How to qualify for full child tax credit
2022 Child Tax Credit: Requirements, How to Claim
You’re our first priority.
Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners.
Taxpayers may be eligible for a credit of up to $2,000 — and $1,500 of that may be refundable.
By
Sabrina Parys
Sabrina Parys
Content Management Specialist | Taxes, investing
Sabrina Parys is a content management specialist on the taxes and investing team. Her previous experience includes five years as a project manager, copy editor and associate editor in academic and educational publishing. Sabrina earned a master's degree in publishing at Portland State University.
Learn More
and
Tina Orem
Tina Orem
Senior Writer/Spokesperson | Small business, taxes
Tina Orem covers small business and taxes at NerdWallet. She has a degree in finance, as well as a master's degree in journalism and a Master of Business Administration. Her work has appeared in a variety of local and national media outlets. Email: <a href="mailto:[email protected]">[email protected]</a>.
Learn More
Edited by Arielle O'Shea
Arielle O'Shea
Lead Assigning Editor | Retirement planning, investment management, investment accounts
Arielle O’Shea leads the investing and taxes team at NerdWallet. She has covered personal finance and investing for 15 years, previously as a researcher and reporter for leading personal finance journalist and author Jean Chatzky. Arielle has appeared as a financial expert on the "Today" show, NBC News and ABC's "World News Tonight," and has been quoted in national publications including The New York Times, MarketWatch and Bloomberg News. Email: <a href="mailto:[email protected]">[email protected]</a>.
She has covered personal finance and investing for 15 years, previously as a researcher and reporter for leading personal finance journalist and author Jean Chatzky. Arielle has appeared as a financial expert on the "Today" show, NBC News and ABC's "World News Tonight," and has been quoted in national publications including The New York Times, MarketWatch and Bloomberg News. Email: <a href="mailto:[email protected]">[email protected]</a>.
Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This may influence which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money.
This article has been updated for the 2022 tax year.
The child tax credit is a federal tax benefit that plays an important role in providing financial support for American taxpayers with children. People with kids under the age of 17 may be eligible to claim a tax credit of up to $2,000 per qualifying dependent when they file their 2022 tax returns in 2023. $1,500 of that credit may be refundable
People with kids under the age of 17 may be eligible to claim a tax credit of up to $2,000 per qualifying dependent when they file their 2022 tax returns in 2023. $1,500 of that credit may be refundable
We’ll cover who qualifies, how to claim it and how much you might receive per child.
What is the child tax credit?
