Kids rash all over body
Skin rashes in children | NHS inform
Childhood rashes are common and aren't usually a cause for concern. Most rashes are harmless and disappear without the need for treatment.
However, see your GP if your child has a rash and seems unwell, or if you're worried. They'll be able to investigate the cause and recommend any necessary treatment.
This page may give you a better idea about what could be causing the rash, but don't use this to self-diagnose your child's condition – always see a GP for a proper diagnosis.
The most common causes of rashes in children are:
- cellulitis
- chickenpox
- eczema
- erythema multiforme
- hand, foot and mouth disease
- impetigo
- keratosis pilaris ("chicken skin")
- measles
- molluscum contagiosum
- pityriasis rosea
- prickly heat
- psoriasis
- ringworm
- scabies
- scarlet fever
- slapped cheek syndrome
- urticaria (hives)
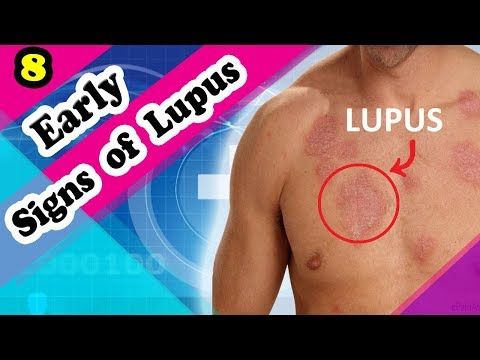
Although meningitis has become less common over recent years, it's important to be aware of the rash and the other signs and symptoms of meningitis.
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is an infection of the deeper layers of skin and underlying tissue. The affected area will be red, painful, swollen and hot. It often affects the legs, but can occur anywhere on the body. Your child will probably also have a fever.
See your GP immediately if an area of your child's skin suddenly turns red, hot and tender. If you can't see your GP on the same day, go to a walk-in centre or minor injuries unit.
Cellulitis can usually be diagnosed by assessing the symptoms and examining the skin. It usually responds well to treatment with antibiotics.
Chickenpox
Chickenpox is a viral illness that most children catch at some point. It most commonly affects children under 10 years of age.
A rash of itchy spots turns into fluid-filled blisters. They crust over to form scabs, which after a while drop off. Some children only have a few spots, whereas others have them over their entire body. The spots are most likely to appear on the face, ears and scalp, under the arms, on the chest and belly, and on the arms and legs.
There's no specific treatment for chickenpox, but you can take steps to relieve the symptoms. For example, paracetamol can help relieve fever (don't give aspirin to children under 16), and calamine lotion and cooling gels can be used to ease itching.
Read more about treating chickenpox.
Eczema
Eczema is a long-term condition that causes the skin to become itchy, red, dry and cracked. The most common type is atopic eczema, which mainly affects children but can continue into adulthood.
Atopic eczema commonly develops behind the knees or on the elbows, neck, eyes and ears. It isn't a serious condition, but if your child later becomes infected with the herpes simplex virus, it can cause the eczema to flare up into an outbreak of tiny blisters called eczema herpeticum, and will cause a fever.
About one in five children in the UK has eczema, and in eight out 10 cases it develops before the age of five, often before a child's first birthday.
Read about treating atopic eczema.
Erythema multiforme
Erythema multiforme is a skin rash (usually mild) that's caused by an allergic reaction to the herpes simplex virus.
The spots look like targets, with a dark red centre and paler ring around the outside. The hands or feet tend to be affected first, followed by the limbs, upper body and face.
Your child will probably feel unwell and may have a fever, which you should be able to treat with over-the-counter medicine. It may take from two to six weeks before they feel better. See your GP if your child has a rash and seems unwell.
In rare cases, erythema multiforme can be triggered by a reaction to certain medications, such as an antibiotic or anticonvulsant. This more severe form is called Stevens-Johnson syndrome and it can be life-threatening.
Hand, foot and mouth disease
Hand, foot and mouth disease is a common, contagious infection that causes mouth ulcers and spots and blisters on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
It's most common in young children (particularly those under 10), but it can also affect older children and adults.
There's no cure for hand, foot and mouth disease and it's easily spread, so you should keep your child away from school or nursery until they're better. Your child's immune system will fight the virus and it should clear up after about seven to 10 days.
Make sure your child drinks plenty of fluid, and if eating and swallowing is uncomfortable, give them soft foods, such as mashed potatoes, yoghurt and soup.
Impetigo
Impetigo is a common and highly contagious skin infection that causes sores and blisters. It isn't usually serious and often improves within a week of treatment. There are two types of impetigo called non-bullous and bullous.
