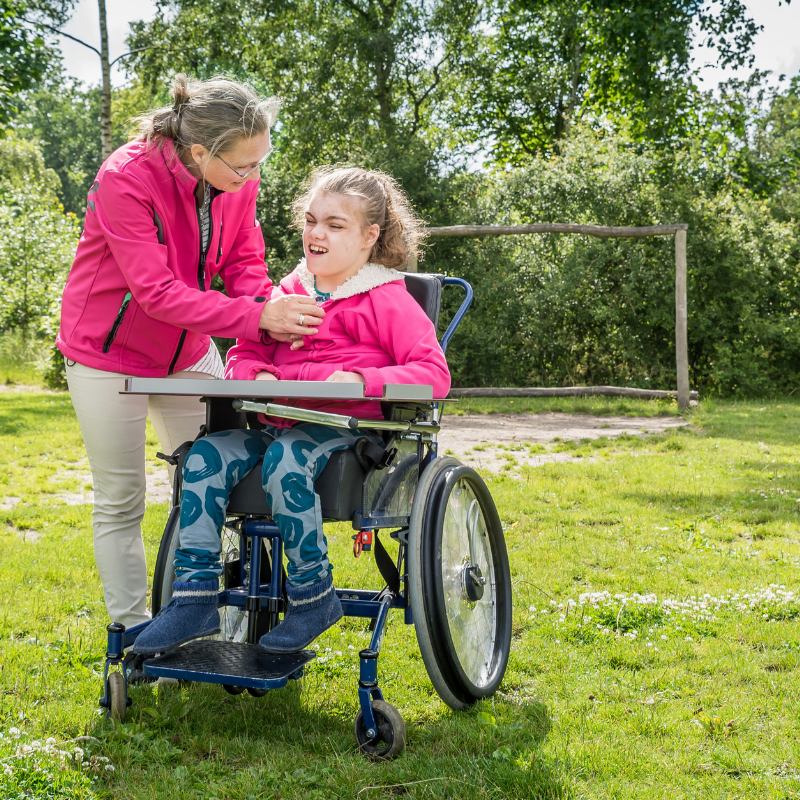
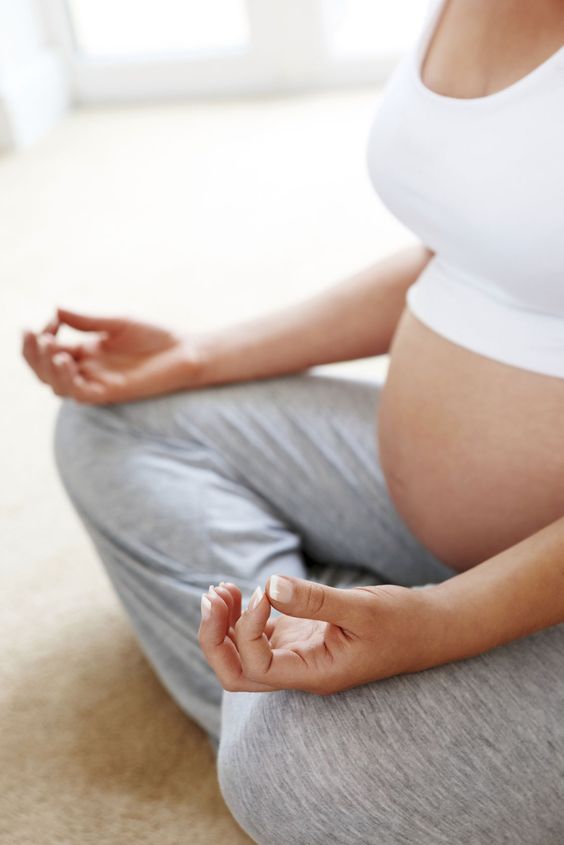
Is reaching bad when pregnant
Physical Demands (lifting, standing, bending) - Reproductive Health | NIOSH
Español (Spanish)
Physical demands at work could increase your chances of miscarriage, preterm birth, or injury during pregnancy. Learn more about reducing physical factors for a healthier pregnancy.
What are physical demands?
Physical factors can include:
- Lifting heavy objects (e.g., waitress carrying a tray or food to customers)
- Standing for long periods of time
- Repeatedly bending at the waist
Why should I worry about physical demands?
