beverages
- medications that can cause fever, such as antibiotics
- vaccines that can cause fever after administration, such as the pneumococcal vaccine or the DTaP vaccine
- sweat gland problems
Some examples of specific conditions that may cause your skin to feel hot to the touch can include, but aren’t limited to:
- viral infections, such as the flu, measles, chickenpox, and infectious mononucleosis
- bacterial infections, like cellulitis, strep throat, and urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- infections that may be either bacterial or viral, including gastroenteritis, pneumonia, and meningitis
- chronic conditions, like rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease
- conditions related to the environment, like sunburn and heat stroke
- skin reactions, such as contact dermatitis and reactions to bug bites or stings
- other health conditions, including cancer and alcohol withdrawal
How you treat skin that feels hot to the touch will depend on what’s causing the condition. Below, we’ll explore some treatment options for some of the common causes of hot skin.
Below, we’ll explore some treatment options for some of the common causes of hot skin.
Fever
If a fever is present, it may be treated with fluids, over-the-counter (OTC) anti-inflammatories, such as aspirin or ibuprofen.
Anyone under the age of 17 shouldn’t use aspirin. None of these drugs should be used to treat environmental heat illness.
In addition to OTC anti-inflammatories and fluids, additional medications may be needed to treat the underlying cause of a fever. These can include things like antibiotics for a bacterial infection or medications to treat underlying conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Environmental causes
During exercise, be sure to stay hydrated by drinking water or sports drinks. Don’t wait until you feel thirsty to hydrate. If a person becomes overheated due to the environment or exercise, move them to a cool, shaded place and remove any outer layers of clothing.
Apply cool wet cloths to their skin. Placing cool compresses on the groin, neck, and armpits helps lower the body temperature. Provide cool fluids as frequently as the person can tolerate.
Provide cool fluids as frequently as the person can tolerate.
If they’re showing signs of heat stroke, call 911. In this case, fluids shouldn’t be given. An ice bath is recommended to help lower body temperature. If this isn’t available, follow the tips above on applying cool cloths and compresses to the skin until help arrives.
Skin conditions
The pain from sunburn can be treated by taking a cool bath or shower. Applying aloe vera or another moisturizer to the affected area may also help. If you’re experiencing swelling and pain, an OTC anti-inflammatory can work to ease these symptoms.
If a bug has bitten you, be sure to clean the area with soap and warm water. A cold compress can help with pain or swelling. You can also use OTC anti-inflammatories or antihistamines to help relieve symptoms like pain, swelling, or itching. Be sure not to scratch.
For something like contact dermatitis, start by applying OTC antihistamines or corticosteroid creams to the affected area. If your reaction is more severe or widespread, you may need to see your doctor for a stronger medication. Try to avoid scratching the area.
If your reaction is more severe or widespread, you may need to see your doctor for a stronger medication. Try to avoid scratching the area.
There are some potential complications of having skin that’s hot to the touch. What they are depends on what’s causing your condition. Some possible complications include:
Complications from fever
One possible complication of a fever is febrile seizures. These most often occur in young children. Although they can be troubling, most times they don’t lead to any lasting effects. You should still contact your child’s doctor if your child has a febrile seizure.
Dehydration can also be a concern with fever. This is when you’re not getting enough fluids or losing more fluid than you’re taking in. Symptoms to look out for include things like intense thirst, dry mouth, and less frequent urination.
Remember that fever is often caused by infections or other underlying illnesses, some of which can be potentially serious. Not seeking timely treatment for these can lead to the worsening of your condition.
Complications from heat
Overheating from high temperatures or exercise can lead to a variety of health problems. These can include dehydration and heat-related illness. A heat illness like heat stroke can rapidly worsen, leading to organ damage and even death.
Complications for skin conditions
One of the main complications from skin conditions like contact dermatitis or insect bites is infection. This can occur if bacteria get into a break in your skin, which can happen if you scratch.
Another possible concern is a life threatening allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. This is a medical emergency. Symptoms to look out for are swelling in the throat or face, difficulty breathing or swallowing, and hives.
Call 911 if the person:
- loses consciousness
- is confused, lethargic, or listless
- has a seizure
- is breathing rapidly or has a rapid pulse
- is nauseous or vomiting
- has a severe headache
- is experiencing chest pain or difficulty breathing
- has a stiff neck
- is in a condition that’s getting worse
- has symptoms of heatstroke
- has symptoms of anaphylaxis
Call a doctor if:
- the person is vomiting and unable to hold down fluids
- the skin forms tents when pinched and doesn’t return to normal
- an infant younger than 3 months has a fever of 100.
 4°F (38°C) or higher
4°F (38°C) or higher - a fever is over 102°F (39°C)
- a skin condition like sunburn or dermatitis affects a large area of your body
There are many potential reasons that your skin may feel hot to the touch. These can include an elevated body temperature or an increase in blood flow near the surface of the skin. Common causes of these things can be fever, skin reactions, or environmental conditions.
It’s important to try to determine what may be making your skin feel hot. That way, you can seek out an appropriate treatment. It’s always a good rule of thumb to contact your doctor if your condition doesn’t get better or gets worse with at-home care.
11 causes of feeling hot with no fever
Fever typically makes a person feel hot, but there are many other possible causes of this symptom. Environmental and lifestyle factors, medications, age, hormones, and certain emotional states can all affect body temperature. However, a persistent feeling of being hot sometimes signals an underlying health condition.
Depending on the cause, a person who feels hot may sweat excessively or not sweat at all. They may have flushed or irritated skin, or their skin may remain unchanged.
In this article, we look at 11 possible causes of feeling hot without a fever. We also explain the treatment options and when to contact a doctor.
A person can check that they do not have a fever by using a thermometer to measure their body temperature. A digital thermometer is the best option, as glass ones can be dangerous.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend that people measure their temperature when they are not taking fever-reducing medications, such as ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol).
If an adult’s body temperature is 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, they have a fever. However, if their body temperature is normal, at 98.6°F (37°C), they do not have a fever.
A child will have a fever if their temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C).
Learn more about fever in adults and children.
