Diet pill while breastfeeding
Diet and medication while breastfeeding
Diet and medication while breastfeeding | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content6-minute read
Listen
Breastfeeding mothers often worry that what they eat and drink (consume) can affect their baby. You don't need to follow a special diet when breastfeeding. But you do need to be careful with some things.
Your diet and breastfeeding
No matter what foods you eat, your body will make healthy breast milk. Eating a nutritious diet and drinking enough fluids will help you produce enough milk.
Breastfeeding uses a lot of calories so you may need to eat a little more than normal.
Make sure to include plenty of protein, calcium and iron in your diet. You may also need an iodine supplement.
You might worry that some foods like spices, garlic, beans or cabbage might make your baby gassy and irritable. Food is rarely the cause, and you should rule out some other possibilities before changing your diet.
There is no need to avoid allergenic foods such as peanuts, egg or milk while you are breastfeeding. The research suggests that this will not stop your baby becoming allergic to these foods.
There is little evidence to support eating foods that claim to boost your milk supply. If you are worried about your milk supply you should talk to your doctor.
Caffeine and breastfeeding
Most breastfeeding mothers can consume a few cups of tea or coffee each day.
But caffeinated energy drinks are not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women.
The amount of caffeine in your breast milk usually peaks about 1 hour after you consume it.
You should not have more than 200mg of caffeine per day while breastfeeding. The following is a handy guide:
- espresso coffee has 60–120 mg per 250 mL cup
- instant coffee (one teaspoon/ cup) has 60–80 mg per 250 mL cup
- tea has 10–50 mg per 250 mL cup
Newborn babies are particularly sensitive to caffeine.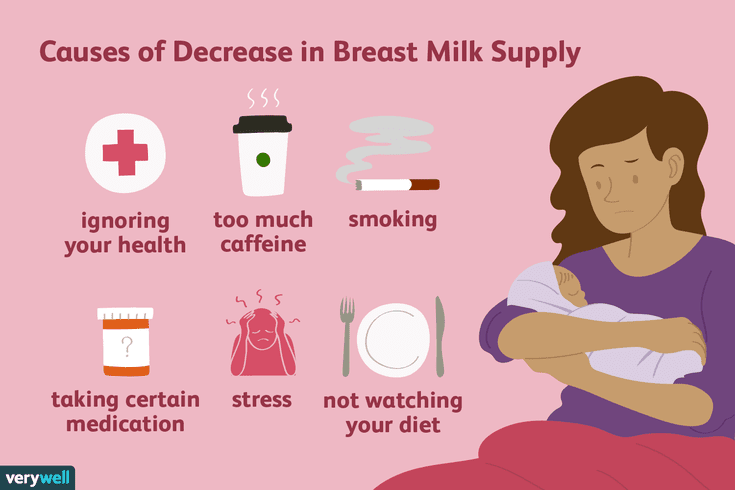 This is because it can take them between 2 and 4 days to process caffeine.
This is because it can take them between 2 and 4 days to process caffeine.
Alcohol and breastfeeding
It’s best to limit alcohol while you’re breastfeeding. The amount of alcohol in your breast milk is the same as in your blood.
Alcohol enters your breast milk 30 minutes to 1 hour after you start drinking. This depends on how much alcohol you drink, whether you have eaten, how much you weigh and how quickly you are drinking.
It takes about 2 hours for your body to get rid of the alcohol from one standard drink.
If you do have an occasional drink, feed your baby and express milk before you start drinking. Your baby can drink the expressed milk while there is still alcohol in your body.
The safest option is to avoid drinking alcohol when you are breastfeeding.
If you do plan on drinking alcohol use the Feed Safe apps.
Medications and breastfeeding
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice on medicines that are safe to take while breast feeding.
Most medicines are safe to take at the recommended dose while breastfeeding. Even if the medicine does pass into your breast milk, it’s usually in such a small amount that it won’t harm your baby.
Take special care if your baby was premature, is sick or on medication.
For more information on medicines that are safe to take while breastfeeding, call the NPS Medicines Line on 1300 MEDICINE (1300 633 424) Monday to Friday, 9am to 5pm AEST.
Contraception and breastfeeding
If you are breastfeeding, you can get still pregnant, even if your periods haven't started again.
