Mild microcephaly symptoms
Microcephaly | Boston Children's Hospital
How is microcephaly diagnosed?
Doctors typically diagnose microcephaly by:
- taking a full medical and family history
- performing a complete physical exam
- measuring the size of the baby’s head as he or she grows, to compare with the average head size for age and gender
- measuring the head size of the parents (sometimes smaller head sizes simply run in the family)
Can microcephaly be found during pregnancy?
If your child has the congenital form of microcephaly — arising before birth — it might be possible to detect the condition with a prenatal ultrasound during the third trimester of pregnancy. Microcephaly is usually not obvious until the third trimester.
What testing is done for microcephaly?
If your child has microcephaly that involves some degree of learning disability or other impairment, your clinician may suggest one of the following tests:
- x-rays
- computed tomography (CT) scan
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan
If a genetic cause of microcephaly is suspected, your clinician may also suggest genetic testing.
Will my child with microcephaly be OK?
Your child’s exact prognosis depends on his or her specific symptoms and circumstances. Keep in mind that head size doesn’t always predict how a child will do.
While microcephaly cannot be cured, support and therapy can help new brain connections grow, even if the brain remains small. Even in the most severe cases, there are treatment options that can help your child feel and function better.
Can microcephaly be prevented?
When microcephaly is genetic, it cannot be prevented, but genetic counseling can be help you learn if the mutation is inherited and the likelihood that future children could be affected.
Those who live in or travel to areas where the Zika virus is common can prevent microcephaly by taking steps avoiding mosquito bites. Some health authorities suggest that women in Zika-affected areas postpone pregnancy until a Zika outbreak is contained.
Expectant mothers can also reduce the risk of having a baby with microcephaly by not using drugs or alcohol, eating a nutritious diet, and avoiding exposure to toxic chemicals and other viruses that can cause microcephaly.
What are the treatment options for microcephaly?
There is no cure for microcephaly, since there is no way to enlarge the brain and head. Instead, the treatment focuses on managing symptoms and any related conditions. Every child with microcephaly is different, so the type of support will be guided by his or her symptoms and severity of disease.
Children who don't have any problems other than a small head size will not need any treatment. Children who have problems with learning, speech or motor skills may benefit from:
- physical therapy to help improve strength, movement, and coordination
- occupational therapy to help build confidence performing day-to-day tasks
- speech therapy to help improve language, voice, and swallowing skills
- psychological counseling to help with self-esteem and feelings about their medical condition
Some children with severe microcephaly can have physical complications, such as seizures and facial deformities.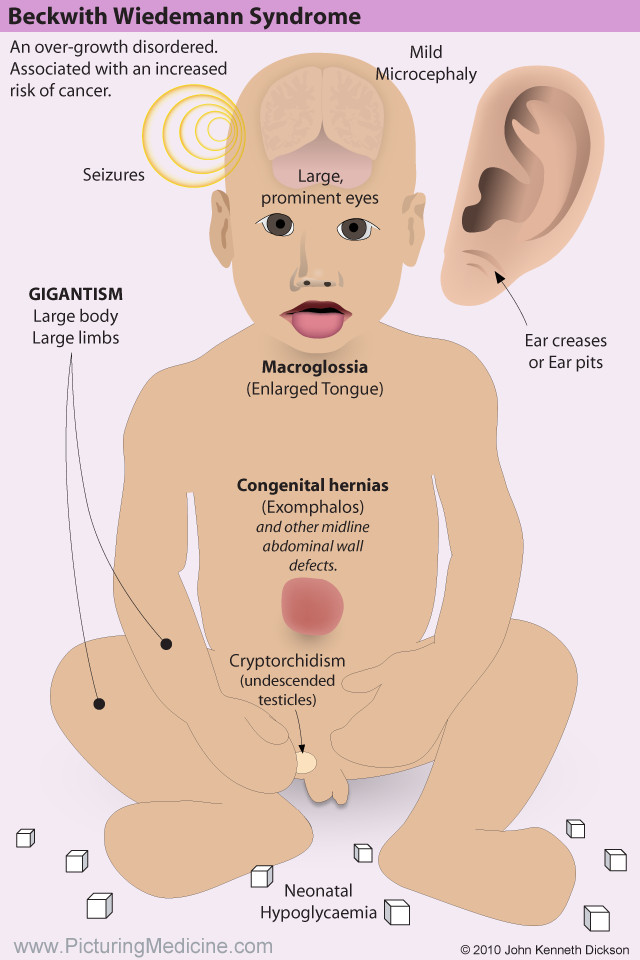 These types of problems are treated separately.
