How do you work out child support payments
Monthly Child Support Calculator | Office of the Attorney General
- About
- News
- Opinions
- Jobs
- Contact Us
This calculator provides an estimate for a single source of income. The actual amount set or approved by the court may differ.
Income
The person paying support is:
an employeeself-employed
Income Frequency:
YearlyMonthlySemi-MonthlyBi-WeeklyWeeklyHourly
Amount:
Deductions
Medical Support
If you are providing (or can provide) health insurance for your children, enter the monthly premium amount.
Dental Support
If you are providing (or can provide) dental insurance for your children, enter the monthly premium amount.
Union Dues
If you are a member of a union and make regular payments to be a member of the union, enter the monthly dues amount.
State Income Tax
If you work or reside in a state where a state income tax is assessed against your income, enter the monthly amount.
Support Order Determination
Children in this Action
Enter the number of children under age 18 in the child support order.
Children outside this Action
Enter the number of other children for whom you have a legal duty to support.
Support Order Calculations
Monthly Gross Income
Monthly OASDI, Medicare, and Federal Taxes
Monthly OASDI Taxes
Monthly Medicare Taxes
Monthly Federal Income Taxes
Monthly Income
Other Deductions
Medical Support Deduction
Dental Support Deduction
Union Dues Deduction
State Income Tax Deduction
Net Resources
Low-Income Child Support Guidelines Percentage:
Texas Family Code Sec. 154.125 Low-Income Child Support Guidelines are used in actions filed on or after 9/1/2021
154.125 Low-Income Child Support Guidelines are used in actions filed on or after 9/1/2021
Projected Monthly Child Support Obligation for net resources up to $9,200
**The Guidelines for the support of a child are specifically designed to apply to monthly net resources not greater than $9,200. This calculator does not calculate support in excess of the $9,200 net resource amount per Texas Family Code Sec. 154.125(a).
Child Support Calculator - HRA
* Orders are paid weekly, biweekly, monthly, or bimonthly. Divide the estimated annual support amount by the frequency that applies to the way the noncustodial parent is paid.
DISCLAIMER: Use the Child Support Calculator to get an idea of how much a noncustodial parent might owe in child support in New York State. It is only an estimate and is adjusted to reduce the gross income by Medicare, FICA and local NYC taxes. The court may, under certain circumstances, deviate from the formula. In addition, other factors are routinely considered in setting the order amount. Read the Child Support Standards Act for more information.
The court may, under certain circumstances, deviate from the formula. In addition, other factors are routinely considered in setting the order amount. Read the Child Support Standards Act for more information.
The Child Support Standards Act
The Child Support Standards Act was developed to ensure that child support awards in New York State were fair and consistent. The goal is to give children the same standard of living they would have if their parents were together. For more information on the law call the New York State Child Support Helpline at 888-208-4485.
| Number of Children | % |
|---|---|
| 1 | 17% |
| 2 | 25% |
| 3 | 29% |
| 4 | 31% |
| 5+ | at least 35% |
The law states that the basic support award be set at a fixed percentage of parental income, depending on the number of children for whom an order is being requested:
These percentages are applied to almost all parental earnings up to $163,000, minus Medicare, FICA and NYC tax deductions. Child or spousal support actually paid, based on a court-order or written agreement, may also be deducted before calculating the child support order. Earnings include worker's compensation, disability payments, unemployment insurance, social security, pensions, and many other forms of income. After $163,000, the court can choose whether or not to use the percentage guidelines.
Child or spousal support actually paid, based on a court-order or written agreement, may also be deducted before calculating the child support order. Earnings include worker's compensation, disability payments, unemployment insurance, social security, pensions, and many other forms of income. After $163,000, the court can choose whether or not to use the percentage guidelines.
In addition to the basic support award, the child support order must include medical support, which means health insurance and payments for any out-of-pocket medical expenses for the child. Either parent may be required to provide health insurance coverage for the child, if it is available at a reasonable cost. The basic award may be increased to include a prorated share of child care expenses, if the custodial parent is working or in school. In addition, the court may increase the award to include a prorated share of educational expenses for the child.
For a more in-depth calculation, refer to the Post-Divorce Maintenance/Child Support – Online Calculator, maintained by the New York State Family Court.
New York State laws protect low-income noncustodial parents:
- If the noncustodial parent's income is below the Federal Poverty Level ($12,140 for 2018), the child support order may be established at $25 per month and the amount of arrears will be capped at $500.
