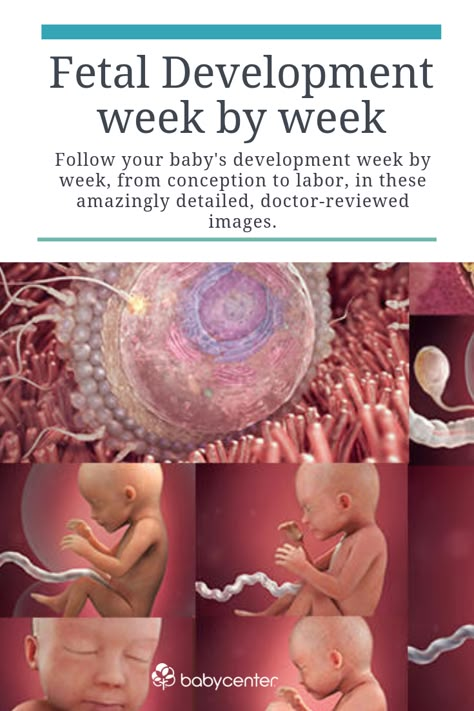
How long are babies in the womb
Baby due date - Better Health Channel
Summary
Read the full fact sheet- The unborn baby spends around 38 weeks in the uterus, but the average length of pregnancy, or gestation, is counted at 40 weeks.
- Pregnancy is counted from the first day of the woman’s last period, not the date of conception which generally occurs two weeks later.
- Since some women are unsure of the date of their last menstruation (perhaps due to period irregularities), a baby is considered full term if its birth falls between 37 to 42 weeks of the estimated last menstruation date.
The unborn baby spends around 37 weeks in the uterus (womb), but the average length of pregnancy, or gestation, is calculated as 40 weeks. This is because pregnancy is counted from the first day of the woman’s last period, not the date of conception which generally occurs two weeks later, followed by five to seven days before it settles in the uterus. Since some women are unsure of the date of their last menstruation (perhaps due to period irregularities), a pregnancy is considered full term if birth falls between 37 to 42 weeks of the estimated last menstruation date.
A baby born prior to week 37 is considered premature, while a baby that still hasn’t been born by week 42 is said to be overdue. In many cases, labour will be induced in the case of an overdue baby.
The average length of human gestation is 280 days, or 40 weeks, from the first day of the woman’s last menstrual period. The medical term for the due date is estimated date of confinement (EDC). However, only about four per cent of women actually give birth on their EDC. There are many online pregnancy calculators (see Baby due date calculator that can tell you when your baby is due, if you type in the date of the first day of your last period.
A simple method to calculate the due date is to add seven days to the date of the first day of your last period, then add nine months. For example, if the first day of your last period was 1 February, add seven days (8 February) then add nine months, for a due date of 8 November.
For example, if the first day of your last period was 1 February, add seven days (8 February) then add nine months, for a due date of 8 November.
Determining baby due date
Irregular menstrual cycles can mean that some women aren’t sure of when they conceived. Some clues to the length of gestation include:
- Ultrasound examination (especially when performed between six and 12 weeks)
- Size of uterus on vaginal or abdominal examination
- The time fetal movements are first felt (an approximate guide only).
Pregnancy ultrasound
A pregnancy ultrasound is a non-invasive test that scans the unborn baby and the mother’s reproductive organs using high frequency sound waves. The general procedure for a pregnancy ultrasound includes:
- The woman lies on a table.
- A small amount of a clear, conductive jelly is smeared on the woman’s abdomen.
- The operator places the small hand-held instrument called a transducer onto the woman’s abdomen.

- The transducer is moved across the abdomen. The sound waves bounce off internal structures (including the baby) and are transmitted back to the transducer. The sound waves are then translated into a two-dimensional picture on a monitor. The mother doesn’t feel or hear the transmission of the sound waves.
- By measuring the baby’s body parts, such as head circumference and the length of long bones, the operator can estimate its gestational age.
The diagnostic uses of pregnancy ultrasound
Apart from helping to pinpoint the unborn baby’s due date, pregnancy ultrasounds are used to diagnose a number of conditions including:
- Multiple fetuses
- Health problems with the baby
- Ectopic pregnancy (the embryo lodges in the fallopian tube instead of the uterus)
- Abnormalities of the placenta such as placenta praevia, where the placenta is positioned over the neck of the womb (cervix)
- The health of the mother’s reproductive organs.

