How to get child support in north carolina
General Information About Child Support Services
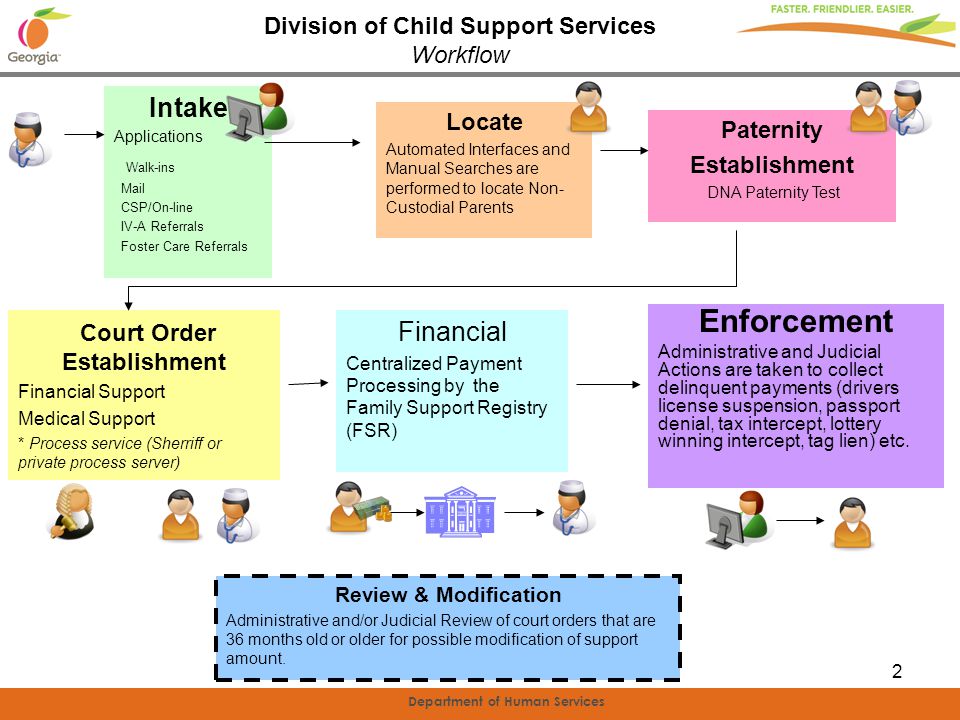
What is the Child Support Services program?
Child Support Enforcement (CSE) is a national program established by Congress in 1975 to ensure that both parents are responsible for the support of their children to the best of their ability. This program, known in North Carolina as Child Support Services (CSS), provides CSS Services to the custodians of minor children regardless of income level.
CSS agents help locate noncustodial parents (NCPs), establish the paternity of the child(ren) and petition the court to order child support payments. Once a court order has been established incoming child support payments are receipted at NC Child Support Centralized Collections (NCCSCC), which manages the collection and disbursement of all ordered child support payments in the state. To enforce child support orders CSS agents can initiate legal action against the NCP, withhold support payments from the NCP’s wages and intercept the NCP’s tax refunds.
Learn more about the Federal Child Support Enforcement Program.
Customer Service
Anyone with a child support case can get information using the web or telephone.
eChild Support: Custodial and noncustodial parents may use this tool to quickly obtain information about their case and payment information.
Customer Service: 1-800-992-9457. The customer service center assists callers 24 hours a day with an automated voice response system as well as personalized assistance between 7:30am and 5:30pm.
Roles and Responsibilities of the CSS Agency
- Gather all available information from individuals and other agencies. Evaluate their cases and determine the support activities to be pursued.
- Contract with attorneys to represent cases in civil court actions. These attorneys represent the CSS agency and not the individual custodial parent (CP) in a case.
- Work with all parties in a case providing information or explanation of case activities when appropriate.
- Keep the information that they receive confidential. Only information that is public record can be divulged. NC law requires CSS to list the Social Security numbers of all parties who are involved in a child support case on documents that establish paternity and support.
- Abide by federal regulations and state laws when handling child support cases. Automation has increased the speed and accuracy of information gathering, taking actions and disbursing support payments for children.
- Continue providing the necessary services to all cases after public assistance is terminated unless the CP requests that services not be provided and no amounts are due and owed to the state.
North Carolina CSS Organization
The Governor of North Carolina has designated the NC Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) as the CSS agency. NC General Statutes 110-128 through 110-142.2 authorize DHHS to supervise the child support program. DHHS has designated the Division of Social Services (DSS) to be responsible for this program. The Child Support Services (CSS) Section exists within DSS.
The Child Support Services (CSS) Section exists within DSS.
Some counties have placed their CSS program under the authority of the county DSS, some counties have placed it under Revenue or the County Attorney and other counties have elected to offer services by contracting with private companies. There are currently 100 Child Support Offices. 74 are under the authority of the county DSS, eight are under the authority of Revenue or the county manager and 18 are under contract with private companies and one tribal office. Regardless of who operates the local CSS office the same regulation, laws and state policies apply.
A staff of CSS regional program representatives is responsible for providing consultation and program assistance to all local programs.
Brief History of the CSS Program
In 1935 Congress enacted the Social Security Act to ease financial problems that had arisen during the Great Depression. Title IV-A of the Social Security Act established a public assistance program that offered financial assistance to families due to death of the father.
In response to increasing numbers of applications for assistance due to parental abandonment, the first actual child support legislation was enacted in 1950. This legislation required welfare agencies to report all applications for assistance due to abandonment by a parent to law enforcement agencies.
