How to miscarry at 6 weeks
Miscarriage - what you might actually see and feel
Miscarriage - what you might actually see and feel | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content7-minute read
Listen
WARNING — This article contains some graphic descriptions of what you might see during a miscarriage.
A miscarriage requires prompt medical care. If you think you are having a miscarriage, call your doctor or midwife for advice and support. Go to the Emergency Department if:
- you are bleeding very heavily (soaking more than 2 pads per hour or passing clots larger than golf balls)
- you have severe pain in your tummy or shoulder
- you have a fever (a temperature above 38 degrees C)
- you are dizzy, fainting or feel like fainting
- you notice fluid coming from your vagina that smells bad
- you have diarrhoea or pain when you have a bowel motion (do a poo)
Miscarriage is a very unfortunate and sad outcome of pregnancy that takes a significant emotional and physical toll on a woman. It also happens more frequently than many people think. It's important to recognise that there's no right or wrong way to feel about a miscarriage.
Despite close to one in 5 pregnancies ending in miscarriage, what actually happens and what a woman needs to know and do when faced with a possible miscarriage are subjects that rarely get discussed.
This article aims to give you an idea of what happens and what a woman needs to know and do at different stages in her pregnancy.
Please call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 if you have any concerns or wish to discuss the topic further.
What might I feel during a miscarriage?
Many women have a miscarriage early in their pregnancy without even realising it. They may just think they are having a heavy period. If this happens to you, you might have cramping, heavier bleeding than normal, pain in the tummy, pelvis or back, and feel weak. If you have started spotting, remember that this is normal in many pregnancies — but talk to your doctor or midwife to be safe and for your own peace of mind.
Later in your pregnancy, you might notice signs like cramping pain, bleeding or passing fluid and blood clots from your vagina. Depending on how many weeks pregnant you are, you may pass tissue that looks more like a fetus, or a fully-formed baby.
In some types of miscarriage, you might not have any symptoms at all — the miscarriage might not be discovered until your next ultrasound. Or you might just notice your morning sickness and breast tenderness have gone.
It is normal to feel very emotional and upset when you realise you’re having a miscarriage. It can take a while to process what is happening. Make sure you have someone with you, for support, and try to be kind to yourself.
What happens during a miscarriage?
Unfortunately, nothing can be done to stop a miscarriage once it has started. Any treatment is to prevent heavy bleeding or an infection.
Your doctor might advise you that no treatment is necessary. This is called 'expectant management', and you just wait to see what will happen.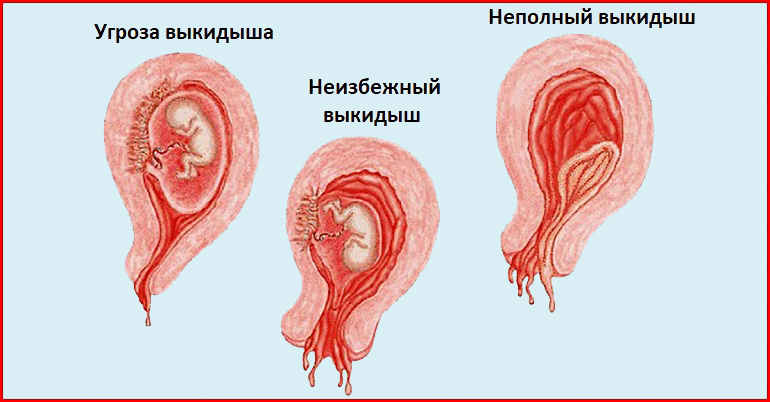 Eventually, the pregnancy tissue (the fetus or baby, pregnancy sac and placenta) will pass naturally. This can take a few days or as long as 3 to 4 weeks.
Eventually, the pregnancy tissue (the fetus or baby, pregnancy sac and placenta) will pass naturally. This can take a few days or as long as 3 to 4 weeks.
It can be very hard emotionally to wait for the miscarriage because you don’t know when it will happen. When it starts, you will notice spotting and cramping and then, fairly quickly, you will start bleeding heavily. The cramps will get worse until they feel like contractions, and you will pass the pregnancy tissue.