- If the noncustodial parent’s income is below the New York State Self-Support Reserve ($18,347), the child support order may be established at $50 per month.
Other Resources
- Office of Child Support Services Home Page
- Information for Custodial Parents
- Information for Noncustodial Parents
- Information for Parents
- Handbook for Custodial Parents
- Handbook for Noncustodial Parents
- OCSS Locations
- New York State Income Withholding Calculator for Employers
Alimony - Help for paying parents
This guide will answer questions about child support that a non-custodial parent may have.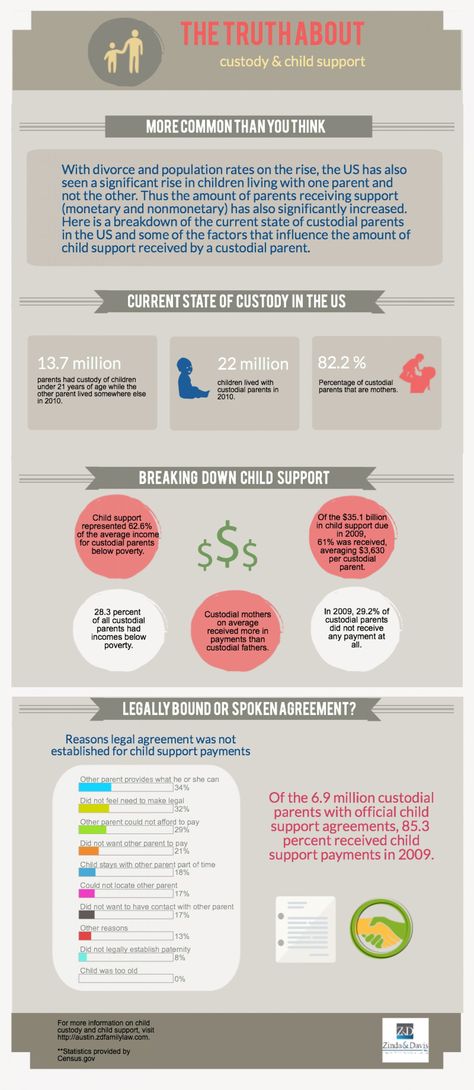 The information below is useful for both custodial parents and non-custodial parents
The information below is useful for both custodial parents and non-custodial parents
Definitions of key terms
Custodial Parent (kas-TO-di-al PER-ent): Parent who lives with the child.
Non-custodial parent : Separated parent.
Why did I get documents telling me that I have to appear in court?
Someone filed a petition (pe-ti-shan) to the court to force you to pay child support. A petition is a written appeal to the court.
Who is eligible to petition for child support?
Petition for child support can be filed by:
- The person who cares for the child
- New York City if the child is or has received public assistance (welfare)
- Child (however, this usually only applies to adult children)
What happens when I go to court?
On the day of the hearing, you will meet with the welfare magistrate (sup-PORT MAD'J-is-trate) who will hear the case and issue a child support order (OR-der for child sup-PORT) . The court's decision is a piece of paper detailing the amount you owe, how often you must pay, and where to send the money. The welfare magistrate is like a judge and has the power to decide on alimony and paternity (pe-TURN-and-tee) . A paternity case is a case to establish who is the real father of a child.
The court's decision is a piece of paper detailing the amount you owe, how often you must pay, and where to send the money. The welfare magistrate is like a judge and has the power to decide on alimony and paternity (pe-TURN-and-tee) . A paternity case is a case to establish who is the real father of a child.
When does child support end?
In New York State, a child may receive child support until the age of 21. Sometimes child support payments may end earlier; for example, this can happen if the child joins the army or gets married.
Can I use a lawyer for my child support case?
In child support cases, the family court is not required to provide a lawyer to the parents, except in cases where the non-custodial parent faces jail time for failure to pay; however, you are free to hire a lawyer if you wish. The welfare magistrate may appoint a lawyer for the child, called a legal guardian or child advocate, to ensure that the best interests of the child are protected. It doesn't happen in every case.
It doesn't happen in every case.
What happens if I don't show up on court day?
If you do not appear on the day of the hearing, the welfare magistrate may issue a default decision (de-FOLT D'JAD'J-mant) . A default judgment is an order issued if the defendant fails to appear in court. In child support cases, the default decision automatically becomes a child support order against the non-custodial parent. This court decision is based on information provided by the custodial parent.
If you wish to contest this decision, you must file a motion to set aside the default decision (MO-shan tou WEI-cate e de-FOLT D'JAD'J-ment) . This is a written petition to the court asking for the annulment of the decree. You must give the court a good reason for not appearing in court.