In 1975, Title IV-D was added to the Social Security Act to establish a nationwide Child Support Enforcement (CSE) program, with the purpose of recouping money paid out to welfare recipients when at least one parent was absent from the home and did not provide support. N.C. General Statutes 110-128 through 110-142.2 established North Carolina’s CSE (now CSS) program. These federal and state laws set forth the requirements for the program.
Additional legislation has been enacted over the years to expand the scope of the CSS program.
In 1981 amendments to the Omnibus Reconciliation Act established the interception of federal (IRS) tax refunds as a means of collecting overdue child support (also known as “arrearages”) and authorized the withholding of unemployment insurance benefits (UIB) to pay child support obligations.
In 1984, Child Support amendments were added to the Social Security Act. Some of these amendments authorized mandatory income withholding when arrearages accrued, the interception of state tax refunds as a means of collecting child support payments and the provision of CSS services to families that do not receive Public Assistance.
In 1988, the Family Support Act included child support provisions that established mandatory guidelines for determining child support obligation amounts and time frames for providing CSS services. States were also required to develop automated collection and payment tracking systems.
In 1994, the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (OBRA) allowed the mother and natural father to voluntarily acknowledge the paternity of a child born outside of marriage while at the birthing hospital. OBRA also required CSS to pursue health insurance coverage for children when establishing a support order.
In 1996, a major overhaul was made to the welfare system in the U. S. The Personal Responsibility & Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act (PRWORA), commonly referred to as “Welfare Reform”, completely changed Public Assistance from an entitlement program to a temporary financial assistance program with opportunities for recipients to become self-supporting. Child support became more crucial to families that could no longer stay on welfare for extended periods of time. Some important components of Welfare Reform included:
S. The Personal Responsibility & Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act (PRWORA), commonly referred to as “Welfare Reform”, completely changed Public Assistance from an entitlement program to a temporary financial assistance program with opportunities for recipients to become self-supporting. Child support became more crucial to families that could no longer stay on welfare for extended periods of time. Some important components of Welfare Reform included:
A requirement that states create a centralized collection operation to process child support payments.
A requirement that states create a central repository of employment information for newly hired employees. In North Carolina, this has resulted in the creation of the N.C. New Hire Directory (NHD). This employment information is transmitted to the National Directory of New Hires and is used to aid in the establishment and enforcement of child support orders. States were also required to notify employers within two (2) business days when their new employees were subject to income withholding.
An Expanded Federal Parent Locator Service (EFPLS) that provides CSS agencies with location, income, asset and employment information for noncustodial parents. States were required to maintain a state case registry with records of their child support cases. These records are submitted to the Federal Case Registry, which is a component of EFPLS.
The Uniform Interstate Family Support Act (UIFSA), which provides for the establishment, registration and enforcement of child support orders when another state is involved.
Financial institution data match (FIDM), which allows CSS to secure information from financial institutions to aid in the enforcement of child support orders.
The revocation of driver, business/occupational and recreational licenses as an enforcement remedy when noncustodial parents are delinquent in their child support payments. (North Carolina began using this remedy before Welfare Reform.)
The denial of passports as an enforcement remedy when noncustodial parents are delinquent in their child support payments and their arrearages are more than $2,500.
In 2012, the CSE program’s name was changed to Child Support Services (CSS).
The ACTS System
The NC CSS program uses a statewide computer system called ACTS (Automated Collection and Tracking System) to assist in the performance of its duties. This system receives and shares data with more than 30 state, federal and private agencies.
ACTS supports the functions needed to perform CSS activities at the local and state level including case management, financial management, document and report generation and supervisory functions.
CSS caseworkers use ACTS to add and update cases, enter and modify court order data after a hearing, review payment and collection activities, perform enforcement activities such as income withholding, assets attachment and tax intercepts, document their activities in the case record online and interact with CSS agencies in other states.
Child Support | North Carolina Judicial Branch
About
- What is child support?
-
Child support is money paid by a parent for the purpose of meeting the reasonable needs of the parent’s child for health, education and maintenance.
- What are the options for arranging child support?
-
Child support can be arranged in several ways.
- Parents can agree on an amount for child support in a Separation Agreement. See the Separation and Divorce Help Topic for more information.
- Parents may sign a Voluntary Support Agreement (VSA). A VSA is a child support agreement signed by both parties and then by the judge. Once a judge signs the VSA, it becomes a court order and is enforceable by the court.
- Child support can be arranged through the Child Support Enforcement Agency (CSE).
- The person who wants to receive child support can file a civil complaint in district court.
- Who can file for child support?
-
Any parent or person who provides care for a minor child living in his or her home can file for child support.
- Do I have to go to court and request custody of a child before I request child support for a child who lives with me?
-
If you are caring for a child who lives with you, you do not have to have a court order granting you custody before requesting child support.
- Who can be required to pay child support?
-
All parents are responsible for supporting their children, unless the parent’s rights have been terminated. If a parent is under the age of 18, his or her parents can be obligated to pay child support until he or she reaches the age of 18. Non-parents are otherwise not responsible for child support.
- What if the parent or child is not a U.S. citizen?
-
All children living in the United States are entitled to child support, regardless of the citizenship or immigration status of the child or the parents.
- What if there is a joint custody arrangement?
-
Parents can be obligated to pay child support even if they have joint custody of their children. See below for more information on how child support is calculated.
- Can I file an action for child support if the father’s name is not on the child’s birth certificate?
-
A child support case can be filed against an alleged father even if his name is not listed on the child’s birth certificate.