Some women opt to have medicine to speed up the process. In this case, the pregnancy tissue is likely to pass within a few hours.
If not all the tissue passes naturally or you have signs of infection, you may need to have a small operation called a ‘dilatation and curettage’ (D&C). You may need to wait some time for your hospital appointment. The operation only takes 5 to 10 minutes under general anaesthetic, and you will be able to go home the same day.
While you are waiting for a miscarriage to finish, it’s best to rest at home — but you can go to work if you feel up to it. Do what feels right for you. You can use paracetamol for any pain. If you are bleeding, use sanitary pads rather than tampons.
Do what feels right for you. You can use paracetamol for any pain. If you are bleeding, use sanitary pads rather than tampons.
What might I see during a miscarriage?
In the first month of pregnancy, the developing embryo is the size of a grain of rice so it is very hard to see. You may pass a blood clot or several clots from your vagina, and there may be some white or grey tissue in the clots. The bleeding will settle down in a few days, although it can take up to 2 weeks.
At 6 weeks
Most women can’t see anything recognisable when they have a miscarriage at this time. During the bleeding, you may see clots with a small sac filled with fluid. The embryo, which is about the size of the fingernail on your little finger, and a placenta might be seen inside the sac. You might also notice something that looks like an umbilical cord.
At 8 weeks
The tissue you pass may look dark red and shiny — some women describe it as looking like liver. You might find a sac with an embryo inside, about the size of a small bean. If you look closely, you might be able to see where the eyes, arms and legs were forming.
If you look closely, you might be able to see where the eyes, arms and legs were forming.
At 10 weeks
The clots that are passed are dark red and look like jelly. They might have what looks like a membrane inside, which is part of the placenta. The sac will be inside one of the clots. At this time, the developing baby is usually fully formed but still tiny and difficult to see.
At 12 to 16 weeks
If you miscarry now, you might notice water coming out of your vagina first, followed by some bleeding and clots. The fetus will be tiny and fully formed. If you see the baby it might be outside the sac by now. It might also be attached to the umbilical cord and the placenta.
From 16 to 20 weeks
This is often called a 'late miscarriage'. You might pass large shiny red clots that look like liver as well as other pieces of tissue that look and feel like membrane. It might be painful and feel just like labour, and you might need pain relief in hospital. Your baby will be fully formed and can fit on the palm of your hand.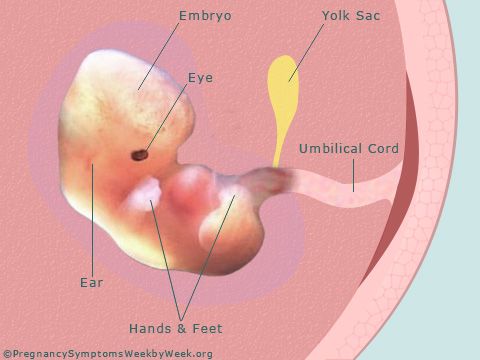
After the miscarriage
You will have some cramping pain and bleeding after the miscarriage, similar to a period. It will gradually get lighter and will usually stop within 2 weeks.
The signs of your pregnancy, such as nausea and tender breasts, will fade in the days after the miscarriage. If you had a late miscarriage, your breasts might produce some milk. You will probably have your next period in 4 to 6 weeks.
Remember, it’ll be normal to feel very emotional and upset at this time.
More information
Read more about miscarriage:
- What is a miscarriage?
- What happens after a miscarriage
- Emotional support after miscarriage
- Fathers and miscarriage
- Experiencing a pregnancy loss
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
KidsHealth (Understanding miscarriage), The Royal Women's Hospital (Treating miscarriage), Pink Elephants Support Network (Sorry for your loss), Women’s and Children’s Health Network (Miscarriage), Patient.com (Miscarriage and bleeding in early pregnancy), Pink Elephants Support Network (Treatments and procedures), New Kids Center (Blood Clots of Miscarriage: What It Looks Like?), Babycenter Australia (Understanding late miscarriage)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: March 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Fathers and miscarriage
- Emotional support after miscarriage
- What happens after miscarriage
- Miscarriage
- Experiencing a pregnancy loss
Need more information?
