Why do my hands hurt so bad
Dignity Health | Why Do My Hands Hurt?: Arthritis and Other Culprits
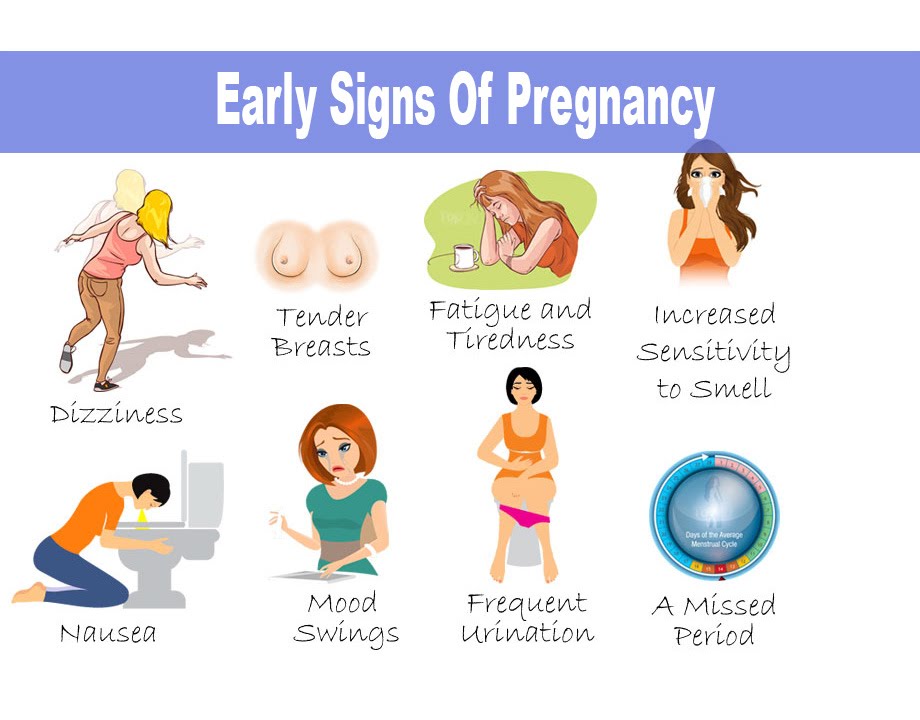
Do you find that sometimes you get an achy feeling in your fingers or wrist? Do you have trouble moving your fingers or gripping things? It might just feel tingly, or it might be a burning pain. It comes and goes, so you're not sure whether to worry about it. You just wonder: Why do my hands hurt? Here are three possible culprits for your hand pain and how to address them.
Arthritis
What It Is
Arthritis is one of the most common causes of hand pain, affecting millions of people every year. Arthritis develops over time and causes inflammation of the joints. You may have it in a finger, your wrist, or multiple spots along your hand.
Osteoarthritis is the most common type. The bones in your hand are cushioned by cartilage and lubricated by a fluid called synovium, which allows you to freely move your hands and fingers. Osteoarthritis is when the cartilage wears down and no longer cushions your bones. They begin to rub, which causes pain, swelling, inflammation, and even changes to the shape of the joint.
Rheumatoid arthritis, the second most common type, works a little differently. It's a chronic disease that can affect other parts of your body, but often starts in the hands. This is when the joint lining swells, causing pain and stiffness.
Both types of arthritis develop slowly over time, but rheumatoid arthritis is more likely to affect the same joints on both sides of the body, whereas osteoarthritis might only affect one side.
What You Can Do
Arthritis is a common condition with many treatment options. Because it worsens over time, it's best to seek medical care early. Even if you think your hand pain is mild, make an appointment with your doctor. You can perform exercises, wear arthritis gloves, and take medications to manage the symptoms.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
What It Is
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passage at the base of your hand that houses ligaments and tendons. When this passage narrows, the nerves get pinched, causing pain, tingling, numbness, and even swelling in your hands and fingers.
When this passage narrows, the nerves get pinched, causing pain, tingling, numbness, and even swelling in your hands and fingers.