- What if I’m not sure that I’m the father?
-
You may request a paternity test.
A judge will decide whether to grant your request. If CSE filed the child support case, the agency will require a paternity test. You may be charged for the cost of the test if you are found to be the father.
- What if the other person doesn’t let me see my child?
-
Child custody and child support are separate legal issues. Even if the other party denies you custody or visitation time, this does not affect your obligation to pay child support. See the Child Custody Help Topic for more information about custody and visitation issues.
- Can I view the status of my child support case or payments online?
-
If your case is filed through CSE, you can create an account here to view the status of your case, payments, and any arrears.
Filing
- How can I begin a case with the Child Support Enforcement Agency (CSE)?
-
You can find the location of your county’s CSE office here.
 Your local CSE office will tell you what information the agency needs to assist you.
Your local CSE office will tell you what information the agency needs to assist you. - Where should I file my case?
-
A child support case may be filed in the county where the child lives or is physically present or in a county where a parent resides.
- Can I get assistance from CSE if I already have a child support case?
-
Yes, you can request assistance from CSE. Contact your local CSE agency for guidance.
- The other parent is not in North Carolina. Can I still get assistance from CSE to obtain child support?
-
Yes. Contact your local CSE agency for guidance.
- What if I don’t know the location of the other parent?
-
CSE has various tools that may be used to locate noncustodial parents. Providing information about the other parent, such as the person’s date of birth, social security number, or last known address, can assist the agency in locating the person.
Court Process
- What happens after a complaint is filed?
-
The other party must be “served” with a copy of the complaint.
 You may have the other party served by a sheriff’s deputy or through certified mail. The other party has 30 days to file an answer.
You may have the other party served by a sheriff’s deputy or through certified mail. The other party has 30 days to file an answer. - I received a complaint for child support. What should I do?
-
You have 30 days after receiving a complaint to file an answer with the court. You may hire an attorney to assist you or represent yourself.
- What should I expect in child support court?
-
Many cases will typically be scheduled for the same day. The judge or the CSE attorney will typically begin court by calling the names of everyone expected to be in court that day, and address each case one at a time.
- What should I bring with me to child support court?
-
- If you are the person entitled to receive child support, you should bring any documentation related to expenses paid on behalf of your child. For example, you should bring day care receipts or medical bills for the children. You should also bring proof of your income.
 If you have other children in the home, you should bring documentation to show that the other children live with you.
If you have other children in the home, you should bring documentation to show that the other children live with you. - If you are the person who will be paying child support, you should bring proof of your income. You also should bring documentation of any payments you have made to the other person or expenses you have paid for the children. For example, you should bring proof of payment of rent, cell phone or car payments for the custodial parent or proof that you have provided groceries, clothing, diapers, etc., for the children.
- If you are the person entitled to receive child support, you should bring any documentation related to expenses paid on behalf of your child. For example, you should bring day care receipts or medical bills for the children. You should also bring proof of your income.
- Do I need to hire an attorney for child support court?
-
If you are the party seeking child support, you may contact your local CSE to provide representation for you, or you may hire a private attorney. If you are the party obligated to pay child support, you may hire a private attorney to represent you or represent yourself. Court officials, such as judges and clerks of court, cannot give you legal advice about your rights and obligations, possible claims or defenses, or the likely outcome of your case.

- When will I start receiving child support?
-
The first payment is typically due on the first of the month after the judge signs an order for child support.
- How should I pay child support?
-
There are several possibilities if your case goes through CSE.
- In many cases, the judge will set up automatic deductions from your paycheck. If the money is not deducted, you are responsible for making the payments.
- You can make payments online using a credit or debit card or by setting up automatic bank drafts. Visit the ePayments site here to register for an account, or here for more information about online payments and statements.
- You can contact North Carolina Child Support Enforcement for more information about payment options or to make a payment at 1-877-361-5437, and can view additional contact information for the agency here.
If your case was not filed by CSE, a judge will instruct you on how to pay.

- What is family court?
-
Family court is available in some districts / counties in North Carolina. A major goal of family court is to consolidate and assign a family's legal issues before a single district court judge or team of judges. Parent education programs also may be available. Together, the dedicated family court judges and staff implement policies that promote prompt and just resolution of family law issues. Learn more.
Calculating Child Support
- How is child support calculated?
-
North Carolina’s Child Support Guidelines set the amount of child support that should be paid depending on each family’s financial circumstances. Judges must order the amount of child support set out in the Guidelines unless applying the Guidelines would not meet or would exceed the reasonable needs of the child, or would otherwise be unjust or inappropriate.
- How can I estimate the amount of child support in my case?
-
There are online calculators that allow you to estimate the monthly child support in your case.
- Calculator if one parent has primary custody
- Calculator if the parents have joint custody
- Calculator if the parents have split custody
- What if I have other children?
-
Having other children in your home or paying child support for other children not living with you are factors in calculating child support.
- What is the minimum that a person can be ordered to pay in child support per month?
-
The Child Support Guidelines require a minimum child support order of $50 per month.
Enforcement
- What can I do if the other party is not paying child support?
-
If you are represented by the local CSE agency, you should contact your caseworker. Otherwise, you can file a Motion for Order to Show Cause, requesting the court to hold the other party in contempt.
- What are the consequences for refusing to pay child support?
-
A judge has a number of enforcement options available to address a parent’s failure to pay child support as ordered.
 Depending upon the circumstances, a parent who fails to pay support as ordered may have wages withheld or be required to serve time in jail.
