White tongue pregnancy
How to Treat Thrush During Pregnancy
Thrush is caused by the fungus Candida albicans, which inhabits the mouth or genitals. If present in excessive amounts, this fungus can cause white lesions, redness, and soreness, among other symptoms. Candida albicans occurs naturally in the body in small quantities. Expecting mothers often want to know how to treat thrush naturally during pregnancy.
However, when the immune system is not functioning at full capacity, the body is unable to keep the levels of fungus in check, and thrush can result. Thrush can occur in the mouth, in the genitals, and on the breasts of mothers who are nursing infants with thrush.
- Creamy white lesions on your tongue, inner cheeks, and sometimes on the roof of your mouth, gums, and tonsils
- Slightly raised lesions with a cottage cheese-like appearance
- Redness or soreness that may be severe enough to cause difficulty eating or swallowing
- Slight bleeding if the lesions are rubbed or scraped
- Cracking and redness at the corners of your mouth (especially in denture wearers)
- A cottony feeling in your mouth
- Loss of taste
Thrush can occur at any age, from babies, to healthy adults, and even to the elderly.
- Being an infant or elderly
- Having a weakened immune system
- Wearing dentures
- Having other health conditions, such as diabetes
- Taking certain medications, such as antibiotics or oral/inhaled corticosteroids
- Undergoing chemotherapy or radiation treatment for cancer
- Having conditions that cause dry mouth
Treat thrush naturally while expecting is possible. Here are a couple of natural options you can take to treat thrush naturally during pregnancy.
Proper oral hygiene
One way you can combat the excessive amounts of oral fungus is practicing good brushing and flossing habits daily. However, it is best to avoid mouthwash during this time since it can affect the original amounts of flora inside your mouth.
Saltwater rinse
Rinsing with salt water might help to alleviate some of the pain caused by the sores in your mouth. The Mayo Clinic recommends the following practice: Dissolve 1/2 teaspoon (2.5 milliliters) of salt in 1 cup (237 milliliters) of warm water. Swish this around in your mouth and then spit it out. Do not swallow it.
The Mayo Clinic recommends the following practice: Dissolve 1/2 teaspoon (2.5 milliliters) of salt in 1 cup (237 milliliters) of warm water. Swish this around in your mouth and then spit it out. Do not swallow it.
There are options you can explore with your health care provider or over the counter when experiencing thrush.
Antifungal cream
An antifungal cream can be used to treat breastfeeding moms who contract thrush from their infants, as well as women who develop thrush in their vagina. Babies with thrush can pass the condition on to the breastfeeding mother.
In this case, the doctor may prescribe an antifungal cream to treat the thrush that is on the breasts. If your infant has thrush, it is likely the fungus is also on the baby’s pacifier and bottles, so they should be washed thoroughly and sanitized. Your doctor can identify further ways to clean these items.
Sometimes, cases of thrush are severe enough that they cannot be cured by natural means alone. In this situation, your doctor may prescribe an antifungal medication to help regulate the levels of Candida albicans in your system. It is important to note that pregnant women should not take the anti-fungal tablets known as fluconazole, as some studies indicate that it could cause birth defects. Consult with your doctor before taking any medications.
In this situation, your doctor may prescribe an antifungal medication to help regulate the levels of Candida albicans in your system. It is important to note that pregnant women should not take the anti-fungal tablets known as fluconazole, as some studies indicate that it could cause birth defects. Consult with your doctor before taking any medications.
If you think you have thrush, it is important to consult your doctor immediately, as thrush can spread into the throat, esophagus, and intestines, leading to eating and digestion issues.
- Yeast Infections During Pregnancy
Compiled using information from the following sources:
Mayo Clinic: Disease Conditions/oral thrush
https://www.nhs.uk/chq/Pages/1101.aspx?CategoryID=54
https://www.healthychildren.org/English/health-issues/conditions/infections/Pages/Thrush-and-Other-Candida-Infections.aspx
Dry Mouth in Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Dry mouth is a very common symptom of pregnancy.:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/2785562/original/028627600_1556001360-shutterstock_1019963743.jpg) That’s in part because you need a lot more water when you’re pregnant, as it helps your baby develop.
That’s in part because you need a lot more water when you’re pregnant, as it helps your baby develop.
But another reason is that your changing hormones can have an effect on your oral health. Besides dry mouth, you may experience gingivitis and loose teeth during pregnancy.
Some conditions during pregnancy, such as gestational diabetes, can also cause dry mouth.
