Gross motor skills examples for preschoolers
What Are Gross Motor Skills for Preschoolers?
- Share
Why are gross motor skills so important for preschoolers to develop and how can parents and teachers build them with simple activities and movement games?
What are Gross Motor Skills?The process that children follow from learning to lift their heads as babies and run as toddlers, all the way to playing a sport in school is known as gross motor development.
Children develop gross motor skills when they learn how their bodies work and how they can move and control them.
Gross motor skills should be developed during infancy, toddlerhood and right through the preschool and early elementary/primary years.
During early childhood, it is important for children to develop skills such as muscle strength, balance, core strength, postural control, endurance and coordination.
Children naturally develop from the centre of the body outwards. This means they need to develop strength in their core and trunk before they develop it in their arms and legs.
Fine motor skills (such as finger strength and control) are therefore dependent on a child first building gross motor skills.
Gross motor skills can be developed in a variety of ways during childhood, through free play as well as adult-guided activities.
Planning movement activities to do with your children allows you to work on specific skills with them, such as balance or catching and throwing.
Why Are Gross Motor Skills Important?When children do not have well-developed gross motor skills, this can result in:
- poor concentration in class
- poor body awareness and control
- difficulty writing
- difficulty sitting at a desk
- inability to cross the midline
- poor posture, balance and coordination
- avoidance of sports and physical activities
What Are Examples of
Gross Motor Skills?Here is a list of gross motor skills examples for preschoolers:
- running, walking, galloping, chasing
- crawling, lifting, reaching
- skipping, hopping, leaping
- catching, throwing, pushing, pulling
- rolling, dribbling, kicking
- balance and coordination
- hitting, bouncing, passing
- climbing, hanging, holding
Here is a list of the gross motor milestones, by age.
This post contains affiliate links for educational products that I personally recommend. If you purchase through one of them, I earn a commission at no extra cost to you. Read the terms and conditions for more details.
Gross Motor Skills Activities for Preschoolers
Here are some ideas to develop preschoolers’ gross motor skills with games and activities.
1. SkittlesThis game can be played with a plastic set of skittles or a homemade set.
Simply take empty plastic cooldrink bottles and pour some sand or water into them so they will stand up. You can also make an art activity out of it and paint the bottles different colours.
They should not be impossible to knock down though. Vary the amount of sand/water depending on your child’s age and strength.
Place the bottles standing up into a V-shape and take turns rolling a ball towards them and knocking them over. The younger your child is, the bigger the ball should be.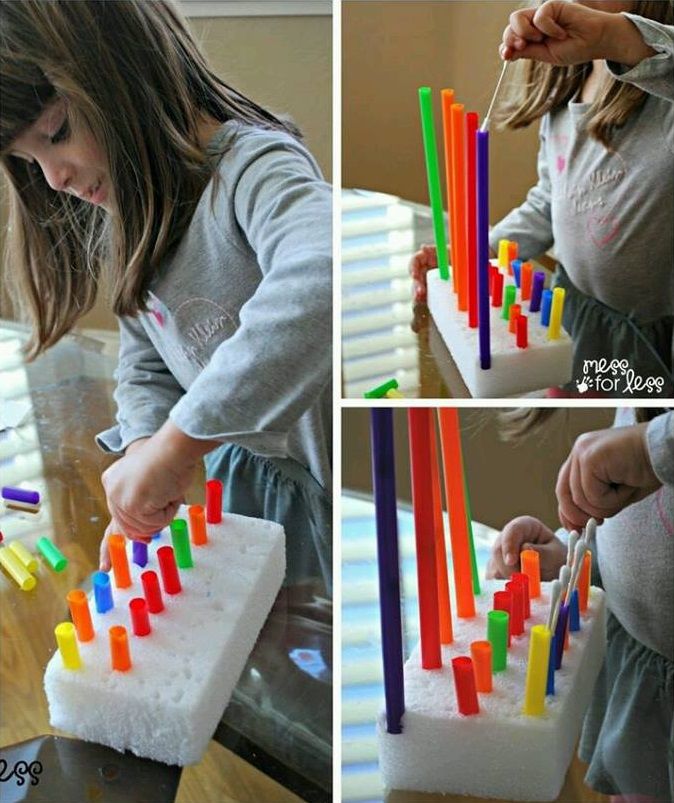
This is an old favourite. Hopscotch is best played outside by drawing the squares with jumbo chalk on concrete or paving.