How is the amount of maintenance determined?
Support amount based on Support Standards Act . First, the court establishes total combined income of for both parents. Total income is the sum of all money earned before taxes. (For incomes of $143,000 or more, the court sometimes applies different rules.) Some special expenses (ex-PEN-ses) will reduce your income for child support. Ordinary expenses are expenses that you pay on a regular basis, such as electricity bills, credit cards, or living expenses. These costs do not reduce your child support income. After the court determines both parents' income, it uses the following formula to determine the amount needed for child support:
Total income is the sum of all money earned before taxes. (For incomes of $143,000 or more, the court sometimes applies different rules.) Some special expenses (ex-PEN-ses) will reduce your income for child support. Ordinary expenses are expenses that you pay on a regular basis, such as electricity bills, credit cards, or living expenses. These costs do not reduce your child support income. After the court determines both parents' income, it uses the following formula to determine the amount needed for child support:
1 child 17% of your income
2 children 25% of your income
3 children 29% of your income
4 children 31% of your income
5 children or more 35% of your income
help.
You may be asked to pay an extra amount for government and child care. Or you may be assigned to include the child in your health insurance.
What if the child support has not yet been paid?
The court may also order the payment of retroactive child support (re-tro-ek-tiv sup-PORT) for the maintenance of the child. This means that you must pay child support from the time the petition is filed, even if it is long before you appear in court. Retroactive child support usually does not accrue from the date of birth of the child, but this can happen if the petition was filed as soon as the child was born. Accrual occurs from the time the custodial parent first files a petition for child support.
This means that you must pay child support from the time the petition is filed, even if it is long before you appear in court. Retroactive child support usually does not accrue from the date of birth of the child, but this can happen if the petition was filed as soon as the child was born. Accrual occurs from the time the custodial parent first files a petition for child support.
If you do not pay child support, you will have debt (e-RIRS) . Debt means non-payment of alimony. If you become indebted, the court may add a set amount to your child support until the entire amount owed is paid.
What if my income is unofficial?
If you work informally or do not receive a stable salary, the court may determine your income based on the following:
- How much did you earn in the past
- How much does the court think you could earn
- What are your family's standards of living
The amount determined by the court is called conditional income (im-PYU-ted In-kam) . The court then uses the amount of conditional income to determine the amount of support you will have to pay.
The court then uses the amount of conditional income to determine the amount of support you will have to pay.
What should I bring to court?
- Carefully completed Financial Disclosure Affidavit
- Proof of your income, such as check stubs from your paycheck
- Documents showing Social Security or disability payments, workers' compensation, unemployment benefits, veterans' benefits, pension funds, investment, bursaries, or annuities.
- Information about the “SSI,” “Medicaid,” “Home Relief,” or “Food Stamps,” you get.
- Proof of expenses such as FICA and city taxes. These expenses will be deducted from your income before the court determines the amount of child support.
- If you are paying support for another child, bring a copy of the court order and proof of payments you have already made. As proof, you can use money order receipts, voided checks, or paycheck stubs showing support was paid.
What if I am not the father of the child?
If you were married to the mother when the child was born, the law implies that you are the child's father. If you were married to the mother but believe you are NOT the father of the child, notify the benefits magistrate immediately. It's called denial of paternity (con-TEST-ing p-TURN-and-tee) . The court must determine paternity (find out who the real father is) before determining child support. To establish paternity, the court may order a DNA test (DNA test) . If the analysis confirms your paternity, the court will issue Decree of Descent (OR-der of fil-i-EI-shan) . This is an official court document that determines who is the father of a child.
If you were married to the mother but believe you are NOT the father of the child, notify the benefits magistrate immediately. It's called denial of paternity (con-TEST-ing p-TURN-and-tee) . The court must determine paternity (find out who the real father is) before determining child support. To establish paternity, the court may order a DNA test (DNA test) . If the analysis confirms your paternity, the court will issue Decree of Descent (OR-der of fil-i-EI-shan) . This is an official court document that determines who is the father of a child.
Will the court give me a lawyer for my paternity case?
If someone opens a paternity case against you and you are unable to hire a lawyer, you can ask the magistrate to appoint a lawyer for you free of charge. You can also hire your own lawyer. If you open a paternity case, the court may not provide you with a lawyer, even if you are unable to pay for one.
How can I pay child support?
You can pay directly to the other parent or through Child Support Collection Unit (SCU) at the address below. If the custodial parent receives public assistance, SCU will automatically deduct child support from it. SCU services are free and they will keep track of all payments.