Premature babies
A baby born prior to week 37 is considered premature. The odds of survival depend on the baby’s degree of prematurity. The closer to term (estimated date of confinement, or EDC) the baby is born, the higher its chances of survival - after 34 weeks gestation with good paediatric care almost all babies will survive.
Premature babies are often afflicted by various health problems, caused by immature internal organs. Respiratory difficulties and an increased susceptibility to infection are common.
Often there is no known cause for a premature labour; however, some of the maternal risk factors may include:
- Drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy
- Low body weight prior to pregnancy
- Inadequate weight gain during pregnancy
- No prenatal care
- Emotional stress
- Placenta problems such as placenta praevia
- Various diseases such as diabetes and congestive heart failure
- Infections such as syphilis.
Overdue babies
Around five out of every 100 babies will be overdue, or more than 42 weeks gestation. If you have gone one week past your due date without any signs of impending labour, your doctor will want to closely monitor your condition. Tests include:
- Monitoring the fetal heart rate
- Using a cardiotocograph machine
- Performing ultrasound scans.
The placenta starts to deteriorate after 38 weeks or so, which means an overdue baby may not get enough oxygen. An overdue baby could also grow too large for vaginal delivery. Generally, an overdue baby will be induced once it is two weeks past its expected date. Some of the methods of induction include:
- Vaginal prostaglandin gel - to help dilate the cervix
- Amniotomy - breaking the waters, sometimes called an artificial rupture of membranes (ARM)
- Oxytocin - a synthetic form of this hormone is given intravenously to stimulate uterine contractions.

Where to get help
- Your doctor
- Your obstetrician
- Midwife or childbirth educator
Things to remember
- The unborn baby spends around 38 weeks in the uterus, but the average length of pregnancy, or gestation, is counted at 40 weeks.
- Pregnancy is counted from the first day of the woman’s last period, not the date of conception which generally occurs two weeks later.
- Since some women are unsure of the date of their last menstruation (perhaps due to period irregularities), a baby is considered full term if its birth falls between 37 to 42 weeks of its estimated due date.
- Common concerns and discomforts: overdue baby, Mother’s Bliss, UK.
- Going Overdue, 2001, Centre for Reproduction and Minimally Invasive Surgery.
- Premmie-L FAQ and advice sheets, Parents of Premature Babies Inc.(Preemie-L). More information here.
- Pregnancy: what to expect when it’s past your due date, Family Doctor, USA.
- Ultrasound, Women Health Information, Royal Women’s Hospital, Melbourne. More information here.
This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:
Baby due date - Better Health Channel
Summary
Read the full fact sheet- The unborn baby spends around 38 weeks in the uterus, but the average length of pregnancy, or gestation, is counted at 40 weeks.
- Pregnancy is counted from the first day of the woman’s last period, not the date of conception which generally occurs two weeks later.
- Since some women are unsure of the date of their last menstruation (perhaps due to period irregularities), a baby is considered full term if its birth falls between 37 to 42 weeks of the estimated last menstruation date.