Many lifestyle and environmental factors can make a person feel hot but not produce a temperature. Factors include:
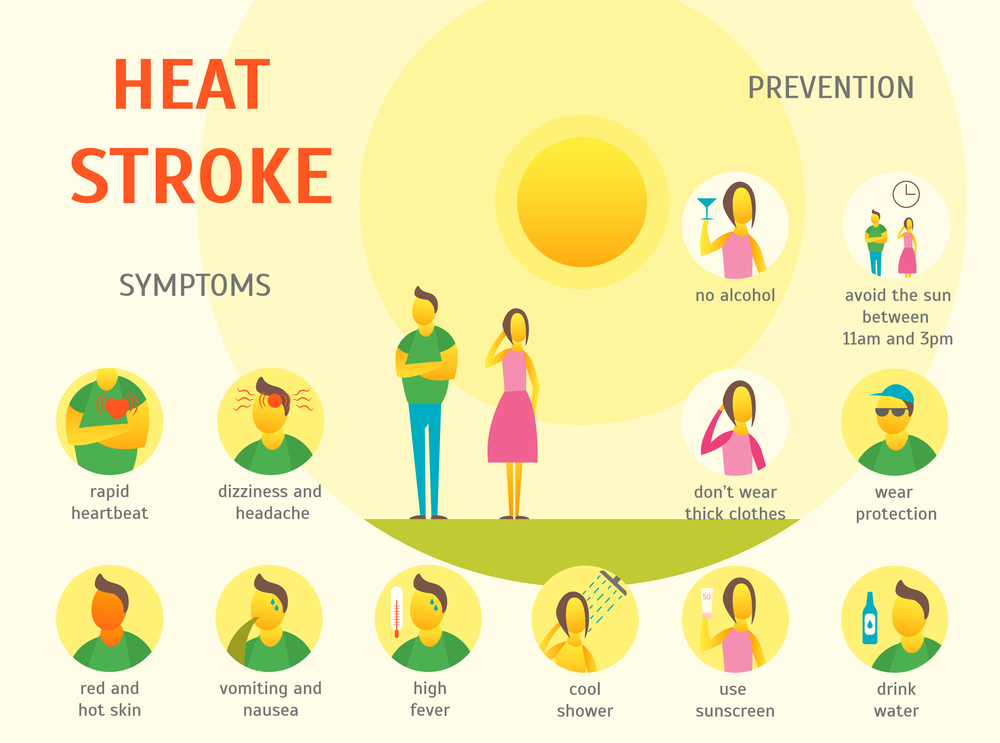
Heat-related illness
Hot or humid weather is taxing for the body, and it may affect some people more than others. In hot weather, a person might feel irritable and tired or find it difficult to concentrate.
In some cases, extreme temperatures or prolonged exposure to the sun can cause heat-related health conditions, such as sunburn, heat exhaustion, and, less commonly, heatstroke.
Sunburn occurs when the sun damages the skin, causing it to feel hot and sore. Heat exhaustion occurs when a person loses too much water and salt through sweating. The CDC notes that the symptoms of heat exhaustion include:
- heavy sweating
- cold, clammy skin
- nausea or vomiting
- tiredness or weakness
- a headache
- dizziness
- muscle weakness or cramping
Children with heat exhaustion may be excessively tired and thirsty, with cool, clammy skin.
A person with heat exhaustion should find a cool area, drink fluids, and stop all physical activity until they feel better. If a person does not cool down or get better within 1 hour, they should seek medical help immediately.
Untreated heat exhaustion can turn into heatstroke, which can be life threatening. The symptoms include confusion, fainting, and skin that is hot and dry or changes color. A person may also become unconscious. Due to this, anyone who is with someone showing signs of heatstroke should call 911 right away.
Learn about the differences between heat exhaustion and heatstroke.
Exercise or strenuous activity
Exercising or carrying out physical tasks can increase a person’s body heat, particularly if they:
- are not used to exercising regularly
- exercise or carry out physical tasks in hot or humid environments
- overexert themselves
The CDC states that athletes who train in hot weather should look out for the signs of heat-related illnesses and stop training if they feel weak or faint.
Avoiding exercise at the hottest times of the day, drinking more water, and pacing activities may help people avoid becoming too hot during exercise.
Food and drink
Certain foods and drinks can make people feel hotter than usual. These include:
- alcohol
- caffeine
- spicy food
- foods and beverages with a high temperature
People may feel extra heat in their skin or sweat more than usual during and after consuming these foods.
Clothing
Tight, restrictive, or dark clothing may increase body heat and prevent air circulation around the skin. Synthetic fibers may also trap heat and prevent sweat from evaporating. This can cause excessive warmth and increased sweating.
A range of conditions and disorders can also cause someone to feel hot. These include:
Anxiety
When a person feels stressed or anxious, they may experience physical symptoms, including feeling hot and sweaty. This happens during the “fight-or-flight” response, which increases the person’s heart rate and the blood supply to their muscles.
A person who is feeling anxious or stressed may also notice:
- increased heart rate
- heart palpitations
- tense muscles
- rapid breathing
Learn more about how anxiety affects the body.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism occurs when a person’s thyroid gland becomes overactive and makes too many thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormones affect how the body uses energy.
People with hyperthyroidism often experience heat intolerance, along with other symptoms, such as:
- shaky hands
- a rapid or irregular heartbeat
- diarrhea or frequent bowel movements
- difficulty sleeping
- fatigue
Anhidrosis
Sweating is how the body keeps cool. Anhidrosis describes the inability to sweat. This symptom can affect a small or large area of the body. It may be due to an underlying condition, a medication, or blocked or injured sweat glands.
If someone cannot sweat — either at all or across a large area of their body — this could be dangerous. A person with this symptom should speak with a doctor.
A person with this symptom should speak with a doctor.
Diabetes
The International Diabetes Federation explains that people with diabetes may be more sensitive to heat than people without the condition. This can be due to:
- Dehydration: People with diabetes become dehydrated more quickly during hot weather. Not drinking enough liquids can also raise blood glucose levels, which causes a person to urinate more. This further exacerbates dehydration.
- Complications: Diabetes can cause complications that damage the blood vessels and nerves, which, in turn, may affect a person’s sweat glands. As a result, a person may sweat less, making it more difficult for them to stay cool.
According to the CDC, the symptoms of diabetes include:
- frequent urination, especially at night
- feeling very thirsty and hungry
- blurry vision
- tingling in the hands or feet
- fatigue
- unintentional weight loss
People may feel hot for a variety of other reasons, including:
Pregnancy and menstrual cycles
The National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom states that it is relatively common to feel hotter than usual during pregnancy and to sweat more. Hormonal changes, which increase blood supply to the skin’s surface, are responsible for these symptoms.
Hormonal changes, which increase blood supply to the skin’s surface, are responsible for these symptoms.
It is also common for the body temperature to rise during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, which begins after ovulation.
Menopause and perimenopause
People may experience hot flashes during, before, and after menopause. The National Institute on Aging (NIA) explains that hot flashes occur due to changing estrogen levels. Hot flashes may last anywhere from 30 seconds to 10 minutes. Other symptoms of a hot flash include:
- flushed skin on the face and neck
- excessive sweating
- night sweats, which may disrupt sleep
- feeling cold or shivery afterward
Learn more about recognizing the signs of menopause.
Medications
The International Hyperhidrosis Society lists a wide range of medications that can cause heat or sweating as a side effect. Medications that might cause a person to feel hot include:
- analgesics, such as naproxen (Aleve) and tramadol (Ultram)
- cardiovascular drugs, such as amlodipine (Norvasc) and losartan (Cozaar)
- hormonal drugs, such as thyroid medication and testosterone
- gastrointestinal drugs, such as omeprazole (Prilosec) and atropine (Atropen)
- skin treatments, such as lidocaine (Xylocaine) and isotretinoin (Accutane)
- psychiatric drugs, such as tranquilizers and fluoxetine (Prozac)
- some antibiotics and antiviral drugs
If a person thinks that their medication might be causing side effects, they can speak with a doctor to discuss their options.
The treatment for feeling hot without a fever depends on the underlying cause.
People who feel hot due to environmental or lifestyle factors, such as sun exposure or dietary habits, may feel better if they adjust their daily routine. The CDC recommends:
- wearing lightweight, pale, loose-fitting clothing
- staying in air-conditioned spaces, if possible
- taking a cool shower or bath
- drinking plenty of fluids and replacing electrolytes lost through sweat
- avoiding spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol
These strategies may also help people who are pregnant and those experiencing hot flashes.