As with arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome starts mild and worsens over time. You will most likely have symptoms in your dominant hand first. It can develop from repetitive use of vibrating tools, an injury, or a cyst in the tunnel. People with diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis may be more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome.
What You Can Do
See a doctor when you first notice symptoms. Addressing the problem early will help you reduce further damage and treat carpal tunnel syndrome. Your doctor can look for other conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or diabetes, and help you manage those conditions to limit your hand symptoms.
Your doctor can recommend modifications to your daily activities and treatment options, such as splints or pain medications, to manage your symptoms.
Diabetic Nerve Problems
What It Is
Nerve damage from diabetes, called diabetic neuropathy, can lead to bone and joint problems and may be the culprit of your hand pain. Diabetes-related joint problems have similar symptoms to arthritis, including pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Diabetes-related joint problems have similar symptoms to arthritis, including pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Common issues that cause hand pain in people with diabetes include:
- Trigger finger: Your finger gets stuck in a bent position and may painfully pop back out when you straighten it. This is caused by a swollen tendon.
- Diabetic hand syndrome: The skin on your hands thickens, making it difficult to move your hands or straighten your fingers.
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage causes pain, numbness, or tingling in the hands.
What You Can Do
The first step to treating or avoiding hand problems from diabetes is to make sure you're managing the disease and controlling your blood sugar. See your doctor if you're having trouble keeping your diabetes under control.
Most conditions that cause pain in the hands can be treated or managed, and it's best to seek treatment early — as soon as possible after you first start to wonder, "Why do my hands hurt?" Your doctor may be able to diagnose the problem and begin managing your symptoms, or you may be referred to an orthopedist, a doctor who specializes in bone and joint health. Getting help early will help you preserve hand function longer and reduce further damage.
Getting help early will help you preserve hand function longer and reduce further damage.
Why Does My Hand Hurt? 5 Causes of Hand & Wrist Pain
Written by Matt McMillen
In this Article
- De Quervain's Tendinitis
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Fractures
- Arthritis
- Trigger Finger
Hand pain can happen for many reasons, from accidents to conditions that are ongoing. It can often be treated so that your symptoms ease up.
This article looks at some of the most common causes of hand pain.
De Quervain's Tendinitis
This is also called de Quervain's tendinosis. It causes pain on the thumb side of the wrist.
The pain may develop gradually or start suddenly. It can travel the length of the thumb and up the forearm.
If you have de Quervain's tendinitis, it can be painful to:
- Make a fist
- Grasp or hold objects
- Turn your wrist
The pain results from irritation or inflammation of the wrist tendons at the base of the thumb. Repetitive activities and overuse are often responsible for de Quervain's.
Repetitive activities and overuse are often responsible for de Quervain's.
New mothers can get it from holding their baby in an awkward position. Wrist fractures can also make you more likely to get de Quervain's.
Pain relief treatments include:
- A splint to rest the thumb and wrist
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Cortisone shots
Surgery may be an option if symptoms remain severe after you have tried other treatments.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
This is one of the most common nerve disorders of the hand. It causes pain in the:
- Palm and some fingers of the hand
- Wrist
- Forearm
Often the pain is worse at night than during the day. Carpal tunnel syndrome can also cause:
- Weakness
- Tingling
- Numbness
You may especially feel it in your thumb, index finger, and middle finger. This can make it hard to grip objects.
The discomfort happens when swelling constricts the median nerve. The median nerve controls sensation and muscle impulses in the thumb and most of the fingers (except for the pinkie finger and the half of the ring finger that’s closest to the pinkie finger).
The median nerve controls sensation and muscle impulses in the thumb and most of the fingers (except for the pinkie finger and the half of the ring finger that’s closest to the pinkie finger).
The median nerve passes through the carpal tunnel. The carpal tunnel is a structure made up of bones and connective tissues that is located at the base of the hand. It is in this narrow space that the median nerve is pinched by inflamed or irritated tendons or other swelling.