The child tax credit, commonly referred to as the CTC, is a tax credit available to taxpayers with dependent children under the age of 17. In order to claim the credit when you file your taxes, you have to prove to the IRS that you and your child meet specific criteria.
You’ll also need to show that your income falls beneath a certain threshold because the credit phases out in increments after a certain limit is hit. If your modified adjusted gross income exceeds the ceiling, the credit amount you get may be smaller, or you may be deemed ineligible altogether.
Who qualifies for the child tax credit?
Taxpayers can claim the child tax credit for the 2022 tax year when they file their tax returns in 2023.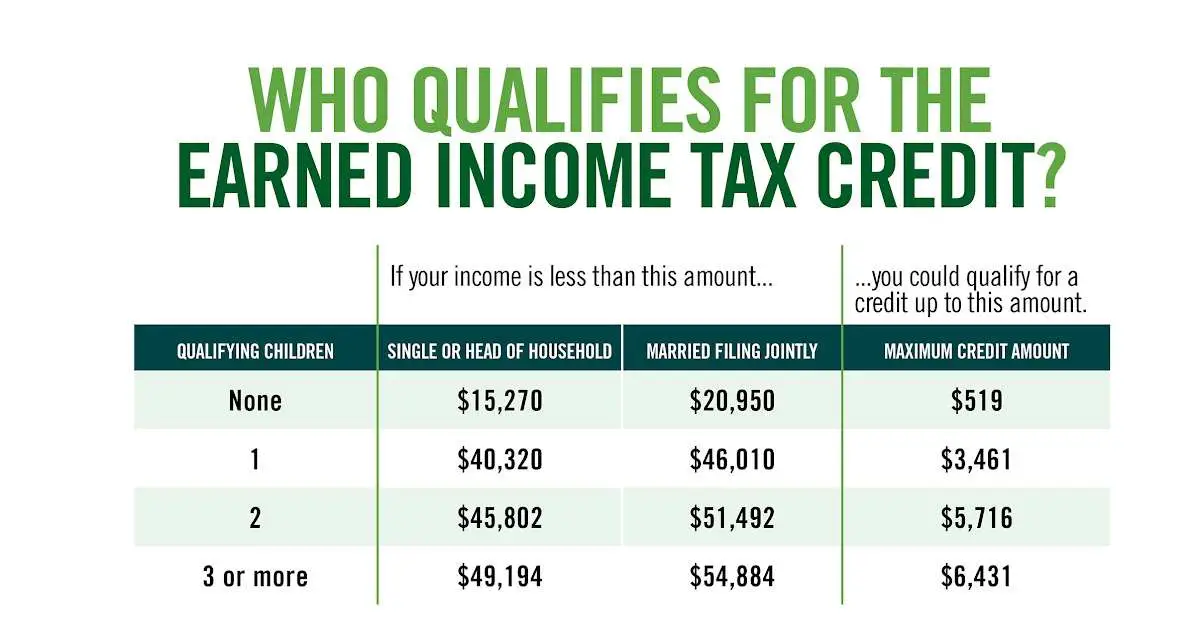 Generally, there are seven “tests” you and your qualifying child need to pass.
Generally, there are seven “tests” you and your qualifying child need to pass.
Age: Your child must have been under the age of 17 at the end of 2022.
Relationship: The child you’re claiming must be your son, daughter, stepchild, foster child, brother, sister, half brother, half sister, stepbrother, stepsister or a descendant of any of those people (e.g., a grandchild, niece or nephew).
Dependent status: You must be able to properly claim the child as a dependent. The child also cannot file a joint tax return, unless they file it to claim a refund of withheld income taxes or estimated taxes paid.
Residency: The child you’re claiming must have lived with you for at least half the year (there are some exceptions to this rule).
Financial support: You must have provided at least half of the child’s support during the last year. In other words, if your qualified child financially supported themselves for more than six months, they’re likely considered not qualified.
Citizenship: Per the IRS, your child must be a "U.S. citizen, U.S. national or U.S. resident alien," and must hold a valid Social Security number.
Income: Parents or caregivers claiming the credit also typically can’t exceed certain income requirements. Depending on how much your income exceeds that threshold, the credit gets incrementally reduced until it is eliminated.
Did you know...
If your child or a relative you care for doesn't quite meet the criteria for the CTC but you are able to claim them as a dependent, you may be eligible for a $500 nonrefundable credit called the "credit for other dependents." Check the IRS website for more information.
How to calculate the child tax credit
For the 2022 tax year, the CTC is worth $2,000 per qualifying dependent child if your modified adjusted gross income is $400,000 or below (married filing jointly) or $200,000 or below (all other filers). If your MAGI exceeds those limits, your credit amount will be reduced by $50 for each $1,000 of income exceeding the threshold until it is eliminated.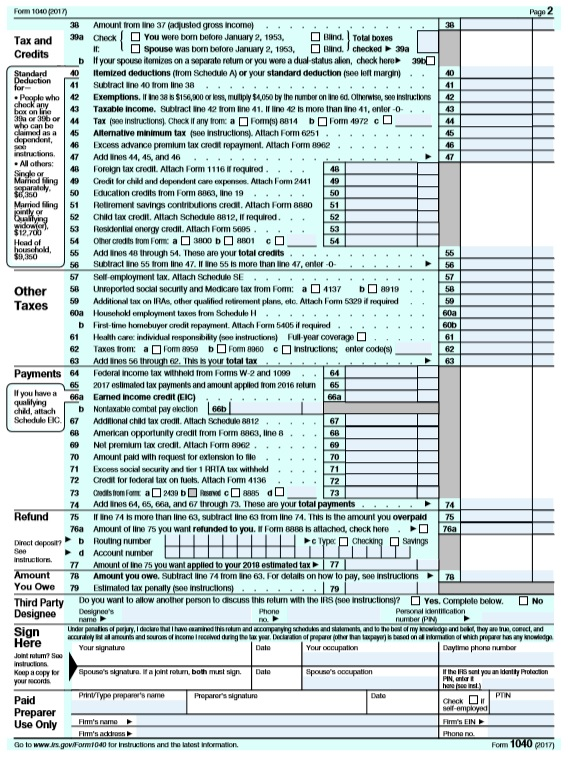
The CTC is also partially refundable; that is, it can reduce your tax bill on a dollar-for-dollar basis, and you might be able to apply for a tax refund of up to $1,500 for anything left over. This partially refundable portion is called the “additional child tax credit” by the IRS.