Except for combined hormonal contraception (products that contain both oestrogen and progestogen), contraception can be safely used immediately after birth. Talk to your doctor about protection while breastfeeding.
Complementary and alternative medicines and breastfeeding
Complementary and alternative medicines (CAMs) include vitamins, dietary supplements, aromatherapy and homeopathic products.
We often think of CAMs as safer than pharmaceutical medicines. But there is little research to support the safety of CAMs.
Many CAMs are not recommended for use when breastfeeding. Talk to your doctor, pharmacist or call the NPS Medicines Line before you take any CAMs while breastfeeding.
If you’re unsure about consuming something while you’re breastfeeding, ask your doctor or lactation consultant about it.
Smoking and breastfeeding
It is best not to smoke if you are breastfeeding.
If you can’t quit smoking, it is still better for your baby to be breastfed.
The amount of nicotine in your breast milk halves about 1.5 hours after each cigarette. So, if you smoke, do so right after a breastfeed. The longer the time you leave between a cigarette and the next feed, the better.
It is very important to protect your baby from cigarette smoke, which puts your baby at risk of chest infections, asthma and sudden infant death syndrome. Don’t smoke around your baby, in the house. Smoking in your car with a child aged under 16 years is illegal.
Smoking in your car with a child aged under 16 years is illegal.
Where to get more advice:
- Pregnancy, Birth and Baby - 1800 882 436
- Poisons Information Centre - 13 11 26
- Australian Breastfeeding Association - 1800 686 268
Sources:
Cochrane Library (Oral galactagogues (natural therapies or drugs) for increasing breast milk production in mothers of non‐hospitalised term infants), Food Standards Australia and New Zealand (Pure and highly concentrated caffeine products), RACGP (Breastfeeding Evidence based guidelines for the use of medicines), RANCOG (FSRH Guideline Contraception After Pregnancy), Australian Breastfeeding Association (Breastfeeding and food sensitivities), Australian Breastfeeding (Breastfeeding and maternal), Australian Breastfeeding Association (Alcohol and breastfeeding), Australian Breastfeeding Association (Breastfeeding and smoking), NSW Health (Smoking with kids in the car is illegal), NHMRC Dept of Health and Ageing (Eat for Health: Infant Feeding Guidelines Information for Health Workers)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: June 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Breastfeeding your baby
Need more information?
Breastfeeding diet, exercise & lifestyle | Raising Children Network
A healthy breastfeeding diet has a wide variety of foods from the five main food groups. Physical activity is also important for your health and wellbeing.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Breastfeeding and your diet - Better Health Channel
Breastfeeding women need to eat regularly and include a wide variety of healthy foods in their diet.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Diet and weight loss while breastfeeding | Australian Breastfeeding Association
A 'perfect' diet is not required for breastfeeding. In general, your diet is important for your own health and energy levels, rather than affecting your breastmilk and your baby. Even in countries where food is scarce, mothers are able to breastfeed and their babies thrive. This article contains tips about what to eat and how to lose weight safely while breastfeeding.
In general, your diet is important for your own health and energy levels, rather than affecting your breastmilk and your baby. Even in countries where food is scarce, mothers are able to breastfeed and their babies thrive. This article contains tips about what to eat and how to lose weight safely while breastfeeding.
Read more on Australian Breastfeeding Association website
Healthy Eating When You’re Pregnant or Breastfeeding | Eat For Health
Eating well during pregancy and while breastfeeding has health benefits for you and your baby.
Read more on NHMRC – National Health and Medical Research Council website
Galactagogues (substances claimed to increase supply) | Australian Breastfeeding Association
Galactagogues are foods, herbs or medications that can help to increase breastmilk supply. The use of a galactagogue to help increase low breastmilk supply requires consultation with a lactation consultant and/or medical adviser.
The use of a galactagogue to help increase low breastmilk supply requires consultation with a lactation consultant and/or medical adviser.
Read more on Australian Breastfeeding Association website
Healthy diet during pregnancy
A healthy diet is an important part of a healthy lifestyle at any time, but especially vital if you're pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding is learnt over the first weeks and months of your child’s life. It is a unique and special experience for families as no two mothers or babies are the same.
Read more on Karitane website
Exercise and breastfeeding | Australian Breastfeeding Association
by Renee Kam, Physiotherapist, IBCLC and ABA Breastfeeding Counsellor.
