Signs your fertile
7 Signs It May Be Easy For You To Get Pregnant
For most people, fertility is a bit of mystery until they begin seriously trying to get pregnant. But despite the many medical conditions and surprises that could make reproducing naturally difficult, there are also lots of little hints you can look out for that may be signs of fertility.
“It’s hard to say [if] someone can feel fertile,” Mache Seibel, M.D., Ob/Gyn, founder of dr.mache.com and member of Harvard Medical School Faculty, tells Bustle. Still, there are lots of ways your body may be communicating to you that it will be easy to get pregnant, if you do decide to try.
Even if you’re not ready to have kids yet, but may like to someday, it can be worthwhile to understand your fertility prospects so you can best take care of your gynecological health. A lot of issues that can cause infertility may also cause other health problems down the line. Plus, if you’re not ready to have kids, knowing that you’re potentially very fertile may help keep you motivated to have safe sex and use protection. So keeping an eye on the signs your body gives you is important at any stage in life.
Here are eight signs it may be easy for you to get pregnant, according to experts.
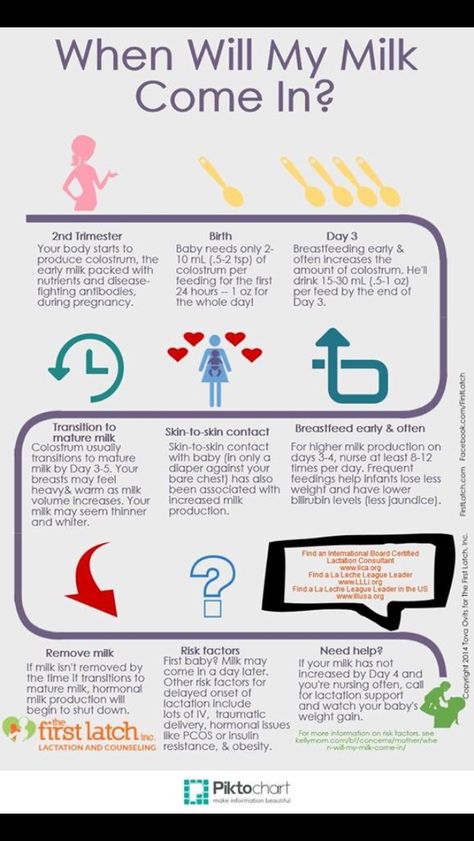
1. You Have A Very Regular Cycle
Having regular cycles, even when you’re off of hormonal birth control, is a good sign of being fertile. “Women with wonderfully regular 28 (plus or minus a day or two) cycles are likely to conceive,” Felice Gersh, M.D., author, founder, and director of the Integrative Medical Group of Irvine, tells Bustle. “Regular cycles are powerful
evidence of regular ovulation — a definite prerequisite to being fertile.” if you are curious to learn more, talk to your doctor, but having regular cycles is definitely a good sign.
2. You Feel Well In General
Having generally good health on a whole is a plus when it comes to fertility as well. “Feeling very well is a very good indicator that you indeed are well and healthy,” Dr. Gersh says.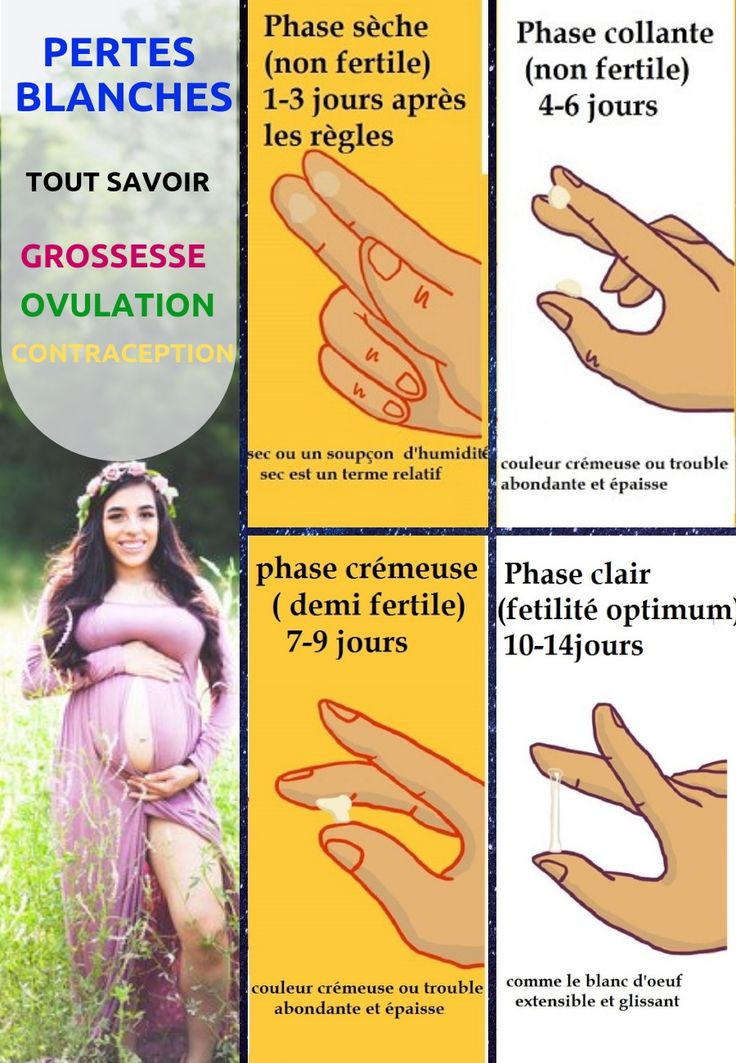 Studies have indicated that struggling with mental
Studies have indicated that struggling with mental
health could make getting pregnant more difficult. So if you’re coming from a place of emotional strength, and not dealing with many outside health problems, you may find it easier than some to get pregnant.
