Post ovulation means
Ovulation Basics: What Happens Pre And Post Ovulation
Unless you’ve been doing your research prior to trying for a baby, you might be a little confused about ovulation. After all, as teenagers we are generally only taught about the period part of our monthly cycle; when it is likely to happen, the bodily changes we might notice, how to handle it and what you need to be aware of in this new stage of life.
What they don't often cover in health class, however, is the ovulation part of the cycle. Every girl who experiences menstruation is also (in most cases) ovulating each month, but without the big red sign to tell you it's happening (otherwise known as blood), you may never even be aware of it.
What is ovulation?
Ovulation is part of your menstrual cycle and occurs when an egg is released from your ovary. It’s around the time of the month when a woman is most fertile, and therefore most likely to get pregnant. This isn’t always guaranteed, however, as it depends entirely on the fertilisation of the egg.
When does ovulation happen?
Every woman’s body is different, and timing varies for everyone just as it does with monthly periods, but typically ovulation will occur around day 14 of a 28-day cycle. This means that as a rough rule, it’s probably happening either four days before or four days after the middle point in your cycle. While you may never have had a reason to think about this before, knowing more about ovulation and when it is happening in your body can help you either achieve or prevent pregnancy.
How do you know ovulation is happening?
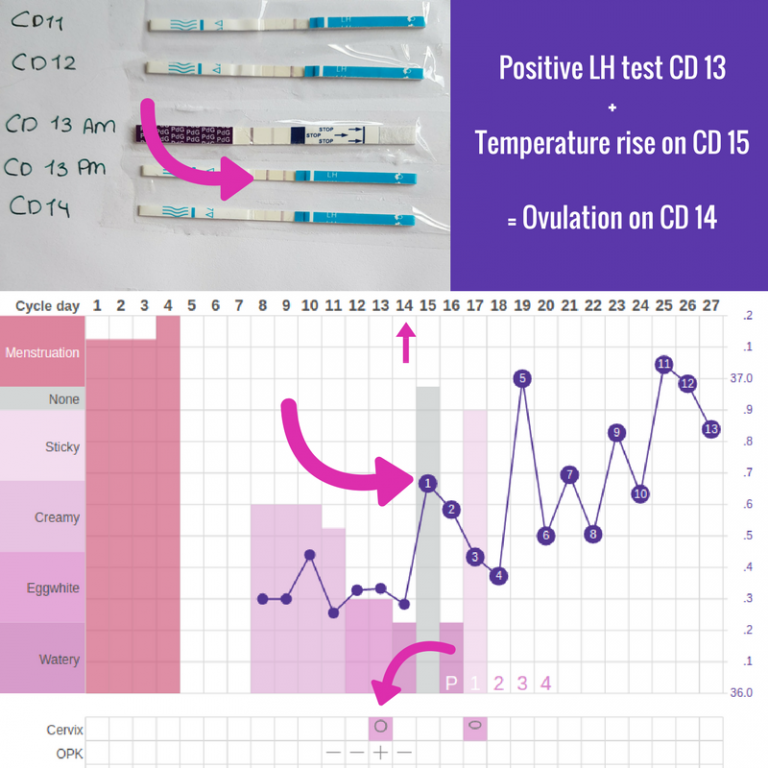
Many women don’t have a clue that they’re ovulating, which is why people who are trying to get pregnant often use ovulation sticks or strips (similar to pregnancy tests) to find out the best time to have intercourse.
That said, some women experience various signs that they have reached the ovulation point in their monthly cycle, so here are some things you may want to look out for:
- The basal body temperature (BBT) experiences fluctuations
- Cervical discharge appears clearer with a consistency similar to egg whites
- Mild cramps or even slight pains occur in the lower abdomen
- An increase in sex drive
- Light spotting when it is not your period
- Slight swelling of the vagina
- Breast tenderness
The signs that you’re ovulating can vary so much from woman to woman, so it is often hard to pinpoint the exact time this takes place in your cycle, though not impossible.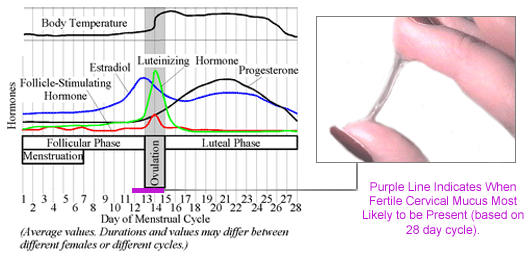
What is happening to your body pre-ovulation?
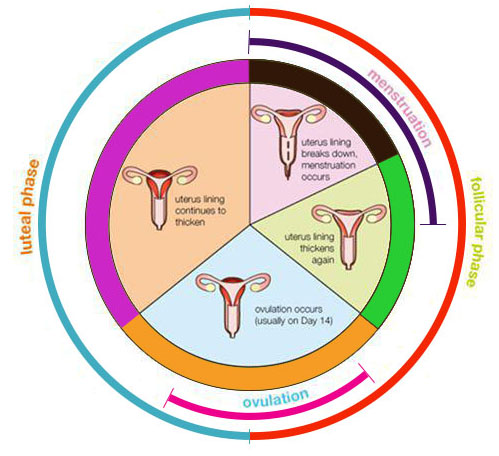
If we count day 1 of the menstrual cycle as the day you first start to bleed, the average woman bleeds for three to five days - though remember everyone is different, so if you bleed for longer this doesn’t mean there is anything wrong. Continuing with this timescale, around day 7 of the cycle your hormones have begun to kick in, in order to prepare your ovaries to release an egg.
From around days 7 to 11, the lining of the uterus thickens in preparation for an egg to potentially latch on. It is during this time that you may notice an increase in discharge, and possibly a change in its consistency.
After roughly day 11 in the cycle, the luteinising hormone signals the egg to be released from the ovary and begin its descent into the fallopian tube, all the way to the uterus. For those trying to get pregnant, this is when things get interesting.
At around day 14, when the egg has been released, is the phase known as ovulation.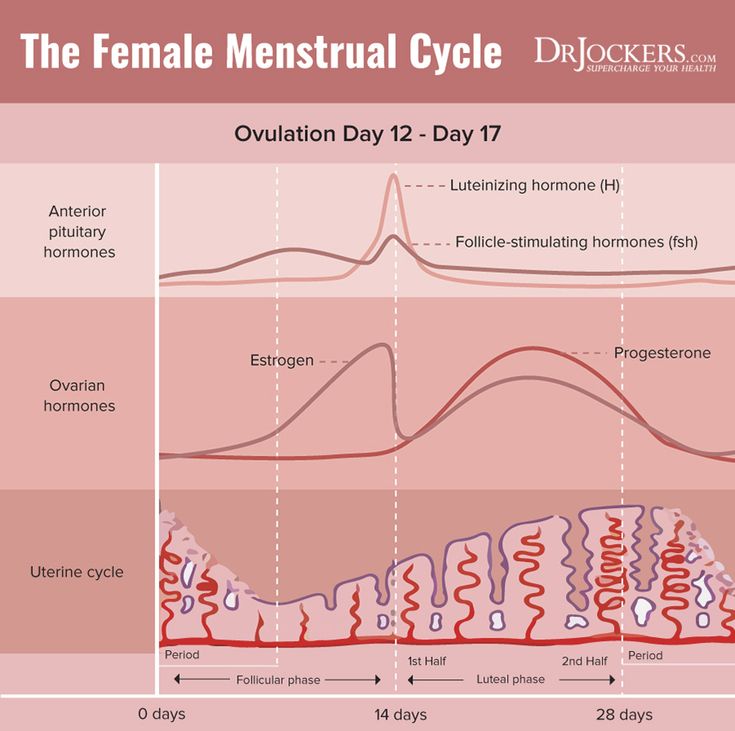
What is happening to your body post-ovulation?
The post-ovulation phase is also known as the luteal phase, and this is when the aforementioned subtle change in body temperature occurs. After ovulation, and if the egg has been fertilised by a sperm, then the egg implants in the uterus, and pregnancy begins.
If the egg is not fertilised then it will essentially “expire” in around 24 hours. When this happens, certain hormone levels will start to decrease, which means the lining of the uterus begins to break down and shed.
This is where the blood comes from when you have your period, and this brings you back to day 1 of the cycle.
Remember, just as periods are unpredictable from woman to woman, everyone is different when it comes to the timing and signs of ovulation. If you want to find out more about your own ovulation phase and menstrual cycle, it is a good idea to keep a cycle diary in order to plan ahead and monitor changes in your body and mood.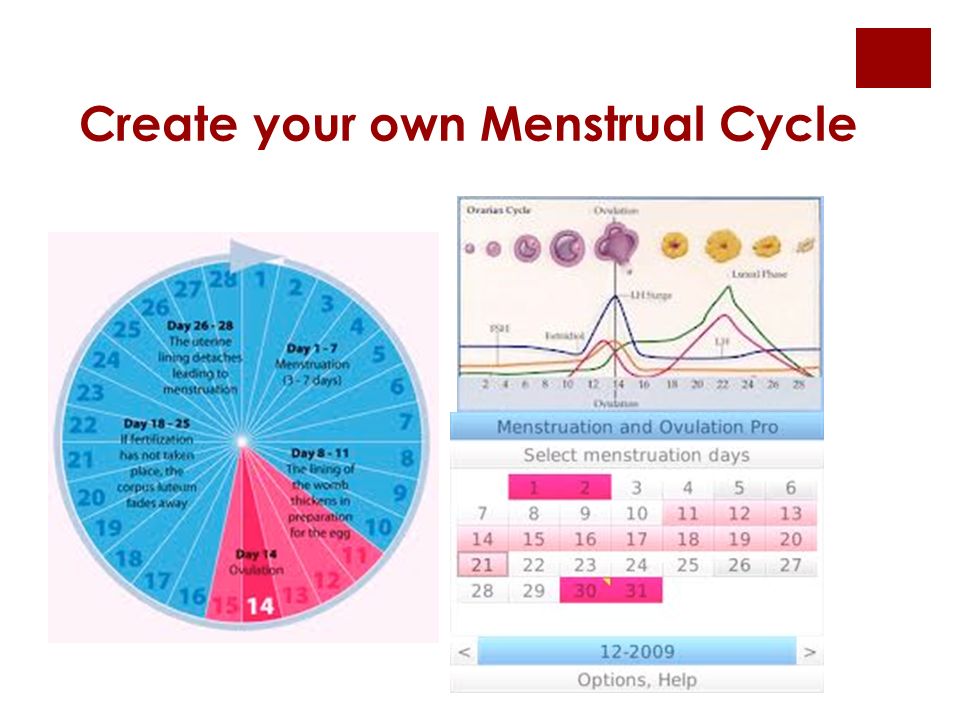
Wondering what more you can learn about ovulation? Reach out in our private Facebook group or drop us a note on Insta @itsyoppie. Don't forget that our personalised period subscription box can get organic tampons, PMS supplements, and much more, delivered easily and regularly through your letterbox. That's one less thing to keep track of!
Fact checked by Doctor Samantha Miller.
Pre & Post Ovulation in Your Menstrual Cycle
Understanding Your Menstrual Cycle
Understanding your menstrual cycle is critical to charting fertility and predicting ovulation. Read about your menstrual cycle – what happens pre and post ovulation – as well as what happens during ovulation.
The menstrual cycle refers to the cyclical development and then shedding of the endometrium, the lining of the uterus. Understanding your menstrual cycle is important if you want to chart your fertility patterns, predict ovulation, and increase your chances of becoming pregnant.
Note: The most reliable way to pinpoint when you ovulate – your most fertile time of month – is by using urine-based ovulation tests. These can be purchased for as little as $0.55 per test (with free same-day shipping). An electronic fertility tracker like the OvaCue can be used to identify even more fertile days each month, and is particularly helpful for women with irregular cycles.