Non-bullous impetigo typically affects the skin around the nose and mouth, causing sores that quickly burst to leave a yellow-brown crust.
Bullous impetigo typically affects the trunk (the area of the body between the waist and neck), and causes fluid-filled blisters that burst after a few days to leave a yellow crust.
See your GP or pharmacist if you think your child has impetigo. Antibiotics, in the form of a cream or tablets, will be prescribed. This should reduce the length of the illness to around seven to 10 days.
Keratosis pilaris ("chicken skin")
Keratosis pilaris is a common and harmless skin condition. The skin on the back of the upper arms becomes rough and bumpy, as if covered in permanent goose pimples. Sometimes, the buttocks, thighs, forearms and upper back can also be affected.
Keratosis pilaris typically begins in childhood and gets worse during puberty. Some people find it improves after this and may even disappear in adulthood.
There's no cure for keratosis pilaris, and it often gets better on its own without treatment. However, there are some measures you can take that may improve your child's rash, such as using non-soap cleansers rather than soap, and an emollient to moisturise their skin. Your GP or pharmacist will be able to recommend a suitable cream.
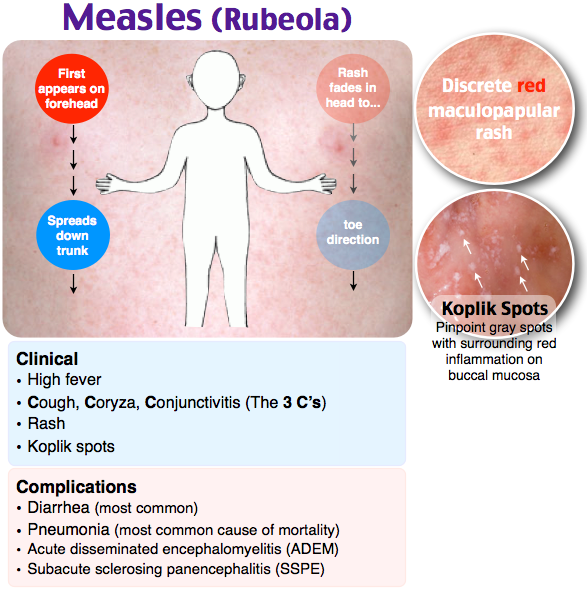
Measles
Measles is a highly infectious illness that most commonly affects young children. It's now rare in the UK because of the effectiveness of the measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) vaccine.
The measles rash is red-brown blotches. It usually starts on the head or upper neck and then spreads outwards to the rest of the body. Your child may also have a fever and cold-like symptoms.
Call your GP surgery immediately if you think your child has measles. It's best to phone before visiting because the surgery may need to make arrangements to reduce the risk of spreading the infection to others.
Measles usually passes in about seven to 10 days without causing further problems. Paracetamol or ibuprofen can be used to relieve fever, aches and pains (don't give aspirin to children under 16). Also, make sure your child drinks plenty of water to avoid dehydration.
Read more about treating measles.
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection that causes clusters of small, firm, raised spots to develop on the skin.
It commonly affects young children aged one to five years, who tend to catch it after close physical contact with another infected child.
The condition is usually painless, although some children may experience some itchiness. It usually goes away within 18 months without the need for treatment.
Molluscum contagiosum is highly infectious. However, most adults are resistant to the virus, which means they're unlikely to catch it if they come into contact with it.
Pityriasis rosea
Pityriasis rosea is a relatively common skin condition that causes a temporary rash of raised, red scaly patches to develop on the body. Most cases occur in older children and young adults (aged between 10 and 35).
The rash can be very itchy. In most cases, it clears up without treatment in 2 to 12 weeks, although in rare cases it can last up to five months.
Emollients, steroid creams and antihistamines can be used to help relieve the itchiness. The rash doesn't usually leave scars, although the skin can sometimes be discoloured afterwards.
Prickly heat (heat rash)
Prickly heat (heat rash), also known as miliaria, is an itchy rash of small, raised red spots that causes a stinging or prickly sensation on the skin.
It occurs when the sweat ducts in the outer layer of skin (epidermis) are obstructed. You can get a heat rash anywhere on your body, but the face, neck, back, chest or thighs are most often affected.
Infants can sometimes get a prickly heat rash if they sweat more than usual – for example, when it's hot and humid or if they're overdressed. It isn't a serious condition and rarely requires any specific treatment.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting (chronic) skin condition that causes red, flaky, crusty patches of skin covered with silvery scales.