Everyday physical activities aren’t a cause for concern. In fact, moderate exercise during pregnancy with your doctor’s approval can help promote a healthy pregnancy. However, physical demands can put some workers at risk.
- High physical demands, like those listed above, may increase risks for adverse birth outcomes.
- Prolonged standing or heavy lifting can cause an increased chance of miscarriage or preterm delivery (premature birth).
- Changes in a pregnant woman’s hormones impact ligaments and joints in the spine to accommodate the developing baby. These changes can make a pregnant woman more prone to musculoskeletal injury from physical job demands. This can happen even before she “looks” pregnant or starts to show.
- During late pregnancy, changes in body size and body weight can impact balance. These changes also impact postures used to perform physical demands at work. Changes in balance and posture may increase the risk of falls and musculoskeletal injury.
- Physical demands at work may be linked with menstrual disorders, which might reduce fertility.
What jobs commonly involve high physical demands?
Many types of jobs can involve physical factors, including:
- Healthcare workers
- Manufacturing workers
- Construction crews
- Service workers
- Flight attendants
- Firefighters
- Childcare providers and teachers
- Farm and greenhouse workers
- Law enforcement officers
What is not known?
- We don’t know what causes most menstrual disorders, miscarriages, or preterm births.
 If one of these events occurs, we often can’t tell if the cause was job-related physical labor or something else.
If one of these events occurs, we often can’t tell if the cause was job-related physical labor or something else. - We don’t know what amount of heavy lifting, prolonged standing, or bending is safe for each pregnant woman. It depends partially on each woman’s health, physical fitness level, and stage of pregnancy. Talk to your doctor about what level of strenuous physical activity is appropriate for you.
What can I do to reduce or eliminate exposure?
- Discuss these recommendations for lifting during pregnancyimage icon with your doctor. (Infografía en españolimage icon)
- If you are pregnant and working, you may want to reduce or avoid:
- Stooping, bending, or squatting often
- Lifting heavy objects from the floor or any location that requires you to bend or reach
- Lifting overhead or reaching
- Standing for 3 hours or more
- If you are pregnant and work in a physically demanding job, you may benefit from sitting down during breaks.

Where can I get more information?
View an infographic on provisional weight limits for lifting during pregnancy. (en español)
Read about provisional recommended weight limits for manual lifting during pregnancy and clinical guidelines for occupational lifting in pregnancy.
Top of Page
By Trimester, How It Feels & When to Avoid
It can feel like pregnancy changes everything.
In some ways, it does. You’re skipping your favorite sushi place and reaching for well-done steak instead. The smallest odors seem to have you rushing to the toilet to throw up, and even sitcoms can leave you in an emotional puddle of tears. You’ve asked your OB everything under the sun, from whether you can have beef jerky to if your belly button will become an outie — and why.
But there’s one subject you’re wondering about that you’ve felt a little uncomfortable bringing up: the big O.
So is it OK to have an orgasm during pregnancy? (And if you’ve already had one, why did it felt really, really good — better than it ever has before?)
The short answer is yes, in most cases, it’s absolutely fine to have an orgasm while pregnant — in fact, it can also be a great for your emotional and mental well-being.
Let’s take a closer look at orgasm safety, sensations in the first, second, and third trimesters, and a big myth about orgasms bringing on labor — debunked.
When it comes to sex during pregnancy, there’s a lot that can cause hesitation: You may not feel “in the mood,” thanks to hormones and morning sickness; your partner may worry about “poking the baby” or otherwise hurting you; and you both may have concerns about orgasms and uterine contractions.
Always check with your doctor about whether you, specifically, are OK to have sex. But if your doctor hasn’t told you otherwise, and your pregnancy is low risk, it’s generally completely safe to get it on between the sheets.
In fact, when researchers looked at studies involving 1,483 pregnant women, they found that there were no significant differences between those who had sex during their pregnancy and those who didn’t when it came to inducing labor contractions.
Researchers also noted that in low risk pregnancies, sex wasn’t associated with “preterm birth, premature rupture of membranes, or low birth weight. ”
”
However, if you have any of the following, your doctor may indeed tell you to abstain from sexual activity:
- spotting or bleeding
- incompetent cervix (when the cervix is shorter than about 22 millimeters and you’re at higher risk for preterm birth)
- vasa previa (when the umbilical cord vessels run too close to the cervix)
- placenta previa (when the placenta covers the cervix)
Also, don’t have sex if your water has already broken. Amniotic fluid forms a protective barrier between your baby and the outside world — without it, you’re more at risk for infection.
