Stomach ache in third trimester
The Third Trimester of Pregnancy: Pain and Insomnia
The Third Trimester of Pregnancy: Pain and Insomnia- Health Conditions
- Featured
- Breast Cancer
- IBD
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Articles
- Acid Reflux
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Bipolar Disorder
- Cancer
- Crohn's Disease
- Chronic Pain
- Cold & Flu
- COPD
- Depression
- Fibromyalgia
- Heart Disease
- High Cholesterol
- HIV
- Hypertension
- IPF
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Skin Disorders and Care
- STDs
- Featured
- Discover
- Wellness Topics
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Skin Care
- Sexual Health
- Women's Health
- Mental Well-Being
- Sleep
- Product Reviews
- Vitamins & Supplements
- Sleep
- Mental Health
- Nutrition
- At-Home Testing
- CBD
- Men’s Health
- Original Series
- Fresh Food Fast
- Diagnosis Diaries
- You’re Not Alone
- Present Tense
- Video Series
- Youth in Focus
- Healthy Harvest
- No More Silence
- Future of Health
- Wellness Topics
- Plan
- Health Challenges
- Mindful Eating
- Sugar Savvy
- Move Your Body
- Gut Health
- Mood Foods
- Align Your Spine
- Find Care
- Primary Care
- Mental Health
- OB-GYN
- Dermatologists
- Neurologists
- Cardiologists
- Orthopedists
- Lifestyle Quizzes
- Weight Management
- Am I Depressed? A Quiz for Teens
- Are You a Workaholic?
- How Well Do You Sleep?
- Tools & Resources
- Health News
- Find a Diet
- Find Healthy Snacks
- Drugs A-Z
- Health A-Z
- Health Challenges
- Connect
- Breast Cancer
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Psoriasis
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph. D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Rachel Nall, MSN, CRNA on September 5, 2018
The third trimester
The third trimester is a time of great anticipation. In a few short weeks, your little one will finally be here.
Some of the symptoms during the third trimester can include insomnia and pain. It’s important to know what’s normal and what’s not, particularly when it comes to the discomfort you may feel over the course of the third trimester.
Pain can occur in seemingly every part of your body during this time. From your back to your hips to your stomach, there are many places that may be sore and uncomfortable.
Though insomnia and pain certainly aren’t pleasant, there’s an end in sight. Soon, you’ll be welcoming your new baby to the world.
Abdominal pain
Stomach pain in the third trimester can include gas, constipation, and Braxton-Hicks contractions (false labor). While these can cause some abdominal discomfort, they shouldn’t cause excessive amounts of pain.
Abdominal pain that’s more severe and concerning can be caused by:
- urinary tract infection (UTI)
- preeclampsia, a condition that causes high blood pressure during pregnancy
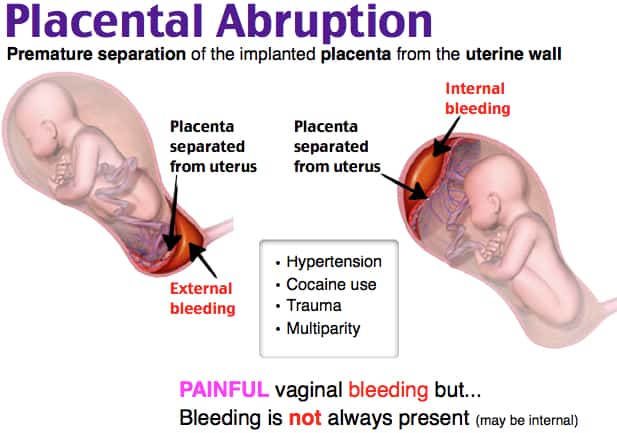
- placental abruption, a condition that occurs when your placenta separates from your uterus too early
Call your doctor if you experience:
- vaginal bleeding
- a fever
- chills
- dizziness
- nausea
- vomiting
Lower back and hip pain
As your body goes through further changes in preparation for childbirth, hormone levels increase so your connective tissue loosens. This enhances flexibility in your pelvis so your baby can pass through the birth canal more easily.
However, women frequently experience hip pain as the connective tissue loosens and stretches. Lower back pain can also occur along with hip pain, as posture changes may cause you to lean more toward one side or another.
Sleeping on your side with a pillow between your legs may help to relieve this pain because it opens the hips slightly.
Try these tips
- Take a warm bath.
- Apply warm compresses or an ice pack, but avoid the abdomen.
- Get a prenatal massage.
- Sit in chairs with good back support.
- Take an over-the-counter pain reliever to reduce soreness and discomfort.
Call your doctor if the pain becomes severe or if you feel pressure radiating toward your thighs. These could be signs of preterm labor.
You should also contact your doctor if your pain is accompanied by stomach cramping, contractions that occur roughly 10 minutes apart, or vaginal discharge that’s clear, pink, or brown.
Sciatica
Your sciatic nerve is a long nerve that runs from your lower back all the way down to your feet. When pain occurs along this nerve, the condition is known as sciatica.
Many women experience sciatica during pregnancy because the enlarged uterus presses down on the sciatic nerve. This increased pressure causes pain, tingling, or numbness in the lower back, buttocks, and thighs. It may affect one side or both sides of the body.
It may affect one side or both sides of the body.
While the pain of sciatica is uncomfortable, it shouldn’t hurt your growing baby.
You may be able to ease the pain by stretching, taking a warm bath, or using pillows to position yourself as comfortably as possible.
Vaginal pain
Vaginal pain during your third trimester can make you feel anxious and stressed. You may wonder if your baby is coming or if the pain is a sign that something’s wrong.
The answer depends on the severity of the pain. Some women experience sharp, piercing pain in the vagina. This could potentially indicate that the cervix is dilating in preparation for delivery.
You should call your doctor immediately if you’re experiencing any of the following:
- severe vaginal pain
- intense pain in the vagina
- intense pain in the lower abdomen
- vaginal bleeding
Even if these symptoms turn out not to be cause for concern, it’s best to get a confirmation from your doctor.