The unborn baby spends around 37 weeks in the uterus (womb), but the average length of pregnancy, or gestation, is calculated as 40 weeks.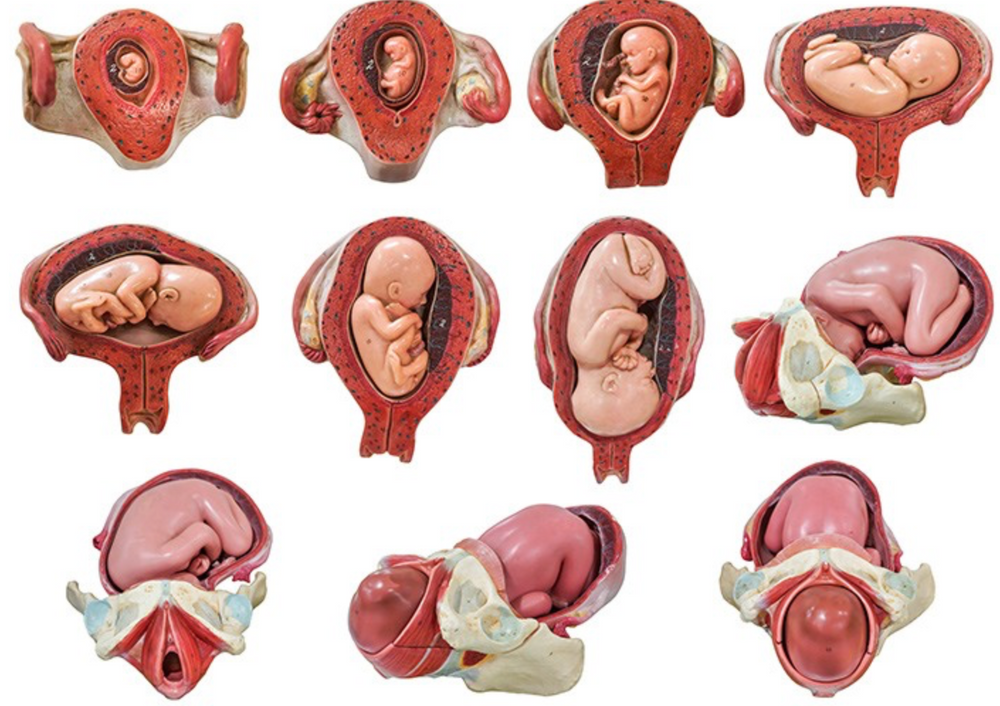 This is because pregnancy is counted from the first day of the woman’s last period, not the date of conception which generally occurs two weeks later, followed by five to seven days before it settles in the uterus. Since some women are unsure of the date of their last menstruation (perhaps due to period irregularities), a pregnancy is considered full term if birth falls between 37 to 42 weeks of the estimated last menstruation date.
This is because pregnancy is counted from the first day of the woman’s last period, not the date of conception which generally occurs two weeks later, followed by five to seven days before it settles in the uterus. Since some women are unsure of the date of their last menstruation (perhaps due to period irregularities), a pregnancy is considered full term if birth falls between 37 to 42 weeks of the estimated last menstruation date.
A baby born prior to week 37 is considered premature, while a baby that still hasn’t been born by week 42 is said to be overdue. In many cases, labour will be induced in the case of an overdue baby.
The average length of human gestation is 280 days, or 40 weeks, from the first day of the woman’s last menstrual period. The medical term for the due date is estimated date of confinement (EDC). However, only about four per cent of women actually give birth on their EDC. There are many online pregnancy calculators (see Baby due date calculator that can tell you when your baby is due, if you type in the date of the first day of your last period.
A simple method to calculate the due date is to add seven days to the date of the first day of your last period, then add nine months. For example, if the first day of your last period was 1 February, add seven days (8 February) then add nine months, for a due date of 8 November.
Determining baby due date
Irregular menstrual cycles can mean that some women aren’t sure of when they conceived. Some clues to the length of gestation include:
- Ultrasound examination (especially when performed between six and 12 weeks)
- Size of uterus on vaginal or abdominal examination
- The time fetal movements are first felt (an approximate guide only).
Pregnancy ultrasound
A pregnancy ultrasound is a non-invasive test that scans the unborn baby and the mother’s reproductive organs using high frequency sound waves. The general procedure for a pregnancy ultrasound includes:
- The woman lies on a table.
- A small amount of a clear, conductive jelly is smeared on the woman’s abdomen.
- The operator places the small hand-held instrument called a transducer onto the woman’s abdomen.
- The transducer is moved across the abdomen. The sound waves bounce off internal structures (including the baby) and are transmitted back to the transducer. The sound waves are then translated into a two-dimensional picture on a monitor. The mother doesn’t feel or hear the transmission of the sound waves.
- By measuring the baby’s body parts, such as head circumference and the length of long bones, the operator can estimate its gestational age.
The diagnostic uses of pregnancy ultrasound
Apart from helping to pinpoint the unborn baby’s due date, pregnancy ultrasounds are used to diagnose a number of conditions including:
- Multiple fetuses
- Health problems with the baby
- Ectopic pregnancy (the embryo lodges in the fallopian tube instead of the uterus)
- Abnormalities of the placenta such as placenta praevia, where the placenta is positioned over the neck of the womb (cervix)
- The health of the mother’s reproductive organs.