Here is an example of the formation of squares, but you can change this:
Take turns with your child jumping through the squares – hop on one foot on single squares and jump with two feet into double squares (one foot in each square). When you get to the end, turn around and hop back to the start.
Learning to hop on one foot or two feet is an important skill for a preschooler and this is a great game to teach this skill.
When your child has mastered how to hop, vary the game by using a beanbag or stone and throwing it into the first square before beginning.
Then, hop over the beanbag and jump into the second square. Hop all the way to number 10, turn around and hop backwards, bending over to pick up the beanbag on one leg on returning to 1.
This awesome indoor hopscotch rug will encourage lots of extra movement.
Test your child’s jumping skills with this game using only a roll of craft tape.
Lay a strip of tape on the ground as a starting point. Then place another few strips spaced closely together and get your child to hop, feet together, from tape to tape.
Then, move the strips slightly further apart and see if your child can jump further. Continue moving them further away until you reach your child’s limit. Measure the distance and watch your child slowly beat that distance every time they play.
4. Balancing BeamUse a beam in your garden (such as a low wooden fence) or create a makeshift balancing beam out of a wooden plank or any other material. Balance it on some bricks or low stools.
Practise walking across the beam and not falling off. Turn it into a game and pretend there are crocodiles in the river below.
Challenge your child to walk across the beam, turn around at the end and walk back without falling off.
Stand a short distance from your child with your legs spread wide apart. Get him to roll a ball “through the tunnel” (through your legs).
With practice, you can begin to stand further away from your child and make the tunnel narrower by stepping your legs closer together, as well as using a smaller ball. This is a good game for developing ball skills and eye-hand coordination.
6. Beanbag TossPlaying with beanbags is another good way to work on eye-hand coordination. You can also replace beanbags with soft balls or even handmade balls or beanbags (stuffed material).
Use a bean bag toss board or find a target such as a laundry basket or a box. Use a target with a large opening for younger children.
Take turns aiming and throwing the beanbags into the basket and counting how many got in each time. Slowly move the target further away, or make it smaller (e.g. use a small bin).
Here are more fun bean bag activities for kids.
Build your child’s strength and agility with a fun homemade obstacle course. These can be built indoors or outdoors.
Be creative and place together several props into a course that you and your child will take turns to follow, or even race through.
Provide a mix of activities in each course, such as opportunities to climb, jump, throw, etc.
Here are a few ideas for props and activities:
- chairs to step/climb over
- Planks to walk along
- beanbags to balance on your head
- an empty box to crawl through
- hopping in between the rungs of a ladder (lying down)
- swinging on a tree branch
The Egg and Spoon Race is a favourite for young children’s sports days. Your kids will love racing you in this fun game.
Simply balance an egg in a tablespoon from the start line to the finish line.
You may want to boil the eggs first unless you’re really in the mood for some fun! Nothing will sharpen the skills and concentration quicker than the threat of an egg cracking open.
Simon Says is a game that can be played to develop many of your child’s skills, including listening skills, concentration, auditory perception, etc. Use this game as a way to stimulate your child’s large muscles.
Make it more fun by taking turns and allowing your child to also give you instructions to follow.
Some ideas of actions:
Simon Says…
- do a crab walk to the wall and back
- run to the tree, do 4 jumping jacks and run back
- do 3 cartwheels, turn around and lie on your back
- hang from the monkey bars for 10 seconds
Incorporating multiple actions will work on your child’s ability to follow instructions at the same time.
10. Balloon TossBlow up some balloons and play a game of Balloon Toss. The object is to see how long you and your child can keep the balloon in the air, by tossing it back and forth, before it drops to the ground.
Time each round and see how long you last. When you can go for at least a minute, try lifting two balloons in the air and keeping them both in the air.
When you can go for at least a minute, try lifting two balloons in the air and keeping them both in the air.
As you can see, gross motor skills are an important part of your child’s overall physical development but are easily built through play.
11. Action Songs
Sing some action songs to get the body moving. They are also great for developing body awareness.