Common treatments include:
- Resting the hand and wrist
- Anti-inflammatory or analgesic painkillers
- Wrist splints
- Steroid shots
- Physical therapy
Your doctor may suggest surgery if your symptoms last for 6 months or more.
Fractures
A fracture, or a break in a bone, can cause a great deal of hand pain. Besides pain, after a fracture you may have:
- Stiffness
- Swelling
- Loss of movement
If you have fractured a finger, for example, you may not be able to move it fully. Your injured finger could be swollen and in some cases slightly shorter than usual.
Your injured finger could be swollen and in some cases slightly shorter than usual.
There are several types of fractures:
- Simple (broken bone is aligned and stable)
- Complex (break may cause bone to shift or become displaced, making treatment more difficult)
- Comminuted (bones broken in more than one place)
- Compound (broken bone breaks through skin)
Fracture treatment depends on the type of the break. Casts or splints are often used for simple breaks. You may need pins, wires, or plates to treat more complicated fractures. Surgery might also be needed to set the broken bone completely.
Arthritis
This is a leading source of hand pain. It causes joints to lose the cartilage that allows them to move smoothly against each other. As the cartilage deteriorates, painful, sometimes debilitating, swelling begins to occur.
In the hand, the areas where this most often occurs are the:
- Base of the thumb
- Middle joint of one or more fingers
- End joint, which is closest to the finger tip
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. It causes progressive degeneration of cartilage. It can happen with aging or following an injury, such as a fracture or dislocation. When it affects the hand, it causes:
It causes progressive degeneration of cartilage. It can happen with aging or following an injury, such as a fracture or dislocation. When it affects the hand, it causes:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Stiffness
Bony nodules may also form at the middle or end joints of the fingers. Osteoarthritis can also cause deep, aching pain at the base of the thumb. The hand may also become weaker, making everyday activities difficult.
Treatment depends on the severity of the pain and disability. Treatment includes:
- Anti-inflammatory or analgesic painkillers
- Splints for the fingers or wrist
- Heat
- Physical therapy
If these treatments do not provide relief, surgery may be recommended.
Trigger Finger
Doctors call this stenosing tenosynovitis. It causes fingers or the thumb to lock in a bent position. It can be painful, especially when you bend or straighten the affected finger or thumb.
The condition develops when the flexor tendons, which control the movements of the fingers and thumb, become irritated. This can make them thicken within the tendon sheath that surrounds the flexor tendons.
This can make them thicken within the tendon sheath that surrounds the flexor tendons.
Nodules may also form on the affected tendons. The sheath itself may thicken, too.
All of this prevents the smooth movement of the tendons. Eventually, the tendon may become stuck when you try to straighten a bent finger or thumb. You may also feel a catching sensation when the finger or thumb locks in place, and then a pop as the tendon is released.
Doctors don’t know what causes trigger finger. You’re more likely to get it if you have:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
- Diabetes
Women get the condition more often than men do. And trigger finger is more common in adults between ages 40 and 60.
Rest, sometimes while wearing a splint, may fix the problem. Over-the-counter pain medications can ease the pain. Corticosteroid injections (steroid shots) often can help relieve symptoms. Your doctor may recommend surgery if other treatments fail.
Pain Management Guide
- Types of Pain
- Symptoms & Causes
- Diagnosis & Tests
- Treatment & Care
- Living & Managing
- Support & Resources
Why the hands hurt - causes, treatment
Home
>
TYPES OF PAIN IN A HUMAN
>
Pain in the hands
Anna Budyevskaya expert, editor, author
Views: 65 866
Last update date: 29. 12.2022 G.
12.2022 G.
Average reading time: 8 minutes
Content:
Causes of pain in the hands of the hands
Muscle overvoltage
tendonitis and tendovaginitis
joint diseases
injuries
cervical osteochondrosis
Features of pains in hands
Diagnostics of pains
Prevention gripping and moving objects 3 , that is, movements that we perform in everyday life - at home and at work. Also, the brush helps us to contact the outside world 3 . Handshakes, touching objects, gestures - all this is done with brush movements, helping us, on the one hand, to receive information, and on the other hand, to express our thoughts and emotions. Therefore, when pain occurs in the hand, a person often falls out of the usual rhythm of life. Let's see why it occurs, how to alleviate discomfort and, most importantly, what to do so that they do not reappear.
