Can a woman still ovulate while pregnant
Can You Get Pregnant While Pregnant? It’s Rare But Possible
There are plenty of reasons to not love every minute of pregnancy — morning sickness, leg cramps, and heartburn, just to name a few — but the freedom to have sex with your partner whenever you want without worrying about birth control is one of pregnancy’s bigger selling points.
After all, you can’t get pregnant when you’re pregnant, right? RIGHT?!
Sorry to be the bearer of mind-blowing news, but everything you thought about pregnancy and fertility is pretty much wrong. OK, not everything… just enough to make it necessary for us to inform you that — technically — you can add another bun to your oven even when one’s already cooking in there.
A double pregnancy, or superfetation, is extremely rare — in fact, there aren’t even stats on how often it happens — but it’s scientifically possible. We’re not saying you should worry about it happening to you, just that you can’t say that it’s impossible. Here’s why.
There are three things that happen to your body when you get pregnant that make it super unlikely you’ll be able to get pregnant again in the next 9 months:
- You stop ovulating. You need to produce a healthy egg in order to get pregnant. Once that egg has been successfully fertilized and implants in your uterus, pregnancy hormones tell your ovaries that you don’t need to ovulate anymore right now.
- Speaking of your uterus, it gets pretty tough for another fertilized egg to implant once the first one has nestled in there. The uterine lining thickens to support the first egg and that makes it hard for another to attach itself.
- During pregnancy, your cervix produces something called a mucus plug, which not only protects your uterus from infection but also prevents sperm from passing through the cervix.
Any one of these things — ovulation, second implantation, or sperm getting through in the first place — happening after conception would be unusual.
Having all three of them happen, resulting in superfetation, is practically unheard of. (We mean this literally: Medical experts can only point to about 10 confirmed cases in the literature, as evidenced by a 2017 article.)
In order to have a double pregnancy, you’d have to either ovulate while pregnant or have two uteri. Both of those scenarios, again, are highly unlikely.
Ovulating during pregnancy happens so infrequently doctors haven’t been able to study why it may occur.
While uterine abnormalities aren’t quite as uncommon, doctors typically see people with a divided or partially formed uterus, not two separate uteri.
This condition, called didelphic uterus, is rare. While it can cause a double pregnancy, it’s more likely to result in a miscarriage than two pregnancies at the same time.
Since double pregnancy happens so infrequently, there’s no definitive info about how close in gestational age the two fetuses would be.
A 2013 study suggests these fetuses are usually conceived between 2 and 4 weeks apart, so it’s likely to be something that happens within a short window of time after the first conception. Considering that the average length of time between menstrual cycles is about 28 days, that makes sense.
Considering that the average length of time between menstrual cycles is about 28 days, that makes sense.
As far as the timing of labor and delivery, a double pregnancy can complicate things a little but not dramatically. You wouldn’t be dealing with, say, a 7-month-old fetus and a 3-month-old one.
Your babies will be close in age. For the most part, babies born between 37 and 38 weeks gestation have healthy outcomes, so you could — in theory — schedule a delivery that falls somewhere in between the younger and older babies’ estimated due dates.
There have been a handful of confirmed double pregnancies over the years, including:
- Jessica Allen agreed to be a surrogate for a Chinese couple. When it was discovered she was carrying two fetuses, doctors assumed the embryo had split into twins. After delivering the babies, however, both Allen and the biological parents were confused about how different in appearance they were. DNA testing eventually confirmed that one baby was the biological child of Allen and her husband while the other was the biological child of the Chinese parents.

- Julia Grovenburg became pregnant with one baby in early 2010 and then conceived another roughly 2 and a half weeks later. The superfetation was discovered by her doctor during an ultrasound, which revealed the babies were growing at two different rates within two different uterine sacs. The babies also had two different due dates but were ultimately born via cesarean section on the same day.
- Kate Hill conceived two babies 10 days apart after receiving treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome. She and her husband were trying to conceive but only had sex once — despite the two eggs being fertilized separately.
Twins happen when a fertilized egg splits in two after implantation (for identical twins) or when two separate eggs are fertilized at the same exact time (for fraternal twins).
These are different from superfetation, which occurs when two eggs are fertilized during separate instances of ovulation.
In other words, twins are conceived during the same ovulatory cycle. In superfetation, one egg is fertilized and implants in the uterus, and then — during a secondary ovulatory cycle — another egg follows suit.
In superfetation, one egg is fertilized and implants in the uterus, and then — during a secondary ovulatory cycle — another egg follows suit.
As far as knowing when a double pregnancy has occurred instead of the more likely twin conception, it’s fairly tough to decipher before the babies are born.
Two of the indicators — a significant difference in gestational size and a second baby suddenly appearing on a later ultrasound — can have other explanations. For example, it’s more reasonable to assume that the fetuses are simply growing differently or that an ultrasound technician missed the second fetus the first time around.
After birth, of course, a marked difference in the babies’ physical appearance (like being of two different ethnicities, as in Jessica Allen’s case) is a strong enough sign that DNA testing may be warranted, which would confirm or rule out superfetation for certain.
Further complicating things, there’s a similar-but-different biological phenomenon called superfecundation, which refers to fraternal twins with two different fathers.
This happens when two eggs are released during one ovulatory cycle, with each one being fertilized by sperm from a different male partner. A woman would need to have sex with two different men within the short window of ovulation, which is typically about 5 days.
Since the eggs are released, fertilized, and implanted during the same ovulatory cycle, superfecundation isn’t the same as a double pregnancy. It’s almost equally as rare, though. One study from way back in 1992 estimated it had happened in about 2 percent of the twin cases examined.
Once more for the people in the back: This situation happens so infrequently that doctors can’t say if the risks of carrying and delivering babies with a double pregnancy are higher or not than in traditional pregnancies.
If both fetuses are developing normally, there may not be any increased risks in carrying them. On the other hand, problems may arise if one is significantly “younger” in gestational age or less developed than the other.
Beyond that, a person facing delivery with a double pregnancy would simply have the same risks as anyone delivering multiples. Those risks include low birth weight, preeclampsia, and preterm delivery, among others.
Do you need to be worried about winding up with a superfetation situation? Probably not. It can happen once in a blue moon — and if you’re an extremely rare case, it could explain why your “twins” aren’t developing along the same growth pattern.
Otherwise, consider this a fun fact to pull out at parties: Yes, you can (in theory) become pregnant while pregnant.
Forget What You Know, You Actually Can Get Pregnant While Pregnant : ScienceAlert
ruigsantos/Shutterstock.com
In a disturbing twist that goes against everything we learned in sex education, a recent New York Times Q&A confirmed that it's actually possible for a woman to get pregnant… while she's already pregnant.
As far-fetched as that sounds, the science on this one actually lines up. In a creepy quirk of the human body, under very exceptional circumstances, a woman can continue to ovulate while pregnant and can conceive another child - something known as 'superfetation'.
In a creepy quirk of the human body, under very exceptional circumstances, a woman can continue to ovulate while pregnant and can conceive another child - something known as 'superfetation'.
That means a woman can have two foetuses developing inside her at the same time, both at different stages of development. And we sort of wish we could immediately scrub that knowledge from our brains.