People who feel hot due to anxiety or stress may also benefit from relaxation techniques that calm the nervous system.
These include deep breathing, yoga, and tai chi. Stress can exacerbate hot flashes, so these techniques may also help people in perimenopause or menopause, according to the NIA.
A person experiencing frequent anxious thoughts may find a form of therapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), helpful for reducing the physical symptoms of anxiety.
However, if these strategies do not help, the individual may have a condition that requires medical treatment.
If someone frequently or continuously feels hot with no fever, they should speak with a doctor. The doctor may need to perform tests, such as blood or urine tests, to diagnose the underlying cause.
If someone is experiencing heatstroke or has symptoms of heat exhaustion that do not improve within an hour, it is important to seek emergency help.
People may feel hot for many reasons other than a fever. Some causes may be temporary and easy to identify, such as eating spicy foods, being in a humid environment, or experiencing stress and anxiety.
However, some people may feel hot frequently for no apparent reason. In such cases, it could be a symptom of an underlying condition. Anyone who is unsure why they are feeling hot with no fever should consider speaking with a doctor.
Fever
Fever and its features in children.
Promotion temperature is the most common symptom of the disease in children, each child has at least 1 time per year fever is noted. Temperature rise is also very common forces the use of medicines, all feverish children receive antipyretic means. This is facilitated by both the idea of many parents about the dangers of high temperature, and the desire of the doctor to alleviate the discomfort associated with febrile reaction or at least make appointment, the effect of which will be obvious.
Wrestling with fever is an important element of treatment, but not an end in itself, since lowering the temperature in most cases does not affect the course of the disease. That's why the desire to reduce the temperature by all means and keep it at normal level indicates only about a weak acquaintance with the causes and significance of fever.
Fever- an increase in body temperature that accompanies most infectious and some non-infectious (injuries, inflammatory, autoimmune and oncological) diseases.
Normal the child's body temperature fluctuates during the day from 360C to 370C.
Fever - a defensive reaction directed against the causative agent of infection. At t 38.50C and above, the synthesis of interferons is enhanced, protein synthesis, leukocytosis is stimulated. All these factors reduce the ability to reproduction of many microorganisms. Fever suppression reduces intensity immune response. Fever is dangerous at temperatures closer to 410 C - mainly in children from risk groups. With a high fever, metabolism increases sharply, oxygen consumption and the release of carbon dioxide, fluid losses increase, there is extra stress on the heart and lungs. Initially healthy child tolerates these changes easily, although experiencing discomfort, but in children with pathology (often the central nervous system and congenital heart defects) can worsen the condition significantly.
With a high fever, metabolism increases sharply, oxygen consumption and the release of carbon dioxide, fluid losses increase, there is extra stress on the heart and lungs. Initially healthy child tolerates these changes easily, although experiencing discomfort, but in children with pathology (often the central nervous system and congenital heart defects) can worsen the condition significantly.
There are "pink" and "white" (pale) fevers. "Pink" fever signals the correspondence of heat production to heat transfer, with it, the skin is pink, hot, moist to the touch, the child behaves normally. With "white" fever, the skin is cyanotic or marbled, often appearing "goose bumps" skin", acrocyanosis, cold extremities.
HAZARDS FEVER
Adverse phenomena caused directly by fever are extremely rare. The danger may be a disease that caused a fever that plays protective role. The main danger of fever is dehydration, which is easily prevented or corrected by the introduction of an additional amount liquids. Violation of microcirculation, the signs of which are a marble pattern skin, "goosebumps", cold extremities, are observed with "white" fever and require restoration of microcirculation. Fever is not harmful actions on the CNS.
K dangers of fever include the possibility of developing febrile seizures, which observed in 2-4% of those predisposed to children, more often at the age of 12-18 months and do not have an unfavorable influence on the central nervous system and its development.
In general, the hazards associated with fever, are largely exaggerated, with most infections the maximum temperature is set within 39.5-40.00 C, which does not threaten persistent health problems.
Fever in a child always indicates a disease, but its severity, as usually does not correlate with its severity. Many common viral (eg, rhinitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis, pneumonia) and bacterial (otitis media, urinary tract infection, impetigo) infections in immunocompetent individuals do not have a severe course, against the background of antibiotic therapy or symptomatic treatment, recovery is fast. Other infections (sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia, purulent infections of bones and joints, pyelonephritis) without treatment often lead to complications and sometimes even death. Most febrile diseases in children is associated with viral infections and those bacterial, which only briefly violate the health and do not pose a threat to the life of the child.
Most febrile diseases in children is associated with viral infections and those bacterial, which only briefly violate the health and do not pose a threat to the life of the child.
. Fever in a child under the age of 3 months of life requires close monitoring due to high risk of developing a serious bacterial infection.
"White (pale)" fever requires restoration of microcirculation.
Fever without catarrhal phenomena, rash and other visible local symptoms of infection common with urinary tract infection, in children 0-3 years of age may indicate the development bacteremia.
Save febrile fever (more than 38.5 C) for more than 3 days, especially with rapid breathing (including in the absence of catarrhal phenomena) may indicate development of pneumonia.
Hemorrhagic a rash (not blanching on pressure) with fever may indicate meningococcemia - in this case, emergency therapy is required.
Rigidity occipital muscles or their soreness, bulging of the fontanel on the background of fever indicates a CNS infection (meningitis).
Fever associated with abdominal pain and vomiting requires exclusion of appendicitis.
Fever with joint pain may be associated with bacterial arthritis, osteomyelitis.
Resistant fever with rash, changes in the oral mucosa, scleritis, an increase in lymph nodes requires the exclusion of Kawasaki disease.
Continuous (more than 2 weeks) fever requires examination to detect long-term ongoing infections, connective tissue diseases, immunodeficiency, oncological pathology.
TREATMENT FEVER
Fever is not an absolute indication for temperature reduction.
In cases where the reduction temperature is necessary, there is no need to strive to bring it to normal - enough decrease by 1-1.50С.
Indications to lower temperature:
In previously healthy children older than 3 months:
- at body temperature above 39. 00C -39.50C; and/or
00C -39.50C; and/or
- in the presence of a muscular or head pain;
- in shock.
In children under 3 months of age:
- at body temperature above 380C.
In children with heart, lung, CNS:
- at body temperature above 38.50C.
Uncontrolled the use of antipyretics, especially "course", creates the illusion well-being and causes a belated appointment of etiotropic drugs.
Selection antipyretics should be founded, first of all, on their safety, and not on the strength of the effect. Ideally, an antipyretic drug for children should have the ability to quickly and effectively reduce the temperature by at least 10C, available in liquid form and as suppositories, rarely cause side effects effects at therapeutic doses and have as wide a gap as possible between therapeutic and toxic dose.
This only two drugs, paracetamol and ibuprofen, currently meet this parameter.
B pediatric practice prohibited the use of acetylsalicylic acid and nimesulide.