Read more on Australian Breastfeeding Association website
Breastfeeding problems | Australian Breastfeeding Association
Common breastfeeding questions: enough milk, too much milk, expressing - Raising Children NetworkCommon breastfeeding questions: challenges, getting help - Raising Children Network
Read more on Australian Breastfeeding Association website
Breastfeeding Confidence | Australian Breastfeeding Association
Breastfeeding Confidence is a quick guide on the essentials of breastfeeding. Download your free copy now.Breastfeeding Confidence has also been translated into other languages.
Read more on Australian Breastfeeding Association website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
The Dangers of Taking Weight-Loss Supplements While Breastfeeding
Taking diet pills when breastfeeding can cause side effects like diarrhea or constipation, which may also affect your baby.
Image Credit: Image Source/Image Source/Getty Images
You had the baby, and now you're ready to lose the weight. Diet pills may be tempting to help you shed pounds quickly, but taking weight-loss supplements while breastfeeding likely isn't safe for you or your child.
Video of the Day
Weight-loss supplements often claim to help burn fat, regulate appetite, speed metabolism or improve nutrition to ultimately help you slim down, according to the Cleveland Clinic. But these products are not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and in fact, there's little scientific evidence to show they work at all, per the Mayo Clinic.
But these products are not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and in fact, there's little scientific evidence to show they work at all, per the Mayo Clinic.
And not only is it unlikely that these supplements will help with weight loss, but some of these products can also harm your health due to side effects and hidden ingredients, according to the Mayo Clinic.
So, can you take weight-loss pills or fat burners while breastfeeding? Here, we explore whether or not you can take appetite suppressants or other diet supplements while breastfeeding, plus safer ways to lose weight postpartum.
Tip
Ask your doctor if you can take any weight-loss pills while breastfeeding (or other supplements, for that matter), as the FDA doesn't require supplements to be proven safe or effective before they are sold, so there’s no guarantee that what you take is safe, contains the ingredients it says it does or produces the effects it claims.
Can You Take Weight-Loss Supplements While Breastfeeding?
If you're wondering whether you should take weight-loss pills while breastfeeding, the short answer is probably not (the same goes for taking diet pills while pregnant).
Here's why: Diet supplements (yes, even the "natural" ones) may have side effects that can affect you and your child, as it's possible to pass potentially harmful ingredients to your baby via breastmilk, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
Per the National Institutes of Health (NIH), potential side effects include:
- Headaches
- Difficulty sleeping
- Muscle or bone pain
- Increased heart rate
- High blood pressure
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Abdominal cramps
- Gas
- Heartburn
- Vertigo
- Weakness
- Anxiety
- Jitteriness
- Kidney stones
- Liver damage
Certain ingredients in diet supplements are explicitly discouraged if you're breastfeeding. For instance, 5-Hydroxytryptophan is a component of certain weight-loss pills that may not be safe for your baby, according to Mount Sinai.
Some of these products also contain prescription drugs without listing them on the label, per the Mayo Clinic, which can produce even more unexpected side effects and potentially harm you or your child.
Additionally, the downstream effects of certain diet pills may not be safe while you're breastfeeding.
For example, many supplements contain caffeine, which acts as a diuretic and eliminates fluid from your body, per the NIH. Staying well-hydrated is important while you're breastfeeding, so losing too much fluid can jeopardize healthy lactation, according to the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP). What's more, shedding water weight alone doesn't support long-term weight loss.
Are There Safe Weight-Loss Supplements for Breastfeeding?
Diet pills and their ingredients aren't tested in babies, so taking any weight-loss supplement while breastfeeding is inherently risky for your child — especially considering these products don't typically support weight loss in the first place, per the Mayo Clinic.
Can You Take Fat Burners While Breastfeeding?
Some people specifically turn to fat burners while breastfeeding to fast-track weight loss. Fat burners are a type of supplement that often contain stimulants and claim to increase your metabolism, reduce fat absorption and suppress your appetite, per the Cleveland Clinic. But like other diet pills, there's no scientific evidence to suggest that these products work or that they're safe for you and your baby.
But like other diet pills, there's no scientific evidence to suggest that these products work or that they're safe for you and your baby.
