Vomit during pregnancy
Vomiting and morning sickness - NHS
Nausea and vomiting in pregnancy, often known as morning sickness, is very common in early pregnancy.
It can affect you at any time of the day or night or you may feel sick all day long.
Morning sickness is unpleasant, and can significantly affect your day-to-day life. But it usually clears up by weeks 16 to 20 of your pregnancy and does not put your baby at any increased risk.
There is a chance of developing a severe form of pregnancy sickness called hyperemesis gravidarum. This can be serious, and there's a chance you may not get enough fluids in your body (dehydration) or not get enough nutrients from your diet (malnourishment). You may need specialist treatment, sometimes in hospital.
Sometimes urinary tract infections (UTIs) can also cause nausea and vomiting. A UTI usually affects the bladder, but can spread to the kidneys.
Non-urgent advice: Call your midwife, GP or 111 if:
you're vomiting and:
- have very dark-coloured urine or have not had a pee in more than 8 hours
- are unable to keep food or fluids down for 24 hours
- feel severely weak, dizzy or faint when standing up
- have tummy (abdominal) pain
- have a high temperature
- vomit blood
- have lost weight
Treatments for morning sickness
Unfortunately, there's no hard and fast treatment that will work for everyone’s morning sickness. Every pregnancy will be different.
But there are some changes you can make to your diet and daily life to try to ease the symptoms.
If these do not work for you or you're having more severe symptoms, your doctor or midwife might recommend medicine.
Things you can try yourself
If your morning sickness is not too bad, your GP or midwife will initially recommend you try some lifestyle changes:
- get plenty of rest (tiredness can make nausea worse)
- avoid foods or smells that make you feel sick
- eat something like dry toast or a plain biscuit before you get out of bed
- eat small, frequent meals of plain foods that are high in carbohydrate and low in fat (such as bread, rice, crackers and pasta)
- eat cold foods rather than hot ones if the smell of hot meals makes you feel sick
- drink plenty of fluids, such as water (sipping them little and often may help prevent vomiting)
- eat foods or drinks containing ginger – there's some evidence ginger may help reduce nausea and vomiting (check with your pharmacist before taking ginger supplements during pregnancy)
- try acupressure – there's some evidence that putting pressure on your wrist, using a special band or bracelet on your forearm, may help relieve the symptoms
Find out more about vitamins and supplements in pregnancy
Anti-sickness medicine
If your nausea and vomiting is severe and does not improve after trying the above lifestyle changes, your GP may recommend a short-term course of an anti-sickness medicine, called an antiemetic, that's safe to use in pregnancy.
Often this will be a type of antihistamine, which are usually used to treat allergies but also work as medicines to stop sickness (antiemetic).
Antiemetics will usually be given as tablets for you to swallow.
But if you cannot keep these down, your doctor may suggest an injection or a type of medicine that's inserted into your bottom (suppository).
See your GP if you'd like to talk about getting anti-sickness medication.
Risk factors for morning sickness
It's thought hormonal changes in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy are probably one of the causes of morning sickness.
But you may be more at risk of it if:
- you're having twins or more
- you had severe sickness and vomiting in a previous pregnancy
- you tend to get motion sickness (for example, car sick)
- you have a history of migraine headaches
- morning sickness runs in the family
- you used to feel sick when taking contraceptives containing oestrogen
- it's your first pregnancy
- you're obese (your BMI is 30 or more)
- you're experiencing stress
Visit the pregnancy sickness support site for tips for you and your partner on dealing with morning sickness.
Find maternity services near you
Sign up for pregnancy emails
Sign up for Start4Life's weekly emails for expert advice, videos and tips on pregnancy, birth and beyond.
Video: how can I cope with morning sickness?
In this video, a midwife gives advice on how to deal with morning sickness during your pregnancy.
Media last reviewed: 27 February 2017
Media review due: 27 March 2020
Page last reviewed: 13 April 2021
Next review due: 13 April 2024
Severe vomiting in pregnancy - NHS
Sickness in pregnancy (sometimes called morning sickness) is common. Around 8 out of every 10 pregnant women feel sick (nausea), are sick (vomiting) or both during pregnancy. This does not just happen in the morning.
This does not just happen in the morning.
For most women, this improves or stops completely by around weeks 16 to 20, although for some women it can last longer.
Some pregnant women experience very bad nausea and vomiting. They might be sick many times a day and be unable to keep food or drink down, which can impact on their daily life.