The severity of psoriasis varies greatly from person to person. For some people, it's just a minor irritation, but for others it can have a major impact on their quality of life.
There's no cure for psoriasis, but there are a number of treatments that can help improve the symptoms and appearance of skin patches.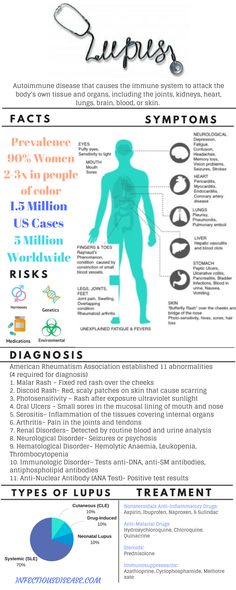 For example, topical corticosteroids are creams and ointments that can be applied to the skin.
For example, topical corticosteroids are creams and ointments that can be applied to the skin.
Ringworm
Ringworm is a highly infectious fungal skin infection that causes a ring-like red or silvery patch on the skin that can be scaly, inflamed or itchy.
Ringworm often affects the arms and legs, but it can appear almost anywhere on the body. Other similar fungal infections can affect the scalp, feet, groin and nails.
Ringworm can usually be easily treated with antifungal medicines, which are available from a pharmacy. Ringworm of the scalp can cause scaling and patches of hair loss. It's treated with antifungal tablets, often combined with antifungal shampoo.
Scabies
Scabies is a contagious skin condition that's intensely itchy. It's caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin.
In children, scabies is usually spread through prolonged periods of skin-to-skin contact with an infected adult or child – for example, during play fighting or hugging.
The mites like warm places, such as skin folds, between the fingers, under fingernails, or around the buttock creases. They leave small red blotches, which are often found on the palms of the hands or soles of the feet. In infants, blisters are commonly found on the soles of the feet.
See your GP if you think your child has scabies. It's not usually a serious condition, but it does need to be treated. Your GP will prescribe a lotion or cream. Read more about treating scabies.
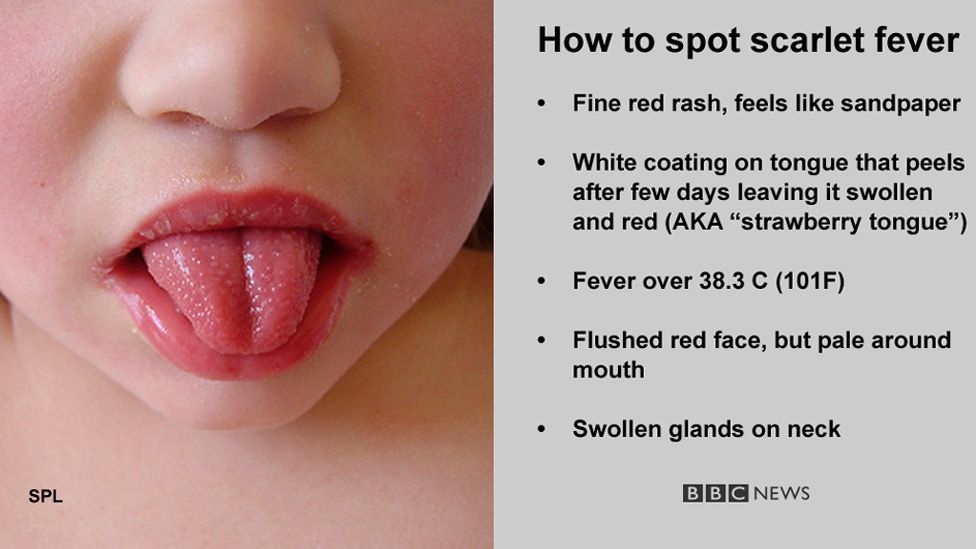
Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is a highly contagious bacterial infection that usually affects children between two and eight years of age. It causes a distinctive pink-red rash, which feels like sandpaper to touch and may be itchy.
It often starts with a sore throat, fever and headache, with the rash developing two to five days after infection. The rash usually occurs on the chest and stomach before spreading to other areas of the body, such as the ears and neck.
Scarlet fever usually clears up after about a week, but see your GP if you think your child may have it. Antibiotics are used to treat it (liquid antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin, are often used to treat children).
Antibiotics are used to treat it (liquid antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin, are often used to treat children).
Slapped cheek syndrome
Slapped cheek syndrome – also known as fifth disease or parvovirus B19 – is a viral infection that's common in children aged six to 10.
It causes a distinctive bright red rash to develop on both cheeks. This can look alarming, but it usually clears up by itself in one to three weeks.