Before you panic, this is highly unlikely to happen to you or anyone you know. In fact, according to a paper published in 2008 in the European Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology it's only happened 10 times in the scientific literature… ever.
Many claims of double pregnancies over the years that have gone on to be debunked, but, according to the researchers, at least 10 of those seem to be the real, evidence-backed deal.
And since that paper came out, there have been a few other cases reported.
In 2009, a couple from Arkansas became pregnant after already conceiving two and a half weeks earlier. Both babies were delivered healthily by c-section on 2 December, with one baby measurably a fortnight more premature than the other.
Both babies were delivered healthily by c-section on 2 December, with one baby measurably a fortnight more premature than the other.
And in 2015, an Australian couple gave birth to two girls that were 10 days apart in age at birth.
So, how is this even possible? Superfetation is actually quite common in mammals outside of humans, and has been seen in species including rodents, rabbits, horse, sheep, and kangaroos.
Sometimes these mammals have two uteri to facilitate the double pregnancy, or sometimes their menstrual cycle simply continues during pregnancy. It's even considered a handy reproductive strategy in some species.
But, in humans, superfetation appears to be a very rare accident - that's because, as soon as a woman becomes pregnant, her body actively blocks a second pregnancy from happening.
"Ordinarily, the release of eggs ceases once a woman is pregnant, and the hormonal and physical changes of pregnancy work together to prevent another conception," C. Clairborne Ray explained in a New York Times' science Q&A this week.
Clairborne Ray explained in a New York Times' science Q&A this week.
But for some reason, in superfetation, a pregnant women still manages to ovulate. A male's sperm then manages to fertilise that egg, somehow bypassing the the mucus plug that blocks up a woman's cervix once she's conceived.
Finally, implantation has to occur - which is an incredibly delicate process even in ordinary pregnancies. And when a woman is already pregnant, her hormones should make the uterus an unfavourable environment for another fertilised egg to implant (not to mention that there wouldn't be much room).
"In order for superfetation to occur in humans … it would appear that three seemingly impossible things need to happen," Khalil A. Cassimally reported for Scientific American back in 2011.
"Ovulation must take place during an ongoing pregnancy, semen must somehow find its way through the blocked cervix to the oviduct, via the occupied uterus and finally, the conceptus has to successfully implant itself in an unsuspecting already-occupied uterus. "
"
Unlike twins - which occur either when a fertilised egg splits into two, or when two eggs are fertilised by two sperm at the same time - superfetation leads to a woman being pregnant with an additional foetus that's younger than the existing pregnancy.
So far, no cases have been reported of the age gap being greater than a few weeks.
According to the 2008 paper in the European Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, whenever superfetation was confirmed to occur, the two foetuses had a separate amniotic sac. And they differed in size throughout the pregnancy and after birth.
Given the small sample size scientists have to work with, it's not yet clear why superfetation sometimes occurs, and whether whether there are any risk factors that can increase the odds of the phenomenon.
But Casimally notes that reports of superfetation are more common in women who've undergone fertility treatments, which could explain how one or two of those checkpoints get passed.
Despite how rare superfetation is, however, surprisingly, most babies conceived through the strange accident end up surviving.
The main risk is the fact that the babies are still born at the same time, despite their age difference - so one of the babies has the additional challenge of being born premature.
If your brain can handle it, you can find out more about superfetation here and here. The more you know…
| Author: http://www.jlady.ru/ |
| January 16, 2012 |
|
Everyone knows where babies come from, for this the sperm must meet with the egg. But for this meeting to take place, the most active sperm needs to “come” to the finish line first, and the egg must mature and leave the follicle. The word "ovulation" comes from the Latin "ovum", which means "egg". Ovulation is the release of a mature egg capable of fertilization from the ovarian follicle. The most important condition for pregnancy is the presence of a good mature egg, so doctors are interested in this issue in order to assess the general condition of the reproductive system. Ovulation TestsOvulation is characterized by individual signs, when a woman experiences discomfort in the lower abdomen around the middle of the menstrual cycle - this is the period of ovulation. On the same days, you can observe bloody discharge from the genital tract and an increase in sexual desire. However, for more accurate results, it is better to use one of the methods described below. Rectal (basal) temperature measurement This is one of the simplest methods that does not require any financial investments, except for the purchase of a thermometer. True, it is not perfectly accurate, since many conditions must be strictly observed here: normal and long sleep, temperature is measured in the morning at the same time, without getting out of bed. Temperature measurement takes place in the rectum. Information about the temperature is plotted on a graph, where the days of the menstrual cycle are indicated along the horizontal axis, and temperature is indicated along the vertical axis. Ovulation Test Strips This is a more accurate method for determining the level of LH (luteinizing hormone), which is one of the gonadotropins responsible for the normal functioning of the female reproductive system. Before ovulation, the level of this hormone increases significantly, thereby causing it. The preovulatory peak point of LH can be guessed on certain days of the menstrual cycle in the urine, for this special test strips are used. With a regular cycle, tests should be started about 17 days before the next menstruation, since the corpus luteum phase lasts about 12-16 days. With a standard cycle of 28 days, the start of testing should be on the 11th day, and with a cycle of 35 days, the 18th day. Dynamic ultrasound and progesterone determination Ultrasound allows you to see the process of formation of a mature dominant follicle in the ovary. After the egg is released, a corpus luteum is formed in this place, which produces progesterone, which contributes to the normal development of pregnancy. By the level of this hormone, you can get effective information about ovulation. Age and ovulation If a young woman is of reproductive age, almost every menstrual cycle will be ovulatory. Moreover, the absence of ovulation in 10-15% of cycles during the year is considered the norm. The general trend can be described as follows: the older a woman becomes, the less often ovulation will occur. Over the age of 40, ovulation occurs no more than six times a year. However, it's not just the lack of ovulation. In women over 40, the likelihood of pregnancy is reduced not only due to a decrease in the number of ovulatory cycles, but also due to a decrease in egg quality. If you can't get pregnant1-1.5 years of regular sexual intercourse is considered a normal period. If, after its expiration, pregnancy does not occur in young women of reproductive age, the doctor makes a diagnosis of infertility in a married couple. After that, both spouses are recommended to be examined to clarify the possible reasons for the lack of pregnancy. Women over 35 are recommended to start examinations much earlier: if pregnancy has not occurred within six months of regular sexual activity. Such recommendations are given in order not to lose time, since with age, ovarian function and egg quality deteriorate. Factors that affect ovulation It can be any reason: environment, different diets, medications. All this can cause hormonal disruptions and, as a result, the lack of ovulation. Constant changes in time zones, long flights, changes in the usual climatic conditions - these factors are also a source of stress for the body, which can disrupt the usual rhythm of the reproductive system. Thoughtless use of drugs for weight loss, fasting often lead to persistent anovulation. A vivid example is patients with anorexia who voluntarily refuse food and bring themselves into a state of severe exhaustion. If the weight falls below the mark of 45 kg, the body clearly reacts to this and begins to inhibit the processes of the normal functioning of the reproductive system. These women stop menstruating and ovulating. Hormonal disorders can also cause disruption of the ovulation process, most of them due to genetic causes. Various conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome, hyperprolactinemia, thyroid dysfunction, syndromes that are accompanied by an increase in the level of male hormones, sexual differentiation disorders can cause the absence of normal ovulation. Some of these conditions are promising in terms of restoring ovulation and pregnancy, while others exclude the process of ovulation altogether. Therefore, the question of the treatment of hormonal disruptions and the choice of medicines should be decided by the doctor. Ovulation can be achieved by correcting hormonal disorders and prescribing drugs to stimulate the ovulation process. For this purpose, many means are intended: starting with tablets and ending with injectables. In the past few years, new means have appeared to stimulate the ovulation process. They contain gonadotropins, which are obtained using genetic engineering methods, this is guaranteed to exclude the presence of impurities. With the advent of such drugs, the effectiveness of the treatment of women with endocrine disorders has dramatically increased, both in order to restore the ovulation cycle, and in terms of pregnancy. How ovulation affects the sex of the baby American scientists from Harvard University David Rorvik and Lendran Shettles spent almost half a century developing a method based on planning sexual contacts relative to a known ovulation period. The method is as follows: empirically, it was found that spermatozoa with the male Y chromosome are more mobile than those that carry the X chromosome, so they can be the first to reach the egg. An interesting point is that there is a certain seasonality, which is proven by many observations.