What is pelvic rest?
If your doctor puts you on “pelvic rest” and hasn’t explained what that means, absolutely ask questions. It usually means no vaginal sex because your pregnancy is considered high risk. Since you can achieve orgasm without penetrative sex, it’s worth clarifying what’s off limits.
If your pregnancy is high risk for other reasons, like multiples, talk to your OB. One review of studies found that there simply isn’t enough research about sex during high risk pregnancies.
One review of studies found that there simply isn’t enough research about sex during high risk pregnancies.
First trimester
Sex in the first trimester may be great, or it may suffer from many “false starts”: You’re in the mood one minute, and a wave of nausea hits you the next.
On the other hand, your body is already becoming more sensitive — your breasts, for example, may be more tender to the touch and therefore more easily stimulated by your partner or yourself. Your libido may increase, too. These things, along with more natural lubrication down there, may result in quicker and more satisfying orgasms.
Or, you may just need to wait for the discomfort of first trimester symptoms to pass. And some women’s libido actually decreases. And that’s OK, too. It’s all within the realm of normal.
Second trimester
This might be the sweet spot when it comes to reaching your, ahem, sweet spot.
With morning sickness (usually) a thing of the past and the discomforts of the third trimester yet to come, sex and orgasm during the second trimester may be the most enjoyable.
Here are a few things that you may experience:
- Your orgasms may be more pleasurable. There are a few reasons for this, with perhaps the main one being increased blood flow during pregnancy. This means your uterus and vaginal area are more engorged, which can mean more sensitivity. This can go either way depending on the person, but for many, it means more pleasure — and easier orgasms.
- You may feel post-orgasm uterine contractions or cramps. These are perfectly normal and even happen when you’re not pregnant — you just may not feel them unless you are. Don’t worry — these contractions aren’t labor, and they’re not going to bring on labor. Cramps will generally subside with rest.
- Your stomach may feel very hard. This is another common occurrence during orgasm, pregnant or not. But with your stretched skin and more extended belly, chances are, you’ll notice this sensation more.
- The release of hormones may be compounded.
 What we mean is this: Your body is already producing more oxytocin (the “love hormone”) during pregnancy. You’ll release even more when you orgasm. And that’s typically going to feel pretty darn good.
What we mean is this: Your body is already producing more oxytocin (the “love hormone”) during pregnancy. You’ll release even more when you orgasm. And that’s typically going to feel pretty darn good.
Third trimester
Sex in general may be more difficult during the home stretch that is the third trimester. For one thing, your adorable baby bump may feel more like an enormous sack of potatoes: awkward to carry and always in the way. (That’s where creative sex positions come in!)
But also, you may have a harder time reaching the big O. With baby taking up so much room in your uterus, the muscles may not be able to fully contract as they need to in order to climax.
An orgasm is an orgasm, no matter whether it involves two people or just one. So masturbation is completely safe during pregnancy — unless you’ve been told to abstain — and so is using sex toys.
Just remember to practice good hygiene and keep any toys you use clean — now is not the time you want to worry about sexually transmitted infections, which can be introduced to your body by a penis, finger, or toy.
Most of us have heard it. Past your due date and ready to get this show on the road already? Take long walks. Eat spicy food. And have sex.
If you believe this myth, it makes sense that you’d hesitate to have an orgasm before your due date for fear of preterm birth. But here’s the thing: This just isn’t true. The rumor persists, but it’s been debunked.
In one 2014 study, researchers divided pregnant women into two groups — ones who had sex twice a week and ones who abstained. The women were at term — meaning, baby was ready to make their appearance. But researchers found no statistically significant difference in the two groups when it came to onset of labor.
And as we’ve already mentioned, a much larger review of studies similarly found that sex didn’t increase risk of spontaneous labor.
(Spoiler alert: There’s no evidence that spicy food brings on labor, either.)
Good news if pregnancy has your hormones raging and your libido through the roof: It’s completely safe to have an orgasm during a low risk pregnancy.
If your pregnancy is high risk and it’s not safe for you, your doctor should tell you. Still, it’s worth having that conversation. And if you feel embarrassed about asking, remember: OBs have heard it all. No topic should be off limits.