A woman’s fertile period during her menstrual cycle, on average, lasts about seven days: seven days before ovulation (the release of the egg), the day of ovulation, and the day after ovulation. After this, chances of conception decrease quickly, as the egg has a short life-span of about 24 hours.
Given this somewhat narrow window of opportunity for conception, understanding the menstrual cycle can help increase a woman’s chances of becoming pregnant. The key is to predict ovulation with as much precision as possible. Of course, both the length and regularity of menstrual cycles vary greatly among women – so successful ovulation prediction depends both on understanding the general dynamics of the menstrual cycle, as well as a woman’s own unique cycles and patterns.
*Editor’s Note: Do you have questions about your cycle, ovulation, fertility charting – anything relating to getting pregnant? We have a wonderful online community at OvaGraph.com where you can ask questions, get information, or just let off a bit of steam! Come join in – we want to hear from you!
The Menstrual Cycle and Ovulation Prediction
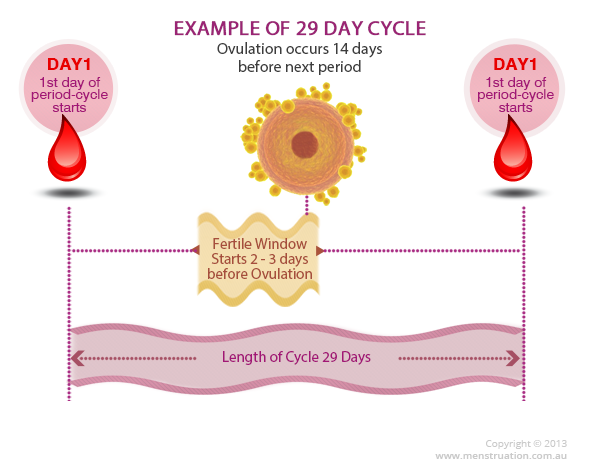
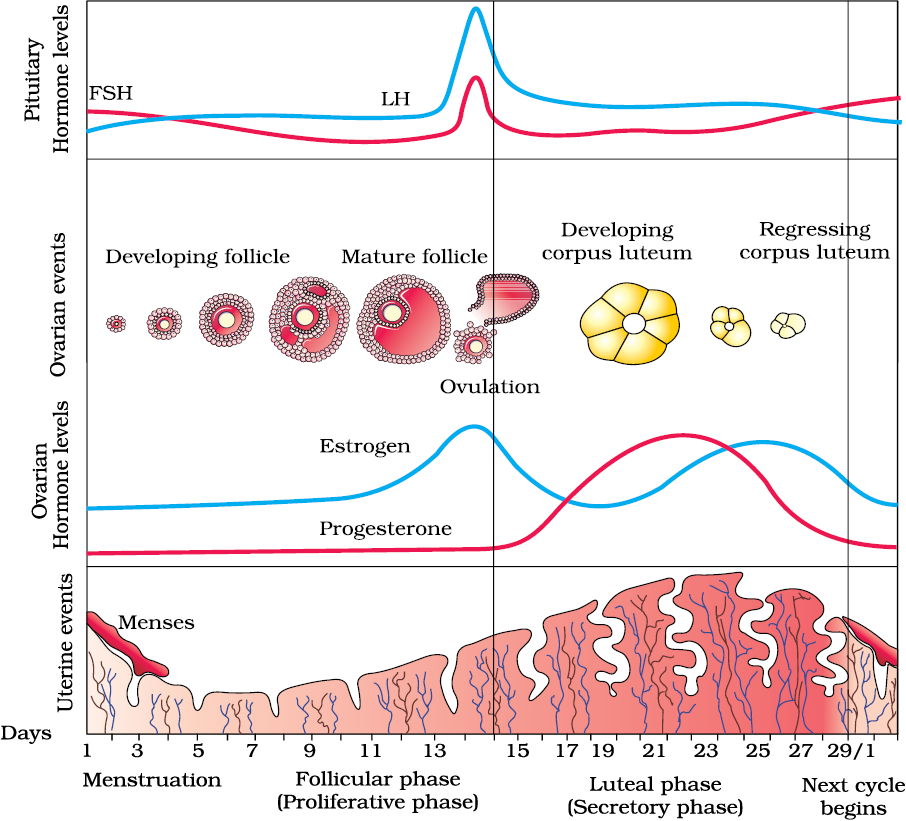
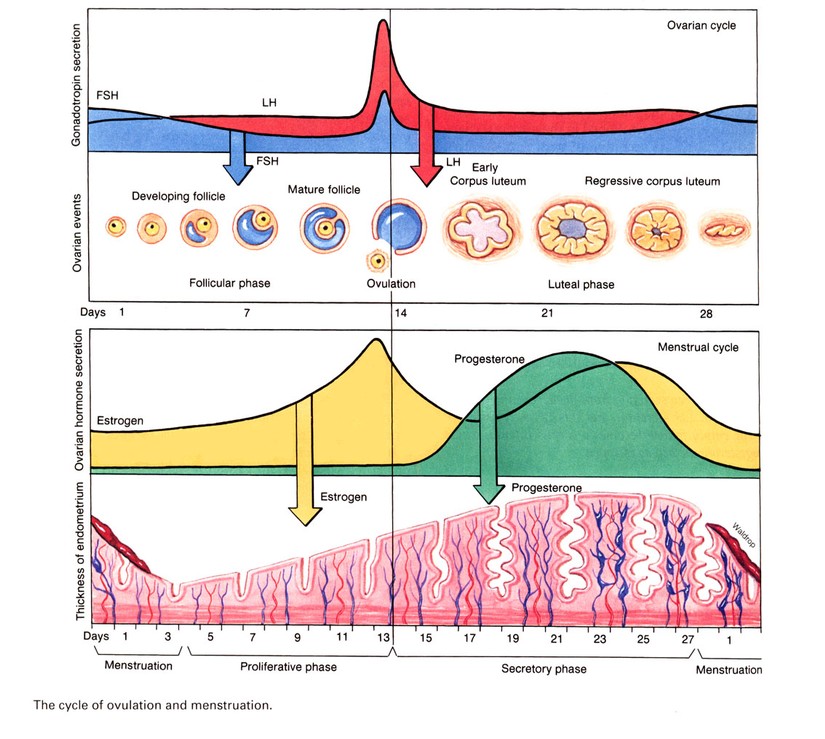
The menstrual cycle is divided into two parts: pre-ovulation and post-ovulation. The ovarian cycle refers to the cyclical development and expelling of the egg from the ovary. Though the length and regularity of a menstrual cycle may differ, the average duration of a complete menstrual cycle is 28 days (though healthy cycles can run from 21-36 days). Below you will find an overview of a typical menstrual cycle with an image map based on a 28 day cycle length.
Pre-Ovulation
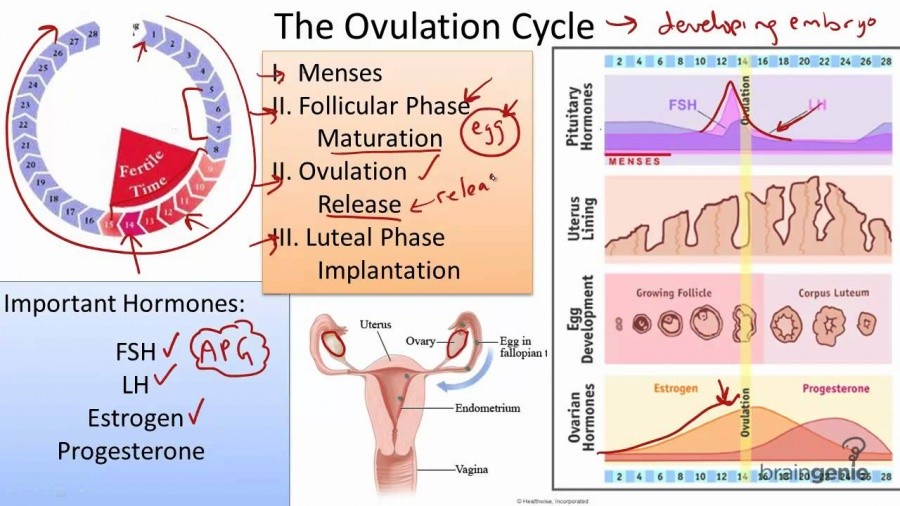
“Day 1” of the menstrual cycle is the day bleeding begins. Bleeding – or “menstrual flow” – last about three to five days. By the seventh day of the cycle, eggs in the ovaries begin to ripen due to various hormonal changes. Between the seventh and the eleventh days, the lining of the uterus begins to thicken and it is possible to observe changes in the presence and consistency of cervical fluids. After the eleventh day, luteinizing hormone cause the egg that is most ripe to be released from the ovary and begin its travel down the fallopian tubes to the uterus. For women with a 28-day cycle, ovulation (the release of the egg) should take place on about the 14th Day – or the very middle – of the menstrual cycle.
Between the seventh and the eleventh days, the lining of the uterus begins to thicken and it is possible to observe changes in the presence and consistency of cervical fluids. After the eleventh day, luteinizing hormone cause the egg that is most ripe to be released from the ovary and begin its travel down the fallopian tubes to the uterus. For women with a 28-day cycle, ovulation (the release of the egg) should take place on about the 14th Day – or the very middle – of the menstrual cycle.
Post-Ovulation
The period after ovulation is called the luteal phase, and it is marked by a slight, but clearly measurable, increase in body temperature. (Note that if the luteal phase is too short, pregnancy cannot occur. This is known as a “luteal phase defect”. Natural fertility supplements, such as FertilAid for Women, may be helpful in addressing issues relating to luteal phase defect.) Following ovulation, the egg travels the fallopian tube toward the uterus. If the egg is fertilized by a sperm (conception), then ” implantation” should take place in the uterus (if implantation takes place outside the womb, this is an ectopic pregnancy.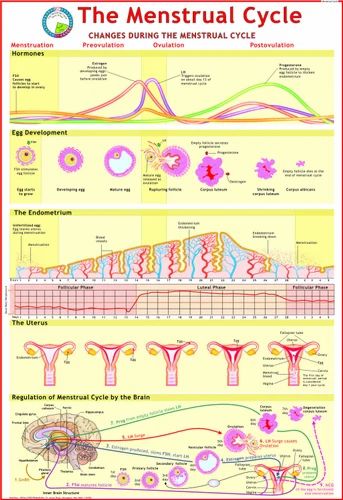 Ectopic pregnancy can occur in several places – but the most common is in the fallopian tube). Pregnancy begins if “implantation” occurs. If the egg is not fertilized, it will “expire” in about 24 hours. Without fertilization, levels of certain hormones will decrease , causing the lining of the uterus to break down and shed – otherwise known as menstruation, or a woman’s “period”. The first day of bleeding is “Day 1” of the next menstrual cycle.
Ectopic pregnancy can occur in several places – but the most common is in the fallopian tube). Pregnancy begins if “implantation” occurs. If the egg is not fertilized, it will “expire” in about 24 hours. Without fertilization, levels of certain hormones will decrease , causing the lining of the uterus to break down and shed – otherwise known as menstruation, or a woman’s “period”. The first day of bleeding is “Day 1” of the next menstrual cycle.
The first part of the cycle, from menstruation to ovulation, may vary from 14 to 20 days in length. The length of the pre-ovulation phase is often different from one woman to another – but it can also differ from month to month for an individual. It is during first part of the cycle that fertilization can occur. Of course, regular menstrual patterns can be altered by illness, insomnia, stress, physical exertion, and physical and emotional changes.
