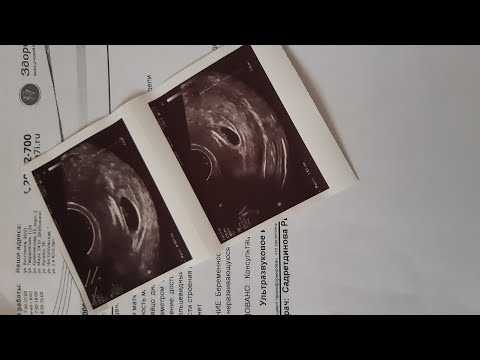
Treatment miscarriage 6 weeks
Treating miscarriage | The Royal Women's Hospital
If a miscarriage has begun, there is nothing that can be done to stop it. Any treatment you have will be aimed at avoiding heavy bleeding and infection.
A discussion with the doctor or nurse will help you to work out which treatment options are best and safest for you.
On this page:
- No treatment (expectant management)
- Treatment with medicine
- Surgical treatment (curette)
- Waiting for treatment
- After a miscarriage
No treatment (expectant management)
You can choose to wait and see what will happen. This is called 'expectant management'. If nothing is done, sooner or later the pregnancy tissue will pass naturally. If it is an incomplete miscarriage (where some but not all pregnancy tissue has passed) it will often happen within days, but for a missed miscarriage (where the fetus or embryo has stopped growing but no tissue has passed) it might take as long as three to four weeks.
While you are waiting you may have some spotting or bleeding, much like a period. When the pregnancy tissue passes, you are likely to have heavier bleeding with crampy, period-like pains. You can use sanitary pads and take pain relieving tablets, such as paracetamol.
If your miscarriage is incomplete, with just a small amount of pregnancy tissue remaining, it’s probably best to take a wait and see approach. But if there is heavy bleeding or signs of infection you will need treatment.
If the tissue does not pass naturally or you have signs of infection, the doctor will recommend a dilatation and curettage (D&C). You and the doctor can discuss and decide the preferred option for you.
Things to know
- There are many reasons why some women prefer to wait and see. It may feel more natural, it may help with the grieving process or it may give you more of a sense of control.
- Some women become worried or frightened when the bleeding gets heavier, especially if blood clots, tissue or even a recognisable embryo is passed.

- Usually, the wait and see approach takes longer than any other approaches such as surgery or medication. Sometimes bleeding can last for up to four weeks.
- Although excessive bleeding and blood transfusion are very rare, they are slightly more common with expectant management than with surgery.
- A few women still need to have surgery – sometimes urgently – if they develop infection, bleed heavily or if the tissue does not pass naturally.
- The waiting time can be emotionally draining for some women.
Treatment with medicine
Medicine is available that can speed up the process of passing the pregnancy tissue. For an incomplete miscarriage, the medicine will usually encourage the pregnancy tissue to pass within a few hours. At most it will happen within a day or two. For a missed miscarriage, it may happen quickly, but it can take up to two weeks and, occasionally, longer.
- Medication is not suitable if there is very heavy bleeding or signs of infection.
 It is usually not recommended for pregnancies that are older than about nine weeks.
It is usually not recommended for pregnancies that are older than about nine weeks. - If the tissue does not pass naturally, eventually your doctor will recommend a dilatation and curettage (D&C).
Things to know
- The pregnancy tissue will pass between four to six hours after taking the medicine, during which time you may be in hospital. After a few hours, if the pregnancy hasn’t passed, you may be sent home to wait. This will depend on where you are and which hospital you are in.
- The medicine has side effects which usually pass in a few hours but can be unpleasant, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, fever and chills. The tablets can be swallowed or dissolved under the tongue, or inserted in the vagina.
- After receiving the medication there may be some spotting or bleeding like a period. When the pregnancy tissue passes, you are likely to notice heavier bleeding and clots with strong cramping, period-like pains. You can use sanitary pads and take pain relieving tablets such as paracetamol.

- Some women may need stronger pain killers or a pain relieving injection.
- A few women still need to have surgery, sometimes urgently, if they develop infection, bleed heavily or if the tissue does not pass.
Surgical treatment (curette)
A D&C (or ‘curette’) is a minor operation. The full name is dilatation and curettage. It is done in an operating theatre, usually under general anaesthetic. There is no cutting involved because the surgery happens through the vagina. The cervix (neck of the uterus) is gently opened and the remaining pregnancy tissue is removed so that the uterus is empty. Usually the doctor is not able to see a recognisable embryo.
The actual procedure usually only takes five to ten minutes, but you will usually need to be in the hospital for around four to five hours. Most of this time will be spent waiting and recovering.
You may have to wait a day or two to have a curette and sometimes, while you are waiting, the pregnancy tissue will pass on its own. If this happens and all of the tissue is passed you may not need to have a curette.
If this happens and all of the tissue is passed you may not need to have a curette.
A curette is done in the following circumstances:
- You have heavy or persistent bleeding and/or pain.
- The medical staff advise that this is a better option for you; this may be because of the amount of tissue present, especially with a missed miscarriage.
- This is an option you prefer.
Things to know
The risks of a D&C are very low, but include:
- some pregnancy tissue remains in uterus. This can cause prolonged or heavy bleeding and the operation may need to be repeated
- infection needing antibiotics
- damage to the cervix or uterus. This is very rare (around 1 in 1000) and, when it does happen, it is usually a small hole or tear which will heal itself
- excessive bleeding (very rare)
- anaesthetic risks. These are very low for healthy women, but no anaesthetic or operation is without risk.