Depending upon the circumstances, a parent who fails to pay support as ordered may have wages withheld or be required to serve time in jail.
Modification
- When can I get a modification of child support?
-
Child support orders can be modified after three years, or if there has been a “substantial change in circumstances.” A difference of 15% or more of the child support paid under an existing order and the amount of child support resulting from the application of the guidelines based on the parents’ current income and circumstances is presumed to be a substantial change in circumstance.
- How can I file to modify child support?
-
If you are represented by the local CSE agency, you should contact your caseworker. Otherwise, you can file for a modification using this form. The judge will hold a hearing on the motion to modify. You should be prepared to show documentation that justifies your request to modify the child support order.
- What if I am required to pay child support, but I lose my job?
-
If you lose your job, you may file a Motion to Modify. A judge will determine how your unemployment impacts the current order of support.
- What if I find out that I am not the father?
-
If you have a child support order and then discover that you are not the biological father of the child, you can file a Motion for Relief within one year of discovering that you are not the father.
Children Age 18 and Older
- What happens when my child turns 18 years old?
-
In general, parents are not obligated to financially support a child once the child reaches the age of 18. Parents are required to support a child until the child turns 20 if the child has not yet graduated and remains in high school. In that case, child support will continue until the child graduates, stops attending school regularly, fails to make satisfactory academic progress, or reaches age 20, whichever happens first.
 Parents can also be required to support a child enrolled in a cooperative innovative high school (CIHS) program until the child reaches age 18 or completes four years in the program, whichever occurs later. You can see a list of CIHS programs here.
Parents can also be required to support a child enrolled in a cooperative innovative high school (CIHS) program until the child reaches age 18 or completes four years in the program, whichever occurs later. You can see a list of CIHS programs here. - Can parents agree that support will be paid until a child graduates from college?
-
Parents can agree in a separation agreement or consent order, for instance, to support a child through college or to continue supporting a disabled child. Any valid agreement between the parents is binding.
- Am I required to go to court to ensure that child support lasts past age 18?
-
If your child qualifies for support after age 18, you are not required to return to court to continue receiving child support.
- Am I required to go to court to end child support when my child reaches age 18 or graduates from high school?
-
In general, no. If you have a CSE case, you should not have to go to court when your child reaches age 18 and has graduated from high school.
 If you do not have a CSE case and your child has reached the age of 18 and graduated from high school, you can file a Motion to Modify to terminate support.
If you do not have a CSE case and your child has reached the age of 18 and graduated from high school, you can file a Motion to Modify to terminate support. - Can child support end before the child turns 18?
-
Yes, if the child marries, joins the U.S. military, or is granted emancipation by a court before reaching the age of 18.
- Am I still responsible for arrears once my child reaches age 18 and graduates from high school?
-
Yes. If arrears are owed after the child reaches the age of 18 and has graduated from high school, child support payments continue in the same amount until all arrears are paid.
Family Law - Sharifov & Associates - Attorneys at Law
division of joint property in New York
Family law is the branch of law that deals with matters relating to the family and family relations. Our family law practice includes representing clients both at the negotiation stage and in court in cases involving domestic violence (usually followed by an order of protection), divorces, separation, residence of children after divorce, and visitation of children. , child and spousal support, property division, domestic violence, prenuptial agreements, and juvenile delinquency lawsuits. We take part in out-of-court negotiations and also conduct court hearings when necessary.
, child and spousal support, property division, domestic violence, prenuptial agreements, and juvenile delinquency lawsuits. We take part in out-of-court negotiations and also conduct court hearings when necessary.
divorce by consent in New York
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the difference between a contested divorce and a non-contested divorce?
When both husband and wife voluntarily agree on all aspects of divorce, including division of joint property, residence and visitation of children, child support and for former spouses, or are able to sign a separation agreement, their divorce is considered a divorce by consent. Arrest for Domestic Violence in New York On the other hand, when spouses cannot agree among themselves on all aspects of divorce and separation, and require the court to make appropriate decisions on the above aspects of divorce, they are forced to deal with a judicial divorce. On the practical side, a legal divorce requires a lot more work, usually takes longer, and tends to cost more.
order of protection in new york
2. How can I get an order of protection in case family violence?
If something threatens your physical or emotional safety or the safety of your children, you should immediately seek the advice of a lawyer or seek the assistance of the Court. You need to take immediate steps to keep you and your children safe. Family courts in all counties in the State of New York are able to make a quick decision on an application for an order of protection; usually, if needed, it can be done within one day. The Summons, Petition and Order of Protection must be delivered to the defendant. This can be arranged through the local police station, privately, or through a professional document delivery agent. The Family Court may order the Sheriff's Department to serve the documents. The case will be rescheduled and the defendant will be subpoenaed to respond to the domestic violence petition. Either by agreement of the parties or after a hearing, the judge may issue a permanent order of protection, limited or complete, for up to 2 years.
Sometimes the police refuse to make an arrest during an investigation into domestic violence; however, the police may advise the victim to go to Family Court and ask the Judge to issue an Order of Protection. Both the New York State Criminal and Family Courts have concurrent jurisdiction over certain domestic violence offenses. The difference between the procedure in these two courts is that in Family Court, you, as the plaintiff, are a party to the process, and you have control of the lawsuit against the defendant (the person you accuse committed acts of domestic violence against you). violence). at any time you can reach an agreement with the defendant as closed; case, or you can just pick up your petition. If the police refuse to arrest the person you complained about, you can file a petition with Family Court. The Family Court Judge has jurisdiction to issue an Order of Protection (full or limited), which will have the same effect as an Order issued by a Criminal Court Judge. For the past few months, due to the Coronavirus pandemic, Family Court has operated largely virtual, with court hearings via Skype or Microsoft Teams Meetings, and filing petitions via email or Electronic Document Delivery (" EDDS").