3. You’ve Never Had A Pelvic Infection
While there are some chronic conditions that can cause infertility, having a history of infection may make getting pregnant harder as well. Because of this, if you haven’t dealt with any pelvic infections, you may be more likely
to conceive. Of course, a history of pelvic infections is part of a larger equation. “If you have regular periods, never had a pelvic infection, and know when your fertile days are, your age is the only limiting factor towards normal
fertility,” Juergen Eisermann, M.D., a South Miami, Fla.-based fertility specialist at Florida’s IVFMD, tells Bustle. If you’re concerned about any of these factors, it’s worthwhile to bring any questions up to your OB/GYN.
4. You Have Other Signs Of Regular Ovulation
If you have regular periods, but are still looking for more signs that it might be easy for you to get pregnant, it might be worthwhile to pay attention to ovulation.
“Signs that you are regularly ovulating [include …] symptoms such as watery vaginal discharge (before ovulation) followed by thicker cervical mucus and breast tenderness (after ovulation),” Dr. Lucky Sekhon, fertility specialist
in Progyny’s Provider Network, tells Bustle. If you notice your body going through these changes, there may be a higher chance you’ll conceive quickly.
5. You Don’t Smoke Cigarettes
Studies have shown that cigarette smoking has a negative impact on fertility. So if you’ve never smoked, you are already giving yourself a leg up when it comes to getting pregnant.
“Cigarette smoking has been shown to accelerate the loss of eggs over time and is associated with shortening a women’s reproductive lifespan,” Dr.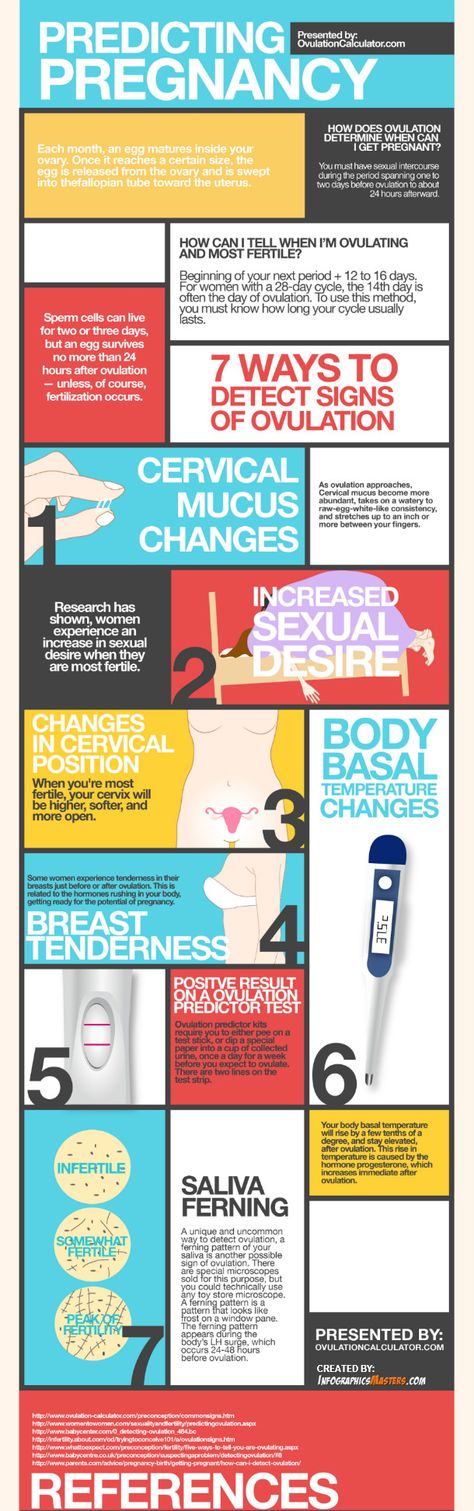 Sekhon says. So just by keeping away from cigarettes, you’ve likely already
Sekhon says. So just by keeping away from cigarettes, you’ve likely already
boosted your chances of getting pregnant.
6. Your Periods Aren’t Extremely Heavy
While everyone’s period is different, your chances of getting pregnant may be related — at least tangentially — to your flow.
“Women with very heavy periods may have fibroids, which are benign tumors that can alter the architecture of their uterus and interfere with embryo implantation and a growing pregnancy,” Dr. Sekhon says. So if you’ve never dealt with fibroids, or particularly heavy periods, you may be more likely to get pregnant easily.