Waiting for treatment
If you have heavy bleeding with clots and crampy pain, it is likely that you are passing the pregnancy tissue. The bleeding, clots and pain will usually settle when most of the pregnancy tissue has been passed. Sometimes the bleeding will continue to be heavy and you may need further treatment.
The bleeding, clots and pain will usually settle when most of the pregnancy tissue has been passed. Sometimes the bleeding will continue to be heavy and you may need further treatment.
You should go to your nearest emergency department if you have:
- increased bleeding, for instance soaking two pads per hour and/or passing golf ball sized clots
- severe abdominal pain or shoulder pain
- fever or chills
- dizziness or fainting
- vaginal discharge that smells unpleasant
- diarrhoea or pain when you open your bowels.
What to do while you are waiting
- You can try to rest and relax at home.
- Usual activity that is not too strenuous will not be harmful. You can go to work if you feel up to it.
- If you have pain you can take paracetamol.
- If there is bleeding, use sanitary pads rather than tampons.
After a miscarriage
- It is usual to have pain and bleeding after a miscarriage.
 It will feel similar to a period and will usually stop within two weeks. You can take ordinary painkillers for the pain. Your next period will usually come in four to six weeks after a miscarriage.
It will feel similar to a period and will usually stop within two weeks. You can take ordinary painkillers for the pain. Your next period will usually come in four to six weeks after a miscarriage. - See a doctor or attend a hospital emergency department if you have strong pain and bleeding (stronger than period pain), abnormal discharge, (especially if it is smelly), or fever. These symptoms may mean that you have an infection or that tissue has been left behind.
- Try and avoid vaginal sex until the bleeding stops and you feel comfortable.
- Use sanitary pads until the bleeding stops (do not use tampons).
- All contraceptive methods are safe after a miscarriage
- See a GP (local doctor) in four to six weeks for a check-up.
Anti-D injection after a miscarriage
It is important to have your blood group checked. If you’re RhD negative and the fetus is RhD positive this can cause problems for future pregnancies. This is because the fetus’s blood cells have RhD antigen attached to them, whereas yours do not. If small amounts of the fetus’s blood mixes with your blood, your immune system may perceive this difference in blood cells as a threat and produce antibodies to fight against the fetus’s blood. Once your body has made these antibodies they can’t be removed. This is unlikely to have caused your miscarriage and is more likely to affect future pregnancies. Women with a negative blood type usually need an Anti-D injection, which will stop the antibodies forming.
If small amounts of the fetus’s blood mixes with your blood, your immune system may perceive this difference in blood cells as a threat and produce antibodies to fight against the fetus’s blood. Once your body has made these antibodies they can’t be removed. This is unlikely to have caused your miscarriage and is more likely to affect future pregnancies. Women with a negative blood type usually need an Anti-D injection, which will stop the antibodies forming.
Future pregnancies after a miscarriage
One of the most common concerns following a miscarriage is that it might happen again. However, if you have had one miscarriage the next pregnancy will usually be normal.
If you do try for another pregnancy, try and avoid smoking, alcohol and excess caffeine as they increase the risk of miscarriage. It is recommended that all women take folic acid while trying to conceive, and continue until three months of pregnancy. In your next pregnancy you are encouraged to see your GP and have an ultrasound at about seven weeks. If ultrasound is done too early in pregnancy the findings are often uncertain and cause unnecessary worry.
If ultrasound is done too early in pregnancy the findings are often uncertain and cause unnecessary worry.
Feelings and reactions
There is no ‘right’ way to feel following a miscarriage. Some degree of grief is very common, even if the pregnancy wasn’t planned. Partners may react quite differently, just as people can respond differently to a continuing pregnancy. Feelings of loss may persist for some time and you may have mixed feelings about becoming pregnant again. Some friends and family may not understand the depth of emotion that can be attached to a pregnancy and may unreasonably expect for you to move on before you are ready.
Some couples decide that they want to try for a pregnancy straight away, while others need time to adjust to their loss. If you feel anxious about a possible loss in future pregnancies, you may find it helpful to talk to someone about this. If it’s difficult to speak with your friends and family about these issues, your doctor, community support group and counsellors can provide information and assistance.
Related Health Topics
-
- Treatment for miscarriage
Treatment for miscarriage is aimed at avoiding heavy bleeding and infection. It is also aimed at looking after you, physically and emotionally.
-
- (English) PDF (302 KB)
- Treatment for miscarriage
The Women’s does not accept any liability to any person for the information or advice (or use of such information or advice) which is provided on the Website or incorporated into it by reference. The Women’s provide this information on the understanding that all persons accessing it take responsibility for assessing its relevance and accuracy. Women are encouraged to discuss their health needs with a health practitioner. If you have concerns about your health, you should seek advice from your health care provider or if you require urgent care you should go to the nearest Emergency Dept.
If you have concerns about your health, you should seek advice from your health care provider or if you require urgent care you should go to the nearest Emergency Dept.
Miscarriage - Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis
Your health care provider might do a variety of tests:
- Pelvic exam. Your health care provider might check to see if your cervix has begun to dilate.
- Ultrasound. During an ultrasound, your health care provider will check for a fetal heartbeat and determine if the embryo is developing as it should be. If a diagnosis can't be made, you might need to have another ultrasound in about a week.
- Blood tests. Your health care provider might check the level of the pregnancy hormone, human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), in your blood and compare it to previous measurements. If the pattern of changes in your HCG level is abnormal, it could indicate a problem.