REMINDER FOR PARENTS
*temperature - protective reaction; her should be reduced only according to the indications given above;
*adequate fluid administration a feverish child is more important than a decrease in his temperature;
*not important in antipyretics "strength", but safety, to improve the patient's condition, it is enough to reduce temperature by 1-1.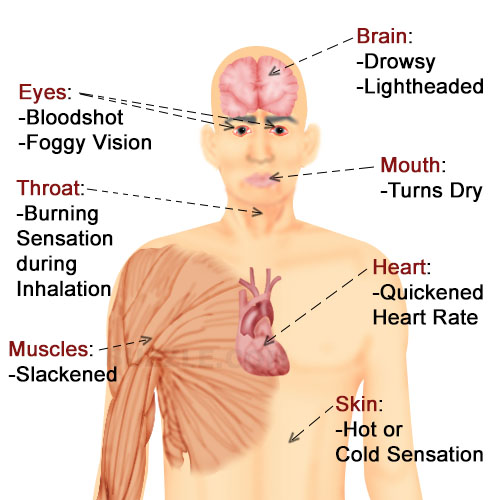 50C;
50C;
* paracetamol and ibuprofen are the most safe drugs, it is important to adhere to the recommended one-time and daily their dosages;
*do not prescribe antipyretic "course" to prevent a rise in temperature, because you can see the progress bacterial infection;
* should not be used for the same reason antipyretic drugs for longer than 3 days without consulting a doctor;
*with the development of "pale" fever with spasm of the skin vessels, the introduction of an antipyretic agent should be combined with vigorously rubbing the baby's skin until redness and immediately call a doctor.
Skin disorders and causes of skin damage
The course will introduce you to various types of skin diseases and conditions. We will talk about the main causes and countermeasures. You can learn how to care for burns and frostbite. Visual illustrations help you learn quickly.
We will talk about the main causes and countermeasures. You can learn how to care for burns and frostbite. Visual illustrations help you learn quickly.
At the moment you cannot watch or distribute a video lesson to students
This and other video courses must be purchased in the catalog and added to your personal account.
Get Great Deals
Course Overview Rough Skin and Its Causes
The skin is constantly exposed to various adverse effects.
The causes of skin damage can be divided into external and internal.
Skin diseases are often caused by several causes at once.
To identify a skin disease, the skin must be carefully observed and inspected. In this case, it is necessary to pay attention not only to the affected areas, but also to the unhealthy ones.
A complete patient history is necessary to establish the cause of the disease and determine the treatment.
This allows you to understand the changes that influenced the development of the disease.
A common skin condition is skin fragility.
Occurs due to mechanical action and may cause dermatitis.
Scratches, diaper rash, peeling of the skin, burns, frostbite, etc.
In addition, the skin is affected by various microorganisms, bacteria and viruses that cause skin diseases. These include lichens, scabies, warts, blackheads (pimples) and fungal infections.
Let's take a closer look at skin wounds and these diseases.
Bumpiness is a superficial injury to the outer covering of the skin caused by friction or pressure from clothing, shoes, belts, etc.
If there is a possibility that the itchy spot will reach, for example, the soles of your feet, after bathing in potassium permanganate, dry the itchy spot, sprinkle it with a powder or grease it with a fat cream.
Instability - an inflammatory disease caused by irritation of skin secretions (and then sebum), damage to skin folds, fungi. Instability occurs most often in natural skin folds.
Instability occurs most often in natural skin folds.
In order to get rid of this disease, it is necessary to lubricate the damaged areas of the skin with special creams.
And for prevention, it is important to observe the rules of personal hygiene and use special products, such as talc. Wear underwear only from natural and breathable materials.
Burns - damage to body tissues due to the action of high temperatures and certain chemicals (alkalis, acids, salts of heavy metals).
The severity of a burn depends on several factors, including the area and depth of the burn.
The combustion area can be roughly determined as follows. It is said that the surface of the skin on the hands is about 9%, on the legs - about 18%, on the chest, back, abdomen and waist - about 9%. That is 18% on the front of the body and 18% on the back of the body.
If the affected area exceeds 10% of the entire body, burn shock is inevitable.
There are four degrees of depth of burn injury.
1 skin redness
11 blisters.
111 Carnity full thickness leather.
1 V degree of carbonization of the structure
The larger the area and the deeper the tissue damage, the more severe the injury.
first aid for burns
High burn temperature requires immediate cooling of the affected skin (replace cold water jet, apply ice). Treat burned skin several times a day with a special spray designed to treat superficial burns.
Second degree burns Never pierce as air bubbles will form and this will protect the surface of the burn from infection. Apply a sterile dressing (sterile bandage or iron bandage) to the burned area. Then see a doctor.
the flame burns requires rapid removal and amputation of clothing from the victim. Pour the burned part of the body with cold water for 15-20 minutes.
For extensive burns Cover the victim with towels, sheets, tablecloths, etc. Give water and 1-2 analytical tablets.
Give water and 1-2 analytical tablets.
Call an ambulance or transport to a medical facility.
Fraud - injury to any part of the body under the influence of low temperatures (up to death).
There are different degrees of frostbite.
(lightest). The skin in the area of the burn is pale, red, hot, followed by swelling.
Level II fluff occurs in more severe cold weather. In the early stages, there comes a turning point when the skin becomes less sensitive. A few days after the injury, air bubbles form, which are filled with transparent contents.
Frostbite occurs with prolonged exposure to cold. The bubble is filled with bloody substance and has a bluish-gray bottom. I have sensitive skin. As a result, all components of the skin die off.
Fruits IV degree occur after prolonged exposure to cold, which leads to a decrease in temperature inside the tissues. All layers of soft tissues are dead, bones and joints are often affected. The damaged part of the limb is bright blue.
The damaged part of the limb is bright blue.
So what should we do when it gets cold?
Warm the casualty first in a warm room. Apply heat to the affected area gradually, slowly, and mostly passively. Do not rub your hands, tissues, alcohol, or even snow on frostbitten areas.
After cooling, wrap the affected area with a cotton-gauze bandage (7 folds) to acclimatize it to heat and prevent rapid heating of superficial tissues.
To prevent frostbite, refrain from going outside in extreme cold and wear warm clothing.
Eat hot food and avoid alcohol (which increases body heat dissipation). After a long journey, take a hot bath and drink hot tea.
Therefore, we examined those with the most skin lesions.
skin diseases.
Synovitis is a fungal parasitism of the skin.
A round-oval inflammatory plaque (or a single point) covered with scales or crusts appears on the skin. Patients usually do not notice anything, except for a slight itch.
When the scalp is affected, all hair is cut off at a height of 4 to 8 mm, forming a large rounded decorative bald spot, and the concomitant disease is called lichen surgery.
Prevention is to avoid contact with stray cats.
They are regularly examined by a veterinarian.
We also strictly adhere to the rules of personal hygiene.
Scabies is an infectious skin disease caused by small parasites, the scabies mite and the scabies worm.
Symptoms are itching and rash, often crusts that form when the infection is scratched.
Usually they are in detention from evening to night. This is caused by an allergic reaction to dust mites and their droppings.
Scabies spreads from sick to healthy people. Often occurs on the arms, which are the most exposed parts of the body.
In case of this disease, you should immediately consult a doctor
To prevent scabies, it is necessary to observe the rules of hygiene for washing exposed skin with soapy water and washing hands before each meal. Wash in the bathroom or toilet at least once a week.
Wash in the bathroom or toilet at least once a week.
The next disease to consider is the very famous wart, a viral skin disease.
The virus enters the skin through cuts and scrapes. As a result, the division of skin cells becomes active, and a tubular thing is formed, that is, a wart.