How to claim the credit
You can claim the child tax credit on your Form 1040 or 1040-SR. You’ll also need to fill out Schedule 8812 (“Credits for Qualifying Children and Other Dependents”), which is submitted alongside your 1040. This schedule will help you to figure your child tax credit amount, and if applicable, how much of the partial refund you may be able to claim.
Most quality tax software guides you through claiming the child tax credit with a series of interview questions, simplifying the process and even auto-filling the forms on your behalf. If your income falls below a certain threshold, you might also be able to get free tax software through IRS’ Free File.
🤓Nerdy Tip
If you applied for the additional child tax credit, by law the IRS cannot release your refund before mid-February.
Consequences of a CTC-related error
An error on your tax form can mean delays on your refund or on the child tax credit part of your refund. In some cases, it can also mean the IRS could deny the entire credit.
If the IRS denies your CTC claim:
You must pay back any CTC amount you’ve been paid in error, plus interest.
You might need to file Form 8862, "Information To Claim Certain Credits After Disallowance," before you can claim the CTC again.
If the IRS determines that your claim for the credit is erroneous, you may be on the hook for a penalty of up to 20% of the credit amount claimed.
State child tax credits
In addition to the federal child tax credit, a few states, including California, New York and Massachusetts, also offer their own state-level CTCs that you may be able to claim when filing your state return. Visit your state's department of taxation website for more details.
Visit your state's department of taxation website for more details.
History of the CTC
Like other tax credits, the CTC has seen its share of changes throughout the years. In 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, or TCJA, established specific parameters for claiming the credit that will be effective from the 2018 through 2025 tax years. However, the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 (the coronavirus relief bill) temporarily modified the credit for the 2021 tax year, which has caused some confusion as to which changes are permanent.
Here's a brief timeline of its history.
1997: First introduced as a $500 nonrefundable credit by the Taxpayer Relief Act.
2001: Credit increased to $1,000 per dependent and made partially refundable by the Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act.
2017: The TCJA made several changes to the credit, effective from 2018 through 2025. This included increasing the credit ceiling to $2,000 per dependent, establishing a new income threshold to qualify and ensuring that the partially refundable portion of the credit gets adjusted for inflation each tax year.

2021: The American Rescue Plan Act made several temporary modifications to the credit for the 2021 tax year only. This included expanding the credit to a maximum of $3,600 per qualifying child, allowing 17-year-olds to qualify, and making the credit fully refundable. And for the first time in U.S. history, many taxpayers also received half of the credit as advance monthly payments from July through December 2021.
2022–2025: The 2021 ARPA enhancements ended, and the credit will revert back to the rules established by the TCJA — including the $2,000 cap for each qualifying child.
Frequently asked questions
Does the child tax credit include advanced payments this year?