7. Your Periods Aren’t Extremely Painful
For a lot of these signs of fertility, the hints that it may be easy for you to get pregnant is more about the absence of symptoms, rather than the presence of anything in particular. In this case, not having particularly painful periods
is another plus.
“Very painful periods can signify a condition called endometriosis, where the tissue that normally lines the uterus, is found outside of uterus (most often in the pelvic cavity or ovaries) where it can cause pain, scarring and inflammation,” Dr.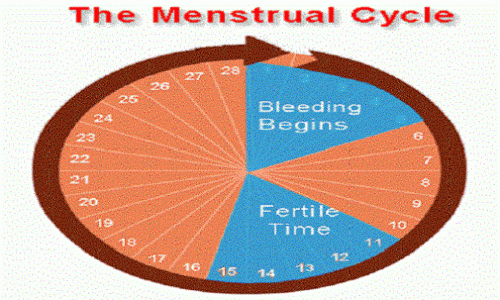 Sekhon says. Making sure you regularly see your OB/GYN, and keeping track of your period symptoms, can keep you more informed about whether or not you’re dealing with this or other chronic
Sekhon says. Making sure you regularly see your OB/GYN, and keeping track of your period symptoms, can keep you more informed about whether or not you’re dealing with this or other chronic
gynecological conditions — many of which may impact fertility.
While being unable to get pregnant is not at all a personal failing, and modern medicine is making it easier than ever to have biological children even if you struggle with fertility, it still can be good to know where you stand when it comes to one day trying to conceive. You can have kids any way that’s right for you, but no matter what, it’s still a good idea to be in tune with your body. Paying attention and going to the doctor regularly may have some really important ripple effects.
Click here to view the original article.
Am I Ovulating? Physical Signs That You Are Fertile
Written by Lisa Fields
In this Article
- What Are Ovulation Symptoms?
- How to Track Ovulation Symptoms
- When Does Ovulation Happen?
- How Long Does Ovulation Last?
- Ask Your Doctor
To boost your chances of getting pregnant, it helps to know when you're ovulating.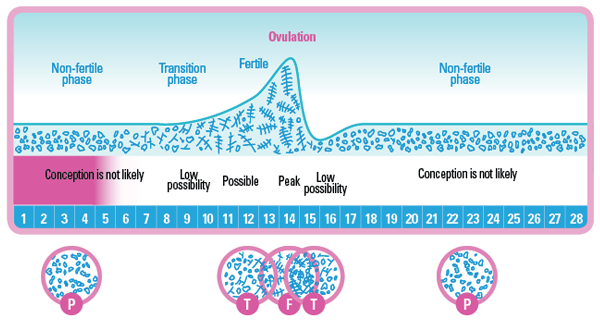 Then you'll know when you and your partner should be having sex.
Then you'll know when you and your partner should be having sex.
Ovulation happens halfway through your cycle. Every woman’s cycle is different, so you have to pay attention to the signs.
There are many ways you can tell if the time is right.
What Are Ovulation Symptoms?
Here are the signs you may have when your body releases an egg:
- Your basal or resting temperature falls slightly, then rises again. You can use a special thermometer to check your temperature every morning before you get out of bed. You’re most fertile 2 or 3 days before your temperature rises.
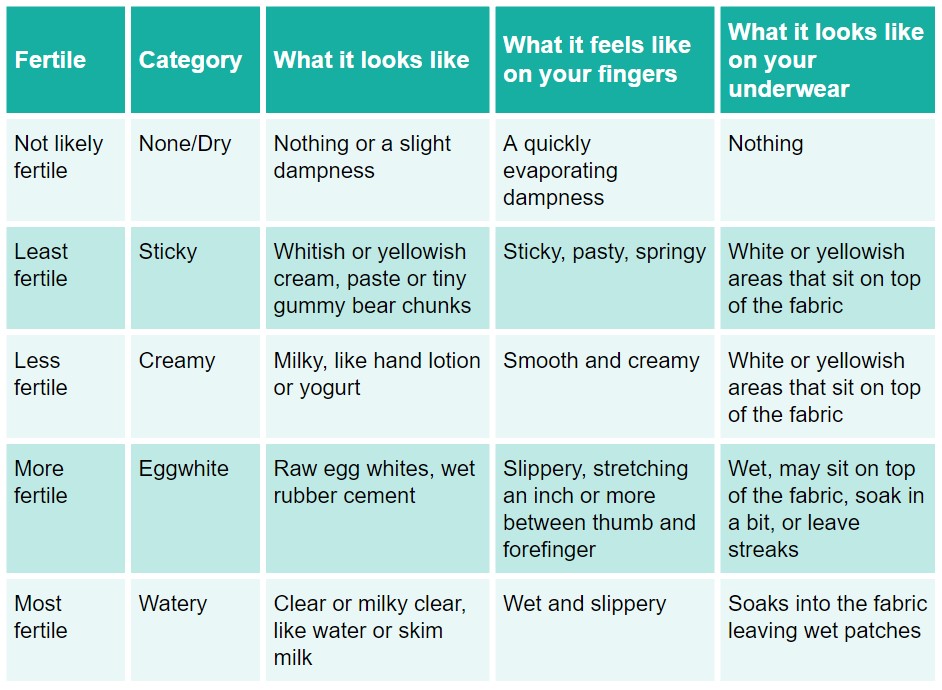
- Your cervical mucus becomes clearer and thinner with a slippery consistency, like egg whites.