Infection with pathogens is confirmed by contact through objects used by the patient.
The only way to treat warts is to remove them. Today, there are several ways to remove warts. Liquid nitrogen is the most common removal method.
fungal skin disease
Fungi that enter the human body affect the skin, mucous membranes and internal organs, multiply and cause disease.
It is spread through essential items such as towels, washcloths, small items such as nail polish, and shoes. Infection is also common in public places (bathrooms, swimming pools, gym showers, etc.).
In order not to get sick with mycosis, it is necessary to observe personal hygiene. Since the feet cannot sweat, it is worth using talc, special creams. wear shoes and clothes.
Since the feet cannot sweat, it is worth using talc, special creams. wear shoes and clothes.
Also avoid walking barefoot in public places. Bring your own beauty and care products.
Consult a dermatologist for infections.
Skin diseases also include diseases of the sebaceous glands. Inflammatory nodules (pimples) are red, often painful and non-inflammatory, painless black dots. Occurs with blockage of the sebaceous ducts and increased secretion of sebum.
Pimples on the face are often caused by hormonal changes in the body. Of course, the most striking example is adolescence. In a person's life, this is the time when the action of hormones becomes active.
In addition, certain medications, the type of work you do, and the air you breathe can contribute to acne.
How to get rid of this disease?
Acne should be possible, because any stimulation leads to their development. Cosmetologists categorically forbid non-professionals to squeeze out pimples. Such an intervention can bring scars not only to the formation of new, more complex acne, but also significantly complicate the fight against them.
Such an intervention can bring scars not only to the formation of new, more complex acne, but also significantly complicate the fight against them.
Generally recommended by experts.
Review your diet when your sebaceous glands are most active. That is, excluding fats, sweets and simple carbohydrates.
Wash your face and hands frequently.
Use antiseptic masks and creams regularly. Protects pores and prevents dirt particles and bacteria that cause skin irritation from entering.
tattoo and perforations.
Remember, not everything that is fashionable is healthy. Some fashion crazes can be harmful or deadly.
Dyes used (especially red ones) can cause complications such as allergic reactions (skin redness, swelling, itching) and dermatitis.
Cases of tetanus, tuberculosis and even AIDS are known.
So think twice before getting a tattoo or piercing.
Finally, remember that the best way out of an unpleasant situation is to avoid it.
To prevent various skin diseases, some very important rules must be observed.
These are personal hygiene, alcohol consumption and proper nutrition. how to work and relax. Rest is as important as work. You should spend more time outdoors. Avoid stressful situations and get more positive emotions.
Course content Basic skin rashes: scratches, diaper rash, burns, frostbite.
As well as skin diseases: Trichophyton; Scabies; Skin diseases. Warts, acne, fungal infections.
In addition to studying the root causes of these diseases, we are also implementing preventive measures.
What is psoriasis? Analyze causes, diagnosis, treatment methods, etc. from the articles of Dr. Sergei Vladimirovich Medvedev, who has 34 years of experience as a dermatologist.
Article by Dr. Sergey Vladimirovich Medvedev was written by literary editor Margarita Tikhonova, scientific editor Sergey Fedosov and editor-in-chief Rada Rodachina.
Definition of disease.
 Causes of disease
Causes of disease Psoriasis is a chronic disease affecting the skin, sometimes nails, joints and internal organs. Itchy and pink rashes-papules appear, which can merge into larger plaques [1]. Papules rise above the surface of the skin. It is covered with silvery scales that are easily detached.
Often accompanied by impotence, ejaculation and Reiter's syndrome. Extensive psoriasis can lead to psoriatic arthritis.
risk factor
The cause of psoriasis has not yet been fully established. Risk factors for developing the disease include:
- Microbial factors - various mold fungi, mycoplasmas.
- neuropsychic trauma, stress
- Endocrine diseases - diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease.
- Development of chronic infections (in particular, streptococcal).
- Immunodeficiency states.
- Lipid and protein metabolism disorders
- skin and joint injuries
Is psoriasis contagious?
Psoriasis is not contagious. Many researchers pay attention to the family nature of psoriasis and are aware of its genetic nature. Moreover, it is not the disease itself that is inherited, but the predisposition to it.
Many researchers pay attention to the family nature of psoriasis and are aware of its genetic nature. Moreover, it is not the disease itself that is inherited, but the predisposition to it.
If you experience these symptoms, contact your doctor. Do not self-medicate - it is harmful to health!
Symptoms of psoriasis
The first symptoms of psoriasis are shiny, pink, scaly patches on the skin. Plaques are simple, grow above the level of healthy skin and appear in the area of the elbows and paranasal sinuses.
Psoriatic plaques often appear on the skin of the knees, elbows, chest, abdomen, back and scalp, but as the disease progresses, they can appear on any other, more amazing, capsule.
Initially, these are small papules, 3-5 mm, bright pink. It gradually grows, becomes covered with silvery scales and fuses into large structures called plaques [4].
Fresh papular components are usually bright red, while the "old" ones are more faded. In the early stages of psoriasis, papules do not exfoliate. It is an overloaded frontier, a by-product of growth [10].
In the early stages of psoriasis, papules do not exfoliate. It is an overloaded frontier, a by-product of growth [10].
Psoriasis is characterized by the Auspitz triad. This triad is observed when the surface of the papules is exposed with a sharp object. It includes three things.
- The stearin fleck phenomenon is a layer of many silvery-white scales that are easily detached when the wings are unfolded.
- A symptom of psoriatic membranes is a disordered surface consisting of layers that open after delamination of the underlying lamina.
- The phenomenon of "bleeding" is the exposure of subsurface capillaries in the form of small bloody spots after exfoliation of the psoriatic membrane [6].
Symptoms of different types of psoriasis
Clinical variety of psoriasis.
- Sandy psoriasis - expressed as pale pink, slightly infiltrated spots. It's like archery.
- Irritant psoriasis - occurs due to exposure of the skin to irritating environmental factors (sun, cold, heat) and irritating drugs.
 The color of the plaque becomes more pronounced, it increases in size, grows more on the surface of the skin, forming reddish strands along the edges.
The color of the plaque becomes more pronounced, it increases in size, grows more on the surface of the skin, forming reddish strands along the edges.
- Seborrheic psoriasis - often found in patients with seborrhea. The clinical picture is very similar to seborrheic eczema.
- Exudative psoriasis: Quite common. Occurs in combination with excessive secretion of inflammatory fluid. Eliminates the formation of flakes and turns them into cocoa flakes.
- Psoriasis of the palms and soles - presents with normal plaques and palms or hyperkeratotic masses resembling calluses or cerebellum.
- Ovarian psoriasis is a rare disease. The rash consists of white army nodules with a funnel-shaped induration in the center.
- Mucosal psoriasis is a rare disease. Occurs on the mucous membranes of the mouth and bladder. Appears as gray-white lobules with a red border [10].

Frequency of psoriasis symptoms
Psoriasis is characterized by periodic exacerbations. Often happens from autumn to spring.
Pathogenesis of psoriasis
Dermatitis is an inflammatory process associated with the action of immune T-cells. This inflammation promotes the proliferation of keratinocytes, the primary cells of the epidermis [15].
Psoriasis, a type of skin disease, is a chronic inflammatory disease. It progresses with the involvement of microbial pathogens, and can also be associated with the skin surface.
