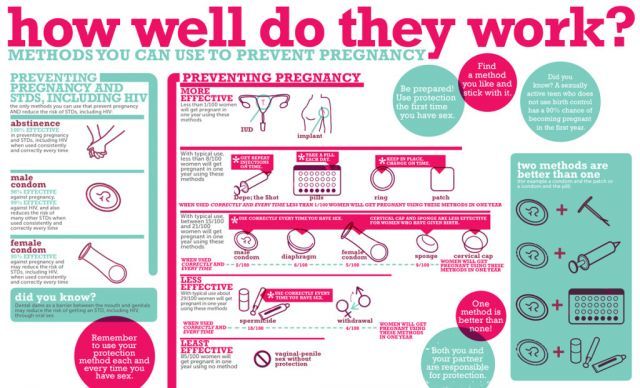
How to tell when pregnant
16 early signs of pregnancy
You’ve got one question on your mind: Could I be pregnant?
A pregnancy test is the only way to know for sure. But if it’s too early to take a test, you may be on the lookout for early signs – or maybe you think you’re already experiencing some early pregnancy symptoms.
Is it too early to tell if you’re pregnant? What symptoms may be the earliest signs of pregnancy? Below, we answer those questions and more.
How early can you tell if you’re pregnant?
Again, you’ll need to take a pregnancy test at the right time to confirm your hopes or suspicions. But when it comes to the first symptoms of pregnancy, everyone is different. Some people start to notice changes within a week after conception. Others might not notice anything until they miss their period.
When should you take a pregnancy test?
It’s usually recommended that you take a pregnancy test after you’ve missed your period. This is because pregnancy tests measure the level of human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) in your body, which is a hormone that starts to build up when you conceive. It can take around three to four weeks from the first day of your last period for there to be enough hCG in your body to show up on a test.
What are the first symptoms of pregnancy?
The most common sign of early pregnancy? A missed period.
Your menstrual cycle is your body’s way of preparing for a possible pregnancy each month. Part of that is the thickening of your uterine lining, which is where a fertilized egg would implant to begin a pregnancy.
If you’re not pregnant, your period is how your uterus sheds that extra lining. If you are pregnant, that lining stays put and you don’t get your normal flow. This is why a missed period is often the earliest sign of pregnancy.
Of course, a delayed or missed period doesn’t always mean you’re pregnant. If your body is under a lot of stress or you have a hormonal imbalance, you could be experiencing an irregular menstrual cycle.
What other symptoms can be early signs of pregnancy?
Every person – and every pregnancy – is different. So, if you are pregnant, you’ll likely experience a unique combination of common, not-so-common and sometimes overlapping symptoms. And, they may show up earlier or later than expected. Here are more than a dozen possible symptoms of early pregnancy.
So, if you are pregnant, you’ll likely experience a unique combination of common, not-so-common and sometimes overlapping symptoms. And, they may show up earlier or later than expected. Here are more than a dozen possible symptoms of early pregnancy.
1. Spotting or light bleeding
Many women are surprised to learn that spotting or light bleeding can be an early sign of pregnancy, but about one-third of women experience it. This is often called implantation bleeding because doctors believe it occurs as the fertilized egg attaches (or implants) itself into the uterine lining. This is different from bleeding that could occur from something like a miscarriage – which is usually heavier.
When does implantation bleeding occur?
Implantation bleeding typically occurs 10 to 14 days after conception, which is just before or right around the time your period is due. So, you may think you’ve gotten your period.
But implantation bleeding is a light flow, which may start and stop over a couple days. And while it can take on a range of colors, it’s more likely to be pink, brown or light red.
And while it can take on a range of colors, it’s more likely to be pink, brown or light red.
Your period, on the other hand, may start off light in flow and in color but after a couple days becomes heavier, changes to a crimson red color and lasts up to a week or so.
2. Lower abdominal pain or cramping
While cramps and lower-abdominal pain can signal a coming period, they can also be a sign of egg implantation.
What do implantation cramps feel like?