Here’s an example:
Head, shoulders, knees and toes,
knees and toes
Head, shoulders, knees and toes,
knees and toes
And eyes and ears and mouth and nose
Head, shoulders, knees and toes,
knees and toes
12. Play With Balls
Playing with balls is one of the most basic activities and one that will keep babies, as well as 10-year-olds, entertained.
Balls are great practice for developing hand-eye and foot-eye coordination.
Throw and catch balls of different sizes
The Effects of Screen Time and Less Play Time on Gross Motor DevelopmentOver the years, there has been a tendency to replace children’s free play time with all kinds of extra activities.
While you may want to send your children for swimming lessons or the occasional extra activity, there is no need to have your 4-year-old attending art class, computer class, multiple dance classes, ball skills class, etc.
These activities are replacing children’s playtime. Playtime is vital for your child’s development, especially for building their gross motor skills.
If you are packing your children’s free time with paid activities and programs, know that many of these are unnecessary and are actually taking away from your child’s natural learning time.
As for screen time, while it is impossible in today’s times to prevent children entirely from watching screens, as a parent you can control how much screen time your child is exposed to.
Your 3-year-old does not need to be sitting on their iPad in the afternoon. They are supposed to be running around outside or getting up to mischief somewhere. They should be learning.
Whatever amazing online program your child is following is not a justifiable replacement for play.
Just these two factors alone – screen time and extramural activities – have had a serious impact on children’s motor development in today’s times.
This translates directly into problems concentrating and working effectively in the classroom.
Here’s some of the research on the effects of screen time on the brain, shared by Debra Bradley Ruder,
Simply put, the more your children play freely, the more they will be learning.
Check out this awesome list of the best gross motor toys for kids and 35 of the best gross motor activities for kids.
Get FREE access to Printable Puzzles, Stories, Activity Packs and more!
Join Empowered Parents + and you’ll receive a downloadable set of printable puzzles, games and short stories, as well as the Learning Through Play Activity Pack which includes an entire year of activities for 3 to 6-year-olds.
Access is free forever.
Signing up for a free Grow account is fast and easy and will allow you to bookmark articles to read later, on this website as well as many websites worldwide that use Grow.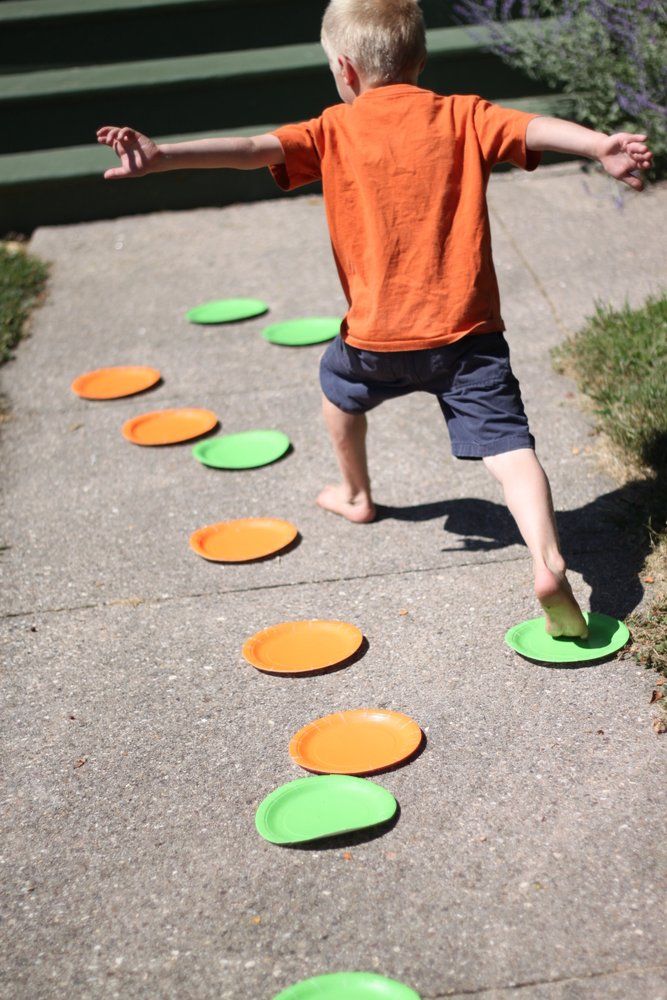
- Share
Gross Motor Skills (walking, running, jumping, climbing, balance, strength)
Preschool Milestones
(walking, running, jumping, climbing, balance, strength)
Gross Motor development involves the larger, stronger muscle groups of the body. In early childhood, it is the development of these muscles that enable the baby to hold his/her head up, sit, crawl and eventually walk, run and skip.