These types of problems are treated separately.
Facts about Microcephaly | CDC
Microcephaly is a birth defect where a baby’s head is smaller than expected when compared to babies of the same sex and age. Babies with microcephaly often have smaller brains that might not have developed properly.
Click here to view a larger image
The images are in the public domain and thus free of any copyright restrictions. As a matter of courtesy we request that the content provider (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities) be credited and notified in any public or private usage of this image.
What is microcephaly?
Microcephaly is a condition where a baby’s head is much smaller than expected. During pregnancy, a baby’s head grows because the baby’s brain grows. Microcephaly can occur because a baby’s brain has not developed properly during pregnancy or has stopped growing after birth, which results in a smaller head size.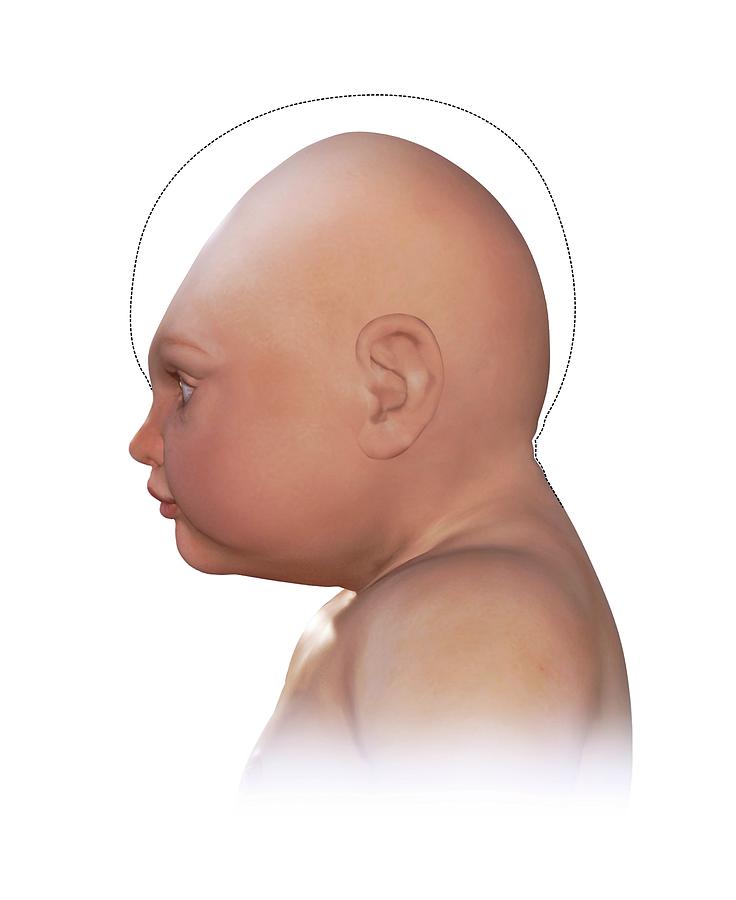 Microcephaly can be an isolated condition, meaning that it can occur with no other major birth defects, or it can occur in combination with other major birth defects.
Microcephaly can be an isolated condition, meaning that it can occur with no other major birth defects, or it can occur in combination with other major birth defects.
What is severe microcephaly?