Miscarriage
Miscarriage Despite being common and widespread, miscarriage can be a heartbreaking experience – with up to one in five pregnancies ending before week 20
Read more on Gidget Foundation Australia website
Miscarriage
A miscarriage is the loss of a baby, usually during the first three months or first trimester of pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Fathers and miscarriage
A miscarriage can be a time of great sadness for the father as well as the mother.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Emotional support after miscarriage
It is important to know that there is no right or wrong way to feel after experiencing a miscarriage.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
What happens after miscarriage
There are a number of things you may need to consider after a miscarriage.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Miscarriage | SANDS - MISCARRIAGE STILLBIRTH NEWBORN DEATH SUPPORT
Helping you understand the complex range of emotions you may experience during fertility treatment or after miscarriage or early pregnancy loss
Read more on Sands Australia website
Miscarriage: a guide for men | Raising Children Network
This Dads Guide to Pregnancy covers miscarriage, the grief men might experience after miscarriage, and how to support partners after pregnancy loss.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
The Pink Elephants Support Network - Medical Options for Recurrent Miscarriage
In some cases, a medical reason for miscarriage or recurrent miscarriage can be found through testing
Read more on Pink Elephants Support Network website
New research on vitamin B3 and miscarriages
Pregnant women are being warned not to start taking vitamin B3 supplements, despite a recent study that suggests it might reduce the risk of miscarriages and birth defects.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy: miscarriage & stillbirth | Raising Children Network
Have you experienced a miscarriage or stillbirth? Find articles and videos about coping with the grief of losing a pregnancy or having a stillbirth.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
What causes Early Miscarriages at 6-8 weeks?
Miscarriages are common and often, unpreventable. Loss of pregnancy before 12 weeks is an early miscarriage and it happens in around 10% of all pregnancies. If you’ve experienced multiple miscarriages soon after conceiving without any logical explanation, it must be very frustrating. So, what causes early miscarriages at 6-8 weeks?
So, what causes early miscarriages at 6-8 weeks?
Normally, the early miscarriages are blamed on chromosomal abnormalities that result in the arrest of embryo growth and while that may be correct in some situations, it is not so for all. Miscarriages are caused by various factors at different times in the pregnancy and not knowing the reason can be frustrating.
To check the embryos for any aneuploidy (chromosomal imbalance), the doctors recommend preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A) before embryo implantation. While it has proven highly useful, this technique is not always accurate because the cells that are tested do not always represent the whole embryo.
The placenta and its precursor (the trophectoderm) tend to have more aneuploid cells and those are the ones tested with PGT-A. So, sometimes, despite being declared aneuploid by PGS testing, an embryo turns into a perfectly normal baby.
Chromosomal abnormalities of the embryo remain the most common cost of pregnancy losses in women but what else could be the reason of early miscarriages? Read below:
Less common reason for early miscarriages at 6-8 weeks:
Hyperactive immune system
An embryo comprises genetic material from both the father and the mother, which means that genetically it is always 50% foreign to the mother’s body and her immune system. In normal situations, during a pregnancy the immune system is reprogrammed to accept this embryo.
In normal situations, during a pregnancy the immune system is reprogrammed to accept this embryo.
However, if your immune system is hyper-active or you have auto-immune diseases, the body may perceive the embryo as a foreign entity and the attack it. This results in embryo implantation problems, clinical pregnancies, and early miscarriages.
Maternal immunity problems are the most common cause of early miscarriages, after chromosomal abnormalities in the embryo.
Other causes of early miscarriages at 6 weeks to 8 weeks
Other than chromosomal and immunologic reasons, there are also other causes of early miscarriages including:
1. Anatomical abnormalities of the uterus
Uterine malformations can cause recurrent miscarriages if they remain undetected. A study published in the Journal Human Reproduction found that more than 65% of the women with septate uterus ended up having a miscarriage. Similarly, a bicornuate, unicornuate, didelphic, T-shaped, or tipped uterus can all cause early miscarriages. If you have large fibroids, your doctor may recommend removing them to allow for a safe pregnancy.