There are many potential causes for dry mouth during pregnancy. Some of the more common causes include:
Dehydration
Dehydration happens when your body loses water faster than it takes it in. It can be especially dangerous for pregnant women. This is because water helps your baby develop. You need more water when you’re pregnant than when you’re not pregnant.
In severe cases, dehydration during pregnancy can lead to birth defects or premature labor.
Other signs of dehydration include:
- feeling overheated
- dark yellow urine
- extreme thirst
- fatigue
- dizziness
- headache
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs only during pregnancy and can cause you to have high blood sugar. It often goes away after you give birth.
It often goes away after you give birth.
You need more insulin than usual during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes happens when your body can’t make that extra insulin.
Gestational diabetes can cause problems for you and your baby, but it can also be managed with proper care. This includes a healthy diet and exercise. You may need medication or insulin.
Many women with gestational diabetes have no symptoms, or only minor symptoms. In this case, it would be detected during a test given to all pregnant women. If you do have symptoms, in addition to dry mouth, they may include:
- excessive thirst
- fatigue
- needing to urinate more often than usual
Thrush
Thrush is an overgrowth of a fungus called Candida albicans. Everyone has it in small amounts, but it can grow out of normal range if your immune system isn’t working as well as it normally does.
Thrush can cause a dry, cottony feeling in your mouth, in addition to:
- white, cottage cheese-like lesions on your tongue and cheeks that may bleed if scraped
- redness in your mouth
- mouth soreness
- loss of taste
Sleep issues
Pregnancy can cause many sleep issues, from not being able to fall asleep to waking up frequently throughout the night. It can also lead to breathing issues, including snoring and sleep apnea.
It can also lead to breathing issues, including snoring and sleep apnea.
Snoring is especially common during the second and third trimesters. It is more common if you are overweight, smoke, are sleep-deprived, or have conditions such as enlarged tonsils.
Your changing hormones can also cause your throat and nasal passages to narrow, which can lead to breathing issues.
Snoring and sleep apnea can make you breath with your mouth open while you sleep. This makes it harder to produce saliva and dries out your mouth.
Sleep apnea can be serious. If you snore and find yourself very tired during the day, see a doctor.
Beyond the feeling of dryness, potential symptoms of dry mouth include:
- constant sore throat
- trouble swallowing
- dryness inside your nose
- burning feeling in your throat or mouth
- trouble speaking
- hoarseness
- change in sense of taste
- tooth decay
In many cases, home remedies are enough to treat your dry mouth. Home remedies that are safe during pregnancy include:
Home remedies that are safe during pregnancy include:
- Chewing sugar-free gum. This can help encourage your mouth to make more saliva.
- Eating sugar-free hard candy. This also encourages your mouth to make more saliva.
- Drinking lots of water. This will help keep you hydrated and relieve some of your symptoms.
- Sucking on ice chips. This not only gives you fluids and moistens your mouth, but it can also help reduce nausea during pregnancy.
- Using a humidifier at night. This is especially helpful if you’re waking up with a dry mouth.
- Practicing good oral hygiene. Brush and floss regularly to help prevent tooth decay.
- Using a mouthwash specifically made for dry mouth. You can find this at your regular drugstore.
- Skipping coffee. Avoid caffeine as much as possible.
In some cases, you might need treatment from a doctor. Potential clinical treatments include:
Potential clinical treatments include:
- Working with your doctor to change medications that may be making your dry mouth worse.
- Wearing fluoride trays at night to help protect your teeth.
- Treating snoring or sleep apnea if that is causing your dry mouth.
- Treating thrush with antifungal medication if that’s the cause of your dry mouth.
- Setting up a gestational diabetes management plan, including diet, exercise, and medication or insulin if necessary.
If home remedies don’t help your dry mouth, you should see a doctor. They can look for an underlying cause and prescribe treatment if necessary.
You should also see a doctor if you have other symptoms of:
- Thrush: White, cottage cheese-like lesions in your mouth and redness or soreness in your mouth.
- Gestational diabetes: Excessive thirst, fatigue, and the need to urinate more often.
- Tooth decay: A toothache that doesn’t go away, tooth sensitivity, and brown or black spots on your teeth.

- Severe dehydration: Being disoriented, having black or bloody stool, and not being able to keep fluids down.
- Sleep apnea: Daytime fatigue, snoring, and frequent wakening during the night.
Your changing hormones and increased water needs might lead to dry mouth while you’re pregnant. Luckily, there are a lot of ways to relieve this symptom, from increasing how much water you drink to chewing sugar-free gum.