This excessive nausea and vomiting is known as hyperemesis gravidarum (HG), and often needs hospital treatment.
Exactly how many pregnant women get HG is not known as some cases may go unreported, but it's thought to be around 1 to 3 in every 100.
If you are being sick frequently and cannot keep food down, tell your midwife or doctor, or contact the hospital as soon as possible. There is a risk you may become dehydrated, and your midwife or doctor can make sure you get the right treatment.
Symptoms of hyperemesis gravidarum
HG is much worse than the normal nausea and vomiting of pregnancy.
Signs and symptoms of HG include:
- prolonged and severe nausea and vomiting
- being dehydrated. Symptoms of dehydration include, feeling thirsty, tired, dizzy or lightheaded, not peeing very much, and having dark yellow and strong-smelling pee
- weight loss
- low blood pressure (hypotension) when standing
Unlike regular pregnancy sickness, HG may not get better by 16 to 20 weeks. It may not clear up completely until the baby is born, although some symptoms may improve at around 20 weeks.
See your GP or midwife if you have severe nausea and vomiting. Getting help early can help you avoid dehydration and weight loss.
There are other conditions that can cause nausea and vomiting, and your doctor will need to rule these out first.
See the healthtalk. org website for videos and written interviews of women talking about their experiences of hyperemesis gravidarum and how they coped.
org website for videos and written interviews of women talking about their experiences of hyperemesis gravidarum and how they coped.
What causes hyperemesis gravidarum?
It's not known what causes HG, or why some women get it and others do not. Some experts believe it is linked to the changing hormones in your body that occur during pregnancy.
There is some evidence that it runs in families, so if you have a mother or sister who has had HG in a pregnancy, you may be more likely to get it yourself.
If you have had HG in a previous pregnancy, you are more likely to get it in your next pregnancy than women who have never had it before, so it's worth planning in advance.
Treating hyperemesis gravidarum
There are medicines that can be used in pregnancy, including the first 12 weeks, to help improve the symptoms of HG. These include anti-sickness (anti-emetic) drugs, vitamins (B6 and B12) and steroids, or combinations of these.
These include anti-sickness (anti-emetic) drugs, vitamins (B6 and B12) and steroids, or combinations of these.
You may need to try different types of medicine until you find what works best for you.
You can visit the Bumps website to find out which medicines are safe to use in pregnancy.
If your nausea and vomiting cannot be controlled, you may need to be admitted to hospital. This is so doctors can assess your condition and give you the right treatment to protect the health of you and your baby.
Treatment can include intravenous fluids, which are given directly into a vein through a drip. If you have severe vomiting, the anti-sickness drugs may also need to be given via a vein or a muscle.
The charity Pregnancy Sickness Support has information and tips on coping with nausea and vomiting, including HG.
Will hyperemesis gravidarum harm my baby?
HG can make you feel very unwell, but it's unlikely to harm your baby if treated effectively.
However, if it causes you to lose weight during pregnancy, there is an increased risk that your baby may be born smaller than expected (have a low birthweight).
Other symptoms you may experience
Pregnancy Sickness Support is in touch with many women who have had HG, and who report having some or all of the following symptoms in addition to the main symptoms listed above:
- extremely heightened sense of smell
- excessive saliva production
- headaches and constipation from dehydration
If you experience these symptoms, you are not alone. Many women have them and they will go away when the HG stops or the baby is born.
How you might feel
The nausea and vomiting of HG can impact your life at a time when you were expecting to be enjoying pregnancy and looking forward to the birth of your baby.
It can affect you both emotionally and physically. The symptoms can be hard to cope with. Without treatment HG may also lead to further health complications, such as depression or tears in your oesophagus.
Severe sickness can be exhausting and stop you doing everyday tasks, such as going to work or even getting out of bed.
In addition to feeling very unwell and tired, you might also feel:
- anxious about going out or being too far from home in case you need to vomit
- isolated because you do not know anyone who understands what it's like to have HG
- confused as to why this is happening to you
- unsure about how to cope with the rest of the pregnancy if you continue to feel very ill
If you feel any of these, do not keep it to yourself. Talk to your midwife or doctor, and explain the impact HG is having on your life and how it is making you feel. You could also talk to your partner, family and friends if you want to.
You could also talk to your partner, family and friends if you want to.
If you want to talk to someone who has been through HG, you can contact Pregnancy Sickness Support's help section. They have a support network across the UK and can put you in touch with someone who has had HG.