 Your health care provider might check to see if you're anemic — which could happen if you've experienced significant bleeding — and may also check your blood type.
Your health care provider might check to see if you're anemic — which could happen if you've experienced significant bleeding — and may also check your blood type. - Tissue tests. If you have passed tissue, it can be sent to a lab to confirm that a miscarriage has occurred — and that your symptoms aren't related to another cause.
- Chromosomal tests. If you've had two or more previous miscarriages, your health care provider may order blood tests for both you and your partner to determine if your chromosomes are a factor.
Possible diagnoses include:
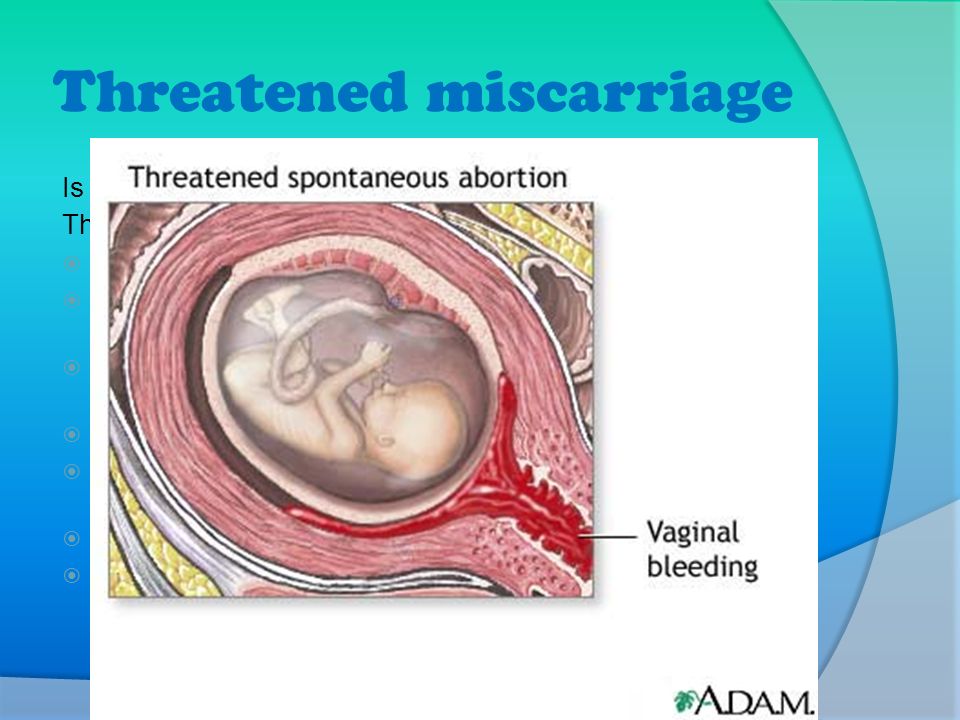
- Threatened miscarriage. If you're bleeding but your cervix hasn't begun to dilate, there is a threat of miscarriage. Such pregnancies often proceed without any further problems.
- Inevitable miscarriage. If you're bleeding, cramping and your cervix is dilated, a miscarriage is considered inevitable.
- Incomplete miscarriage.
 If you pass fetal or placental material but some remains in your uterus, it's considered an incomplete miscarriage.
If you pass fetal or placental material but some remains in your uterus, it's considered an incomplete miscarriage. - Missed miscarriage. In a missed miscarriage, the placental and embryonic tissues remain in the uterus, but the embryo has died or was never formed.
- Complete miscarriage. If you have passed all the pregnancy tissues, it's considered a complete miscarriage. This is common for miscarriages occurring before 12 weeks.
- Septic miscarriage. If you develop an infection in your uterus, it's known as a septic miscarriage. This can be a severe infection and demands immediate care.
More Information
- Pelvic exam
- Ultrasound
Treatment
Threatened miscarriage
For a threatened miscarriage, your health care provider might recommend resting until the bleeding or pain subsides. Bed rest hasn't been proved to prevent miscarriage, but it's sometimes prescribed as a safeguard. You might be asked to avoid exercise and sex, too. Although these steps haven't been proved to reduce the risk of miscarriage, they might improve your comfort.
In some cases, it's also a good idea to postpone traveling — especially to areas where it would be difficult to receive prompt medical care. Ask your health care provider if it would be wise to delay any upcoming trips you've planned.
Miscarriage
With ultrasound, it's now much easier to determine whether an embryo has died or was never formed. Either finding means that a miscarriage will definitely occur. In this situation, you might have several choices:
- Expectant management. If you have no signs of infection, you might choose to let the miscarriage progress naturally. Usually this happens within a couple of weeks of determining that the embryo has died. Unfortunately, it might take up to three or four weeks. This can be an emotionally difficult time. If expulsion doesn't happen on its own, medical or surgical treatment will be needed.
- Medical treatment. If, after a diagnosis of certain pregnancy loss, you'd prefer to speed the process, medication can cause your body to expel the pregnancy tissue and placenta. The medication can be taken by mouth or by insertion in the vagina. Your health care provider might recommend inserting the medication vaginally to increase its effectiveness and minimize side effects such as nausea and diarrhea. For about 70 to 90 percent of women, this treatment works within 24 hours.
- Surgical treatment. Another option is a minor surgical procedure called suction dilation and curettage (D&C). During this procedure, your health care provider dilates your cervix and removes tissue from the inside of your uterus. Complications are rare, but they might include damage to the connective tissue of your cervix or the uterine wall. Surgical treatment is needed if you have a miscarriage accompanied by heavy bleeding or signs of an infection.