And the old folk wisdom that says that sex brings on labor? It’s just not supported. So whether you’re 8 weeks or 42 weeks, feel free to get busy with your partner — or yourself — and enjoy the O.
1st, 2nd and 3rd trimester
During the period of carrying a baby, the expectant mother carefully monitors her well-being, worrying, first of all, about the health of the fetus.
Important!
To avoid groundless worries, a woman should know which symptoms are quite normal for pregnancy or, on the contrary, pose a danger to both her and the child. Acquaintance with relevant literature or conversations with specialists will be especially useful for girls who are preparing to become a mother for the first time.
A woman already has her own experience with a second pregnancy. She can compare her feelings, catch possible deviations from the norm.
She can compare her feelings, catch possible deviations from the norm.
Well-being during pregnancy depends on the age of the expectant mother, on the initial state of her health and even on the sex of the child (although the latter statement has not been scientifically proven and is in the nature of a sign). A young girl without malformations and chronic ailments will more easily endure pregnancy. And qualified specialists will help a woman with certain diseases to give birth to a healthy baby.
Despite the fact that bearing a child is a unique and highly individual process, there are a number of characteristic features in the state of health at different stages of pregnancy:
- The first trimester is often accompanied by some emotional instability of the expectant mother. At the same time, her general well-being is characterized by weakness and drowsiness. A rare woman in the first trimester bypasses toxicosis: its mild degree in the form of morning sickness is a completely expected phenomenon.

- The second trimester of pregnancy is considered the most comfortable and carefree. The expectant mother will soon feel the timid movements of her baby. Her appetite is noticeably improving.
- Pregnancy in the third trimester, approaching its end, brings a number of physical difficulties due to a significant increase in the size of the uterus. The psychological well-being of the expectant mother is characterized by a balance of two processes - the fear of childbirth and the anticipation of the joy of the upcoming meeting with the baby.
Feeling well in the first trimester of pregnancy
Shortly after conception, a kind of revolutionary transformation of the hormonal background takes place in the body of a woman. The endocrine system of the mother tries to create the most favorable conditions for the intrauterine development of the fetus. A woman's well-being during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, changes primarily under the influence of progesterone - the ovaries begin to actively synthesize this hormone after fertilization. Thanks to progesterone, the vessels that feed the pelvic organs expand. Thus, the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the embryo improves, and other organs of the expectant mother find themselves in a somewhat deprived position.
Thanks to progesterone, the vessels that feed the pelvic organs expand. Thus, the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the embryo improves, and other organs of the expectant mother find themselves in a somewhat deprived position.
Important!
The redistribution of blood in a woman's body in the first trimester of pregnancy leads to a slight drop in blood pressure, which may cause increased drowsiness, absent-mindedness, fatigue and general weakness.
In the early stages of bearing a child, a woman's well-being can be overshadowed by toxicosis of varying severity - from mild nausea to persistent vomiting in response to food intake or certain odors. Experts will help to cope with malaise by recommending fractional meals and a special medical and protective regimen of the day in the first trimester. Prolonged toxicosis can cause hospitalization: it interferes with the normal absorption of food, as a result, the full supply of the baby with the necessary substances.
During pregnancy, taste preferences may change, some quirks may appear. A woman begins to feel an aversion to meat, gravitates towards salty foods and is ready to absorb chalk, tooth powder or dry pasta with pleasure. Such a perversion of taste is often explained by the development of iron deficiency anemia during pregnancy.
A woman begins to feel an aversion to meat, gravitates towards salty foods and is ready to absorb chalk, tooth powder or dry pasta with pleasure. Such a perversion of taste is often explained by the development of iron deficiency anemia during pregnancy.
In the first trimester, the expectant mother notes discomfort in the mammary glands, pigmentation of the nipples, increased vaginal discharge, increased urination. These processes are physiological. But the appearance of pulling pains in the lower abdomen and blood from the genital tract are pathological symptoms. To maintain pregnancy, you should immediately seek medical help.
The well-being of the expectant mother: the second trimester
The first three dangerous (due to the relatively high risk of miscarriage) months of pregnancy have passed. The second trimester of childbearing has begun. The baby and mother are used to coexistence. Toxicosis receded, general well-being improved. The woman's tummy is noticeably rounded and clearly pleasing to the eye.
Closer to the 20th week of pregnancy, the expectant mother listens especially carefully to her well-being, waiting for the first time to feel the baby moving.