Premature babies
A baby born prior to week 37 is considered premature. The odds of survival depend on the baby’s degree of prematurity. The closer to term (estimated date of confinement, or EDC) the baby is born, the higher its chances of survival - after 34 weeks gestation with good paediatric care almost all babies will survive.
Premature babies are often afflicted by various health problems, caused by immature internal organs. Respiratory difficulties and an increased susceptibility to infection are common.
Often there is no known cause for a premature labour; however, some of the maternal risk factors may include:
- Drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy
- Low body weight prior to pregnancy
- Inadequate weight gain during pregnancy
- No prenatal care
- Emotional stress
- Placenta problems such as placenta praevia
- Various diseases such as diabetes and congestive heart failure
- Infections such as syphilis.

Overdue babies
Around five out of every 100 babies will be overdue, or more than 42 weeks gestation. If you have gone one week past your due date without any signs of impending labour, your doctor will want to closely monitor your condition. Tests include:
- Monitoring the fetal heart rate
- Using a cardiotocograph machine
- Performing ultrasound scans.
The placenta starts to deteriorate after 38 weeks or so, which means an overdue baby may not get enough oxygen. An overdue baby could also grow too large for vaginal delivery. Generally, an overdue baby will be induced once it is two weeks past its expected date. Some of the methods of induction include:
- Vaginal prostaglandin gel - to help dilate the cervix
- Amniotomy - breaking the waters, sometimes called an artificial rupture of membranes (ARM)
- Oxytocin - a synthetic form of this hormone is given intravenously to stimulate uterine contractions.

Where to get help
- Your doctor
- Your obstetrician
- Midwife or childbirth educator
Things to remember
- The unborn baby spends around 38 weeks in the uterus, but the average length of pregnancy, or gestation, is counted at 40 weeks.
- Pregnancy is counted from the first day of the woman’s last period, not the date of conception which generally occurs two weeks later.
- Since some women are unsure of the date of their last menstruation (perhaps due to period irregularities), a baby is considered full term if its birth falls between 37 to 42 weeks of its estimated due date.
- Common concerns and discomforts: overdue baby, Mother’s Bliss, UK.
- Going Overdue, 2001, Centre for Reproduction and Minimally Invasive Surgery.
- Premmie-L FAQ and advice sheets, Parents of Premature Babies Inc.(Preemie-L). More information here.
- Pregnancy: what to expect when it’s past your due date, Family Doctor, USA.
- Ultrasound, Women Health Information, Royal Women’s Hospital, Melbourne. More information here.
This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:
What does a child do while it is in the mother’s stomach
August 17, 2018
In 9 months, a child goes a long way from a tiny embryo to a chubby baby and already in the womb acquires some features that will remain with him for life: for example, you can understand whether he will become right-handed or left-handed and what kind of food he will prefer. In a fairly short period of time, a lot of interesting things happen to a child, and today we invite you to go through the path from birth to birth with your baby.
1st trimester of pregnancy
1st–2nd week
So the long journey began. For the first 4 days, the future person is smaller than a grain of salt - its size is only 0.14 mm. However, starting from the 5th day, it begins to grow and by the 6th it almost doubles - up to as much as 0. 2 mm. On the 4th day, the embryo "comes" to where it will spend the next 9 months - into the uterus, and on the 8th day it is implanted in its wall.
2 mm. On the 4th day, the embryo "comes" to where it will spend the next 9 months - into the uterus, and on the 8th day it is implanted in its wall.
3rd–4th week
© EDITORIAL USE ONLY/East News
Embryo at the 4th week of pregnancy.
Around the 20th day of pregnancy, a very important event occurs: the neural tube appears, which will then turn into the spinal cord and brain of the child. Already on the 21st day, his heart begins to beat and all important organs, such as the kidneys and liver, begin to form. The eyes have not yet taken their usual position - the bubbles from which they will then take shape are located on the sides of the head. By the end of the 1st month, the embryo has a circulatory system, and the spine and muscles begin to develop.
5th–6th week
© EDITORIAL USE ONLY/East News © lunar caustic/wikimedia
At the 5th week, the hands appear in the embryo, however, the fingers are still very difficult to distinguish, but in the joints the arms and legs are already bent. It was at this time that the external genitalia begin to form, but it is not yet possible to see on an ultrasound whether it is a boy or a girl. By the way, since its appearance, the embryo has grown a lot - it has increased by as much as 10 thousand times. Already now, the baby's face is beginning to form, and the eyes, which will be closed for a very long time, darken, becoming more human-like.