Everything that occurs in the skin under the influence of pathogens is a typical inflammatory reaction in the early stages of RTCD.
- Rubor - redness.
- Volume - bumps, swelling.
- Fever - fever, fever.
- Dolor - Pain.
- Functia laesa - Violation of function.
Redness and thickening of the skin at the site of injury, itching, development of keratinization and subsequent formation of scales - all this is a manifestation of the inflammatory process, a protective reaction of the body aimed at combating microbial pathogens. Without timely outside help, the body is often damaged.
Without timely outside help, the body is often damaged.
Some scientists suggest that there is a genetic predisposition to disruption of cell division. This violation leads to cell death and keratinization, followed by cell proliferation and the appearance of a large number of unexcised epithelial cells. However, this theory does not contradict the microbial theory mentioned above.
Classification and stages of development of psoriasis
There is no generally accepted classification of psoriasis.
Traditionally, four types are distinguished.
- Psoriasis vulgaris - seborrheic, follicular, warty, exudative, bullous, palmoplantar psoriasis, psoriasis of the mucous membranes.
- Pustular psoriasis.
- Psoriatic erythroderma.
- Psoriatic arthritis [2].
Underlined according to ICD-10.
- L40.0 Psoriasis (nummular and plaque psoriasis) is common.
- L40.1 Systemic impetus psoriasis (impetitis, tsumubushi disease).

- L40.2 is resistant.
- L40.3 Pustules on palms and soles.
- L40.4 Breeds of psoriasis.
- L40.5 Psoriatic arthritis
- L40.8 Other psoriasis
- L40.9 Psoriasis is not suitable [21].
Complications of psoriasis
Without timely and appropriate treatment, psoriasis begins to affect vital organs and systems such as joints, heart, kidneys and nervous system. These conditions can lead to disability and even death.
What is psoriatic arthritis?
Psoriatic arthritis is the most serious form of psoriasis because it is often disabling [16].
Doctors treat this complication more often. Occurs as a result of inflammatory changes in the joints.
Hands, wrists, feet and knees hurt the most. Over time, it can also migrate to the hip, shoulder, and spinal joints. As the joint advances further, the muscle begins to hurt. Patients complain of stiffness, especially in the morning. Body temperature in such people is often elevated during the day [14].
Body temperature in such people is often elevated during the day [14].
The clinical picture of psoriatic arthritis is similar to that of ordinary arthritis: first pain, then swelling, stiffness and limitation of movement. A characteristic sign of this complication is a rustic finger. This is probably because all interfaces are defeated.
Other complications of psoriasis
Psoriatic erythroderma is somewhat less common. This symptom occurs with complete skin lesions. Patients complain of itching and burning, extensive rejection of old tissues, severe skin reactions to temperature changes.
The next most common is psoriasis. Secondary infections such as staphylococci and streptococci join this complication. Clinical pustular psoriasis is accompanied by the appearance of buckwheat-sized pustules. Pustules can occur in various places. It grows on the surface of the skin, grows quickly, merges easily. The symptoms present are associated with high fever and signs of severe poisoning.
Damage to internal organs in psoriasis is currently extremely rare. As a rule, it is focused on people leading a social lifestyle. In the reproductive system, the kidneys, bladder mucosa and urethra are most often affected. As a result, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, cystitis, urethritis develop.
On the part of the heart, psoriasis can cause damage to the mitral valve, inflammation of the heart muscle and the outer lining of the heart - myocarditis and pericarditis. When the nervous system is damaged, patients complain of a crawling sensation, increased irritability or depression, constant fatigue, drowsiness, lethargy [13].
Diagnosis of psoriasis
Terms of medical examination
When the first symptoms of psoriasis appear, bright pink spots with a rough surface, you should consult a doctor.
Preparation for medical examination
Do not apply medicated ointments to the skin 3 days before the visit. Otherwise, no special training is required.
Psoriasis is a well-known disease that is easy to diagnose by its appearance. In many cases, patients can be diagnosed, as they say, "from the backyard." If necessary, the doctor will scrape the surface of the skin to detect the Auspitz triads.
Doctoral candidate of medical sciences OV Teretsky together with co-authors proposed a diagnostic method developed according to the American College of Rheumatology. It includes the following tests:
- Complete blood count (including platelets).
- Complete urinalysis.
- Acute biological reaction - C-reactive protein and rheumatoid factor
- Immunoglobulins - IgA, IgG, IgM, IgE)
- Complement fixation reaction with Neisseria gonorrhoeae-Chlamydia antigen.
- Answer by Wright and Heddelson.
- picacoagulation - assessment of blood clotting.
- Blood tests for borreliosis and toxoplasmosis (as indicated).
- Blood test for HLA [1] .
- However, there are many diseases that appear under the name of psoriasis.
 In this regard, differential diagnosis between blast syphilis, Reiter's syndrome, neurodermatitis, pink lichen, systemic lupus erythematosus and seborrheic eczema is especially necessary [7]. To do this, use:
In this regard, differential diagnosis between blast syphilis, Reiter's syndrome, neurodermatitis, pink lichen, systemic lupus erythematosus and seborrheic eczema is especially necessary [7]. To do this, use:
Biopsy - piercing a piece of skin with subsequent histological examination.
- Laboratory diagnostics. Often used to differentiate between psoriasis and bladder syphilis.
- Get blood tests for other potential infections and make better choices of antibiotics.
- Instrumental diagnostics is used mainly in complex forms of psoriasis with damage to the joints and internal organs. These include x-rays of the joints and ultrasound of the heart, kidneys, and bladder [2].
Are there effective treatments for psoriasis?
Treatment of psoriasis
Psoriasis is a persistent, relapsing disease, but it can be completely cured if you consult a dermatologist in time, who can identify the true cause of psoriasis.
 In the last decade, a number of systemic and local drugs have appeared, aimed at eliminating the cause or inhibiting the mechanism of the onset of the disease. Drugs that interact via chemical signals (cytokines) have proven to be very effective. They eliminate the increased proliferation of creatinine cells in the skin [9].
In the last decade, a number of systemic and local drugs have appeared, aimed at eliminating the cause or inhibiting the mechanism of the onset of the disease. Drugs that interact via chemical signals (cytokines) have proven to be very effective. They eliminate the increased proliferation of creatinine cells in the skin [9]. phototherapy
In 1994, the team of the Department of Dermatology and Vascular MAPO St. Petersburg published a method of treating psoriasis with ultraviolet blood irradiation - ultraviolet blood phototherapy.
Since ancient times, sunlight has been known to be effective for skin with many conditions, including psoriasis. At the beginning of the 20th century, German scientists suggested that "ultraviolet rays have a therapeutic effect and act on exposed skin, so this effect most likely occurs when exposed to ultraviolet rays in the blood." After all, it is also a kind of fabric. Hypothesis supported the first UFO blood exposure session in Germany in Germany at 1924 year.
The therapeutic effect of ultraviolet blood is accompanied by a profound structural change at the molecular and atom level, and this is reflected in the immunosuppressive organs, spleen, bone marrow and lymphatic tissue. These changes are recognized as organ alarms, and as a result, immune complexes are produced 10 times more. In this case, ultraviolet rays are a kind of "junk" that quickly boosts the body's defenses to fight the disease.