For the past few months, due to the Coronavirus pandemic, Family Court has operated largely virtual, with court hearings via Skype or Microsoft Teams Meetings, and filing petitions via email or Electronic Document Delivery (" EDDS").
The Domestic Violence Petition, in the absence of agreement by both parties, will be decided by the Family Court Judge at the conclusion of the hearing on the merits. The New York State Family Court has jurisdiction over other types of petitions, such as Child Visit and Residence, Child Support, Neglect of a Child, Establishment of Paternity, etc.
Sometimes, after an arrest and first appearance in criminal court, a Domestic Violence Petition is also filed in Family Court, requiring the client to attend both courts for both of the relevant cases. If there are minor children in the family, the Criminal Court will often include such children in the Protective Order, however, making an exception for Family Court modifications of the order. In such a case, the defendant who wishes to maintain a relationship with his children must go to Family Court and register a child visitation petition, asking the Judge to schedule visits to the children. Depending on the circumstances of the original case that led to the Order of Protection, the judge may allow limited visits, supervised visits, or even supervised visits by a welfare agency.
Depending on the circumstances of the original case that led to the Order of Protection, the judge may allow limited visits, supervised visits, or even supervised visits by a welfare agency.
legal guardianship
3. I can't find my spouse, can I file for divorce?
Personal delivery of original divorce papers (Summon Notice or Summons of Complaint) is required by law. However, in the event that the plaintiff (the person initiating the divorce case) cannot find his/her spouse, the plaintiff must obtain court permission for alternative delivery of documents by filing a written petition with the court.
4. When am I officially divorced?
The parties to a divorce proceeding are considered divorced from the moment the judge signs the divorce decree. In the case of a divorce by consent, if a postcard has been filed in advance, the court will notify the final divorce by mail. In the event of a judicial divorce, although the judge may verbally announce during the trial that the parties are divorced, the divorce is officially finalized after the parties' lawyers have submitted the documents to the court and the judge has signed the divorce decree.
5. What is custody and how is the issue of child custody after divorce resolved?
There are two types of custody – legal custody and physical custody. Legal custody essentially means the right to make decisions. During marriage, both parents have rights to raise the child. This includes the right to make decisions about all aspects of a child's upbringing, including religion and education, as long as the parent's decisions do not pose a threat to the child. After a divorce, one of the spouses who has received legal custody of the child makes all decisions independently. You can consult with the other parent, and this is even recommended, however, if you are unable to agree with the other parent or do not wish to consult, you can make your own parenting decisions. Note that the court can always review a parent's decision to raise a child to ensure that the decision is in the best interests of the child. Joint legal custody essentially means that both parents have equal rights to make significant decisions that affect their children's lives. If the parents agreed to joint legal custody, then they essentially agreed to set aside their personal differences in order to effectively raise their children. If the parents are unable to agree on legal custody, then such a decision will be made by the court.
If the parents agreed to joint legal custody, then they essentially agreed to set aside their personal differences in order to effectively raise their children. If the parents are unable to agree on legal custody, then such a decision will be made by the court.
Post-divorce custody means the right of a parent to have a child permanently reside with that parent in the same family and be responsible for their child as long as they live with that parent. If one of the parents received the right to live with the child after the divorce, then the other parent is likely to receive the right to visit the child (visitation). If the parents cannot agree on a visitation schedule for the child, the court will provide such a schedule. Sometimes it is possible to have a joint right of residence of a child with parents in turn in equal shares (joint physical custody). In this case, the child will live half the time in the family of one parent, and half the time in the family of the other.
6.
 Will I have less time to visit my child if the other parent has exclusive legal custody?
Will I have less time to visit my child if the other parent has exclusive legal custody? Optional. Legal custody means the right to make decisions, not the right to spend time with the child. The parent with exclusive legal custody has the right to make most parenting decisions if both parents cannot agree on that decision. If the parents agreed to joint legal custody, then they essentially agreed to set aside their personal differences in order to effectively raise their children. Each parent in this case has equal rights to make decisions regarding the child. Regardless of whether your spouse has exclusive legal custody or both of you, you still have the opportunity to see your child as much as his schedule allows. Visitation of a child is usually independent of legal custody.
7. How is child support calculated?
New York State offers a formula for calculating the amount of child support payable by a parent as specified in Family Code section 240(1-b). This is a rather complicated article of law that must be read and interpreted carefully in order to accurately calculate the amount of child support. Usually, after the allowed deductions from the parent's total earnings, a certain percentage is applied to the balance of earnings to calculate basic child support. The percentage depends on the number of dependent children under 21:
Usually, after the allowed deductions from the parent's total earnings, a certain percentage is applied to the balance of earnings to calculate basic child support. The percentage depends on the number of dependent children under 21:
17% per child, 25% for two children, 29% for three children, 31% for four children, and 35% for five or more children;
It is necessary to carefully and carefully interpret the article of the law in order to accurately calculate child support, as there are many factors and conditions prescribed in the law that affect these calculations.
8. Who pays child support?
Generally, the parent with whom the child does not live most of the time will pay child support to the other parent.
child support in New York
9. Will I be able to pay less child support than is legally allowed?
The best chance to achieve this is to negotiate a reduction in child support as part of a common agreement between the parties. Do not forget, however, that the other party is not obliged to agree to this. Only in rare cases does the court find reasons not to apply the formula provided by law.
