What is another name for the placenta
PLACENTA Synonyms: 10 Synonyms & Antonyms for PLACENTA
See definition of placenta on Dictionary.com
- as inbag of waters
- as inmembrane
synonyms for placenta
- afterbirth
- amnion
- arachnoid membrane
- water bag
- sheath
- sheet
- film
- lamina
- leaf
- mucosa
Roget's 21st Century Thesaurus, Third Edition Copyright © 2013 by the Philip Lief Group.
QUIZ
Feeling Frazzled? Take October’s Synonym Of The Day Quiz!
START THE QUIZHow to use placenta in a sentence
Thus, the false narrative goes, the immune system will not be able to differentiate between the two and will create antibodies that interfere with proper development of the placenta.
THE CASE FOR GETTING A COVID-19 VACCINE DURING PREGNANCYMATTHEW WOODRUFFAUGUST 26, 2021QUARTZ
Another protein similar to gag, dubbed PEG10, can grab onto RNA and also form bubbly spaceships to help develop the placenta and aid reproduction.
SURPRISE! OUR BODIES HAVE BEEN HIDING A TROJAN HORSE FOR GENE THERAPYSHELLY FANAUGUST 24, 2021SINGULARITY HUB
Some people have confused these spike proteins with a completely different kind of protein called syncytin-1, which is part of placenta formation during pregnancy.
STILL UNSURE ABOUT GETTING THE COVID-19 VACCINE? START HERE.KALEIGH ROGERSAUGUST 11, 2021FIVETHIRTYEIGHT
Bleeding heavily from what she later learned was a tear between her uterus and her baby’s placenta, Benitez later bargained with her doctors.
A PROGRAM PROMISED TO PAY FOR BRAIN-DAMAGED INFANTS’ CARE. THEN IT SENT FAMILIES TO MEDICAID INSTEAD.BY DANIEL CHANG AND CAROL MARBIN MILLER, MIAMI HERALDJUNE 1, 2021PROPUBLICA
All the vaccines have that material, the placenta and the embryos.
FIVE DAYS, 100 VACCINE DOSES AND A WILDFIRE OF CONSPIRACY THEORIESJOSE DEL REALMAY 28, 2021WASHINGTON POST
In reality, though, by now these rowdy fetal cells — which cross the placenta and enter the maternal blood stream — have probably settled down and embedded in various body parts, permanently integrating with my kidneys, say, or my heart.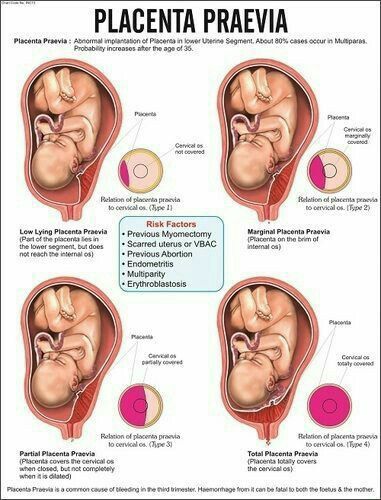
MOMS: YOU SHAPED YOUR CHILDREN, BUT THE REVERSE IS TRUE, TOO — DOWN TO YOUR VERY CELLSABIGAIL TUCKERMAY 6, 2021WASHINGTON POST
The discovery illuminates not only several mysteries about the placenta itself but also some underlying connections to cancer.
NEW GENOMIC STUDY OF PLACENTA FINDS DEEP LINKS TO CANCERMAX KOZLOVAPRIL 8, 2021QUANTA MAGAZINE
Around this time, something “magical” happens within the blastocyst, such that it churns out cells that eventually develop into the placenta, and others that give rise to a fetus.
SCIENTISTS CREATED AN ARTIFICIAL EARLY EMBRYO FROM HUMAN SKIN CELLSSHELLY FANMARCH 23, 2021SINGULARITY HUB
For example, the artificial embryos generated cells that form the placenta, which is critical for a viable embryo that could, in theory, develop further or even until birth.
SCIENTISTS CREATED AN ARTIFICIAL EARLY EMBRYO FROM HUMAN SKIN CELLSSHELLY FANMARCH 23, 2021SINGULARITY HUB
One layer, for example, was populated by cells with a genetic signature that destined them as part of a placenta.
SCIENTISTS CREATED AN ARTIFICIAL EARLY EMBRYO FROM HUMAN SKIN CELLSSHELLY FANMARCH 23, 2021SINGULARITY HUB
WORDS RELATED TO PLACENTA
- afterbirths
- amnions
- arachnoid membranes
- placentas
- water bags
- film
- lamina
- leaf
- mucosa
- placenta
- sheath
- sheet
Roget's 21st Century Thesaurus, Third Edition Copyright © 2013 by the Philip Lief Group.
Placenta Definition & Meaning | Dictionary.com
- Top Definitions
- Quiz
- Related Content
- Examples
- British
- Scientific
- Cultural
This shows grade level based on the word's complexity.
[ pluh-sen-tuh ]
/ pləˈsɛn tə /
Save This Word!
See synonyms for placenta on Thesaurus.com
This shows grade level based on the word's complexity.
noun, plural pla·cen·tas, pla·cen·tae [pluh-sen-tee]. /pləˈsɛn ti/.
Anatomy, Zoology. the organ in most mammals, formed in the lining of the uterus by the union of the uterine mucous membrane with the membranes of the fetus, that provides for the nourishment of the fetus and the elimination of its waste products.
Botany.
- the part of the ovary of flowering plants that bears the ovules.
- (in ferns and related plants) the tissue giving rise to sporangia.
QUIZ
SHALL WE PLAY A "SHALL" VS. "SHOULD" CHALLENGE?