You may also notice:
- Tender breasts
- Bloating
- Cramps
But these symptoms don’t always mean you’re ovulating.
How to Track Ovulation Symptoms
Mark your calendar
Take note of when your period begins and ends and know how long your cycle lasts.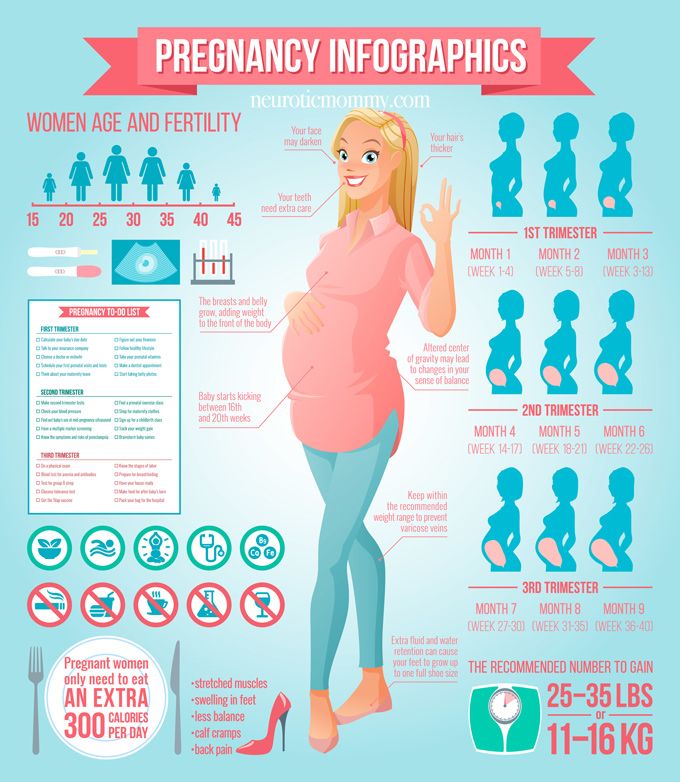 Doctors say it's best to have sex at least every other day, especially during the 5 days before you ovulate. They call this your "fertile window." Your egg only lives for about 12 to 24 hours. But sperm can survive for a few days inside your body, so it's ideal to have them already there waiting for your egg.
Doctors say it's best to have sex at least every other day, especially during the 5 days before you ovulate. They call this your "fertile window." Your egg only lives for about 12 to 24 hours. But sperm can survive for a few days inside your body, so it's ideal to have them already there waiting for your egg.
Watch for body changes
Your hormone levels change throughout your menstrual cycle. During the first half, your ovaries give off the hormone estrogen. When your estrogen levels get high enough, your ovary releases an egg. Then your body starts to make progesterone, another hormone. It makes your body temperature rise slightly.
Your hormones also change the texture of your cervical mucus, the sticky fluid that comes from your cervix, the bottom of your uterus. As your body gets ready to ovulate, you have more of it, and it feels more stretchy and slippery, like raw egg whites. The texture helps sperm swim inside your body. When your mucus feels like this, you should be in your fertile window.
Ovulation predictor kits
These tests, which you can buy at drugstores, give you a more precise idea of when to expect your fertile window. They test your urine to measure your levels of luteinizing hormone (LH), which go up in the 24 to 36 hours before you ovulate. When your LH levels are highest, you're in the fertile window.
The kits have enough test strips to let you check your LH levels several times during your menstrual cycle. Start testing a few days before you think you might ovulate, then repeat a few times over the next few days to pinpoint the exact day. When your LH levels are highest, you're in the fertile window.
Progesterone ovulation tests
These tests can find out whether you have ovulated. They look at the levels of progesterone metabolite (pregnanediol glucuronide, or PdG) in your urine.
PdG levels typically rise 24-36 hours after you ovulate, so the tests are highly accurate. Start testing your levels before your anticipated menstrual cycle.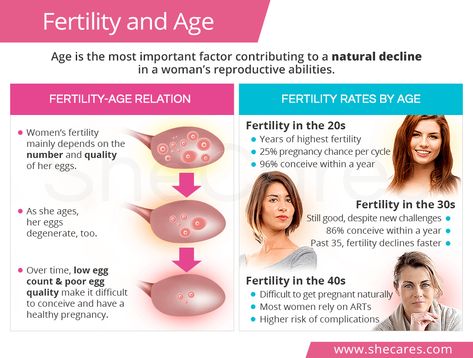 These tests also have several strips to allow you to check your progesterone levels throughout your cycle.
These tests also have several strips to allow you to check your progesterone levels throughout your cycle.
A twinge of pain
It's possible to feel yourself ovulate, but many women don't notice it. You might notice a slight pain in your side about halfway through your menstrual cycle. But if you're trying to get pregnant, don't wait for the twinge. That means your fertile window is soon closing.