The luteal phase, or post-ovulation (from ovulation to menstruation), is generally the same length for most women – averaging about 14 days.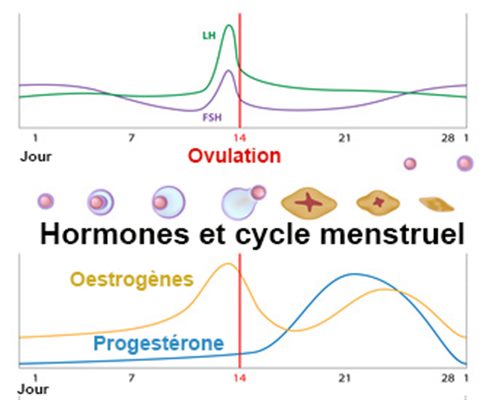 As a rule, the egg is released 10 to 16 days before menstruation, or the start of the next menstrual cycle. If you have heard the term DPO on preconception chats, this refers to “days past ovulation”. High sensitivity pregnancy tests can allow you to begin testing for pregnancy at around 7-10 days past ovulation.
As a rule, the egg is released 10 to 16 days before menstruation, or the start of the next menstrual cycle. If you have heard the term DPO on preconception chats, this refers to “days past ovulation”. High sensitivity pregnancy tests can allow you to begin testing for pregnancy at around 7-10 days past ovulation.
Preparations for ovulation stimulation. Pregnancy injections and pills
There are three types of ovulation inducers: follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), lutein maker (LH), HCG drug, and progesterone.
To get pregnant, you need to meet three basic conditions.
1) A woman is ovulating. 2) Sperm fertilized by an egg. 3) The embryo is firmly attached to the uterus.
handle.
1) A drug that enhances the secretion of FSH and LH, which helps pregnancy, promotes ovulation, which is the development of follicles in the ovaries. 2) HCG helps increase the size of enlarged follicles to release eggs to be fertilized by sperm. 3) Progeosterone prepares to fix the embryo into the inner layer of the uterus and helps to transport the embryo.
A little theory: the mechanism of ovulation
Ovulation is when mature eggs are released from the ovaries. The egg then travels through the fallopian tube to the uterus. This usually occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle, 1 to 4 days after the onset of menstrual bleeding. Women with normal cycles probably won't ask themselves, "Can you get pregnant?" In a normal cycle, ovulation usually occurs regularly.
If you've been consulted about why you haven't gotten pregnant or "you can't get pregnant in one year", it's probably not ovulation. Women cannot get pregnant without ovulating.
If you have a question about why you are not pregnant, you can take an ovulation test. You can buy it at a pharmacy. If there is no continuous ovulation, be sure to consult a doctor.
Ovulation may not occur for various reasons, such as hormonal imbalance and pelvic inflammatory disease. If you don't get pregnant within one year due to not ovulating, you may be given injections and pills to make it easier for your doctor to get pregnant, i.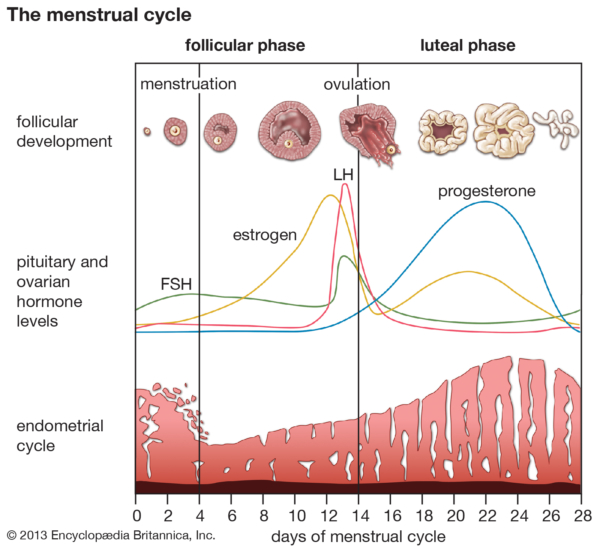 e. medication.
e. medication.
Who is eligible for ovulation stimulation
If the question of why you cannot get pregnant is related to you, you can take the test. If your spouse does the same, you can determine the cause of infertility.
Physicians should recommend ovulation induction after a series of tests to obtain accurate evidence of the cause of independent pregnancy problems. In this case, we prescribe a drug that promotes ovulation.
- The patient noticed an unusual phenomenon that the eggs mature and are released from the ovaries.
- The couple tried to get pregnant for over a year, but failed.
- Spouse over 35 to 40 not pregnant for six months.
In this case, ovulation stimulation is prohibited in the following cases.
- infertility
- Presence or absence of inflammation of the attached device, presence of disease
- Those with uterine lesions
- When the opening of the fallopian tube is bad
FSH and LH preparations.
 Goal - ovulation
Goal - ovulation The follicle is affected by FSH and the egg begins to mature in a "pouch" on the surface of the ovaries. To promote follicle growth, the following medications seem to be often prescribed to help ease pregnancy.
- Klostilbegit; "klostilbegit";
- "Klostilbegit"; "Puregon"?
- "Pureogon?"
- Drugs that are useful for pregnancy are selected individually, depending on the results of tests and ultrasound. This document describes the most famous drugs, but not all existing drugs.
"Klostilbegit"
"Cute drugs that are easy to get pregnant" - Crozil l-Fetto is the name of women who have fulfilled their dreams of giving to children. Promotes the secretion of pituitary hormones. LH (lutein o-hormo n-hormone) - oterus ovulation, that is, eggs are released from the follicles. Milk proractin in the mammary gland.
The instructions say that these drugs that make pregnancy easier should not be taken 5-6 times or more in a lifetime.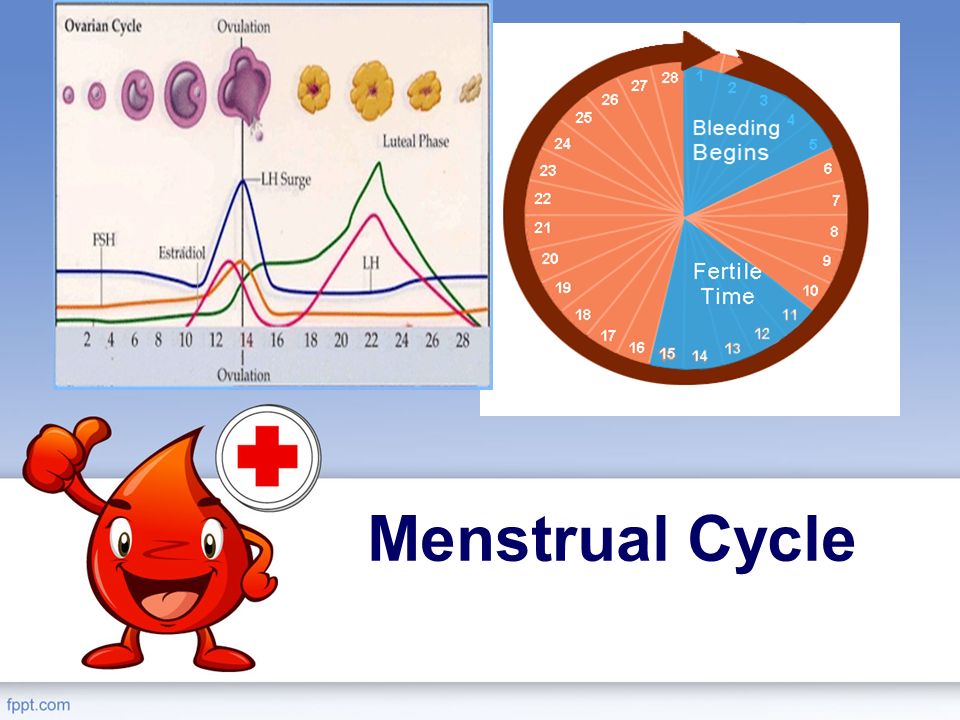 Otherwise, the ovaries may be depleted early and as a result all the eggs may be used and pregnancy may not be possible. "Clostir Extt", which promotes the maturation of eggs, in principle from 5 to 9day after the onset of menstruation. This pill helps pregnancy and takes once a day.
Otherwise, the ovaries may be depleted early and as a result all the eggs may be used and pregnancy may not be possible. "Clostir Extt", which promotes the maturation of eggs, in principle from 5 to 9day after the onset of menstruation. This pill helps pregnancy and takes once a day.
This drug has an adverse effect on the development of the endometrium. If ultrasound tests reveal that the endometrium is thinner than 8 mm, another drug should be used to promote ovulation. If the endometrium is thin, a fertilized egg is difficult to install in the uterus, and even if you become pregnant, you cannot answer the question "how to get pregnant."
Puregon is included in the list of gonodoric drugs to stimulate the production of pituitary hormones (FSH and LH). Puragon helps the ovaries develop some follicles and ovulate during the menstrual cycle. It is suitable for ovulation induction with both natural pregnancy and artificial insemination in in vitro fertilization.
It complements the absence of FSH and LH, which is the sex hormone, and enhances the concentration of estrogen, the female hormone.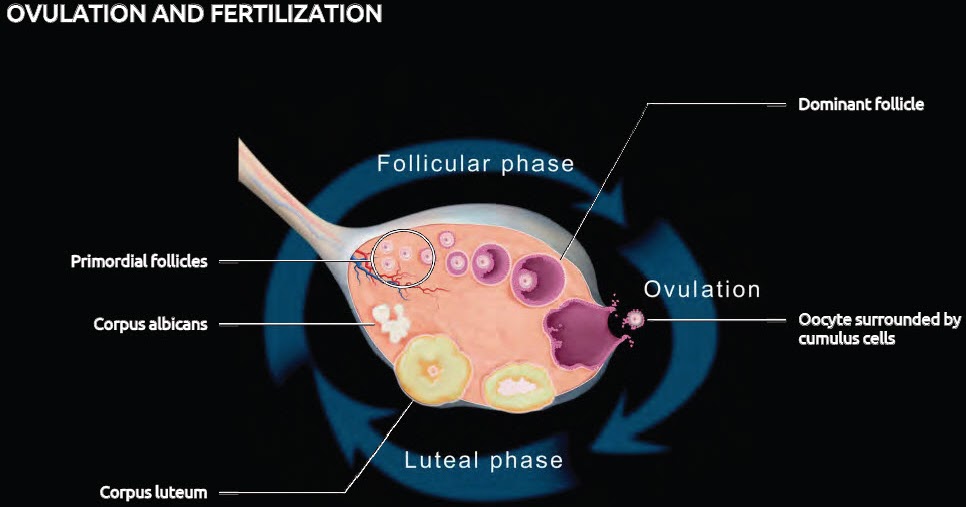 As a result, the ovarian follicles begin to grow, and the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) grows, preparing for the possibility of pregnancy.
As a result, the ovarian follicles begin to grow, and the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) grows, preparing for the possibility of pregnancy.
Gonadotropin (pituitary activation) such as Pure Gon and Menogon starts to get hemorrhagic hemorrhage on the second day. The period is 10 days, but you need to adjust it with the help of a doctor by observing the reaction of the ovaries with ultrasound.