Should you take this quiz on “shall” versus “should”? It should prove to be a quick challenge!
Question 1 of 6
Which form is commonly used with other verbs to express intention?
Origin of placenta
1670–80; <New Latin: something having a flat, circular form, Latin: a cake <Greek plakóenta, accusative of plakóeis flat cake, derivative of pláx (genitive plakós) flat
OTHER WORDS FROM placenta
pla·cen·tal, plac·en·tar·y [plas-uhn-ter-ee, pluh-sen-tuh-ree], /ˈplæs ənˌtɛr i, pləˈsɛn tə ri/, adjectivein·ter·pla·cen·tal, adjectivenon·pla·cen·tal, adjectivepre·pla·cen·tal, adjective
sub·pla·cen·ta, noun, plural sub·pla·cen·tas, sub·pla·cen·tae. sub·pla·cen·tal, adjective
sub·pla·cen·tal, adjective
Words nearby placenta
placeman, place mat, placement, placement test, placename, placenta, placental, placentate, placentation, Placentia, Placentia Bay
Dictionary.com Unabridged Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, © Random House, Inc. 2022
Words related to placenta
sheath, sheet, film, lamina, leaf, mucosa, afterbirth, amnion, water bag
How to use placenta in a sentence
Thus, the false narrative goes, the immune system will not be able to differentiate between the two and will create antibodies that interfere with proper development of the placenta.
The case for getting a Covid-19 vaccine during pregnancy|Matthew Woodruff|August 26, 2021|Quartz
Another protein similar to gag, dubbed PEG10, can grab onto RNA and also form bubbly spaceships to help develop the placenta and aid reproduction.
Surprise! Our Bodies Have Been Hiding a Trojan Horse for Gene Therapy|Shelly Fan|August 24, 2021|Singularity Hub
Some people have confused these spike proteins with a completely different kind of protein called syncytin-1, which is part of placenta formation during pregnancy.

Still Unsure About Getting The COVID-19 Vaccine? Start Here.|Kaleigh Rogers|August 11, 2021|FiveThirtyEight
Bleeding heavily from what she later learned was a tear between her uterus and her baby’s placenta, Benitez later bargained with her doctors.
A Program Promised to Pay for Brain-Damaged Infants’ Care. Then It Sent Families to Medicaid Instead.|by Daniel Chang and Carol Marbin Miller, Miami Herald|June 1, 2021|ProPublica
All the vaccines have that material, the placenta and the embryos.
Five days, 100 vaccine doses and a wildfire of conspiracy theories|Jose Del Real|May 28, 2021|Washington Post
Nothing much to use in cleaning up the baby and his mother after the birth, no place to dispose of the placenta.
Jesus Wasn’t Born Rich. Think About It.|Gene Robinson|December 25, 2014|DAILY BEAST
Usually, the disease resolves with the birth of the baby and placenta.
Beyond ‘Downton Abbey’: Preeclampsia Maternal Deaths Continue Today|Eleni Tsigas, Christine Morton|January 28, 2013|DAILY BEAST
It normally occurs during weeks six and eight of pregnancy, when the placenta takes over production of hormones from the ovaries.

What Exactly Is Wrong With Kate (And Is She Vomiting Blood?) Experts Rush To Explain...|Tom Sykes|December 3, 2012|DAILY BEAST
You get the biting of the placenta and you get Renesmee biting her without necessarily seeing it.
Bill Condon and Melissa Rosenberg on 'Twilight Saga: Breaking Dawn'|Marlow Stern|November 21, 2011|DAILY BEAST
I had to tell her she had a condition with her placenta that made abortion risky.
The Abortion Ban Is Bad Medicine|Willie J. Parker|November 16, 2009|DAILY BEAST
Dugung nagpúgul sa inunlan, Placenta filled with a big clot of blood.
A Dictionary of Cebuano Visayan|John U. Wolff
Finally, some persons make use of the method of corrosion to prepare and preserve the placenta.
History of Embalming|J. N. Gannal
They pass up the sides of the bladder towards the navel, enter the sheath of the cord, and so reach the placenta.
The Matron's Manual of Midwifery, and the Diseases of Women During Pregnancy and in Childbed|Frederick Hollick
The diameter of the placenta is about six inches, and its thickness about one inch and a half.
The Matron's Manual of Midwifery, and the Diseases of Women During Pregnancy and in Childbed|Frederick Hollick
Some have even averred that the Placenta is not required at all, to supply nourishment, but is merely a purifying organ.
The Matron's Manual of Midwifery, and the Diseases of Women During Pregnancy and in Childbed|Frederick Hollick
British Dictionary definitions for placenta
placenta
/ (pləˈsɛntə) /
noun plural -tas or -tae (-tiː)
the vascular organ formed in the uterus during pregnancy, consisting of both maternal and embryonic tissues and providing oxygen and nutrients for the fetus and transfer of waste products from the fetal to the maternal blood circulationSee also afterbirth
the corresponding organ or part in certain mammals
botany
- the part of the ovary of flowering plants to which the ovules are attached
- the mass of tissue in nonflowering plants that bears the sporangia or spores
Word Origin for placenta
C17: via Latin from Greek plakoeis flat cake, from plax flat
Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 2012 Digital Edition © William Collins Sons & Co.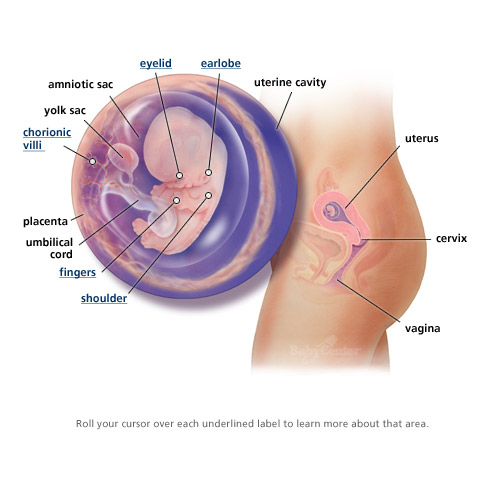 Ltd. 1979, 1986 © HarperCollins Publishers 1998, 2000, 2003, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2012
Ltd. 1979, 1986 © HarperCollins Publishers 1998, 2000, 2003, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2012
Scientific definitions for placenta
placenta
[ plə-sĕn′tə ]
The sac-shaped organ that attaches the embryo or fetus to the uterus during pregnancy in most mammals. Blood flows between mother and fetus through the placenta, supplying oxygen and nutrients to the fetus and carrying away fetal waste products. The placenta is expelled after birth.