When Does Ovulation Happen?
If your menstrual cycle lasts 28 days and your period arrives like clockwork, it's likely that you'll ovulate on day 14. That's halfway through your cycle. Your fertile window begins on day 10. You're more likely to get pregnant if you have sex at least every other day between days 10 and 14 of a 28-day cycle.
How Long Does Ovulation Last?
Your fertile window typically lasts 4-5 days. These are the days leading up to when you ovulate.
Ask Your Doctor
Some women don't ovulate on a set schedule. If you can't figure out when it happens or if your menstrual cycle isn't regular, ask your doctor for help.
Methods for increasing fertility | Rosselkhoznadzor Office for the Chelyabinsk Region
Rosselkhoznadzor Office for the Chelyabinsk Region recalls that any intervention in the environment changes the ecosystem. The soil is always changing during operation, the quality of these changes depends on the owner of the land. Today we will talk about methods to improve soil fertility and give some tips on how to make the soil nutritious and fertile.
Soil is home to countless helpers, ecosystem engineers who change the physical properties of the soil. It is they who create stable soil structures and passages. Pores and microtunnels provide habitat for smaller soil organisms. Large and small worms, centipedes, mites maintain a high level of aeration and soil porosity. Aerobic bacteria live in 15 cm of the topsoil, then anaerobic bacteria. Aerobic bacteria require oxygen to live; For anaerobic bacteria, oxygen is a poison. Deep plowing of the earth turns the top layer with aerobic bacteria down into an oxygen-free space, and sends anaerobic bacteria into an oxygen environment. As a result of regular plowing, the microflora of the earth is significantly reduced, and instead of increasing the yield of our plants in symbiosis with the roots, these living creatures spend time and energy restoring their habitat.
As a result of regular plowing, the microflora of the earth is significantly reduced, and instead of increasing the yield of our plants in symbiosis with the roots, these living creatures spend time and energy restoring their habitat.
Any roots of both cultivated plants and weeds grow to great depths for water and minerals, and when they die, they leave channels with humus in which soil life boils. All animals, eating dead roots, make their smallest passages and channels and deposit coprolites in them. After hoeing, loose soil is preserved until the first watering and rain, and from the work of weed roots and other soil engineers accompanying them, structural soil remains all year round. So the roots of weeds become catalysts for life and preserve fertility.
Introducing organics into the soil, without plowing, superficially
If we got a new plot on which the soil was killed by previous improper exploitation, there is no organic matter in it, there is no established balance of soil life, it is contaminated with pesticides and pathogenic microorganisms, having once dug up, poured manure for digging, we will not start the processes of self-healing of the soil, on the contrary, pests and diseases will multiply intensively in the buried manure.
The soil must first be cured, and it should be treated with composts, compost extracts, alternating with ACC (aerated compost tea), planting plants resistant to root rot (green manure).
As long as the soil is poor, you should add a little organic matter, any, in layers no more than 3-5 cm and water it.
- Mowed fresh grass is a nitrogenous fast-acting fertilizer.
- Dried grass - lignin (long-lasting energy of carbon, leads to the accumulation of humus).
- Manure of unknown quality is a breeding ground for disease if placed under anaerobic conditions.
- Crushed thin branches of deciduous trees. They do not have much nitrogen, they will not feed the plants, and the basidiomycetes will begin to develop, and they will process the lignin from the wood chips into long-lasting humus.
- Mature manure is not food for plants, but medicine for the soil. It is food for fungi, bacteria and soil engineers.
- It is recommended to apply fresh manure only on healthy soil, leave it to rot or make composts.
- Yeast; lactic acid bacteria; infusions from herbs, manure, compost - quick-acting fertilizer, food for microorganisms.
To create a soil ecosystem of a new, higher order, it is not enough just to add any organic matter to the beds.
The introduction of effective microorganisms
The basis of the foundations is the care of the plant rhizosphere. It is that very thin layer of soil microbes that surrounds the root hairs of plants, which the plants themselves create, attract with their root secretions, supply the plants with active hormonal substances and antibiotics and make them as resistant as possible to the harmful effects of the environment.
Soil, especially depleted by agriculture, does not always contain all useful microorganisms, so ACh can be used to restore the soil ( aerated compost tea , based on ready-made compost with a high content of bacteria, fungi and other microorganisms), as well as the compost itself.
When we use ACS, we introduce with the solution not only effective microorganisms that will process organic matter and make it available for plant nutrition (as is the case with purchased EO preparations), but more importantly, stimulate root growth and create a very active rhizosphere in the root zone. This will help plants to enter into symbiosis with microorganisms, symbiotic fungi, by increasing the secretion of carbohydrates by the roots. The process of soil formation in the root zone is accelerated at times. The roots will intensively release carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, together with microbes and fungi, will destroy the mother rock and make minerals available for nutrition, nitrogen fixers, using root secrets, absorb and accumulate nitrogen from the air in the soil. Thus, our plants will not only consume nutrition from the soil, but even accumulate it for future generations.