Implantation cramps can occur with or without spotting or bleeding, and may feel different from period cramps. For example, you might feel mild to moderate prickling, pulling or tingling that comes and goes over a few days.
But menstrual cramps can often feel like a throbbing or dull ache, and typically start a day or two before your period.
3. Higher basal body temperature
If you’ve been tracking your basal body temperature (BBT) to increase your chances of getting pregnant, you probably know that your BBT goes up slightly right after ovulation. If you’re pregnant, your temperature may remain elevated rather than dipping back down.
If you’re pregnant, your temperature may remain elevated rather than dipping back down.
Of course, you could be running hot for other reasons, but if it lasts more than a few weeks, pregnancy may be the explanation.
4. Changes in cervical mucus
If you’ve already been checking your cervical mucus to figure out when you’re most fertile, here’s a reason to continue: In the first few weeks of pregnancy, the amount of cervical discharge may increase and become stickier and whiter.
5. Breast tenderness, swelling or tingling
When you’re pregnant, your body experiences big changes in hormones – specifically, increases in estrogen and progesterone – to support your growing baby. This change in hormones can contribute to many symptoms, including breast tenderness.
Oftentimes, increased breast tenderness, swelling or tingling start to become noticeable a few days before a missed period.
If you usually experience breast tenderness leading up to your period or shortly after it begins, pregnancy-related breast tenderness and swelling will likely be more intense than you’re used to and stick around. You may also experience nipple soreness.
You may also experience nipple soreness.
6. Fatigue
Fatigue in early pregnancy is common, and some women might notice it before they know they’re pregnant. In fact, fatigue may set in as soon as one week after conception. This is thanks to those sudden changes in hormone levels, particularly increasing progesterone.
7. Frequent urination
If you’re making more trips to the bathroom than usual around the time your next period is due, it may be a sign of pregnancy.
Certainly, your drinking habits play a big role in how many times you pee in a day. However, pregnancy increases the amount of blood in your body, which gives your kidneys more fluid to filter and more waste to get rid of.
So if you’re pregnant, you may notice you’re peeing a lot more – a symptom that can start early on and (unfortunately) last throughout your pregnancy.
8. Nausea or vomiting
Morning sickness might be the most well-known of all pregnancy symptoms, taking the form of food aversion or nausea, and even vomiting for some. This symptom can set in as early as two weeks after conception, which is around the fourth week of pregnancy and right around the time you’d miss your period if you were pregnant.
This symptom can set in as early as two weeks after conception, which is around the fourth week of pregnancy and right around the time you’d miss your period if you were pregnant.
But some may not experience nausea or vomiting at all. And despite its name, morning sickness can actually happen at any time of the day or night.
9. Darkening areolas
When you’re pregnant, your areolas (the areas round your nipples) will likely grow and darken. Usually, these changes are gradual and continue throughout pregnancy. However, some women notice these changes really early on in combination with other symptoms.
10. Bloating or constipation
We all experience bloating or constipation from time to time, but both are quite common during pregnancy. Once again, those changing hormones are the culprit. They slow down digestion, which can cause a buildup of air in the gut and lead to constipation.
Early on, bloating or constipation may be mild and accompanied with other pregnancy symptoms. But – as a heads up – if you really are pregnant, these symptoms may stick around throughout your whole pregnancy.
But – as a heads up – if you really are pregnant, these symptoms may stick around throughout your whole pregnancy.
11. Metallic taste in your mouth
Many women report a metallic taste in their mouth during pregnancy. Once again, hormones are to blame – specifically, estrogen.
Typically, this symptom (as well as changes in taste overall) is common in the first trimester but may occur at other times too – including before a missed period.
12. Sensitivity to smell
Many women report that sensitivity to smell was one of their first signs of pregnancy. In fact, as many as two-thirds of women become more sensitive or reactive to the smells around them during pregnancy.
And oftentimes, this heightened sense of smell can stick around through the first trimester or beyond, and contribute to other symptoms such as nausea, and food cravings or aversions.