An increase in the level of estrogen and, as a result, the retention of excess fluid in the body of a pregnant woman can adversely affect her well-being in the second trimester. It is not so much the obvious swelling of the lower extremities that is dangerous, but the swelling of the placenta that is not visible to the eye, the development of which can disrupt the blood supply to the fetus. Refusal of liquid food is not the best solution to the problem. After all, water, along with foods rich in vegetable fiber, helps to avoid the development of constipation in the second trimester.
The expectant mother's appetite has noticeably improved. When catching up, do not overdo it, remember the list of prohibited foods: fast food, fatty, spicy, smoked dishes, raw eggs, sushi, moldy cheeses, carbonated drinks, coffee, alcohol. Give preference to healthy food: meat, lean fish, cereals.
Give preference to healthy food: meat, lean fish, cereals.
The second trimester is a time of strict control over body weight. An increase of no more than 300 g is allowed weekly. In the third trimester of pregnancy, this increase should not exceed 400 g. In case of excess weight, the doctor will review the diet of a pregnant woman and prescribe fasting days.
Pregnant woman's well-being: third trimester
From the 27th obstetric week, the third trimester of childbearing begins. Pregnancy, approaching completion, introduces a number of physical inconveniences into the well-being of the expectant mother. By the end of the third trimester, the maximally enlarged uterus causes some displacement of the internal organs. The woman is worried about shortness of breath, lower back pain, frequent urination, possible constipation, varicose veins in the legs.
Psychological well-being in the third trimester is often disturbing, fear of childbirth may appear.
Important!
In the third trimester, you need to carefully monitor your well-being in order to timely detect possible pathological phenomena (preeclampsia, placental abruption) and seek help.
In the last months of pregnancy, the growing baby becomes cramped in the uterine cavity, and the expectant mother no longer feels timid movements, but active pushes with her hand or heel.
In the third trimester, the harbingers of childbirth (sagging abdomen, training contractions, mucus plug discharge) will tell the woman that the meeting with the baby will take place very soon.
Good health during pregnancy is an indicator of its favorable course. The deterioration of the condition of the expectant mother is the reason for a visit to a specialist.
Early toxemia of pregnancy - causes and treatment
- When does early toxemia begin in pregnancy
- Manifestation of early toxicosis
- Early causes of toxicosis
- Severity of toxicosis during pregnancy
- How to manage morning sickness and relieve symptoms
- Principles of treatment of early toxicosis
Most women, having barely learned about the onset of pregnancy, are waiting for poor health, nausea and even vomiting. Indeed, early toxicosis often becomes a constant companion of many expectant mothers in the early stages of pregnancy. Is there any way to alleviate these unpleasant symptoms?
Indeed, early toxicosis often becomes a constant companion of many expectant mothers in the early stages of pregnancy. Is there any way to alleviate these unpleasant symptoms?
Toxicosis (and doctors call this condition preeclampsia) is a syndrome that is defined as a violation of a woman's adaptation to pregnancy. According to the time of occurrence, early preeclampsia is distinguished, which will be discussed in this article, and late preeclampsia, which appears in the last 2-3 months of pregnancy and is manifested by edema, increased blood pressure and the appearance of protein in the urine.
When early morning sickness begins in pregnancy
Early morning sickness usually occurs in the first half of pregnancy. As a rule, after the end of the formation of the placenta, that is, at 12-13 weeks of pregnancy, the phenomena of toxicosis stop. During a normal pregnancy, adaptive changes in the function of almost all organs and systems occur in a woman's body, which are regulated by the nervous system with the participation of endocrine glands. Toxicosis also occurs due to the impossibility of the adaptive mechanisms of the body of the expectant mother to adequately meet the needs of the developing fetus.
Toxicosis also occurs due to the impossibility of the adaptive mechanisms of the body of the expectant mother to adequately meet the needs of the developing fetus.
Manifestation of early toxicosis
The most common manifestation of toxicosis is vomiting. Other forms of early toxicosis are very rare:
- Pregnancy dermatosis is a group of skin diseases that occur during pregnancy and disappear after it. When it occurs in early pregnancy, dermatosis is caused by immune disorders in the body of a pregnant woman, and is also most often found in patients with diseases of the digestive and endocrine systems. The most common form of dermatoses of pregnancy is pruritus gravidarum, which can be on a small area of the skin or spread throughout the body, including the feet and palms.