The American Rescue Plan Act made several temporary modifications to the credit for tax year 2021, including issuing a set of advance payments from July through December 2021. This enhancement has not been carried over for this tax year as of this writing.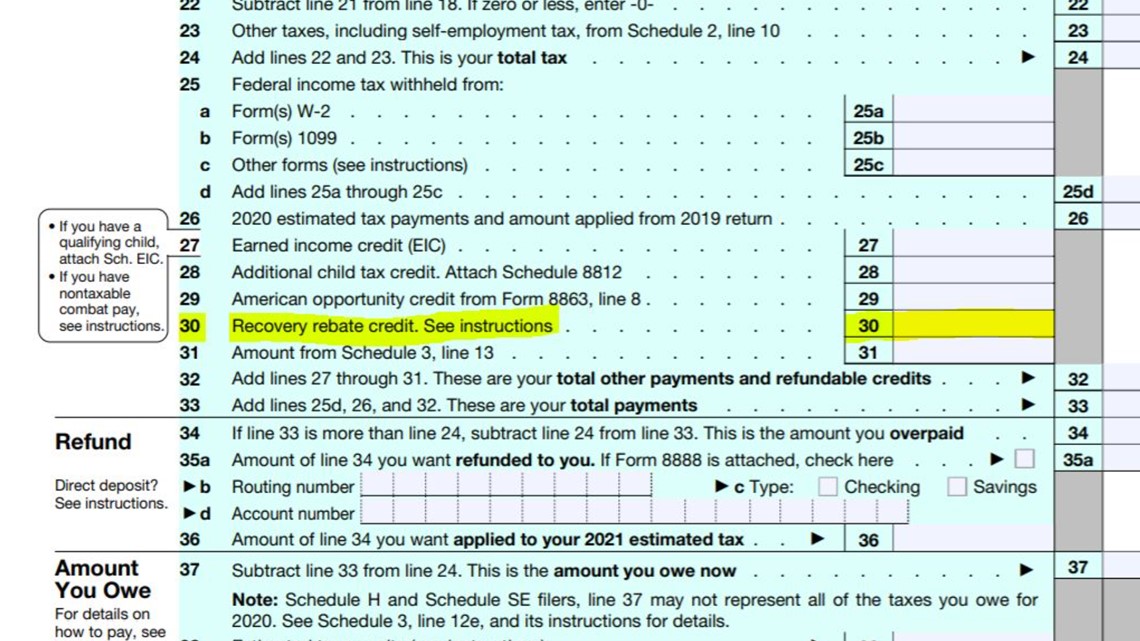
Is the child tax credit taxable?
No. It is a partially refundable tax credit. This means that it can lower your tax bill by the credit amount, and if you have no liability, you may be able to get a portion of the credit back in the form of a refund.
Is the child tax credit the same thing as the child and dependent care credit?
No. This is another type of tax benefit for taxpayers with children or qualifying dependents. It covers a percentage of expenses you made for care — such as day care, certain types of camp or babysitters — so that you can work or look for work. The IRS has more details here.
I had a baby in 2022. Am I eligible to claim the child tax credit when I file in 2023?
If you also meet the other requirements, yes. You'll also need to make sure your child has a Social Security number by the due date of your 2022 return (including extensions).
About the authors: Sabrina Parys is a content management specialist at NerdWallet. Read more
Read more
Tina Orem is NerdWallet's authority on taxes and small business. Her work has appeared in a variety of local and national outlets. Read more
On a similar note...
Get more smart money moves – straight to your inbox
Sign up and we’ll send you Nerdy articles about the money topics that matter most to you along with other ways to help you get more from your money.
Tax Credits vs. Tax Deductions
You’re our first priority.
Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners.
Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners.
Tax deductions reduce your taxable income, but tax credits reduce your bill dollar for dollar.
Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This may influence which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money.
Tax credits and tax deductions may be the most satisfying part of preparing your tax return. Both reduce your tax bill, but in very different ways.
Tax credits directly reduce the amount of tax you owe, giving you a dollar-for-dollar reduction of your tax liability. A tax credit valued at $1,000, for instance, lowers your tax bill by the corresponding $1,000.
Tax deductions, on the other hand, reduce how much of your income is subject to taxes. Deductions lower your taxable income by the percentage of your highest federal income tax bracket. So if you fall into the 22% tax bracket, a $1,000 deduction saves you $220.