Removal of the uterus (or hysterectomy) is a fairly common surgical operation. Indications for it can be different: uterine fibroids, various neoplasms and tumors (including postmenopausal ovarian cystomas), endometriosis. This volume of surgery is offered in the case when the preservation of the diseased organ is no longer possible, since it is accompanied by a high risk of complications (bleeding, malignancy, progression of the process) Similar operations began to be carried out about a hundred years ago, so a lot of experience has been accumulated in this field of gynecology. A large number of clinical studies have also been conducted, which allow drawing certain conclusions regarding the consequences of the operation and the quality of life of the operated patients. However, almost every woman whose doctors recommend hysterectomy is much more concerned about the consequences of the operation. Although, quite often, you need to worry more about the pathology that is an indication for surgery. How will life change? Will it be necessary to change something radically, to adapt to the work of the body, deprived of such an important organ as the uterus? How will the operation affect your sexual life, and how will you now need to build your relationship with your sexual partner? Will the operation entail changes in appearance: excess weight, rapid aging of the skin, the growth of dark hair on the face and body? If you try to answer all these questions briefly, the answer will be: "No radical changes will occur - neither in lifestyle, nor in appearance. And if you want more detailed explanations, then read on. Why do such questions arise?A stable stereotype works in the mind of a woman: No uterus - no menstruation - menopause. Climax = old age. Women are sure that the removal of the uterus will entail an artificially induced unnatural restructuring of the body, which will lead to premature aging, a decrease in libido, and the extinction of many functions. There will be problems with health and well-being, frequent mood swings, causeless fatigue - which, in turn, will affect relationships with others, especially with loved ones. Psychological problems will be superimposed on physiological problems, it will become difficult to achieve mutual understanding and trust in the family. The result is sad - early old age, loneliness, a sharp decline in the quality of life, a feeling of guilt and inferiority. In fact, this stereotype is quite easy to destroy if you understand the anatomical structure of the female body and understand the purpose of the uterus, the mechanism of menstruation and menopause. The uterus and its functions (briefly about the main things)The uterus is an organ of the female body that performs certain functions (for more details, see the section "Normal anatomy of the pelvic organs"). It is designed for the development of the embryo and the bearing of the fetus. In the process of childbirth, the uterus also takes a direct and very active part - it contracts, thereby contributing to the expulsion of the fetus. Inside the uterus, as it were, is “lined” with a mucous membrane, the endometrium. The endometrium is saturated with blood vessels, and the blood supply increases markedly by the middle of the menstrual cycle and in the second phase (medics say: "the endometrium thickens"). The body needs this so that the fertilized egg is safely fixed in the uterus and begins to develop. If fertilization does not occur, then the vessels do not receive nutrition, the upper layer of the endometrium is separated and rejected by the body. When the uterus is removed, there can be no menstruation, because there is no endometrium, the body simply has nothing to expel. However, such a state has a completely different nature than menopause. It's called "surgical menopause." What is menopauseMenopause is the extinction of ovarian function. They produce less and less sex hormones (estrogen, testosterone, progesterone), the egg does not mature in them. Estrogens (female sex hormones) are very important for the state of bone tissue and blood vessels, so their absence very often leads to problems with the musculoskeletal system and blood circulation. Reduced production of testosterone (male sex hormone) leads to a lack of sexual desire (libido). An active hormonal restructuring takes place in the body - it is this that can lead to such external changes as excess weight, skin aging, hair loss. Removal of the uterus cannot cause hormonal changes, because the ovaries will continue to function and produce sex hormones. Clinical studies prove that when the uterus is removed, the ovaries work in the same mode and during the same period that is planned, “programmed” by the body genetically. Estrogens are produced regardless of whether the uterus is removed or left, they continue to have a positive effect on bone tissue and the cardiovascular system. Testosterone is also produced, so libido does not decrease, and the quality of sexual life does not change in any way. Moreover, if you are familiar with such a condition as premenstrual syndrome (PMS), then it will continue. Because PMS is caused by the cyclic work of the ovaries. Approach to surgeryJust because the doctor thinks that it is necessary to remove the uterus, this does not mean that the adnexa (ovaries and fallopian tubes) should also be removed. The modern approach unequivocally says that the ovaries, as well as the cervix, can be left if they are healthy. The risk of developing ovarian cancer has also been shown to decrease after hysterectomy. Psychological consequences of hysterectomy
The right mental attitude is the key to your good health, quick recovery after surgery and return to your usual way of life. For a favorable psychological state, first of all, you need trust in the doctor and confidence that your body will function in the same way as it did before the operation (which is really true). A positive attitude and support from loved ones is very important. Many women attach some symbolism to the uterus, endow it with super-significance. In their minds, the uterus is, as it were, identified with the female essence. You can read above that the actual situation is different. If you attach great importance to the opinions of others and want to protect yourself from their negative psychological impact, then you do not have to dedicate them (including all close relatives, except for your husband) to the details of the operation. Sexual life after hysterectomy
Within 1-1.5 months, sexual intercourse after removal of the uterus (as well as after other operations) is prohibited. This is primarily due to the necessary time required for wound healing. When your body recovers and you realize that you can again lead a normal life, then there will be no obstacles to sexual intercourse. The sensitive zones that bring pleasure to a woman during intercourse are located not in the uterus, but in the vagina and external genitalia. Of course, the degree of trust in your relationship with your sexual partner plays a very important role here. It is possible that he will feel constrained and insecure, will try to adapt to your new state, be wary of sudden movements and experience banal fear. At the same time, his feelings will be determined solely by yours. Remember that your partner also needs reliable information. Feel free to discuss his questions and concerns with him. If necessary, contact a gynecologist for a joint consultation - perhaps your partner will treat his words with a greater degree of trust. He must be sure that your sexual desire and sensations will not undergo major changes, and you can still be a desirable and sensual woman for him. The way you were before. So you just have to weigh the pros and cons. The consequences of removing the uterus will not bring you discomfort. The choice between the state of health after the removal of a diseased organ, and your imaginary fears about changing your appearance and lifestyle, always remains with you. In the first phase of the menstrual cycle, the growth and maturation of the main follicle, which is called dominant, occurs. Ovulation is the rupture of the wall of the dominant follicle and the release of the egg.