It was at this time that the external genitalia begin to form, but it is not yet possible to see on an ultrasound whether it is a boy or a girl. By the way, since its appearance, the embryo has grown a lot - it has increased by as much as 10 thousand times. Already now, the baby's face is beginning to form, and the eyes, which will be closed for a very long time, darken, becoming more human-like.
7th–8th week
The 7th week of pregnancy is the time when the baby begins to move, however, so far completely unnoticed by the mother, and the fingers and toes become almost the same as in adults. At this stage, the rudiments of milk teeth appear in the embryo and the reproductive system develops, and the kidneys begin to produce urine. Despite the fact that the growth of the fetus is only 2.5 cm, it acquires its own facial expressions, it has eyelids, and the tip of the nose becomes more defined.
9th–10th week
© lunarcaustic/wikimedia
Baby at 9-10 weeks of gestation.
By this time, the baby has already grown well - its weight is 4 grams, and its height is 2-3 cm. Despite its tiny size, the brain is already divided into two hemispheres, and milk teeth and taste buds are beginning to form. The baby's tail and membranes between the fingers on the hands disappear, he begins to swim in the amniotic fluid and move even more actively, although still unnoticed by the mother. It was at this time that the child's individual facial features appear, and hair begins to grow on the head.
11–12 weeks
At this time, the genital organs are formed in the child, so it is already possible to find out his sex on an ultrasound scan, although the probability of an error is still high. The child still looks a little alien: he has a big head and a small body, but his face is more and more like an adult. The ears are almost in the right position, eyebrows and eyelashes appear. The cartilage that makes up the skeleton gradually ossifies, new blood vessels appear, and hormone production begins. By the way, the baby has already grown up to 6 cm and weighs about 20 grams.
By the way, the baby has already grown up to 6 cm and weighs about 20 grams.
13th-14th week
Baby at 14 weeks pregnant.
Despite the fact that the child's head is half the length of the entire body, the face is more and more reminiscent of an adult, and the rudiments of all 20 milk teeth have already been formed in the oral cavity. The child is already able to put his finger in his mouth, but he will learn to suck a little later. Due to the active formation of blood vessels, the baby's skin is red and very thin, so vellus hair appears on the body - lanugo, which is necessary to maintain a special lubricant that protects against hypothermia.
2nd trimester of pregnancy
15th–16th week
By the 15th week, the baby has grown to 10 cm and is gaining weight - now he weighs about 70 grams. Despite the fact that the eyes are still quite low, the face is already quite recognizable, moreover, the child begins to “make faces”, since the facial muscles are well developed. By this time, he already knows how to suck his thumb, and the sebaceous and sweat glands begin their work.
By this time, he already knows how to suck his thumb, and the sebaceous and sweat glands begin their work.
17th–18th week
And finally, the child's auditory canals are formed, so he begins to distinguish sounds well and hears the mother's voice, moreover, he is able to recognize it. In addition to the milk teeth, the embryos of the molars also appear, the bones are finally formed and begin to harden. By the way, the bones of the skull will remain mobile until birth - when passing through the birth canal, they will overlap each other to make it easier for the baby to be born. But the mother is finally beginning to feel the movements of the child, who has grown to 14 cm and 190 grams.
19th-20th week
Baby at 20 weeks pregnant.
Despite the fact that the child's eyes are still closed, he is already well oriented in the surrounding space. Moreover, now you can understand whether the child will be right-handed or left-handed, because right now he begins to use his dominant hand more actively. Fingerprints appear on the baby's fingers - another unique sign of each of us. By the way, the child is already beginning to gradually distinguish day from night and is active at a certain time.
Fingerprints appear on the baby's fingers - another unique sign of each of us. By the way, the child is already beginning to gradually distinguish day from night and is active at a certain time.
21–22 weeks
The 21st week is the time when the baby begins to gain weight due to the formation of subcutaneous fat. Soon, the folds that newborns have will appear on his arms and legs. On the 22nd week, those neurons are formed in the brain that will be with a person all his life. Very soon the child will open his eyes, he is already trying to do this, and the eyeballs move almost like an adult.