If you have large fibroids, your doctor may recommend removing them to allow for a safe pregnancy.
Not all fibroids need removal. A fibroid’s potential of causing miscarriage depends upon its location within your uterus.
2. Infections
Around 15% of all early miscarriages are caused by infections of some kind. Bacterial vaginosis (imbalance of vagina’s normal bacteria), HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), Gonorrhea, and cytomegalovirus (CMV) were all found to increase the risk of miscarriage.
3. Uncontrolled diabetes or high blood pressure
1,228 women with at least one previous miscarriage were examined. During the study, 797 women became pregnant and 188 or about 24 percent again suffered loss of pregnancy.
Even if they achieved normal blood pressure before the pregnancy, each 10 mm increase in systolic blood pressure was found to cause an 8 percent higher risk of miscarriage and each 10mm increase in diastolic blood pressure showed an 18 percent increased risk of miscarriage.
4. Thyroid disease
Hypothyroidism and raised TSH levels increase the chances of miscarriage in early pregnancy. TSH levels higher than 4.5 mU/L are associated with a greater risk of early miscarriage.
5. Blood clotting
Having genetic or hereditary thrombophilia raises your predisposition to blood clotting. Blood clots that develop in the placenta increase the risk of miscarriage and fetal loss. Some doctors advise all patients seeking IVF to test for “antiphospholipid syndrome,” so in case, it exists, it can be managed with medications for better chances of a successful pregnancy.
6. Medications
Medicines like Misoprostol, Methotrexate, retinoids, and some NSAIDS are harmful to pregnancy and may cause an early miscarriage. Never take any over-the-counter medication without your doctor’s advice during pregnancy.
7. Food poisoning
It will not always be the reason for miscarriage but some cases of food poisoning may be lethal for the growing embryo. Listeria, a bacteria that is sometimes found in soft, unpasteurized cheeses and other uncooked foods may cause miscarriage. Besides, undercooked eggs, raw meat may cause Salmonella, Toxoplasmosis, which can result in a miscarriage.
Listeria, a bacteria that is sometimes found in soft, unpasteurized cheeses and other uncooked foods may cause miscarriage. Besides, undercooked eggs, raw meat may cause Salmonella, Toxoplasmosis, which can result in a miscarriage.
8. Environmental causes
Excessive exposure to harmful chemicals such as Lead, Arsenic, Mercury, pesticides, etc. may raise your risk of miscarriage. Be sure to discuss with your doctor to understand if your environment may be responsible for miscarriages.
While any of the above may be responsible for an early miscarriage at 6-8 weeks, the most common reasons for miscarriages are either chromosomal abnormalities in the embryo or immunologic problems in the mother.
If miscarriage is a concern, the doctors usually advise to do Karyotype testing in both parents to check the size, shape, and number of your chromosomes. If it comes out normal [normal female (45, XX) and normal male (46, XY)], the mother must be evaluated for immunological issues.
After a miscarriage happens, the doctor may also advise to test the products of conception (the fetus, placenta, and other pregnancy tissues) to check for chromosomal abnormalities.
If everything is normal, the maternal immune response and other causes must be evaluated before attempting a pregnancy again.
If you find the reason for your early miscarriage, it may be avoided. Consult with our top fertility specialists for early miscarriages and pregnancy problems.