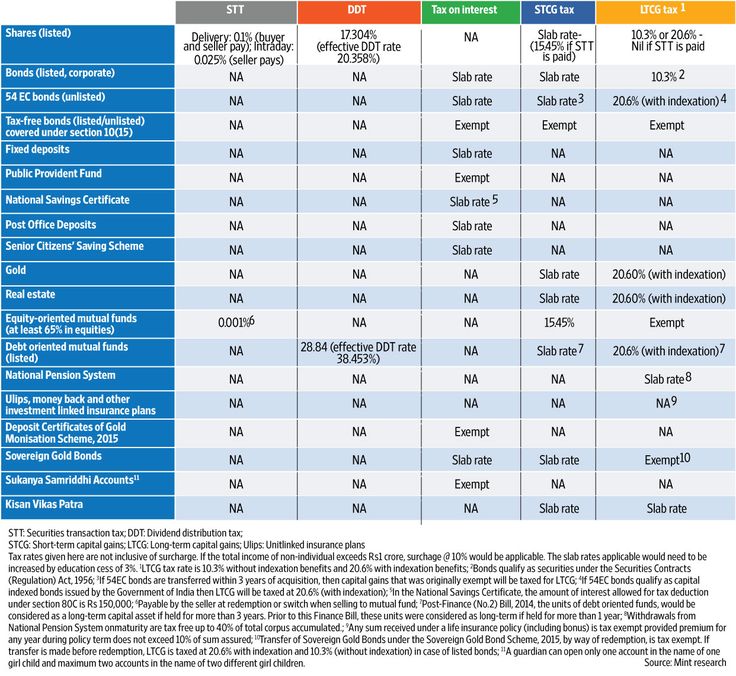
Would you rather have: | ||
A $10,000 tax deduction… | …or a $10,000 tax credit? | |
Your AGI | $100,000 | $100,000 |
Less: tax deduction | ($10,000) | |
Taxable income | $90,000 | $100,000 |
Tax rate* | ||
Calculated tax | $22,500 | $25,000 |
Less: tax credit | ($10,000) | |
Your tax bill | $22,500 | $15,000 |
The catch to tax credits
Some tax credits are nonrefundable.
 That means that if you don’t owe a lot in taxes to begin with, you don’t get the full value if the credits take your tax bill below zero. In other words, a $600 tax bill combined with a $1,000 nonrefundable credit doesn’t get you a $400 tax refund check.
That means that if you don’t owe a lot in taxes to begin with, you don’t get the full value if the credits take your tax bill below zero. In other words, a $600 tax bill combined with a $1,000 nonrefundable credit doesn’t get you a $400 tax refund check.Some tax credits are refundable. If you qualify to take refundable tax credits — things such as the earned income tax credit or the child tax credit — the value of the credit goes beyond your tax liability and can result in a refund check.
The IRS lays out specific criteria you must meet to qualify for both nonrefundable and refundable credits.
A big decision about tax deductions
There are two types of tax-deduction strategies: taking the standard deduction or itemizing.
The standard deduction
The standard deduction is a one-size-fits-all reduction in the amount of your income that’s subject to tax.
 You don’t have to do anything to qualify for the standard deduction or provide any documentation.
You don’t have to do anything to qualify for the standard deduction or provide any documentation.You can claim the standard deduction on Form 1040. The amount varies depending on your filing status.
Filing status | 2021 tax year | 2022 tax year |
|---|---|---|
Single | $12,550 | $12,950 |
Married, filing jointly | $25,100 | $25,900 |
Married, filing separately | $12,550 | $12,950 |
Head of household | $18,800 | $19,400 |
Itemizing
Itemizing allows you to take advantage of deductions such as home mortgage interest, medical expenses or charitable donations. If together your itemized deductions exceed the value of the standard deduction, you'll want to itemize so you pay less tax.
 You'll need to use the regular Form 1040 and Schedule A.
You'll need to use the regular Form 1040 and Schedule A.Just as with tax credits, taking certain deductions requires meeting certain qualifications based on your filing status, current life events and the amount of your income that’s taxable. Be sure you meet IRS criteria to qualify for both tax credits and deductions.
Promotion: NerdWallet users get 25% off federal and state filing costs. | |
Promotion: NerdWallet users can save up to $15 on TurboTax. | |
|
On a similar note...
Get more smart money moves – straight to your inbox
Sign up and we’ll send you Nerdy articles about the money topics that matter most to you along with other ways to help you get more from your money.
Tax deduction - Medline Clinic in Barnaul
Have you paid taxes? Take them back to the state!
A significant part of the Russian population pays taxes. However, this amount can be reduced. There is a tax deduction for this. What's this? When making such a deduction, the state reduces the amount on which taxes are paid. It is also called the return of a certain part of the previously paid personal income tax (personal income tax) when buying real estate, spending on treatment or training. It is important to note that you can get a tax deduction not only when paying for your examinations and medicines. The tax is returned even from the amount of expenses for the treatment of close relatives
It is important to note that you can get a tax deduction not only when paying for your examinations and medicines. The tax is returned even from the amount of expenses for the treatment of close relatives
What expenses can be included in the deduction for treatment
The following expenses can be included in the deduction:
- Medical services - tests, examinations, doctor's appointments, procedures in paid clinics. Provided that you paid for it, that is, the services are not under the CHI policy, but at your expense.