Severe microcephaly is a more serious, extreme form of this condition where a baby’s head is much smaller than expected. Severe microcephaly can result because a baby’s brain has not developed properly during pregnancy, or the brain started to develop correctly and then was damaged at some point during pregnancy.
Other Problems
Babies with microcephaly can have a range of other problems, depending on how severe their microcephaly is. Microcephaly has been linked with the following problems:
- Seizures
- Developmental delay, such as problems with speech or other developmental milestones (like sitting, standing, and walking)
- Intellectual disability (decreased ability to learn and function in daily life)
- Problems with movement and balance
- Feeding problems, such as difficulty swallowing
- Hearing loss
- Vision problems
These problems can range from mild to severe and are often lifelong.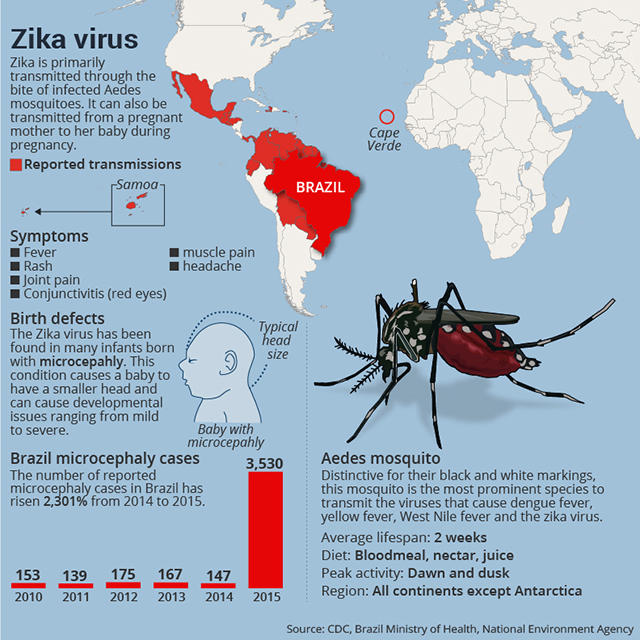 Because the baby’s brain is small and underdeveloped, babies with severe microcephaly can have more of these problems, or have more difficulty with them, than babies with milder microcephaly. Severe microcephaly also can be life-threatening. Because it is difficult to predict at birth what problems a baby will have from microcephaly, babies with microcephaly often need close follow-up through regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor their growth and development.
Because the baby’s brain is small and underdeveloped, babies with severe microcephaly can have more of these problems, or have more difficulty with them, than babies with milder microcephaly. Severe microcephaly also can be life-threatening. Because it is difficult to predict at birth what problems a baby will have from microcephaly, babies with microcephaly often need close follow-up through regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor their growth and development.
How Many Babies are Born with Microcephaly?
Microcephaly is not a common condition. Researchers estimate that about 1 in every 800-5,000 babies is born with microcephaly in the United States.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of microcephaly in most babies are unknown. Some babies have microcephaly because of changes in their genes. Other causes of microcephaly, including severe microcephaly, can include the following exposures during pregnancy:
- Certain infections during pregnancy, such as rubella, toxoplasmosis, or cytomegalovirus
- Severe malnutrition, meaning a lack of nutrients or not getting enough food
- Exposure to harmful substances, such as alcohol, certain drugs, or toxic chemicals