Ultrasound tests confirm that the follicles have grown to the desired size (20 to 25 mm) and a human gonadotropin (HCG) injection is given. These are also hormones that help pregnancy. HCG is administered one day after the last administration of menogon and puregon. HCG hormones contain drugs such as Pristen, Hrongon, Profra and Gonakor. HCG hormone preparations are only prescribed in doses of 5,000 to 10,000 IU. Ovulation occurs one day after the injection. To aid treatment, he does not have sex for 24 hours after the day before injecting the HCG drugs and after having sex.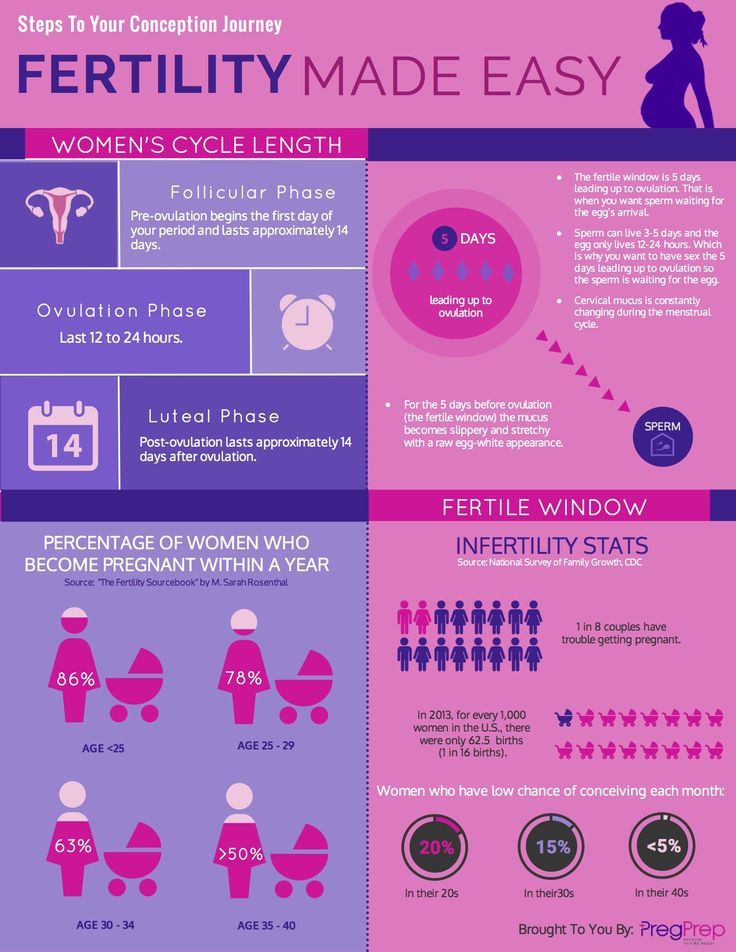
HCG preparations
Progesterone preparation
If the result of the preparation is positive, proterorone is prescribed. It helps pregnancy "correction". Dufaston and other prozhe locks that are easy to get pregnant are prescribed individually.
In order to solve problems that cannot be given or have children, there are many cases where the above hormone therapy is performed. And because of the development of medicine, more and more women forgot that the thread "can not be born", stood on the bulletin board and realizes the happiness of becoming a mother.
1. Can I get pregnant with polycystic properties? In the case of polycystic ovaries, the chance of a retrieval is very low. The greater the number and size of cysts, the lower the chances of becoming a child.
Frequently asked questions related to the possibility of getting pregnant
2. Can I get pregnant even if I have uterine fibroids? If you have fibroids, the chance of pregnancy will be much lower. The larger the diameter of the nodes, the lower the likelihood of pregnancy.
The larger the diameter of the nodes, the lower the likelihood of pregnancy.
3. Can I get pregnant from endometriosis? Even if you are diagnosed with endometriosis, you may be pregnant, but it is very rare. Severe endometriosis can cause infertility.
4. Can I get pregnant if my fallopian tubes are blocked? High probability of pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy. It must be removed surgically. However, it is possible to get pregnant with IVF. Implantation of a fertilized egg in the uterus and obstruction of the fallopian tubes is not a problem. In this case, the answer to the question “is it possible to get pregnant?” - "Yes".
5. If the first pregnancy ended in an abortion, can I get pregnant again? Doctors do not recommend terminating a first pregnancy with a surgical abortion. In this case, infertility is more likely. However, this is not the norm and some women successfully give birth to children after multiple abortions.
6. Is it possible to get pregnant from chewing gum? 6.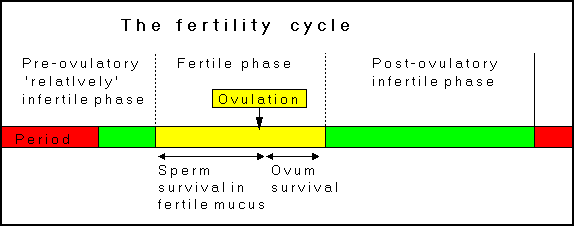
7. Is it possible to get pregnant if the uterus is bent? Curvature of the uterus is diagnosed as "infertility", but this is by no means an indication, and there are women with a curvature of the uterus who successfully give birth to many children.
8. Can I have a future pregnancy if the fetus from a previous pregnancy was frozen? If a previous pregnancy did not produce an embryo within nine months, the cause should be investigated. Pregnancy is possible.
9. Is it possible to get pregnant after multiple miscarriages? Pregnancy is possible, but it is necessary to find out why previous pregnancies were not tolerated.
10. Can I get pregnant if I have a hormonal imbalance? This is possible, but there may be problems maintaining the pregnancy. Hormone therapy is effective.
11. Is it possible to get pregnant with cervical erosion? Erosion (ectopic) does not affect fertility.
12. Is it possible to get pregnant after 40? Women can get pregnant before menopause.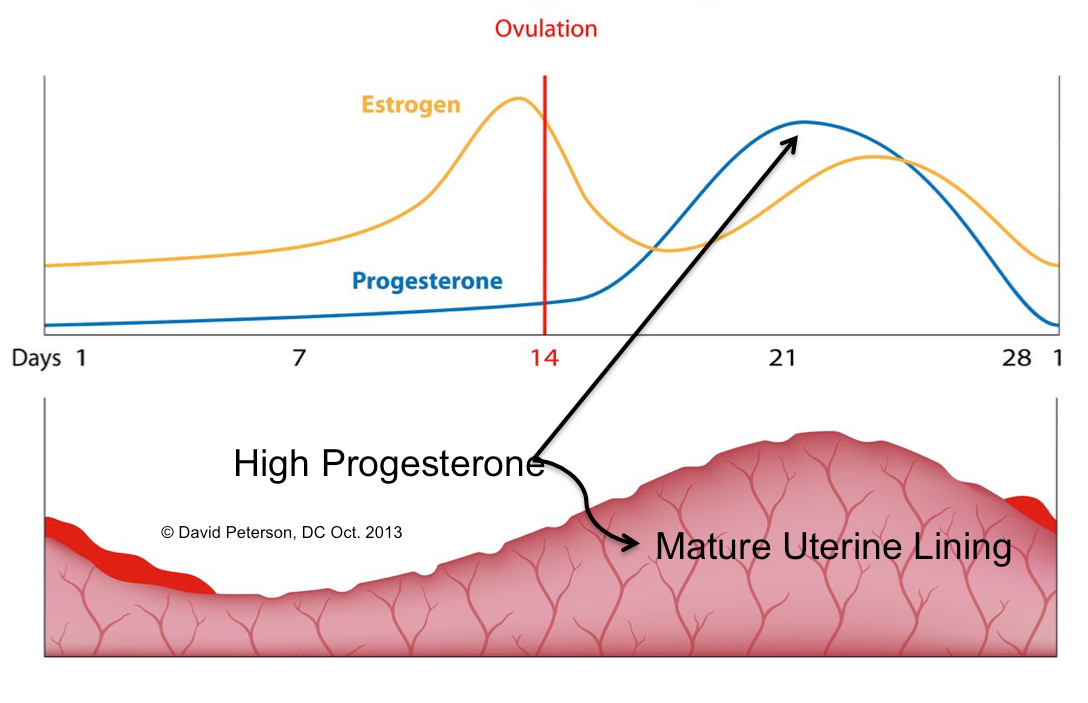
13. Can I get pregnant with rubella? Does not affect fertility, but may interfere with fetal development.
14. Can I get pregnant after a medical abortion? Medical abortion does not affect the ability to conceive a child in the future.
15. Is it possible to get pregnant with thin endometrium? The thickness of the endometrium does not affect fertility. However, in a thinned embryo, the embryo cannot "take root" and the pregnancy cannot continue.
16. Can I get pregnant after an ectopic pregnancy? 16. However, in the case of an ectopic pregnancy, it is possible that the new zygote will not be able to enter the uterus and will become fixed in the duct. Talk to your doctor about how to prevent another ectopic pregnancy.
17. Can I get pregnant even if I have irregular periods? Yes, it's possible. It is wise to find out what causes an irregular menstrual cycle in order to rule out hormonal problems or other abnormalities that may affect the course of pregnancy.
18. Can I get pregnant with an STD? Sexually transmitted diseases, especially sexually transmitted diseases, are the second leading cause of infertility. In such cases, pregnancy is unlikely.
There are a number of so-called folk remedies that promote ovulation and help to conceive a child naturally, but their effectiveness has not been proven by specialists.
Ovulation Stimulation Folk Remedies
When assisting ovulation at home, you can use sage, ghost, aloe vera, etc., which stimulate the necessary processes. The effect is obtained because the vegetable estrogen contained in the herbs works in a similar way to female hormones and causes ovarian storage. The storytelling action is most effective at the beginning of the menstrual cycle. In the second stage, the progesterone secreted from the woman's body and the northern uterus decoction, which is a drug-like drug, is more suitable. The use of essential oils based on siprostradina, basil and anisides, which promote the secretion of estrogen in the body, can promote ovulation. Special diets can help you ovulate just like taking a vitamin, but these places should consult with reproductive medicine and nutritionists to help you choose the most effective and appropriate methods.
Special diets can help you ovulate just like taking a vitamin, but these places should consult with reproductive medicine and nutritionists to help you choose the most effective and appropriate methods.
In most arts (reproductive care technology), which contains in vitro fertilization (reproductive care technology), the call for such y-ovulation is performed, and the essence is the ovaries receive. This is an incentive. Therefore, it can increase the chance of success in the entire program. Currently, ovulation-induction is performed according to various protocols and medications using it are prescribed. In addition to the trigger, a drug is prescribed to prepare the endometrium for implantation of a fertilized egg. In many cases, gonadotropin, progesterone, chromphene citrate and gonadotropinluticin tropica and an antagonist are included in the regimen. Usually protocols contain drugs from different groups.
The clinician selects the dose from the selected stimulus protocol and the patient's individual characteristics.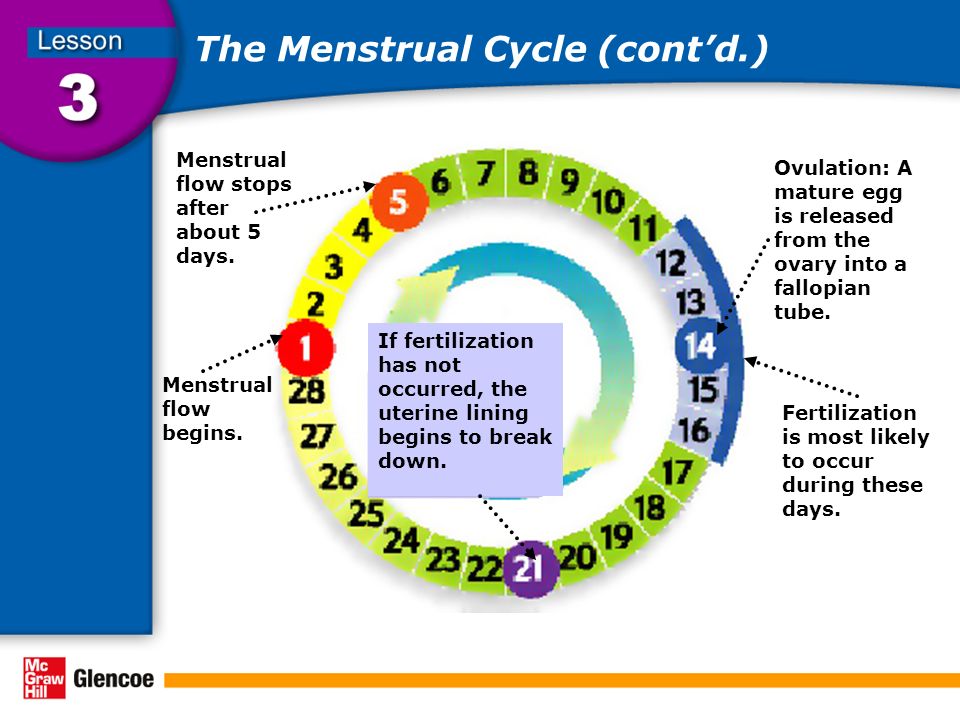 Dose adjustments are made according to the results of follicular ultrasound monitoring. Let's take a closer look at the listed group of drugs.