Resources:
Gleicher, N., Vidali, A., Braverman, J., Kushnir, V. A., Barad, D. H., Hudson, C., Wu, Y. G., Wang, Q., Zhang, L., Albertini, D. F., & International PGS Consortium Study Group (2016). Accuracy of preimplantation genetic screening (PGS) is compromised by degree of mosaicism of human embryos. Reproductive biology and endocrinology: RB&E, 14(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-016-0193-6
Tullio Ghi, Francesca De Musso, Elisa Maroni, Aly Youssef, Luca Savelli, Antonio Farina, Paolo Casadio, Marco Filicori, Gianluigi Pilu, Nicola Rizzo, The pregnancy outcome in women with incidental diagnosis of septate uterus at first trimester scan, Human Reproduction, Volume 27, Issue 9, September 2012, Pages 2671–2675, https://doi. org/10.1093/humrep/des215
org/10.1093/humrep/des215
Sevi Giakoumelou, Nick Wheelhouse, Kate Cuschieri, Gary Entrican, Sarah E.M. Howie, Andrew W. Horne, The role of infection in miscarriage, Human Reproduction Update, Volume 22, Issue 1, January/February 2016, Pages 116–133, https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmv041
Preconception Blood Pressure Levels and Reproductive Outcomes in a Prospective Cohort of Women Attempting Pregnancy https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10705
Thyroid Status and Risk of Miscarriage: https://www.thyroid.org/patient-thyroid-information/ct-for-patients/volume-7-issue-12/vol-7-issue-12-p-3
Medical termination of pregnancy in the early stages in Nizhny Novgorod at the Tonus clinic, medical abortion, mini abortion
Termination of pregnancy is an important step in the life of a woman who is going to do this. It is important to think carefully about everything, and also, to choose a clinic where you would like to have an abortion. After you have made up your mind, the question arises, where to have an abortion? Not all clinics are licensed to perform abortions, so if you want to do abortion, clinic , in which it will be performed, must have the appropriate permission.
After you have made up your mind, the question arises, where to have an abortion? Not all clinics are licensed to perform abortions, so if you want to do abortion, clinic , in which it will be performed, must have the appropriate permission.
In our country, at her own request, a woman can have an abortion for up to 12 weeks. There are also various indications for termination of pregnancy. Abortion for social reasons a woman can do up to 22 weeks, for medical - at any stage of pregnancy.
Abortion in this case is performed after determining the indications for it by a gynecologist and related specialists. The reason for termination of pregnancy for medical reasons can be both a serious pathology on the part of the woman and on the part of the fetus. Only a competent and experienced gynecologist will help you decide on the choice of the method of abortion - medical, mini-abortion or surgical.
The best is early termination of pregnancy . Early termination of pregnancy reduces the risk of complications in the future and can be carried out without the use of invasive techniques.
Early termination of pregnancy reduces the risk of complications in the future and can be carried out without the use of invasive techniques.
Early termination of pregnancy. Medical abortion
Medical abortion is one of the safest methods and an excellent alternative to surgical abortion. Medical abortion is performed up to 6 weeks of pregnancy. When holding medical termination of pregnancy in the early stages, drugs are used that, by their mechanism of action, inhibit the synthesis of progesterone.
Medical abortion is performed only under the strict supervision of a gynecologist. After medical termination of pregnancy, an ultrasound scan is required to examine the uterine cavity.
Early termination of pregnancy by medical abortion method does not impair the woman's reproductive function. According to many studies, after medical termination of pregnancy, ovulation is restored in the shortest possible time.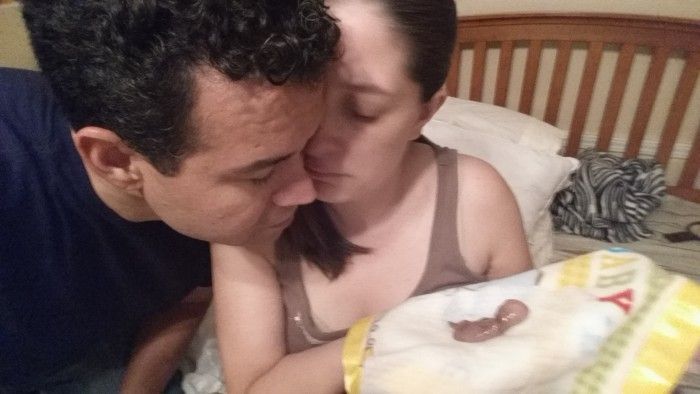 An additional positive quality of medical abortion is the possibility of its implementation directly on the day of treatment.