The part of the ovary of a flowering plant to which the ovules are attached. In a green pepper, for example, the whitish tissue to which the seeds are attached is the placenta.
The American Heritage® Science Dictionary Copyright © 2011. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Cultural definitions for placenta
placenta
[ (pluh-sen-tuh) ]
An organ that forms in the uterus after the implantation of a zygote. The placenta moves nourishment from the mother's blood to the embryo or fetus; it also sends the embryo or fetus's waste products into the mother's blood to be disposed of by the mother's excretory system.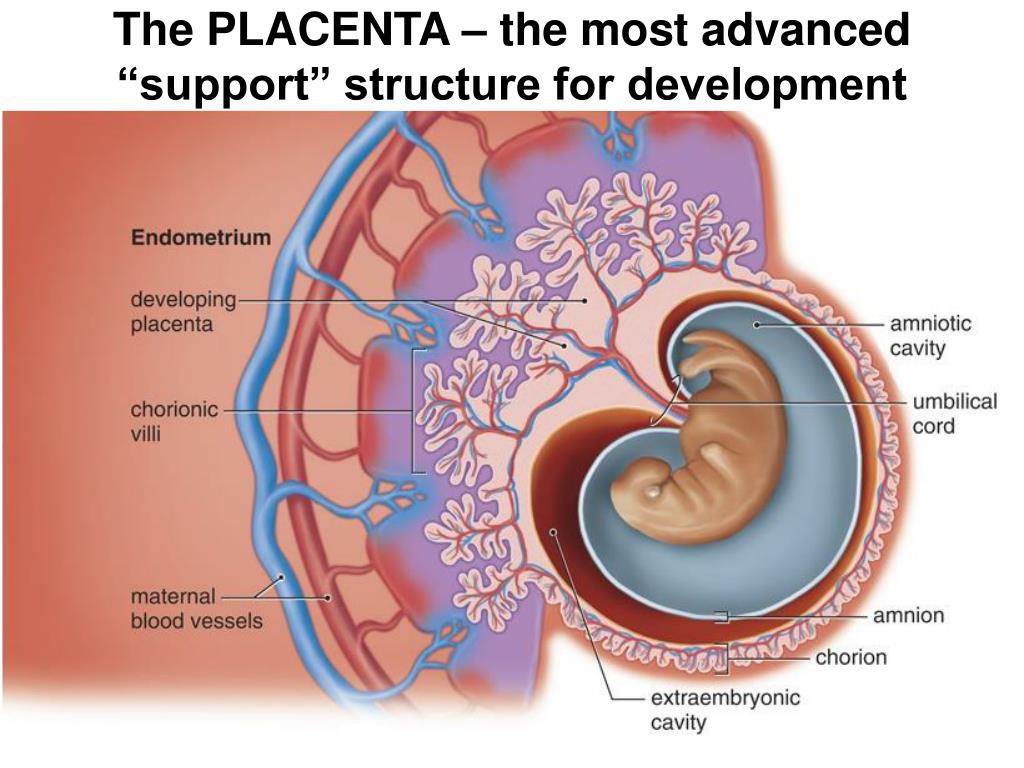 The embryo or fetus is attached to the placenta by the umbilical cord. After birth, the placenta separates from the uterus and is pushed out of the mother's body.
The embryo or fetus is attached to the placenta by the umbilical cord. After birth, the placenta separates from the uterus and is pushed out of the mother's body.
The New Dictionary of Cultural Literacy, Third Edition Copyright © 2005 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Maternity hospital №7, Novosibirsk - What is the placenta?
Anna Valentinovna Yakimova, obstetrician-gynecologist, MD talks about the placenta and placental insufficiency.
Picture from the site http://s7ya7.zdorovo-zivi.ru
Placenta. The name of the organ comes from lat. placenta - cake, cake, pancake. This is an extra-embryonic organ, consisting of villi, thanks to which the fetus is nourished, respired, and waste products are removed from its blood. There are free and fixing (anchor) villi. The placenta is formed in the place where the embryo was implanted, arises as a result of the connection of the chorion - extraembryonic tissue with a thickened uterine mucosa (decidual tissue). Despite the fact that the blood of the mother and fetus does not mix, as they are separated by the placental barrier, the fetus receives all the necessary nutrients and oxygen from the mother's blood. In addition, the placenta produces hormones that ensure the preservation of pregnancy. The placenta has two surfaces. The surface that faces the fetus is called the fetal. It is covered with a smooth shell - the amnion, through which large vessels shine through. The one that is attached to the wall of the uterus is called maternal.