13. Mood changes
From a stressful day at work to the natural wonders of your menstrual cycle, there are a lot of things that can affect your mood. But changes in mood are very common during pregnancy – and they may be especially noticeable early on as your body gets a sudden burst of estrogen and progesterone.
But changes in mood are very common during pregnancy – and they may be especially noticeable early on as your body gets a sudden burst of estrogen and progesterone.
If you are pregnant, any mood changes you’re experiencing are likely coupled with other symptoms such as fatigue or nausea. You may feel more sensitive or weepy. Or perhaps your fuse is a little shorter and you’re more easily annoyed.
14. Headaches
Headaches are a part of life. They come with colds and allergies. They come with stress or fatigue, or when you cut down on caffeine to help prepare your body for pregnancy. But they can also come with pregnancy.
Headaches can happen thanks to the increasing blood volume and hormonal changes that occur in early pregnancy. You can also get headaches if you’re dehydrated as a result of nausea.
15. Dizziness
As blood flow increases during pregnancy, blood pressure can also decrease and lead to dizzy spells. Usually, dizziness is more of a second trimester symptom, but some women may notice it very early on, too.
16. Nasal congestion
A lot of people are shocked to learn that nasal congestion can be a pregnancy symptom. You may wonder if you’re coming down with something or your allergies are acting up. But if you’re noticing a stuffy or runny nose along with other pregnancy signs, you might be taking a pregnancy test in the near future.
The mucous membranes in the nose are also affected by hormones and increased blood flow throughout your body. This can cause blood vessels to swell, resulting in congestion and even sneezing.
Could you have early pregnancy symptoms and not be pregnant?
Yes. As we’ve mentioned, many early pregnancy symptoms can overlap with symptoms of other conditions, especially premenstrual symptoms. So, the best way to know if the symptoms you’re experiencing are pregnancy related is to try to relax and patiently wait until it’s time to take a pregnancy test.
When should you see a doctor about a new pregnancy?
If you’ve taken a pregnancy test and it’s positive, go ahead and make your first prenatal visit right away. This is also a great time to start looking into educational resources like the myHealthyPregnancy app.
This is also a great time to start looking into educational resources like the myHealthyPregnancy app.
At the first prenatal visit, you’ll get a physical exam and other tests to make sure everything is looking healthy, and you’ll learn about the rest of your prenatal appointment schedule. You’ll also get to talk through any expectations and questions you have, such as which foods to eat and avoid while pregnant.
Questions or concerns about your symptoms? Our 24/7 nurse line is free for our members and patients.
Positive pregnancy test? Schedule a visit.
What to eat when pregnant
You’ve probably heard about some of the common dietary restrictions that come with pregnancy – like no alcohol or sushi. But not everyone knows the complete list of foods that are off-limits during pregnancy, or the reasons behind it. And when it comes to the foods that you can eat while pregnant, you may wonder how much is enough.
You don’t have to eat for two in terms of volume, but you do need to eat for two in terms of quality. Below, we explain which foods to keep in and out of your diet for the next nine months, and why.
Below, we explain which foods to keep in and out of your diet for the next nine months, and why.
Healthy food to eat during pregnancy
Your pregnancy diet doesn’t need to be built around a strict set of specific foods. Instead, you can focus on getting enough of the nutrients that have been proven to contribute to healthy pregnancies. Your care provider will likely recommend that you meet your nutrient needs through a combination of food and vitamin supplements. These nutrients include:
Folate and folic acid
Folate (or folic acid when taken as a supplement) is a B vitamin that helps prevent birth defects in your baby’s brain and spine. Generally, people who are pregnant or planning to get pregnant need about 600 micrograms (mcg) daily, starting at least one month before conception.
Foods high in folic acid to eat during pregnancy include fortified grain products (cereals, bread, pasta), as well as foods like spinach, beans and asparagus. It’s hard to reach 600 mcg through food alone, so a supplement containing at least 400 mcg folic acid is usually recommended to help reach the ideal daily dosage.