Between the ages of 3 – 4 years, your toddler should:
|
|
Between the ages of 4 – 5 years, your preschooler should:
|
|
Red Flags for Gross Motor Development (1 – 5 years)
If you notice or are concerned about some of the following things about your child, you may want to talk to your physician or another health professional.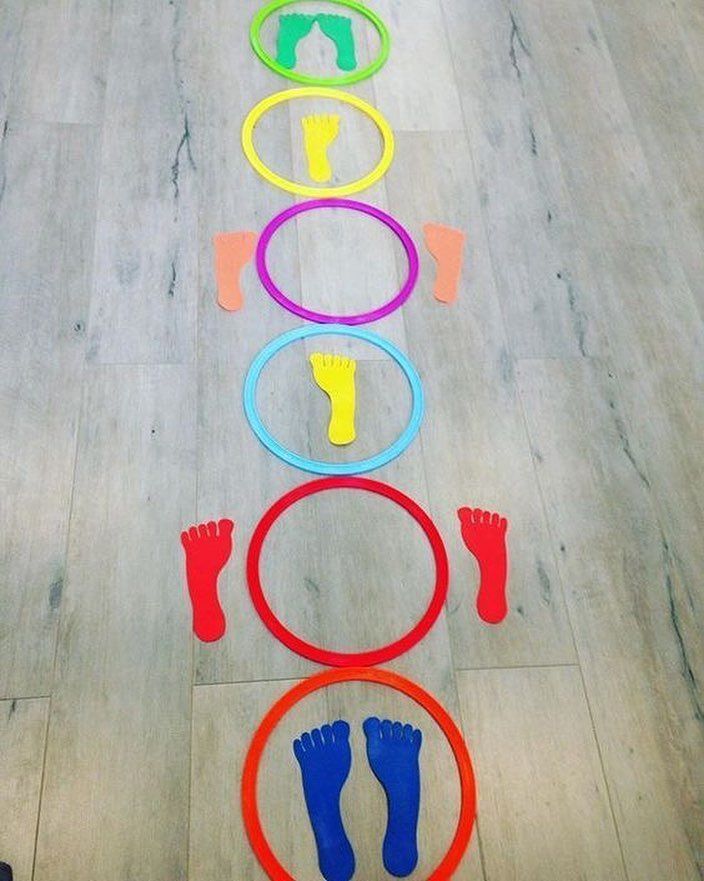
|
|
If you have concerns about your child at any age, please feel free to contact us to speak to a professional. You can also make a referral to our centre at anytime.
Development of gross motor skills in children
Parents, and often teachers, underestimate the need for the development of gross motor skills in children. And it is the basis for the formation of fine motor skills, which is important in preparing for school. Let's figure out what gross motor skills are, why and how to develop them.
Let's figure out what gross motor skills are, why and how to develop them.
Article content:
- What is gross motor skills
- Why develop
- Gross motor disorder in children
- How to develop gross motor skills
- Developmental games and exercises
- Output
What is gross motor skills
Gross motor skills, or general, are active body movements that involve arms, legs, torso, head. In fact, adults use these skills without thinking, and children have to master them gradually.
In the first year of life, the baby develops rapidly and learns to control his body:
- focuses the eye;
- holds his head;
- controls arms and legs;
- is learning to sit;
- crawling;
- tries to get up;
- walks, runs, jumps.

The success of all these important processes depends on the health and life of the child.
- By the age of 2, a child masters complex general motor skills of arms and legs. The kid throws and kicks objects. Holding hands, he climbs the stairs.
- Children at the age of 3 learn to walk, run, jump more confidently.
Gross motor skills are formed through any movement: active games, copying the actions of adults and animals, sports, dancing, aerobics.