Despite the fact that the blood of the mother and fetus does not mix, as they are separated by the placental barrier, the fetus receives all the necessary nutrients and oxygen from the mother's blood. In addition, the placenta produces hormones that ensure the preservation of pregnancy. The placenta has two surfaces. The surface that faces the fetus is called the fetal. It is covered with a smooth shell - the amnion, through which large vessels shine through. The one that is attached to the wall of the uterus is called maternal.
The main structural unit of the placenta is cotelidone. Cotyledon of the placenta is conditionally comparable to a tree. Each cotyledon is formed by a stem villus, from which, like branches of a tree, villi of the second and third order extend, containing vessels. The central part of the cotyledon forms a cavity, which is surrounded by many villi. Between the cotyledons there is a space - mejvirus, which on the maternal side is limited by partitions (septa) extending from the mucous membrane of the uterus. Most of the placental villi are freely immersed in the intervillous space (free villi) and are bathed in maternal blood. The spiral arteries, which are small branches of the arteries that supply the uterus, open into the intervillous space and supply oxygen-rich blood to the intervillous space. Due to the pressure difference, which is higher in the mother's arterial bed compared to the intervillous space, oxygenated blood from the mouths of the spiral arteries is directed through the center of the cotyledon to the villi, washes them, reaches the chorionic plate and returns to the maternal circulation through the venous orifices through the separating septa. . In this case, the blood flow of the mother and fetus are separated from each other. Those. maternal and fetal blood does not mix. Thus, the concept of the placental barrier appears: the blood of the mother of the fetus does not mix, because they are separated by the wall of the villus, loose connective tissue inside the villus and the wall of the vessel that is inside the villus, and in which the blood of the fetus circulates.
Most of the placental villi are freely immersed in the intervillous space (free villi) and are bathed in maternal blood. The spiral arteries, which are small branches of the arteries that supply the uterus, open into the intervillous space and supply oxygen-rich blood to the intervillous space. Due to the pressure difference, which is higher in the mother's arterial bed compared to the intervillous space, oxygenated blood from the mouths of the spiral arteries is directed through the center of the cotyledon to the villi, washes them, reaches the chorionic plate and returns to the maternal circulation through the venous orifices through the separating septa. . In this case, the blood flow of the mother and fetus are separated from each other. Those. maternal and fetal blood does not mix. Thus, the concept of the placental barrier appears: the blood of the mother of the fetus does not mix, because they are separated by the wall of the villus, loose connective tissue inside the villus and the wall of the vessel that is inside the villus, and in which the blood of the fetus circulates.
At the end of pregnancy, the placenta is a soft disk 15-18 cm in diameter, 2-4 cm thick in the central part, weighing about 500-600 g. their capillaries - 12 m2. The placenta, membranes, and umbilical cord together form the afterbirth, which is expelled from the uterus after the baby is born.
Normally, the placenta is attached to the uterine cavity on its anterior or posterior surface, sometimes in the fundus. If the placenta is attached in the lower part of the uterine cavity, close to the internal opening of the cervix - the internal pharynx, then its blood supply is often insufficient and the fetus may suffer from lack of oxygen and nutrients - a phenomenon called placental insufficiency occurs.
Placental insufficiency is a violation of all or some of the functions of the placenta, ultimately leading to oxygen starvation (hypoxia), fetal growth retardation or death and / or early termination of pregnancy.
Placental insufficiency may occur early in pregnancy due to impaired placental formation, for example, if the spiral arteries that supply blood to the villi do not lose the ability to narrow their lumen in response to exposure to vasoconstrictor substances. It is possible that there is a violation of the development of blood vessels inside the villi, the vessels can form in the central part of the villus, and not close to its wall, then the transfer of nutrients from the mother's blood to the fetal blood and the flow of metabolic products back will be difficult. The process of development of the placenta (in particular, vascular formation) occurs to a greater extent in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, ending at about 30-32 weeks. After this period, involutive processes predominate ("aging", immuring the villi with fibrinoid). Along with the processes of involution in the placenta during pregnancy, young villi develop, more often avascular, which, however, only partially compensate for the function of mature villi containing vessels that have “fallen out” of the circulation.
It is possible that there is a violation of the development of blood vessels inside the villi, the vessels can form in the central part of the villus, and not close to its wall, then the transfer of nutrients from the mother's blood to the fetal blood and the flow of metabolic products back will be difficult. The process of development of the placenta (in particular, vascular formation) occurs to a greater extent in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, ending at about 30-32 weeks. After this period, involutive processes predominate ("aging", immuring the villi with fibrinoid). Along with the processes of involution in the placenta during pregnancy, young villi develop, more often avascular, which, however, only partially compensate for the function of mature villi containing vessels that have “fallen out” of the circulation.
In another scenario, placental insufficiency occurs at a later date, as a result of damage to the placenta in inflammatory processes, diabetes in a pregnant woman, or high blood pressure, when blood flow to the uterus is disturbed, which can also occur with increased maternal blood clotting .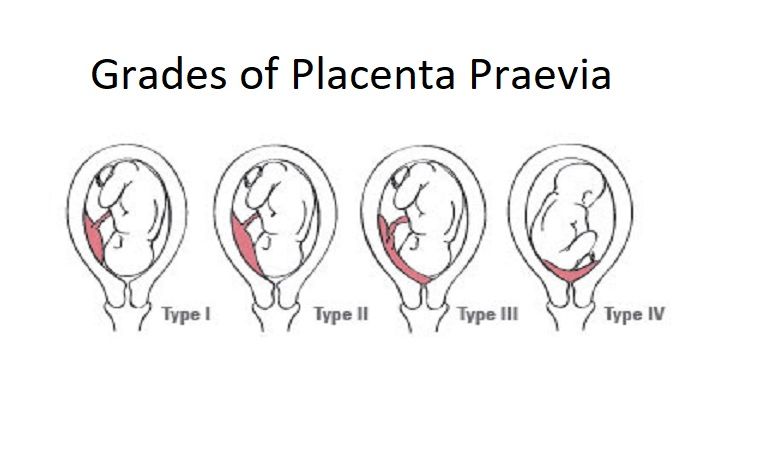 It is believed that it is the violation of the uteroplacental circulation that plays the main role in the formation of the intrauterine growth retardation syndrome. Before the advent of Doppler ultrasound research methods in obstetric practice, there were no non-invasive methods for studying blood flow in the mother-placenta-fetus system. To date, Doppler is the most preferred instrumental method that provides useful information in relation to the detection of blood flow disorders and the determination of pregnancy management tactics for placental insufficiency. If there are symptoms of placental insufficiency - a mismatch in the height of the uterine fundus, signs of a threat of early termination of pregnancy, rapid or slow fetal heart rate (normal: 120-160 beats per minute), an altered amount of amniotic fluid - it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination, Doppler blood flow in the vessels of the uterus, umbilical cord and fetus, and in the third trimester - cardiotocography.