Do not forget, however, that the other party is not obliged to agree to this. Only in rare cases does the court find reasons not to apply the formula provided by law.
10. What if the children spend a significant part of their time with me, or even 50% of the time?
Once again, if you are unable to negotiate a reduction in child support with the other party, it will be extremely difficult for you to persuade the court not to apply the statutory formula. To illustrate this, note that even if the parents spend the same amount of time with the children, there is case law stating that the parent with the higher income counts as the parent not living with the child for purposes of calculating child support, and such parent would have to pay formula support! ! This shows how much more beneficial it is for clients to take good faith negotiations seriously as the best way to resolve a dispute.
11. Until what age should a parent support a child?
In New York State, a child is entitled to parental support until the age of 21, unless he/she begins independent living earlier. If a child chooses not to attend college and instead joins the military or starts working full-time, then parental support ends when the child reaches 18 years of age.
If a child chooses not to attend college and instead joins the military or starts working full-time, then parental support ends when the child reaches 18 years of age.
12. Will a child be eligible for support if she stays in college after her 21st birthday to complete her studies and earn a bachelor's or graduate degree?
No. If child support continues after his 21st birthday, it will only be as a result of the agreement of both parents. The law does not require parents to continue supporting their children after they turn 21, regardless of whether higher education is completed.
OK with this parent?
The Court takes the issue of changing the residence of children very seriously. The main criterion for the court is the issue of the welfare of the children. In attempting to make such a decision, the court will ask the question: "If such a change in the place of residence of the child is allowed, will it significantly change the nature of the relationship between the child and the parent who does not move to a new place with him?" The court will try to find out as much as possible about the nature of the relationship with the parent. (For example, how often do you see your children? Do you go to their school events? Do you meet with your children during the school week? Do you make use of all the visits that you have assigned to your children? How good are your visits to children?) will evaluate all reasons for the expected relocation of children to determine whether the parent with whom the child lives has explored all possibilities to avoid such a relocation. The distance over which the proposed move is made is also an important factor. Is this the distance that will prevent you from regularly visiting your children? The latest trend in jurisprudence is to generally allow moves up to 2 hours by car from the children's previous residence (assuming the parent with whom the children live generally has a good reason for the move). These decisions were determined by the circumstances, so don't try to reassure yourself ahead of time based on what the court has decided in other cases.
(For example, how often do you see your children? Do you go to their school events? Do you meet with your children during the school week? Do you make use of all the visits that you have assigned to your children? How good are your visits to children?) will evaluate all reasons for the expected relocation of children to determine whether the parent with whom the child lives has explored all possibilities to avoid such a relocation. The distance over which the proposed move is made is also an important factor. Is this the distance that will prevent you from regularly visiting your children? The latest trend in jurisprudence is to generally allow moves up to 2 hours by car from the children's previous residence (assuming the parent with whom the children live generally has a good reason for the move). These decisions were determined by the circumstances, so don't try to reassure yourself ahead of time based on what the court has decided in other cases.
14. Will my spouse be required to pay me alimony or maintenance after the divorce, and if so, for how long?
A recent change to the law that went into effect in 2016 provides for a formula on how to calculate temporary alimony, as well as a recommended formula for calculating permanent alimony after divorce and how long it lasts. There are also additional factors that the court must consider when determining the amount and duration of child support.
There are also additional factors that the court must consider when determining the amount and duration of child support.
Here are a few factors that are considered the most significant:
- length of marriage; the age and state of health of each spouse;
- present and future earning potential for each spouse;
- your opportunity to become financially independent;
- reduced or lost earning opportunity due to denial or delay in education, training, employment, or career development during marriage;
- having children in your home;
This is a complex decision and will be influenced by many factors.
15. Can my spouse evict me from our home?
Unless you have physically, verbally, or mentally abused your spouse, or have already found another place to live, it will be extremely difficult for your spouse to evict you from their home. Unless you agree to move out voluntarily, your spouse will have to file a petition with the court for you to be evicted, and the court will give you an opportunity to respond to it.
16. Can I and my children continue to live in our house after the divorce?
Assuming that the children will be living with you, and if you have a child under 18, the court will generally try to keep the child in the home, neighborhood, and school to which the child is already accustomed, assuming that the child is fine in that environment, and also implying that financial circumstances allow it.
17. Am I entitled to a share in the value of the house, even if the title is not in my name?
If the house was purchased during the marriage with funds earned during the marriage (regardless of which spouse earned the money), then it is likely that you will be entitled to a share in the price of the house, even if the house is not registered on you. There are many factors to calculate the size, value and percentage of this share.
18. I bought our house before our marriage with funds I bought before our marriage. Will I have to share the cost of my home with my ex/ex-spouse?
Usually not. However, if the house increased in value during the marriage as a result of your spouse's efforts, or as a result of a joint investment in the house, then your spouse may claim a share of the excess price during the marriage. Please note that if you put your spouse's name on the home title deeds, this may cause your spouse to be able to claim a share of the total value of the home.
However, if the house increased in value during the marriage as a result of your spouse's efforts, or as a result of a joint investment in the house, then your spouse may claim a share of the excess price during the marriage. Please note that if you put your spouse's name on the home title deeds, this may cause your spouse to be able to claim a share of the total value of the home.
19. Will the court force me to sell my house?
If there are no children, and assuming the house is jointly owned, the court will allow each spouse to buy out the other spouse's share. If neither spouse has the ability to buy out the other's share, or is not interested in doing so, the court may order the sale of the house and divide the proceeds from the sale at the discretion of the court.