23–24 weeks
At 23 weeks, the baby may begin to dream, and his face is so formed that an ultrasound can determine whose facial features he has inherited. His skin becomes opaque, his eyes open, and the child can already react to light, moreover, bright flashes can scare him. By the 24th week, the baby grows to almost 30 cm, and its weight reaches 0. 5 kg.
5 kg.
25th–26th week
At this time, the taste buds of the child are finally formed and, tasting the amniotic fluid, he can frown if he does not like it. By the way, this is how eating habits are formed - already in the womb we have our favorite and unloved foods. Very soon the child will learn to blink and can already see a little, however, so far it is very, very vague.
3rd trimester of pregnancy
27th–28th week
Baby at 27–28 weeks of gestation.
If you do an ultrasound at this time, you can see how the baby smiles and intensively sucks his thumb. At this time, the baby has the first "toy" - his own umbilical cord, and he actively studies his body. At the end of the 7th month of pregnancy, the child develops an individual metabolism, which he will have all his life. The baby is already quite large - his weight reaches 1.2 kg, and his height is 35 cm.
29th-30th week
© East News
Baby at 30 weeks pregnant.
The layer of subcutaneous fat is increasing, and the baby is becoming more and more plump and well-fed. In addition, he already knows how to cry, cough, and even sometimes hiccups - this happens, most likely, when he swallows too much amniotic fluid. By the 30th week, the baby's brain is already so developed that it is quite capable of remembering and even analyzing information.
31–32 weeks
At this time, a person has all 5 senses, and his daily routine is more and more reminiscent of the one he will follow after birth. The child hears the work of all the organs of the mother, knows her voice perfectly, thanks to which, immediately after birth, he is able to distinguish her from all other people. The baby's immune system begins to produce antibodies that will protect him from all kinds of infections that may lie in wait in the first days and months after birth.
33–34th week
And finally, subcutaneous fat is already formed, and lanugo disappears from the body of the fetus. By this time, the baby has grown a lot - the length of his body reaches 40 cm, and the weight is very close to or even exceeds 2 kg. The baby's nervous system is already fully formed, but the lungs are still developing.
By this time, the baby has grown a lot - the length of his body reaches 40 cm, and the weight is very close to or even exceeds 2 kg. The baby's nervous system is already fully formed, but the lungs are still developing.
35th–36th week
© East News
The child yawns. 3D ultrasound at 36 weeks pregnant.
At this time, the child looks almost exactly the same as when he was born. He is still quite thin, but the layer of subcutaneous fat is increasing more and more intensively. However, his hair and nails are already fully developed, and he himself becomes so big that he has almost no room to maneuver, so he can move less than in earlier stages.
37–38th week
And finally, the process of forming a person has finally ended - now he is completely ready for birth, and obstetricians consider the pregnancy to be full-term. Lanugo completely disappears from his body and can only sometimes remain on his arms and legs. Since there is almost no space left in the uterus, it may seem to the mother that the child has begun to move more intensively, but in fact the force of the blows has increased, because the child's muscles have already completely formed and strengthened.
Since there is almost no space left in the uterus, it may seem to the mother that the child has begun to move more intensively, but in fact the force of the blows has increased, because the child's muscles have already completely formed and strengthened.
39th–40th week
© depositphotos.com
The first minutes after birth.
The lungs of a child continue to form until the very birth, and only at the time of birth they release the right amount of surfactant - a substance that prevents the alveoli from sticking together after the first independent breath. Very soon, the baby will announce its birth with the first cry and begin its long journey through a large and interesting world.
show all
Child development by weeks | Regional Perinatal Center
Expectant mothers are always curious about how the fetus develops at a time when it is awaited with such impatience. Let's talk and look at the photos and pictures of how the fetus grows and develops week by week.
What does the puffer do for 9 whole months in mom's tummy? What does he feel, see and hear?
Let's start the story about the development of the fetus by weeks from the very beginning - from the moment of fertilization. A fetus up to 8 weeks old is called embryo , this occurs before the formation of all organ systems.
Embryo development: 1st week
The egg is fertilized and begins to actively split. The ovum travels to the uterus, getting rid of the membrane along the way.
On the 6th-8th days, implantation of eggs is carried out - implantation into the uterus. The egg settles on the surface of the uterine mucosa and, using the chorionic villi, attaches to the uterine mucosa.