- Prescribed medicines. Starting in 2019, you can get a deduction for the cost of any drug, not just those on the government's list. nine0022 Expensive treatment. This is the only type of medical expenses for which there is no limit: any amount is accepted for deduction without restrictions. Types of expensive treatment are in a special list, this is followed by a medical organization when it issues a certificate of the cost of services.
- Contributions under the VHI agreement.

Relatives for which the deduction for treatment is given
The deduction for treatment can be received not only when paying for your examinations and medicines. The tax is returned even from the amount of expenses for the treatment of close relatives, but not any, but only from a limited list. nine0004
Here is a complete list of relatives whose treatment can be included in your tax deduction:
- Parents. The deduction will be given only when paying for the treatment of their parents. If you pay for the spouse's parents or adoptive parents, the tax will not be refunded. There are no parental requirements. They can work under an employment contract, or they can be pensioners, unemployed or self-employed individual entrepreneurs.
- Children or wards under 18 years of age. The deduction for treatment is only for your children. If you pay for tests and examinations of your spouse's children, even when they are fully supported, personal income tax cannot be returned.
 There is also an important condition regarding age: the child must be no more than 18 years old. Moreover, the fact of studying at a full-time university does not extend this age to 24 years: this is possible with education, but with treatment - only up to 18 years. nine0023
There is also an important condition regarding age: the child must be no more than 18 years old. Moreover, the fact of studying at a full-time university does not extend this age to 24 years: this is possible with education, but with treatment - only up to 18 years. nine0023 - Spouses. If a husband pays for his wife, he can get a deduction. And the wife will return the tax when paying for the treatment of her husband. But the marriage must be officially registered. A certificate of payment for medical services and checks for the purchase of drugs can be issued to any spouse: their expenses are still considered general.
You cannot get a deduction for other relatives. Unlike training, there are no siblings on this list. If you pay for dental treatment or surgery for your sister, you will not receive a deduction. For grandparents, common-law spouse, children of the wife from the first marriage, nephews or mother-in-law, the tax cannot be refunded. nine0004
The list of relatives is closed and there can be no additional conditions.
How to return money for treatment
How much money can be returned when paying for the treatment of relatives
Cost limit. The deduction for treatment has a limit - 120,000 R per year. This is a general limit for several social deductions, for example, it also includes tuition costs. 120,000 R is a restriction not for each type of expense, but for all.
Here are the expenses that will be included in the limit:
- Training.
- Treatment.
- DMS.
- Voluntary contributions to pensions.
- Voluntary life insurance.
- Additional contributions to the funded part of the pension.
- Independent qualification assessment.
When paying for the treatment of relatives, an additional deduction will not be given: both your own and their expenses must be included in this limit.
120,000 R does not include only the cost of educating children - there is a separate limit of 50,000 R for each child - and expensive types of treatment that are accepted for deduction without taking into account the limit. There is also a social deduction for charity, but it has separate conditions and the limit is calculated as a percentage.
There is also a social deduction for charity, but it has separate conditions and the limit is calculated as a percentage.
How much money will be returned
The amount of the deduction depends on your salary and the cost of treatment. In any case, the tax office will not return more money than the personal income tax paid for the year. Let's look at an example:
Vasily works as a manager and receives 40,000 R per month. In a year, he earned 480,000 R. He gives 13% of his salary to the state as a tax (personal income tax). For the year he paid 480,000 × 0.13 = 62,400 R.
In 2015, he spent 80,000 RUR on treatment. Vasily collected documents and applied for a tax deduction. After submitting the application, the tax authority will deduct the amount of treatment from Vasily’s income for the year and recalculate his personal income tax: (480,000 − 80,000) × 0.13 = 52,000 R.
It turns out that Vasily had to pay 52,000 R, but in fact he paid 62,400 R. The tax office will return the overpayment to him: 62,400 − 52,000 = 10,400 R.
The tax office will return the overpayment to him: 62,400 − 52,000 = 10,400 R.
The deduction can be made within three years following the year of treatment payment.
This money will go directly to the card, but you will have to wait.