It is important to start working with your child as early as possible. The good physical development of a preschooler is the key to his further success in school, life and the ability to avoid many problems.
Read also: what a 2-year-old child should be able to and know
Why develop
Without developed gross motor skills, it is impossible to fully develop a person. Benefits of developing motor skills:
- strengthen the musculoskeletal system;
- improve coordination;
- provide muscle protein synthesis;
- stimulate cognitive activity;
- increase efficiency;
- develop independence;
- improve speech;
- help develop reading and writing skills;
- motivate to vigorous activity;
- form interhemispheric interaction;
- develop creativity;
- contribute to successful socialization;
- learn to control their body in space;
- contribute to the knowledge of the world and themselves.

As you can see, the value of developing gross motor skills is great. This work allows you to preserve and increase the physical and mental development of children.
Difficulties of a child with a lack of gross motor skills
Each baby is individual and its development is uneven. It is better not to compare your child with other children. One child may start walking at 9 months and another after a year. This is fine. The main thing is to exercise regularly with the baby. However, there are criteria by which it can be determined that a child has poorly developed gross motor skills:
- drawing and writing skills are difficult;
- inability to dress and use cutlery independently;
- inability to maintain a sitting posture;
- loses orientation in space: falls, stumbles, crashes;
- lethargy;
- speaks poorly;
- cannot play with small toys;
- badly switches to a new activity;
- low self-esteem;
- is hard to communicate with peers.

If gross motor impairment is suspected, see a physician for correction.
How to develop
The main objectives of the development of gross motor skills are:
- creation of conditions for the implementation of the child's motor activity;
- development of skills to control and manage movements;
- learning coordination of actions;
- development of motor activity.
Based on the tasks, parents need to equip the space in the room, stock up on the necessary equipment and control the process. The room should have enough space for running, jumping, bending. Start with the simplest: teach your baby to do morning exercises. If you can do it outside, even better. Simple exercises are quite enough: squats, walking, turns, bends.
Buy a variety of equipment for outdoor games: balls, jump ropes, hoop. At home with a child, you can play skittles, basketball, gorodki, dodgeball. The ideal option would be to arrange a special sports corner in the room. If this is not available, you can simply dance to your favorite music, alternating slow and fast movements.
The ideal option would be to arrange a special sports corner in the room. If this is not available, you can simply dance to your favorite music, alternating slow and fast movements.
For walks on the street, stock up on a bicycle, scooter, roller skates and other equipment according to age. In winter - skates, skis, slides. In addition, for the development of the child's motor activity, you can sign up for the nearest children's center or sports section, where ideal conditions are created for a full-fledged formation.
Household chores also help develop gross motor skills. It is necessary to load the child with feasible chores around the house. For example, sweep the floor, wipe off the table, arrange toys, hang or fold laundry.
Games and exercises for the development of gross motor skills
There are a great many exercises and games for the development of speech and gross motor skills. These can be exercises to strengthen the muscular corset, to coordinate to create spatial representations in preschool children. Games are played in pairs or groups.
Games are played in pairs or groups.
- Boat. Lying on the back with outstretched arms. The child needs to simultaneously raise straight arms, head and legs. Hold the pose for as long as possible. The same exercise can be done lying on your stomach.
- Log. Starting position as in the previous exercise. Roll with the whole body alternately to the right and left side.
- Lying on your stomach, put your hands behind your head. Elbows apart. Slowly raise your upper body while keeping your legs straight.
- "Spider". Squat down, palms lean behind. Crawl like an insect.
- Goose step. Squatting position, only hands on knees. Walk in different directions: forward, backward, left, right. You can complicate the exercise by putting a flat object on your head.
- "Narrow path". Lay out a long rope on the floor with bends and turns. Invite the child to walk along it.
 On an imaginary track, you can roll cars and other toys.
On an imaginary track, you can roll cars and other toys. - Stand alternately on the right and left legs, on the toes, on the heels. Make a "swallow".
- March in place with high legs.
- Exercises with cross movements of arms and legs.
- "Hit the target." The game develops the eye well. You can purchase a traditional ring thrower or build your own from improvised material. Any container where you need to throw objects at a distance will do. This also includes options for bowling, towns, skittles.
