When does teething usually start
Baby teething symptoms - NHS
When it comes to teething, all babies are different. But your baby will probably get their first tooth some time during their first year.
Find out how to spot when your baby is teething and what order your baby's teeth are likely to appear in.
When do babies start teething?Some babies are born with their first teeth. Others start teething before they are 4 months old, and some after 12 months. But most babies start teething at around 6 months.
Teething symptomsBaby teeth sometimes emerge with no pain or discomfort at all.
At other times, you may notice:
- their gum is sore and red where the tooth is coming through
- they have a mild temperature of less than 38C
- they have 1 flushed cheek
- they have a rash on their face
- they're rubbing their ear
- they're dribbling more than usual
- they're gnawing and chewing on things a lot
- they're more fretful than usual
- they're not sleeping very well
Read tips on how to help your teething baby.
Some people think that teething causes other symptoms, such as diarrhoea, but there's no evidence to support this.
You know your baby best. Get medical advice if they have any symptoms that are causing you concern. You can call NHS 111 or contact a GP.
Read more about spotting the signs of serious illness in babies and toddlers.
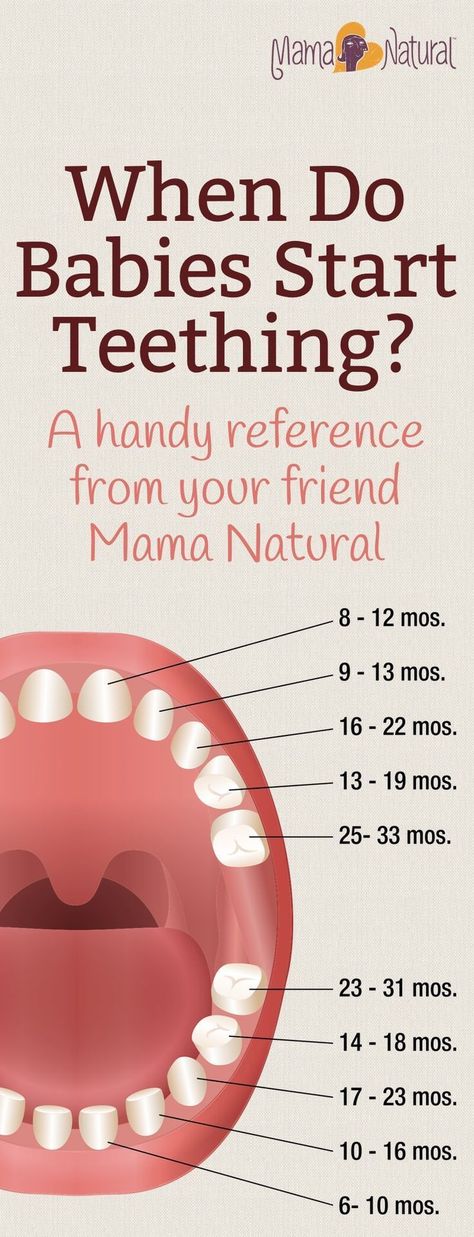
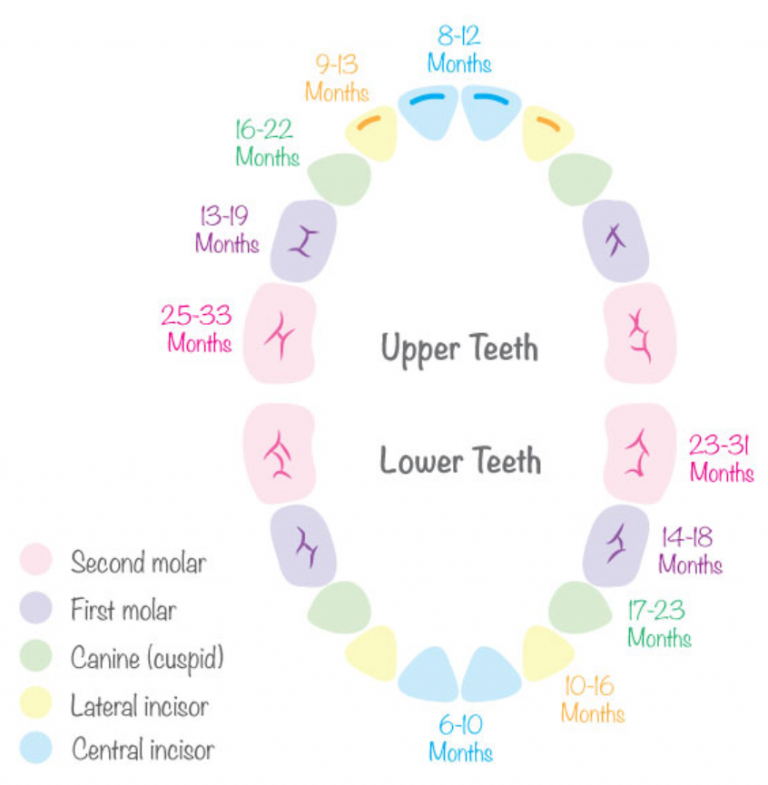
What order do baby teeth appear in?Here's a rough guide to how babies' teeth usually emerge:
- bottom incisors (bottom front teeth) – these are usually the first to come through, usually at around 5 to 7 months
- top incisors (top front teeth) – these tend to come through at about 6 to 8 months
- top lateral incisors (either side of the top front teeth) – these come through at around 9 to 11 months
- bottom lateral incisors (either side of the bottom front teeth) – these come through at around 10 to 12 months
- first molars (back teeth) – these come through at around 12 to 16 months