- tetany (chorea) of pregnant women. This condition occurs when the function of the parathyroid glands decreases, as a result of which calcium metabolism in the body is disturbed.
 Clinically, the disease is manifested by muscle cramps, more often cramps occur in the fingers, sometimes in the muscles of the face.
Clinically, the disease is manifested by muscle cramps, more often cramps occur in the fingers, sometimes in the muscles of the face. - salivation - increased secretion of saliva, in connection with which there is a large loss of fluid (up to 1 liter per day). Salivation can be an independent manifestation of toxicosis or accompany vomiting of pregnant women. In the development of salivation, not only changes in the central nervous system are important, but also local disturbances in the salivary glands and their ducts under the influence of hormonal changes.
- Pregnancy bronchial asthma is an extremely rare form of preeclampsia.
- pregnancy osteomalacia - softening of the bones due to a violation of calcium and phosphorus metabolism, while the bones of the pelvis and spine are more often affected
- neuropathy and psychopathy of pregnancy.
Causes of toxicosis in the early stages
There are many theories trying to explain the causes and mechanisms of early toxicosis: the most recognized are the so-called neuro-reflex and immunological.
According to the neuro-reflex concept , vomiting occurs as a result of a violation of the relationship between the cerebral cortex and subcortical structures. During pregnancy, the subcortical centers of the brain begin to work more intensively than usual, which are responsible for most protective reflexes, including breathing and cardiac activity. In the same areas of the subcortical structures are the vomiting and salivary centers, the nuclei of the olfactory system of the brain. Excitation processes also capture them. Therefore, nausea and vomiting may be preceded by such phenomena as deepening of breathing, increased heart rate, an increase in the amount of saliva, pallor due to vasospasm, and a change in smell.
Immunological disorders play a certain role in the development of preeclampsia . The timing of the onset of vomiting usually coincides with the formation of blood circulation in the placenta, increased reproduction of white blood cells - lymphocytes, which are involved in immune reactions. The fetus is foreign to the mother's body, and her immune system reacts to it in this way. After the full maturation of the placenta, which accumulates all these immune cells, toxicosis usually disappears.
The fetus is foreign to the mother's body, and her immune system reacts to it in this way. After the full maturation of the placenta, which accumulates all these immune cells, toxicosis usually disappears.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) plays a certain role in the development of vomiting in pregnant women. This hormone is produced by the placenta during pregnancy. Its high concentration can provoke vomiting.
The severity of toxicosis during pregnancy
The main symptom of early toxicosis of pregnant women is vomiting. Depending on the frequency of its occurrence, as well as the degree of metabolic disorders in the body of the expectant mother, doctors distinguish three degrees of severity of vomiting during pregnancy.
How to manage morning sickness and relieve symptoms
Treatment for mild morning sickness is usually done at home. But, nevertheless, a pregnant woman should be under the supervision of doctors, take all the tests recommended by the doctor, and follow the appointments. This will allow the doctor to monitor the condition of the future mother's body and prevent possible complications in time. A woman needs to organize a normal sleep and rest regimen, walks in the fresh air, a calm atmosphere in the family are shown.
This will allow the doctor to monitor the condition of the future mother's body and prevent possible complications in time. A woman needs to organize a normal sleep and rest regimen, walks in the fresh air, a calm atmosphere in the family are shown.
Proper nutrition
You need to eat in small portions, fractionally, every 2-3 hours. Food should be easily digestible, high-calorie and fortified whenever possible. In connection with a decrease in appetite, they recommend varied and pleasant food for the expectant mother, that is, products are selected taking into account the desires of the pregnant woman, with the exception of spicy dishes and smoked meats. It is important to remember that very hot or very cold food often induces vomiting, so the dishes should be warm. Reception of alkaline mineral waters in small volumes 5-6 times a day is shown.
If nausea and vomiting occur in the morning, immediately after waking up, it is recommended to have breakfast while lying in bed without getting up. For breakfast, you can eat dry crackers, crackers, drink tea or water with lemon, light yogurt is allowed. It is better to put all this next to the bed in advance or ask someone to bring breakfast.
For breakfast, you can eat dry crackers, crackers, drink tea or water with lemon, light yogurt is allowed. It is better to put all this next to the bed in advance or ask someone to bring breakfast.