Physical recovery
In most cases, physical recovery from miscarriage takes only a few hours to a couple of days. In the meantime, call your health care provider if you experience heavy bleeding, fever or abdominal pain.
You may ovulate as soon as two weeks after a miscarriage. Expect your period to return within four to six weeks. You can start using any type of contraception immediately after a miscarriage. However, avoid having sex or putting anything in your vagina — such as a tampon — for two weeks after a miscarriage.
Future pregnancies
It's possible to become pregnant during the menstrual cycle immediately after a miscarriage. But if you and your partner decide to attempt another pregnancy, make sure you're physically and emotionally ready. Ask your health care provider for guidance about when you might try to conceive.
Miscarriage is usually a one-time occurrence. Most women who miscarry go on to have a healthy pregnancy after miscarriage. Less than 5 percent of women have two consecutive miscarriages, and only 1 percent have three or more consecutive miscarriages.
Less than 5 percent of women have two consecutive miscarriages, and only 1 percent have three or more consecutive miscarriages.
If you experience multiple miscarriages, generally two or three in a row, consider testing to identify any underlying causes. Such causes could include problems with the uterus, blood clotting or chromosomes. If the cause of your miscarriages can't be identified, don't lose hope. About 60 to 80 percent of women with unexplained repeated miscarriages go on to have healthy pregnancies.
More Information
- Dilation and curettage (D&C)
Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and support
Emotional healing can take much longer than physical healing. Miscarriage can be a heart-wrenching loss that others around you might not fully understand. Your emotions might range from anger and guilt to despair. Give yourself time to grieve the loss of your pregnancy, and seek help from loved ones.
Your emotions might range from anger and guilt to despair. Give yourself time to grieve the loss of your pregnancy, and seek help from loved ones.
You'll likely never forget your hopes and dreams surrounding this pregnancy, but in time acceptance might ease your pain. Talk to your health care provider if you're feeling profound sadness or depression.
Preparing for your appointment
If you have signs or symptoms of miscarriage, contact your health care provider right away. Depending on the circumstances, you might need immediate medical care.
Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment, and what to expect from your health care provider.
What you can do
Before your appointment, you might want to:
- Ask about pre-appointment restrictions. In most cases you'll be seen immediately. If that's not the case, ask whether you should restrict your activities while you wait for your appointment.
- Find a loved one or friend who can join you for your appointment.
 Fear and anxiety might make it difficult to focus on what your health care provider says. Take someone along who can help remember all the information.
Fear and anxiety might make it difficult to focus on what your health care provider says. Take someone along who can help remember all the information. - Write down questions to ask your health care provider. That way, you won't forget anything important that you want to ask, and you can make the most of your time with your health care provider.
Below are some basic questions to ask your health care provider about miscarriage:
- What are the treatment options?
- What kinds of tests do I need?
- Can I continue to do my usual activities?
- What signs or symptoms should prompt me to call you or go to the hospital?
- Do you know what caused my miscarriage?
- What are my chances for a successful future pregnancy?
In addition to the questions you've prepared, don't hesitate to ask other questions during your appointment — especially if you need clarification or you don't understand something.
What to expect from your health care provider
Your health care provider is likely to ask you a number of questions, too. For example:
- When was your last menstrual period?
- Were you using any contraceptive methods at the time you likely conceived?
- When did you first notice your signs or symptoms?
- Have your symptoms been continuous or occasional?
- Compared with your heaviest days of menstrual flow, is your bleeding more, less or about the same?
- Have you had a miscarriage before?
- Have you had any complications during a previous pregnancy?
- Do you have any other health conditions?
- Do you know your blood type?
By Mayo Clinic Staff
Related
Associated Procedures
Products & Services
Miscarriage, how to avoid - Planning and management of pregnancy in the gynecology of the Literary Fund polyclinic after a miscarriage
- Gallery
- News
- Blog
- Reviews
- Jobs
- Licenses
- Insurance partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule of reception of citizens on personal appeals
- What you need to know about coronavirus infection?
- Rules for patients
- Online doctor's consultation
- to corporative clients
- The documents
A miscarriage is always associated with severe consequences for the whole body of a woman and for her reproductive organs in particular, it also affects the family situation, disrupts the woman's work schedule. An unfavorable outcome of pregnancy requires great mental and physical costs on the part of parents. Therefore, contacting doctors to find out the causes of the problem is the very first and correct step towards the birth of a child.
An unfavorable outcome of pregnancy requires great mental and physical costs on the part of parents. Therefore, contacting doctors to find out the causes of the problem is the very first and correct step towards the birth of a child.
Any competent gynecologist will tell you that the problem of miscarriage can be solved. With proper preparation for pregnancy and its management, the next time you will have a successful pregnancy. Most girls after a miscarriage go to extremes: they try to get pregnant again as soon as possible. And if this succeeds, then the miscarriage is very often repeated. And you need to give the body a rest for 2-3 months, then identify and eliminate the cause. And only then try.
Causes of miscarriage
Many are convinced that miscarriages are due to a fall, bruise, or some other physical shock. Any woman who has had a miscarriage can remember that not long before she either fell or lifted something heavy. And I am sure that she lost her unborn child precisely because of this. However, those women whose pregnancy was normal also fall and lift heavy things. Most sudden miscarriages do not occur for this reason. The reason is in violations of the pregnancy itself. Approximately half of miscarriages are due to abnormal genetic development of the fetus, which can be hereditary or accidental. Merciful nature, following the principles of natural selection in everything, destroys the defective and unviable fetus. But you should not be afraid of this. The fact that there is a defect in one embryo does not mean at all that all the others will be the same.