Why does insomnia occur during the third trimester?
Insomnia is a sleep disorder that makes it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep on a regular basis. Chances are, both of these symptoms may affect you at some point during your third trimester.
There are several factors that can contribute to insomnia in the third trimester:
Baby’s growing size
During the final trimester, your baby is getting much larger. This can make it harder to breathe while sleeping and more difficult to find a comfortable position.
The lower back pain you may experience during pregnancy can also affect your ability to get a good night’s sleep.
Snoring
Your sleep may also be impacted by snoring. Nasal congestion occurs in up to 42% women during pregnancy and can cause snoring.
The baby’s increased size also puts additional pressure on the diaphragm, or breathing muscles. While some moms-to-be can sleep through the snoring, others may wake themselves up with their snoring.
Leg cramping and restless legs
You may start to develop leg cramping and restless leg syndrome (RLS) in the third trimester.
Cramping can occur as a result of too much phosphorus and too little calcium in the body.
RLS, or the overwhelming need to constantly move your leg, can be a symptom of an iron or folic acid deficiency. For this reason, it’s important to let your doctor know if you’re experiencing the symptoms of RLS. These can include:
- an uncomfortable sensation in the legs
- a strong urge to move one or both legs
- nighttime leg twitching
- sleep interruption
Your doctor may want to perform certain blood tests to determine the cause of RLS.
Preventing and fighting insomnia
Insomnia can be a challenging condition. However, there are some steps you can take to get better sleep in your third trimester. Try the ones below:
- Sleep on your left side to promote blood flow to your baby. Place a pillow underneath your belly to support it.
 If you experience heartburn or acid reflux while lying flat, add extra pillows under your upper body.
If you experience heartburn or acid reflux while lying flat, add extra pillows under your upper body. - Avoid sleeping on your back when possible, as this restricts blood flow.
- Avoid foods known to contribute to leg cramps, especially carbonated and caffeinated beverages.
- Drink plenty of water to help reduce cramping.
- Share your symptoms with your doctor. If you do experience nasal swelling that causes snoring, your doctor may want to run certain tests to ensure it isn’t a symptom of preeclampsia, or high blood pressure.
- Stretch your legs before going to bed. Try straightening your legs and flexing your feet to help reduce leg cramping that keeps you up at night.
- If you can’t fall asleep, don’t force it. Try reading a book, meditating, or doing another relaxing activity.
Medications
It’s best to avoid taking medications in pregnancy and for insomnia generally, but if other remedies don’t appear to be helping, you can try using a short-term sleep aid.
Make sure to consult with your doctor to choose the best medication. There are some safe sleep aids to use during pregnancy, though some of these can be addictive even when taken short term.
While you can expect some sleep disruptions during your last trimester, talk to your doctor if they’re happening on a daily basis or if you can’t seem to sleep for more than a few hours each night. Sleep is important for both you and your growing baby.
Last medically reviewed on September 5, 2018
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Health
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Balserak B I. (2015). Sleep disordered breathing in pregnancy.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4818216/ - Do I have insomnia? (2020).
thensf.org/?s=insomnia - How to handle sciatica during your pregnancy. (2014).
health.clevelandclinic.org/how-to-handle-sciatica-during-your-pregnancy - Karadag-Saygi, E, et al. (2010). Plantar pressure and foot pain in the last trimester of pregnancy. DOI:
10.3113/FAI.2010.0153 - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2017). Third trimester pregnancy: What to expect.
mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/pregnancy/art-20046767 - Pregnancy calendar: Third trimester. (n.d.).
publichealth.org/public-awareness/prenatal-care/third-trimester - Stomach pain in pregnancy. (2018).
nhs.uk/conditions/pregnancy-and-baby/stomach-pain-abdominal-cramp-pregnant
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Sep 5, 2018
Written By
Rachel Nall, MSN, CRNA
Edited By
Phil Riches
Medically Reviewed By
Debra Rose Wilson, PhD, MSN, RN, IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Rachel Nall, MSN, CRNA on September 5, 2018
related stories
What Might Go Wrong in the Third Trimester?
Why Vaginal Pressure During Pregnancy Is Totally Normal
Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy: Is It Gas Pain or Something Else?
How to Safely Exercise in the Third Trimester of Pregnancy
The Third Trimester of Pregnancy: Weight Gain and Other Changes
Read this next
What Might Go Wrong in the Third Trimester?
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Weeks 28 through 40 bring the arrival of the third trimester.
 This exciting time is definitely the home stretch for expectant mothers, but it’s also a…
This exciting time is definitely the home stretch for expectant mothers, but it’s also a…READ MORE
Why Vaginal Pressure During Pregnancy Is Totally Normal
Medically reviewed by Nicole Galan, RN
Many pregnant women experience vaginal and/or pelvic pressure. Here's why it happens and how to find relief.
READ MORE
Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy: Is It Gas Pain or Something Else?
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Gas pain is common during pregnancy. Sometimes, though, your stomach pain could be a sign of something more serious. Here's what to look out for.
READ MORE
How to Safely Exercise in the Third Trimester of Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.
 D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHTJust 20 minutes a day of low- to moderate-intensity activity can help improve pregnancy symptoms and strengthen your body for delivery. You can still…
READ MORE
The Third Trimester of Pregnancy: Weight Gain and Other Changes
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
The third trimester of pregnancy produces the most rapid changes for your baby. Your body will also go through significant changes to support your…
READ MORE
The Third Trimester of Pregnancy: Concerns and Tips
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
For many people, the third trimester of pregnancy can be an anxious time. Here’s a list of concerns you might have, including traveling, sleeping…
READ MORE
The Third Trimester of Pregnancy: Shortness of Breath and Edema
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.
 D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI
D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COIShortness of breath and swelling (or edema) are both common in the last trimester of pregnancy. Learn some techniques than can help.