20. Credit cards: Should they be cancelled?
If you think your spouse will use credit cards beyond justified living expenses, consider closing the account. Most accounts can be closed by either paying off the debt or transferring to another credit card. If your name is first on the account, you can achieve the same goal simply by removing your spouse's name from the account. The final liability for debts will be determined by the court or by agreement. In most cases, it is recommended that you inform your spouse of your actions (after the accounts have already been changed) so that he/she is not unpleasantly surprised or embarrassed when the payment is unexpectedly declined.
If your name is first on the account, you can achieve the same goal simply by removing your spouse's name from the account. The final liability for debts will be determined by the court or by agreement. In most cases, it is recommended that you inform your spouse of your actions (after the accounts have already been changed) so that he/she is not unpleasantly surprised or embarrassed when the payment is unexpectedly declined.
21. Do I have to withdraw money from all joint accounts to protect myself from my spouse taking or hiding the money?
The courts do not approve of either spouse withdrawing all the money from a joint account or withdrawing money without good reason. The husband should think seriously before withdrawing money. Do not forget that the court has the right to demand liability from the spouse if it is proved that he squandered or hid the joint funds.
22. If I own a business or share in a business, will my spouse get a share of the business?
If your business was created during your marriage, or you acquired an interest in a business during your marriage, then your spouse will likely be able to claim a portion of that business or a portion of your interest in the business. If you acquired the business before marriage, or you acquired an interest in the business using funds from an inheritance or a gift, then your spouse may claim an excess (if any) of the value of the business that occurred during the marriage if you or your spouse is actively contributed to the value of the business. Usually an accountant is hired to do this calculation and there are many factors that go into this calculation. Once the overall valuation of the business has been made, it is calculated what percentage of that value should be used to calculate the spouse's share. There are many factors the court will take into account to determine this percentage, including but not limited to the length of the marriage, your spouse's contribution to the business, family earnings or assets invested in the business, etc.
If you acquired the business before marriage, or you acquired an interest in the business using funds from an inheritance or a gift, then your spouse may claim an excess (if any) of the value of the business that occurred during the marriage if you or your spouse is actively contributed to the value of the business. Usually an accountant is hired to do this calculation and there are many factors that go into this calculation. Once the overall valuation of the business has been made, it is calculated what percentage of that value should be used to calculate the spouse's share. There are many factors the court will take into account to determine this percentage, including but not limited to the length of the marriage, your spouse's contribution to the business, family earnings or assets invested in the business, etc.
23. Can my spouse claim the estimated value of my professional license or higher education diploma?
For divorces initiated before 2016, by law, if all or part of a professional license or higher education occurred during marriage and was paid for by joint family funds, then it is likely that the spouse will be able to claim a portion of the assessed value of such a license or diploma. Following recent changes to the New York State Family Code that went into effect in 2016, the court must no longer consider increased earning potential due to a professional license, college degree, celebrity status, or career advancement as part of a family partnership. assets. However, when deciding on an equitable division of joint marital property, the court must take into account each spouse's direct and indirect contribution to enhancing the earning potential of the other spouse. NY Dom. Rel. L. § 236B(5)(d)(7).
Following recent changes to the New York State Family Code that went into effect in 2016, the court must no longer consider increased earning potential due to a professional license, college degree, celebrity status, or career advancement as part of a family partnership. assets. However, when deciding on an equitable division of joint marital property, the court must take into account each spouse's direct and indirect contribution to enhancing the earning potential of the other spouse. NY Dom. Rel. L. § 236B(5)(d)(7).
24. Which courts can hear divorce, custody and alimony cases?
The Supreme Court has exclusive jurisdiction over divorce cases; however, Family Court has concurrent jurisdiction over custody, visitation, and child support matters. If a person wants to get a divorce, he needs to fill out the original documents in the Supreme Court. If the child's parents are not seeking a divorce, or are not married at all, and want to sue for domestic violence, custody, visitation, or child support, they should file an application in Family Court.
25. What is a juvenile delinquency trial?
This is a New York State Family Court lawsuit involving a juvenile delinquency case between the ages of 7 and 16. When such a minor is arrested in New York State, he/she may obtain a subpoena from the police in Family Court in the county where the alleged offense was committed. On the other hand, when the allegations are serious enough and/or the minor child has had previous police referrals, the child may be detained overnight in a special detention center for children and brought to Family Court the next day when the court is open.
When a child comes to court with a parent or guardian, he/she and the parent will be interviewed by a probation officer and, depending on the charges, previous criminal convictions, the wishes of the victim and his parents, if the victim himself is a minor, the case may be referred to probation department. In this case, the petition against the juvenile delinquent is not filed and the child agrees to follow the rules of the probation department for an initial period of up to 60 days. The child must attend school, report to the probation department when required, write an essay and/or do community service under the direction of a probation officer, and also have no new drives. If the child complies with all this, the case will be dismissed.
The child must attend school, report to the probation department when required, write an essay and/or do community service under the direction of a probation officer, and also have no new drives. If the child complies with all this, the case will be dismissed.