Iron
Iron helps your red blood cells carry oxygen around your body. Because your body will be making more blood to support your baby, you’ll need about twice as much iron in your second and third trimesters as you do when you’re not pregnant. Generally, this looks like 27 milligrams (mg) a day.
You can find iron in fortified grain products, lean red meat, dark green leafy vegetables and beans. Iron is also included in most prenatal vitamins.
Calcium
Your body uses calcium to build your baby’s bones, and you generally need around 1000 mg per day. This can be met with four servings of dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt) per day. Other good sources of calcium include fortified grain products, fortified orange juice, fish, dark green leafy vegetables and almonds.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D also contributes to bone development. 600 international units (IUs) is the recommended dose for all women, regardless of whether they’re pregnant. You can get vitamin D from fortified milk, fortified orange juice and fortified grain products. Good sources of naturally occurring vitamin D include fatty fish (such as salmon) and eggs.
Good sources of naturally occurring vitamin D include fatty fish (such as salmon) and eggs.
Protein
Protein provides long-lasting energy and contributes to growth and development. Your pregnancy meal plan can include protein from a variety of sources, including meat, fish, eggs, beans, soy products, nuts and nut butters. Try to include a protein source in every meal.
Water
Water helps your body function. And during pregnancy, water is also used to form amniotic fluid. To meet your pregnant body’s increased demand for water, it’s recommended that you drink around 8-12 cups of water daily.
Herbs and supplements to take during pregnancy
Even though there’s a large variety of healthy foods containing key nutrients during pregnancy, it can be hard to get as much of those nutrients as you need from food alone, particularly folate and iron. Because of this, your doctor or midwife will likely recommend or prescribe certain supplements.
Prenatal vitamins are a common example. As the name implies, prenatal vitamins are made specifically for pregnant people and people planning to get pregnant. Prenatal vitamins provide a combination of vitamins and minerals that support healthy pregnancies (frequently the same ones listed above), and are available over the counter in a wide range of stores.
As the name implies, prenatal vitamins are made specifically for pregnant people and people planning to get pregnant. Prenatal vitamins provide a combination of vitamins and minerals that support healthy pregnancies (frequently the same ones listed above), and are available over the counter in a wide range of stores.
Your care provider may also prescribe supplements based on other factors, like dietary restrictions. If you’re lactose intolerant and can’t eat dairy, for example, you may be prescribed a calcium supplement.
You may also want to use herbal supplements to help provide relief from pregnancy symptoms. Peppermint leaf and ginger root are commonly used to help with nausea and morning sickness. However, there are some herbs to avoid.
Herbs and supplements to avoid during pregnancy
Though herbs are natural, not all are safe to consume during pregnancy. According to the American Pregnancy Association, herbs that should be avoided when pregnant include saw palmetto, goldenseal, dong quai, black cohosh, and several others.
You may also want to be cautious when choosing herbal tea blends to drink during pregnancy. They could contain an herb that may not be safe. Supplements aren’t tightly regulated by the Food and Drug Administration, so it’s important to talk to your care provider about herbs and teas that you are taking.
What not to eat when pregnant
There are two main factors that determine what foods to avoid during pregnancy – foods with a likelihood of containing bacteria or viruses and foods that may contain harmful substances (toxins or contaminants). Here are some examples:
1. The potential presence of bacteria or viruses
Being pregnant naturally weakens your immune system. This increases your risk of foodborne illnesses, including food poisoning from bacteria or viruses, which can have serious effects on you and your baby. To minimize your risk, avoid foods that could potentially contain bacteria or viruses, such as:
Raw or undercooked seafood
Raw or undercooked meat and eggs
Lunch meat
Unpasteurized foods and drinks
Unwashed fruits and vegetables
Uncooked sprouts
2.