Bear in mind that HG is much worse than regular pregnancy sickness. It is not the result of anything you have or have not done, and you do need treatment and support.
Another pregnancy
If you have had HG before, it's likely you will get it again in another pregnancy.
If you decide on another pregnancy, it can help to plan ahead, such as arranging child care so you can get plenty of rest.
You could try doing things that helped last time.
Talk to your doctor about starting medicine early.
Blood clots and hyperemesis gravidarum
Because HG can cause dehydration, there's also an increased risk of having a blood clot (deep vein thrombosis), although this is rare.
If you are dehydrated and immobile, there is treatment that you can be given to prevent blood clots.
Read more about how to prevent deep vein thrombosis.
We fight against toxicosis - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Alexandrova Anna Evgenievna
Embryologist
Clinic "Mother and Child" South-West
rest more
Very often in the first trimester, the expectant mother feels weak, drowsy, she wants to lie down to rest, and sometimes she simply does not even have the strength to move. This, of course, is not toxicosis, but if such sensations arise, then they must be indulged so as not to inadvertently provoke another attack of nausea. Get plenty of rest and do not make any sudden movements, because even if you just fail to get up from a chair, you can provoke an attack of nausea.
Get plenty of rest and do not make any sudden movements, because even if you just fail to get up from a chair, you can provoke an attack of nausea.
Sleep with the windows open: the air in the bedroom should be fresh and cool. Go to bed on time, do not sit at midnight in front of the TV or at the computer, eliminate all irritating factors: an uncomfortable mattress, blanket, pillow, hard bedding - lack of sleep can respond with morning sickness.
eat right
Eat small meals, 5-6 times a day, or even more often. When you wake up, don't get out of bed right away. One of the most effective methods against toxicosis is breakfast in bed. In the evening, put crackers, yogurt, or any product that you can tolerate well next to your bed. Eat it before you get up, and then lie down for a while. Most likely, morning sickness will either not appear at all, or will be very weak.
Usually, in case of toxicosis, it is not recommended to eat fatty, smoked, salty, pickled, drink soda (the usual set of food hazards). But it is likely that some not very healthy product will now be well tolerated, and something from healthy food, on the contrary, will cause nausea. "Pregnant whims" - a cake with herring or pineapples at night - these are the requests of the body that it needs one or another component in food. For example, the desire to chew chalk is a sign of calcium deficiency. So eat what you like and what you want, within reason, of course. And if you don’t feel like something, even if this product is extremely useful and necessary, don’t eat it. If you feel sick from some dish, it means that the body signals you: I don’t need this now!
But it is likely that some not very healthy product will now be well tolerated, and something from healthy food, on the contrary, will cause nausea. "Pregnant whims" - a cake with herring or pineapples at night - these are the requests of the body that it needs one or another component in food. For example, the desire to chew chalk is a sign of calcium deficiency. So eat what you like and what you want, within reason, of course. And if you don’t feel like something, even if this product is extremely useful and necessary, don’t eat it. If you feel sick from some dish, it means that the body signals you: I don’t need this now!
drink more often
Toxicosis may not be limited to nausea, some may also vomit. This means fluid is lost. Therefore, between meals, drink more often: a sip or two of mineral water or tea with lemon will help to cope with nausea and replenish lost fluids. But drink in small sips. Also, you should not drink food and you should give up soups for a while - a large amount of food drunk and eaten, on the contrary, only provokes nausea and vomiting.
breathe fresh air
Outdoor walks are good for everyone, but especially for toxicosis. Firstly, when walking, the blood of the expectant mother and baby is saturated with oxygen, which is very important for health, and secondly, walking calms the nervous system. Together, this helps to reduce the unpleasant symptoms of toxicosis. You need to walk at least two hours a day - but not just along the street, but in a place where the air is really fresh: in a forest, park, square, and best of all outside the city. Before you go out, think over the route: go away from gas-polluted highways, street cafes, tents with food and other "fragrant" places.
eliminate fragrances
Taste and smell preferences change during the first trimester. Now even your favorite perfumes can cause nausea, headaches and allergic reactions. Therefore, put away all fragrant cosmetics that irritate you: perfumes, deodorants, creams, and so on. You will have to stop using your favorite perfume for both your husband and loved ones. Explain to others that this is not a whim, but a temporary measure, very soon everything will return to normal.
Explain to others that this is not a whim, but a temporary measure, very soon everything will return to normal.