READ MORE
The Third Trimester: Which Test Could Save Your Baby?
Medically reviewed by Nicole Galan, RN
Learn about the types of tests your doctor might use at your prenatal checkups in the third trimester, for both you and your baby’s health.
READ MORE
What Bodily Changes Can You Expect During Pregnancy?
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
The hormonal and physiologic changes during pregnancy are unique in the life of women. Discover what they are here.
READ MORE
Can I Take Ambien During Pregnancy?
Medically reviewed by Darren Hein, PharmD
Pregnant and having trouble falling or staying asleep? Find out if Ambien is a safe option to treat insomnia during pregnancy.

READ MORE
Upper stomach pain during pregnancy: Third trimester
Many people experience pain in the upper part of their stomach or abdomen during pregnancy. This is usually nothing to worry about, but sometimes it might be necessary to see a doctor.
The third trimester is notoriously difficult. From breathing through Braxton–Hicks contractions and wondering whether they are the real thing to stretching skin and crowded organs, people may feel exhausted and ready to give birth by the end of the third trimester.
Stomach pain is a common pregnancy complaint. Some people report pain in the upper stomach or upper abdomen during their third trimester. This pain may be sharp and shooting or a dull ache.
Many of the causes of upper abdominal pain are harmless, but feeling intense pain here can signal a serious problem. Talk to a doctor or midwife about any unusual or very painful sensations.
In this article, we look at the possible causes of upper abdominal pain during pregnancy, how to ease the symptoms, and when to see a doctor about it.
Stomach or abdomen pain is more common during early pregnancy, when hormonal shifts can trigger the nausea and vomiting of morning sickness. In the middle of the second trimester, at around 20 weeks, stomach pain usually goes away.
In the third trimester, abdominal pain can reappear as the uterus begins to crowd the organs. Some women experience heartburn or a sensation that the skin of the stomach is stretching.
Having stomach pain in the third trimester may indicate a more serious problem if it:
- occurs with other symptoms, such as itching
- feels sudden or intense
- is constant
- is in a specific location
- appears alongside a fever, nausea, or vomiting
- appears alongside vaginal bleeding
Many causes of upper abdominal pain in the third trimester are harmless. However, because premature labor, placenta issues, and other concerns can endanger the woman and the baby, it is important to be cautious and tell a doctor or midwife about any unusual symptoms.
Possible causes of upper abdomen pain during the third trimester include:
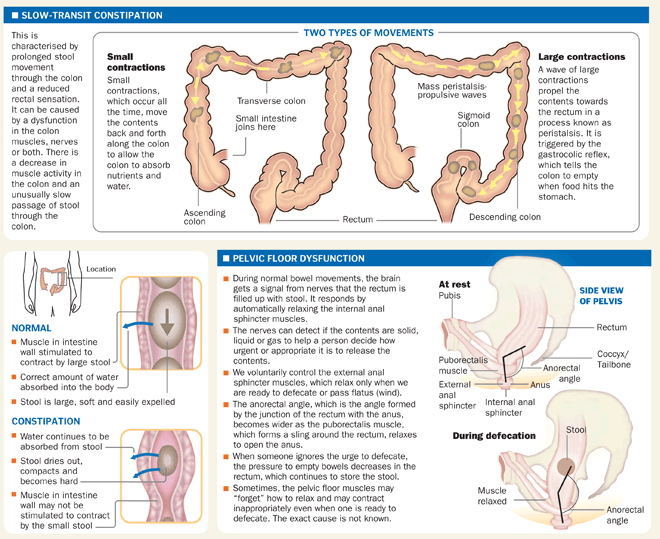
Constipation and gas
Constipation is one of the most common pregnancy complaints.
During the first trimester, hormonal shifts may trigger constipation. By the third trimester, the uterus is putting significant pressure on the intestines and making it more difficult for a person to have a bowel movement.
Having a vague feeling of fullness in the upper stomach or abdomen is sometimes a symptom of severe constipation. Other symptoms might include gas, straining to have a bowel movement, and having very hard or small bowel movements.
Eating fiber-rich foods may help. Taking laxatives can also provide relief, but it is important to talk to a doctor or midwife before taking any medication when pregnant.
Acid reflux
Heartburn is a common symptom, affecting an estimated 17–45 percent of women during pregnancy. A pregnancy hormone called progesterone can cause acid reflux and heartburn.
As the uterus grows, pressure on the digestive tract can make this problem more severe. Many pregnant women experience acid reflux when lying down.
Pain in the upper abdomen may be from acid reflux if the pain extends up the chest and into the throat or includes a burning sensation. Some women belch or experience gas.
Taking over-the-counter heartburn medications, eating smaller meals, and opting for a less acidic diet may help.
Stretching skin
Some pregnant people report feeling an intense sensation of stretching skin. As the uterus expands, this sensation can extend to the upper abdomen. If the skin itches and feels tight, and the pain is on the outside of the stomach rather than deep in the abdomen, stretching skin could be the culprit.
Gently massaging the area, applying lotion to it, and taking warm showers can sometimes help relieve the discomfort.
Muscle pain and strain
The abdominal muscles must stretch to accommodate the growing fetus. The pressure of the uterus on the lower body can also change the way a person walks or moves, increasing the likelihood of sustaining an injury.
The pressure of the uterus on the lower body can also change the way a person walks or moves, increasing the likelihood of sustaining an injury.
Feeling pain when bending or lifting may mean an injury to the stomach or chest muscles. Resting and stretching can help with minor injuries. People can see a doctor about injuries that do not go away on their own.
Gallbladder issues
Pain in the upper right part of the abdomen, under or near the ribs, may mean that there is a problem with the liver or gallbladder.
If there is nausea or vomiting, or if the pain comes in waves or attacks, it may be a sign of gallstones. Left untreated, gallstones can block the bile duct and cause liver problems.
If the gallstones do not pass on their own, a doctor might recommend removing the gallbladder.