The land should not be empty
The more roots of cultivated plants, green manure, weeds penetrate the soil, the more organic matter of root secretions and dead roots enters the soil, the faster and to a greater extent the soil biota grows, and the faster your fertility grows soils.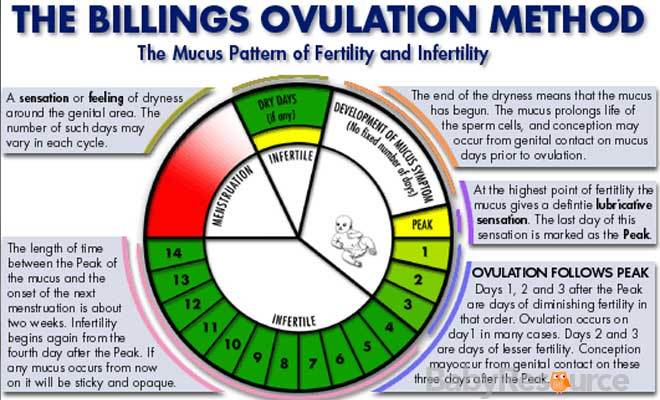
Any roots of cultivated plants and weeds grow to great depths for water and minerals, and when they die, they leave channels with humus in which soil life boils. All organisms, eating dead roots, make their smallest passages and channels and deposit coprolites in them. So the roots of weeds become catalysts for life and preserve fertility.
Each green manure has its own qualities and is useful in its own way for the soil and in the human economy. Any green manure is a former weed, but due to the usefulness of its use in fields or gardens, it has become a "green manure".
As an example, the use of white and yellow sweet clover, which is a phytosanitary. Its roots, releasing its own substances, create conditions for the life of the corresponding microorganisms that suppress pathogens in the soil. Sweet clover also has a high competitive ability to suppress weeds, high nitrogen fixation, does not allow the development of erosion processes, and contributes to soil decompaction due to its deep root system.
If the land is without vegetation cover (pure fallow, black fallow), then almost all soil moisture in the upper layers of the soil evaporates into the atmosphere. If the soil loses moisture, then it loses the life in it.
If a field is plowed every year and nothing is sown in it, then after some time the land will turn into either mud or desert, depending on the area.
Also uses mulch to protect the soil from drying out, suppress weeds and as an additional organic fertilizer.
Mulch is any material that covers the soil from above. It retains moisture, keeps cool or warm depending on the area, conducts air and creates comfort for living soil rippers. Humus mulch is also a food for these living creatures, a source of nutrition and carbon dioxide. Bare soil is a dying open wound.
The application of mineral fertilizers over the entire area inhibits soil microorganisms
The mineral fertilizer applied to the soil over the entire surface increases the yield for the first time, but in the long term it inhibits soil organisms and worsens soil fertility. Moreover, mineral fertilizers are the main source of soil pollution with heavy metals and toxic elements. This is due to the content of strontium, uranium, zinc, lead, mercury, vanadium, cadmium, lanthanides and other chemical elements in the raw materials used for the production of mineral fertilizers.
Moreover, mineral fertilizers are the main source of soil pollution with heavy metals and toxic elements. This is due to the content of strontium, uranium, zinc, lead, mercury, vanadium, cadmium, lanthanides and other chemical elements in the raw materials used for the production of mineral fertilizers.
In nature, useful substances for a plant (minerals, organics) are always found in separate clots or inclusions, in separate piles or stripes, i.e. locally. And plants have learned to make the most of it. The roots find "local nutrition" adapt to them and consume the right minerals in the right quantities. The roots are able to consume nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium separately, if they themselves find "deposits" of these salts, and not we "make droppers" for the entire volume of the roots. Therefore, with local top dressing, the roots and leaves grow simultaneously, in a balanced way, without waves and stress. Soil biota at 90% of the area is not oppressed by “excessive chemistry”, and most importantly, high-salt roots, consuming deficient nitrogen, and having unoppressed leaves and a large volume of low-salt roots, begin to secrete secrets with the whole mass of these remaining roots and form a rhizosphere.
It is necessary to look at mineral fertilizers not as food for plants, but as corrective (improving, correcting) additives for different crops. Therefore, it makes sense to apply fertilizer locally: surface (manure) or in holes (organic mineral fertilizer).
HOW TO RESTORE THE FERTILITY OF THE SOIL | Nauka i Zhizn
Already in a year or two, potatoes will grow again on a plot overgrown with a variety of grasses.
Peas rise like a green wall above the bed.
Clover, like lupine, beans, not only restores soil fertility, but also enriches it with nitrogen.
Science and life // Illustrations
Science and life // Illustrations
Pikulnik, popovnik, horsetail - lovers of acidic soils.
Science and life // Illustrations
Science and life // Illustrations
Field bindweed grows on slightly acidic or neutral soil.
Squash tolerates slightly acidic soils.
Cucumbers do not tolerate acidic soils.
‹
›
View full size
I remember when I became seriously interested in soil science and agronomy, I was struck by such numbers. It turned out that at least a million different insects (that is, 95 percent of the total number of species known to scientists) are somehow connected with the soil. Some spend their whole lives in the ground, the second lay eggs, the third - pupae lie in it, the fourth - larvae live. And each of these living creatures leaves its mark in the earth, either helping to increase the fertility of the soil, or laying passages in it through which water and air enter, and the carbon dioxide formed by living organisms is removed.