And do not worry that now you will be left without your usual beauty products. Both the cosmetic store and the pharmacy are full of different creams, tonics, shampoos without fragrance or with a minimal smell.
work with yourself
Psychologists believe that the cause of toxicosis is not only in hormonal changes, but also in the psychological state of a woman. The more a woman experiences, the more anxieties and fears she has, the more pronounced toxicosis can be. Ideally, it is better to limit yourself during pregnancy from any stress. Of course, it’s not always possible to eliminate nervous work or crowding in public transport, but watch less TV, don’t read negative news and various pregnant “horror stories” on the Internet, and don’t react to minor or even major everyday troubles everyone can do. Therefore, if you are worried about toxicosis, create your own comfortable world during pregnancy. If you can’t cope on your own, contact a specialist (psychologist). Toxicosis is really well treated with psychotherapy. The main thing is that the expectant mother should want to get rid of her own anxiety.
If you can’t cope on your own, contact a specialist (psychologist). Toxicosis is really well treated with psychotherapy. The main thing is that the expectant mother should want to get rid of her own anxiety.
No matter how unpleasant toxicosis is, it does not last forever. It is necessary to suffer until the beginning or (less often) the middle of the II trimester. And very soon all the unpleasant symptoms of toxicosis will remain in the past!
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Alexandrova Anna Evgenievna
Clinic "Mother and Child" South-West
ICSIECO
By clicking on the send button, I consent to the processing of personal data
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select a clinic
Clinical Hospital MD GROUPClinical Hospital Lapino-1 "Mother and Child"Clinic KG "Lapino" in Odintsovo (branch)Clinic "Mother and Child" Khodynskoye PoleClinic "Mother and Child" KuntsevoClinic "Mother and Child" SavelovskayaClinic "Mother and Child" Yugo-ZapadMother and Child Clinic NovogireevoMother and Child Clinic Lefortovo
All directionsSpecialist consultations (adults)Specialist consultations (children)Laboratory of molecular geneticsGeneral clinical studiesTreatment roomTelemedicine for adultsTherapeutic studiesUltrasound examinations for adults
01.
Consultations of specialists (adults)
02.
Consultations of specialists (children's)
03.
Laboratory of molecular genetics
04.
General studies
05.
05.
Cabinet
06 06.
Adult Telemedicine
07.
Therapeutic Research
08.
Adult Ultrasound
Nothing found
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to timely update the price list posted on the website, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we advise you to clarify the cost of services and the timing of tests by calling
causes of nausea and stomach pain in pregnant women
{{if type === 'partner-stocks'}}
{{/if}}
{{/if}} {{each list}}${this} {{if isGorzdrav}}
Delete
{{/if}}
{{/each}} {{/if}} Search by drug, disease, substance: DERMAKOSMETIKA, SOLGAR, NaturAge, Otrivin,Home
Articles
What to do if your stomach hurts during pregnancy
Pregnant women experience hormonal changes that may exacerbate chronic diseases or introduce new diseases.![]() The digestive system is also being rebuilt. Therefore, many complain that the stomach hurts during pregnancy, although there was no such symptom before. In order not to miss a serious pathology and start treatment on time, you can learn to distinguish between different painful conditions and eliminate their causes.
The digestive system is also being rebuilt. Therefore, many complain that the stomach hurts during pregnancy, although there was no such symptom before. In order not to miss a serious pathology and start treatment on time, you can learn to distinguish between different painful conditions and eliminate their causes.
How to understand that it is the stomach that hurts
If you put three fingers in the midline on the area just below the xiphoid process, which connects the right and left halves of the ribs, you can find the approximate position of the stomach. This is a hollow muscular organ, which is usually located almost vertically. Its glands produce hydrochloric acid and mucus, which does not allow the walls of the organ to be digested and prevents damage.
If the mucous membrane becomes inflamed, pain occurs. It can be sharp, cutting, burning, aching and is localized in the intercostal region, slightly below and to the left of the xiphoid process of the sternum. Hungry pains during pregnancy are not uncommon, sometimes they are accompanied by nausea, belching, appear at night in a dream. In some diseases, pain increases after eating.
Hungry pains during pregnancy are not uncommon, sometimes they are accompanied by nausea, belching, appear at night in a dream. In some diseases, pain increases after eating.
But gastric pathology is not characterized by girdle pain, a feeling of fullness in the right hypochondrium, bitterness in the mouth, cramps in the lower abdomen. These are signs of diseases of the pancreas, liver or intestines.