Liver issues
Pregnancy-related hormone changes can cause a condition called intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (IHP), or cholestasis. For most women, the first symptom is itching. Some also experience pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, vomiting, or yellowing eyes or skin.
Some also experience pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, vomiting, or yellowing eyes or skin.
A doctor must carefully monitor liver health in a person with IHP. In some cases, they will need to deliver the baby early to prevent serious complications, including liver failure and injuries to the developing baby.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is inflammation in the pancreas. Infections, injuries, and problems with other organs, including the liver and gallbladder, can cause pancreatitis.
Pancreatitis may cause upper abdomen pain, exhaustion, nausea, or changes in the color of stool.
Depending on the cause of pancreatitis, a woman may need to stay at the hospital. In some cases, a doctor may recommend antibiotics or fluids.
Spleen injury
Pain in the upper abdomen, especially the left side, may mean that there is a problem with the spleen.
A blow to the stomach can bruise or injure the spleen. Infections can cause the spleen to rupture. Rarely, a person’s spleen may rupture for no clear reason.
Spleen injuries cause intense, sudden pain. A woman may feel dizzy or lightheaded, and they must seek emergency treatment. A surgeon may need to remove the spleen.
Contractions
True labor contractions typically start at the top of the uterus, causing an intense tightening sensation that becomes progressively more painful. A woman who feels contractions beginning in the top of the abdomen may be going into labor.
Call a medical professional straight away. If there is vaginal bleeding, go to the emergency room.
The risk of missing a serious problem far outweighs any benefits of trying home remedies. If the cause of the problem is unclear, call a doctor or midwife first.
If they feel that the pain is not dangerous or does not need medical treatment, some home remedies that may help ease upper abdomen pain during pregnancy include:
- stretching to ease muscle pain and tension
- eating fewer acidic foods
- with a doctor or midwife’s permission, using an antacid to deal with heartburn
- eating smaller, more frequent meals to reduce the pain of a full stomach and heartburn
- massaging the area to ease muscle tension and stress
Call a doctor or midwife within a day for any unusual pain in the stomach or abdomen. At each visit with a provider, talk about any recent symptoms, as well as any symptoms that have changed in severity.
At each visit with a provider, talk about any recent symptoms, as well as any symptoms that have changed in severity.
Go to the emergency room or immediately call a medical professional for:
- intense upper abdominal pain, especially if it is on the right side or if the pain is unbearable
- abdominal pain accompanied by vaginal bleeding
- contractions that come at regular intervals
- abdominal pain and a fever
- symptoms of high blood pressure, such as dizziness, difficulty breathing, a bad headache, or intense fatigue
- itching, yellowing skin or eyes, or vomiting
Most causes of stomach or abdominal pain in the third trimester are not fully preventable. As the fetus grows, the organs must shift. This can cause some aches and pains.
For some women, hormonal shifts trigger serious complications, such as IHP.
The best strategy to prevent serious pregnancy complications is to get regular prenatal care. Talk to a provider about any concerns, and ask about lifestyle strategies to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
For most women, eating a healthful and balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and devising healthful strategies for managing stress can all help with the aches and pains of pregnancy.
Abdominal pain is one of the most common pregnancy complaints. This does not mean that a woman should ignore it. Only a doctor or midwife can diagnose the problem, so do not hesitate to call them.
They can either reassure a person that there is nothing to worry about or offer medical care to prevent an emerging condition from becoming more serious.
Read the article in Spanish.
Treatment of pain in the abdomen - Network of clinics "OSTEOMED"
Pain in the abdomen during pregnancy can be of different localization and in most cases they do not conceal anything threatening. Basically, this is a normal reaction of the body to the increasing weight and growth of the uterus. The most hectic period of pregnancy is the first trimester, because ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous abortion and the like can take place here. Anxiety contributes to a lot of hormonal failure in the body. After all, during this period they need to quickly reorganize in a new way, which will allow them to endure, give birth to a healthy child without problems, and even set up proper lactation. Moreover, in each of these stages there is a certain hormonal jump, in which the emotional state of the pregnant woman is often changeable. nine0003
Anxiety contributes to a lot of hormonal failure in the body. After all, during this period they need to quickly reorganize in a new way, which will allow them to endure, give birth to a healthy child without problems, and even set up proper lactation. Moreover, in each of these stages there is a certain hormonal jump, in which the emotional state of the pregnant woman is often changeable. nine0003
Quite often, pain in the lower abdomen is felt during pregnancy in the early stages. If they do not bring much discomfort, there is no spotting, as well as other symptoms of a possible pathology or disease, then treatment is not required. At the beginning of pregnancy, such pains can be associated with hormonal changes, in the middle - with the rapid growth of the uterus, and at the end - with the preparation of the uterus for childbirth.