 Harmful substances
Harmful substances Some foods contain toxins or contaminants that can be harmful to your baby’s development, and some drinks may have their own negative effects. The biggest sources of concern are:
High mercury content fish
Many fish naturally contain mercury, which in high amounts may affect the development of your baby’s nervous system. To protect your baby, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends that you avoid fish that have high mercury content, including:
- King mackerel
- Marlin
- Orange roughy
- Shark
- Swordfish
- Tilefish
- Bigeye tuna
However, ACOG also has a list of lower-mercury fish and seafood that pregnant women can eat two to three servings of per week. A lot of common fish and seafood are on this list, including:
- Salmon
- Tilapia
- Catfish
- Cod
- Shrimp
- Scallops
- Crab
- Clams
Local fish
There may be local fish advisories in your area due to pollution. If you’re buying locally sourced fish, look up your state’s advisories. Minnesotans can also use chooseyourfish.org to learn about state guidelines, find recipes and more.
If you’re buying locally sourced fish, look up your state’s advisories. Minnesotans can also use chooseyourfish.org to learn about state guidelines, find recipes and more.
Alcohol
No amount of alcohol is known to be safe during pregnancy. Drinking alcohol during pregnancy increases your risk of miscarriage and stillbirth, and your baby’s risk of developing Fetal Alcohol Syndrome, which may lead to physical and mental issues.
Caffeine
Research isn’t conclusive about how high amounts of caffeine affect pregnancies. Because of this, the general rule is to limit caffeine intake to 200mg per day. That’s roughly one to two 8-ounce (oz) cups of coffee, depending on how it’s made.
The caffeine content of tea is generally lower, but this again depends on the type and amount of leaves used. A 6-oz cup of black tea usually has around 50 mg, while a similarly sized cup of oolong tea has about 30-40 mg. For green tea, it’s about 20-30 mg, and for white tea it’s around 15-20 mg.
Herbal teas
Herbal teas are naturally caffeine-free, making them a good choice during pregnancy. However, there isn’t a lot of research available for all the herbs that can be included in herbal teas. And like other supplements, herbal teas aren’t tightly regulated. While herbal teas made from common ingredients like peppermint and ginger are likely to be safe, it’s best to check with your care provider.
Nitrites
Some studies suggest that there may be a link between preterm birth and eating a diet high in nitrites while using certain medicines during pregnancy. Nitrites are commonly found in bacon, deli meat and other processed meat products in the form of sodium nitrite, which is used as a preservative.
Although more research is needed, it may be a good idea to limit or avoid meat products that list sodium nitrite in their ingredients list. Talk to your care provider if you have questions about eating foods with nitrites during your pregnancy.
How much should you eat while pregnant?
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, people need to eat around 340 extra calories per day during their second trimester, and a bit more in their third trimester. These numbers may be higher or lower based on a few factors, including your weight at the beginning of your pregnancy, your body mass index (BMI), your activity level and whether you’re having multiples.
These numbers may be higher or lower based on a few factors, including your weight at the beginning of your pregnancy, your body mass index (BMI), your activity level and whether you’re having multiples.
These extra calories are essential for supporting the natural, gradual weight gain that you’ll experience as your body changes to support your growing baby.
What to do about cravings during pregnancy
Cravings are real, and you don’t have to resist them. A treat here and there (assuming it isn’t from the “foods to avoid” list) is perfectly fine, and not something to feel bad about. Instead, limit the portion sizes of the unhealthy foods you crave, or satisfy cravings with healthy alternatives. For example, use a small bowl to limit a serving of ice cream or chips, or choose dark chocolate over milk chocolate. What’s most important is that unhealthy foods aren’t your main source of extra calories.
What to eat if you have morning sickness
There may be times when you can’t stick to your usual pregnancy eating patterns. Bouts of morning sickness are a perfect example. If you can’t keep most food down, focus on eating what you can keep down. In these cases, something is better than nothing. Foods such as bananas, rice, crackers and applesauce tend to be easier to eat when you’re looking to get relief from morning sickness.
Bouts of morning sickness are a perfect example. If you can’t keep most food down, focus on eating what you can keep down. In these cases, something is better than nothing. Foods such as bananas, rice, crackers and applesauce tend to be easier to eat when you’re looking to get relief from morning sickness.