If home remedies don’t relieve your dry mouth, or you have other symptoms of conditions such as gestational diabetes, see your doctor.
symptoms, treatment, causes, consequences, photos, prices in Moscow
Services
Stomatitis during pregnancy is a frequent problematic disease that is diagnosed in the "Professor's Author's Dental Clinic on Arbat" and prescribed treatment that allows you to completely and quickly get rid of the disease. The nature of the inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa is different, the symptoms are traditional for most fungal infections. If you suspect stomatitis, do not delay your visit to the dentist, so as not to harm the fetus.
If you suspect stomatitis, do not delay your visit to the dentist, so as not to harm the fetus.
The following symptoms testify to the development of the disease:
- discomfort when talking and eating;
- hypersensitivity of the tongue and inner cheeks;
- increased salivation;
- sores on the mucosa;
- bad taste and odor in the mouth;
- subfebrile temperature.
If you do not consult a doctor at this stage, stomatitis in pregnant women progresses rapidly, sores become covered with bubbles, swelling of the mucous membrane is observed, eating becomes difficult.
Causes of stomatitis and its types during pregnancy
There are certain types of stomatitis that differ precisely in the causes of the disease and the peculiarity of the hormonal background: contact with an already ill person or non-compliance with oral hygiene;

What happens if stomatitis is not treated during pregnancy?
A woman who is expecting a baby is much more susceptible to attack by pathogenic microorganisms than other people. Her body spends its defenses on itself and the fetus, so it does not always fully cope with the task without medical help.
Pregnancy stomatitis: treatment of diseases of various nature
In modern dentistry, there are several options for treating the disease. Therapy depends on its nature and the individual characteristics of the patient's body:
- bacterial damage to the oral mucosa due to insufficient hygiene;
- allergic reaction to products, hygiene products;
- viruses causing herpetic lesions of tissues;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- avitaminosis of pregnant women;
- fungus;
- immunosuppression;
- temperature fluctuations leading to dehydration;
- manifestation of infection on the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx, eyes;
- transition to a chronic form with the development of a disease in a newborn;
- preeclampsia (toxicosis).

If stomatitis is caused by a fungus, an antifungal rinse is prescribed. Viral tissue damage requires taking antiviral drugs, treating sores with sea buckthorn oil, vitamin A. Allergic stomatitis is treated by eliminating the allergen and taking antihistamines. The bacterial form is eliminated with antibiotics, selected in strict accordance with the position of the patient.
Book an urgent appointment with our dental clinic and get effective treatment of stomatitis during pregnancy at the most reasonable cost in Moscow.
You can make an appointment for a consultation by calling 8 (495) 695-59-60 or in the form of an electronic application, and the clinic administrator will call you back to clarify the details of the appointment!
Book a consultation
Advantages of dental treatment in our clinic
Painless
Before treatment, the doctor will administer anesthesia using an individually selected anesthetic
Carefully
During treatment, the doctor uses modern instruments and equipment to speed up recovery
Exactly
Before treatment, the doctor makes a diagnosis, determines the condition of the teeth and draws up a procedure plan
Request a call
Appointment
To get the consultation
Leave feedback
Ask a question to the doctor
Thank you for contacting
Our operator will contact you soon
Thank you for contacting
Our operator will contact you shortly to clarify the details
Thanks for the feedback
We will add it to our website soon.
Thank you for contacting
Soon the answer to your question will appear on our website
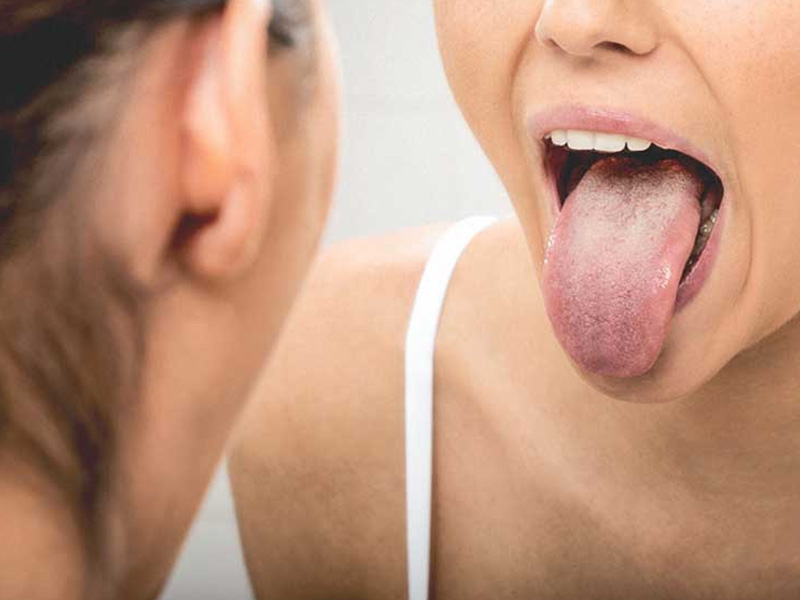
Plaque on the tongue - the norm or the beginning of serious problems
The tongue is an indicator of a person's health, a kind of business card that a doctor requires to "show" when examining a patient. By the color of the tongue and the presence of plaque, an experienced specialist can identify the presence of diseases and evaluate the functioning of the digestive system.