But besides insects, other animals live in the earth, for example, earthworms. Creeping out of the minks at night, they look for last year's leaves, the remains of plants and drag them to themselves. Eaten and passed through the intestines, these remains fall into the ground in the form of small dark lumps.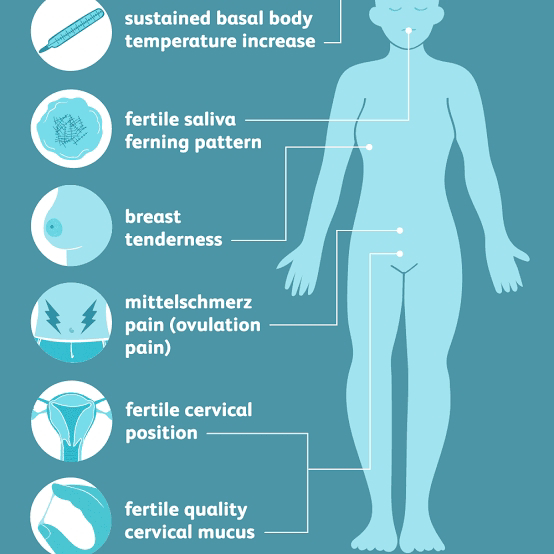 So earthworms fertilize it, in their own way answering for fertility. And through their minks, water and air enter the soil, soil drainage is carried out, and often very deep.
So earthworms fertilize it, in their own way answering for fertility. And through their minks, water and air enter the soil, soil drainage is carried out, and often very deep.
I remember one more figure: on one hectare of unplowed land, there are about 200 kilograms of microorganisms. The total mass of all living beings inhabiting this piece of land reaches a ton. Is it a lot or a little? In order to grow a good harvest of turnips, 500 kilograms of mineral fertilizers must be applied per hectare of land, when planting carrots - 800 kilograms, and beets - already one ton. As you can see, the mass of living beings inhabiting the soil is greater than the mass of mineral fertilizers applied to the ground when growing turnips and carrots. But after all, all living creatures inhabiting the earth, after the expiration of the life span allotted to them, die and remain in the earth, giving it the accumulated organic substances. The remains of animals are decomposed by microorganisms, and microorganisms, in turn, dying off, provide the soil with nutritious humus.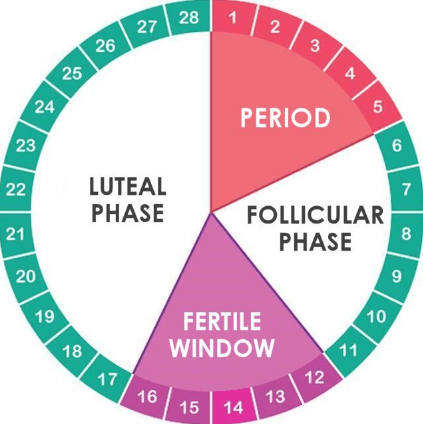
This is how a healthy, not exhausted, not exhausted land lives, which until recently wise peasants affectionately called living.
Living earth has one amazing property: it not only provides plants with the necessary nutrition, but is also able to restore fertility if life is not destroyed in it.
The peasant has long known that the land that has lost its strength, yielding smaller and smaller crops from year to year, should be left alone for several years, not touched with a plow and wait until it again protects itself with a layer of turf and organic matter accumulates in it. And all this without fertilization.
Having taken possession of the land to my house, I mastered the former meadow that occupied a high, dry place, and successfully grew potatoes for two years in a row, practically without introducing any fertilizer into the soil - except for pouring into each hole prepared for a potato tuber, half a handful of ash, but did it more so that the potatoes were tastier.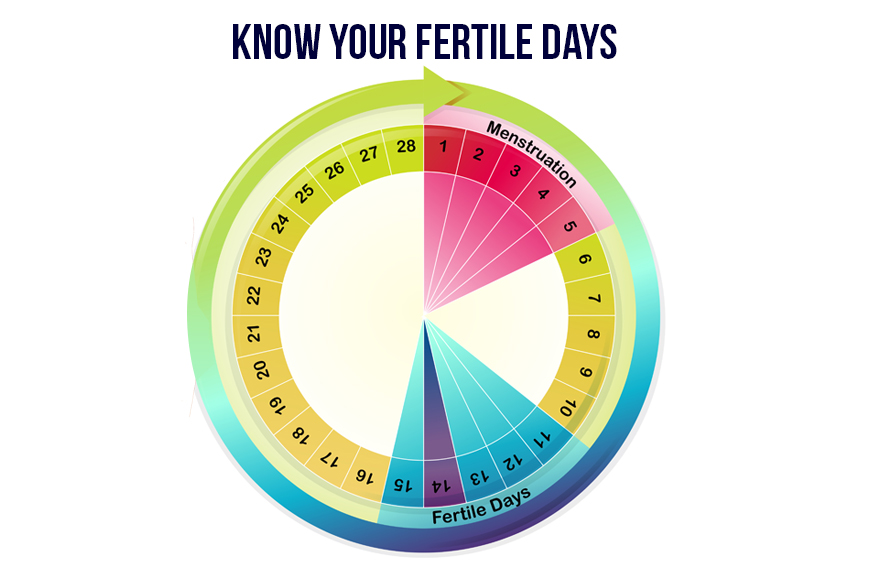 But in the third year, I did not wait for the potato harvest in this, until recently, virgin garden. There was not enough manure then, and I left this place for a while. For the third year in a row it has been overgrown with grass, which grows thicker and thicker year after year. I do not mow the grass and do not bury it in the soil. Former grasses die off, and their remains are processed by microorganisms. This is how the strength of my garden is gradually restored. I think that in a year or two I will again get decent potato crops here.