The corpus luteum functions for 10–12 days. If conception does not occur, then the egg dies, the corpus luteum regresses, resulting in menstruation. Symptoms of ovulation
Most women ovulate completely asymptomatically, although some representatives of the weaker sex say that they can experience the onset of such days in advance. During ovulation, a woman may feel pain in the lower abdomen. They can be very pronounced. This disorder is called ovulatory syndrome. The discomfort lasts for several days. A woman's discharge may change, become more viscous.
Studies during one cycle are considered non-indicative. The duration of the menstrual cycle directly depends on the rate of maturation of the egg in its first phase, before the onset of ovulation. After the release of the egg, the second phase of the cycle (luteal) begins and in the same woman it is constant - from 12 to 16 days, but most often 14. In a long cycle, the period of egg maturation is longer than in the standard one, and ovulation occurs later. For example, if a woman has a cycle duration of 32-35 days, then the release of the egg is not in the middle of the cycle, as many people think, but on the 18-21st DC or two weeks before the start of the next menstruation. Ultrasonic folliculometrySeveral ultrasound procedures using a vaginal probe can calculate the day of ovulation or conception in a woman. A visit to the ultrasound room is carried out 3-4 times per cycle with an interval of every 2-3 days. If the cycle is irregular, the doctor will have to visit 3-4 times, starting from the 7th day after the end of menstruation - every 2-3 days. If the cycle is regular, it is worth doing an ultrasound 2-3 days before the expected day.
Ovulation TestsIf you can track the follicle using ultrasound, then ovulation tests can be done at home. They act like this: 24-36 hours before the release of the egg from the ovary in the urine, the amount of luteinizing hormone (LH) sharply increases. A day or two before that, he seems to “push out” the egg through the wall of the ovary. Ovulation tests determine if the amount of the hormone is elevated. They also allow you to calculate fertile days. 5-6 days before the expected ovulation, tests are carried out twice a day. Since we are interested in ovulation with a cycle of 30 days, measurements should be started from about day 13. If ovulation is not observed, then the second strip will be absent. But on the eve or on the 15th day, the test line will be as bright as the control line. A similar sign says that the upcoming ovulatory period is coming, which must be expected in the next 24 hours. It is necessary to lower the strip into a container with fresh urine for a few seconds, then put it on a dry surface and after about five minutes read the result.
Basal Temperature Method This method involves measuring the temperature in the rectum (rectal). It is measured immediately after sleep during the cycle. To do this, you need to use one thermometer. You need to shoot it down on the eve of sleep. Measurements are taken in the morning, immediately after waking up. The correct measurement of basal temperature will help determine whether the patient is normal, early or late ovulating. This is one of the easiest ways to determine favorable days for conception. This should be done after waking up in the morning, while you can’t get out of bed. Just woke up, and immediately for the thermometer. All results must be scrupulously noted on a special chart. At the end of the cycle, all points with measurement results are connected into a broken line. During monthly measurements are not carried out. On the first day of the cycle, the temperature reaches 36. Calendar methodThis method of determining ovulation is suitable for those who have a regular menstrual cycle. It is 14 days before the start of a new cycle that full ovulation occurs. In order to determine the calendar of days for conception, it is necessary to analyze the last 3 months. The first day of the menstrual cycle is the first day of menstruation. It is 12-14 days before the start of a new cycle that full-fledged ovulation occurs. The cycle changes under the influence of various factors - health, nervous strain, stress, physical activity, climate change when traveling, and so on. Cervical Mucus Assessment Method Before ovulation, a woman's ovaries experience a surge in estrogen production. This leads to an increase in the production of mucus by the cells of the vagina and cervix. Why doesn't ovulation occur?Ovulation may be absent for various reasons. They can be divided into 2 groups: physiological and pathological. Do not worry about the lack of ovulation in such cases:
Ovulation - reasons for absence
Early rupture of the follicle can also provoke
Not in all cases the female body works like a clock. The absence of ovulation during regular periods is called anovulation. If this phenomenon occurs no more than 2 times a year, there is no need to worry. The absence of ovulation with regular menstruation can only be judged after a long-term observation of the body (at least 3 months).
Warsaw
Krasnopresnenskaya
Annino
This question worries both those women who dream of a child and those who want to protect themselves from unwanted pregnancy. In this article, together with the Health clinic, we will analyze what ovulation is from a physiological point of view and how to detect its onset. Ovulation is the short period in a woman's menstrual cycle when conception is most possible. Ovulation lasts from 12 to 24 hours and traditionally falls in the middle of the cycle - 11-21 days - depending on its length. Only women with an impeccable menstrual cycle can calculate ovulation according to the calendar with high accuracy. It should be noted that there are few of them. Most women have to go to the gynecologist or try to determine ovulation by a set of symptoms characteristic of this period. Fortunately, we live in the 21st century, which offers us several methods for determining ovulation at once. Methods for determining ovulation1. Calendar method This method is very popular, but not very accurate. As we wrote above, using the calendar, only those women who do not have any disruptions in the menstrual cycle can determine ovulation. If, for example, your cycle from month to month is 29days, your period is right on time, and you don't have any reproductive health issues, then the calendar method might work for you. True, it is better to use it if you want to conceive a child. If not, it will be safer to use protection regardless of the day of the cycle. 2. Ovulation tests for determining ovulation are sold in any pharmacy and are now available to women in all developed countries. It is worth using such a test from the 11th day of the cycle, not earlier. 2 days before ovulation, both bands (test and control) will be bright, which indicates the onset of a favorable period for conception. However, the test shows only a peak of luteinizing hormone, which contributes to the rupture of the follicular capsule. 3. Folliculometry A modern and accurate method for determining ovulation, which is performed using . During the procedure, a special sensor is inserted into the vagina, with the help of which the doctor evaluates the condition of the follicles on each ovary. Among the follicles, at the time of ovulation, one dominant matures, and when it reaches 20 mm, the ideal moment for conception comes. It is necessary to carry out this procedure at least 3 times per cycle - on the first day after the end of menstruation, on days 11-12 and on days 24-25. During the first ultrasound, the doctor will assess the condition of the ovaries and the number of follicles, during the second ultrasound - the probability and date of ovulation, during the third ultrasound - the probability of pregnancy. In any case, a gynecologist should be consulted before the ultrasound procedure. The doctor will give precise instructions and recommendations. 4. Symptoms of ovulation Method with unspecified effectiveness, but also very popular among women. A few days before and during ovulation, a number of symptoms appear that indicate a convenient moment for conception. There are some nuances here: in some women, the symptoms appear brightly, in others - almost imperceptibly. But we will talk about them in the next part of the article. Symptoms of ovulationSo, what you should pay attention to: Basal body temperature (lowest body temperature after sleep). On the day of ovulation, it sharply decreases by about 0.5 * C, and the next day it rises sharply and continues to grow until the 23-27th day of the cycle. To calculate the exact day of ovulation, the temperature must be taken immediately after waking up daily on each day of the cycle and plotted with a curve of changes. Temperature is measured rectally, that is, by inserting a thermometer into the rectum. Changes in cervical mucus. In the period suitable for conceiving a child (4-6 days), the mucus becomes like egg white - almost transparent, watery, slippery, but at the same time dense and elastic. If you pay attention to such changes, then the probability of conception increases markedly. Swelling of the mammary glands. The breasts may become tighter and more painful, the nipples more sensitive. Increasing sexual desire. A few days before ovulation, a woman's attraction to a partner increases. Some women note that the condition of the skin and hair improves, there is greater self-confidence. Pain or unpleasant pulling sensations in the lower abdomen from the side of the ovary in which the maturation of the egg has occurred. It lasts no more than 5 days. To track all these symptoms, a woman has to make an effort and monitor the state of her body throughout the cycle for several months. Symptoms of the end of ovulationThere are also a number of symptoms that indicate that ovulation has ended:
How to accurately determine the days of ovulation?Today, only folliculometry can determine the day of ovulation and the possibility of conception with high accuracy. For the reason that ultrasound makes it possible to see and evaluate the condition of the follicles before and after ovulation. For example, in the second phase of the cycle, the follicle could degenerate into a functional cyst - this will immediately become clear on ultrasound. Sometimes ovulation simply does not occur due to various reasons - stress in a woman's life, sudden weight loss, climate change or hormonal disorders. Is it possible to get pregnant not on ovulation, but on other days of the cycle? Yes, you can. A woman's body is not a clockwork mechanism strictly in accordance with medical reference books. Sometimes ovulation occurs later than expected, sometimes earlier. You can calculate it yourself, but it is time-consuming and energy-consuming. If you are planning to conceive a baby or, conversely, want to protect yourself from an unwanted pregnancy, contact for advice. This increases the chances of success in both the first and second cases. Version of the site for the visually impaired |
Ovulation and pregnancy | Huggies® Official Website
PreviousNext
- How does ovulation and fertilization occur?