An additional positive quality of medical abortion is the possibility of its implementation directly on the day of treatment.
Early termination of pregnancy - mini-abortion
Mini-abortion as a method of early termination of pregnancy can be performed from 6 to 12 weeks. The main technique for mini-abortion is vacuum aspiration. The fertilized egg is removed from the uterine cavity using a special electric suction. This option for early termination of pregnancy is more gentle than the standard options for surgical abortion.
We must not forget that the sooner have an abortion , the lower the risk of complications.
The procedure takes about 5 minutes and the woman can go home within a few hours after the procedure. The uterine mucosa, unlike curettage, is slightly injured. A contraindication to abortion in this way is the presence of infection in the acute period. After the mini-abortion, a control ultrasound examination of the uterine cavity is performed.
Where to have an abortion?
Many women (especially young women), in order not to advertise their pregnancy, start looking for options, where to have an abortion . It must be remembered that it is most correct to have an abortion in a clinic, under the supervision of specialists, and not with the help of folk remedies.
An abortion made outside the walls of a medical institution that has the right to perform this manipulation is called criminal. A self-performed abortion by untested means can lead to serious consequences. In this case, a woman risks not only the possibility of having children in the future, but also her health.
Medical abortion
Termination of pregnancy by indications or at the request of a woman for a period of 6 to 12 weeks can be performed by curettage of the uterine cavity. This procedure is a surgical procedure and requires preparation. As with any other operation, all the necessary tests are given. Termination of pregnancy is carried out on an empty stomach, as the woman is given anesthesia.
Termination of pregnancy is carried out on an empty stomach, as the woman is given anesthesia.
In the postoperative period during the month you need to refrain from sexual intercourse, do not go to the sauna, bath, bathing in water, it is not recommended to take a bath. All these measures are aimed at preventing infection.
It is also not advisable to overcool, be subjected to excessive stress and physical exertion for some time. It is necessary to give the body a rest, so that in the future there will be no problems with conception.
After the abortion, it is necessary to visit a gynecologist. During the appointment, the doctor will conduct a comprehensive examination with obligatory ultrasound control, as well as select the optimal method of contraception, which will help to avoid unwanted pregnancies in the future, and therefore new abortions. A large number of abortions brings with it a large number of complications that can affect the reproductive potential of a woman.
Psychological support for a woman is also important, both before and after an abortion. The doctor in this case should be not only a competent specialist, but also a sensitive psychologist who can encourage the patient.
A great role is given to conversations with a woman, since she must understand that the doctor is on her side and in no case condemns the perfect act.
Within a month after the abortion, women should monitor their well-being.
If you experience pain, bleeding, fever or other unusual phenomena, you should definitely visit a gynecologist for a comprehensive examination and identify the cause of the symptoms.
Where to have an abortion in Nizhny Novgorod?
Termination of pregnancy in Nizhny Novgorod is performed by experienced specialists at Tonus Medical Center. It is possible to carry out manipulations at various stages of pregnancy. An abortion performed at Tonus Medical Center is a safe procedure carried out by highly qualified doctors who choose an individual approach to each woman and provide reliable medical care.
You can make an appointment at the Center for Obstetrics and Gynecology by calling 8 (831) 411-11-22
Mini-abortion (up to 5 weeks 6 days) close to home - outpatient operations
Paracelsus Medical Center
Recording in 1 click
Mini-abortion (up to 5 weeks 6 days)
Mini-abortion is an artificial termination of pregnancy in a specialized medical institution, performed up to 5 weeks 6 days. A mini-abortion can only be done in a medical institution that has the appropriate license. Artificial termination of pregnancy should be carried out by a qualified obstetrician-gynecologist.
Indications for mini-abortion: woman's desire.