- canines (between the lateral incisors and the first molars) – these come through at around 16 to 20 months
- second molars – these come through at around 20 to 30 months
Most children will have all of their milk teeth by the time they are between 2 and 3 years old.
Page last reviewed: 9 August 2022
Next review due: 9 August 2025
When Do Babies Start Teething? Symptoms, Remedies, and More
You love watching your baby hit those sweet milestones — the first smile, first giggle, and rolling over for the first time. But one that’s sometimes not so sweet (for you or for them) is cutting their first tooth.
Teething is when a baby’s teeth start to come through their gums. Although this is a typical part of growing for babies, it is one of those milestones that can bring discomfort, tears (from you and baby), and even sleepless nights (yep, more of those!).
As for when your baby will actually start the process, it depends.
A baby’s teeth can sometimes emerge with no pain or discomfort, so you might not realize they’re teething until you see the first sign of a tiny white tooth. For other babies, though, teething does cause discomfort.
Common symptoms of teething may include:
- drooling
- face rash from drooling
- chewing on different objects
- irritability and crankiness
- crying
- refusing to eat
- swollen, sore, or tender gums
- trouble sleeping
- flushed cheeks
- pulling on their ears
- slightly elevated temperature to around 99°F (37.2°C)
Note
On the other hand, a rectal temperature 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, vomiting, or diarrhea are not usually signs of teething. If your baby has these symptoms, contact their pediatrician.
Symptoms of teething in breastfed babies
Teething symptoms can occur whether you breastfeed or bottle-feed your baby. But if you breastfeed or chestfeed, you might notice other changes, too. For example, gum pain or soreness might cause your baby to latch on differently.