However, those women whose pregnancy was normal also fall and lift heavy things. Most sudden miscarriages do not occur for this reason. The reason is in violations of the pregnancy itself. Approximately half of miscarriages are due to abnormal genetic development of the fetus, which can be hereditary or accidental. Merciful nature, following the principles of natural selection in everything, destroys the defective and unviable fetus. But you should not be afraid of this. The fact that there is a defect in one embryo does not mean at all that all the others will be the same.
The woman's body is almost always to blame for the other half of miscarriages. They are caused by various known and unknown factors, such as: acute infectious diseases suffered in the first trimester of pregnancy, poor environment or difficult working conditions, excessive psychological or physical stress, abnormal development of the uterus, radiation, alcohol, smoking and certain types of drugs.
The causes of early and late miscarriage may differ, although they may overlap. The most important thing is to find out and eliminate or compensate for your own cause of miscarriage. Having discovered the cause, the gynecologist will tell you how to avoid another loss.
The most important thing is to find out and eliminate or compensate for your own cause of miscarriage. Having discovered the cause, the gynecologist will tell you how to avoid another loss.
Miscarriage
Miscarriage statistics also include “missed pregnancy”. Sometimes it happens that the embryo dies and lingers in the uterine cavity. Most often, this fact is detected by ultrasound. The dead fetus may begin to decompose, and this, thereby, will lead to poisoning of the mother's body.
Doctors resort to surgical curettage, which is associated with a risk of inflammation and complications. With such a miscarriage, the next pregnancy is planned after the body is fully restored - not earlier than a year. During this year, you will have to find out the cause of the missed pregnancy and treat it.
Miscarriage up to 6 weeks
The main causes of miscarriage on this line are malformations of the embryo itself. Statistics say that from 70-90% of embryos had chromosomal abnormalities: they are random and will not occur in other pregnancies. You may have been ill, taken medication, or were under the influence of other harmful factors. Fate saved you from a child with malformations.
You may have been ill, taken medication, or were under the influence of other harmful factors. Fate saved you from a child with malformations.
The human body is perfect and finds a way to correct the situation by miscarriage. Today is a tragedy for you. The real tragedy would be the preservation and birth of a sick, non-viable child. So don’t cry and understand: everything is for the best, you won’t help grief with tears ... And after three months, try again - it will almost certainly turn out to be successful.
It should also be noted that the fact of a miscarriage does not mean that you have lost something. So for a period of 7-8 weeks, the absence of an embryo in the fetal egg is found - "anembryony". It is believed that in 80-90% of cases, miscarriages are undiagnosed non-developing pregnancies.
Miscarriage between 6 and 12 weeks
Miscarriage in this period is also considered early. Its most common causes are:
Endocrine disorders
Endocrine disorders, when the ovaries do not synthesize enough hormones to keep the fetus in the womb, or the amount of male sex hormones is increased, is one of the most common causes of miscarriage and miscarriage.
Imbalance of hormones in a woman's body is very likely to lead to an early termination of pregnancy. With a lack of the main hormone progesterone produced by the ovaries, this happens most often. Another hormonal problem is an increase in the tone of the uterus, which provokes the expulsion of the fetus.
Progesterone prepares the uterine mucosa for implantation and is the hormone for maintaining pregnancy in the first months. If conception occurs, the fetus cannot properly establish itself in the uterus. As a result, the fertilized egg is rejected. But pregnancy can be saved with the help of progesterone preparations if this problem is detected in time.
An excess of male sex hormones that suppress the production of estrogen and progesterone can also be the cause of an early miscarriage. Often, the cause of recurrent miscarriages are androgens that affect the formation and development of pregnancy; as well as thyroid and adrenal hormones. Therefore, a change in the function of these glands can lead to miscarriage.
Undertreated sexual infections
This problem must be solved before conception. Often the cause of miscarriage is sexually transmitted infections: syphilis, trichomoniasis, toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, cytomegalovirus and herpetic infections. Their effect on the fetus and the course of pregnancy is different for each woman and depends on the timing of infection, the activity of the microorganism, the degree of immune protection and the presence of other adverse factors. Depending on the situation, they can lead to the formation of fetal malformations, intrauterine infection, feto-placental insufficiency, early miscarriage or premature birth. Infection of the fetus and damage to the membrane of the fetus leads to miscarriage. To avoid this, infections should be treated before pregnancy. The use of therapy is possible during pregnancy as prescribed by a doctor.
Viral infections and other diseases
Any disease accompanied by intoxication and fever above 38 about C can lead to a miscarriage. Rubella, influenza and viral hepatitis occupy a leading position in this list. At a period of 4-10 weeks for pregnancy, ordinary tonsillitis can also become tragic, pneumonia carries a more serious risk. Pyelonephritis and appendicitis can cause early labor. When planning a pregnancy, it is imperative to undergo a medical examination in order to identify and treat foci of infections.
Rubella, influenza and viral hepatitis occupy a leading position in this list. At a period of 4-10 weeks for pregnancy, ordinary tonsillitis can also become tragic, pneumonia carries a more serious risk. Pyelonephritis and appendicitis can cause early labor. When planning a pregnancy, it is imperative to undergo a medical examination in order to identify and treat foci of infections.