Embryo development: 2-3 weeks
Picture of embryo development at 3 weeks.
The embryo is actively developing, starting to separate from the membranes. At this stage, the beginnings of the muscular, skeletal and nervous systems are formed. Therefore, this period of pregnancy is considered important.
Therefore, this period of pregnancy is considered important.
Embryo development: 4–7 weeks
Fetal development by week in pictures: week 4
Fetal development by week photo: week 4
Photo of an embryo before the 6th week of pregnancy.
The heart, head, arms, legs and tail are formed in the embryo :) . Gill slit is defined. The length of the embryo at the fifth week reaches 6 mm.
Fetal development by week photo: week 5
At the 7th week, the rudiments of the eyes, stomach and chest are determined, and fingers appear on the handles. The baby already has a sense organ - the vestibular apparatus. The length of the embryo is up to 12 mm.
Fetal development: 8th week
Fetal development by week photo: week 7-8
The face of the fetus is determined, you can distinguish the mouth, nose, auricles. The head of the embryo is large and its length corresponds to the length of the body; the fetal body is formed. All significant, but not yet fully formed, elements of the baby's body already exist. The nervous system, muscles, skeleton continue to improve.
The head of the embryo is large and its length corresponds to the length of the body; the fetal body is formed. All significant, but not yet fully formed, elements of the baby's body already exist. The nervous system, muscles, skeleton continue to improve.
Fetal development in the photo already sensitive arms and legs: week 8
The fetus developed skin sensitivity in the mouth area (preparation for the sucking reflex), and later in the face and palms.
At this stage of pregnancy, the genitals are already visible. Gill slits die. The fruit reaches 20 mm in length.
Fetal development: 9–10 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 9
Fingers and toes already with nails. The fetus begins to move in the pregnant woman's stomach, but the mother does not feel it yet. With a special stethoscope, you can hear the baby's heartbeat. Muscles continue to develop.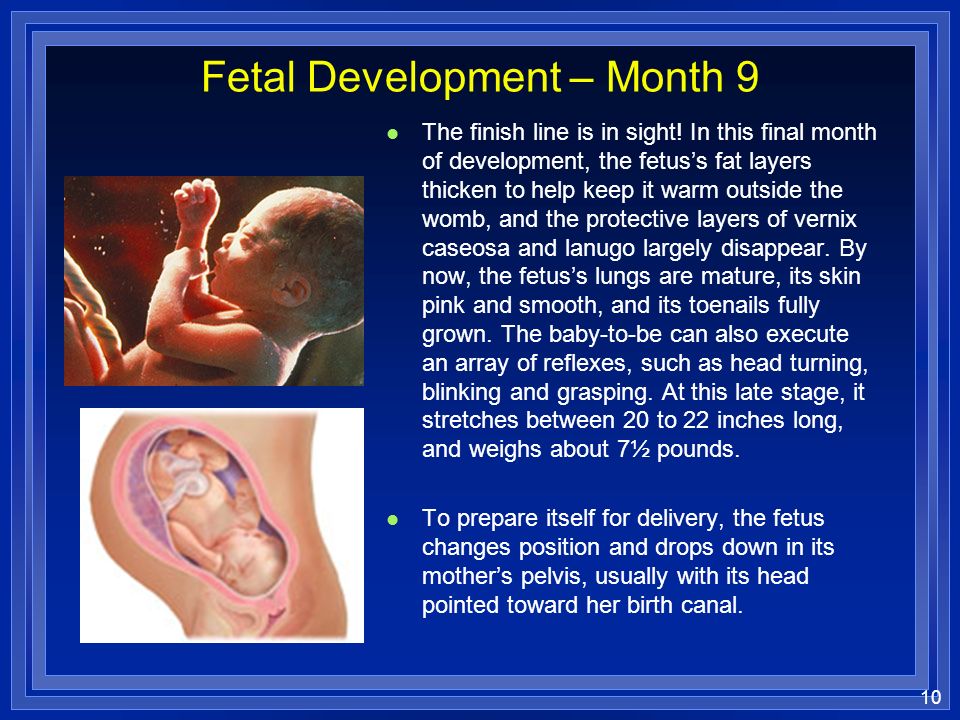
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 10
The entire surface of the fetal body is sensitive and the baby develops tactile sensations with pleasure, touching his own body, the walls of the amniotic sac and the umbilical cord. It is very curious to observe this on ultrasound. By the way, the baby first moves away from the ultrasound sensor (of course, because it is cold and unusual!), And then puts his hands and heels trying to touch the sensor.