Unless your child is feeling unwell, they don't need to stay away from school. Once the rash appears, the infection is no longer contagious. However, it's a good idea to notify your child's school about the infection.
Urticaria (hives)
Urticaria – also known as hives, weals, welts or nettle rash – is a raised, itchy rash that can affect one part of the body or be spread across large areas. It's a common skin reaction that often affects children.
Urticaria occurs when a trigger causes high levels of histamine and other chemical messengers to be released in the skin. These substances cause the blood vessels in the skin to open up, resulting in redness or pinkness, and swelling and itchiness.
These substances cause the blood vessels in the skin to open up, resulting in redness or pinkness, and swelling and itchiness.
There are many possible triggers of urticaria, including allergens, such as food or latex, irritants, such as nettles, medicines, and physical factors, such as heat or exercise. Sometimes, a cause can't be identified.
The rash is usually short-lived and mild, and can often be controlled with antihistamines.
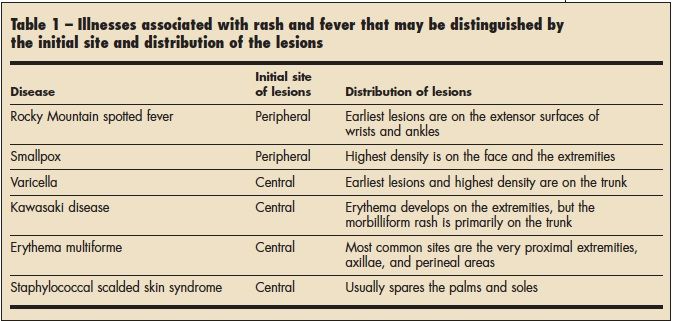
Rash or Redness - Widespread
Is this your child's symptom?
- Red or pink rash over large parts or most of the body (widespread)
- Sometimes, just on hands, feet and buttocks - but same on both sides of body
- Small spots, large spots or solid red skin
Causes of Widespread Rash or Redness
- Viral Rash. Most rashes are part of a viral illness. Viral rashes usually have small pink spots. They occur on both sides of the chest, stomach and back. Your child may also have a fever with some diarrhea or cold symptoms.
 They last 2 or 3 days. More common in the summer.
They last 2 or 3 days. More common in the summer. - Roseola. This is the most common viral rash in the first 3 years of life. (See details below).
- Chickenpox. A viral rash with a distinctive pattern. (see that Care Guide)
- Hand-Foot and-Mouth Disease. A viral rash with a distinctive pattern. It starts with tiny red spots and blisters on the palms and soles. (see that Care Guide)
- Monkeypox. A rare viral rash that often starts on the face or genital area. It then spreads to the arms and legs. Not usually seen in children unless someone in the home has monkeypox.
- Scarlet Fever. Scarlet Fever is a speckled, red rash all over. Has a sandpaper feel. Caused by the Strep bacteria. Starts on upper chest and quickly spreads to lower chest and stomach. No more serious than a Strep throat infection without a rash.
- Drug Rash. Most rashes that start while taking an antibiotic are viral rashes.
 Only 10% turn out to be allergic drug rashes. (see details below)
Only 10% turn out to be allergic drug rashes. (see details below) - Hives. Raised pink bumps with pale centers. Hives look like mosquito bites. Rashes that are bumpy and itchy are often hives. Most cases of hives are caused by a virus. Hives can also be an allergic reaction. (See that Care Guide for details)
- Heat Rash. A fine pink rash caused by overheating. Mainly involves neck, chest and upper back.
- Insect Bites. Insect bites cause small red bumps. Flying insects can cause many bumps on exposed skin. Non-flying insects are more likely to cause localized bumps.
- Hot Tub Rash. Causes small red bumps that are painful and itchy. Mainly occurs on skin covered by a bathing suit. Rash starts 12-48 hours after being in hot tub. Caused by overgrowth of bacteria in hot tubs.
- Petechiae Rash (Serious). Petechiae are purple or dark red colored tiny dots. They come from bleeding into the skin.
 Scattered petechiae with a fever are caused by Meningococcemia until proven otherwise. This is a life-threatening bacterial infection of the bloodstream. Peak age is 3 to 6 months old. Unlike most pink rashes, petechiae don't fade when pressed on.
Scattered petechiae with a fever are caused by Meningococcemia until proven otherwise. This is a life-threatening bacterial infection of the bloodstream. Peak age is 3 to 6 months old. Unlike most pink rashes, petechiae don't fade when pressed on. - Purpura Rash (Serious). Purpura means bleeding into the skin. It looks like purple or dark red larger spots. Widespread purpura is always an emergency. It can be caused by a bacterial bloodstream infection. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever is an example.