- When does pregnancy occur? Right after ovulation?
- So how do you calculate ovulation?
- What should be the sensations after ovulation?
- When will signs of pregnancy appear after ovulation and conception?
- Why did not conception occur after ovulation?
Contents:
Ovulation is a special event. It means that a woman has begun a period in which she can give a new life. How to calculate the date of ovulation? What are the best days for getting pregnant? How long after ovulation does conception occur? We answer the questions of expectant mothers.
It means that a woman has begun a period in which she can give a new life. How to calculate the date of ovulation? What are the best days for getting pregnant? How long after ovulation does conception occur? We answer the questions of expectant mothers.
How does ovulation and fertilization occur?
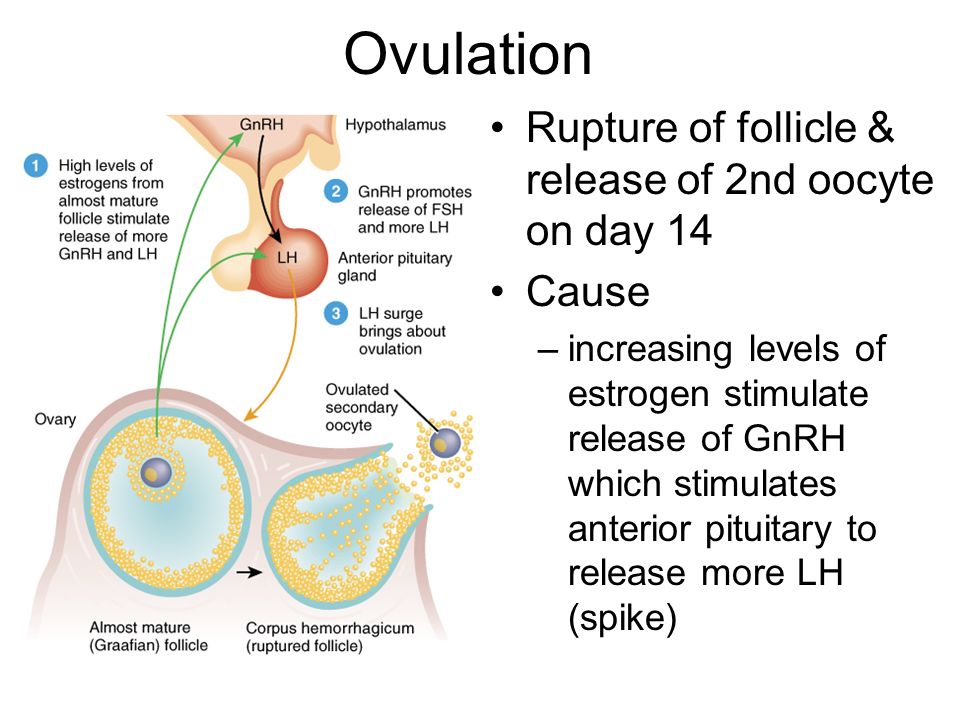
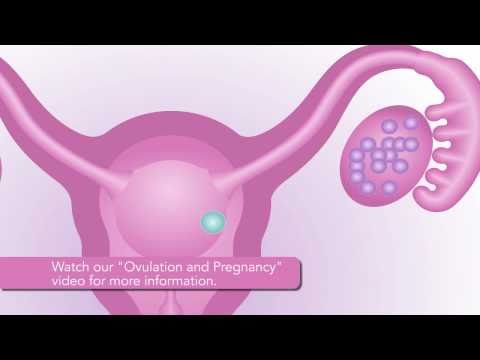
In the first phase of the menstrual cycle, the maturation of the follicle begins in one of the ovaries. This small vesicle consists of an ovum enclosed in a "shell" of connective tissue. The follicle grows from 1 mm to 12–16 mm 1 and then bursts, releasing the egg into the fallopian tube. This moment is called ovulation.
What happens after ovulation? The egg becomes available for fertilization. For this to happen, there must be enough sperm in the fallopian tube. Contrary to popular belief, the winner will not be the most agile of them all. The ovum is surrounded by a special membrane called the "radiant crown" 2 (sounds very nice, doesn't it?). First, many fighters will die trying to destroy the protective shell, and only then one lucky one will get inside and fertilize the egg.
First, many fighters will die trying to destroy the protective shell, and only then one lucky one will get inside and fertilize the egg.
When does pregnancy occur? Right after ovulation?
The period in which a woman can become pregnant does not last very long: the egg cell lives only about 24 hours 3 . This gives us the answer to the question of how long after ovulation conception occurs - at any point in this short period. In particular, fertilization can happen almost immediately if the spermatozoa made their way into the fallopian tube even before the egg is released from the follicle.
Some women report that they did not become pregnant on the day of ovulation, but earlier or later. This is impossible in principle, and they are wrong - it's just that the actual date of this event may not coincide with the calculated one. It is normal if ovulation happened a day or two earlier or later than the plan, and under certain conditions (hormonal changes, stress, and others), it can go beyond this.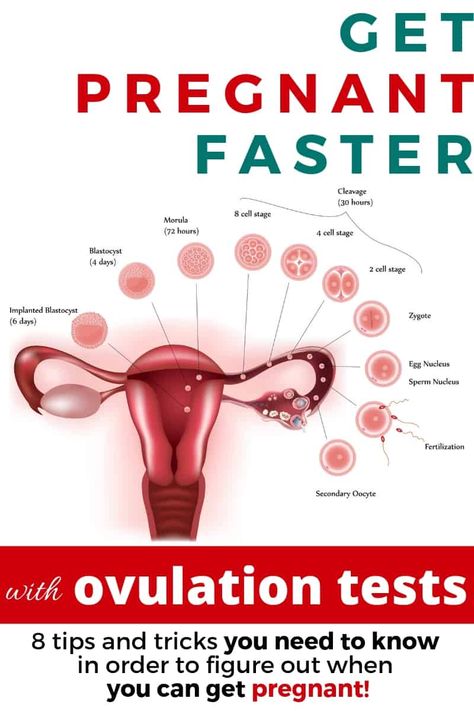 More details in this article.