- Interruption of the blood supply to the baby’s brain during development
Some babies with microcephaly have been reported among mothers who were infected with Zika virus while pregnant.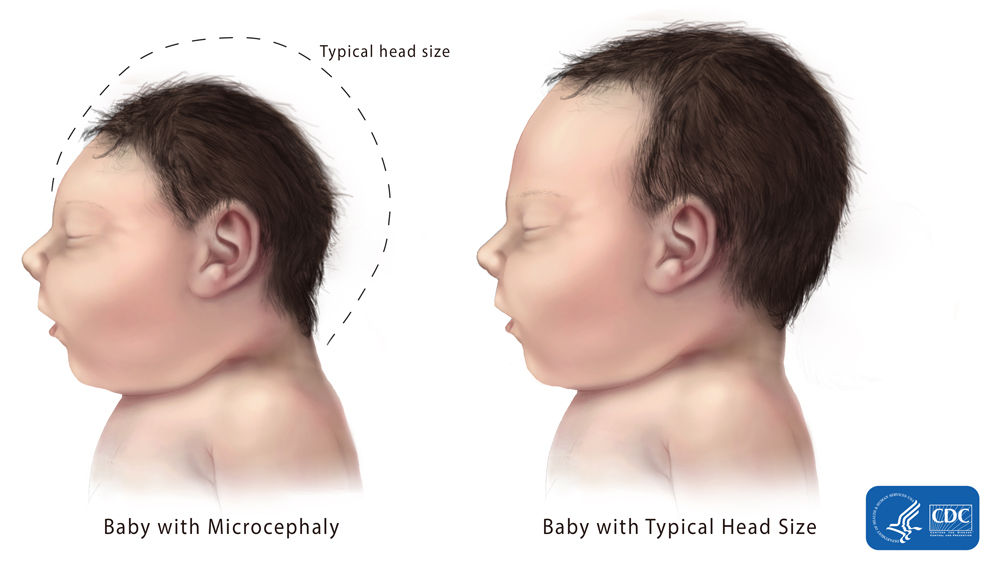 CDC scientists announced that enough evidence has accumulated to conclude that Zika virus infection during pregnancy is a cause of microcephaly and other severe fetal brain defects.
CDC scientists announced that enough evidence has accumulated to conclude that Zika virus infection during pregnancy is a cause of microcephaly and other severe fetal brain defects.
CDC continues to study birth defects, such as microcephaly, and how to prevent them. If you are pregnant or thinking about becoming pregnant, talk with your doctor about ways to increase your chances of having a healthy baby.
For information about the effects of Zika virus infection during pregnancy, visit CDC’s Zika and Pregnancy web page.
Diagnosis
Microcephaly can be diagnosed during pregnancy or after the baby is born.
During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, microcephaly can sometimes be diagnosed with an ultrasound test (which creates pictures of the body). To see microcephaly during pregnancy, the ultrasound test should be done late in the 2nd trimester or early in the third trimester. For more information about screening and confirmatory tests during pregnancy, visit CDC’s birth defects diagnosis web page.
After the Baby is Born
To diagnose microcephaly after birth, a healthcare provider will measure the distance around a newborn baby’s head, also called the head circumference, during a physical exam. The provider then compares this measurement to population standards by sex and age. Microcephaly is defined as a head circumference measurement that is smaller than a certain value for babies of the same age and sex. This measurement value for microcephaly is usually more than 2 standard deviations (SDs) below the average. The measurement value also may be designated as less than the 3rd percentile. This means the baby’s head is extremely small compared to babies of the same age and sex.
Head circumference growth charts for newborns, infants, and children up to age 20 years in the United States can be found on CDC’s growth charts website. Head circumference growth charts based on gestational age at birth (in other words, how far along the pregnancy was at the time of delivery) are also available from INTERGROWTH 21stexternal icon.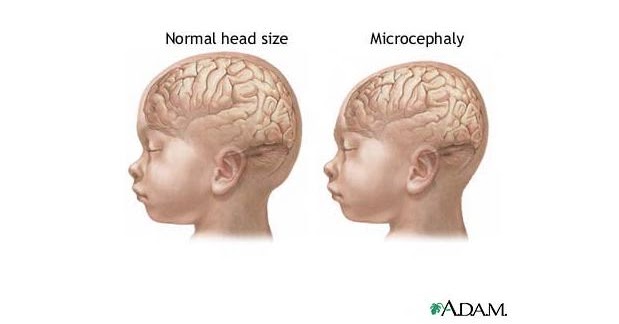 CDC recommends that health care providers use the WHO growth charts to monitor growth for infants and children ages 0 to 2 years of age in the United States.