- Blister Rash (Serious). Widespread blisters on the skin are a serious sign. It can be caused by infections or drugs. Stevens Johnson Syndrome is an example.
- Caution. All widespread rashes with fever need to be seen. They need to be diagnosed. Reason: some serious infections that can cause this type of rash.
Drugs and Rashes
- Prescription medicines sometimes cause widespread rashes. Some are allergic, but most are not.

- Non-prescription (OTC) medicines rarely cause any rashes.
- Most rashes that occur while taking an OTC medicine are viral rashes.
- Fever medicines (acetaminophen and ibuprofen) cause the most needless worry. Reason: most viral rashes start with a fever. Hence, the child is taking a fever medicine when the rash starts.
- Drug rashes can't be diagnosed over the phone.
Roseola - A Classic Rash
- Most children get Roseola between 6 months and 3 years of age.
- Rash: pink, small, flat spots on the chest and stomach. Then spreads to the face.
- Classic feature: 3 to 5 days of high fever without a rash or other symptoms.
- The rash starts 12 to 24 hours after the fever goes away.
- The rash lasts 1 to 3 days.
- By the time the rash appears, the child feels fine.
- Treatment: the rash is harmless. Creams or medicines are not needed.
Localized Versus Widespread Rash: How to Decide
- Localized means the rash occurs on one small part of the body.
 Usually, the rash is just on one side of the body. An example is a rash on 1 foot. Exceptions: athlete's foot can occur on both feet. Insect bites can be scattered.
Usually, the rash is just on one side of the body. An example is a rash on 1 foot. Exceptions: athlete's foot can occur on both feet. Insect bites can be scattered. - Widespread means the rash occurs on larger areas. Examples are both legs or the entire back. Widespread can also mean on most of the body surface. Widespread rashes always occur on matching (both) sides of the body. Many viral rashes are on the chest, stomach and back.
- The cause of a widespread rash usually spreads through the blood stream. Examples are rashes caused by viruses, bacteria, toxins, and food or drug allergies.
- The cause of a localized rash usually is just from contact with the skin. Examples are rashes caused by chemicals, allergens, insect bites, ringworm fungus, bacteria or irritants.
- This is why it's important to make this distinction.
When to Call for Rash or Redness - Widespread
Call 911 Now
- Purple or blood-colored spots or tiny dots with fever within the last 24 hours
- Trouble breathing or swallowing
- Not moving or too weak to stand
- You think your child has a life-threatening emergency
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Bright red skin that peels off in sheets
- Large blisters on skin
- Bloody crusts on the lips
- Taking a prescription medication within the last 3 days
- Fever
- Your daughter is having her period and using tampons
- Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- Widespread rash, but none of the symptoms above.
 Reason: all widespread rashes need to be checked by a doctor.
Reason: all widespread rashes need to be checked by a doctor.
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
Care Advice for Widespread Rashes
- What You Should Know About Widespread Rashes:
- Most rashes with small pink spots all over are part of a viral illness.
- This is more likely if your child has a fever.
 Other symptoms (like diarrhea) also point to a viral rash.
Other symptoms (like diarrhea) also point to a viral rash. - Here is some care advice that should help until you talk with your doctor.
- Non-Itchy Rash Treatment:
- If you suspect a heat rash, give a cool bath.
- Otherwise, no treatment is needed.
- Itchy Rash Treatment:
- Wash the skin once with soap to remove any irritants.
- Steroid Cream. For relief of itching, use 1% hydrocortisone cream (such as Cortaid). Put it on the most itchy areas. No prescription is needed. Do this 3 times per day.
- Cool Bath. For flare-ups of itching, give your child a cool bath. Do not use soap. Do this for 10 minutes. Caution: avoid any chill. Option: Can add 2 ounces (60 mL) of baking soda per tub.
- Scratching. Try to keep your child from scratching. Cut the fingernails short. Reason: prevents a skin infection from bacteria.
- Allergy Medicine for Itching.
 If itching becomes severe, give an allergy medicine, such as Benadryl. No prescription is needed. Age limit: 1 and older. If needed longer than a few days, switch to a long-acting antihistamine, such as Zyrtec. Age limit: 2 and older.
If itching becomes severe, give an allergy medicine, such as Benadryl. No prescription is needed. Age limit: 1 and older. If needed longer than a few days, switch to a long-acting antihistamine, such as Zyrtec. Age limit: 2 and older.