Extremely dangerous during pregnancy rubella - it leads to severe fetal malformations, so infection during pregnancy is an indication for medical abortion.
Any disease during pregnancy can lead to non-viability of the fetus. And the body, through a miscarriage, insures you against unwanted offspring. With such a miscarriage, the next pregnancy has every chance of going well.
Immune causes of miscarriage
Sometimes antibodies that are hostile to the fetus are formed in the blood of a pregnant woman. This cause can be predicted and eliminated in advance. Most often, the conflict occurs when the embryo inherits the positive Rh factor of the father, and the negative Rh factor, the mother's body rejects the embryonic tissues that are alien to it. Constant monitoring of antibody titer and the introduction of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins allows you to maintain and maintain pregnancy. In case of an immune conflict, progesterone preparations are also used to prevent miscarriage, which in this case has an immunomodulatory effect.
Most often, the conflict occurs when the embryo inherits the positive Rh factor of the father, and the negative Rh factor, the mother's body rejects the embryonic tissues that are alien to it. Constant monitoring of antibody titer and the introduction of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins allows you to maintain and maintain pregnancy. In case of an immune conflict, progesterone preparations are also used to prevent miscarriage, which in this case has an immunomodulatory effect.
Reduced immunity
Reduced immunity during pregnancy also refers to immune causes. The body is simply not able to grow a new life in itself. You need to take care of yourself and recover before the next conception.
Anatomical causes of miscarriage
Anatomical causes of miscarriage are the most intractable. Malformations of the uterus are a serious reason for miscarriage. Sometimes you just have to deal with it.
Miscarriage between 12 and 22 weeks
Such a miscarriage is considered late. Its causes coincide with the causes of miscarriages in the early stages (anatomical, immune, infectious, endocrine).
Its causes coincide with the causes of miscarriages in the early stages (anatomical, immune, infectious, endocrine).
At this time, miscarriage also occurs due to isthmic-cervical insufficiency - a weak cervix cannot hold the fetus and opens. For this reason, a miscarriage can occur in the 2nd or 3rd trimester. Isthmic-cervical insufficiency is observed in 15.0-42.7% of women suffering from miscarriage. Careful monitoring of the pregnant woman allows you to identify the problem in time and make surgical correction of the cervix before the onset of childbirth.
In isthmic-cervical insufficiency, there is only one method of treatment - mechanical narrowing of the cervical canal. To do this, the neck is either sewn up or a special ring is put on it. However, the latter method is less efficient, because the ring can easily slide off the neck, then it will no longer hold back the process of opening it.
After suturing, if necessary, it is possible to use antibiotics and drugs that normalize the microflora of the vagina. The treatment of the vagina and the control of the state of the seams are carried out daily for 5 days. Stitches are removed at 37-38 weeks and with premature onset of labor.
The treatment of the vagina and the control of the state of the seams are carried out daily for 5 days. Stitches are removed at 37-38 weeks and with premature onset of labor.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency may be primary (for no apparent reason), may be the result of abortion or hormonal disorders (increased levels of androgens - male sex hormones or their precursors).
Miscarriage after 22 weeks
Such a loss is hard to forget. Obstetricians talk about premature birth after the 28th week of pregnancy. Traditionally, a child born after this period is considered viable. But medicine knows many cases when it was possible to save the life of earlier children.
We recommend that you be carefully examined for miscarriage, check the above factors. In addition to them, the cause of a miscarriage can be antiphospholipid syndrome, while the woman's body perceives the child as something alien and rejects it. This disease, like the others listed, can be corrected; you have a very real chance of bearing a child.
Miscarriages due to hemostasis disorders
All of the above causes account for only 30-40%. Up to 70% of miscarriages are caused by disorders in the blood coagulation system (hemostasis).
Blood coagulation disorders leading to pregnancy loss can be divided into thrombophilic (increased clotting) and hemorrhagic (bleeding tendencies). Both of these extremes are dangerous to the fetus. Various disorders leading to the formation of small blood clots lead to the fact that the fetus loses sufficient blood supply, development is disturbed and the fetus is rejected.
The main hemorrhagic changes can appear even in childhood in the form of increased bleeding during cuts, tooth extractions, the onset of menstruation. But sometimes they declare themselves only during pregnancy and are the cause of a miscarriage. Bleeding in the early stages and detachment of the chorion is difficult to stop.
You may not guess, but incomprehensible headaches, weakness, fatigue, temporary loss of smell or hearing may be symptoms of disorders in the blood coagulation system.
When planning a pregnancy, a genetic examination should be carried out and, if necessary, treatment should be initiated.
It is advisable to be examined for hidden hemostasis defects even for those who consider themselves healthy. This will allow you to predict the occurrence of complications and prevent loss. Early therapy can prevent miscarriage at 98% of cases. If defects in hemostasis are already detected during pregnancy, it can be difficult to maintain it.
What to do after a miscarriage?
Find the cause! The ideal option is to be examined by future parents: it is much more reasonable to postpone conception and spend two or three months to identify the causes than to risk getting pregnant again, spend two months waiting, and then lose everything again and still go to the doctors.
Until you understand the reason, it will not evaporate. In most cases, the answers lie on the surface. Take care of your health and your future baby.