CDC recommends that health care providers use the WHO growth charts to monitor growth for infants and children ages 0 to 2 years of age in the United States.
Microcephaly can be determined by measuring head circumference (HC) after birth. Although head circumference measurements may be influenced by molding and other factors related to delivery, the measurements should be taken on the first day of life because commonly-used birth head circumference reference charts by age and sex are based on measurements taken before 24 hours of age. The most important factor is that the head circumference is carefully measured and documented. If measurement within the first 24 hours of life is not done, the head circumference should be measured as soon as possible after birth. If the healthcare provider suspects the baby has microcephaly, he or she can request one or more tests to help confirm the diagnosis. For example, special tests like like magnetic resonance imaging can provide critical information on the structure of the baby’s brain that can help determine if the newborn baby had an infection during pregnancy. They also can help the healthcare provider look for other problems that might be present.
They also can help the healthcare provider look for other problems that might be present.
Download slidespdf icon | Download transcriptpdf icon
Treatments
Microcephaly is a lifelong condition. There is no known cure or standard treatment for microcephaly. Because microcephaly can range from mild to severe, treatment options can range as well. Babies with mild microcephaly often don’t experience any other problems besides small head size. These babies will need routine check-ups to monitor their growth and development.
For more severe microcephaly, babies will need care and treatment focused on managing their other health problems (mentioned above). Developmental services early in life will often help babies with microcephaly to improve and maximize their physical and intellectual abilities. These services, known as early interventionexternal icon, can include speech, occupational, and physical therapies. Sometimes medications also are needed to treat seizures or other symptoms.
Other Resources
The views of these organizations are their own and do not reflect the official position of CDC.
Mother To Babyexternal icon (on behalf of the Organization of Teratology Information Specialists)
This website provides comprehensive information to mothers, healthcare professionals, and the general public about exposures during pregnancy.
References
- National Birth Defects Prevention Network. Major birth defects data from population-based birth defects surveillance programs in the United States, 2006-2010. Birth Defects Research (Part A): Clinical and Molecular Teratology. 2013;97:S1-S172.
causes, symptoms, treatment, life expectancy
Microcephaly ( Giacomini's syndrome ) in newborns is a state of underdevelopment of the brain in combination with a decrease in head circumference by 5 cm in circumference and a further lag in the growth of the skull (microcrania). The incidence of microcephaly is approximately 1 in 5,000 newborns.
The incidence of microcephaly is approximately 1 in 5,000 newborns.
Unfortunately, these children often have other malformations in addition to neurological deficits. With a pronounced defect, the development of a convulsive syndrome, the presence of severe muscle paresis and other neurological manifestations is also common.
Information for doctors. The diagnosis of microcephaly according to ICD 10 is coded under the code Q02. The diagnosis can also indicate the existing concomitant disorders of the nervous system, such as paresis of the limbs, oculomotor disorders, mental retardation, the presence of symptomatic epilepsy, etc.
Causes
There are two types of microcephaly, primary (true, genetically predisposed) and secondary.
Primary microcephaly is most often the result of genetic defects inherited in an autosomal recessive manner or arising from chromosomal abnormalities. There are more reasons for secondary microcephaly. These include the following states:
- Prenatal infections (toxoplasmosis, rubella, measles, etc.
 ).
). - Intoxication (use of drugs, alcohol, nicotine, certain teratogenic drugs).
- Asphyxia during childbirth.
- Birth or intrauterine trauma.
- Severe eclampsia.
Symptoms
Symptoms of microcephaly are the following manifestations:
- Reduction in the size of the cerebral skull in at least two dimensions.
- Reducing the mass of the brain.
- Thickening of the skull bones with the formation of diploid canals preventing the development of hydrocephalus.
- Lagging behind in mental as well as in physical development (begins to speak, walk late, does not study well at school, etc.). Up to 15% of cases of oligophrenia are attributed to patients with microcephaly.