Causes of pain in the hands
The hand has a complex structure and consists of the wrist, metacarpus and short tubular bones (phalanges) of the fingers, as well as tendons, ligaments and muscles 3 . Pain can mean damage to any of these structures, which means that there are a lot of reasons for the appearance of such a symptom. Next, let's talk about them in more detail.
Pain can mean damage to any of these structures, which means that there are a lot of reasons for the appearance of such a symptom. Next, let's talk about them in more detail.
Back to top
Muscle strain
The most common cause of pain in the hands is muscle strain 6 . For example, due to monotonous repetitive movements, the transverse ligament of the wrist swells, thickens and compresses the median nerve under it, causing carpal (carpal) tunnel syndrome 6 .
If earlier movements that provoke nerve compression were typical for manual laborers or athletes, today, in the age of global computerization, work at the computer 1 or prolonged (many hours) use of smartphones 13 causes overload.
Scientists have calculated: gamers who play computer games up to 12 hours a day, perform up to 8 thousand clicks on the keyboard and computer mouse 1 . But just 4 hours of daily work at the computer is enough to overload the muscles of the hand and fingers 1 .
Tendinitis and tendovaginitis
Pain in the hands can be a problem for athletes (tennis players and golfers) when the tendons (tendinitis) or the membrane that covers them (tendovaginitis) become inflamed. 5.16 .
Women aged 30-50 often develop de Quervain's tendovaginitis. It is associated with overload and damage to the tendons that coordinate the mobility of the thumb 5.14 . The disease is more often observed in young mothers who constantly hold the baby in their arms 14 .
De Quervain's Tenosynovitis also did not bypass the generation that does not part with mobile gadgets 13 . Soreness in the wrist area in young people has become so widespread that it has acquired the popular name “selfie wrist”. However, studies have shown that pain in the hands is not associated with the habit of often taking selfies. The reason is in the microtraumas of the muscles that we use to hold the smartphone in our hand, type text on it or scroll the screen with our thumb 13 .
Tenosynovitis can be caused by an infection, a chronic systemic disease (rheumatism) or trauma 5 , so don't be too quick to attribute hand pain to overload. For the treatment to be effective, consult your doctor.
Back to top
Diseases of the joints
Arthritis of the hand can be caused by:0046 10 . Depending on the cause, arthritis occurs both at a young age and in people older than 40-50 years 10 .
Do not self-medicate for diseases of the joints of the hand. Therapy for arthritis and arthrosis is different, and only a specialist can determine the exact cause of the pain.:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/2417866/hurtinjured.0.jpg)
Back to top
Injuries
Bruises, sprains of tendons and ligaments, dislocations and fractures can be another cause of pain in the hand 12,14,16 . Acute injury occurs when tissue is compressed, hit 12 or falls on an open hand 2 . Sometimes damage to the wrist area results from prolonged exposure to vibration 6 , strenuous work in which the hand is constantly in the position of flexion or extension 6 .
Almost any injury can disrupt the blood circulation in the tissues, and this, in turn, aggravates the degree of damage 12 and often leads to malunion of the fracture and arthrosis 3 .
Serious injury is the first thing to rule out when pain occurs in the hand, especially if it gets worse when you try to grab and squeeze an object in your hand 2 . Consult a doctor to get qualified medical care and avoid unwanted consequences.
Cervical osteochondrosis
Pain in the hands may be associated with changes in the cervical vertebrae 15 with osteochondrosis. The fact is that the ulnar nerve stretches to the muscles of the forearm and hand, which originates from the nerve roots of the cervical spine 14 . With osteochondrosis, the distance between the vertebrae gradually decreases, as a result of which the nerve roots are often compressed 11 . Neck movement 14 , coughing or sneezing 15 provoke pinching of the nerve and cause "long pain", which is felt in the neck and "radiates" along the nerves of the upper limb - to the shoulder, forearm, reaching the fingers of the hand 15 .