It is believed that it is the violation of the uteroplacental circulation that plays the main role in the formation of the intrauterine growth retardation syndrome. Before the advent of Doppler ultrasound research methods in obstetric practice, there were no non-invasive methods for studying blood flow in the mother-placenta-fetus system. To date, Doppler is the most preferred instrumental method that provides useful information in relation to the detection of blood flow disorders and the determination of pregnancy management tactics for placental insufficiency. If there are symptoms of placental insufficiency - a mismatch in the height of the uterine fundus, signs of a threat of early termination of pregnancy, rapid or slow fetal heart rate (normal: 120-160 beats per minute), an altered amount of amniotic fluid - it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination, Doppler blood flow in the vessels of the uterus, umbilical cord and fetus, and in the third trimester - cardiotocography.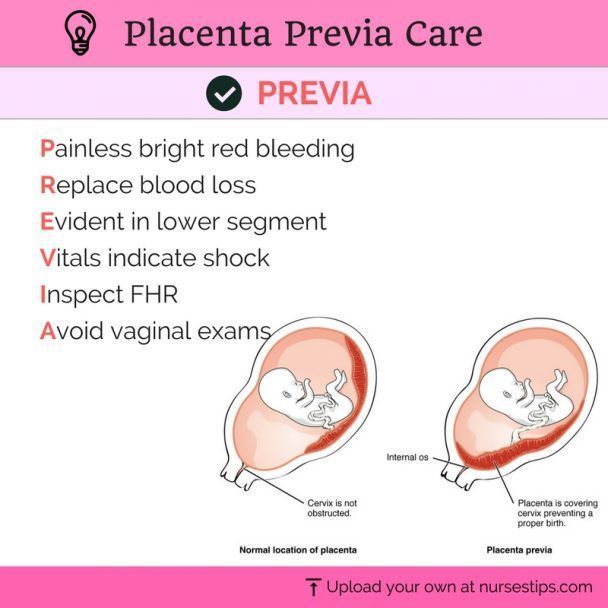 The earliest sign of placental dysfunction is a decrease in its production of hormones and proteins, therefore, in pregnant women with a known risk of placental dysfunction (for example, if she has a chronic inflammatory process or often / constantly increased blood pressure, etc.), you can examine the level placental lactogen, progesterone, unconjugated estriol in the blood. And on the basis of the data obtained, predict the further development of pregnancy and take preventive measures.
The earliest sign of placental dysfunction is a decrease in its production of hormones and proteins, therefore, in pregnant women with a known risk of placental dysfunction (for example, if she has a chronic inflammatory process or often / constantly increased blood pressure, etc.), you can examine the level placental lactogen, progesterone, unconjugated estriol in the blood. And on the basis of the data obtained, predict the further development of pregnancy and take preventive measures.
Can placental insufficiency be treated? The answer to this question is ambiguous. It is possible to influence the development of the placenta when it is incomplete, improving the conditions for development - by eliminating, for example, the inflammatory process, normalizing blood pressure, lowering the tone of the uterus, and normalizing blood clotting. You can influence the metabolism in the cells of the placenta - by doing this, for example, by introducing drugs into the body of a pregnant woman that help improve the utilization of glucose by cells. It is possible to influence the tone of the vessels, reduce the permeability of the wall and, in this way, the swelling of the tissues decreases and the penetration of oxygen into them improves. But we must understand that we do not cure placental insufficiency, we are only trying to influence the compensatory mechanisms that exist in the placenta, if this succeeds, the manifestations of placental insufficiency disappear. But more often, treatment is aimed at prolonging the pregnancy to the term of a viable fetus.
It is possible to influence the tone of the vessels, reduce the permeability of the wall and, in this way, the swelling of the tissues decreases and the penetration of oxygen into them improves. But we must understand that we do not cure placental insufficiency, we are only trying to influence the compensatory mechanisms that exist in the placenta, if this succeeds, the manifestations of placental insufficiency disappear. But more often, treatment is aimed at prolonging the pregnancy to the term of a viable fetus.
But if the signs of placental insufficiency increase, and the gestation period is more than 32 weeks, when even in a normal placenta it undergoes involution, the placenta initially developed incorrectly, and now it performs its functions worse, the fetus suffers, then it is useless to treat placental insufficiency, it is better to carry out early delivery and to nurse the newborn without the risk of intrauterine death, which is possible if the placenta depletes its reserves. Sometimes it is necessary to make a decision on early delivery and at an earlier date, when the treatment of placental insufficiency is impossible and the delay threatens the life of the fetus.