Every woman chooses for herself a remedy that helps to fight nausea. Someone helps a slice of orange, lemon or apple, some expectant mothers carry crackers or mint sweets with them to alleviate the symptoms of toxicosis. Pumpkin juice has a good antiemetic effect. Many pregnant women benefit from ginger tea. It is prepared very simply:
ginger root finely chopped or grated on a coarse grater is poured with boiling water and infused for 15-20 minutes. Tea can be drunk warm or chilled, adding lemon, mint or honey to it.
Fats and proteins of animal origin are recommended to be consumed in the morning, when pancreatic enzymes are more active. Dairy products are best eaten after dinner or before bed.
Do not use food with preservatives, broiler meat, fast food, fast food.
To maintain metabolic processes in the body, it is advisable to drink 2-2.5 liters of fluid per day. With increased vomiting, it is not recommended to consume solid and liquid food at the same time. Liquids should not be drunk 30 minutes before and within 1.5 hours after eating, as this provokes vomiting by stretching the walls of the stomach and affecting the receptors.
Decoctions and infusions
Oat broth
As an enveloping agent, that is, a substance that forms a mucous film and prevents irritation of receptors on the walls of the stomach and intestines, oat broth is recommended. It is prepared as follows: 2-3 tbsp. spoons of oat grains are washed, pour 500-700 ml of water, boil over low heat under a lid for 30 minutes. The broth is drained, the grains are crushed and poured with new water and boiled until fully cooked. The resulting mass is crushed with a blender. You need to use the decoction on an empty stomach and in the evening before going to bed, but not earlier than 2 hours after dinner, and also throughout the day in small portions.
It has a particularly good effect in combination with rosehip infusion.
Rosehip tincture
This tincture is a good source of vitamins and microelements – it contains vitamins C, K, P and PP, potassium, manganese, iron, it contributes to the normalization of the gallbladder function. To prepare it, you need 1 tbsp. pour a spoonful of crushed rose hips with 250 ml of boiling water and insist in a thermos for about 2 hours.
The following infusions and decoctions contribute to reducing nausea and improving the condition of the expectant mother.
Phytonast
Take equally: valerian root, common anise fruits, fireweed leaves, linden flowers, marigold flowers, common blueberry shoots, blood-red hawthorn fruits. 1 st. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over a spoonful of the mixture ground in a coffee grinder and insist in a thermos for 2 hours, then strain. Take the infusion as needed, up to 6 times a day in a heated form, 1/3 cup.
Benediktov's collection
To prepare this collection you will need: common yarrow (10 g), peppermint herb (20 g), shepherd's purse herb (20 g), valerian officinalis rhizomes (10 g), calendula officinalis inflorescences (20 g) and inflorescences of chamomile officinalis (20 g). Pour 10 g of the mixture with 400 ml of water, soak in a water bath for 30 minutes, strain. Take 50 ml 6 times a day for 25 days, three courses with 15-day breaks.
Pour 10 g of the mixture with 400 ml of water, soak in a water bath for 30 minutes, strain. Take 50 ml 6 times a day for 25 days, three courses with 15-day breaks.
Viburnum with honey
Grind 2 tbsp. tablespoons of fresh viburnum berries, pour 250 ml of boiling water over them, heat for 10 minutes in a water bath, strain, add a little honey. Take 1/3 cup of warm infusion before meals 3-4 times a day.
Cranberries with mint, honey and lemon
Squeeze the juice from 250 g of cranberries, cool it, boil the pulp in 1 liter of water, add 1 tbsp. a spoonful of mint leaves and leave for 15 minutes under the lid. Strain, dissolve in a hot broth 2-3 tbsp. tablespoons of honey, let cool to room temperature, add chilled cranberry juice and a slice of lemon. Drink 0.5 cup after meals or when nausea occurs.
Rose hips with apples
Crushed rose hips (approx. 1 tbsp) pour 250 ml of boiling water, add 0.5 tbsp. tablespoons of dried apples, heat in a water bath for 15-20 minutes. This drink can be consumed throughout the day instead of tea.
This drink can be consumed throughout the day instead of tea.
Rosehip with garden berries
To make a drink you will need: 1 tbsp. a spoonful of rose hips, 1 tbsp. spoon of raspberries, 1 tbsp. spoon of blackcurrant leaves, 1 tbsp. a spoonful of lingonberry leaves. 2 tbsp. spoons of the mixture pour 500 ml of boiling water, boil for 5 minutes, leave for 1 hour, strain. Take 100 ml of decoction 3 times a day.