Causes of pain in the stomach in pregnant women
After pregnancy, progesterone is intensively synthesized in the ovaries, and from the 12th week it is produced by the placenta. One of the functions of this hormone is to reduce the tone of the smooth muscles of the internal organs so that the uterus does not contract and reject the embryo. But at the same time, the muscles of the digestive tract also fall under the influence of progesterone. Therefore, in pregnant women, peristalsis slows down, the muscular sphincter located between the stomach and esophagus relaxes.:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/2785562/original/028627600_1556001360-shutterstock_1019963743.jpg)
With increasing gestational age, the uterus grows and displaces organs. Therefore, the stomach moves from a vertical position to a horizontal one. At the same time, intra-abdominal pressure increases, gastric juice during the digestion of food can be thrown into the esophagus and burn the mucous membrane. This process is more pronounced after thirty weeks, but the first signs may appear early.
The nature of pain during exacerbation of gastritis
Causes of severe pain in the abdomen may be associated with acute gastritis or exacerbation of chronic. Various factors lead to it:
- malnutrition - lack of protein, iron or vitamins;
- irritant effect of drugs - antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- infections - more often the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- the impact of harmful substances - alcohol abuse, smoking, as well as work in hazardous industries.
The disease can be exacerbated by stress, lack of diet or gout, chronic kidney pathologies.
In case of exacerbation of gastritis, the stomach begins to hurt after eating, the sensations increase when overeating due to stretching of the walls of the stomach. Often the symptoms are associated with the use of spicy, fried, fatty foods or carbonated drinks. The pregnant woman feels that she has pain in the right hypochondrium, under the pit of the stomach. She is sick, there is an eructation sour, sometimes vomiting. Protracted gastritis disrupts the digestion of food, so there is flatulence, rumbling in the abdomen and a violation of the stool.
If the secretion of hydrochloric acid is reduced in chronic inflammation of the stomach, then the symptoms of the disease are less pronounced.
Features of pain in gastric ulcer or mucosal erosion
In most pregnant women, the symptoms of peptic ulcer disappear due to a decrease in acidity and an increase in mucus production. But in 1 out of 4,000 women, the pathology worsens. This occurs in the autumn-spring period in the 1st or 3rd trimester.
An ulcer is characterized by severe hunger pains that bother between meals or at night. A woman is often sick, sometimes vomiting appears, which alleviates the condition. Additional symptoms are heartburn, sour belching, constipation.
If the ulcer is left untreated, anemia develops and, in severe cases, gastrointestinal bleeding. In the latter case, the pregnant woman will vomit clotted blood that resembles coffee grounds, the pain in the abdomen will become severe, blood pressure will drop, and the skin will turn pale.
Sometimes, after overeating or physical exertion, the ulcer perforates and a through hole is formed in the wall of the stomach. At the same time, the stomach hurts very badly and unbearably sharply, sticky sweat appears on the skin, dry mouth, and thirst intensifies. Vomiting with perforation of the ulcer is rare. Then flatulence appears and after two hours the condition improves, but this is the appearance of well-being. Later, the pregnant woman develops peritonitis.
Bleeding and perforation of the ulcer are dangerous for the pregnant woman and the fetus. When the first symptoms appear, you need to call an ambulance. Otherwise, the likelihood of death from complications is high.
Other causes of stomach pain
In the later stages, stomach pain is more common and is not always associated with gastritis or ulcers. Sometimes other diseases or lifestyle habits are to blame:
- overeating;
- eating stale food;
- irritant effect of spicy, salty, sour or fatty foods;
- stress or nervous tension;
- long break between meals;
- concomitant diseases of the liver, gallbladder or intestines;
- chronic constipation;
- toxicosis;
- acute infections, including food poisoning.
Sometimes inflammation of the duodenum, or duodenitis, is masked behind gastric pain. Pathology often occurs in the 1st trimester or 4-5 weeks before delivery. Duodenitis is characterized by nocturnal hungry pains, which decrease after eating. Pregnant women have reduced appetite, nausea, vomiting, a feeling of fullness in the upper abdomen.
Pregnant women have reduced appetite, nausea, vomiting, a feeling of fullness in the upper abdomen.
Pain in the stomach in early pregnancy
According to statistics, from 21 to 80% of women experience a pathology of the digestive tract for the first time during pregnancy, and symptoms appear already at an early stage of gestation. They may be associated with toxicosis. Why it develops is not exactly known, but it is associated with a violation of the hormonal and nervous regulation of metabolism in the body. This leads to nausea, vomiting, salivation, gradual dehydration and deterioration. In severe cases, the metabolism of fats and carbohydrates is disturbed in a pregnant woman, body weight decreases.