Most fat burners use stimulants like caffeine, green tea extract and yohimbe, per the Cleveland Clinic. While small amounts of caffeine are typically safe while you're breastfeeding, fat burners aren't regulated by the FDA and thus don't always list dosage information, so you run the risk of overloading yourself and your child with stimulants. This can lead to side effects like:
- Headaches
- Anxiety
- Agitation
- Increased blood pressure
- Increased heart rate
- Difficulty sleeping
In high doses, yohimbe can also cause heart problems or kidney failure, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
The takeaway: Skip the fat burners (and all other diet supplements) while breastfeeding, as the risk certainly outweighs the potential reward.
Is L-carnitine Safe for Breastfeeding?
Certain fat burners contain carnitine, a compound that supports metabolism and energy levels, per the Cleveland Clinic. If you have a diagnosed carnitine deficiency and are breastfeeding, you and your baby may benefit from carnitine supplementation, according to August 2020 research in the Drugs and Lactation Database.
If you have a diagnosed carnitine deficiency and are breastfeeding, you and your baby may benefit from carnitine supplementation, according to August 2020 research in the Drugs and Lactation Database.
However, that doesn't mean you should take a fat burner while breastfeeding. Instead, talk to your doctor about the best carnitine-specific supplement — not a diet pill that contains the ingredient — for you.
Safer Alternatives to Diet Pills While Breastfeeding
If your goal is to shed pounds after giving birth, taking weight-loss supplements while breastfeeding is not the solution.
Instead, lose weight the safe and sustainable way by eating a nutritious diet and exercising regularly, all of which can help you burn more calories than you eat. According to the Mayo Clinic, your diet should include:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Whole grains like oats, whole-wheat bread and brown rice
- Low-fat dairy products like yogurt and milk
- Lean protein sources like skinless poultry, beans, and nuts
When it comes to physical activity, talk to your doctor about when it's safe to start exercising. Typically, you can start moving as soon as you feel ready, although you may have to wait for your doctor's clearance if you're recovering from a C-section, extensive vaginal repair or a difficult delivery, per the Mayo Clinic.
Typically, you can start moving as soon as you feel ready, although you may have to wait for your doctor's clearance if you're recovering from a C-section, extensive vaginal repair or a difficult delivery, per the Mayo Clinic.
Once you're able, though, a combination of strength training and cardio exercises can help you not only lose weight, but also increase your strength, improve your energy levels and support your mental health, according to the Mayo Clinic.
And through it all, don't forget to stay hydrated to support your wellbeing and the breastfeeding process, per the Mayo Clinic. It takes extra energy to produce milk for lactation, so it's important to get plenty of fuel, fluid and rest to sustain the health of you and your baby, according to CHOP.
How to lose weight after childbirth while breastfeeding
09/18/2018 Visitors: 75555
The article is devoted to the main issues of life and health of a modern woman.
How to get slim after childbirth while breastfeeding? After childbirth, the main goal of a woman is the full development of the baby, the basis of which is breastfeeding. While enjoying breastfeeding, many young mothers notice that the former prenatal harmony does not want to return. Sometimes, despite all efforts, the weight continues to increase.
While enjoying breastfeeding, many young mothers notice that the former prenatal harmony does not want to return. Sometimes, despite all efforts, the weight continues to increase.
How to lose weight after childbirth while breastfeeding - the principles of a healthy diet
Usually the problem of unwanted pounds is solved with the help of a special diet. But is there an expert-approved balanced diet for new mothers who are breastfeeding their babies? After all, their diet should be complete, containing the full range of nutrients needed by the baby. It is important to understand that, contrary to popular belief, eating for two is not worth it during pregnancy. The amount of food eaten is unlikely to increase the amount of breast milk, but the lifeline at the waist will definitely grow.
How to choose a diet for weight loss after childbirth
Of course, the baby's health is above all. It requires such a selection of products that would contain all the essential amino acids necessary for the growth of the newborn. How to lose weight after childbirth while breastfeeding in this situation? Therefore, strict diets for a young mother during breastfeeding are strictly contraindicated. But a rational balanced diet, for young mothers, will contribute to safe weight loss, the return of a slim figure. The diet will ensure the presence in the milk of proteins, fats and carbohydrates that are healthy for the baby.
How to lose weight after childbirth while breastfeeding in this situation? Therefore, strict diets for a young mother during breastfeeding are strictly contraindicated. But a rational balanced diet, for young mothers, will contribute to safe weight loss, the return of a slim figure. The diet will ensure the presence in the milk of proteins, fats and carbohydrates that are healthy for the baby.