The fact is that the ulnar nerve stretches to the muscles of the forearm and hand, which originates from the nerve roots of the cervical spine 14 . With osteochondrosis, the distance between the vertebrae gradually decreases, as a result of which the nerve roots are often compressed 11 . Neck movement 14 , coughing or sneezing 15 provoke pinching of the nerve and cause "long pain", which is felt in the neck and "radiates" along the nerves of the upper limb - to the shoulder, forearm, reaching the fingers of the hand 15 .
Features of pain in the hands
Constant soreness may be associated with muscle spasm and swelling of the joints, especially if the pain is dull, aching or exhausting 10 . For some it is more pronounced in the morning, accompanied by stiffness, but goes away or gets better in the daytime 10 , for others it appears at the end of the working day and subsides after rest 10 . Often the pain bothers even at night and disturbs sleep 6 .
Often the pain bothers even at night and disturbs sleep 6 .
Depending on the cause, hand pain can be triggered by various factors - driving a car, drawing, working at a computer or sports 6 . Usually the pain goes away if you take a break and let your hands rest. But, when the cause of pain persists, the usual activity becomes impossible, and the person is forced to change profession 6 .
Back to top
Diagnosis of pain in the hands
Various doctors are involved in identifying the causes of pain in the hands - traumatologists, orthopedists, rheumatologists and neuropathologists. To the right specialist, as a rule, the therapist directs after the examination. If necessary, the specialist prescribes an x-ray or MRI and sends for tests.
At the appointment, tell the doctor what symptoms bother you, in addition to pain:
- if redness or swelling was observed in the area of the wrist or fingers 10 ;
- is there any restriction of movement in the joints 10 ;
- how long ago the deformations occurred 10 ;
- which movements provoke pain 6 ;
- if she has numbness and weakness of her hands 6 .

Back to top
Hand pain treatment
Therapy depends on the cause of the hand pain. To unload the wrist joint, the doctor may recommend wearing orthoses 5 , using bandages 6 or taping 6.9 . The treatment also includes:
- rest and cold compress 2 :
- special training regimen 5 ;
- physiotherapy 6.12 ;
- massage 12 ;
- physiotherapy exercises 4.5 ;
- medical treatment 5,6,18 .
Surgical 2 Orthopedic correction if necessary 10 .
MOTRIN® may be used to relieve pain. Its active ingredient, naproxen, has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. MOTRIN® can be used to combat pain after sprains and bruises, in osteoarthritis, tendovaginitis, osteochondrosis and soft tissue lesions in rheumatism 7 . One dose of MOTRIN® is sufficient up to 12 hours 7 .
Prevention of pain in the hands
At the first sign of tension in the hands, rest the hands. Even if you take a 30-second break every 10 minutes, this is enough to restore the function of the muscles and ligaments of the hand and prevent the occurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome 1 .
If you work in the office at the computer:
- Do a set of exercises regularly. Flexion and extension of the hands and fingers are performed both for pain prevention and treatment 8 .
- Type with keyboard in neutral position (not tilted) 1 .
- Opt for a chair with a functional curved back 8 .
- Position the chair so that its height is equal to the length of the lower leg, and the depth is at least 2/3 of the length of the entire thigh 8 .
- Keep your elbows off the table and keep your shoulders level. This position will allow you to evenly distribute the load on the muscles of both hands 8 .

The hand is an important part of our body. Small to medium joints, ligaments and muscles are designed to provide ease of movement, but overuse, injury, and chronic illness can cause pain. Limiting the movements of the hands and fingers brings only temporary relief. Therefore, it is important to establish a diagnosis and eliminate the cause of pain in the hands. To do this, you should consult with your doctor.
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional medical advice. For diagnosis and treatment, contact a qualified specialist.