Ultraviolet RT treatment is also noticeable. This treatment is important because psoriasis is chronic and has many visceral complications from various microorganisms. The longer the microorganisms in the body, the wider the habitat. This small creature on the blood and lymph will capture more and more anatomical parts. When you hit the tissue, you try to get as deep into the cells as possible. Hence, they form a microcolony protected by a debris of dead or damaged cells and a leukocyte axis. Due to this, microorganisms may not work for many years of antibiotics. It easily complements nutritional deficiencies and introduces an animation status between life and death.
It easily complements nutritional deficiencies and introduces an animation status between life and death.
The ability of ultraviolet rays helps to destroy the "hidden home" of microorganisms. They have created conditions that are beneficial for the penetration of antibiotics and other drugs that affect psoriasis.
In addition, the cost of UV rays is also high. The best known treatment using this principle is the Puva Therapy. Although the effect is inferior to UFO blood. The effect of the treatment does not last long and may recur two weeks after the end of the treatment.
Drug therapy
Among drugs, this has been proven to work well.
The mature rate of vitamin A derivative (Neoig Tazon, Chigazon) and keratinocytes is reduced and cell differentiation is normalized.
- This reduces the activity of the T-lymphocyte that promotes epidermal cell hyperplasia, an immunosuppressive agent (Cyclosporin A).
- A malignant tumor therapeutic drug (Metotlexart) that inhibits the regeneration and proliferation of variant skin cells (16].
- What are effective masks and creams for the treatment of psoriasis?
Ointment and cream containing anti-inflation ingredients relieve the patient's symptoms. Dommerity Light, Psoleil, Acrydam, Continuus, etc.
How to treat scalp psoriasis
Ointments are not effective in treating scalp psoriasis. In addition to drug therapy and UV rays, special shampoos such as Nizoral can be used.
Treatment for psoriasis, which can be obtained in the elbows and hands
Psoriasis on the elbows and hands is treated in the same way as in other areas. A feature of the course of psoriasis of this part is that the skin of the hands is subjected to physical, mechanical and chemical influences, which are considered aggravating factors in the course of the disease.
Is the treatment of psoriasis with monoclonal antibodies effective?
Treatment of psoriasis with monoclonal antibodies is highly effective. Monoclonal antibody preparations are laboratory antibodies similar to those produced by human immune cells.
 Monoclonal antibodies selectively act on targets involved in the development of the disease. Infliximab, adalimumab, and ustekinumab are used to treat psoriasis.
Monoclonal antibodies selectively act on targets involved in the development of the disease. Infliximab, adalimumab, and ustekinumab are used to treat psoriasis. How to recognize and treat psoriasis in children
In children, psoriasis is difficult to diagnose because it progresses quickly and often mimics other conditions (eczema, erysipelas, herpes). Treatment methods - phototherapy, drug therapy and topical therapy - are the same as in adults.
Which bath salts are effective against psoriasis?
Baths with aloe vera (lat. aloe vera) can reduce inflammation and itching [22].
How pegano treats psoriasis
Treatment for peganopsoriasis includes colon cleansing, diet, and herbal drips. The effectiveness of this method has not been proven by clinical trials.
The role of diet in therapy.
Diet strongly influences the course of psoriasis. Alcohol, salt, spices, pickles, nuts, citrus fruits, honey, chocolate, smoked meats, etc.
 should be avoided during treatment.
should be avoided during treatment. Which spa hotel offers bed rest for the treatment of psoriasis?
For psoriasis, balneotherapy by the sea is preferable in areas with a warm, dry climate and sunny days. Crimean resorts are most suitable for this.
folklore method
Some folk remedies can help reduce itching and flaking of the skin in people with mild to moderate psoriasis. These methods are:
Aloe vera extract cream (lat. Aloe vera).
- Fish oil was applied to the bandaged skin 6 hours a day for 4 weeks.
- Cream with Oregon grape extract (lat. Mahonia aquifolium) [22].
- Psoriasis is not a death sentence. If you timely seek help from a specialist who can identify the true cause of your disease and prescribe an effective treatment, your disease will be cured.
Forecast. Prevention
Psoriasis simplex occurs when the skin is imperfect. Therefore, the patient does not need special working conditions.![]() However, working in a chemical plant is an exception, in which case staying at the workplace should be excluded.
However, working in a chemical plant is an exception, in which case staying at the workplace should be excluded.
It is also worth remembering that psoriasis can have complications. The most common is psoriatic arthritis. In severe cases, this limits your ability to work at work and can lead to permanent disability in the future.
Prevention of psoriasis is the most important treatment for one of the most serious skin diseases. After recovery, you should completely reconsider your lifestyle, get rid of bad habits, pay attention to the treatment of chronic diseases of other organs, adjust your diet, include outdoor walks and sports in your daily routine.
take psoriasis into the army
A severe form of psoriasis is a sufficient reason for unfitness for military service, and a mild form of psoriasis is partially.
Nedoplasma is the medical name for a tumor, which means the overgrowth of all tissues in the body. Since the tumor is not yet mature, it is the result of disorderly reproduction, which cannot fully perform its functions.
Tumors may occur on internal organs or on the surface of the skin. Many people who don't know what skin is like misunderstand the new creature on the skin. In fact, this is not always the case.
In the main classification, the skin of the skin is divided into benign and malignant. There is also a lesion from cancer, that is, two types of borders. Each type has a variant, each has its own characteristics, and it requires proper diagnosis in order to make an accurate diagnosis.
Belonble's new products usually do not affect cell differentiation. In other words, while retaining the original function, it has the same structure as normal cells. However, these cells grow slowly, compress nearby tissue, but do not penetrate the tissue.
Benign neoplasms of the skin
Type of benign new skin creatures.
Atheroma is a tumor made by blocking the sebaceous glands. It is often found in places with a lot of sebaceous glands (neck, back, head and groin).
- A hemangioma is a blood vessel tumor derived from cells in blood vessels. The color is blue from red to blue.
- It forms as ground or verrucous small nodules or nipples. The cause is the human papilla virus (HPV). Usually stress, reduced immunity, sprouting disorders, etc. are used in the background. It often occurs in the groin under the armpits. Nipitoma is the most common new creature that can be done on the skin of the eyelids.
- Lymphoma is a tumor made from the wall of the lymphatic tube and may be in the uterus. The appearance is a small layer with hangose or an irregular reddish surface.
- Lipoma a-tumor in the fat layer (“warm”). It is found in the subcutaneous layer, often found on the back, shoulder and outer thigh. The tumor is soft and mobile without pain.
- Fibroma is a form of joint tissue. It is common in young women and women with an average level. It looks like a spherical new creature protruding from the surface of the skin.

- Nervous fibroma is a tumor of the nerve sheath cells. Appearance looks 0.1 to 2.3 cm in dense mass.
- Another group of new creature contains Nevus (eyelashes). This is a new product in various colors such as brown, red, black, purple. In most cases, the nevus is the congenital skin that is the catch. However, moles can appear throughout their lives and many of them are affected by sunlight. Dews are difficult to degenerate malignant, but in some cases it can be caused by damage to the mole or scratches.
Although not immediately dangerous, all benign new creatures that may be made on the skin, such as the face and limbs, should always be monitored. You need to make sure that the tumor does not grow, does not grow and that the color does not change. If not, you need to see a doctor.