- Fever Medicine:
- For fevers above 102° F (39° C), give an acetaminophen product (such as Tylenol).
- Another choice is an ibuprofen product (such as Advil).
- Note: Fevers less than 102° F (39° C) are important for fighting infections.
- For all fevers: Keep your child well hydrated. Give lots of cold fluids.
- Return to School:
- Most viral rashes can be spread to others (especially if a fever is present).
- If your child has a fever, avoid contact with other children. Also, avoid pregnant women until a diagnosis is made.
- For minor rashes, your child can return after the fever is gone.
- For major rashes, your child can return to school after the rash is gone.
 If your doctor has given medical clearance, your child can return sooner.
If your doctor has given medical clearance, your child can return sooner.
- What to Expect:
- Most viral rashes go away within 48 hours.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.
Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 01/07/2023
Last Revised: 12/30/2022
Copyright 2000-2023. Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Rash in a child on the body, legs, back
We treat children according to the principles of evidence-based medicine: we choose only those diagnostic and treatment methods that have proven their effectiveness. We will never prescribe unnecessary examinations and medicines!
Make an appointment via WhatsApp
Prices Doctors
The first children's clinic of evidence-based medicine in Moscow
No unnecessary examinations and medicines! We will prescribe only what has proven effective and will help your child.
Treatment according to world standards
We treat children with the same quality as in the best medical centers in the world.
The best team of doctors in Fantasy!
Pediatricians and subspecialists Fantasy - highly experienced doctors, members of professional societies. Doctors constantly improve their qualifications, undergo internships abroad.
Ultimate treatment safety
We made pediatric medicine safe! All our staff work according to the strictest international standards JCI
We have fun, like visiting best friends
Game room, cheerful animator, gifts after the reception. We try to make friends with the child and do everything to make the little patient feel comfortable with us.
You can make an appointment by calling or by filling out the form on the website
Other Pediatric services
- Pediatrician's consultation
- Child Health Management Program
Frequent calls
- Acute bronchiolitis in children: diagnosis and treatment
- SARS
- Angina streptococcal tonsillitis
- Frequently ill child nine0034
- Intestinal infections
- Pneumonia (pneumonia) in children
- Colic
- Feeding problems
- Prolonged cough in a child: diagnosis and treatment
- Acute bronchitis in children: diagnosis and treatment
- Pneumonia (pneumonia) in children: diagnosis and treatment nine0034
- False croup in a child
- Coxsackie virus in a child
- The child was bitten by a tick! What to do?
Online payment
Documents online
Online services
- nine0079
Rashes on the child's body
Many parents have noticed suspicious rashes on the body of their children.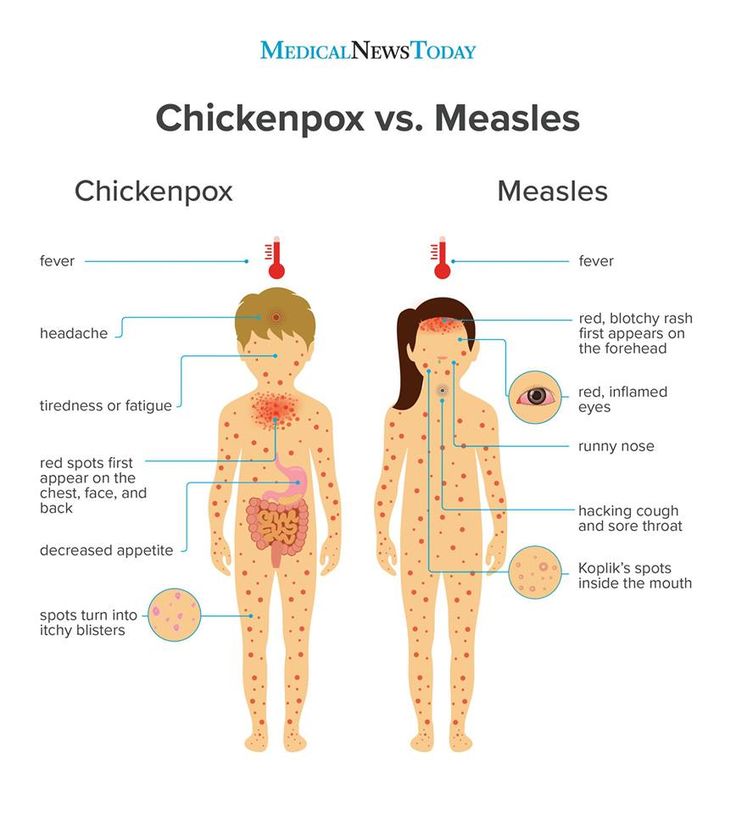 This symptom indicates the presence of any disease of the body or simply its painful condition. In any case, a rash on a child's body can be very dangerous. Therefore, if you notice a rash on the skin, you should immediately make an appointment with the child's pediatrician. nine0003
This symptom indicates the presence of any disease of the body or simply its painful condition. In any case, a rash on a child's body can be very dangerous. Therefore, if you notice a rash on the skin, you should immediately make an appointment with the child's pediatrician. nine0003
Help with rashes
Make an appointment with a doctor
Online appointment
Phones:
+7 (812) 30-888-03
+7 (812) 242-53-50 Clinic address: 900 900 50 Petersburg, Vyborgsky district, st. Asafiev, 9, building 2, lit. A (metro station Ozerki, metro station Prosveshcheniya)
Causes of rashes