Dose adjustments are made according to the results of follicular ultrasound monitoring. Let's take a closer look at the listed group of drugs.
The essence of the ovaries is the stimulus of the ovaries to get some fertilization in most technology (reproductive care medical care) that contains in vitro fertilization (reproductive care), and receive some fertilization drugs and receive some fertilization. implemented. Therefore, it can increase the chance of success in the entire program. Currently, ovulation-induction is performed according to various protocols and medications using it are prescribed. In addition to the trigger, a drug is prescribed to prepare the endometrium for implantation of a fertilized egg. In many cases, gonadotropin, progesterone, chromphene citrate and gonadotropinluticin tropica and an antagonist are included in the regimen. Usually protocols contain drugs from different groups.
Find a doctor by referral IVF drugs
The doctor chooses the dose from the selected stimulus protocol and individual patient characteristics. Dose adjustments are made according to the results of follicular ultrasound monitoring. Let's take a closer look at the listed group of drugs.
Dose adjustments are made according to the results of follicular ultrasound monitoring. Let's take a closer look at the listed group of drugs.
The essence of the ovaries is the stimulus of the ovaries to get some fertilization in most technology (reproductive care medical care) that contains in vitro fertilization (reproductive care), and receive some fertilization drugs and receive some fertilization. implemented. Therefore, it can increase the chance of success in the entire program. Currently, ovulation-induction is performed according to various protocols and medications using it are prescribed. In addition to the trigger, a drug is prescribed to prepare the endometrium for implantation of a fertilized egg. In many cases, gonadotropin, progesterone, chromphene citrate and gonadotropinluticin tropica and an antagonist are included in the regimen. Usually protocols contain drugs from different groups.
Gonadotropins
Helps the growth of follicles (FSH) and follicles.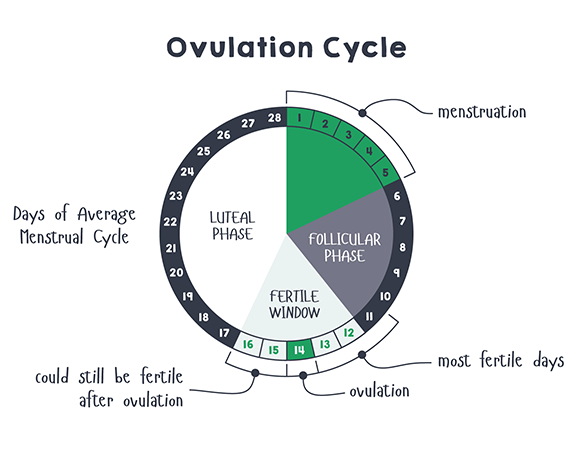
- Luteinization (LH), estrogen secretion, induces ovulation.
- Some ovulatory agents contain FSH while others contain both FSH and LH. Commonly used are Menopor, Elomba, Pyragon and Gonar F.
While taking gonadotropins, side effects such as bloating, emotional disorders, and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome may develop. These phenomena usually disappear immediately after the follicle puncture.
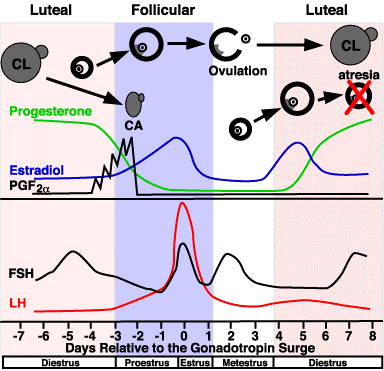
GnRH is produced in the hypothalamus and released in small doses every hour and a half. Under its influence, gonadotropins are formed in the pituitary gland. GnRH agonists are synthetic analogues of this hormone. When more α-GnRH enters the body than nature intended, the pituitary gland becomes insensitive to the hormone and ovulation stops. Thus, the combination of gonadotropin and a-GnRH gives the doctor complete control over the course of the ovarian cycle. The main objectives of such protocols are:
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (a-GnRH) agonists
prolong ovulation period
- prolong pregnancy; prolong pregnancy
- If necessary, slow down the hypersynthesis of gonadotropins.
- Therefore, ovulation should coincide with the time of full maturation of the follicles. For this purpose, drugs such as Decapeptil and Diferelin are often used.
Side effects of α-GnRH administration are associated with changes in the level of sex hormones and are relatively rare. These effects include decreased libido, mood disturbances, and hot flashes. Since agonists do not accumulate in the body, these changes disappear without a trace when taking gonadotropins.
Antagonists generally solve the same tasks as the previous group of drugs, only in a slightly different way. It inhibits the formation of gonadotropins in the pituitary gland and neutralizes the activity of its own gonadotropin-releasing hormone. GnRH Anti-GnRH is used in various protocols to control ovulation, coinciding with the full maturation of follicles. Side effects from the use of antagonists are due to lower estrogen levels and are transient. Specialists in this group usually prescribe Oglartran, which is available in the form of a syringe tube.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (ant-GnRH) antagonists
Progesterone and estrogen are necessary to prepare the endometrium for embryonic egg implantation. These hormones are normally secreted by a special gland, the so-called corpus luteum, where the follicle opens. If fertilization is successful, the corpus luteum continues to actively secrete progesterone for 10-12 weeks, preventing the release of new eggs and menstruation. From now on, the necessary concentration of progesterone will be supplied by the placenta.
Progesterone and estradiol preparations
Therefore, a certain level of progesterone is necessary to maintain and maintain pregnancy. For this purpose, you can use drugs in the form of capsules and tablets: Utrozhestan, Duphaston.
After completion of any stimulation protocol, the follicle should be prepared for puncture to allow final oocyte maturation. For this purpose, chorionic gonadotropin is prescribed 34-36 hours before aspiration of the follicles.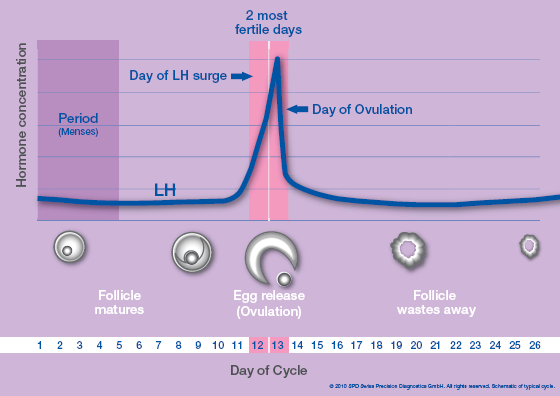 In addition, in some protocols, the absence of LH extrusion peaks indicates that ovulation does not occur. Thus, the introduction of human chorionic gonadotropin is the trigger dose that initiates this process.
In addition, in some protocols, the absence of LH extrusion peaks indicates that ovulation does not occur. Thus, the introduction of human chorionic gonadotropin is the trigger dose that initiates this process.
Chorionic gonadotropin
Ovulation occurs 40-42 hours after injection. Otherwise, the egg will already break away from the follicle and the entire stimulation cycle will go awry. Give this drug once.
Strictly speaking, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone that is secreted by fetal cells in the placenta as early as 6-8 days after implantation of the ovum and whose measurement is used to diagnose pregnancy. In medicine, hCG preparations obtained from the urine of pregnant women and genetically modified microbial preparations are used. It comes out under different product names like transfer, projection, and chorus, but there really isn't any difference between the two.
How you take your medication depends on your stimulation protocol and should be strictly followed by your physician.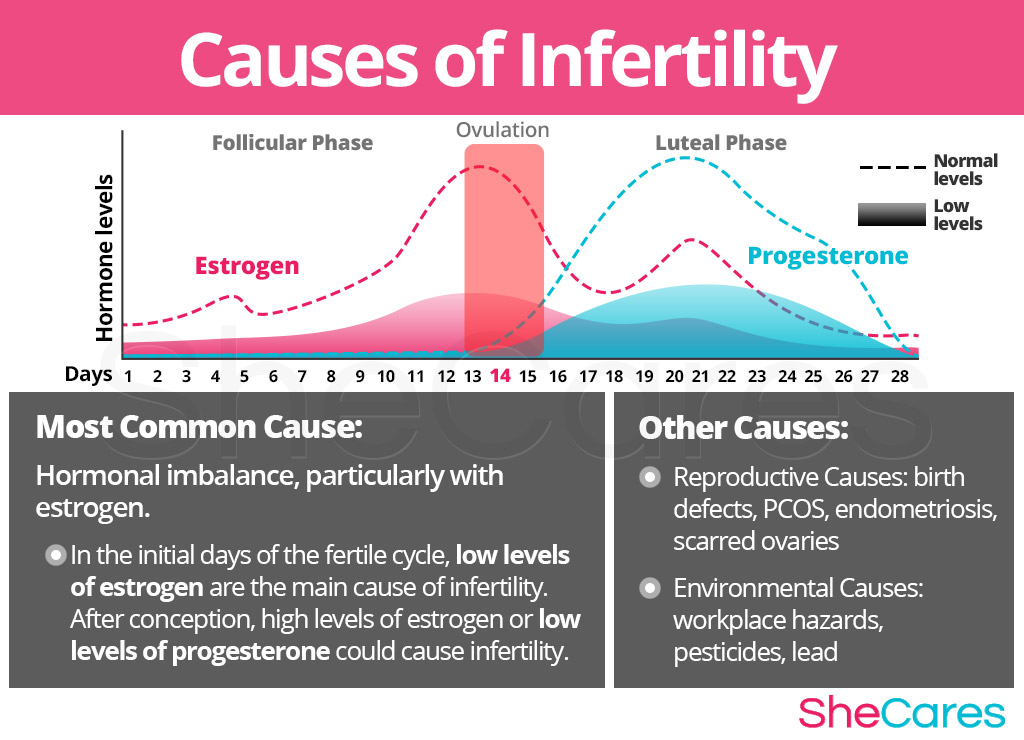 Most drugs are administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Many of them have unique characteristics regarding the use and storage associated not only with the drug itself, but also with the form of release offered by the manufacturer. Therefore, we recommend doing the first injection in our treatment room. There, the nurse explains how the medicine is administered and, more importantly, shows it to you. We strongly do not recommend giving injections according to instructions on the Internet - the price of a mistake can be very high.
Most drugs are administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Many of them have unique characteristics regarding the use and storage associated not only with the drug itself, but also with the form of release offered by the manufacturer. Therefore, we recommend doing the first injection in our treatment room. There, the nurse explains how the medicine is administered and, more importantly, shows it to you. We strongly do not recommend giving injections according to instructions on the Internet - the price of a mistake can be very high.
How to use prescribed drugs
Many infertile women have hormonal disorders that affect the development and maturation of follicles. Let me tell you what it is, which sensations are normal and which are not.
How long IVF stimulation lasts depends on what drugs are used and what protocols are used. In this case, the prevention of premature ovulation plays an important role. This is achieved by suppressing the secretion of luteinizing hormone, which reaches an overwhelming peak. To inhibit this process, two types of drugs are used: gonadotropin-activating hormones and agonists. The type of drug and how long it is used determines how the ecosystem is stimulated.
To inhibit this process, two types of drugs are used: gonadotropin-activating hormones and agonists. The type of drug and how long it is used determines how the ecosystem is stimulated.