Sign up for a consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist by phone +7 (495) 150-60-01
Tyan Oksana Alexandrovna
Head of the department, obstetrician-gynecologist Doctor of the highest category Work experience: 26 years
Volkova Polina Dmitrievna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, doctor of ultrasound diagnostics Doctor of the highest category Experience: 35 years
Postnikova Nadezhda Anatolyevna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound specialist Work experience: 35 years
Moiseeva Alla Vitalievna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, doctor of ultrasound diagnostics Doctor of the first category Work experience: 37 years
Zabolotnova Olga Valentinovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist Doctor of the first category Experience: 25 years
Shchelokova Elena Nikolaevna
Obstetrician-gynecologist Doctor of the highest category Work experience: 38 years
Pass or medical card number:
Contact phone: *
Select the day of your appointment:
Additional information:
I am not a robot
By clicking the "Submit Application" button, you agree to the terms Privacy Policy and User Agreement
Early Miscarriage Help
- home /
- Blog /
- How to avoid early miscarriage
A miscarriage occurs when the fetus is shed from the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus. According to experts, two out of 10 clinically established pregnancies end in spontaneous abortion. It is necessary to understand in more detail the causes, symptoms and methods of dealing with miscarriage.
How an early miscarriage occurs
There are three steps in this process. First, the fetus dies, after which it detaches from the endometrial layer. This is manifested by the fact that bleeding begins.
At the third stage, everything that has exfoliated is removed from the uterine cavity. The process may be complete or incomplete. In the early stages - five to six weeks - the process resembles ordinary menstruation. They are characterized by painful and much more unpleasant sensations. You can find out that it was just an early miscarriage by taking tests for the ratio of hCG in the blood.
You can find out that it was just an early miscarriage by taking tests for the ratio of hCG in the blood.
Symptoms of a miscarriage
Signs of miscarriage are abdominal cramps, cramps or bloody discharge. However, they do not always appear. It is necessary to note the most typical manifestations of the presented state and their main characteristics.
Temperature
For a short period of time, hyperthermia may well not be observed. Fever is not the most common symptom. In some cases, the thermometer readings really rise to 38 degrees or more.
At the same time, when hyperthermia is accompanied by a number of additional symptoms, septic miscarriage is likely. These are its symptoms:
- severe pain in the abdomen and deep in the vagina;
- increase in the tone of the uterus, which is felt by jerks inside;
- pungent, pungent and unpleasant odour.
All this indicates that the infection has joined. In such a case, emergency hospitalization is strongly recommended to stop the development of the process. It is better not to engage in self-medication or the use of folk recipes.
In such a case, emergency hospitalization is strongly recommended to stop the development of the process. It is better not to engage in self-medication or the use of folk recipes.
Discharge
Early miscarriage can indeed be accompanied by discharge. They may be habitual, as during menstruation. Also, the discharge may be smearing, insignificant.
Secretion brown, scanty, much less likely to end in spontaneous abortion. Most often, this is indicated by abundant and bright red discharge. It is blood that normally appears when the fetus is rejected from the inner layer of the uterus.
Pain
The severity of unpleasant and specific sensations may differ from each other depending on the duration of pregnancy. Probably the accession of pain, similar to menstruation. Most often, a similar symptom indicates an early miscarriage - no more than six weeks.
Probably cramping pains in the abdomen, pulling in the back. Their strength can vary from subtle to much more pronounced. In the rarest cases, when the clinical picture is complicated by a long course, this leads to a state of shock.
In the rarest cases, when the clinical picture is complicated by a long course, this leads to a state of shock.
Another typical manifestation of pain is discomfort in the back or abdomen. Only then are the discharges identified. A similar situation is most typical for spontaneous abortion at the seventh or eighth week of pregnancy.
Causes of miscarriage
The first factor is genetic abnormalities in the development of the fetus. It is they who most often lead to miscarriage in the early stages. Violations can be expressed in qualitative or quantitative failures in chromosomes. In this regard, the female body recognizes the defect, and therefore does not allow such a fetus to develop further. Most often, such rejection is noted in the third week of pregnancy.
The next reason that an early miscarriage has developed may be disturbances in the work of the endocrine gland. Hormones determine not only the success and regularity of the cycle, but also how well the fetus is attached to the mucous surface of the uterus.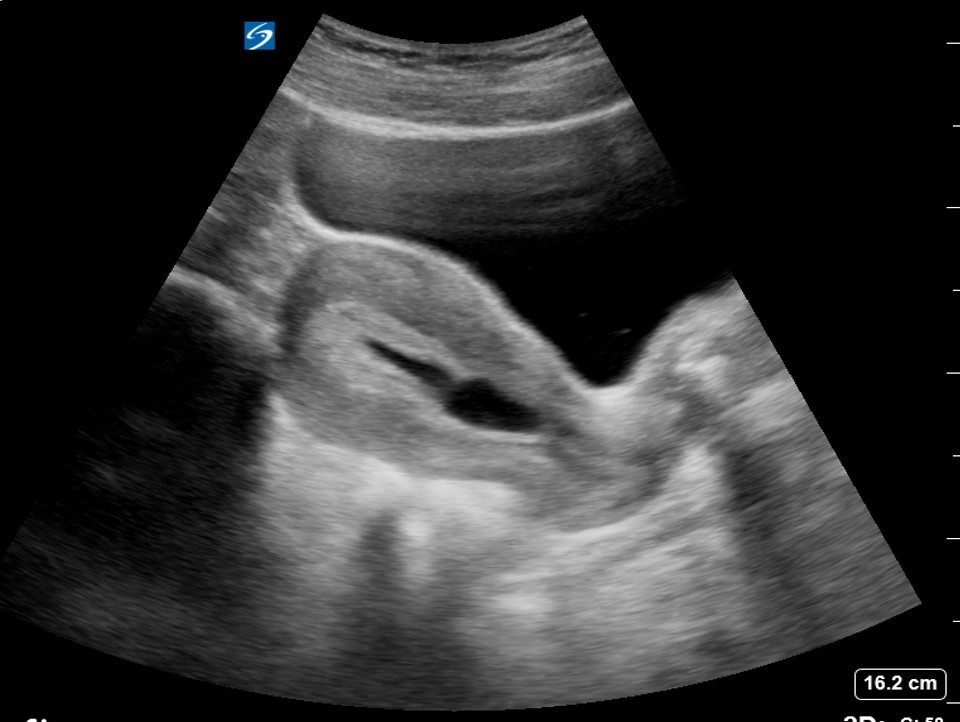 If, due to a malfunction of the thyroid gland, the endometrium is not able to provide the fetus with all the necessary components, the pregnancy will not go well. Most often, a miscarriage occurs at the beginning or at the end of the fourth week.