A rash in children can appear for various reasons. The most “safe” case is when rashes appear due to poor hygiene. In addition, the cause of the rash is allergies, blood diseases, cardiovascular diseases, as well as infections and microbes. In the case of an infection, a rash is not the only symptom: fever, runny nose, sore throat, severe cough, chills, etc. are added to it. Often infections are accompanied by indigestion and vomiting. The rash in such cases does not occur immediately, but appears after a few days. nine0003
Often infections are accompanied by indigestion and vomiting. The rash in such cases does not occur immediately, but appears after a few days. nine0003
Rash most often occurs as a symptom of diseases that are commonly referred to as "children's". We are talking about chicken pox, rubella, measles, scarlet fever and some other infections that people get sick, mainly in childhood. Moreover, depending on the disease, the nature of the rash changes, so that doctors can diagnose only one type of rash. The most dangerous rash, which refers to the symptoms of meningitis.
Diseases causing rashes on the skin of children
Let's analyze the types of rash in a child in more detail, depending on the disease.
- Chicken pox. Perhaps the most famous disease that is accompanied by a rash. With chickenpox, reddish spots appear on the entire surface of the body, which grow and become bubbles filled with a clear liquid. The growth of the bubbles is accompanied by itching, but over time they dry out and fall off, sometimes leaving characteristic “pockmarks”.
 Chicken pox often causes fever, and doctors recommend treating blisters of the rash with brilliant green. nine0034
Chicken pox often causes fever, and doctors recommend treating blisters of the rash with brilliant green. nine0034 - Measles. Initially, a rash in the form of large red spots appears on the face, but literally within 2-3 days it spreads “from top to bottom” along the body to the very legs. In addition, the child begins to have a sore throat, runny nose and cough, and the temperature rises. The largest spots merge into large inflamed areas.
- Meningococcal infection. The most dangerous infection, as it causes meningitis. It is very important to recognize the disease in time, as it develops very quickly. The rash is expressed in the form of large spots resembling bruises. If you see a doctor as soon as possible, the chances of a cure are very high. nine0034
- Rubella. The rash is accompanied by fever and inflammation of the lymph nodes. A rash on the body of a child in the form of small red spots appears mainly on the buttocks and in the places where the limbs are bent.
 After a few days, the rash disappears without leaving any consequences.
After a few days, the rash disappears without leaving any consequences. - Scarlet fever. With scarlet fever, a rash in the form of small pimples appears on the second day all over the body, but their highest concentration is noted in the groin, in the places of the folds of the arms and legs and in the lower abdomen. After a few days, the rash disappears, and the skin in these places begins to peel off strongly. Also during the peak of the disease, swelling, rash and redness of the entire skin are noted. nine0034
- Enteroviral infection. Redness and rash appear on the third day after infection and last for about two to three days. Their other symptoms, doctors note vomiting, diarrhea, fever and general weakness of the body.
- Parasites. In this case, the rash is not caused by infections, but by scabies mites or other parasites that live on the human body. The scabies mite "drills" holes in the skin, leaving entrances and exits in the form of dots. The most “attractive” parts of the body for a tick are places with thin skin: groin, wrists, areas between fingers, etc.
 Since the tick can be transmitted from one person to another, urgent treatment is necessary after the detection of this pathology. nine0034
Since the tick can be transmitted from one person to another, urgent treatment is necessary after the detection of this pathology. nine0034 - Cardiovascular diseases. As a rule, these diseases are not typical for children, although they occur in them. Vascular disease can be recognized by small hemorrhages under the skin. Larger areas form bruises.