If a juvenile is charged with a felony, or if the victim wants the case to continue, the New York City Law Department, which in such cases acts as a prosecutor, will file a petition against the juvenile delinquent, and the child will be required to appear before judge. A case on juvenile delinquency is similar to a criminal case of an adult in a criminal court, however, there are significant differences: there is no bail for the release of the defendant to freedom for a minor - either he is left in custody or released without bail on bail to the parent / guardian; no right to a jury trial, instead a court hearing before a judge; no criminal conviction - instead, recognition as a juvenile delinquent; punishment options also vary, including case closure, conditional closure, suspended sentences of up to 2 years, or detention with varying degrees of security for an initial period of up to 18 months. For the most serious crimes allegedly committed by minors 13 years of age or older, the prosecutor has the option to refer the case to an adult criminal court.
For the most serious crimes allegedly committed by minors 13 years of age or older, the prosecutor has the option to refer the case to an adult criminal court.
26. What is marriage annulment and how is it different from divorce?
A man and a woman must be legally capable of entering into a legal marriage. If the parties are not authorized to enter into a marriage, such a marriage can be annulled, that is, declared invalid. Grounds for marriage annulment are untraceable disability, minority, lack of consent, or consent obtained through fraud or intimidation, and incurable mental illness for five years.
- If one of the spouses is terminally incapable of sexual activity, the marriage can be annulled.
- Both parties must be over 18 years of age to marry without parental consent. A marriage between persons under the age of 18 may be annulled, at the discretion of the court, if the spouse under 18 wishes to annul the marriage.
- If, after marriage, either partner becomes terminally ill for 5 years or more, the marriage may be annulled.
 However, a healthy spouse may be required to maintain a mentally ill spouse for life.
However, a healthy spouse may be required to maintain a mentally ill spouse for life. - The parties must knowingly consent to the marriage. A marriage can be declared invalid if either party consented to the marriage as a result of violence or threats from the other party, or if either party did not understand the meaning and consequences of marriage.
- A marriage may be annulled if the consent was obtained by fraud, provided that the fraud was such as to deceive an ordinary reasonable person and was essential to obtain the consent of the other party. Fraud must be at the heart of the marriage contract. Only the injured party can annul the marriage on the grounds of lack of consent.
27. What is a declaration of invalidity of a marriage and how does it differ from annulment?
Unlike an annulment, where a marriage can be declared invalid, some marriages are invalid from the moment they are contracted. Such marriages include incest and bigamy.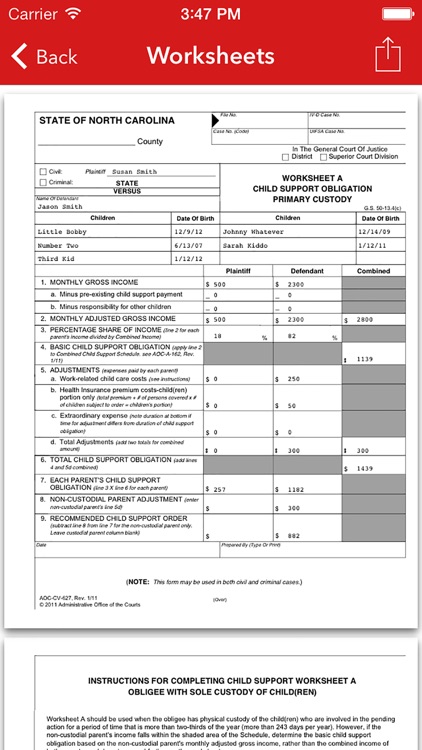 In the case of incest, this is a marriage between ancestors and descendants, brothers and sisters (including half blood). In the case of bigamy, one of the parties is already married to another person.
In the case of incest, this is a marriage between ancestors and descendants, brothers and sisters (including half blood). In the case of bigamy, one of the parties is already married to another person.
For more information, please contact our company.
Tel 516-505-2300
Te l 718-368-2800
Email [email protected]
Family Court | North Carolina Judicial Branch
eCourts
Find eCourts information, training, and resources. Read more
The NC Judiciary continues to closely monitor the spread of the coronavirus (COVID-19) throughout the state. You can check county announcements if and how your case has been affected by the COVID-19 situation.. Also, see the county page in which your case is being litigated to read local announcements, a link to the closings and advisories page, then contact the Clerk of the High Court if necessary. contact the clerk of superior court office.
Family Court makes timely, consistent, and thoughtful decisions in family and juvenile cases.
District court judges who serve in family court hear cases that involve the following:
- Juvenile delinquency
- Suspected abuse, deprivation of attention and care, addiction
- Termination of parental rights
- Domestic violence
- Child custody and visitation rights
- Divorce and divorce-related financial matters: child support, alimony to former wife or husband, fair division of property
Family Court Judges are highly experienced in dealing with family issues and receive special training to enhance their professional competence in this area.
An important purpose of family court is to consolidate family legal disputes and have them heard by a single district judge or a team of judges. This allows family court judges to better understand the concerns of each family; families do not have to tell the same story at every hearing to a different judge.
Family Court judges and other court staff work together to enforce a policy of prompt and fair family law decisions. The Family Court conducts intensive and efficient case management, which includes the following:
The Family Court conducts intensive and efficient case management, which includes the following:
- Judicial control of the progress of the case
- Case Transfer System
- Delay control
- Early Decisions and Fixed Dates of Litigation
Standard time limits depend on the type of claim, ideally the family court decides within a year from the commencement of the proceedings.
Parent Training Programs
NC State Law 1999-237 House Bill 168 Section 17.16 authorizes the Administrative Office of the Courts of North Carolina (NCAOC) to establish a training program for parents suing for custody or visitation rights of a child; any parenting training program is conducted in conjunction with family court programs under Section 25 of Session Law 1998-202.
Parenting education programs help parents who are divorced or separated to understand the needs of children during divorce, after divorce, and when children are raised in different families.