Back to top
Literature
- Berezutsky V.I. Computer mouse, keyboard and carpal tunnel syndrome // Medical Perspectives. 2018. No. 3-1. URL: https : //cyberleninka . ru/article/n/kompyuternaya-mysh-klaviatura-i-sindrom-zapyastnogo-kanala (date of access: 08/17/2021).
- Causes and Treatment of Wrist Pain By Jonathan Cluett, MD https : //www .
 verywellhealth . com/wrist-pain-causes-symptoms-and-treatments-2549458
verywellhealth . com/wrist-pain-causes-symptoms-and-treatments-2549458 - Deikalo, Tolstik, Boloboshko Clinical anatomy of the hand and surgical approaches//Vitebsk:-2013, 123p.
- Olyunin Yu.A. Osteoarthritis of the joints of the hands. Differential diagnosis with inflammatory diseases of the joints and treatment tactics. Modern rheumatology. 2015;9(4):77-82. https : //mrj . ima-press . net/mrj/article/view/657/644
- Torshin I.Yu., Gromova Olga Alekseevna, Lila A.M., Limanova O.A. Systematic analysis of the molecular pathophysiology of tendovaginitis: the prospects for the use of chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine sulfate // Neurology, neuropsychiatry, psychosomatics. 2020. №2. URL: https : //cyberleninka . ru/article/n/sistematicheskiy-analiz-molekulyarnoy-patofiziologii-tendovaginita-perspektivnost-primeneniya-hondroitina-sulfata-i-glyukozamina
- Yarikov A. V., Tutkin A. V., Boyarshinov A.
 A., Fraerman A. P., Perlmutter O. A. Carpal tunnel syndrome: clinic, diagnosis and modern approaches to treatment (brief review) // Medical Almanac . 2020. No. 3 (64). URL: https : //cyberleninka . ru/article/n/karpalnyy-tunnelnyy-sindrom-klinika-diagnostika-i-sovremennye-podhody-k-lecheniyu-kratkiy-obzor
A., Fraerman A. P., Perlmutter O. A. Carpal tunnel syndrome: clinic, diagnosis and modern approaches to treatment (brief review) // Medical Almanac . 2020. No. 3 (64). URL: https : //cyberleninka . ru/article/n/karpalnyy-tunnelnyy-sindrom-klinika-diagnostika-i-sovremennye-podhody-k-lecheniyu-kratkiy-obzor - Instructions for use of the drug MOTRIN ® tablets // Reg. number R N002874/01// GRLS RF. – URL: https : //grls.rosminzdrav . en/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGuid=868bad0c-d10e-47a9-b9d8-2595d9a01ac7&t=
- A set of exercises for the prevention and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis of the hands. Author's technique N.K. Novikova / M.-2021 / / Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation Federal State Budgetary Institution "National Medical Research Center for Therapy and Preventive Medicine" https : //gnicpm . en/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/kompleks-uprazhnenij-kistej-ruk-kniga.pdf
- Jung KS, Jung JH, Shin HS, Park JY, In TS, Cho HY.
 The Effects of Taping Combined with Wrist Stabilization Exercise on Pain, Disability, and Quality of Life in Postpartum Women with Wrist Pain: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 30;18(7):3564. doi: 10.3390/ijerph28073564. https : //pubmed . ncbi . nlm . nih.gov/33808137/
The Effects of Taping Combined with Wrist Stabilization Exercise on Pain, Disability, and Quality of Life in Postpartum Women with Wrist Pain: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 30;18(7):3564. doi: 10.3390/ijerph28073564. https : //pubmed . ncbi . nlm . nih.gov/33808137/ - Outpatient aspects of the management of patients with articular syndrome: textbook.-method. allowance / I. L. Mesnikova. - Minsk: BSMU, 2007. - 46 p. ISBN 978–985–462–675–8.
- Treatment and prevention of osteochondrosis A.A. Pilipovich // Medical business 2. 2015 - P. 15-22
- Rodomanova, L.A. Prevention of ischemic contractures of the hand after severe traumatic injuries: a guide for doctors / L.A. Rodomanova, D.I. Kutyanov, K.S. Melikhov. - St. Petersburg. : RNIITO im. R.R. Vredena, 2013. - 24 p.