Sometimes it is necessary to make a decision on early delivery and at an earlier date, when the treatment of placental insufficiency is impossible and the delay threatens the life of the fetus.
What is the placenta
It connects two organisms - the mother and the fetus, providing it with the necessary nutrients.
Where is the placenta located and what does it look like?
In a normal pregnancy, the placenta is located in the body of the uterus along its posterior (more often) or anterior wall. It is fully formed by the 15-16th week of pregnancy, after the 20th week, active exchange begins through the placental vessels. From the 22nd to the 36th week of pregnancy, an increase in the mass of the placenta occurs, and by the 36th week it reaches full functional maturity.
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the location of the placenta in the uterus of a pregnant woman. Photo: Wikipedia (Public Domain) In appearance, the placenta looks like a round flat disk.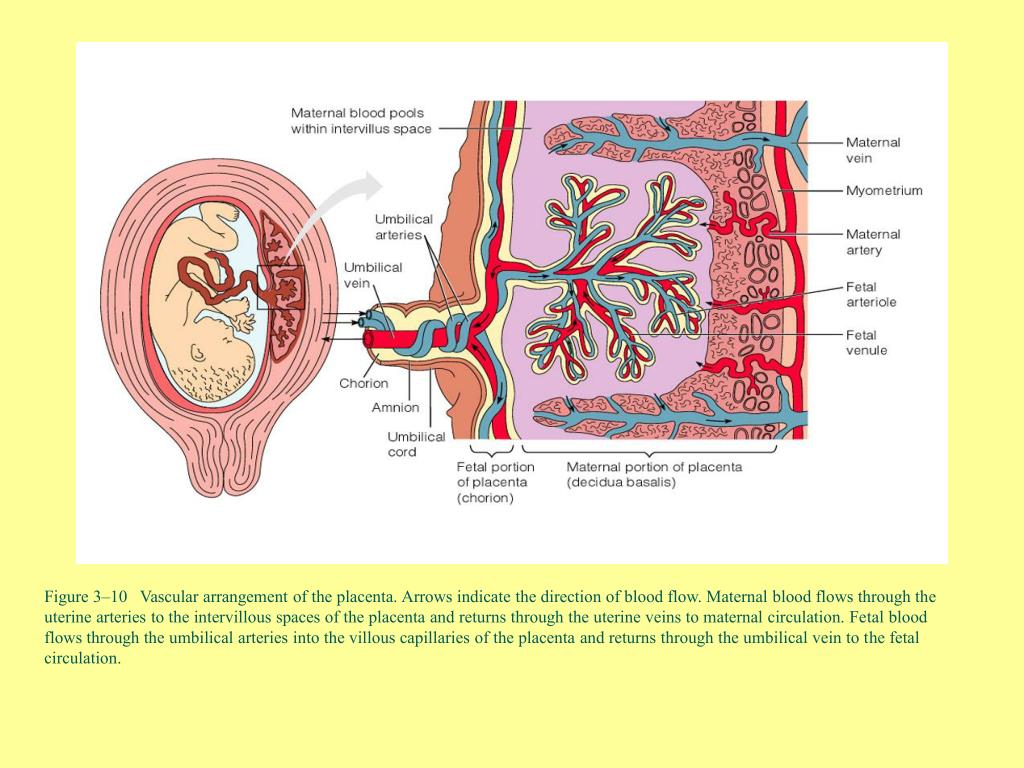 By the time of delivery, the weight of the placenta is 500-600 g, the diameter is 15-18 cm and the thickness is 2-3 cm.
By the time of delivery, the weight of the placenta is 500-600 g, the diameter is 15-18 cm and the thickness is 2-3 cm.
Functions of the placenta
Photo: zffoto / freepik.com- First, gas exchange occurs through the placenta: oxygen penetrates from the mother's blood to the fetus, and carbon dioxide is transported in the opposite direction.
- Secondly, the fetus receives through the placenta the nutrients necessary for its growth and development. It must be remembered that many substances (alcohol, nicotine, drugs, many drugs, viruses) easily penetrate through it and can have a damaging effect on the fetus. In addition, with its help, the fetus gets rid of the products of its vital activity.
- Thirdly, the placenta provides immunological protection to the fetus, delaying the cells of the mother's immune system, which, having penetrated to the fetus and recognized a foreign object in it, could trigger its rejection reactions. At the same time, the placenta passes maternal antibodies that protect the fetus from infections.
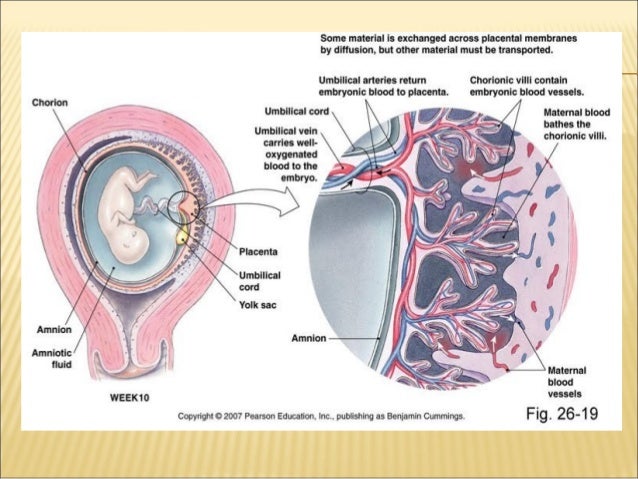
- Fourthly, the placenta plays the role of an endocrine gland and synthesizes hormones (human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), placental lactogen, prolactin, etc.) necessary to maintain pregnancy, growth and development of the fetus.