How to draw up documents if you pay for relatives
- For your spouse. When paying for the treatment of a husband or wife, documents can be issued to anyone. The contract and receipts can be in the name of the husband or wife, it does not matter for the deduction. It is believed that they have everything in common. The same expenses can be deducted by either spouse, but only by one. They can also be divided among themselves, this helps to return more tax, taking into account the limit. nine0023
- For children and parents. Payment documents must be issued to the person who pays and wants to receive a deduction. If receipts and a certificate are issued to the mother, the son will not be given a deduction for these expenses.
 Although you can try to resolve this issue with the help of a conventional written power of attorney. The contract for medical services should contain a wording from which it is clear that it is concluded with this person - the one who claims the deduction - for the treatment of this relative. But if this did not work out, this usually does not interfere with the return of the tax. The tax first of all looks at payment documents and a certificate. This is really important. nine0023
Although you can try to resolve this issue with the help of a conventional written power of attorney. The contract for medical services should contain a wording from which it is clear that it is concluded with this person - the one who claims the deduction - for the treatment of this relative. But if this did not work out, this usually does not interfere with the return of the tax. The tax first of all looks at payment documents and a certificate. This is really important. nine0023
How to return personal income tax from the costs of treatment for the last year
For the last year, you can return the tax only on the declaration. Through the employer return only in the current year.
Here is the instruction:
- Get medical bills. This is a special document, it must be issued by the organization to which you paid for the treatment. Now everything is stored electronically, so usually you don’t even need to show receipts. The help will indicate the code - "1" or "2".
 If it is "1", then you need to take into account the limit, if "2" - the entire amount will be deducted. nine0023
If it is "1", then you need to take into account the limit, if "2" - the entire amount will be deducted. nine0023 - Make copies of documents that confirm your relationship: birth and marriage certificates.
- Fill out the 3-personal income tax declaration in your personal account on the nalog.ru website. It can be filled out in a special program or handed in on paper, but through the site - this is the easiest, fastest and most convenient way that will insure you against mistakes and speed up the verification. Scans or photographs of documents must be attached to the declaration.
To receive documents for a tax deduction, you can apply to the administrator-cashier at our Center or send a request electronically by filling out the form below. nine0017
Dear patients, when filling out the form, be sure to indicate:
- contact details
- period for which documents must be submitted
- list of required documents
Tax deduction application form
Sergey
Hello, I was treated at the clinic with my own problem, which was helped by a wonderful surgeon, coloproctologist Galyatin Denis Olegovich.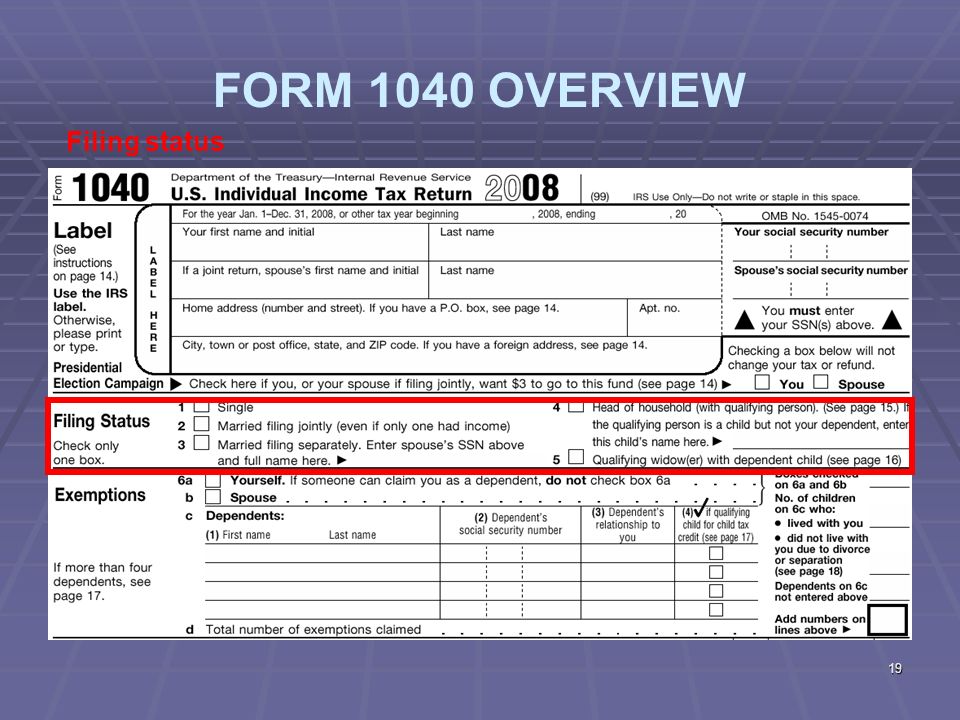 Many thanks to the team of the clinic "Medline". All health! nine0004
Many thanks to the team of the clinic "Medline". All health! nine0004
Vladimir
I want to express my gratitude to Galyatin Denis Olegovich for a successful and easy operation and my quick recovery. A very good center and excellent specialists! Thank you all! I recommend 100% to everyone who has a problem in urology and proctology.