- Ball games or fitball exercises.
Also find out what are the exercises for the development of fine motor skills in children.
Conclusion
Gross motor skills are the motor skills a child needs for full physical and mental development. Abilities are formed from an early age through simple exercises, housework, outdoor games and active sports activities.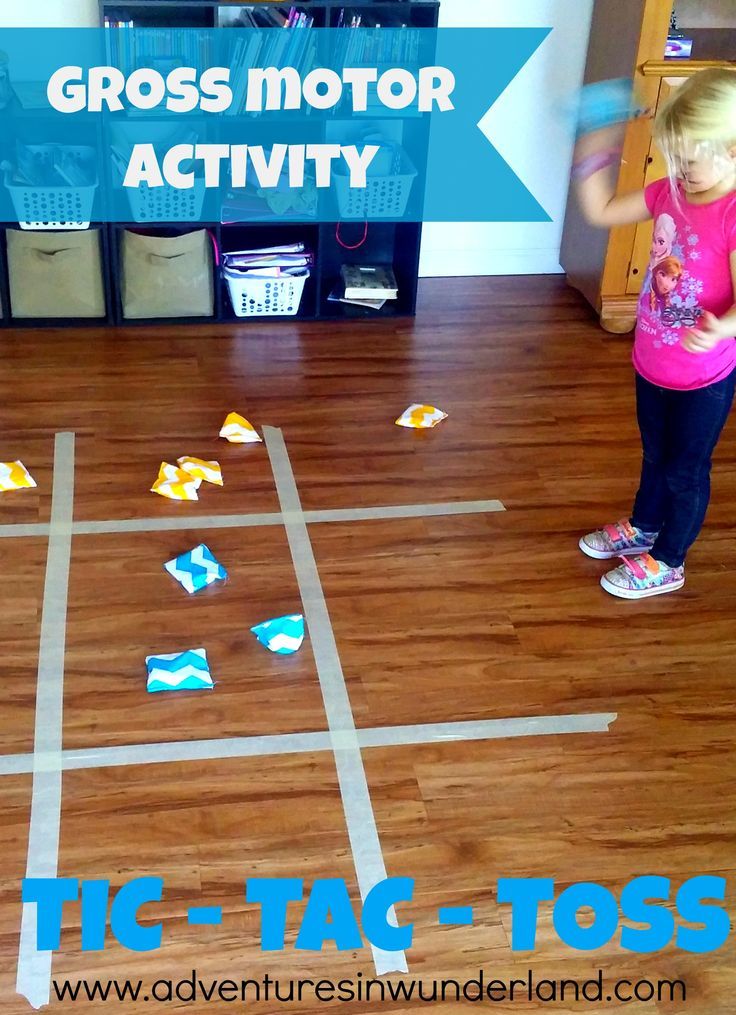
In the Baby Club child development centers we pay attention to both gross and fine motor skills. We use only proven, popular development methods. Our specialists will be happy to prepare your child for kindergarten or school and help him develop as a person.
What is gross motor skills and how does it affect speech initiation?
What is gross motor skills and how does it affect the start of speech?
Parents pay a lot of attention to the development of the child's fine motor skills, and gross motor skills are often left unattended. But it plays an equally important role in the overall harmonious development of the baby and in particular in the development of speech.
We will talk about the importance of gross motor skills for a future student with the coach of the Mowgli club Anna Kulik. At the big Bookids family festival, Anna gave a master class on this topic, talked about the influence of gross motor skills on the development of speech in children aged 3-4 and showed exercises that can be done at home or on a walk.
At the big Bookids family festival, Anna gave a master class on this topic, talked about the influence of gross motor skills on the development of speech in children aged 3-4 and showed exercises that can be done at home or on a walk.
Photos of our sports ground here
- What is gross motor skills?
- These are the movements of the large muscles of the body: the muscles of the neck, arms, legs, torso. Gross motor skills develop much earlier than fine motor skills. It begins with the development of the neck muscles: the baby learns to hold and turn his head. Then he begins to rise on his elbows, roll over from his back to his stomach and back, sit down, crawl, walk, bend over, squat, jump. Gross motor skills include hand-eye coordination. For example, the ability to throw or catch a ball, climb ladders. Undeveloped gross motor skills lead to the fact that the child spends too much effort to perform simple actions.