First trimester abdominal pain
If the stomach hurts during early pregnancy, then this does not always indicate some kind of pathology. With mild, rarely occurring and quickly passing pains, you should not worry. But for greater certainty, as soon as the test showed two strips, it is worth contacting a gynecologist as soon as possible. This will not only relieve the hassle, but also morally set you up for the upcoming event. With frequent aching, intense and cramping pains, it is urgent to find time and be sure to see a doctor. After all, this may indicate an ectopic pregnancy, which will require urgent surgical intervention. In addition, spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) can also be the cause. However, often, but not always, abdominal pain is accompanied by lower back pain and bleeding. If all indicators of pregnancy are normal, but the stomach still aches, this is explained very simply. The body is rebuilt, the tissues supporting the uterus become softer, looser, while the uterus itself grows and shifts, which contributes to tingling and sipping pains in the lower abdomen. nine0003
With mild, rarely occurring and quickly passing pains, you should not worry. But for greater certainty, as soon as the test showed two strips, it is worth contacting a gynecologist as soon as possible. This will not only relieve the hassle, but also morally set you up for the upcoming event. With frequent aching, intense and cramping pains, it is urgent to find time and be sure to see a doctor. After all, this may indicate an ectopic pregnancy, which will require urgent surgical intervention. In addition, spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) can also be the cause. However, often, but not always, abdominal pain is accompanied by lower back pain and bleeding. If all indicators of pregnancy are normal, but the stomach still aches, this is explained very simply. The body is rebuilt, the tissues supporting the uterus become softer, looser, while the uterus itself grows and shifts, which contributes to tingling and sipping pains in the lower abdomen. nine0003
Pain in the lower abdomen
Pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy, and especially in the later stages, are often due to internal pressure, that is, the growing uterus presses on the internal organs, thus disrupting their full-fledged work. The intestine reacts very sensitively to the hormones of "pregnancy" with a decrease in motility, a violation of peristalsis, which is a common cause of constipation, bloating and colic. To avoid this, you need to move more often, eat foods rich in fiber (fruits, vegetables, whole grain bread) and, of course, drink more fluids. Also, pain concentrated in the lower abdomen can be caused by a sprain due to the rapid growth of the uterus, or it can be triggered by premature detachment of the placenta. In the latter case, urgent medical attention is needed, because irreparable harm can be done to the mother and child. In this case, rapid delivery and immediate stopping of bleeding are indicated. In addition, during pregnancy, new or exacerbated chronic diseases can develop, which can also give signals in the lower abdomen. These are cholecystitis, intestinal dysbacteriosis and others. In some cases, emergency surgery is indicated, and therefore it is worth paying attention to the slightest changes in the nature of the pain.
The intestine reacts very sensitively to the hormones of "pregnancy" with a decrease in motility, a violation of peristalsis, which is a common cause of constipation, bloating and colic. To avoid this, you need to move more often, eat foods rich in fiber (fruits, vegetables, whole grain bread) and, of course, drink more fluids. Also, pain concentrated in the lower abdomen can be caused by a sprain due to the rapid growth of the uterus, or it can be triggered by premature detachment of the placenta. In the latter case, urgent medical attention is needed, because irreparable harm can be done to the mother and child. In this case, rapid delivery and immediate stopping of bleeding are indicated. In addition, during pregnancy, new or exacerbated chronic diseases can develop, which can also give signals in the lower abdomen. These are cholecystitis, intestinal dysbacteriosis and others. In some cases, emergency surgery is indicated, and therefore it is worth paying attention to the slightest changes in the nature of the pain.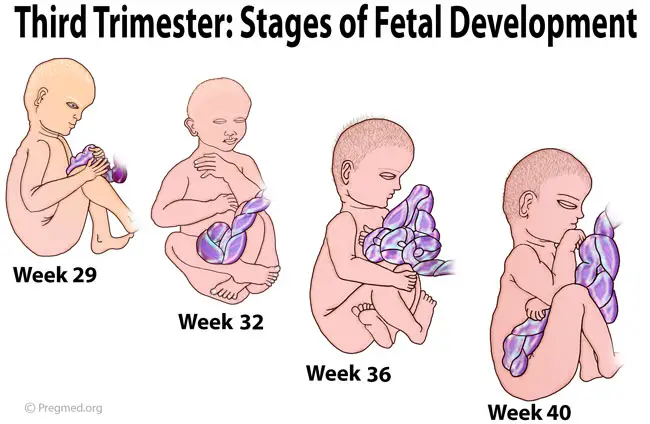 If there is even the slightest doubt, you should urgently consult a doctor, otherwise it may be too late. In addition, problems with the genitourinary system are quite possible, which can also provoke pain in the lower abdomen. nine0004
If there is even the slightest doubt, you should urgently consult a doctor, otherwise it may be too late. In addition, problems with the genitourinary system are quite possible, which can also provoke pain in the lower abdomen. nine0004
Uterine tone
Uterine tone is painless or slightly painful uterine contractions. If a pregnant woman feels a spasm in the lower abdomen, the stomach becomes like a stone (this is especially noticeable in the second half of pregnancy) - this is a tone. The tone is diagnosed by a gynecologist during an external examination. The fact that the tone was recorded on the ultrasound, contrary to popular belief, is not an indication for treatment and hospitalization. The uterus is a muscular organ, and it is quite normal that it contracts periodically. The key word here is periodically, and, of course, painlessly and for a short time. With uterine tone, doctors recommend taking a horizontal position, lying on your side, you can take an antispasmodic pill and use a Papaverine suppository. nine0004
nine0004
Preliminaries
As a rule, there are minor pains in the lower abdomen during late pregnancy - these are preparatory contractions. Thus, the uterus prepares for the upcoming birth. In some women, the uterus begins to “prepare” like this at 32 weeks, in others for 1-2 weeks, and someone either does not notice these weak contractions, or considers this the norm, and therefore does not pay attention. It is very important to learn to distinguish between preliminary contractions and true ones, those that begin already in childbirth. Preliminary contractions last for several seconds, and they are not regular, unlike true ones, and do not intensify. It has been observed that nulliparous women are more likely to experience pre-contractions than multiparous women. This kind of pain is removed very easily by non-drug methods - you can just take a deep breath, lie down and relax. In many cases, taking a warm (not hot!) bath helps. nine0004
Gynecological pathologies
Those 4 reasons that we described above are variants of the norm. However, it is urgent to consult a doctor if these conditions are accompanied by bloody or brown vaginal discharge, clear or greenish vaginal discharge (they may turn out to be amniotic fluid), if the pain lasts for several minutes, is not relieved by antispasmodics and only increases when weakness appears, dizziness, flies before the eyes, etc. In a word, if the condition worsens. Such symptoms may indicate a threat or a spontaneous miscarriage, a frozen or ectopic pregnancy (when an early pregnancy, pain in the lower abdomen), premature or term birth, etc. nine0004
However, it is urgent to consult a doctor if these conditions are accompanied by bloody or brown vaginal discharge, clear or greenish vaginal discharge (they may turn out to be amniotic fluid), if the pain lasts for several minutes, is not relieved by antispasmodics and only increases when weakness appears, dizziness, flies before the eyes, etc. In a word, if the condition worsens. Such symptoms may indicate a threat or a spontaneous miscarriage, a frozen or ectopic pregnancy (when an early pregnancy, pain in the lower abdomen), premature or term birth, etc. nine0004
Other reasons
However, not always abdominal pain in expectant mothers occurs precisely because of gynecological problems and is a consequence of pregnancy. Here are some other possible reasons.