When can you start to lose weight after childbirth? Then, after 5-6 months, eliminate light carbohydrates and trans fats from the diet. What should be the diet for nursing mothers who want to lose weight after childbirth while breastfeeding? How to get back in shape?
5 principles of a diet for weight loss during breastfeeding
1. The very first rule of a diet for weight loss after childbirth during breastfeeding can be formulated as follows: we eat only what the body really needs. Try not to get carried away with fried, floury and sweet, giving preference to cereals and vegetables.
2. Fat in the daily diet of a young mother who wants to return the figure to prenatal forms should not exceed 40%. Therefore, buy dairy products with the lowest possible fat content, and give up seeds and nuts for a while. Meat, especially beef, is essential during lactation, but they should not be eaten more than once a day.
3. The diet of a nursing mother implies mandatory control over the amount of food eaten. The daily number of calories for medium-sized and short women should be reduced to 1500, and for tall and large women by nature - up to 2000.
4. An important guarantee of weight loss after childbirth is the correct diet. If you intend to lose weight, you should eat small portions (no more than 250 g), but often: 5-7 times a day.
5. A hypoallergenic diet for weight loss after childbirth during breastfeeding means avoiding foods that contain allergens - substances that can cause an allergic reaction in an infant. These products include: citrus fruits, strawberries, chocolate, eggs, various canned food. In no case should you take dietary supplements for weight loss! Thirst should be quenched with the most ordinary clean water and fresh fruits, but not with sweet water. Exclude soda, sweet tea, factory kvass.
In no case should you take dietary supplements for weight loss! Thirst should be quenched with the most ordinary clean water and fresh fruits, but not with sweet water. Exclude soda, sweet tea, factory kvass.
According to these principles, a diet for nursing mothers for weight loss can be compiled independently. To simplify the task, we offer an approximate menu.
Breakfast options:
25 g cereal (unsweetened) with milk, banana.
25 g cheese with bran toast, apple.
Lunch options:
100 g light cod steak, garnished with mashed potatoes with herbs and green peas; low-calorie yogurt; green salad.
Spaghetti with tomato sauce, lean minced meat, garlic, herbs and cheese; mixed salad; small apple.
Dinner options:
125 g boiled beans; 2 toasts; banana.
Any boiled vegetables with a sauce of yoghurt, lemon juice and Edam cheese; whole grain bun.
Snack options:
25 g cheese and a couple slices of whole grain bread, 2 tomatoes.
You can eat a small wholemeal bun with a glass of low-fat kefir or curdled milk.
Based on personal experience, I want to say that this diet helped me get rid of extra 35 kg in 3-4 months. Dear girls, do not forget about sports. Allocate for yourself, your beloved, 2 hours 3 times a week for physical activity. Trust me, it's worth it!
The article was prepared by an obstetrician-gynecologist, head. antenatal clinic BU "Megion City Hospital No. 1" - Vanina O.S .
Breastfeeding and drug use
And now the birth is behind, the labor pain has been forgotten, lactation has been established, and at any moment a new problem may arise in front of the young mother: how the medicine will affect the newborn baby when breastfeeding. Unfortunately, not every mother can boast of excellent health and there is a need to take medication.
The degree of adverse effect of the drug on the body of the newborn is determined by the following factors:
- drug toxicity;
- the true amount of the drug that entered the child's body;
- a feature of the effect of the drug on the immature organs of the child;
- the duration of the drug excretion from the child's body;
- the duration of taking the medicine by a nursing mother;
- individual sensitivity of the child to this drug;
- the risk of developing allergic reactions.

Of the most commonly used drugs, most are not very toxic drugs that cause significant toxic effects on organs and tissues. Therefore, it is believed that in many cases, with medical treatment, breastfeeding can be continued.
If a woman combines breastfeeding and treatment, then it may be useful to select the optimal scheme for alternating the drug and feeding. It is necessary to take the medicine in such a way that the time of feeding does not fall on the period of its maximum concentration in the blood.
When using the medicine, a woman during breastfeeding should be aware that the side effects caused by this drug may also occur in a child.