Normally, the tongue should be light pink in color and free from coating. If, upon examination of the oral cavity, a white, yellow, or black-brown plaque was detected, most likely you need medical attention.
There are situations when a plaque on the tongue does not mean the body's cry for help. If you have identified a white coating on the tongue without an unpleasant odor, and its thickness allows you to see the pink color of the tongue - this is not a reason to sound the alarm.
At different times of the year you may notice a white coating. For example, in summer it will be more pronounced than in spring. In winter, there may be a yellow coating on the tongue, the presence of which is considered the norm.
The appearance of plaque is often associated with poor daily oral hygiene. During hygiene procedures, it is necessary to clean the tongue. In adolescence, tongue lining is often observed, the occurrence of which is associated with hormonal changes.
In such situations, plaque on the tongue does not indicate any disease. However, if you find a plaque of a dense structure of white, yellow or black, it is better to make an appointment with a doctor and undergo an examination.
Why is there a white coating on the tongue?
A thick white coating on the tongue often indicates the presence of a disease. A thick white coating is sometimes a symptom of atonic constipation. If you have a fever and weakness, the plaque most likely indicates an infection.
If the tongue is completely covered with a slippery white coating, this is a signal of an excess of mucus and a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract. Such a sign may indicate problems with the gallbladder or liver. If the plaque resembles a spot in shape, this indicates a large amount of toxins in the body.
In the normal state of the body, the root of the tongue has a loose white coating. If a thickening of plaque is found at the root, or an unpleasant aftertaste occurs, there may be a focus of inflammation in some part of the gastrointestinal tract. If the root has a loose plaque of a heterogeneous structure, most likely, this may be a sign of enterocolitis.
A coating on the tongue sometimes indicates respiratory problems. So, if a white coating has formed along the contour of the tongue, this may be a symptom of pulmonary diseases. Also, such localization of white plaque is one of the signs of kidney disease.
White coating may indicate the presence of a fungus in the oral cavity. The most common of them is Candida fungus, which can be identified by a characteristic cheesy plaque in the form of individual plaques. If small sores in the oral cavity are added to such signs, there is a suspicion of stomatitis.
The most common of them is Candida fungus, which can be identified by a characteristic cheesy plaque in the form of individual plaques. If small sores in the oral cavity are added to such signs, there is a suspicion of stomatitis.
The presence of dry white plaque, through which a pale pink tongue is visible, may indicate inflammation in the stomach or spleen. This may indicate a gastrointestinal infection. Also, such a plaque can mean a lack of fluid.
If you find a white coating on the left side of the tongue, check the liver and gallbladder.
White coating may be a signal of the presence of a viral infection, the localization of which can be determined by additional signs.
Why is there a yellow coating on the tongue?
Normally, yellowing of the tongue can occur in hot, dry weather.
If you see a yellow coating on your tongue, this often indicates a serious health problem. Yellow plaque signals any digestive disorders, both minor and serious.
If there is a yellow coating of a loose structure on the tongue, which can be easily removed with a toothbrush, this indicates slagging of the body. It is safe to talk about an overabundance of toxins if such a plaque appears in the morning. The more slag, the denser and yellower the plaque. If, after removing the yellow plaque, it does not appear again within 3-4 hours, then it is necessary to correct the diet, and the digestive system will improve.
A yellow coating that is loose and accompanied by an unpleasant odor or taste in the mouth is a sign of a more serious problem. If nausea is added to this symptom, urgently contact a gastroenterologist and examine the stomach.
Diseases of the liver or pancreas may also present with yellow patches on the tongue. A distinctive feature in this case will be a taste of bitterness, the presence of which almost always indicates a violation of the outflow of bile. Here it is necessary to follow a strict diet and connect the treatment with drugs. Eat a lot of fiber, which will cleanse the intestines and improve the functioning of the digestive tract.
Eat a lot of fiber, which will cleanse the intestines and improve the functioning of the digestive tract.