The so-called dysembryogenesis stigmas (developmental disorders in the prenatal period) also occur in microcephaly. These include a sloping forehead, thick brow ridges, large earlobes, etc. Noteworthy is the marked predominance of the size of the facial skull over the brain.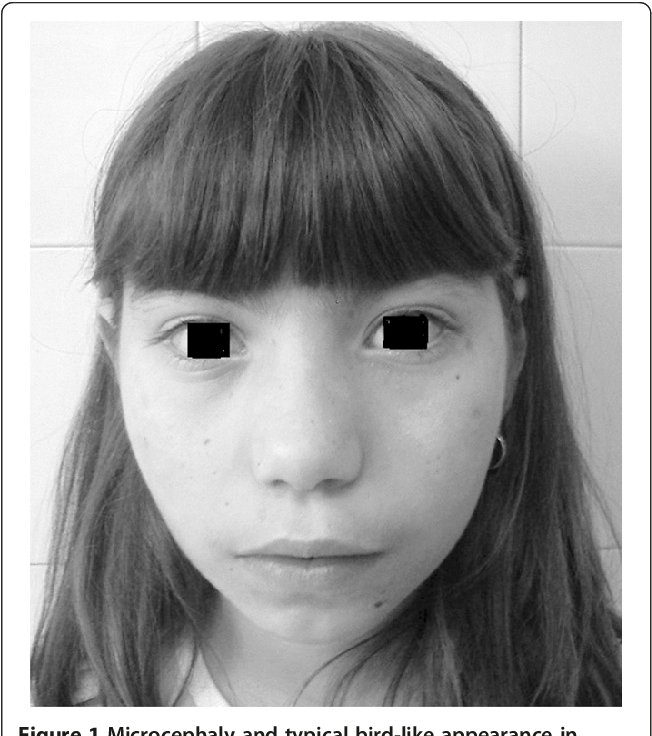
An instrumental neuroimaging study (MRI) can reveal the presence of an abnormal structure of the cerebral cortex with a relatively intact architectonics of the cerebellum and brain stem.
Treatment
There is no specific therapy for the disease. The most important role is given to the prevention of the disease, including genetic counseling in the presence of microcephaly in any of the relatives of the spouses. Also an important means is the refusal to use drugs, drugs, alcohol, restriction in work with difficult working conditions.
A child with an existing defect needs a favorable atmosphere in the family . With mild and moderate changes, it is possible for such a child to adapt to society.
Life expectancy
With small changes in the skull and good social adaptation, the patient's life expectancy can be equal to the average for the country's population (read as "you can live with this disease"). With gross defects of the brain, concomitant congenital malformations from other organs, life expectancy is reduced until death in childbirth.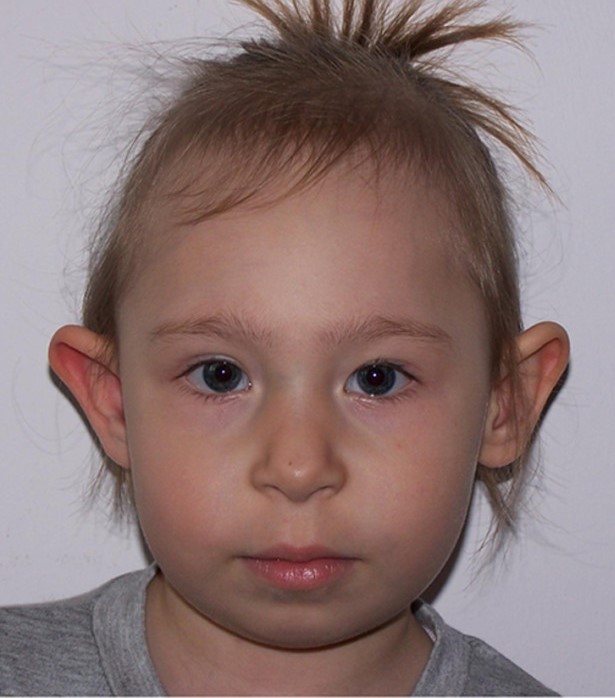
Treatment of microcephaly in Israel | Assutahospital.ru
Microcephaly is one of the serious diseases of children, mainly newborns, which affects the brain. As a result of this serious defect, a decrease in head circumference is observed (unlike hydrocephalus), as a rule, by 2-3 sigmoid deviations. This disease can be congenital, when the child already has deviations in the development of the brain even in the prenatal period, or postpartum, when the disease develops in the first months and years of the child's life, due to birth injuries. Microcephaly is treated in Israel by leading neuropathologists who draw up an individual treatment plan for each specific case, depending on the characteristics of the baby's body and the causes of the disease.