- Stacy, Monica, "Assessment of Antebrachial and Carpal Muscle Activity During Smartphone Use: is “Selfie Wrist” a Real Phenomenon?" (2020).
 Honors Theses. 1339. https : //egrove . olemiss . edu/hon_thesis/1339/
Honors Theses. 1339. https : //egrove . olemiss . edu/hon_thesis/1339/ - Shehab, Ramsey, and Mark H Mirabelli. “Evaluation and diagnosis of wrist pain: a case-based approach.” American family physician vol. 87.8 (2013): 568-73. https : //www . aafp . org/pubs/afp/issues/2013/0415/p568.html
- Sadokha K.A., Golovko A.M., Krotov V.V. Cervical compression radiculopathy // Medical News. 2019. No. 3 (294). URL: https : //cyberleninka . ru/article/n/sheynaya-kompressionnaya-radikulopatiya
- A systematic approach to a painful wrist. R Wang, J Reed, J Leone, M Bhandari, JK Moro. Canadian Journal of Diagnosis 18(8), 86-97, 2001
You may also be interested in:
- Bursitis
- Joint restoration: a myth or a real opportunity to regain freedom of movement?
- Headache treatment
Pain in the hands: causes, consequences, methods of treatment
Pain in the arm is one of the most common complaints of patients visiting a neurologist or orthopedist. This symptom is not specific, as it can indicate the development of several diseases at once - arthritis, arthrosis, osteochondrosis, hernia, localized in the cervical or thoracic spine.
This symptom is not specific, as it can indicate the development of several diseases at once - arthritis, arthrosis, osteochondrosis, hernia, localized in the cervical or thoracic spine.
At the stage of diagnosis, the nature of the pain, which can be burning, aching or shooting, and the place of its localization are of great importance. In some cases, pain in the shoulders and upper limbs is only a consequence of problems with the back or neck, in others it indicates inflammation of the joints (in the elbows and wrists).
When should I see a doctor?
Practice shows that the vast majority of patients practice self-diagnosis, traditional medicine and uncontrolled use of painkillers. This approach always leads to one result: a neglected disease requires more serious, long-term and expensive treatment.
We strongly recommend that you see a specialist if you have any of the following symptoms:
- The pain persists for 3 days and is aggravated by any physical activity.

- The arm is swollen.
- Pain in the arm reduces its strength. Patients note the inability to perform the usual actions, stiffness of movements.
The sooner the diagnosis is made, the more effective the treatment will be. Our goal is to find and eliminate the cause, relieve a person from pain, and restore mobility.
What does arm pain indicate? The most common diseases
Does your arm hurt? There may be several reasons. In this article, we will talk about the most serious and common of them:
- Arthritis - inflammation of the joints and periarticular space.
The main symptoms are pain, swelling, deterioration of mobility, local hyperemia or hyperthermia, reaction to weather changes. Lack of treatment leads to joint deformity, changes in cartilage, ligaments and capsule. At the initial stage, arthritis affects the hands, feet, elbow and shoulder joints, then descends to the pelvis and knees. In the presence of several foci of inflammation, a diagnosis of polyarthritis is made. This pathology develops against the background of injuries, bruises and other damage to the ligamentous apparatus, infections, deficiency of bone or cartilage tissue, poor heredity, and disorders in the immune system. At risk are the elderly.
This pathology develops against the background of injuries, bruises and other damage to the ligamentous apparatus, infections, deficiency of bone or cartilage tissue, poor heredity, and disorders in the immune system. At risk are the elderly.
- Arthrosis – destruction of cartilage and joint capsule.