But in the third year, I did not wait for the potato harvest in this, until recently, virgin garden. There was not enough manure then, and I left this place for a while. For the third year in a row it has been overgrown with grass, which grows thicker and thicker year after year. I do not mow the grass and do not bury it in the soil. Former grasses die off, and their remains are processed by microorganisms. This is how the strength of my garden is gradually restored. I think that in a year or two I will again get decent potato crops here.
Of course, it is unlikely that such an experiment can be carried out on several summer cottages - every piece of land is valuable. But even on your 6-8 acres, you can very well take advantage of the ability of the living earth to restore its strength, and besides, you will help it in this.
Some garden bed ceases to produce crops, it would be necessary to fertilize it with organic fertilizer. If there is no such fertilizer, sow peas in early spring, preferably undersized, and plant them thicker - then it will rise like a solid green wall and will not allow any weeds. The time will come to harvest, pluck the pods, cut off the tops and leave to lie in an even layer. By spring, almost all stems will perepere. Then again loosen the grooves on this bed with a garden pitchfork and spread the pea seeds. Again, collect only the pods and leave the stems. And in the new spring, with a garden pitchfork or a shovel, close the half-rotted stalks of peas into the soil and you can safely grow root crops. For cabbage or potatoes, and even for cucumbers of two seasons, such a natural restoration of soil fertility is not enough - these plants take out, as they say, a lot of nutrients from the ground in one summer, and radishes, lettuce, carrots and beets will be quite good.
The time will come to harvest, pluck the pods, cut off the tops and leave to lie in an even layer. By spring, almost all stems will perepere. Then again loosen the grooves on this bed with a garden pitchfork and spread the pea seeds. Again, collect only the pods and leave the stems. And in the new spring, with a garden pitchfork or a shovel, close the half-rotted stalks of peas into the soil and you can safely grow root crops. For cabbage or potatoes, and even for cucumbers of two seasons, such a natural restoration of soil fertility is not enough - these plants take out, as they say, a lot of nutrients from the ground in one summer, and radishes, lettuce, carrots and beets will be quite good.
In addition, peas, like clover, lupine, also enrich the soil with nitrogen. You can plant beans on a resting bed, but they will not be able, like peas, to resist weeds - they will not cover the whole earth with a solid green mass.
I have long adopted this method of soil restoration with the help of peas: peas in my garden are a respected crop.
The ability of the soil to self-repair, accumulate organic matter, and improve its structure depends on many factors. The climate and the acidity of the soil also affect. The higher the acidity, the slower the fertile layer grows. This is explained by the fact that under conditions of increased acidity, the work of microorganisms that are busy processing organic residues slows down.
The yield also depends on the acidity of the soil. Of all cultivated plants, only potatoes feel good on acidic soil. Tolerate slightly acidic soils sorrel, tomatoes, zucchini, radish, radish, carrots. But cabbage, beets, onions, garlic, lettuce, cucumbers and peas simply do not tolerate acidic soils.
There are special instruments for measuring the acidity of the soil, but even without instruments it is possible to determine whether it is suitable for certain crops.
If the soil is acidic, unsuitable for garden plants, near the beds it is easy to find horsetail, pikulnik, veronica, plantain, small sorrel, field mint, buttercup, popovnik. If the soil is slightly acidic or neutral, that is, suitable for all garden plants, such savage plants as field bindweed, odorless chamomile, clover, coltsfoot, wheatgrass, and garden thistle will grow on it.
If the soil is slightly acidic or neutral, that is, suitable for all garden plants, such savage plants as field bindweed, odorless chamomile, clover, coltsfoot, wheatgrass, and garden thistle will grow on it.
Plants that help to immediately determine the acidity of the soil in the garden are commonly called indicator weeds.
Acidic soils are usually found in low, damp places and where spring water stagnates longer. There is a so-called natural acidification of the soil. But in our time, acidic soils can also be found in high places - the earth is "gifted" with acid by acid rains. Industrial acidification of the soil for some places becomes almost a national disaster.
You can reduce the acidity of the soil with fluff lime (slaked lime), cement dust, chalk, ground lime.
Furnace ash will help too. Even in ancient times, peasants used ashes to "bring horsetail" out of their gardens. Ashes are applied to the soil during autumn digging: 100-150 grams per 1 m 2 (up to 1.