How stimulation works before IVF: how many days it lasts, what the consequences may be
Protocol for the use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists. This group of drugs can immediately stop the natural synthesis of the lutein hormone. It is prescribed approximately 6-8 days after the start of gonadotropins and promotes the growth and maturation of several follicles at once.
- With a long protocol, hormone therapy is started a week before the expected menstruation. This puts the woman's body into a brief state of menopause, which can be reached in the next menstrual cycle, with all follicles the same (this process is called "follicular synchronization"). After the menstrual reaction, the introduction of gonadotropins, which stimulate the growth of follicles, begins.
 The puncture is carried out after about 3-4 weeks.
The puncture is carried out after about 3-4 weeks. - Protocols for the use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists. There can be 3 types depending on the duration./li>
The Ultradrin protocol is technically no different from the Long protocol, except that the agonists are started at least 2-3 months before artificial insemination. This method of stimulation is recommended for severe endometriosis, when it is necessary to normalize existing disorders first.
All events occur during the same menstrual cycle in which gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists and gonadotropins are administered. It takes about two weeks until the follicle is received.
Many IVF protocols artificially activate the ovaries. In vitro fertilization in a natural cycle, that is, without or with minimal hormonal activation, is performed in a small number of women. Such methods are sometimes recommended not only with a normal menstrual cycle, but also with a too weak menstrual cycle or, conversely, with too strong classical stimulation.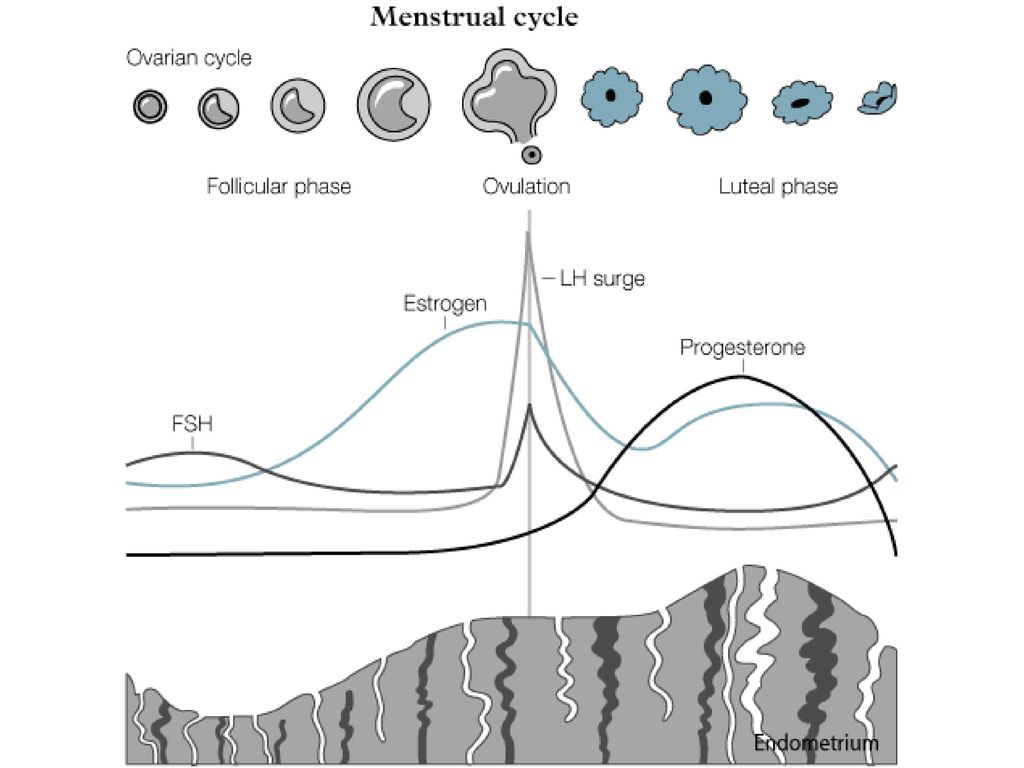 Otherwise, Classic ECO is recommended. with stimulation.
Otherwise, Classic ECO is recommended. with stimulation.
Who needs ovarian stimulation in IVF
First, an ultrasound examination is performed to determine the condition of the follicular apparatus. When using long-term schemes, gonadotropin-releasing hormone pre-initiates the release of gonadotropin architecture. Otherwise, gonadotropins are administered from about the 2nd to the 3rd day and at the same time promote the development of multiple follicles. At the same time, gonadolibrin agonists or antagonists are used to prevent premature ovulation. When the follicle size reaches 18-20 mm, insert the ovulation inducer. Helps separate eggs, including male and female, from the walls of the follicle.
Procedure
Approximately 34-36 hours later, the ovaries are perforated to collect follicles. In laboratory conditions, eggs are extracted from the follicles, fertilized with sperm, and the embryos are cultured before implantation in the uterine cavity. After the puncture, the woman begins taking progesterone preparations.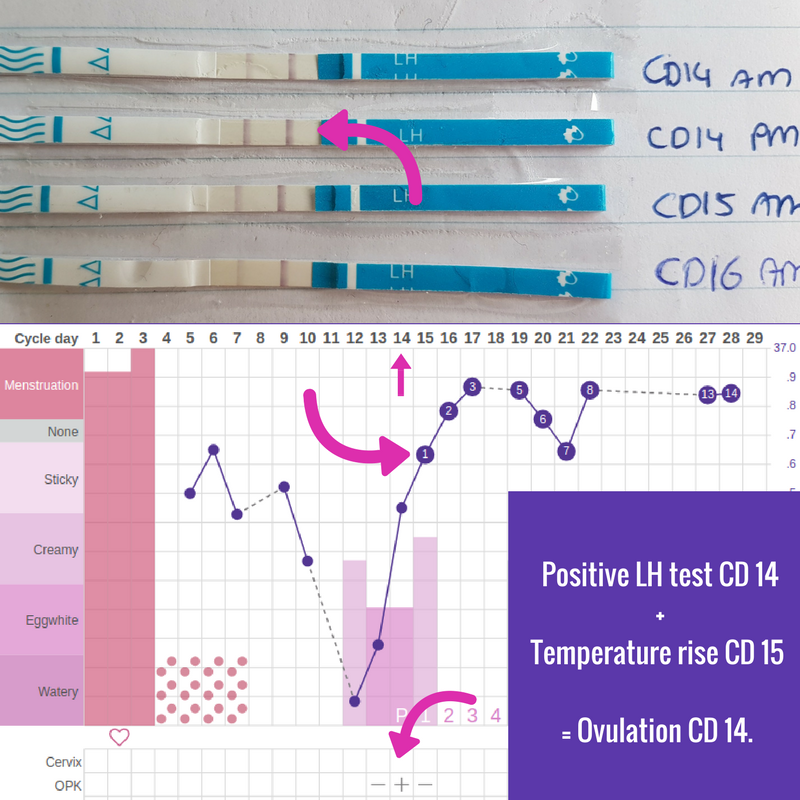
Depending on the stage of treatment, different groups of drugs are used. Promotes the simultaneous development and maturation of many follicles in the same sense as gonadotropins (recombinant hormones or menopausal hormones). At this stage of reproduction, unpleasant situations await when the follicles begin to develop, but preventively "molt", i.e. premature ovulation occurs. To prevent this, it blocks the peak of ovarian hormones. Ovulation begins when its concentration in the blood rises. Both gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists and antagonists can be used for blocking.
Ovarian stimulants
Follicles continue to grow during hormone therapy. When the size reaches 18-20 mm, an ovulation inducer is introduced. Ultimately, it seems that they will also help prepare for artificial insemination. Chorionic gonadotropin often acts as an inductor. After the end of ovarian stimulation, the gynecologist prescribes progesterone preparations for successful conception and maintaining pregnancy.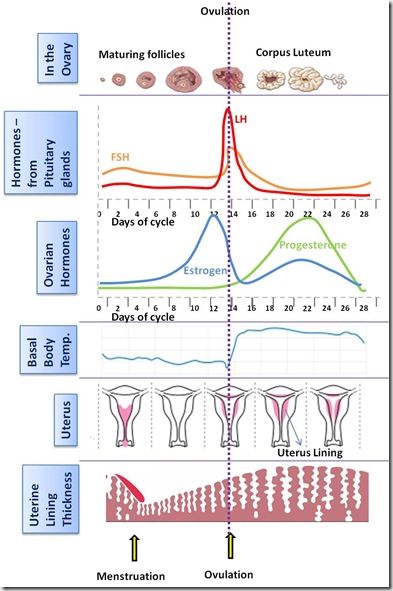 It prepares the endometrium for the placement of the embryo. This stage is very important because the corpus luteum, often found in stimulated cycles, is defective.
It prepares the endometrium for the placement of the embryo. This stage is very important because the corpus luteum, often found in stimulated cycles, is defective.
Ovulation induction usually lasts 2 weeks for the "short" protocol and 3-4 weeks for the "long" protocol. The next two weeks after the follicle puncture is the time of implantation of the fertilized egg. If this treatment is successful, serum chorionic gonadotropin β-blast levels begin to rise after 14 days.
How long can the stimulation last? The reception table is clearly held and issued to women.
How to behave during stimulation
In most cases, ovulation induction is carried out without complications. However, at a rate of 5 to 10%, a hybridized syndrome may occur. The initial pattern will appear a few days after ovulation induction (usually 48 hours) and the final pattern will appear 10 days or more later. For early diagnosis for women, it is important to assess the feeling of stimulation. First sign
First sign
Possible complications
Help nausea.
- Pain in the abdomen, especially pain in the groin (protrusion of the ovaries).
- The area around the belly is a little exciting.
- These symptoms are caused by exposure to hormone therapy, increased blood clarity and released into the plasma on the way outside the blood vessels. If you do not notice this condition, the pleural effusion begins to overgrow in the chest cavity, causing shortness of breath. The decrease in plasma circulating plasma lies in the amount of urine as filtration in the kidneys decreases. These are symptoms that can show serious progress in ovarian syndrome. This condition increases the risk of complications of thrombocytosis. Therefore, if you feel uncomfortable with the stimulus, you need to contact your doctor immediately. Over time, treatment has become safe and effective using reproductive health care.
Taking hormonal drugs affects the synthesis of blood vessels.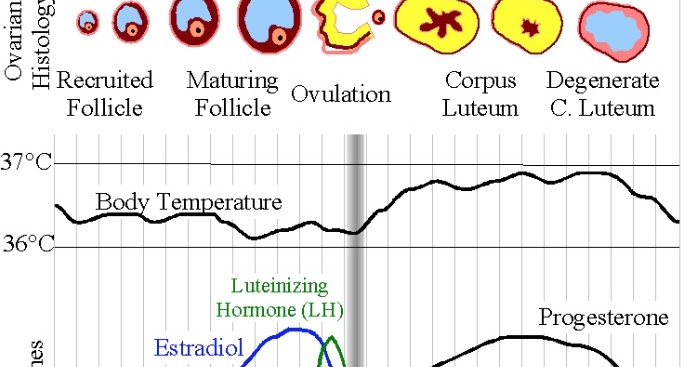 Expand blood vessels and increase the distance between cells. As a result, body fluid is easily transported to the external blood vessel. As a result, the overall state changes as the stimulus continues to stimulate in the Vitro fertilization protocol.
Expand blood vessels and increase the distance between cells. As a result, body fluid is easily transported to the external blood vessel. As a result, the overall state changes as the stimulus continues to stimulate in the Vitro fertilization protocol.
Why the head, chest, ovaries can hurt when stimulated
Headache occurs when the blood vessels in the brain dilate. When fluids are released into the cells of the mammary glands, compression of the nerve leads to dyspnea disorders and the development of chest pain. The ovaries are normal, but may be slightly diseased, that is, if there is no a-irrigation syndrome. This is because the blood flow to these organs is increased through hormones. This increases the volume and compresses the end of the nerve. These symptoms usually do not require much discomfort for women, so there is no need for pharmacological correction.