If, due to a malfunction of the thyroid gland, the endometrium is not able to provide the fetus with all the necessary components, the pregnancy will not go well. Most often, a miscarriage occurs at the beginning or at the end of the fourth week.
Other reasons why pregnancy is terminated:
- Rhesus conflict. If the parents have different Rh factors, then the risk that a miscarriage will occur after the first weeks of pregnancy increases significantly. This happens if a woman has a negative Rh, and the child has a positive, inherited from the father. In such a situation, the female body recognizes the fetus as a foreign object. Therefore, it is excreted from the uterus. Timely diagnosis allows you to save the child through full-fledged drug therapy.
- Sexually transmitted diseases, other infections. Similar problematic conditions also lead to spontaneous abortion. In this case, the embryo is infected at a very early stage. That is why the body will perceive it as a foreign object.
 In this regard, a miscarriage will occur already in the fifth week.
In this regard, a miscarriage will occur already in the fifth week. - Previous abortions. Another common reason why a miscarriage occurred. Abortion is a huge stress for the reproductive system, which leads to thinning of the lining of the uterus. That is why the risk of miscarriage may be greater.
Abdominal injuries should not be excluded from the list. Sharp pressure on the peritoneum, including when lifting weights, can provoke an abortion. Also on the list are severe stress, anxiety and depression. Anything that violates the normal state of a woman can lead to serious consequences.
How to avoid miscarriage
The main goal of treatment is to relieve tension in the uterus. It will be equally important to stop the bleeding and prolong the pregnancy, but only on the condition that the fetus is viable. The sooner medical assistance is provided, the higher the likelihood of preserving the fetus, without the need to determine the expected timing of miscarriages.
Our specialists will help you with this. Only we have the most qualified and experienced doctors who know exactly how to treat even the most difficult cases. They will conduct a full diagnosis and prescribe the most effective, effective medicines.
Drug treatment
Hormonal drugs are used. They at an early stage determine the normal course of pregnancy. Medicines based on the hormone progesterone are effective.
- The use of hemostatic drugs. In the case of pregnant women, droppers are used with drugs such as Dicinon or Tranexam. They are needed to stop bleeding.
- Antispasmodics. Experts recommend injections of Drotaverin, followed by a switch to painkillers such as No-shpa. Papaverine suppositories, droppers with the addition of magnesia are also used. All of them are necessary in order to remove a number of signs of a pathological condition, namely, an increased tone of the uterus and pronounced pain.
- Use of Tocopherol. Vitamin E is an indispensable component for women, including pregnant women.
 It ensures the normal and full functioning of the ovaries. Tocopherol also strengthens the vascular walls, eliminates the formation of blood clots.
It ensures the normal and full functioning of the ovaries. Tocopherol also strengthens the vascular walls, eliminates the formation of blood clots. - Sedative preparations. Use motherwort or valerian tincture. The presented measure is recommended for increased irritability or nervousness of a pregnant woman.
To prevent early miscarriage, the specialists of our clinic recommend glucocorticosteroids. Apply Dexamethasone or Metipred. They are prescribed to patients with diagnosed immune disorders that can lead to early termination of pregnancy.
A special relief ring can be fitted as an option. The presented procedure is carried out in the second trimester, or rather after the 20th week of gestation.
Remove this device not earlier than 38 weeks. It is necessary for a woman to maintain the correct position of the uterus. Also, the unloading ring helps to prevent premature birth.
Additional measures
To prevent early miscarriage, it is recommended to stop physical activity. Especially when it comes to jumping, lifting weights. Rest, lack of sudden physical activity and adherence to bed rest will help to keep the pregnancy.
Especially when it comes to jumping, lifting weights. Rest, lack of sudden physical activity and adherence to bed rest will help to keep the pregnancy.
Another preventive measure will be the exclusion of sudden movements. At any stage of pregnancy, they can provoke detachment of the embryo or lead to serious complications in its development.
To exclude an early miscarriage will allow:
- emotional peace and absence of stress;
- refusal to take a hot bath or visit a bath, sauna - this is due to the fact that high temperatures provoke increased bleeding, as well as detachment of the fetus;
- restriction of sexual intercourse - if there is a threat that an early miscarriage will occur, they refuse to have sex;
- exclusion of alcohol, nicotine addiction.
It is also important to stop eating certain foods. The ban applies to chocolate, coffee, and any other caffeinated drinks. In no case should you self-medicate.