- What are the difficulties faced by a first grader with a lack of gross motor skills?
- Maintaining a sitting position at a desk for 45 minutes will be difficult for children with undeveloped gross motor skills. These children have low energy levels, are slow to respond to the teacher's words, appear tired and lethargic. They lack the stamina to cope with the school load. Lack of gross motor skills is also expressed in clumsiness: children often fall, stumble, touch furniture, crash into walls and people, drop objects. Gross motor skills affect the independence of the child - the ability to serve himself.
These children have low energy levels, are slow to respond to the teacher's words, appear tired and lethargic. They lack the stamina to cope with the school load. Lack of gross motor skills is also expressed in clumsiness: children often fall, stumble, touch furniture, crash into walls and people, drop objects. Gross motor skills affect the independence of the child - the ability to serve himself.
If even before school the child had problems with mastering the skills of drawing and writing, then he will get very tired from writing or drawing during the lesson. The result of all these difficulties is low self-esteem, physical inactivity, difficulty communicating and playing with peers. But the child definitely needs to move a lot in order to throw out the accumulated tension and stress during the day.
- It turns out that the development of a child's intellectual abilities directly depends on his physical health?
- Yes, when doing physical exercises, the child thinks about his movements. This involves both hemispheres of the brain. The coordinated work of the two hemispheres is needed in most school assignments. Gross motor skills, like fine motor skills, affect the development of memory and attention. Poor articulation of sounds is a consequence of not only undeveloped fine motor skills, but also large motor skills. Because articulation is the same motor skill!
This involves both hemispheres of the brain. The coordinated work of the two hemispheres is needed in most school assignments. Gross motor skills, like fine motor skills, affect the development of memory and attention. Poor articulation of sounds is a consequence of not only undeveloped fine motor skills, but also large motor skills. Because articulation is the same motor skill!
I can give real life examples. My daughter is now 10 years old. She enjoys going to school and studying for 9and 10. Besides school, she has many other interests. I have been doing gymnastics with her since birth. She spoke early and went on her own. In "Mowgli" daughter from 2 years old. She is interested in many sports, but has not yet chosen one. I see how her mood improves after physical activity. With a positive attitude, homework is done quickly and correctly, and free time is left for rest, hobbies and chatting with friends.
But, unfortunately, there are many young mothers in my environment who do not pay any attention to the physical development of their children. Hence the delay in speech, and the inability to participate in joint games with other children, and the unwillingness to learn something new. Many times I invited them to developmental gymnastics, but I constantly heard excuses “no time”. I hope that I will be able to "reach out" to them and convince them of the importance of physical culture for the harmonious development of their children.
Hence the delay in speech, and the inability to participate in joint games with other children, and the unwillingness to learn something new. Many times I invited them to developmental gymnastics, but I constantly heard excuses “no time”. I hope that I will be able to "reach out" to them and convince them of the importance of physical culture for the harmonious development of their children.
- What exercises and games will help develop gross motor skills?
- Accuracy games train the eye and develop the ability to concentrate. The child uses concentration skills in school. These are games with skittles, throwing rings and rag balls at the target.
Catching ball games are important for the development of literate speech and articulation. We speak, and we have a change of different sounds, it works on the skill of switching. In playing with the ball, the child needs to constantly switch his body, adjust to catch and throw the ball. Use 3 balls of different sizes: large, small and medium.
Use 3 balls of different sizes: large, small and medium.
Stairs, walking, bicycle develop endurance, which in the future will shape the child's perseverance.
Climbing, Swedish walls, rope ladders, rope will teach you to track your body, develop strategic thinking, the ability to analyze. Because the child in the process of climbing needs to calculate his path for several steps.
Balance games balance the processes of excitation and inhibition and work to develop the skill of concentration. Use balance pads and fitness balls. You can come up with exercises for stepping over sticks, stripes on the pavement. In the gym we give an exercise in stepping on the platforms.
The flexibility of the body gives the plasticity of the mind. Without stretching, one workout does not begin in any sport. Stretching saturates the body and brain with oxygen.