More details in this article.
So how do you calculate ovulation?
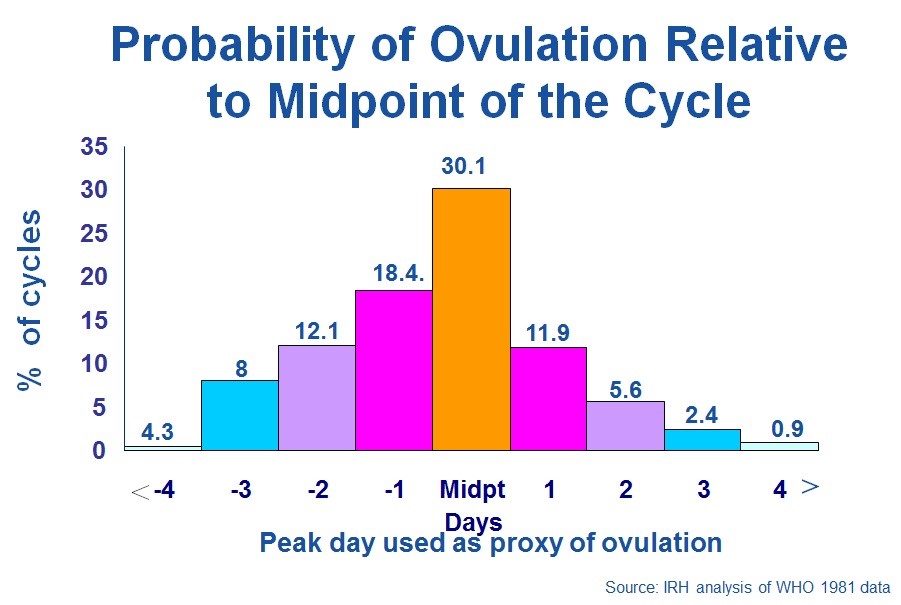
Pregnancy begins after ovulation and fertilization of the egg by sperm. It's up to the small thing - to understand when this important event will happen. Take a calendar and look at our drawing. With it, you can calculate the approximate date of ovulation. But remember, this is just a prediction, and that's why we've drawn high, medium, and low pregnancy probability areas around the central day.
Do not try to get pregnant exactly at ovulation. It is better to cover the entire period of high probability with a “queue”. Start having sex for pregnancy 4 days before the planned date and do it every other day: 4th day before, 2nd day before, day of ovulation, 2nd day after, 4th day after. This will greatly increase your chances of success.
Approximate menstrual cycle schedule. Calculations are given for cycles with a duration of 25 to 31 days.
The ideal menstrual cycle is 28 days. In many articles on conception and ovulation, all the reasoning is built around this textbook case. Indeed, it is very convenient - ovulation in it occurs on the 14th day, dividing the cycle into two equal halves. Life is different from the ideal: the duration of the cycle for different women varies, but usually ranges from 25 to 31 days 4 .
In many articles on conception and ovulation, all the reasoning is built around this textbook case. Indeed, it is very convenient - ovulation in it occurs on the 14th day, dividing the cycle into two equal halves. Life is different from the ideal: the duration of the cycle for different women varies, but usually ranges from 25 to 31 days 4 .
Most likely, you will find your case in this figure, but if your cycle is shorter or longer, there is nothing strange in this - the duration is considered to be from 21 to 35 days 5 . The following knowledge will help calculate the day of ovulation: with a change in the length of the cycle, its first part usually decreases or grows, while the second remains unchanged and is always about two weeks. Set aside 14 days back from the planned first day of menstruation - get the approximate day of ovulation.
There are many more signs of ovulation that you can check out in this article.
In terms of conception, the menstrual cycle can be divided into the following phases (shown in the figure):
-
Menstruation.
 Sex during this period can only lead to conception under very unusual circumstances. For now, relax - auspicious days ahead.
Sex during this period can only lead to conception under very unusual circumstances. For now, relax - auspicious days ahead. -
From the end of menstruation to the 6th day before the planned ovulation. The probability of conception at this time is minimal. Most likely, the egg has not only not left the ovary, but has not even matured yet.
-
5 to 3 days before estimated ovulation date. The chance of getting pregnant increases, and there are two reasons for this. Firstly, the real day of ovulation does not always coincide with the calculated one. Secondly, spermatozoa know how to wait. Most of them will die in the vagina within a couple of hours - its acidic environment fights well not only with bacteria. However, those that can penetrate the uterus are able to live up to three, sometimes up to five days 6 .
-
Planned day of ovulation plus or minus two days. During this period, a woman is most fertile. Given the lifespan of the egg and sperm, sex these days is highly likely to lead to pregnancy.
 Of course, if there are no factors that can interfere with this.
Of course, if there are no factors that can interfere with this. -
3 to 4 days after estimated ovulation date. The chance of getting pregnant is decreasing, but still remains. Do you remember that calculating the day of ovulation is not a very exact science? So anything is possible.
-
From the 5th day after the planned ovulation until the end of the cycle. Do not seriously expect that you will be able to conceive these days, have sex just for fun. If you have tried to get pregnant on your fertile days, you may have already conceived!
What should be the feeling after ovulation?
During the menstrual cycle there is only one period in which a woman feels the changes taking place in her body. This is menstruation itself, and the sensations from it are very familiar to you. All other phases of the cycle are "asymptomatic".
The answer to the question of how to understand that ovulation was successful is prosaic: no way. The woman's body simply does not have a mechanism that would tell the brain about it. So, if you woke up with the certainty that today is that very day, these are just mind games that frolicked in a dream with the thought you desired about the joy of motherhood. Although, coincidences also happen :)
The woman's body simply does not have a mechanism that would tell the brain about it. So, if you woke up with the certainty that today is that very day, these are just mind games that frolicked in a dream with the thought you desired about the joy of motherhood. Although, coincidences also happen :)
When will signs of pregnancy appear after ovulation and conception?
Reliable - not yet soon. A regular pregnancy test will show two cherished strips only after a delay, a test with increased sensitivity or laboratory analysis - 3-4 days earlier. The final confirmation with the help of ultrasound will have to wait another couple of weeks.