Normally, the placenta together with the membranes (afterbirth) is born 10-15 minutes after the birth of the fetus. She is carefully examined and sent for a morphological study. First, it is very important to make sure that the whole placenta was born (that is, there are no damages on its surface and there is no reason to believe that pieces of the placenta remained in the uterine cavity). Secondly, according to the state of the placenta, one can judge the course of pregnancy (whether there was an abruption, infectious processes, etc.).
What do doctors want to know about the placenta?
During pregnancy, it is important to look for signs of placental dysfunction - placental insufficiency. To do this, during an ultrasound study, the structure of the placenta, its location in the uterine cavity, thickness, and the correspondence of the size of the fetus to the gestational age are studied.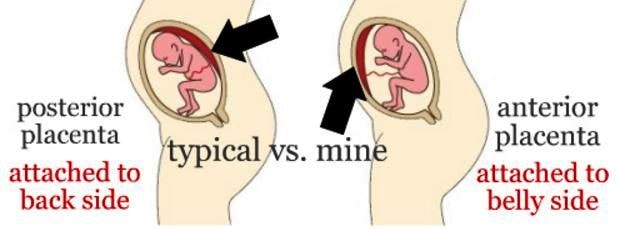 In addition, the blood flow in the placental vessels is studied.
In addition, the blood flow in the placental vessels is studied.
Degree of maturity
Photo: wavebreakmedia-micro / freepik.comThis parameter, as doctors say, is "ultrasonic", that is, it depends on the density of the structures of the placenta determined by ultrasound.
There are four degrees of placental maturity:
- Normally, zero degree of placental maturity should be determined before 30 weeks of pregnancy.
- The first degree is considered valid from 27 to 34 weeks.
- Second - from 34 to 39.
- Starting from 37 weeks, the third degree of placental maturity can be determined.
At the end of pregnancy, the so-called physiological aging of the placenta occurs, accompanied by a decrease in the area of its exchange surface, the appearance of areas of salt deposition.
Place of attachment
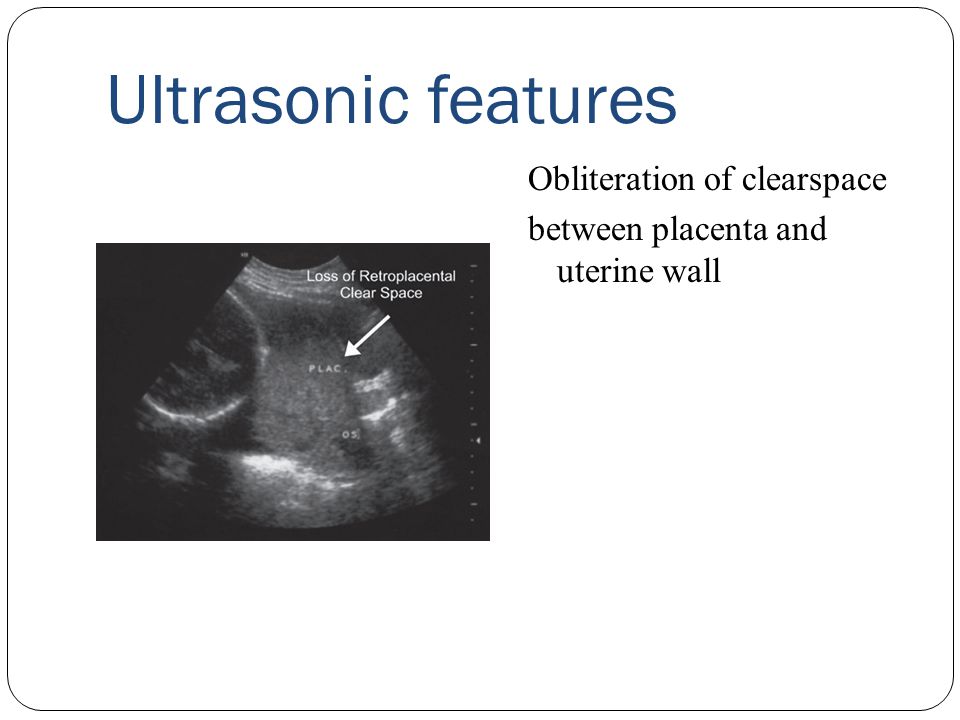
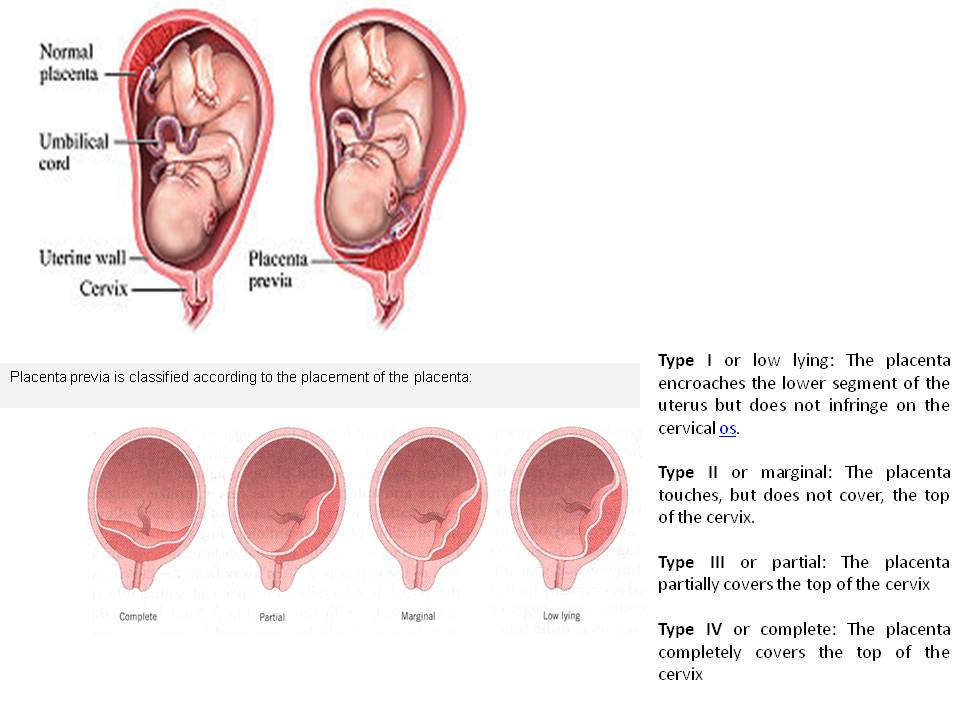
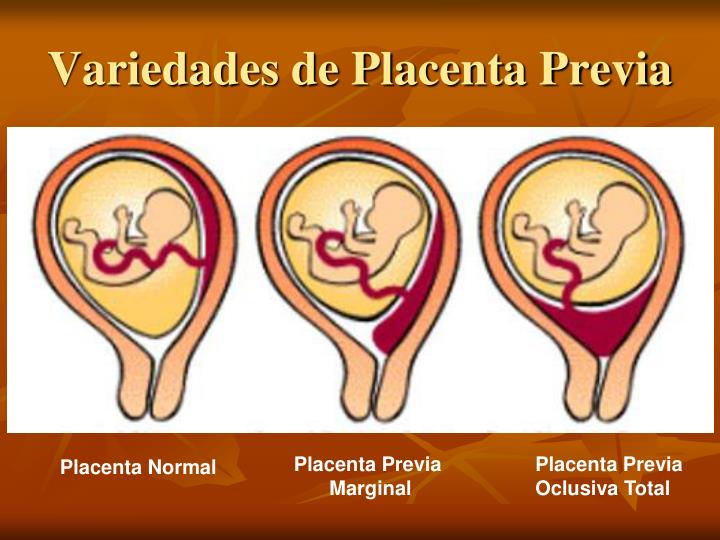
Photo: kuprevich / freepik.com Determined by ultrasound. As mentioned above, during a normal pregnancy, the placenta is located in the body of the uterus. Sometimes, during an ultrasound examination in the first half of pregnancy, it is found that the placenta is located in the lower parts of the uterus, reaching or even overlapping the area of the internal os of the cervix. In the future, as pregnancy progresses, the placenta most often shifts from the lower sections of the uterus to the top. However, if after 32 weeks the placenta still overlaps the area of the internal os, this condition is called *placenta previa**, which is a serious complication of pregnancy.
Sometimes, during an ultrasound examination in the first half of pregnancy, it is found that the placenta is located in the lower parts of the uterus, reaching or even overlapping the area of the internal os of the cervix. In the future, as pregnancy progresses, the placenta most often shifts from the lower sections of the uterus to the top. However, if after 32 weeks the placenta still overlaps the area of the internal os, this condition is called *placenta previa**, which is a serious complication of pregnancy.