Pre-carcinogenesis refers to a new entity that is more likely to turn into a malignant tumor and due to the consequences of congenital or modern causes. Basically, it is a chronic disease that people can see people for a long time.
Precancerous neoplasms (precancroses)
Thus, the anterior tumor is a dangerous new creature that can be made from the skin, which can lead to the oncology process. These are the following.
Keratinosis of the elderly is keratinia in which dry crusts and scales appear on the skin of older people. Victory can cause light bleeding.
- This is a genetic tumor that develops when the skin becomes more sensitive to ultraviolet rays. There are rarely spots that become warts.
- Angle of skin is a conical tumor like an angle. The color is yellow or brown. It occurs in the open part of the body, which always receives friction and pressure. Features of the elderly
- Boren's disease is a positive endometrium. If you don't treat it, it can change to invasive skin cancer. Boren's disease has small reddish-brown spots ranging from 2 to 50 mm in the early days. There is a scraping on the surface, and the edge has a roughness. After removing the scales, there is no bleeding, but the surface sheds tears.

- Among the new creatures that can be on the skin, the most dangerous are malignant tumors. Unlike benign, it is characterized by rapid growth, penetration into the surrounding tissue and goes to the part from the focus. In such a tumor, the body cannot control cell division and lose its original function.
Malignant neoplasms of the skin
Signs of rehabilitation of benign tumors, a kind of malignant skin skin.
The size of the tumor increases rapidly or rapidly.
- Ulcers, bleeding.
- Distributed to adjacent tissue.
- Changes in color or saturation of pigments.
- The main type of skin of a malignant tumor.
Melanoma is the most common type. In many cases it is caused by the fate of injuries and excessive ultraviolet light.
- Bazarioma is a flat skin cancer generated from atypical cells on a layer of skin. Appearance looks like a dry film on a white bag. As it develops, the width becomes larger and the ulcer deep.
- Kaposi's sarcoma. Numerous tumors, purple, purple and purple. They bind and become ulcers.
- Liparcoma is a malignant tumor of adipose tissue generated in the background of the lips and atria.
- Fibrosarcoma is a new entity of the Union organization and usually occurs in the lower extremities. The color is dark blue brown, and may stand out against the skin.
- Experts recommend removal of both benign and malignant new creatures. If there are no contraindications, this is the best method of treatment. In the case of a benign neoplasm or condition before the foreshortening, the prognosis is good also due to timely treatment.
In the case of malignant tumors, more effort is required and the prognosis may not be very good, especially when metastases are observed. Therefore, if you are suspected of malignant tumors, it is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Most infectious diseases are caused by streptococci and staphylococci. It lives in the environment and lives in mucous membranes such as the skin, mouth, nose, and genitals. In cases of 9-12% inflammation is generated from the cornea, hops, tuberculosis and Campylobacter.
It lives in the environment and lives in mucous membranes such as the skin, mouth, nose, and genitals. In cases of 9-12% inflammation is generated from the cornea, hops, tuberculosis and Campylobacter.
Healthy skin does not pass through germs. These are the structure of the epidermis, the pH of sweat, the pH of sebum and the anti-rotation of the sebaceous glands. If there is a breach of protection, a rash of feathers will appear.
Promote the invasion of microorganisms.
How skin becomes infected
Wounds, scratches, cracks, abrasions, etc.
- Dehydration of the epidermis (skin).
- Hypothermia, overheating
- Reduce immunity.
- Diseases - diabetes, tumor disease
- Take adrenocortical hormones, contraceptives, and cell proliferation inhibitors.
- Bacterial infections often have scratches, burns, itching of the skin and allergic diseases.
Lubricant
Superficial bacterial infections of the skin
- Inflammation of the hair parcel: an abscess forms around the hair and the surroundings are red.

Neonatopipox
- Inflammatory blisters have inflammatory blisters all over the child's body that form crusts and ulcers.
Face of eczema
- Painless blisters with a dirty content appear against the background of redness. After that, the blister shrinks into a yellow bark and leaves sloppy.
Wax wax is common in children and young women. Location: face, lower hair, limbs. When staph binds, the bark becomes green or full of blood. This disease is spreading rapidly in the local community. It is necessary to suspect this, isolate the child and wrap him around the wound.
This occurs when the microorganism enters deep into the dermis.
Bacterial infection of the deep layer of the skin
Fullchel
A painful nodule appears first and the abscess has matured in the center. 5-7 days later, purulent nuclei are released, and the wounds are scars. If this happens several times, it is said to be concentration.
Ruby
This is a widespread invasion of some kind of edema.
 This place is like a purple blue tumor. The pain grows, I feel sick, and my body temperature rises. After the opening of the formation, a deep ulcer remains, leaving scars and healing.
This place is like a purple blue tumor. The pain grows, I feel sick, and my body temperature rises. After the opening of the formation, a deep ulcer remains, leaving scars and healing. Acne (pimples)
- inflammation of the pores and due to obstruction of the sebaceous glands. Form pustules on the face, chest and shoulder. The content shrinks and becomes crusty, leaving scratches and blue spots upon discharge.
LEMA Enteritis
Suurbast Inflammation of the sweat glands. This process is often repeated. Such sites: under the armpits, groin folds, under the mammary glands. The appearance is blue and red, and there is a nodule with deep pain. Opened by separation of liquid pus.
It occurs in people with individual differences. Inflammatory damage is clearly limited. The affected area is swelling, warm, bright red, and blistering. It is a disease with fever, drunkenness and severe pain.
Profound Pyoderma can combine lymphatic vessels and inflammation of the lymph nodes, abscess and sepsis.
The blood supply in organs such as the head, face and brain membrane is closely related. Inappropriate treatment and contraction of acne is dangerous and dangerous thanks to the blood and lymph. Terrible complications can be achieved, such as meningitis, abscess, inflammation and inflammation of the eyes, as well as an increase in the area of the affected areas.
Features of facial skin infections
Before deciding on cosmetic procedures such as cleansing, cleansing and mesotherapy, it is necessary to find and treat the cause of the intermediate rash after testing by a dermatologist.
Under the guidance of a specialist, this must be done from the beginning. In some cases, a sufficient amount of local treatment through the use of antibacterial ointments and preservatives. A wide range of rashes and deep pyoderma require the administration of a systemic antibiotic. In the case of a chronic course, doctors may recommend self-assessment and immune formulas.
Treatment of bacterial skin infections
If the abscess does not open on its own or the scar does not become rough, surgical treatment is performed. Laser photocoagulation and physiotherapy are performed to repair the tissue.
It is important to eliminate the recognition and treatment of diseases that arise, and eliminate the adverse effects on the skin from the outside and choose nutrition.
Follow the following rules.
Prevention
After visiting the gym, wipe the area where supplies come into contact with disinfectant.
- Cuts and wounds are treated with antibacterial agents (iodine, salicylic alcohol, hydrogen peroxide) as soon as they occur.
- Do not share body products and cosmetics with others.
- Abscess and impetigo must not be rinsed with water, combed or pressed.
- Avoid fatty and sugary foods.
- Please apply to consult dermatologists in advance. Doctors explain the cause of the inflammation, the tests needed, the selection of treatments, and the appropriate types and stages of Pyoderma.