Before a tooth emerges (and even afterward), you might feel your baby gnaw or bite down on your breasts.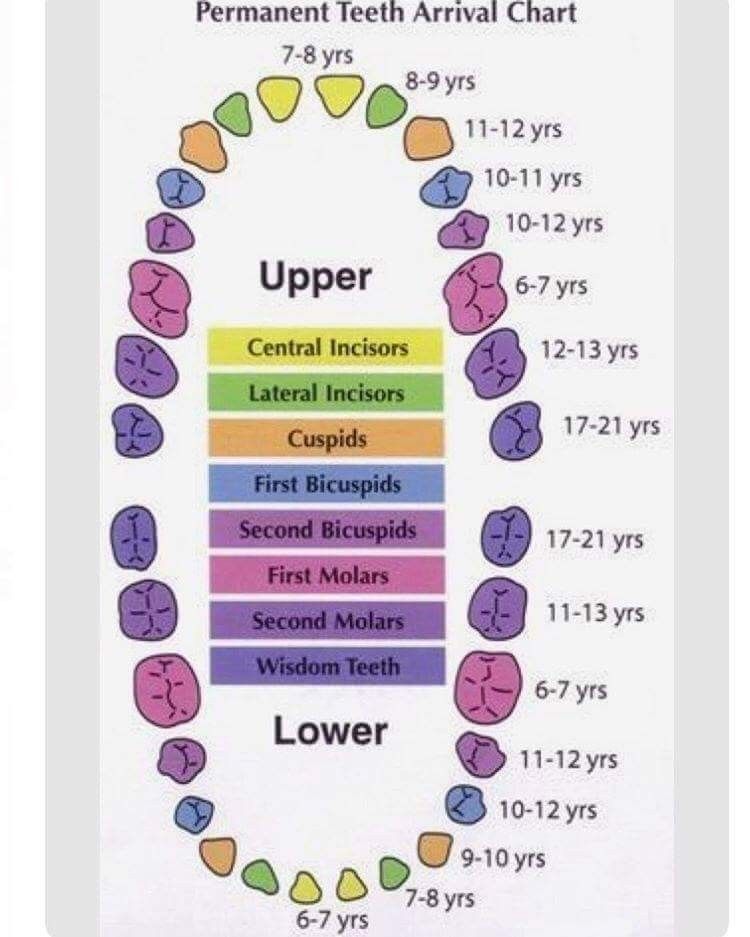 And since breastfeeding is soothing for babies, they might feed more often while teething.
And since breastfeeding is soothing for babies, they might feed more often while teething.
Keep in mind that teething symptoms occur before a tooth breaks through the gum, so don’t be alarmed if you notice these changes in your baby but don’t see any sign of a tooth.
Most babies get their first tooth between 4 and 7 months old.
But there’s a wide range of when it’s considered “typical” to start teething. So don’t panic if your little one hasn’t cut a tooth by 7 or 9 months old. If you’re concerned, you can always speak with their pediatrician at their next checkup.
To get even more specific, most infants begin teething at around 6 months old. Your little one will likely have a full set of their first teeth by age 3, and all the joys of the teeth-brushing routine will have been long established.
But “typical” doesn’t mean “best” or “all.” Exactly when your baby will start teething may even be hereditary.
And though it may seem impossible, some babies are born with one or two teeth! This occurs in about 1 in 6,000 to 1 in 800 cases — so it’s uncommon. It makes for some incredibly adorable pictures, but let’s be honest — toothless grins are pretty darn cute, too.
It makes for some incredibly adorable pictures, but let’s be honest — toothless grins are pretty darn cute, too.
Infants born with teeth should have them closely monitored since they can present a choking risk.
Some infants are early teethers — and it usually isn’t anything to worry about! If your little one starts showing signs of teething around 2 or 3 months old, they’re simply ahead of the curve in the teething department. And if your baby is a late teether, try not to worry about this either (easier said than done, we know).
Every baby is different, so don’t be concerned if all your child’s little friends have started to cut teeth already — yours will too, in their own time. In fact, if you’re going to compare at all, it’s better to consider when their siblings (if they have them) got their first tooth.
The bottom two teeth are usually the first to appear, followed by the four upper teeth. So keep an eye on that area and prepare for cuteness overload when they do.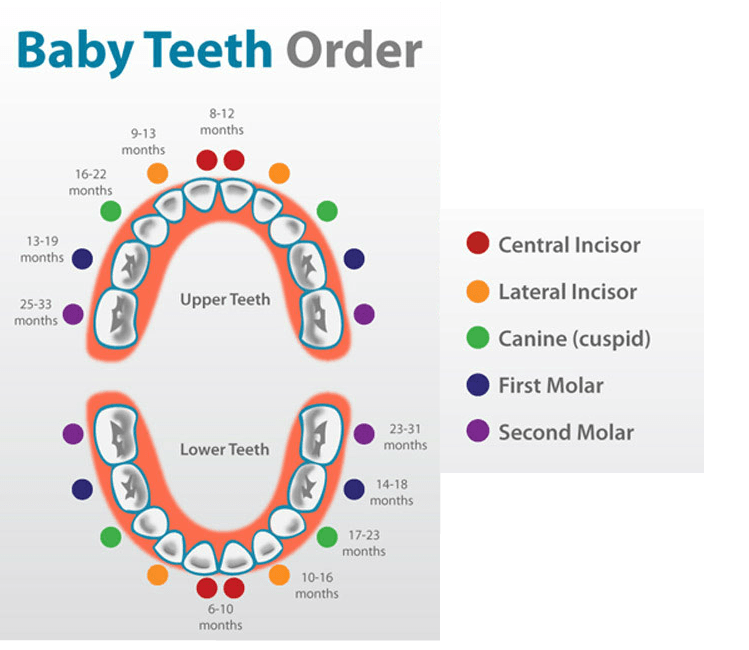
Next, their teeth may come in two at a time, one on each side of the mouth. But this pattern can vary, and many factors can influence the timeline (like if your baby was born early or at a low birth weight, for example).