At risk are people over 45 years of age. Today, arthrosis occurs in every tenth inhabitant of the planet, so it is important to diagnose the disease in time and contact specialists. Main symptoms: inflammation, swelling, swelling, crunching in the joints, pain in the hands, elbows, feet, knees, hips and lower back. Primary arthrosis is an independent disease that occurs due to the fact that the cartilage tissue wears out faster than it is restored. If the pathological process occurs after injuries, against the background of endocrine disorders, osteoporosis, varicose veins, hormonal imbalance, physical inactivity and other problems, arthrosis is called secondary.
- Thoracic osteochondrosis is a disease in which intervertebral discs, joints and ligaments are destroyed.
Attack-like or shooting pain is the most striking symptom that occurs against the background of pinched spinal nerves. Among other manifestations, the most common paresis, "goosebumps", a tingling sensation and muscle tension on palpation. Symptoms of osteochondrosis are similar to the manifestation of coronary heart disease, so we do not recommend postponing a visit to a specialist on the back burner. The disease develops for a number of reasons, including due to spinal injuries, posture disorders and periodic hypothermia, it can be combined with cervical osteochondrosis, one of the manifestations of which is pain in the right arm.
- Herniated disc in the thoracic spine.
A rather rare disease with serious consequences. The thoracic spine begins with the collar zone and ends with the lumbar lordosis. The spinal nerve fibers located in this area activate the upper limbs, the respiratory center, the anterior chest wall, affect the functioning of the liver, esophagus, reproductive and urinary systems. By pinching the nerve roots, intervertebral hernias cause severe pain, as well as dysfunction of the organs listed above. The main reason for the formation of a hernia is the wear of the disc tissues against the background of advanced osteochondrosis. Main symptoms: shooting, aching or dull pain in the chest and between the shoulder blades; tingling sensation, numbness of the extremities and muscle weakness.
By pinching the nerve roots, intervertebral hernias cause severe pain, as well as dysfunction of the organs listed above. The main reason for the formation of a hernia is the wear of the disc tissues against the background of advanced osteochondrosis. Main symptoms: shooting, aching or dull pain in the chest and between the shoulder blades; tingling sensation, numbness of the extremities and muscle weakness.
This is important!
According to statistics, cervical disc herniation occurs in 8% of cases, thoracic hernia - in 1%. The permanent "leader" among diseases of the spine is protrusion in the lumbar region. The top five, along with osteochondrosis, includes arthritis, in particular, humeroscapular periarthritis - a reactive inflammatory process in the movable joint that connects the arm bone with the scapula.
In the absence of adequate treatment, in about 40% of cases, the pain syndrome becomes chronic, every fifth patient inherits severe vertebral neurological disorders.
Causes and consequences
The reasons for the development of diseases of the spine are different:
- Old age. Organs and systems age with us. Bones become more fragile, cartilage wears out.
- Genetic predisposition. Let's just say that this is not a diagnosis. An active lifestyle, the rejection of bad habits, the right diet can delay or prevent the development of pathology.
- Spinal injuries. There are circumstances beyond our control, for example, an accident or an unfortunate fall on ice, but in most cases we endanger ourselves: we perform physical exercises without preliminary stretching, ride tubing - high-speed, dangerous and uncontrollable, jump into the lake from a springboard, without thinking that you can break your neck. Your health is in your hands!
- Posture disorders. Don't hold back? Know that your muscles are in constant tension. Kyphosis, scoliosis, lordosis - this is not a "cosmetic problem", but constant pain and disruption of the internal organs.

Among other factors, it is worth noting excessive physical activity, overweight, refusal to treat other chronic diseases.
Why go to the doctor?
Early diagnosis and proper treatment significantly improve the prognosis and increase your chances, if not for a complete recovery, then for slowing down the development of the pathological process, getting rid of pain, returning joint mobility and, as a result, improving the quality of life.
How to treat?
What should I do if my arm hurts?
- The first stage of treatment is aimed at removing swelling, spasms, inflammation and pain. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed painkillers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, decongestants and muscle relaxants. High efficiency in the fight against the consequences of intervertebral hernia, osteochondrosis, neuralgia, myositis and spinal injuries was shown by therapeutic drug blockade and plasmolifting.
- Treatment of spinal diseases is not limited to drugs and injections.