Why choose Israel for microcephaly treatment?
Every parent wants their child to be healthy and, at the slightest opportunity, chooses treatment only from the world's leading specialists. Israeli medicine has been at a high level of development for more than a year, which attracts foreign patients. Here, anyone who has applied to Israeli clinics can be sure that he will be provided with qualified and effective assistance. The private multidisciplinary medical center Assuta is one of the largest clinics in the country, where the most comfortable conditions for the treatment of patients are created. Comfortable diagnostic and operating rooms with all the necessary innovative equipment have been created here, the best specialists of the country work here, who save people's lives every day. The main advantages of the medical center are the lack of queues, compared to public clinics, as well as the ability to choose the attending physician. In addition, the diagnosis takes on average no more than 3 days, and with our help, patients can count on an individual approach and the provision of an indicative program for the treatment of microcephaly in Israel even before arriving in the country. We will also take care of the patient's accommodation in Israel, provide transfers to the hospital and be in touch with the client around the clock.
Here, anyone who has applied to Israeli clinics can be sure that he will be provided with qualified and effective assistance. The private multidisciplinary medical center Assuta is one of the largest clinics in the country, where the most comfortable conditions for the treatment of patients are created. Comfortable diagnostic and operating rooms with all the necessary innovative equipment have been created here, the best specialists of the country work here, who save people's lives every day. The main advantages of the medical center are the lack of queues, compared to public clinics, as well as the ability to choose the attending physician. In addition, the diagnosis takes on average no more than 3 days, and with our help, patients can count on an individual approach and the provision of an indicative program for the treatment of microcephaly in Israel even before arriving in the country. We will also take care of the patient's accommodation in Israel, provide transfers to the hospital and be in touch with the client around the clock.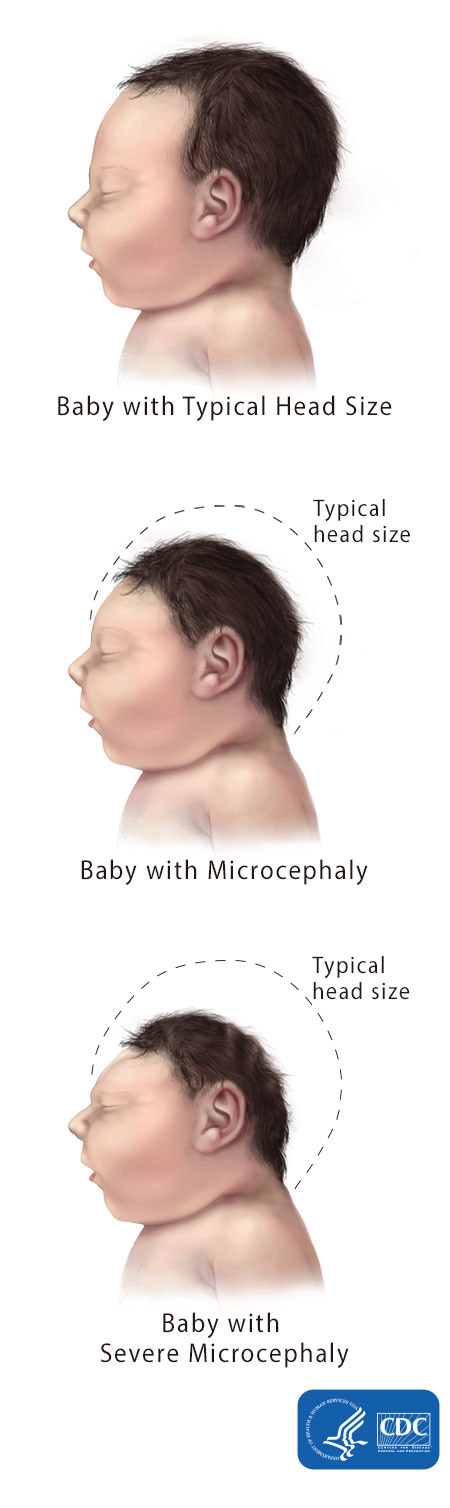
get a free consultation
Types of the disease and methods of its treatment
Depending on the causes of the disease, microcephaly can be of two types - primary and secondary. What exactly is their difference? The first type of microcephaly develops in utero, under the influence of various infectious factors. As a rule, this occurs in the early stages of a woman's pregnancy. Secondary microcephaly develops in the postpartum period, during childbirth, or in late pregnancy. It is on the type of disease that the microcephaly treatment program in Israel will depend.