If the risk of adverse effects of the drug on the child's body is high, then for the duration of treatment you need to stop breastfeeding, but continue pumping milk to maintain lactation. After the end of the course of treatment, it is necessary to resume breastfeeding. It is believed that after a course of antibiotics incompatible with breastfeeding, you can feed 24 hours after the last dose of the drug. And when using a number of radioactive agents, the radioactivity of milk can persist from 3 days to 2 weeks.
And when using a number of radioactive agents, the radioactivity of milk can persist from 3 days to 2 weeks.
Features of the use of various groups of drugs during breastfeeding
Medicines contraindicated while breastfeeding:
Cytostatics and radioactive preparations (drugs used to treat tumors and autoimmune diseases, rheumatoid arthritis). These drugs significantly suppress immunity and cell division. If necessary, these drugs stop breastfeeding.
Antibiotics are used to treat various infectious and inflammatory diseases. Penicillins, cephalosporins, macrolides, aminoglycosides are usually not contraindicated in breastfeeding. These antibiotics pass into milk in small amounts, so their toxicity to the child is low.
Macrolides (erythromycin, sumamed, vilprofen, etc.) penetrate milk well, but their use during breastfeeding is possible. There is a potential risk of developing complications associated with the occurrence of allergic reactions, disruption of the normal intestinal flora (diarrhea), reproduction of fungi (candidiasis - thrush). For the prevention of dysbacteriosis, it is recommended that the child be given probiotics (Bifidum Bacterin, Linex). If an allergic reaction occurs in a child, you should stop taking this antibiotic or temporarily stop breastfeeding.
For the prevention of dysbacteriosis, it is recommended that the child be given probiotics (Bifidum Bacterin, Linex). If an allergic reaction occurs in a child, you should stop taking this antibiotic or temporarily stop breastfeeding.
Tetracyclines, sulfonamides (Bactrim, Biseptol, etc.), Metronidazole, Clindamycin, Lincomycin, Ciprofloxacin penetrate into milk, and the likelihood of negative reactions is high. Therefore, the use of these drugs during breastfeeding is contraindicated.
Side effects of tetracyclines - growth retardation of the child, a violation of the development of bone tissue and tooth enamel of the child. Side effect of Clindamycin - risk of gastrointestinal bleeding; and Levomycetin - toxic damage to the bone marrow, the effect on the cardiovascular system.
Antihypertensives are used in hypertension.
When breastfeeding, the following drugs can be used with caution: Dibazol, Dopegit, Verapamil.
Contraindicated in breastfeeding: Cordaflex, ACE inhibitors (Enap, Kapoten), Diazoxide, Reserpine.
The use of antihistamines for allergies during breastfeeding is possible. It is advisable to use Cetirizine, Loratadine. It is not desirable to use 1st generation drugs (Suprastin, Tavegil), which can cause drowsiness in a child. Erius is contraindicated in breastfeeding.
Antithyroid drugs for breastfeeding
Antithyroid drugs are used in diseases of the thyroid gland, occurring with an increase in its function. These drugs are used when breastfeeding with caution, controlling the condition of the child. They suppress the function of the child's thyroid gland.
Salbutamol, terbutaline, fenoterol are approved for use during breastfeeding. It is necessary to monitor the condition of the child, since their side effect is excitement, increased heart rate.
Hormones (prednisolone, dexamethasone, hydrocortisone) are used for autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic connective tissue diseases, autoimmune hepatitis, etc., with adrenal insufficiency) are usually not contraindicated in breastfeeding.
However, if it is necessary to treat them for more than 10 days, the issue of continuing breastfeeding is decided individually. If a woman needs long-term hormonal treatment at a high dose, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Paracetamol is not contraindicated during breastfeeding if used in the usual dose (1 tablet up to 3-4 times a day, no more than 2-3 days). Exceeding the dose and long-term use of paracetamol should be avoided, since the side effect of the drug is a toxic effect on the liver and blood.
Contraceptives for breastfeeding
When breastfeeding, drugs containing progesterone are allowed. Other medicines are contraindicated during breastfeeding.
Expectorants during breastfeeding
- Ambroxol, Bromhexine, ACC can be used during breastfeeding.
- Pre- and probiotics (Linex, Hilak forte, etc.) are compatible with breastfeeding.
It should be noted that in our Center for Mother and Child, all medications used are safe for the health of the baby and mother.