Start eating for (the health of) two
From your first trimester onward, you do have to avoid eating and drinking a few things. But your pregnancy diet doesn’t have to be stale. You have a lot of options for getting your nutrient intake, and if you have questions, your doctor or midwife will be happy to answer them at your next prenatal appointment.
And if you aren’t pregnant yet, you can get a head start on your tests, questions and more by scheduling a preconception appointment.
How to determine pregnancy without a test
How to determine pregnancy without a test and what signs indirectly indicate that your beloved baby will be born soon? Of course, only a blood test can give a 100% guarantee, but the presence of certain signs may indicate its possible onset.
Classic signs of pregnancy
The most common early signs and symptoms may include
- Delayed menses. Problems with the regularity of the menstrual cycle may be associated with hormonal imbalance in the body. But if the delay arose for the first time, and before that the cycle was as accurate as a clock, then it is likely that you are pregnant.
- Early toxicosis with severe nausea and vomiting - the most common sign of an interesting situation, but not every woman has.
- Pain in both breasts or enlargement. Nipples can become very sensitive and change color. Sometimes in the early stages, colostrum is released from them with slight pressure.
- Pain in the pelvic region, similar to menstruation. But this sign can also indicate such a serious pathology as an ectopic pregnancy.
- Increased amount of discharge from the genitals. This can usually be observed during ovulation.
 Normal discharge is clear and odorless. When a whitish tint or a curdled structure appears, thrush can also be assumed, which is a common problem for expectant mothers. But in this case, you can not do without treatment. During the period of bearing a child, it is necessary to protect your body as much as possible from any, even such a safe disease.
Normal discharge is clear and odorless. When a whitish tint or a curdled structure appears, thrush can also be assumed, which is a common problem for expectant mothers. But in this case, you can not do without treatment. During the period of bearing a child, it is necessary to protect your body as much as possible from any, even such a safe disease. - Increased or vice versa reduced libido. Every woman experiences jumps in sexual desire in one direction or the other due to hormonal changes occurring in the body. Therefore, men should treat this with understanding, knowing that they have not become less loved, but these are just signs of pregnancy.
- Frequent urination, despite the fact that you do not drink more often and there are no inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. A similar phenomenon is associated with a slight relaxation of the sphincter of the bladder due to hormonal processes. And with the growth of the uterus and, accordingly, with the increase in pressure on the bladder, going to the toilet will become even more frequent.

Additional symptoms of pregnancy
There are less obvious signs that may occur during the first trimester. These include:
- Strange Desires . For example, at night I sharply wanted chocolate, and during the day - salted fish. Such desires may not be mere whims. If you want sour, then perhaps there is not enough vitamin C in the body. You want to gnaw on the wall with calcium deficiency, and sniff gasoline - with a lack of iron, anemia.
- Constant irritability, tearfulness. The flow of hormones in a woman's body in the early stages can make her unusually emotional. So-called mood swings can be a clear sign of pregnancy.
- Bloating . Hormonal changes can cause feelings of fullness in the abdomen, as at the beginning of the menstrual cycle.
- Bloody discharge pale pink. This symptom is called implantation bleeding. This happens when a fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus, about 10 to 14 days after conception.
 Usually occurs during the normal periods of the menstrual period. But not all women have such bleeding is a sign of a normal pregnancy. Therefore, in case of detection of deviations from the normal cycle, consult a gynecologist.
Usually occurs during the normal periods of the menstrual period. But not all women have such bleeding is a sign of a normal pregnancy. Therefore, in case of detection of deviations from the normal cycle, consult a gynecologist. - Chair problems . Hormonal changes cause the digestive system to slow down, which can lead to constipation.
- Food aversions . When you are pregnant, you may become more sensitive to certain smells and your sense of taste may change. Like most other symptoms, these eating habits can be attributed to hormonal changes.
- Nasal congestion . An increase in hormone levels and blood production can lead to swelling of the nasal mucosa. This can cause congestion or runny nose, nosebleeds.