all clinic reviews
Certificate for tax deduction
How to get Social tax deduction for paid medical services
All personal income tax payers who receive income taxed at a rate of 13% have the right to apply for a social tax deduction (paragraph 3 of Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
According to subparagraph 3 of paragraph 1 of article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a social tax deduction is provided to the Taxpayer for medical services paid for and received by the taxpayer himself, his legal spouse (legal spouse), parents, children (including adopted children) under the age of 18 years, wards under the age of 18 (in accordance with the list of medical services approved by the Government of the Russian Federation), as well as in the amount of the cost of medicines for medical use prescribed by their doctor and purchased by the taxpayer at his own expense.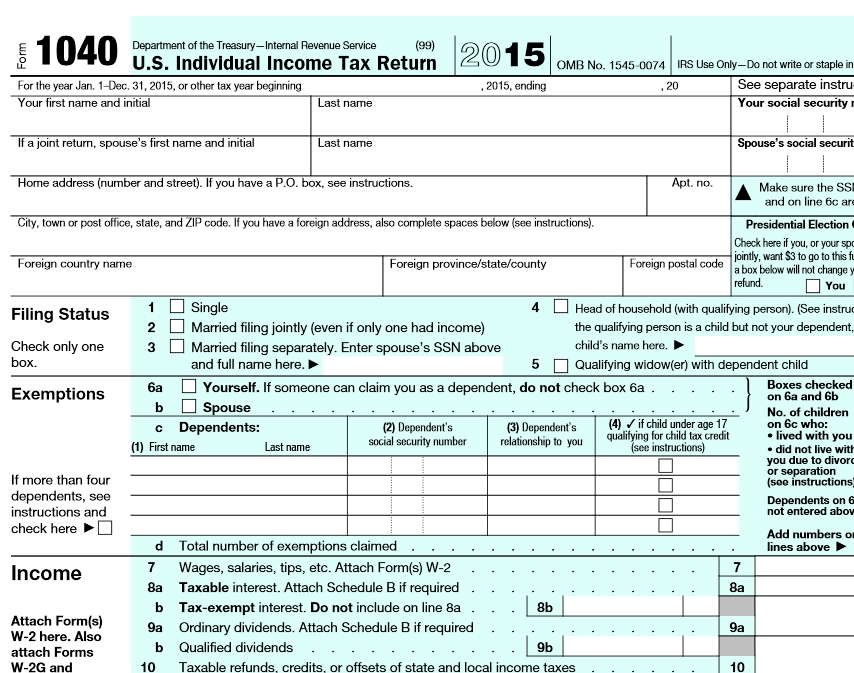 nine0004
nine0004
To receive this deduction, you must submit a 3-NDFL declaration to the tax office at the place of residence along with an application for a social deduction. Supporting documents must be attached to the declaration:
- certificates of income in the form 2-NDFL,
- copies of the contract for treatment,
- copies of payment receipts,
- original certificate of payment for services for submission to the medical authorities (is issued in accordance with the Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation N 289, Ministry of Taxation of the Russian Federation N BG-3-04 / 256 of 07/25/2001),
- marriage certificate, taxpayer's birth certificate, child's birth certificate,
- a copy of the license of the medical institution (if necessary, it can be obtained from the website of the medical organization).
Our license is here >>
FOR ISSUING A CERTIFICATE ON PAYMENT FOR MEDICAL SERVICES TO THE CSTO STATE HEATER, THE TAXPAYER MUST SUBMIT:
who plans to receive a tax deduction and paid for the services:
- for himself,
- for his spouse, who is in a registered marriage,
- for their parents (but not the spouse's parents),
- for their children under the age of 18.