Is there an effective treatment for microcephaly? Unfortunately, modern medicine cannot provide an effective method of treating this disease, which would contribute to the complete cure of the child. Nevertheless, leading scientists in the medical field are developing new methods of therapy that would reduce the symptoms of the disease and slow down the development of brain deformity. A conservative method of treatment is mainly used, which consists in the use of drugs (absorbable, sedative, anticonvulsants in combination with vitamins).![]() In addition, the participation of the child in a variety of developmental programs for children, physiotherapy and other methods of treating microcephaly in Israel contribute to the minimum deviation of brain functions and the maximum development of the baby's mental abilities. The main goal of the therapy program is to prevent the deterioration of the child's condition, but rather to contribute to its improvement.
In addition, the participation of the child in a variety of developmental programs for children, physiotherapy and other methods of treating microcephaly in Israel contribute to the minimum deviation of brain functions and the maximum development of the baby's mental abilities. The main goal of the therapy program is to prevent the deterioration of the child's condition, but rather to contribute to its improvement.
What diagnostics are needed to determine the treatment program
Effective treatment of microcephaly in Israel begins with accurate diagnosis, which ensures the selection of the optimal therapy program in the future. The presence of modern equipment in the diagnostic wards of the Assuta clinic makes it possible to carry out all the necessary examinations. Israeli clinics provide everything that may be required during therapy. It is possible to diagnose the primary type of the disease even before the birth of the child, using a prenatal ultrasound examination. To date, the effectiveness of this method is about 70%, and the disease itself can be detected only at 25-30 weeks of pregnancy. If primary microcephaly is suspected, in addition to ultrasound, other invasive examinations may also be required, which can confirm the pre-established diagnosis.
To date, the effectiveness of this method is about 70%, and the disease itself can be detected only at 25-30 weeks of pregnancy. If primary microcephaly is suspected, in addition to ultrasound, other invasive examinations may also be required, which can confirm the pre-established diagnosis.
After birth, a child with suspected microcephaly is examined by a doctor who, based on a visual examination, can confirm or refute the diagnosis. In addition, a number of additional diagnostic procedures are also carried out, which make it possible to determine the degree of complexity of the disease. With microcephaly, mandatory examinations are MRI of the brain, CT, EEG and neurosonography.
calculate the cost of treatment
Forecasts
The life expectancy of a child diagnosed with microcephaly varies, since there are many causes of the disease, and very often the disease is accompanied by other abnormalities in the child's body. As a rule, children with this disease live less, and their quality of life depends on the right therapy.