Placenta previa can lead to bleeding, which can occur during the second or third trimester of pregnancy or during childbirth.
Ultrasound with placenta previa. Turk J Obstet Gynecol / ResearchGate (Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 Generic license)Thickness
Also determined by ultrasound - placentometry: after establishing the placenta attachment, the area where it has the largest size is found, which is determined. The thickness of the placenta, as already mentioned, continuously increases until 36-37 weeks of pregnancy (by this time it ranges from 20 to 40 mm). Then its growth stops, and in the future the thickness of the placenta either decreases or remains at the same level.
Then its growth stops, and in the future the thickness of the placenta either decreases or remains at the same level.
Deviation from the norm of at least one of these indicators may indicate trouble during pregnancy.
References
- Tiwari D., Das CR., Sultana R., Kashyap N., Islam M., Bose PD., Saikia AK., Bose S. Increased homocysteine mediated oxidative stress as a key determinant of hepatitis E virus ( HEV) infected pregnancy complication and outcome: A study from Northeast India. // Infect Genet Evol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.104882; PMID:33905889
- Salmanian B., Belfort M.A., Shamshirsaz A.A. The risk of placenta accreta spectrum in women with in vitro fertilization in different populations. // Am J Obstet Gynecol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33905744
- Olmos-Ortiz A., Olivares-Huerta A., García-Quiroz J., Zariñán T., Chavira R., Zaga-Clavellina V., Avila E., Halhali A., Durand M., Larrea F., Díaz L. Placentas associated with female neonates from pregnancies complicated by urinary-tract infections have higher cAMP content and cytokines expression than males.
 // Am J Reprod Immunol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.e13434; PMID:33905581
// Am J Reprod Immunol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.e13434; PMID:33905581 - Tandl V., Hoch D., Bandres-Meriz J., Nikodijevic S., Desoye G., Majali-Martinez A. Different regulation of IRE1α and eIF2α pathways by oxygen and insulin in ACH-3P trophoblast model. // Reproduction - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33904834
- Ji S., Gumina D., McPeak K., Moldovan R., Post MD., Su EJ. Human placental villous stromal extracellular matrix regulates fetoplacental angiogenesis in severe fetal growth restriction. // Clin Sci (Lond) - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33904582
- Shmeleva EV., Colucci F. Maternal natural killer cells at the intersection between reproduction and mucosal immunity. // Mucosal Immunol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33903735
- Moreno-Sepulveda J., Espinós JJ., Checa MA. Lower risk of adverse perinatal outcomes in natural versus artificial frozen-thawed embryo transfer cycles: a systematic review and meta-analysis. // Reprod Biomed Online - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.