CM-Clinic Reproductive Medicine is compatible with reproductive medical specialists suitable for each case.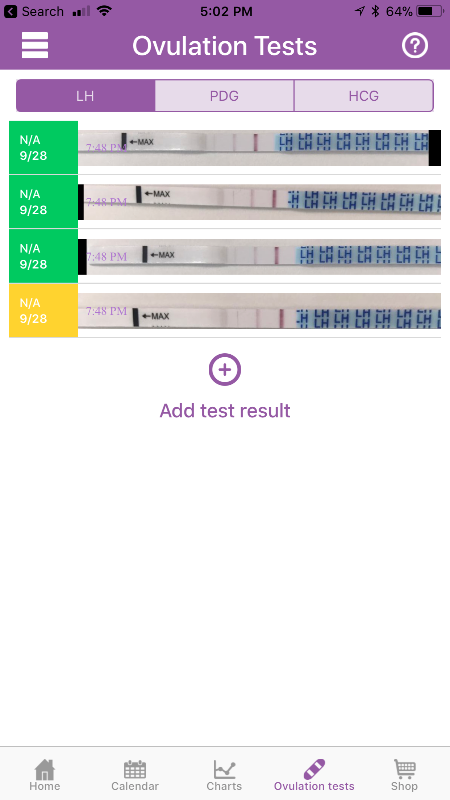 In order to choose the method of optimal stimulation, the first step is to examine the woman in detail. First, evaluate the ovarian reserve and predict the response of the ovary against stimulation. In response, a specific protocol, drug and initial dose is selected. At the same time, we also prevent complications. Set the optimal number of fertilized eggs to establish the optimal conditions for establishing a pregnancy. If there is a hereditary disease, the couple is diagnosed before the transplant. With them, you can treat as effectively and safely as possible.
In order to choose the method of optimal stimulation, the first step is to examine the woman in detail. First, evaluate the ovarian reserve and predict the response of the ovary against stimulation. In response, a specific protocol, drug and initial dose is selected. At the same time, we also prevent complications. Set the optimal number of fertilized eggs to establish the optimal conditions for establishing a pregnancy. If there is a hereditary disease, the couple is diagnosed before the transplant. With them, you can treat as effectively and safely as possible.
Treatment at the SM-Clinic Reproductive Center
SM-Clinic represents cutting-edge results in reproductive medicine and excels. Get expert advice in reproductive medicine to protect your future and that of your children
In the 1980s of the last century, in vitro fertilization began a steady step in reproduction. The number of couples relying on this program, looking for the joy of becoming a mother, is growing year after year.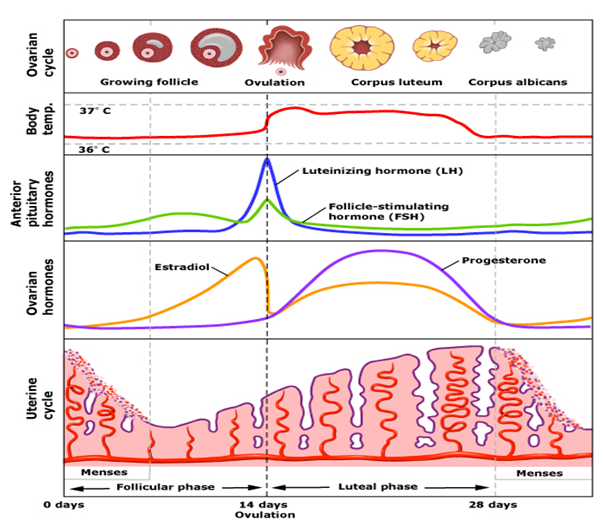 However, in vitro fertilization is the only way to fulfill a child's old dream, doctors always weigh the benefits and risks after in vitro fertilization. Taking into account the latest developments in medicine, only a woman's careful attitude to the body allows for the most effective and safe treatment.
However, in vitro fertilization is the only way to fulfill a child's old dream, doctors always weigh the benefits and risks after in vitro fertilization. Taking into account the latest developments in medicine, only a woman's careful attitude to the body allows for the most effective and safe treatment.
In vitro fertilization is a multi-step program. The introduction will conduct a detailed study of the couple to determine the cause of the decrease in reproductive capacity and avoid the failure that may occur. Composite tests such as ultrasound tests, hormonal tests, sperm tests, and infectious disease assessment are performed.
The essence of the IVF procedure
After checking, start the ovarian stimulation method. Perform both short-term protocols (stimulating the same cycle as hormone drug administration) and long-term protocols (gonadriberin agonist administration in a previous stimulus to synchronize the ovarian follicle formation process). It's possible.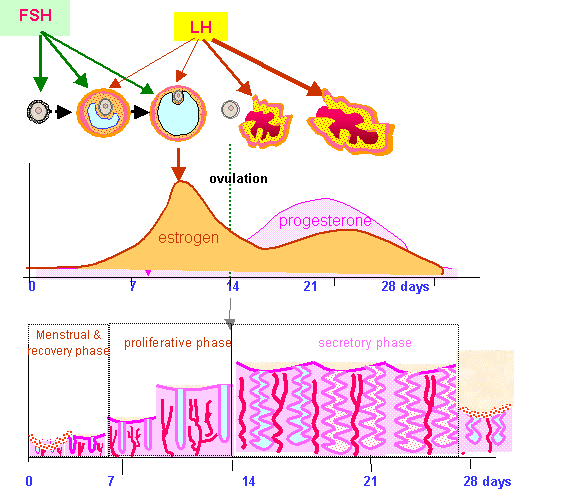 When the follicle reaches 18-20 mm, open the piercing. The embryo then cultured the egg from the follicle solution. It is prepared by a special method and bound to the spermatozoon in the laboratory. It hatches in 3-5 days and is transferred to the uterine cavity. Transplantation can be performed both in a stimulated cycle and in another cycle (first frozen and preserved). After about two weeks, measure the concentration of choriconadotropin in the blood and confirm the pregnancy.
When the follicle reaches 18-20 mm, open the piercing. The embryo then cultured the egg from the follicle solution. It is prepared by a special method and bound to the spermatozoon in the laboratory. It hatches in 3-5 days and is transferred to the uterine cavity. Transplantation can be performed both in a stimulated cycle and in another cycle (first frozen and preserved). After about two weeks, measure the concentration of choriconadotropin in the blood and confirm the pregnancy.
There is a risk of in vitro fertilization for women, but it's not that big compared to the general public, so you don't have to be afraid. The gynecologist calculates the complications that may occur for each patient and strives to minimize the possibilities. O.
Should I be afraid of IVF consequences?
An external pregnancy is generated in the fallopian tube, excluding the uterine cavity, and is usually caused by dysfunction of the tissue tube. The disease rate during natural pregnancy is 1-2%, which occurs at the same percentage even after in vitro fertilization.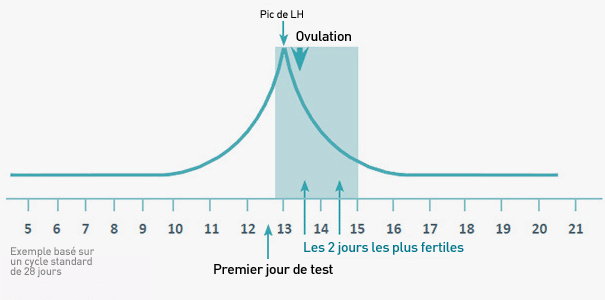 To prevent this complication, a woman with an abnormally altered fallopian tube (called a fallopian tube resection) is removed during the preparation stage.
To prevent this complication, a woman with an abnormally altered fallopian tube (called a fallopian tube resection) is removed during the preparation stage.
- A multiple pregnancy is a pregnancy with two or more fertilized eggs. In in vitro fertilization, it can be formed as a result of two or more rewritings, but this is associated with the formation of identical twins (absolutely the same twins are born). A little.
- Ovarian torsion is a condition in which the reproductive stalk in women is distorted and arterial blood flow is obstructed. In this condition, ovarian tissue may be necrotic. Ovarian torsion is a very rare occurrence that occurs at a rate of 0.1% or less per cycle.
- And, although many patients are afraid, we will also touch on the risk of a tumor, which has not been scientifically confirmed.
Ovarian stimuli in infertility treatment for ovarian cancer has been shown to slightly increase the incidence of ovarian cancer compared to a normal reproductive contrast group. However, an increase in risk associated with tumors has been shown not for stimulation, but in the infertility of the patient. In general, ovulation is known to increase the risk of ovarian cancer and the use of hormonal contraceptives that prevent ovulation reduces the risk.
However, an increase in risk associated with tumors has been shown not for stimulation, but in the infertility of the patient. In general, ovulation is known to increase the risk of ovarian cancer and the use of hormonal contraceptives that prevent ovulation reduces the risk.
- For women who have slow onset breast cancer fetuses and first pregnant women, the risk of developing breast cancer is increased. This explains that the baseline risk of infertility in women is high. Serious large studies have shown that the tumor does not increase even if the ovaries are stimulated by the risk of an instant baseline of infertility.
- Uterine cancer (endometrial cancer). Studies have shown that polycystic ovaries and obese women increase the risk of endometrial cancer with increased ovulation stimulation. However, in these patients, the baseline risk of uterine cancer was six times higher regardless of the stimulus in a normal-weight woman.
- Therefore, hormonal stimulation of the ovulation process does not increase the risk of tumors.
 The increase in the possibility of malignant tumors in the uterus, ovaries and mammary glands is mainly due to infertility and baseline risk and due to its cause. Therefore, it is very important to have a normal weight and a suitable hormonal background, and if there is a deviation.
The increase in the possibility of malignant tumors in the uterus, ovaries and mammary glands is mainly due to infertility and baseline risk and due to its cause. Therefore, it is very important to have a normal weight and a suitable hormonal background, and if there is a deviation.
In the process of excessive stimulation, the risk of ovarian syndrome may increase. It is characterized by larger ovaries, enlarged blood vessels, and edema in which fluid accumulates in the abdomen and thoracic cavity. Against the background of a blood thief, the risk of thrombosis increases, which prevents thrombosis.
Risks in the process of inducing superovulation
Ovariate syndrome can last up to 12 weeks of pregnancy. In the first days, a few days after the follicle puncture, and in the second half, about 10 days after stimulation, that is, the time when pregnancy is secreted and villogenadotropin is secreted.