It's amazing when a mother puts her hand to her stomach, the baby tries to master the world and tries to touch with his pen "from the back".
Fruit development: 11–14 weeks
Development of the fetus in the photo of the legs: Week 11
In the baby's arms, legs and eyelids, and the genitals become distinguishable (you can find out the floor child). The fetus begins to swallow, and if something is not to its taste, for example, if something bitter gets into the amniotic fluid (mother ate something), then the baby will begin to frown and stick out his tongue, making less swallowing movements.
Fruit skin appears translucent.
Fruit development: Week 12
Photo of the fetus 12 weeks on 3D ultrasound
9000 9000 9000 9000
DEVELOPMENT OF NEXTS Photo: Week 140150 9000 9000 urine. Blood forms inside the bones. And hairs begin to grow on the head. Moves more coordinated.
Fetal development: 15-18 weeks
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 15
The skin turns pink, the ears and other parts of the body, including the face, are already visible. Imagine, a child can already open his mouth and blink, as well as make grasping movements. The fetus begins to actively push in the mother's tummy. The sex of the fetus can be determined by ultrasound.
Fetal development: 19-23 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 19
Baby sucks his thumb, becomes more energetic. Pseudo-feces are formed in the intestines of the fetus - meconium , kidneys begin to work. During this period, the brain develops very actively.
Pseudo-feces are formed in the intestines of the fetus - meconium , kidneys begin to work. During this period, the brain develops very actively.
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 20
The auditory ossicles become stiff and now they are able to conduct sounds, the baby hears his mother - heartbeat, breathing, voice. The fetus intensively gains weight, fat deposits are formed. The weight of the fetus reaches 650 g, and the length is 300 mm.
The lungs at this stage of fetal development are so developed that the baby can survive in the artificial conditions of the intensive care unit.
Fetal development: 24-27 weeks
Lungs continue to develop. Now the baby is already falling asleep and waking up. Downy hairs appear on the skin, the skin becomes wrinkled and covered with grease. The cartilage of the ears and nose is still soft.
Fetal development by week photo: week 27
Lips and mouth become more sensitive. The eyes develop, open slightly and can perceive light and squint from direct sunlight. In girls, the labia majora do not yet cover the small ones, and in boys, the testicles have not yet descended into the scrotum. Fetal weight reaches 900–1200 g, and the length is 350 mm.
The eyes develop, open slightly and can perceive light and squint from direct sunlight. In girls, the labia majora do not yet cover the small ones, and in boys, the testicles have not yet descended into the scrotum. Fetal weight reaches 900–1200 g, and the length is 350 mm.
9 out of 10 children born at this term survive.
Fetal development: 28-32 weeks
The lungs are now adapted to breathe normal air. Breathing is rhythmic and body temperature is controlled by the CNS. The baby can cry and responds to external sounds.
Child opens eyes while awake and closes during sleep.
The skin becomes thicker, smoother and pinkish. Starting from this period, the fetus will actively gain weight and grow rapidly. Almost all babies born prematurely at this time are viable. The weight of the fetus reaches 2500 g, and the length is 450 mm.
Fetal development: 33–37 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 36
The fetus reacts to a light source. Muscle tone increases and the baby can turn and raise his head. On which, the hairs become silky. The child develops a grasping reflex. The lungs are fully developed.
Muscle tone increases and the baby can turn and raise his head. On which, the hairs become silky. The child develops a grasping reflex. The lungs are fully developed.
Fetal development: 38-42 weeks
The fetus is quite developed, prepared for birth and considered mature. The baby has mastered over 70 different reflex movements. Due to the subcutaneous fatty tissue, the baby's skin is pale pink. The head is covered with hairs up to 3 cm.
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 40
The baby perfectly mastered the movements of his mother , knows when she is calm, excited, upset and reacts to this with her movements. During the intrauterine period, the fetus gets used to moving in space, which is why babies love it so much when they are carried in their arms or rolled in a stroller. For a baby, this is a completely natural state, so he will calm down and fall asleep when he is shaken.
The nails protrude beyond the tips of the fingers, the cartilages of the ears and nose are elastic.