On average, babies have:
- 4 teeth by 11 months
- 8 teeth by 15 months
- 12 teeth by 19 months
- 16 teeth at 23 months
Those sometimes distressing (but always perfectly usual) teething symptoms may come and go during this time period. Or they may be more consistent as your little one cuts new teeth or starts to feel the first symptoms of a tooth emerging.
If your child doesn’t have any teeth by 18 months, see a pediatric dentist for evaluation. In rare cases, an underlying medical issue may cause a delay in teething. These may include:
- malnutrition
- vitamin deficiency
- underactive thyroid
If you’re concerned that it’s been a while since your child cut their last one or two teeth, speak with their pediatrician.
When your little one is teething, you may feel more inclined to reach for that bottle of wine or chocolate bar because it’s tough to see your baby in pain. (No? Just us?)
Well, baby needs some soothing, too.
Home remedies
These are some tried and true — and most importantly, safe — home remedies you can try:
- Gently massage your baby’s gums with a clean finger, knuckle, or moistened gauze pad.
- Hold a cold washcloth, spoon, or chilled teething ring on your baby’s gums.
- Use plastic or rubber toys that are chilled — never frozen solid (ouch!).
- Offer cold foods like a chilled little slice of cucumber if your baby is already eating solids — but always keep a watchful eye on them, because this could be a choking hazard.
Medical treatment
Currently, there aren’t any medical treatments to soothe teething pain in a baby. The good news, though, is that babies typically respond positively to home remedies.
If these remedies don’t relieve symptoms, feel free to ask your pediatrician about the occasional use of over-the-counter baby acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Your pediatrician can advise whether this is an OK treatment and provide guidance on proper dosing.
And an important note: No matter how attractive the item or the claims of its manufacturers, avoid teething necklaces or bracelets — worn by adults or babies — made of amber, wood, or silicone. These can quickly turn into choking hazards, and it’s just not worth it.
Also on the no-go list: homeopathic teething tablets and medicated topical gels. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued warnings against using both of these products.
Medicated topical gels contain the ingredient benzocaine, which is an anesthetic. It’s found in products like Anbesol, Orajel, Baby Orajel, and Orabase.
Benzocaine is linked to a rare but serious condition called methemoglobinemia.
Keep in mind that good oral health isn’t important for only older children, teens, and adults. Your baby’s oral health matters too. So start brushing those pearly whites as soon as the first tooth grows in.
How do you keep their tiny, delicate teeth healthy? There really isn’t much to do at this age, but the first step is to buy an infant toothbrush that is soft and gentle. You’ll brush their teeth twice a day, once in the morning and once at night.
And yes, it’s OK to use a fluoride toothpaste, but not too much. You only need a small grain-size amount until they’re 3 years old; then, increase to a pea-sized amount.
Brushing helps prevent tooth decay, which can occur when sugar from milk, juice, or formula remains on their teeth and damages the enamel.
Have questions about teething? Here are answers to a few frequently asked questions.
What are the first signs of teething?