1. Cystitis and other diseases of the female excretory system. The ureter is located next to the internal genital organs, because this pain is often confused with "gynecological". Usually the pain occurs in such cases suddenly, has a "stabbing" character.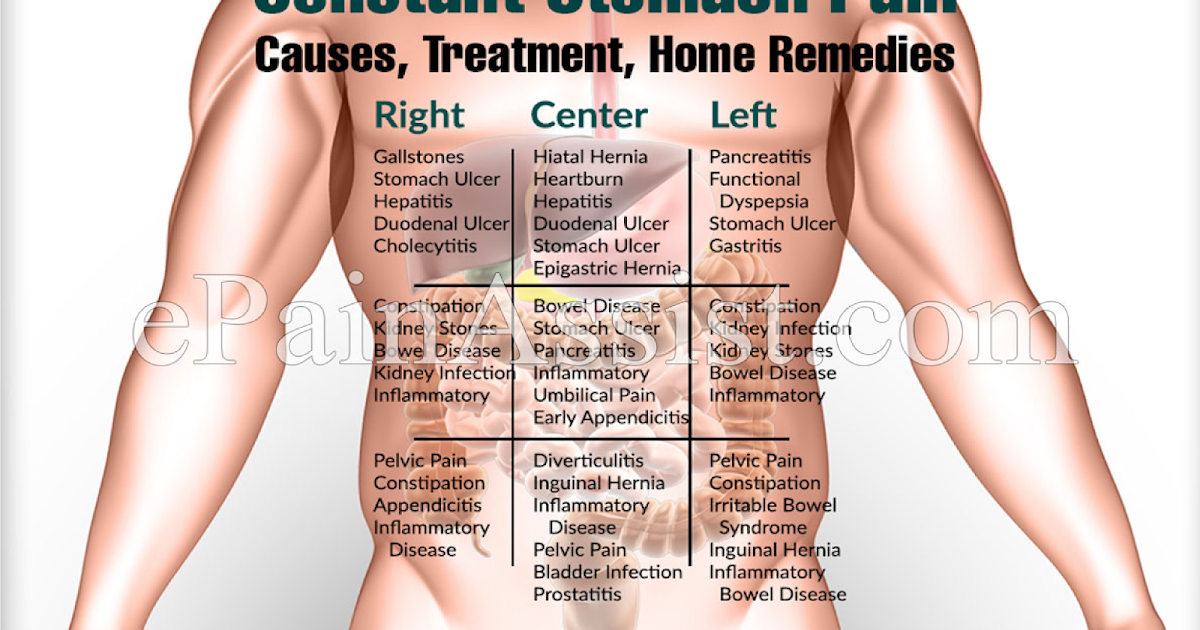 Pain in the lower abdomen is accompanied by frequent and painful urination. The urologist treats the genitourinary system. You should not start the disease, because it is caused by an infection that is unsafe for the child. Folk remedies, like bearberry, do not help well, but the doctor can prescribe effective medications that are approved for use by pregnant women. nine0004
Pain in the lower abdomen is accompanied by frequent and painful urination. The urologist treats the genitourinary system. You should not start the disease, because it is caused by an infection that is unsafe for the child. Folk remedies, like bearberry, do not help well, but the doctor can prescribe effective medications that are approved for use by pregnant women. nine0004
2. Problems with the intestines: diarrhea, constipation, bloating. It should be noted that the last 2 are frequent occurrences in expectant mothers. Constipation is caused by a decrease in physical activity, displacement of internal organs due to the growth of the uterus, malnutrition, and insufficient fluid intake. Bloating is caused by the consumption of appropriate foods, as well as soda. Sometimes it is enough to go to the toilet for the pain in the abdomen to go away if it's constipation.
3. Poisoning or rotovirus infection. Their symptoms are very similar. Usually it all starts with cramping pains in the lower abdomen, sometimes the pain goes to the navel. Then comes diarrhea and/or vomiting. nine0004
Then comes diarrhea and/or vomiting. nine0004
4. Appendicitis. If you have pregnancy, pulling pains in the lower abdomen do not always indicate tone or minor ailments, this may be a symptom of appendicitis, especially if the pain is right-sided, accompanied by fever. The correct diagnosis can be made by the surgeon. If the pain does not go away within an hour or two, but only increases, you should not attribute everything to an intestinal disorder and drink drugs like "smecta", this is very dangerous. If surgery is not carried out in time, it can lead to peritonitis. nine0004
And this is not all the reasons. Pregnant women, not for the first time, can quite easily distinguish the pain caused by uterine spasm from other types of pain. But in any case, it does not hurt to see a doctor.