Please remember: Always include the case number on your SCU payments to ensure your payment is recorded. Don't use cash - especially if you're paying directly to the other parent! Always pay by money order or check.
What if the SCU makes a mistake?
You need to go to the SCU office (located at 151 West Broadway, 4th floor in Manhattan) and speak to a customer service representative. You can also call the Support Enforcement Office at (888) 208-4485.
How long is the benefit order valid?
Once a benefit order is issued, it remains in effect until someone asks the court to reverse it, your child is 21, or your child is independent (e-MAN-C-Pay-ted) . Children are considered independent if they live separately from the custodial parent, are self-supporting, married, or in the military.
Children are considered independent if they live separately from the custodial parent, are self-supporting, married, or in the military.
If you pay through SCU, they automatically review your case every three years. When they review the case, the SCU may add a living wage allowance (COLA). SCU is free to do so without going to court. If they make changes, they will send you an email.
What if I do not agree with the allowance order?
You have the right to tell the court if you disagree with the order. This is called objection (ob-D' JEK-shan) . If you receive a copy of the order on the day the order was issued, you have 30 days to file a written objection. However, if the order was mailed, you have 35 days (from the date the letter was sent) to file a written objection. You can file an objection through the clerk of the Family Court where the decision was made. The judge will decide on your case. You may not have to go to court for a new hearing, but you must continue to pay child support until the court changes the order. The decision will be mailed to you. For more information, see the Family Legal Care booklet – “How to File an Objection or Rebuttal Against a Child Support Order”
The decision will be mailed to you. For more information, see the Family Legal Care booklet – “How to File an Objection or Rebuttal Against a Child Support Order”
If you lose your job or are unable to pay for any other reason - such as a change in your income or you are sent to prison - the court will not automatically change your child support amount. If you are unable to pay child support, you must immediately report to the Family Court where the decision was made and file a Petition for Change for Deterioration shan) . This is a written request to the court to reduce the amount of your child support. To convince the court to reduce your child support, you must provide evidence to the court of evidence of a significant change in circumstances (sig-NIF-i-kant change of ser-kam-STEN-ses) that have occurred in your life since the magistrate on the allowance made the final decision.
- An example of a significant change in circumstances would be imprisonment, provided that the imprisonment is not related to non-payment of support or a crime against the custodial parent or child.
- You can also ask for a change in your child support amount if it has been 3 years since the last order was made.
- Also, if your or the custodial parent's income has changed (up or down) by 15% or more since the last instruction, you can petition for a change due to the downside.
Learn more about what to do if you can't pay
When you go to court, you must show evidence of a significant change in your income. You must ask the court to reduce your child support from the date of the petition. Until the court decides otherwise, you must continue to pay the original amount of support.
The court may look at your previous earnings and determine that you can earn more than you currently earn. In this case, the court may leave the order unchanged.
What happens if I don't pay?
If there is a court order for child support, you must pay. If you don't pay, your debts will continue to pile up. This debt WILL NOT DISAPPEAR, even if your child turns 21. Declaring bankruptcy will also not cancel the payment of debt.
Declaring bankruptcy will also not cancel the payment of debt.
The SCU can force you to pay in a variety of ways.
- SCU can force your employer to calculate child support from your wages/cheque. (Your employer is required by law to do this, but they can't fire you for it.) This is called withholding your paycheck (GAR-nish-ing yor WAID'J-es).
- SCU can collect your federal and state tax refund before you receive it. SCU can also take money directly from your bank account.
- If your debt exceeds a few months, SCU may suspend your driver's license or other professional licenses until you pay off the debt.
- If you owe a very large amount of money and the SCU or custodial parent asks the court to check for willful violation (WIL-full-and WAI-0-lay-ting) of child support payments, you may be SENT IN JAIL for up to 6 months. Intentional violation means willful disobedience to a court order.
What if I support my children?
Make sure you keep all receipts for any child support payments. Paying for services or buying gifts is not a substitute for paying child support. You must pay regularly. You are also required to pay any accumulated debt.
Paying for services or buying gifts is not a substitute for paying child support. You must pay regularly. You are also required to pay any accumulated debt.
Who gets the money if my children get public assistance and I pay child support?
If the custodial parent receives public assistance, SCU will automatically collect support. If you are not in debt, $100 of your monthly payment will go to the custodial parent. This $100 per month is for the maintenance of the household, not for each child. If you are in debt, the alimony will go towards paying off the debt in the first place. The city will continue to pay child support even if you give money directly to the custodial parent. The city may also reduce the child support budget to account for the extra money received by the family.