Do not expect pregnancy symptoms immediately after ovulation. While the fertilized egg slowly gets from the fallopian tube to its destination, almost no changes occur in the body. The first signs of pregnancy will appear only 6-10 days after ovulation, when the embryo attaches to the wall of the uterus 7 .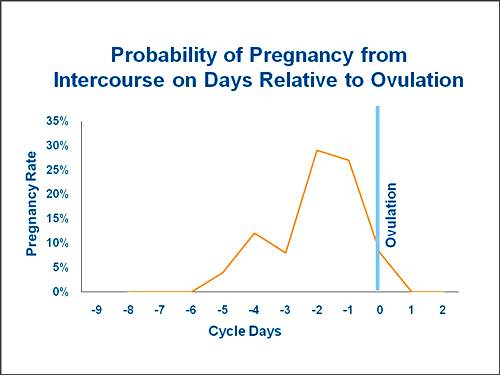 And they will be almost invisible:
And they will be almost invisible:
-
Change in basal body temperature. If you have been measuring your basal temperature all this time, you will notice a slight drop on the chart, and then a rise to a new, higher level.
-
Implantation bleeding. In the process of attaching the embryo to the wall of the uterus, the endometrium is damaged - its inner mucosa. In this case, the expectant mother may notice slight spotting.
-
Pain or cramps in the lower abdomen. Along with bleeding, mild pain may come. Therefore, women often attribute these first signs of pregnancy to early menstruation.
Why did not conception occur after ovulation?
You tried to get pregnant, but your next period started right on time. Why did it happen? Only your doctor can accurately answer this question, but we will list some likely causes.
-
Anovulatory cycle. Some menstrual cycles do not ovulate and this is perfectly normal 8 .
 They are called anovulatory and are needed by the body so that it can take a little break from the constant preparation for pregnancy. During the year, a woman experiences 1–2 anovulatory cycles.
They are called anovulatory and are needed by the body so that it can take a little break from the constant preparation for pregnancy. During the year, a woman experiences 1–2 anovulatory cycles. -
Gynecological diseases. Sometimes conception after ovulation does not occur because the woman has gynecological diseases. Inflammation of the ovaries, blockage of the fallopian tubes, and some other conditions can significantly reduce the likelihood of pregnancy, and under certain conditions, even make conception impossible. A gynecologist can identify such diseases and prescribe treatment.
-
Immune or autoimmune reactions. Spermatozoa are very unusual cells. They contain only half of the chromosome set, and from the point of view of the immune system, they look like mutants. Everything is so bad that nature even had to collect them in special refrigerated bags and hang them outside the man's body. In some cases, the immune mechanisms of a woman can deal with spermatozoa at the time of passage of the cervix 9 .
 Autoimmune reactions also occur when a man's body destroys them. If the doctor considers that this may be the reason for unsuccessful attempts at conception, he will prescribe tests for both the expectant mother and the future dad.
Autoimmune reactions also occur when a man's body destroys them. If the doctor considers that this may be the reason for unsuccessful attempts at conception, he will prescribe tests for both the expectant mother and the future dad. -
Poor semen quality. After intercourse, spermatozoa will have to overcome the champion's obstacle course - survive in the aggressive environment of the vagina, break through the cervical mucus in the cervix, get to the right fallopian tube, destroy the protection of the egg. If the spermatozoa of the future dad are not very active, they can go the distance before conception. To exclude this cause, it is necessary to make a spermogram.
When conception occurs after ovulation, future parents take it for granted. If pregnancy does not occur, they often begin to panic and think with horror that they will never hear ringing children's laughter and light steps of tiny legs in their house. Drive unconstructive thoughts away - many couples were able to conceive far from the first time. Try again next month. We believe you will definitely succeed!
Try again next month. We believe you will definitely succeed!
Links to sources:
-
Ovaries: follicles, growth and development disorders. Link: http://humbio.ru/humbio/eclin/002645db.htm
-
Pansky, Ben (1982), "Chapter 12: Fertilization", Review of MEDICAL EMBRYOLOGY. Link: https://discovery.lifemapsc.com/library/review-of-medical-embryology/chapter-12-fertilization
-
Depares J, Ryder RE, Walker SM, Scanlon MF, Norman CM (1986). Ovarian ultrasonography highlights precision of symptoms of ovulation as markers of ovulation. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 292 (6535): 1562. Link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1340563/?page=1
-
Chiazze L, Brayer FT, Macisco JJ, Parker MP, Duffy BJ (February 1968). "The length and variability of the human menstrual cycle". JAMA. 203(6): 377–80. Link: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/337826
-
Menstruation and the menstrual cycle fact sheet.




 Main reasons:
Main reasons: 
 Quite common causes of infertility in women are the lack of ovulation and various hormonal disruptions.
Quite common causes of infertility in women are the lack of ovulation and various hormonal disruptions.  The menstrual cycle can be considered ovulatory if the temperature difference in the first and second phases is at least 0.3 °C. The first phase is the period before ovulation, with a "classic" regular cycle of 28 days, its duration is 14 days. The second phase of the cycle is the remaining two weeks.
The menstrual cycle can be considered ovulatory if the temperature difference in the first and second phases is at least 0.3 °C. The first phase is the period before ovulation, with a "classic" regular cycle of 28 days, its duration is 14 days. The second phase of the cycle is the remaining two weeks.  Positive test results indicate that ovulation will begin in about 28-42 hours.
Positive test results indicate that ovulation will begin in about 28-42 hours.  This, in turn, affects the likelihood of pregnancy, its normal development and the quality of the embryos.
This, in turn, affects the likelihood of pregnancy, its normal development and the quality of the embryos.  However, these disturbances are usually transient.
However, these disturbances are usually transient. 
 When entering the acidic environment of the vagina, the activity of Y-spermatozoa decreases, since they quickly die there and, thereby, open the way for slower, but also more viable, X-spermatozoa. Scientists believed that X-spermatozoa can survive in the uterine environment for several days in anticipation of ovulation, unlike sperm with a Y-chromosome, which are not capable of this. As the day of ovulation approaches, the vaginal discharge becomes more alkaline, which increases the likelihood of survival of sperm with a Y chromosome. If you know exactly the day of ovulation, then you can try to increase the chances of certain spermatozoa to participate in the fertilization process, and, therefore, plan the sex of the unborn child.
When entering the acidic environment of the vagina, the activity of Y-spermatozoa decreases, since they quickly die there and, thereby, open the way for slower, but also more viable, X-spermatozoa. Scientists believed that X-spermatozoa can survive in the uterine environment for several days in anticipation of ovulation, unlike sperm with a Y-chromosome, which are not capable of this. As the day of ovulation approaches, the vaginal discharge becomes more alkaline, which increases the likelihood of survival of sperm with a Y chromosome. If you know exactly the day of ovulation, then you can try to increase the chances of certain spermatozoa to participate in the fertilization process, and, therefore, plan the sex of the unborn child.  Girls are most often born in early winter, spring, early summer, early and late autumn. Boys are most often born in the first two winter months, at the beginning and end of spring, late summer and mid-autumn. Based on these observations, you can plan the time of conception and increase the likelihood of having a child of a certain gender.
Girls are most often born in early winter, spring, early summer, early and late autumn. Boys are most often born in the first two winter months, at the beginning and end of spring, late summer and mid-autumn. Based on these observations, you can plan the time of conception and increase the likelihood of having a child of a certain gender.  The modern level of gynecology and medical equipment make it possible to perform hysterectomy using laparoscopy (in the case when the size of the uterus makes it possible), which guarantees high accuracy during the operation and a quick recovery after it.