Upper abdominal pain
Pain at the top of the abdomen during pregnancy mainly occurs in the later stages. Their cause is the same uterus, which is constantly growing, slowly begins to reach the upper organs of the peritoneum. This primarily affects the liver, gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, disturbances in which lead to symptoms such as belching, bitterness in the mouth. In addition, very often in the last trimester of pregnancy, the stomach throws gastric juice up the esophagus, causing considerable discomfort. To avoid these unpleasant moments, you need to eat a balanced diet, which should be eaten in small portions. It is desirable, of course, to exclude fried, spicy, too salty and too sweet. nine0004
This primarily affects the liver, gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, disturbances in which lead to symptoms such as belching, bitterness in the mouth. In addition, very often in the last trimester of pregnancy, the stomach throws gastric juice up the esophagus, causing considerable discomfort. To avoid these unpleasant moments, you need to eat a balanced diet, which should be eaten in small portions. It is desirable, of course, to exclude fried, spicy, too salty and too sweet. nine0004
Stitches
Stinging abdominal pain during pregnancy occurs for many reasons. This may be stagnation of feces in the intestines, which also provokes flatulence and constipation. By the way, the latter, in the future, can become one of the causes of hemorrhoids. It is also necessary to pay attention to the intensity of pain. If it is weak, rarely occurring, then you should not dwell on it. But if the pain is severe, especially sharp, you need to consult a doctor. Acute pain may be due to the development of appendicitis, inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), pancreas. Often, during the filling of the bladder, expectant mothers complain of pains of a pulling nature in this area, which turn into stitches, and become more painful when urinating, which indicates cystitis. In addition, stabbing pains may indicate the presence of infectious diseases, which are most often sexually transmitted. nine0004
Often, during the filling of the bladder, expectant mothers complain of pains of a pulling nature in this area, which turn into stitches, and become more painful when urinating, which indicates cystitis. In addition, stabbing pains may indicate the presence of infectious diseases, which are most often sexually transmitted. nine0004
Abdominal pain on the left
Abdominal pain on the left during pregnancy can be caused by various diseases of the internal organs. They can signal various lesions of the stomach and pancreas, the splenic flexure of the colon and, in fact, the spleen itself, as well as the left kidney. In addition, pain localized in the left side of the abdomen is possible when a hiatal hernia occurs.
Abdominal pain on the right
Abdominal pain on the right during pregnancy most often occurs with diseases of the gallbladder, liver, duodenum, and right kidney. If the pain is accompanied by other symptoms, you should consult a doctor. For example, the symptoms of inflammation of the gallbladder include not only pain in the right side of the abdomen, but also nausea and vomiting (which are often confused with toxicosis). As a rule, following a salt-free diet with the complete exclusion of fatty, fried and spicy foods helps to cope with this problem. Possible formation of sand or kidney stones. Basically, during pregnancy, they try not to affect this organ, because it is of great importance when carrying a child. But if the doctor sees some kind of pathology or the hopelessness of the current situation, which can affect the further course of pregnancy, then measures will be taken to eliminate the cause of pain, with the maximum benefit for the fetus and woman. nine0004
For example, the symptoms of inflammation of the gallbladder include not only pain in the right side of the abdomen, but also nausea and vomiting (which are often confused with toxicosis). As a rule, following a salt-free diet with the complete exclusion of fatty, fried and spicy foods helps to cope with this problem. Possible formation of sand or kidney stones. Basically, during pregnancy, they try not to affect this organ, because it is of great importance when carrying a child. But if the doctor sees some kind of pathology or the hopelessness of the current situation, which can affect the further course of pregnancy, then measures will be taken to eliminate the cause of pain, with the maximum benefit for the fetus and woman. nine0004
Abdominal pain when walking
Often, the stomach hurts when walking in a pregnant woman, causing some discomfort. Basically, this problem concerns the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, that is, those periods when the uterus begins to actively grow, thereby causing a change in the center of balance. This is one of the reasons for the so-called duck walk. Many pregnant women are ashamed of this and try hard to walk the same way as they used to walk, which causes pain. The second reason is the softening of the joints located between the pelvic bones. Thus, the body prepares for the passage of the baby through the birth canal. To reduce or even get rid of pain, you should pay attention to the position of your body when walking. The correct position of the torso during pregnancy is to take the shoulders back, shifting the center of gravity from the toe to the heel, and the use of a special bandage for pregnant women will also bring invaluable help, which will not only reduce the load from the abdomen, but also remove tension from the spine. nine0004
This is one of the reasons for the so-called duck walk. Many pregnant women are ashamed of this and try hard to walk the same way as they used to walk, which causes pain. The second reason is the softening of the joints located between the pelvic bones. Thus, the body prepares for the passage of the baby through the birth canal. To reduce or even get rid of pain, you should pay attention to the position of your body when walking. The correct position of the torso during pregnancy is to take the shoulders back, shifting the center of gravity from the toe to the heel, and the use of a special bandage for pregnant women will also bring invaluable help, which will not only reduce the load from the abdomen, but also remove tension from the spine. nine0004
Severe pain
The stomach hurts a lot during pregnancy during the course of some, at least not very good changes. Normally, there should be no severe pain. But if they have already arisen, then you should not endure them, it is imperative to consult with the district gynecologist. Severe pain can be the result of ectopic pregnancy, placental abruption, miscarriage, premature birth, as well as diseases associated with inflammation and chronic diseases of the internal organs. In principle, in any of these cases, it is necessary to call an ambulance as soon as possible, because untimely assistance can lead to disastrous consequences. The most important thing in this matter is not to miss the precious time that can give life to a small miracle, and maybe more than one. nine0004
Severe pain can be the result of ectopic pregnancy, placental abruption, miscarriage, premature birth, as well as diseases associated with inflammation and chronic diseases of the internal organs. In principle, in any of these cases, it is necessary to call an ambulance as soon as possible, because untimely assistance can lead to disastrous consequences. The most important thing in this matter is not to miss the precious time that can give life to a small miracle, and maybe more than one. nine0004
Abdominal pain can be of different localization, intensity and etiology. If you have any doubts about this, you should immediately consult a doctor. If other symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, loss of consciousness, and the like, join pain in the abdomen, you should urgently, without delay, call an ambulance.
OSTEOPATHICS AND ABDOMINAL PAIN
We recommend that you use our services and prevent abdominal pain without the use of medicines that are harmful to the expectant mother. Osteopathy will help you not only get rid of pain, but also prevent their occurrence. Our specialists, absolutely safely, will carry out the treatment very carefully and efficiently. As a rule, osteopathic treatment is an excellent alternative to surgery in the treatment of many gynecological diseases. nine0004
Osteopathy will help you not only get rid of pain, but also prevent their occurrence. Our specialists, absolutely safely, will carry out the treatment very carefully and efficiently. As a rule, osteopathic treatment is an excellent alternative to surgery in the treatment of many gynecological diseases. nine0004
Osteopathy is a universally recognized scientific method of treatment, the main medical tool of which is the hands of a specialist.