Mini-abortion - surgery performed at 5 weeks 6 days of pregnancy. Operative interruption is done only in a gynecological hospital. For anesthesia, intravenous anesthesia is used. After anesthesia, mechanical dilation of the cervix is performed.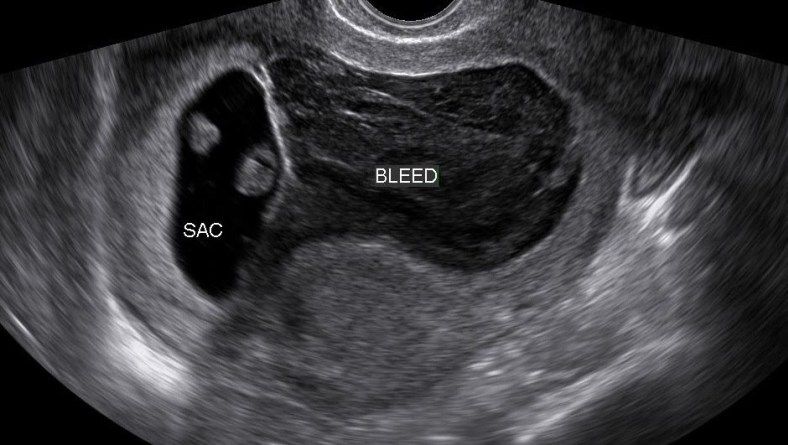 Next, the doctor performs a vacuum aspiration of the fetal egg with a special instrument, removing the inner layer and the embryo with membranes. Honey abortion in this case lasts about 10-15 minutes. After it, the woman spends a few more (2-3) hours in the ward under observation.
Next, the doctor performs a vacuum aspiration of the fetal egg with a special instrument, removing the inner layer and the embryo with membranes. Honey abortion in this case lasts about 10-15 minutes. After it, the woman spends a few more (2-3) hours in the ward under observation.
Any artificial termination of pregnancy can lead to serious consequences. Early complications of abortion can be damage to the body and cervix, bleeding and inflammation. Blood loss in severe cases can threaten a woman's life. Inflammation of the genital organs after a medical abortion can be acute and chronic. More often, the infectious process proceeds without complaints, but leads to adhesions and infertility. Mini-abortion has a number of delayed consequences. A number of women may experience menstrual irregularities, infertility, miscarriage.
You can undergo the entire scope of the preoperative examination at Our Medical Center Paracelsus in one day! Examination for surgery and the validity of the results of the examination:
- - Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
- - Ultrasound of the veins of the lower extremities - 3 months
- - Flora smear -10 days
- - Oncocytology from the cervix - 6 months Urinalysis - 10 days,
- - Complete blood count and reticulocytes -10 days,
- - Electrocardiogram with interpretation -14d,
- - Blood for HIV, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Syphilis 3 months.

- - Biochemical blood test: general, direct, indirect Bilirubin., total protein, albumin, urea, glucose, creatinine, uric acid, -10 days;
- - coagulogram - 10 days;
- - Blood type and Rh factor
- - Fluorography - 6 months
Other tests may be added as indicated.
The price of a mini abortion in Yekaterinburg
- Mini abortion in Yekaterinburg qualitatively and inexpensively!
- ☏ Sign up for a mini abortion and find out the price by phone: 8(343)272-03-03 or online.
- ✔ Outpatient operations - mini-abortion (up to 5 weeks 6 days) in the Paracelsus multidisciplinary clinic.
Recording in 1 click
Please wait, download may take time
Loading...
You know which doctor you want to book
You know the service you want to book
Service selection
A second consultation is considered to be a consultation of one specialist within 30 days from the date of the previous appointment. On the 31st day from the previous visit to a specialist of this profile, the consultation will be primary.
On the 31st day from the previous visit to a specialist of this profile, the consultation will be primary.
The choice of a specialist
Service selected:
Choosing a specialist service
A second consultation is considered to be a consultation of one specialist within 30 days from the date of the previous appointment. On the 31st day from the previous visit to a specialist of this profile, the consultation will be primary.