Therapeutic exercise
Among non-drug treatments, exercise therapy has a good effect. The complex of exercises includes walking, deep breathing with stretching of the muscles of the trunk and limbs. It is necessary to exclude inclinations, they can increase nausea. The complex includes dynamic exercises for training the muscles of the arms, legs, relaxation exercises. Remedial gymnastics also includes training in breathing techniques. As a result, the body is saturated with oxygen, the excitability of the vomiting center decreases - toxicosis is relieved.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Among the physiotherapeutic procedures for the treatment of early toxicosis, electrosleep, acupuncture, laser therapy are used. Electrosleep is a method that uses low frequency currents to induce sleep. The duration of the procedure is from 60 to 90 minutes, the course of treatment is 6-8 sessions.
Laser therapy
In the complex therapy of early toxicosis, blood is irradiated with a helium-neon laser through a light guide passed through a needle placed in the cubital vein. The procedure lasts 15-20 minutes. The therapeutic effect is achieved due to the influence of the laser on blood cells, changes in its properties, accumulation of biologically active substances in the blood. As a result, the metabolism in cells changes, the resistance of tissues and the body to adverse conditions increases, and the vitality increases.
Acupuncture, acupuncture
These are methods of treatment based on irritation of biologically active points and zones on the body and face. With early toxicosis, such an effect changes the tone of the nervous system of a pregnant woman. A session of acupuncture is carried out 1-2 times a week and lasts 15-30 minutes.
With early toxicosis, such an effect changes the tone of the nervous system of a pregnant woman. A session of acupuncture is carried out 1-2 times a week and lasts 15-30 minutes.
With morning sickness and vomiting of pregnant women, the method of acupressure is effective. To do this, you need to press your finger on a point that is located on the inside of the wrist, in the middle, 3 transverse fingers above the palm.
Aromatherapy
The use of plant aromas has a positive effect on the expectant mother and baby. By inhaling pleasant aromas, you can achieve a good psychological effect, create a good mood, and reduce the effects of toxicosis. During pregnancy, aroma lamps, aroma medallions, pads - sachets are mainly used. To relieve nausea and vomiting, oils of noble laurel, lemon, lavender, cardamom present, dill, lemon balm, peppermint, anise, eucalyptus, ginger are suitable. To flavor the air, you can use the following mixture 0 3 drops of lavender oil, 1 drop of peppermint oil, 1 drop of eucalyptus oil.
Principles of treatment of early toxicosis
Even with a mild course of early toxicosis of pregnant women, the attending physician will definitely prescribe a number of tests - a general blood test, a general urinalysis, a biochemical blood test, a hemostasiogram. This is necessary to control the condition of a pregnant woman and to timely prescribe medications to correct the changes that occur in the body.
If non-drug remedies are ineffective, the doctor prescribes medications that help fight toxicosis. First of all, these are herbal sedatives, homeopathic medicines for nausea, vitamin B6 preparations, antiemetics.
If, despite all therapy, vomiting increases, the doctor detects changes in blood and urine tests, and body weight continues to progressively decrease, hospitalization is indicated.
The hospital provides intravenous infusion of medicines that restore fluid, trace elements and proteins lost by the body. A pregnant woman receives at least 2-2. 5 liters of fluid intravenously per day.
5 liters of fluid intravenously per day.
To improve blood flow through the placenta and improve oxygen supply to the fetus, oxygen therapy can be prescribed - inhalation of an oxygen-air mixture for 20-30 minutes twice a day.
Most often, the effects of toxicosis gradually decrease by 12-13 weeks of pregnancy.
Mild
Mild vomiting on an empty stomach or after eating occurs 3 to 5 times a day. Despite vomiting, part of the food is still retained and significant weight loss is not observed in such pregnant women. The general condition does not suffer significantly, there are no changes in blood and urine tests. Such vomiting is easily treatable with various non-drug means, and often resolves on its own after the normalization of the diet and rest.
Moderate vomiting
Moderate vomiting (or moderate vomiting) is expressed in the increase in vomiting up to 10 times a day, regardless of food intake. Characterized by persistent nausea. There comes dehydration of the body, a decrease in body weight by 3-5 kg (6% of the initial weight).