90,000 first signs of pregnancy in the early stages
Basket
0 ₽
Basin
0 ₽
Publication date: 05/17/2021
For pregnant and nursing forces StressstressArticle 9000
Svetlana Bukharova,
Nutritionist, fitness instructor
12 years of experience. Diploma of Medical Education: DVS 1724848
Diploma of Medical Education: DVS 1724848
Article content
- How to understand the first signs of pregnancy without a test
- Signs of pregnancy in the early stages will help to determine the measurement of basal temperature
- Pregnancy symptoms - "Grandma's" methods of determining
- Determination of pregnancy by changes in well-being and mood
- Ask an expert on the topic of the article
Since ancient times, women have been looking for ways to find out about pregnancy as early as possible. Documents found during the study of the Egyptian pyramids (1370 BC) describe this method of early detection of pregnancy: a woman should urinate on barley and wheat seeds. If the grain sprouted shortly thereafter, the woman was considered pregnant. The method was tested by modern scientists in 1963, and it turned out that such a text is really effective in 70% of cases. This is due to an increase in the level of estrogen in the body of the expectant mother, which is excreted along with urine and accelerates the process of grain germination.
The method was tested by modern scientists in 1963, and it turned out that such a text is really effective in 70% of cases. This is due to an increase in the level of estrogen in the body of the expectant mother, which is excreted along with urine and accelerates the process of grain germination.
And at the end of the 17th century, the so-called "olfactory" method was popular. They set fire to a cloth soaked in women's urine. If the woman did not like the smell formed during burning, it was concluded that the lady was in position. However, there are many such methods, many of them have been tested for centuries and have the right to exist. In the article we will talk about the most effective testless methods for determining the "interesting position" - both medical and folk. The latter do not guarantee 100% reliability, since they do not have scientific justification and confirmation, but they will help not to delay a visit to the gynecologist.
How to understand the first signs of pregnancy without a test
Medical methods are the most reliable in determining pregnancy without a test. If you suspect that you are in an interesting position, go to the antenatal clinic. The gynecologist will examine you and direct you to donate blood for the hCG hormone.
If you suspect that you are in an interesting position, go to the antenatal clinic. The gynecologist will examine you and direct you to donate blood for the hCG hormone.
HCG
Blood should be taken in the morning on an empty stomach. The concentration of chronic genadotropin increased throughout pregnancy. If the egg is not fertilized, the indicator is 0-5 mU / ml. If the gestational age is from one to two weeks - 25-156 mU / ml.
Ultrasound
From the seventh day, the fact of conception can be determined by ultrasound. Ultrasound is needed not only to confirm pregnancy. The doctor will also determine the condition of the reproductive organs, the location of the embryo, and exclude an ectopic pregnancy.
Don't have time to read long articles? Follow us on social networks: listen to the video in the background and read short notes about beauty and health.
Megapharmacy in social networks: VKontakte, Telegram, OK, Viber
Signs of pregnancy in the early stages will help determine the measurement of basal body temperature
Gynecologists call this method one of the most reliable. At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, the basal temperature (BT) is kept at around 36.5 - 36.7 ° C, rises to 37 ° C by ovulation. In the event that there was no conception, after the cessation of ovulation, BT again decreases to average values. If you are pregnant, the temperature will be kept within 37 ° C.
At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, the basal temperature (BT) is kept at around 36.5 - 36.7 ° C, rises to 37 ° C by ovulation. In the event that there was no conception, after the cessation of ovulation, BT again decreases to average values. If you are pregnant, the temperature will be kept within 37 ° C.
How to measure basal body temperature?
A conventional thermometer is inserted into the rectum or vagina. The procedure should be carried out every day at the same time in the morning, without getting out of bed. When measuring temperature:
- Stay in the same position in which you woke up
- Measure BBT 5-8 minutes
- Write down the values (with date and time)
Important! During the period of determining the basal temperature, it is advisable not to smoke or drink alcohol.