A yellow coating on the tongue is sometimes a sign of:
- cholecystitis;
- digestive disorders;
- hepatitis.
If at first there was a white coating, and then it turned yellow, this may mean that the acquired infection is spreading throughout the body.
Yellow plaque is a faithful companion of those people who are addicted to excessive consumption of tea or coffee. If you smoke, this state of the tongue will be the norm for you. With colds, yellow coating on the tongue is a common occurrence. Such a symptom in combination with temperature may indicate pharyngitis, viral tonsillitis, etc.
Why is there a dark coating on the tongue?
The richer and darker the shade of the coating on the tongue, the worse. Dark plaque can express the presence of serious diseases.
If you find a brown coating on the tongue, this is a common symptom of the following diseases:
- Thrush.
 Usually, a dark coating indicates the transition of the disease to a chronic form, which requires immediate medical attention. With treatment, the plaque will gradually lighten.
Usually, a dark coating indicates the transition of the disease to a chronic form, which requires immediate medical attention. With treatment, the plaque will gradually lighten. - Acidosis. This is a violation of the acid-base balance in the body. Such a diagnosis is made on the basis of an additional examination.
- Acute infectious diseases, incl. cholera. Brown or black plaque indicates the presence of foci of infection. Plaque is usually accompanied by high fever and general weakness.
- Viral angina. In this case, there is a sharp pain in the throat and fever.
Brown or even black coating on the tongue is often the result of long-term use of strong drugs, especially antibiotics. Such drugs change the microflora of the oral cavity, disrupting its balance. Usually such a plaque disappears on its own after a while.
Before diagnosing yourself with a black coating on your tongue, remember what you ate the day before. Many products have a coloring effect and can remain on the tongue and teeth in the form of characteristic stains. Brush your teeth and tongue. If the raid does not occur again - you can not worry.
Brush your teeth and tongue. If the raid does not occur again - you can not worry.
If you notice a dark coating on a daily basis and have additional symptoms that cause concern, consult your doctor.
Examination and treatment
If you find it difficult to determine the cause of tongue coating and decide to visit a doctor, depending on the color, density and localization of plaque, he will offer to undergo an examination:
- take a general blood test;
- do a blood test for the presence of Helicobacter pylori;
- pass bakposev on the flora of the oral cavity;
- do a biochemical blood test;
- undergo a coprogram;
- to do FGDS and ultrasound of the digestive system.
Treatment should begin with oral hygiene. Plaque is an ideal habitat for bacteria that can provoke infection and inflammation. In addition to regular cleaning of the tongue and teeth, rinse your mouth with decoctions of herbs. A decoction of oregano, plantain or linden is well suited. You can try herbal preparations, such as mint, sage and chamomile.
A decoction of oregano, plantain or linden is well suited. You can try herbal preparations, such as mint, sage and chamomile.
Diagnosis of the condition of the tongue should be carried out in the morning in natural light. If the plaque does not go away, be sure to consult a doctor.
Based on the results of the examination and detailed diagnosis, the doctor makes a diagnosis. Initially, it is worth contacting a therapist who will write out tests, on the basis of which it will become clear which organ or system needs treatment. Further, the patient can be “transferred” to a specialized specialist who will examine and inquire about the accompanying symptoms of the disease. Usually the patient is referred to a gastroenterologist, toxicologist, dentist or infectious disease specialist. A specialist doctor may prescribe additional diagnostics, on the basis of which an accurate diagnosis is established.
If you have digestive problems, you will likely be put on a strict diet and medication. It will be necessary to completely exclude any fatty, fried foods, as well as starchy, sweet and spicy foods. Depending on the severity of the disease and the location of the focus of inflammation, the diet can be adjusted.
It will be necessary to completely exclude any fatty, fried foods, as well as starchy, sweet and spicy foods. Depending on the severity of the disease and the location of the focus of inflammation, the diet can be adjusted.
If an infection is found, treatment with antibiotics or antivirals will be necessary.
Plaque on the tongue often informs its owner about the presence of inflammation. In this case, you will be prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs with a softening effect and adjust the diet.
In the treatment of tongue plaque, the most important thing is timeliness. The spectrum of diseases, a symptom of which is a coated tongue, is quite wide - from the common cold to cancer and HIV infection.
Timely examination and diagnosis of the causes of plaque almost always guarantees successful treatment of the cause of this symptom. Do not self-medicate. Firstly, you are unlikely to be able to accurately establish the diagnosis, and secondly, you risk “masking” the symptom and complicating the work of the doctor.