The osteopathic doctor can determine the cause of the pain with just soft touches and, if possible, eliminate it. Osteopathy treats the human body very carefully, believing that the basis of health is its balanced activity, which means that this method will not harm either the expectant mother or the baby. nine0004
What should I know about abdominal pain during pregnancy?
A pregnant woman is especially sensitive to any manifestations of her body. She listens to the behavior of the baby, pays attention to pain or discomfort. Abdominal pain during pregnancy is one of the most common symptoms that can disturb a woman.
Abdominal pain during pregnancy is one of the most common symptoms that can disturb a woman.
In addition to simple food poisoning, these pains may be accompanied by additional symptoms. Also, pain can be caused by a number of other reasons. In this matter, the main thing is to identify the true cause and assess the risk of its effect on the fetus inside the mother. nine0004
Definitely do not ignore any pain symptoms if you are not sure of their origin. Pulling or sharp pains can be caused by various reasons, up to the threat of miscarriage. Therefore, to make a diagnosis and solve this problem, it is better to contact the specialists of the IPF clinic so that further pregnancy proceeds without complications.
Abdominal pain in normal pregnancy, cause of pain
Causes of abdominal pain in pregnancy can be classified into harmless and abnormal. Let's consider safe pains, when they do not pose a particular threat to the child and can be eliminated by a simple change in position, breathing, or dietary adjustments. nine0004
nine0004
- Growing pains - the fetus is constantly growing. At some point, due to stretching of the uterus and tension of the ligaments, you may feel discomfort in the abdomen.
- Training contractions are common at the end of the 3rd trimester when a woman may experience cramping pain that subsides after a while.
- Movement of the internal organs - due to the growth of the fetus, the internal organs are displaced, causing some discomfort.
- Appendicitis - this inflammation can also occur during pregnancy, it is accompanied by a sharp pain in the right side. The operation to remove it will not affect the child in any way. The only inconvenience is the need for anesthesia. nine0122
- Bloating - due to hormonal changes in the body, the work of the intestines changes. The digestion process can slow down, and certain foods can cause gas and bloating.
- Constipation - abdominal pain during early pregnancy sometimes causes bowel problems.
 Some foods may not be digestible well even if you ate them without problems before pregnancy.
Some foods may not be digestible well even if you ate them without problems before pregnancy.
Symptoms of abnormal pain: when to see a doctor
In addition to aching or sharp pains in the abdomen, other unpleasant symptoms may occur:
- Back pain.
- Bloody discharge from the vagina.
- Pain when urinating.
- Pain during intercourse, etc.
The nature of the pain can also indicate several specific causes. For example, pain in the navel can be caused by stretching of the abdominal muscles during the growth of the fetus, the presence of a weak press that feels uncomfortable while the skin is stretched.
If you feel a sudden colitis in your stomach during pregnancy and after a while this pain only intensifies, then you should definitely consult a doctor. Also, the main signal to go to the hospital is additional symptoms in the form of brown or bloody discharge from the vagina. nine0004
nine0004
Causes of abnormal pain:
- Ectopic pregnancy - may be accompanied by severe pain when the egg attaches to the wall of the fallopian tube and stretches it.
- Placental abruption - due to a lack of the hormone progesterone, the placenta can begin to detach from the uterus, causing pain in the lower abdomen and causing internal bleeding.
- Pre-eclampsia - there is a sharp increase in blood pressure, together with stomach pain, nausea, headache, swelling of the extremities, respiratory failure. In this case, outpatient treatment or hospitalization is necessary in case of critical preeclampsia. nine0122
- Risk of miscarriage - in case of possible loss of the fetus, pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy. The nature of the pain is aching or spasmodic. The next stage is the appearance of spotting or the development of rapid bleeding.
- Urinary tract infections - accompanied not only by aching pain in the lower abdomen, but also there is frequent or uncontrolled urge to urinate, pain during urination.
 The infection can later affect the kidneys and cause nausea, back pain, high fever, etc.
The infection can later affect the kidneys and cause nausea, back pain, high fever, etc.
My stomach hurts during pregnancy, what should I do?
If you have abdominal pain during pregnancy, the first thing to do is to calm down and start listening to your body in more detail. If, in addition to abdominal pain, you do not experience any other unpleasant sensations (pain in the back, limbs) or there is no vaginal discharge, then you can try to cope with the pain yourself.
- First you need to lie down. nine0122
- Choose a comfortable position. Especially if you are in the 3rd trimester, you need to find the optimal position of the abdomen to minimize any pressure. For example, lie on your right side, put a pillow near your stomach.
- Drink water. Discomfort from heartburn can always be distinguished. Therefore, if you have eaten something new that provokes heartburn, then you can drink water saturated with mineral salts.

- You can take a warm shower.
If during all the manipulations, the pain became stronger or additional symptoms appeared, then you should call an ambulance or go to the hospital yourself. nine0004
How can you tell if pain is not dangerous?
In 70% of cases, a woman can determine why her stomach hurts during pregnancy. For example, if a new product or food was consumed that provokes bloating, heartburn. These foods include onions, tomatoes, citrus fruits, milk, carbonated drinks, fried or fatty foods. Also, if a woman has a second pregnancy, then training contractions can be recognized immediately.
Any pain can be considered harmless if it does not get worse and stops after a while. If, nevertheless, you feel that the pain has a dangerous cause, then you can always consult a doctor, do an ultrasound scan and take tests. nine0004
Benefits of choosing IPF
The IPF Family Planning Institute is a specialist center for pregnancy management, examination and treatment.