Pregnancy symptoms - "Grandma's" methods of determination
You can determine pregnancy without a test using folk methods. They are affordable, harmless to health and help you get quick results without leaving your home.
They are affordable, harmless to health and help you get quick results without leaving your home.
How does iodine help determine pregnancy?
You can find out that you are pregnant with regular iodine.
What you need:
- Napkin or sheet of paper
- Plastic or glass containers
- Iodine
- Pipette
What to do:
- Collect some urine in a container
- Soak tissue/paper in urine
- Lay out on a flat surface
- Pipette iodine
- Place a few drops on paper
Result:
- If the color of the iodine has not changed or changed to a bright dark blue, there is no pregnancy.
- If iodine has changed color to lilac or lilac, you are pregnant.
Advantages of the method:
- Everything you need is at hand
- Early pregnancy detection
Cons of the method:
- No 100% guarantee
- Accurate adherence to instructions
- Time limit: you only have 25 minutes for the test, then the urine becomes unusable
Find out about pregnancy with soda
What you need:
- Soda
- Urine
- container
What to do:
- Collect about 150-200 ml of morning urine in a container
- Pour 1 teaspoon baking soda into the urine
Results:
- The mixture bubbles and hisses, which means that the acidity is normal.
 you are not pregnant
you are not pregnant - Soda settled at the bottom, which means that my acidity is lowered. There is a high probability that conception has occurred.
Advantages of the method:
- Cheap
- Accessibility
Cons of the method:
- Efficiency not confirmed by studies
- May give a false result (due to the nature of the urine)
There is another method to test for a possible pregnancy, which does not require "chemical experiments". It consists of palpation of the pulse on the abdomen. Place your fingers on your abdomen two fingers below your navel. During pregnancy, the blood supply to this area increases, the pulse becomes more frequent and well audible.
Feeling and Mood Changes in Pregnancy Detection
There are several symptoms in early pregnancy before your period that might suggest you are pregnant before you see your doctor or buy a test. Listen to your body. You are probably pregnant if:
Listen to your body. You are probably pregnant if:
- No menstruation
- Feeling dizzy, there is a veil in front of the eyes
- Body temperature rises to 37 - 37.5°C for a long time
- Stuffy nose
- Enlarged, swollen breasts, the color of the nipples changed, they became hypersensitive
- Feeling of heaviness and pain in the navel, in the lower abdomen
- You feel sick, your sense of smell and touch are acute
- Overweight
- Frequent mood swings, tearfulness
- Weakness, increased drowsiness
- Gastronomic "shifts" - the desire to "taste" unsuitable for food substances, such as chalk. Cravings for salty, sweet, sour
- A sharp decrease or increase in sexual desire
There are many ways to determine pregnancy without a test, but you should not rely only on physiological changes occurring in your body and “grandmother's” tests. Finding out that you may soon become a mother is best from a gynecologist. Only a specialist will be able to prevent abnormalities in the development of the fetus and determine an ectopic pregnancy, if any. Modern diagnostic methods are very effective, and using them you can endure and give birth to a healthy baby.
Only a specialist will be able to prevent abnormalities in the development of the fetus and determine an ectopic pregnancy, if any. Modern diagnostic methods are very effective, and using them you can endure and give birth to a healthy baby.
Sources:
- Cyberleninka.ru L.A. Terebneva: The history of pregnancy tests and modern methods for determining short-term pregnancy. GBOU DPO Russian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education of the Ministry of Health of Russia
- Elibrary.ru Pregnancy. Week after week. Desktop. book-calendar for expectant mothers and their caring loved ones. Glade Curtis; [Trans. from English: N.A. Shishkov]. - Ser. We are expecting a baby
- Сyberleninka.ru V.E. Kupchenko: Psychology of pregnancy: main directions of research. Omsk State University F.M. Dostoyevsky
- Elibrary.ru Peretyako L.P., Nazarov S.B., Fateeva N.V., Kuznetsov R.A.: Method for morphological determination of gestational age. FSBI "Ivanovo Research Institute of Motherhood and Childhood named after V.