Address selection:
st.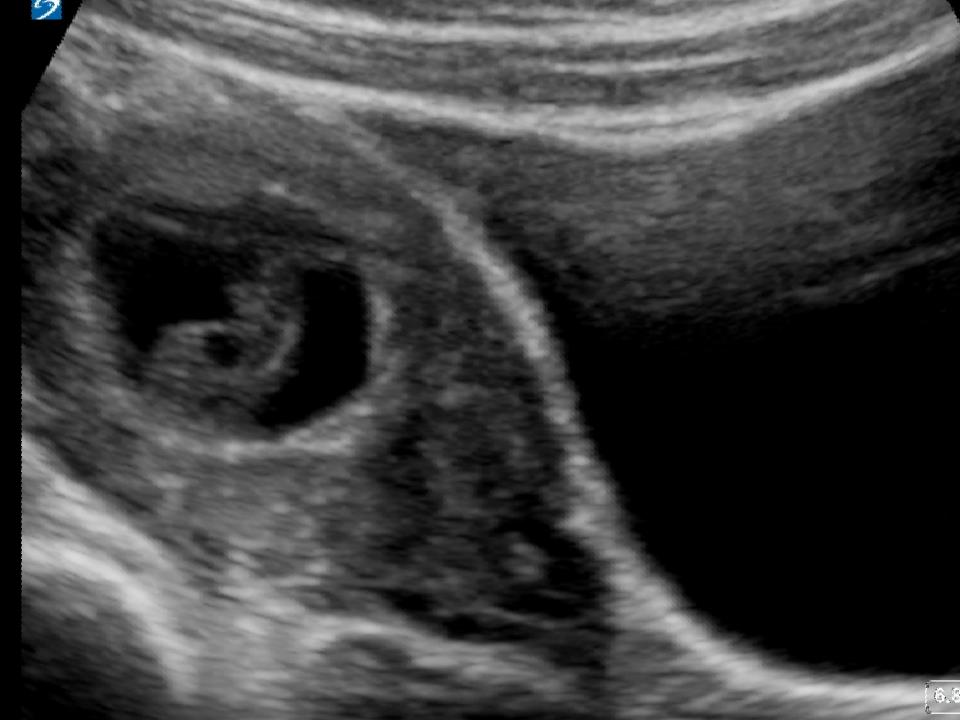 Vikulova, 33, building 2 st. Bolshakova, d. 68
Vikulova, 33, building 2 st. Bolshakova, d. 68
Date selection:
Time of receipt:
Password
Password
Register Can't login? account activation
To gain access to your personal account, enter the e-mail that was specified during registration, we will send instructions for password recovery
To gain access to your personal account, enter the e-mail that was specified during registration, we will send instructions for reactivating your account
Your application has been accepted, our specialists will answer your question as soon as possible!
Telephone
Comment
Dear patients!
Multidisciplinary Clinic and Maternity Hospital "Paracelsus" informs you, according to the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation to the Federal Tax Service dated March 25, 2022. N BS-4-11 / 3605, that subparagraph 3 of paragraph 1 of Article 219The Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the right of a taxpayer to receive a social tax deduction in the amount paid by him in the tax period for medical services provided by medical organizations engaged in medical activities to him, his spouse, parents, children (including adopted children) in under the age of 18, wards under the age of 18 (in accordance with the list of medical services approved by the Government of the Russian Federation).
N BS-4-11 / 3605, that subparagraph 3 of paragraph 1 of Article 219The Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the right of a taxpayer to receive a social tax deduction in the amount paid by him in the tax period for medical services provided by medical organizations engaged in medical activities to him, his spouse, parents, children (including adopted children) in under the age of 18, wards under the age of 18 (in accordance with the list of medical services approved by the Government of the Russian Federation).
Joint order of the Ministry of Taxation of Russia and the Ministry of Health of Russia dated July 25, 2001 N 289 / BG-3-04 / 256 (hereinafter - the order of July 25, 2001) approved the form of the Certificate of payment for medical services for submission to the tax authorities of the Russian Federation (hereinafter - the Certificate payment for medical services).
This certificate certifies the fact of receiving a medical service and its payment through the cash desk of a healthcare institution at the expense of the taxpayer.