If a woman is often sick and vomits, the lining of the esophagus becomes irritated and inflamed. Therefore, from the first weeks there is pain in the stomach.
Due to toxicosis, a pregnant woman develops an aversion to certain types of food or smells, and her appetite decreases. Irregular eating can increase pain in the stomach, and later lead to gastritis.
Irregular eating can increase pain in the stomach, and later lead to gastritis.
Treatment of stomach pain during pregnancy
Caution must be exercised in the choice of treatment in pregnant women. Many drugs are dangerous for the fetus, so a general practitioner should select a therapy regimen. He will also conduct an examination to distinguish early toxicosis from exacerbation of gastritis, peptic ulcer or other pathology.
A pregnant woman is prescribed a diet. All spicy, irritating foods are excluded from the diet. You can not drink coffee, strong tea, carbonated drinks, chocolate, fatty and fried foods that relax the esophageal sphincter. Recommend food in small portions, but at least 5 times a day.
Coating preparations are used to reduce pain. They are not absorbed into the bloodstream, so they will not harm the fetus, but they protect the gastric mucosa and alleviate the condition. In addition to them, doctors recommend drinking tea from chamomile flowers or alder seedlings, which has astringent and anti-inflammatory properties.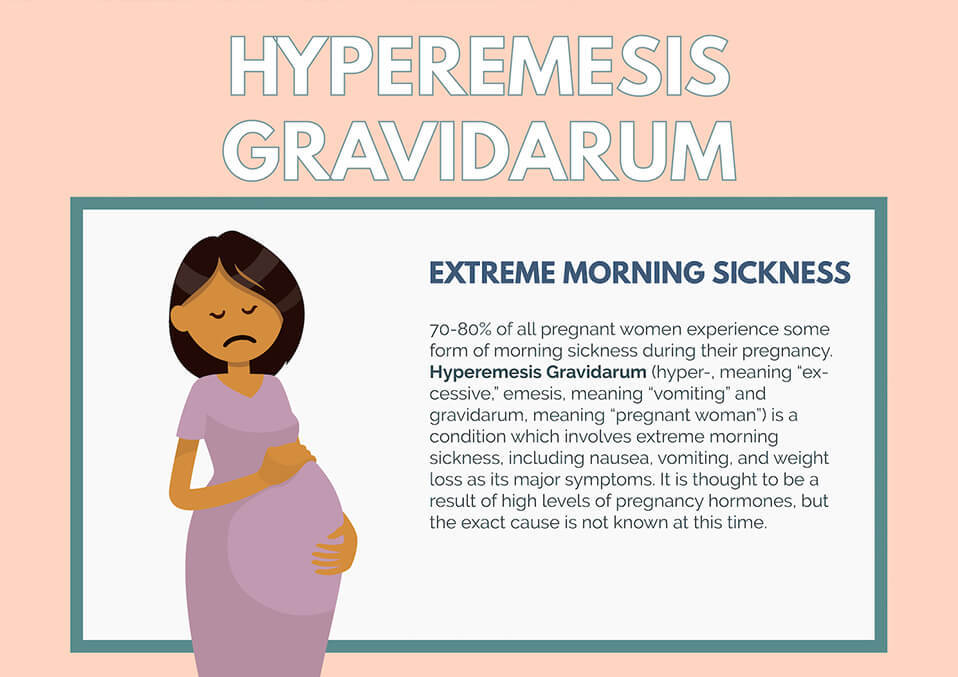
Pregnant women with exacerbation of chronic gastritis or ulcers are additionally prescribed antispasmodics based on drotaverine or papaverine to relieve pain. Drugs that increase intestinal tone, which include metoclopramide, also help.
How can I reduce or prevent stomach pain?
In order not to get sick during pregnancy or to prevent digestive problems, you need to eat right. For this, dishes are boiled, stewed, baked, cooked from vegetables, cereals, dairy products and lean meat. Spicy seasonings, fried and fatty foods, other heavy foods during pregnancy should be excluded.
To relieve the condition, do not overeat during the day, it is better to eat 5 times, but in small portions. Sleeping on an empty stomach is bad, but late dinner is also harmful. Therefore, it can be replaced with a glass of unsweetened yogurt or kefir.
Doctors do not recommend lying down immediately after eating, as there is a higher risk of stomach contents entering the esophagus and heartburn.