The modern level of gynecology and medical equipment make it possible to perform hysterectomy using laparoscopy (in the case when the size of the uterus makes it possible), which guarantees high accuracy during the operation and a quick recovery after it.  "
"  We will try to help you do it!
We will try to help you do it!  Menstruation begins.
Menstruation begins. 
 Some sources cite the following statistics: the risk of developing ovarian cancer in women after a hysterectomy is 1/300, while in women with a preserved uterus - 1/80.
Some sources cite the following statistics: the risk of developing ovarian cancer in women after a hysterectomy is 1/300, while in women with a preserved uterus - 1/80.  This is the case when "a lie is for salvation." Remember that the most important thing in this case is your health. Both physical and psychological.
This is the case when "a lie is for salvation." Remember that the most important thing in this case is your health. Both physical and psychological.  He will perceive everything adequately with your positive attitude towards the situation.
He will perceive everything adequately with your positive attitude towards the situation.  It enters the fallopian tube. During the day, it can be fertilized. The dominant follicle in the 2nd phase of the cycle transforms into the corpus luteum, the main function of which is the synthesis of progesterone.
It enters the fallopian tube. During the day, it can be fertilized. The dominant follicle in the 2nd phase of the cycle transforms into the corpus luteum, the main function of which is the synthesis of progesterone.  During ovulation, her sexual desire increases. Egg maturation changes by day as follows:
During ovulation, her sexual desire increases. Egg maturation changes by day as follows: 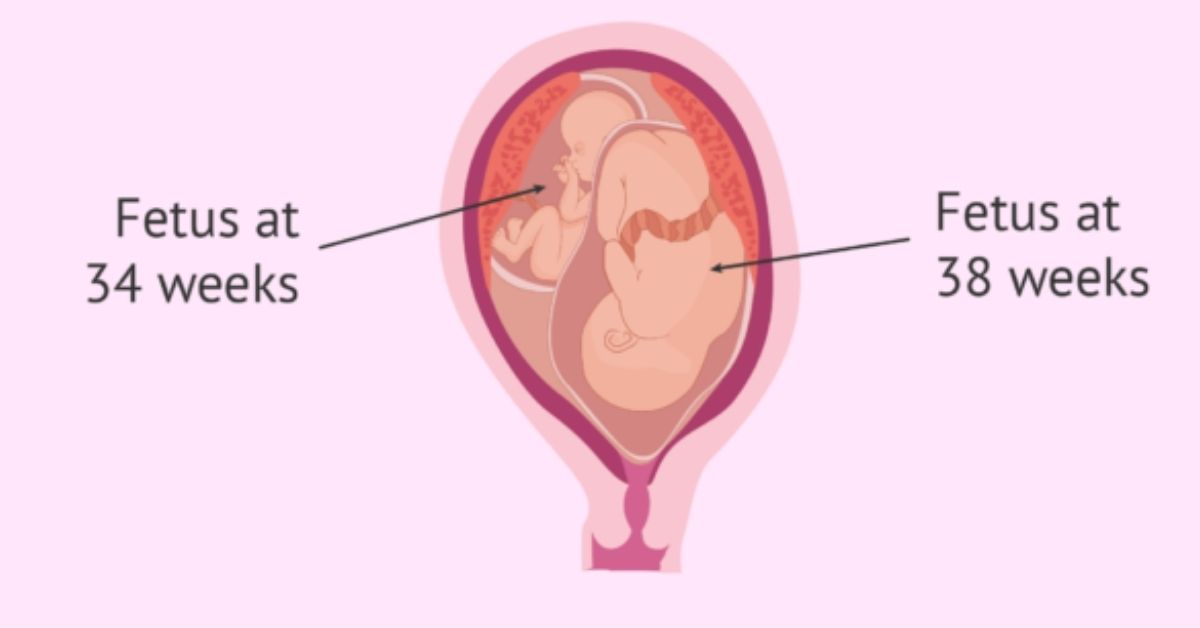 The standard classic option is 14 days with a 28-day cycle.
The standard classic option is 14 days with a 28-day cycle.  With a 30-day cycle, ultrasound monitoring begins on the 10-11th day of the cycle, i.e., approximately 4-5 days before the middle of the monthly cycle. Subsequent sessions of ultrasonic monitoring of the egg are carried out every two days and last until the release of the egg. The onset of the ovulatory period is confirmed by ultrasound diagnostics, when the size of the follicle was 20-24 mm the day before, and now the growth of the corpus luteum has begun. The procedure can be performed through the vagina or through the abdominal wall. With an intravaginal examination, no preliminary preparation is required, the main thing is to empty the bladder. In an abdominal examination, a traditional examination is performed through the abdominal wall. In order for it to pass without difficulty, three days before the monitoring, it is necessary to exclude all products that can provoke flatulence or bloating, and on the day of the examination, you must not eat and drink at least a liter of water.
With a 30-day cycle, ultrasound monitoring begins on the 10-11th day of the cycle, i.e., approximately 4-5 days before the middle of the monthly cycle. Subsequent sessions of ultrasonic monitoring of the egg are carried out every two days and last until the release of the egg. The onset of the ovulatory period is confirmed by ultrasound diagnostics, when the size of the follicle was 20-24 mm the day before, and now the growth of the corpus luteum has begun. The procedure can be performed through the vagina or through the abdominal wall. With an intravaginal examination, no preliminary preparation is required, the main thing is to empty the bladder. In an abdominal examination, a traditional examination is performed through the abdominal wall. In order for it to pass without difficulty, three days before the monitoring, it is necessary to exclude all products that can provoke flatulence or bloating, and on the day of the examination, you must not eat and drink at least a liter of water.
 testing is carried out by analogy with tests to detect conception.
testing is carried out by analogy with tests to detect conception.  9°C A few days before ovulation, it can be 36.2 ° C - 36.4 ° C. An increase in temperature to 37°C - 37.4°C indicates that ovulation is occurring. If the temperature rises after ovulation, the woman is probably pregnant.
9°C A few days before ovulation, it can be 36.2 ° C - 36.4 ° C. An increase in temperature to 37°C - 37.4°C indicates that ovulation is occurring. If the temperature rises after ovulation, the woman is probably pregnant.  This mucus is viscous, which can be tested by stretching a small amount of it between the fingers about 2 cm.
This mucus is viscous, which can be tested by stretching a small amount of it between the fingers about 2 cm. 


 This does not guarantee 100% ovulation. Even in perfectly healthy women, the probability of conception on the day of ovulation rarely exceeds 40%. And if for some reason the dominant follicle has not matured, then the probability tends to zero.
This does not guarantee 100% ovulation. Even in perfectly healthy women, the probability of conception on the day of ovulation rarely exceeds 40%. And if for some reason the dominant follicle has not matured, then the probability tends to zero. 

 Six days before ovulation and two days after, there is a 16 to 30% chance that conception will occur. No one will give exact numbers, since each organism has its own biological rhythms. But it is worth remembering that on no single day of the menstrual cycle is the probability of conception equal to zero! Even during menstruation.
Six days before ovulation and two days after, there is a 16 to 30% chance that conception will occur. No one will give exact numbers, since each organism has its own biological rhythms. But it is worth remembering that on no single day of the menstrual cycle is the probability of conception equal to zero! Even during menstruation.