Can I withdraw my child from public assistance?
A non-custodial parent cannot withdraw their child from public assistance. Only the custodial parent who started the public assistance case can do so.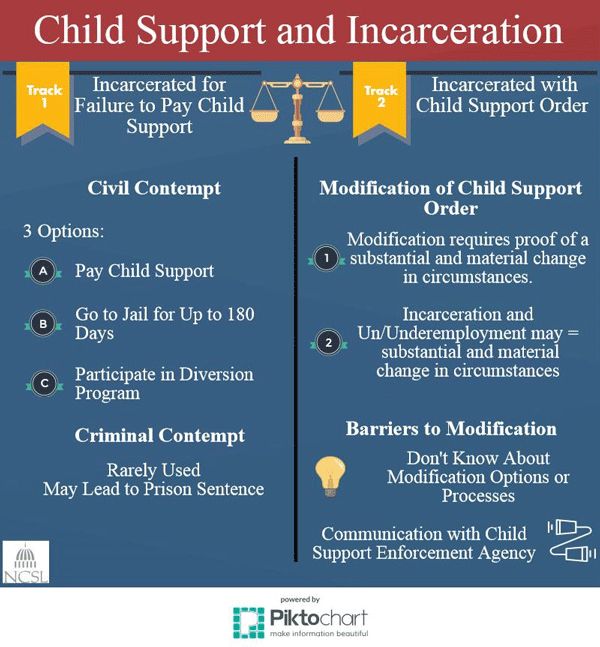
Why might a custodial parent want to remove their child from public assistance?
If your income is high enough, your children may receive more cash assistance from you than from government assistance. For example, if you are the father of all the children in your mother's house, and she can certify that you support them, there should be no problem getting the children off state aid. If a mother has children from other fathers in her public assistance budget, the process will be more complicated. The state wants all children in the home to have the same income. Therefore, it is possible that the mother will not be able to remove only your children from public assistance.
If I pay child support, can I also get visitation?
Optional. Alimony and visits (vi-zi-TAI-shan) are not related. If you are not allowed to see your children, you must file a petition to visit with the court. Whether you see your child or not, you remain responsible for paying child support. For more information about visiting, read the Family Legal Care booklet Custody and Visits.
For more information about visiting, read the Family Legal Care booklet Custody and Visits.
What if there is no child support case, but I want to support my child?
Non-custodial parent cannot start a support case. If you want to support your children but don't know where they are, you can save money in a separate bank account.
Where else can I go for help?
If the SCU is involved in your case, you can contact 151 West Broadway, 4th floor, Manhattan to speak with a customer service representative.
You can also call the Support Enforcement Office at (888) 208-4485.
This document does not replace legal advice. Family Legal Care recommends that all people facing the Criminal Court or Family Court systems consult with a lawyer.
How to recover child support from a working debtor? - Lawyer in Samara and Moscow
Legislation provides for a different procedure for paying and calculating child support.
1. On voluntary payment of alimony by a parent
On voluntary payment of alimony by a parent
cash desks. The amount of alimony and the terms of payment are determined and indicated in the application by the parent paying the alimony. The administration will transfer alimony to the specified details or issue them when calculating wages. The payment of alimony in this manner does not apply to cases of deductions from wages for the purposes of labor legislation (clause 1, article 80 of the IC of the Russian Federation; article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
2. On the payment of alimony on the basis of a notarial agreement
The amount of alimony is determined by agreement of the parties, however, it cannot be less than what would be relied on a child in the recovery of alimony in court (clause 1, article 80, art. Articles 99, 103 of the RF IC). The agreement may provide for a different procedure for the payment of alimony: as a percentage of earnings, in a fixed amount of money paid at a time or periodically, etc.
on the basis of this agreement in accordance with the stipulated conditions for the timing and amount of payments (Article 109RF SC). Their size is calculated on the basis of wages and income (except for payments from which alimony is not withheld) minus tax payments. The types of income from which alimony for minor children is paid are defined in the List, approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 18, 1996 N 841. Withholding by agreement cannot exceed 70% of earnings (Article 110 of the RF IC; Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The administration pays or transfers alimony to the beneficiary's account no later than within 3 days from the date of payment of wages to the alimony payer. The costs of paying alimony (for example, a bank commission or a postal order fee) are borne by their payer.