Other causes of rashes
Sometimes, even with all the rules of hygiene and the absence of diseases, a rash on the body of a child appears with enviable regularity. In this case, it is most likely an allergic reaction of the body to various substances. If this is true, then allergies can be recognized by other symptoms that will inevitably appear along with the rash: a runny nose, cough, tears, and itching. Also, a rash on the body of a child may appear from burns by plants or insect bites. Even a simple mosquito bite often causes a severe rash in children, which is accompanied by itching. nine0003
And, of course, very often a rash appears due to poor hygiene. Unlike adults, children's skin is much thinner and more delicate, so even a short-term lack of care for it can lead to a rash. Children, especially the smallest, should be washed and washed regularly. But wearing a lot of clothes on him or leaving him in wet diapers is not worth it - this can lead to diaper rash, irritation, and a rash.
Unlike adults, children's skin is much thinner and more delicate, so even a short-term lack of care for it can lead to a rash. Children, especially the smallest, should be washed and washed regularly. But wearing a lot of clothes on him or leaving him in wet diapers is not worth it - this can lead to diaper rash, irritation, and a rash.
Rash Help
If you find a rash on your child's body, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. You can make an appointment at our Poem Health clinic. In addition, you can call a doctor at home if the child is in a serious condition. Moreover, sometimes a doctor's house call is mandatory, since many diseases with symptoms in the form of a rash are easily transmitted to such children. You need to be especially careful with rubella, as it seriously affects the health of pregnant women. And if you suspect meningitis, you need to call not just a doctor, but an ambulance team. nine0003
Do not try to get rid of the rash on your own before seeing a doctor.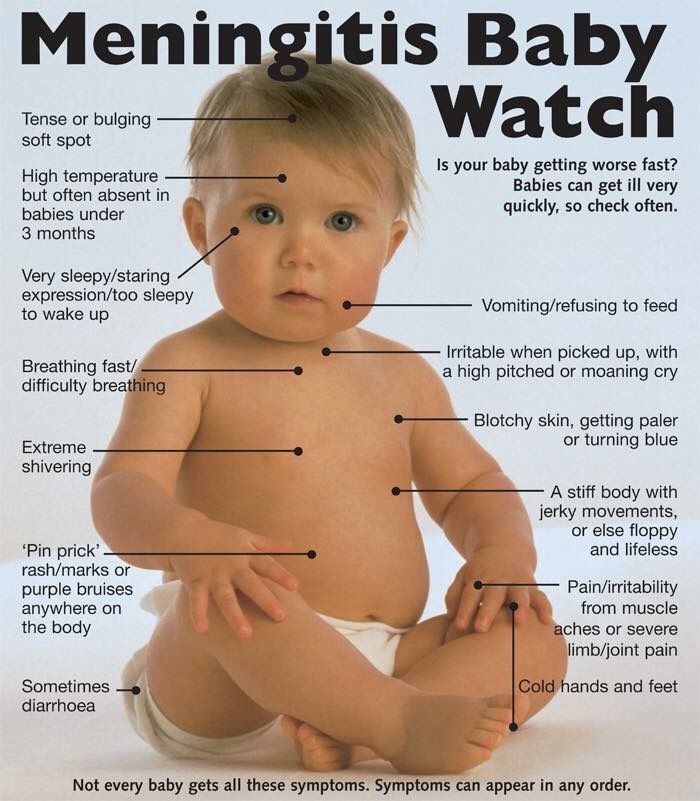 Firstly, it will make it difficult for a doctor to determine the diagnosis. Secondly, it can lead to even more rashes in the child. It is best to wait for the examination of the doctor and listen to his recommendations for further treatment of the rash. Bacterial rashes are treated with antibiotics, scabies - with special means against ticks, allergies - with appropriate drugs with isolation from the source of allergies, etc. More complex treatment is needed for cardiovascular diseases, but, in the end, a rash on the body of a child is always treated successfully. nine0003
Firstly, it will make it difficult for a doctor to determine the diagnosis. Secondly, it can lead to even more rashes in the child. It is best to wait for the examination of the doctor and listen to his recommendations for further treatment of the rash. Bacterial rashes are treated with antibiotics, scabies - with special means against ticks, allergies - with appropriate drugs with isolation from the source of allergies, etc. More complex treatment is needed for cardiovascular diseases, but, in the end, a rash on the body of a child is always treated successfully. nine0003
Rash Prevention
To avoid a rash on the body, you need to take steps to prevent it. First of all, we are talking about the basic rules of personal hygiene. At the earliest age, parents should take care of this, later they should teach this to their child as early as possible. Compliance with hygiene helps to get rid of not only rashes, sweating and dirt, but also prevents many infectious diseases.