In clinical sites, the three severity levels are different.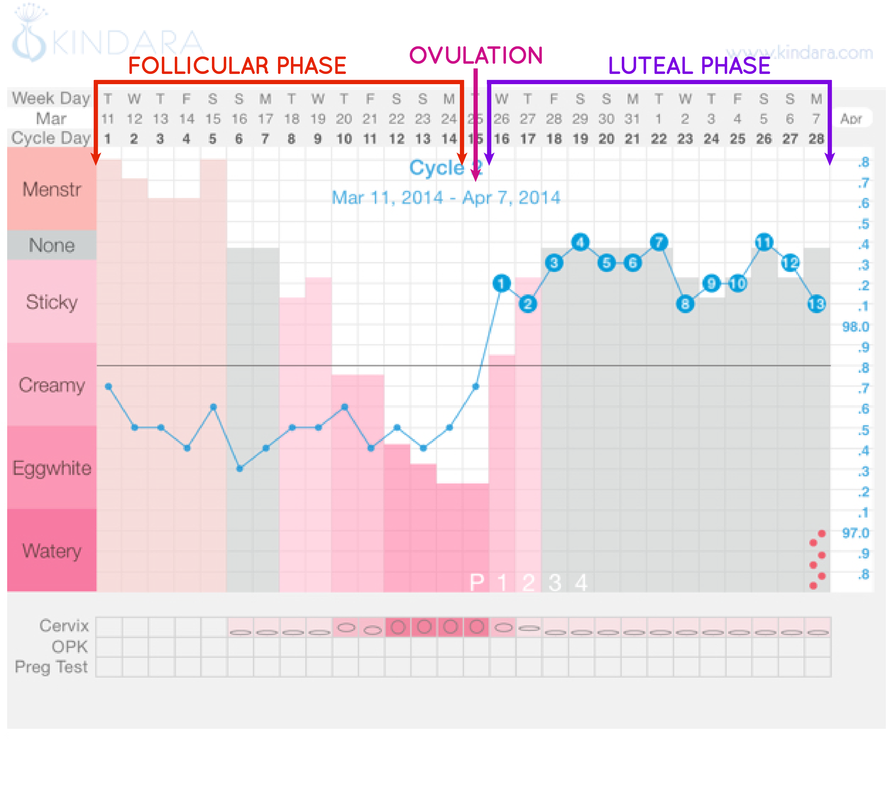 Soft ones make up 5-10%, and heavy ones are often found. Appropriate planning of an ovulation induction program can reduce the risk of these complications, and if an onset develops, the latest medications can quickly stop existing symptoms.
Soft ones make up 5-10%, and heavy ones are often found. Appropriate planning of an ovulation induction program can reduce the risk of these complications, and if an onset develops, the latest medications can quickly stop existing symptoms.
The first symptoms of hyper-asthenia syndrome are as follows.
Feels full in the stomach.
- Enlargement of the abdominal circumference-hemophilia of the stomach;-included germophilia of the abdominal circumference;-Education in the circumference of the abdominal cavity-gastric hemorrhage
- My stomach hurts.
- Sometimes I will participate later.
- irregular breathing
The amount of urine is reduced and the urine is completely out of the urine.
- If you have any symptoms after starting treatment, be sure to consult your doctor.
- Pregnancy that occurs after in vitro fertilization is usually a risk. In fact, luteal phase failure is often seen in the ovaries.
 To make up for the lack of progesterone, a bio-rewarding analogue is prescribed. This prevents a natural pregnancy from ending and prevents placental failure.
To make up for the lack of progesterone, a bio-rewarding analogue is prescribed. This prevents a natural pregnancy from ending and prevents placental failure. - During in vitro fertilization, there are situations where risks are classified. These are the following.
Inflammation of the uterus and attached device.
Risks during childbearing
Repeat rubbing the uterine cavity.
Risk factors contributing to the development of complications
Intervention on the internal organs of the pelvis.
- Obstruction of the ovarian tube (partial or total).
- Overweight or obese
- Polycystic ovary
- The value of ant-mullerian hormone is 4 ng/ml or more.
- For patients at risk, choose the most reasonable treatment. If the risk of fallopian tube pregnancy is high, a fallopian tube ligation is performed. If there is a risk of over-setting syndrome, the use of preserved regimens, etc. is applicable.
 It is recommended that obese women normalize their weight before entering an in vitro fertilization program.
It is recommended that obese women normalize their weight before entering an in vitro fertilization program. - Physicians should use technologies that are appropriate for this age, over time, the number of follicles left in the ovaries is small, the quality of the eggs decreases, and infertility rates accumulate by the age of five. In addition, the frequency of miscarriage increases. So about 15% for 30 years, about 30% for 40 years, and about 50% for women aged 45 and over naturally.
- All patients 40 years of age and older will be assessed for ovaries (number of follicles remaining in the ovaries) prior to in vitro fertilization planning. To do this, the values of ant-Mulle hormone (AMH) should be measured, an ultrasound test of the ovaries is carried out on the 5th-7th day of the menstrual cycle, and a study of the number of male cells. If the AMH value is 1 ng/mL or less, the response to the ovarian stimulus is considered low. But everything may not be. Approximately 10-20% of patients with lower AMH show a good response to stimulation therapy in in vitro fertilization programs.

Fertility treatment for women over 40 years of age is a struggle with time and the low chance of pregnancy. And because of the large individual differences depending on the patient, there is no universal stimulus protocol for patients with low responses in the in vitro fertilization program. However, there are several ways to increase the impact of reproductive medicine as a doctor's weapon. The preliminary use of male steroids and somatotropin (very expensive drugs), which has a positive effect on the formation of follicles, seems promising.
Consequences after IVF after 40-50 years
If the ovaries are very low, they are preferable, for example, in vitro fertilization in a natural cycle and in vitro fertilization with minimal incentives so as not to be depleted.
The risk assessment associated with fertility treatment has its own characteristics. Therefore, although this risk is relatively low, it will exist in both females and females.
In addition, infertility is suffered by the couple and gives a high motivation for success, making risk assessment difficult.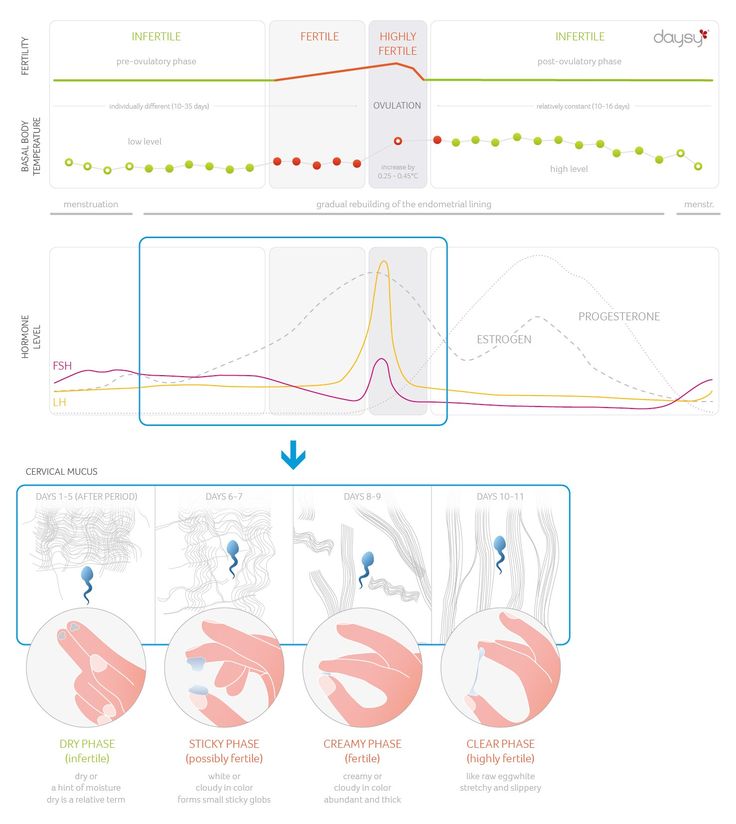 However, SM-Clinic's Reproductive Medicine Specialists will be responsible for addressing the problem of overcoming infertility and will be responsible for the selection of treatments that will affect treatment outcomes.
However, SM-Clinic's Reproductive Medicine Specialists will be responsible for addressing the problem of overcoming infertility and will be responsible for the selection of treatments that will affect treatment outcomes.
In this way, reproductive medicine can achieve high efficacy while reducing the possibility of side effects.
Physician's expert opinion
In vitro fertilization increases the risk of genital cancer. As a result, it was found that the risk is not an in vitro fertilization method, but a pathological condition associated with infertility (polycystic ovaries, obesity, endocrine diseases, etc.).
In vitro fertilization may be harmful to health. For the use of reproductive medicine, it is necessary to take a large number of hormonal drugs that are metabolized in the liver. Therefore, before starting an in vitro fertilization program, a biochemical study is carried out to assess the functional activity of hepatocytes. If it is normal, the treatment will not harm the body.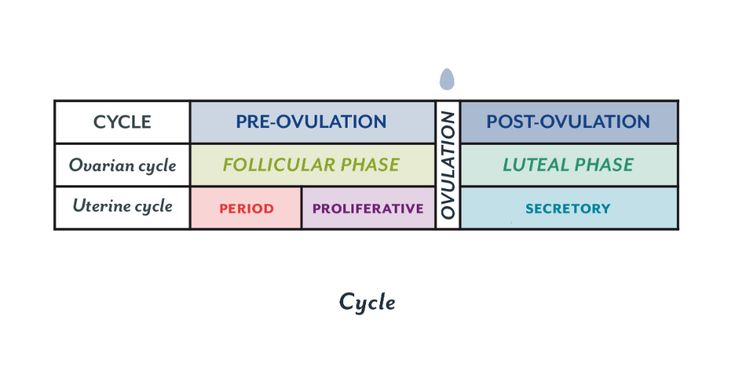
In vitro fertilization results in weight gain. Yes, weight can increase. However, this is, in principle, also due to progesterone antioreturia. Weight gain occurs to maintain water in the body.
Myths and Reality
- Therefore, if the pregnancy ends properly and the administration of progesterone is stopped, the weight will return. A stored diuretic may be given to stimulate the elimination of water from the body.
- In general, the methodology of in vitro fertilization programs in modern reproductive medicine has been complex. Therefore, this operation, which is performed taking into account the individual condition of the patient's body on the basis of an international protocol, is considered effective and relatively safe. The SM-Clinic Center for Reproductive Medicine has a reproductive medical specialist and a gynecologist, and it regularly expands its experience by referring to major clinics around the world.
- Preparing for ovulation induction.
 Injections and tablets for pregnancy
Injections and tablets for pregnancy
Sintsina Elena, Vladimirovna
Berova, Elena Vladimirovna
Preparations for stimulating ovulation: gonal and puregon
Aimed Clinic uses the latest generation combined laser for hatching embryos. Women of older reproductive age have a high percentage of embryo implantation
The most common cause of female infertility is hormonal problems. Therefore, hormonal drugs that act on the endocrine system are used to treat infertility.
These include:
- thyroid preparations;
- adrenal preparations;
- ovarian preparations.
Of the thyroid preparations, thyroxine has received the greatest use.
Adrenal preparations are: Prednisolone , Dexamethasone .
Ovarian preparations: estrogens and progesterone . Synthetic analogues of estrogen and progesterone are: norkolut , dufaston , proginova , microfollin , primolut-nor , esterlan , femoston .
This group of drugs is prescribed by a doctor when a woman has a menstrual cycle and replacement therapy is indicated.
If the problem is in the excessive production of the hormone prolactin, then parlodel is prescribed, which effectively suppresses the secretion of prolactin.
Often the cause of infertility in women is anovulation, that is, the failure of the follicle to mature. Then reception is shown: clomiphene citrate and clostilbegit . These drugs stimulate the growth and maturation of follicles.
The same group of drugs, widely used in the modern treatment of infertility, includes: puregon , gonal-f , alterpur , menopur (gonadotropins).
Puregon Stimulation
Puregon - indicated for the treatment of infertility in women if it is caused by the absence of ovulation, as well as in polycystic ovary syndrome; in men with insufficiency of spermatogenesis; in the program of assisted reproductive technologies.
Gonal stimulation
Gonal-f – is prescribed for anovulation in women and polycystic ovary syndrome, as well as for spermatogenesis in men; in the program of assisted reproductive technologies.
Other drugs
Alterpur - is indicated for anovulation in women with polycystic ovary syndrome, if clomiphene is not effective; for ovarian hyperstimulation (controlled), for obtaining follicles in the program of assisted reproductive technologies (in vitro, transfer of gametes, zygotes inside the fallopian tubes).
Menopur - is prescribed for infertility in women suffering from hypo- or normogonadotropic ovarian insufficiency to stimulate the growth of follicles; for ovarian hyperstimulation (controlled), for obtaining follicles in the program of assisted reproductive technologies.
Gonadotropins are an indispensable component in the treatment of infertility with IVF (in vitro fertilization).