Such an agreement has the force of an executive document, and if the parent does not want to pay alimony voluntarily under a notary agreement, they can be collected forcibly through the bailiff service (clause 3, part 1, article 12, article 30 of the Law of 02. 10.2007 N 229-FZ).
10.2007 N 229-FZ).
The bailiff will calculate the debt for the payment of alimony.
Alimony arrears for the past period can be collected on the basis of an agreement on the payment of alimony within the three-year period preceding the presentation for collection.
If non-payment of alimony was due to the fault of the debtor parent, they can be calculated for the entire past period.
The bailiff calculates the debt based on the terms of the agreement on the payment of alimony and earnings and other income of the person obliged to pay alimony, for the period during which the alimony was not collected (Article 113 of the RF IC).
In case of non-payment of alimony voluntarily and the absence of a notarized agreement on the payment of alimony, alimony can be collected in court.
3. About the recovery of maintenance from a parent in court
There are two ways to collect child support in court: on the basis of an application for a court order or filing a claim for the recovery of alimony.
Issuance of a court order is a simplified procedure for the collection of alimony. The judge issues a court order within five days from the date of receipt of the application without a trial, summoning the debtor and the recoverer and hearing their explanations (Article 126 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
The judge sends a copy of the court order to the debtor, who, within ten days from the date of receipt of the order, has the right to file objections regarding its execution (Article 128 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
The judge cancels the court order if the debtor raises objections regarding its execution within the prescribed period. If no objections are received from the debtor within the prescribed period, the judge issues the second copy of the court order to the recoverer to present it for execution or, at the request of the recoverer, sends it to the bailiff for execution (Article 129, 130 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
A court order cannot be issued in the case of an application for the payment of alimony in a fixed amount of money (paragraph 11 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of 10.25.1996 N 9).
As a general rule, alimony will be assigned from the moment of applying to the court. In rare cases, if payment evasion is proven, they can be recovered for the past period, but not more than three years (clause 2, article 107 of the RF IC).
Alimony is assigned as a fixed amount or as a percentage of the parent's income.
Assignment of alimony as a percentage of the parent's income
If the parent has one job and a steady income, then alimony can be assigned as a percentage of income - for one child in the amount of one quarter, for two children - one third , for three or more children - half of the earnings and (or) other income of the parent (Article 81 of the RF IC). The court may increase or decrease the size of these shares depending on the financial or marital status of the parties and other circumstances of the case (for example, the disability of family members to whom the party is obliged by law to provide maintenance, the onset of disability or the presence of a disease that prevents the continuation of the previous work, the child's admission to work or engaging in entrepreneurial activity).
Assignment of alimony in a fixed amount of money
Alimony in a fixed amount of money is assigned if there is no agreement between the parents on the payment of alimony and the parent does not have a permanent income, or if there are several sources of income, or if the income is unstable, or if this parent receives earnings and (or) other income in whole or in part in kind or in foreign currency, and in other cases when it is impossible to collect alimony in percentage terms (Article 83 of the RF IC).
A fixed amount of maintenance is also determined taking into account the financial and marital status of the parties and other noteworthy circumstances in order to maintain the child's previous level of support. Alimony must be set in a fixed amount of money corresponding to a certain number of minimum wages for further indexation (clause 2 of article 117 of the RF IC).
Alimony can be collected in a fixed amount of money, for example, if the alimony payer hides his income.
Employer withholds child support based on a court order or court order in the same way as a child support agreement. If a court order or court decision is not executed voluntarily, then their enforcement through the bailiff service is possible. The bailiff will calculate the debt on the basis of a court order or decision in the manner indicated above.
Remember, at any stage of a family dispute, Anatoly Antonov's Family Law Center is ready to provide you with legal support. Call us by phone in Samara + 7 (846) 212-99-71 right now and sign up for a consultation at a convenient time for you.
Legal Center for Family Affairs of Attorney Anatoly Antonov provides the following legal services regarding the payment of alimony for minor children, as well as other family members:
- legal advice;
- drawing up an agreement on the payment of alimony;
- drawing up a statement of claim for the issuance of a court order;
- preparation of a statement of claim for the recovery of alimony and attachments to it, as well as filing it with the court;
- preparation of objections regarding claims for the recovery of alimony, for a reduction in the amount of alimony;
- familiarization with the materials of the case on the recovery of alimony, on the reduction of the amount of alimony;
- participation in court hearings (possibly without the presence of the principal) for the recovery of alimony;
- obtaining a court decision on the recovery of alimony;
- appeal against the decision of the court in a higher instance.