The teething experience can differ for each individual baby, but some of the first signs include:
- drooling
- gnawing
- trouble sleeping
- irritability or crying
- a mild increase in body temperature
Some babies also develop flushness around their cheeks or a rash.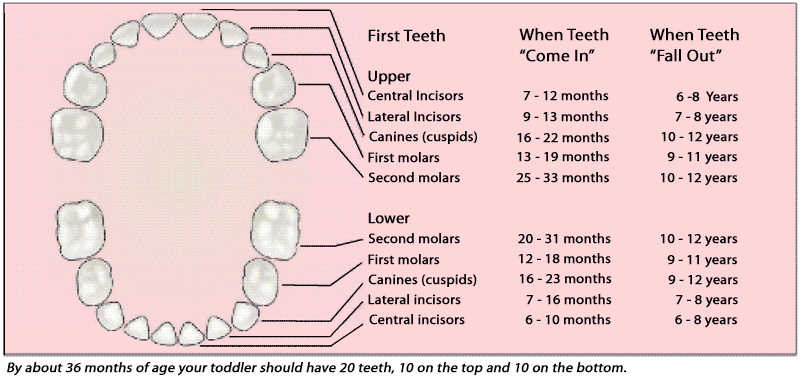 And if you breastfeed or chestfeed, teething might change the way your baby latches, or they might feed more often to soothe themselves.
And if you breastfeed or chestfeed, teething might change the way your baby latches, or they might feed more often to soothe themselves.
How early do babies show signs of teething?
Teething typically occurs around 6 months of age. However, some babies start teething as early as 2 or 3 months. Then again, some babies teeth later and don’t cut their first tooth until 8 or 9 months (or later).
How long does teething last for babies?
The teething timeframe differs for each baby. But regardless of whether a baby starts teething at 6 months or 9 months, they typically stop teething before age 3. Some babies stop teething around 24 months, while others don’t stop until 36 months.
Do babies get sick when teething?
Even though your baby may have physical discomfort, teething doesn’t make them sick. So if your baby has a runny nose, productive cough, diarrhea, vomiting, or a high fever, these symptoms aren’t associated with teething. This could be a sign of an infection, so speak with their pediatrician.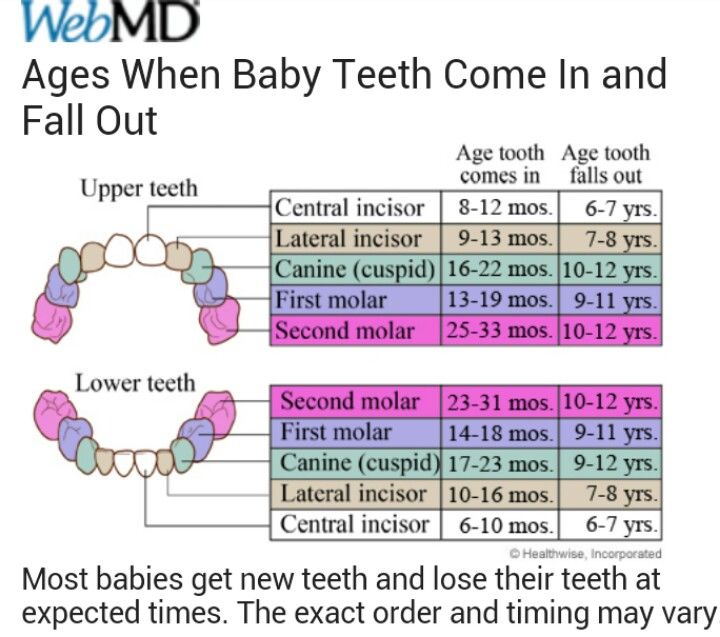
When your baby cuts their first tooth usually says nothing about their development — as with most things baby, there’s such a wide range of totally OK. Most infants end up with a full set of baby teeth by the time they’re 3 years old, regardless of when they cut that first tooth.
But if your baby hasn’t cut a tooth by the time they’re 18 months old, talk with your dentist. Ideally, you’ve already brought your baby to a pediatric dentist by age 1, as recommended by the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (and the American Dental Association and American Academy of Pediatrics, too).
So if you haven’t seen a dentist yet, this would be a good time to have your sweet babe’s mouth and gums checked out.
While visiting the dentist for the first time may sound scary, remember these two things: Your baby hasn’t yet had a negative dental experience to create dread, and pediatric dentists are great at making the visit comfortable — it can even be even fun.
Once your little one does cut a tooth or two, be sure to take good care to clean around the area each day with a damp, cool washcloth or soft-bristle baby toothbrush.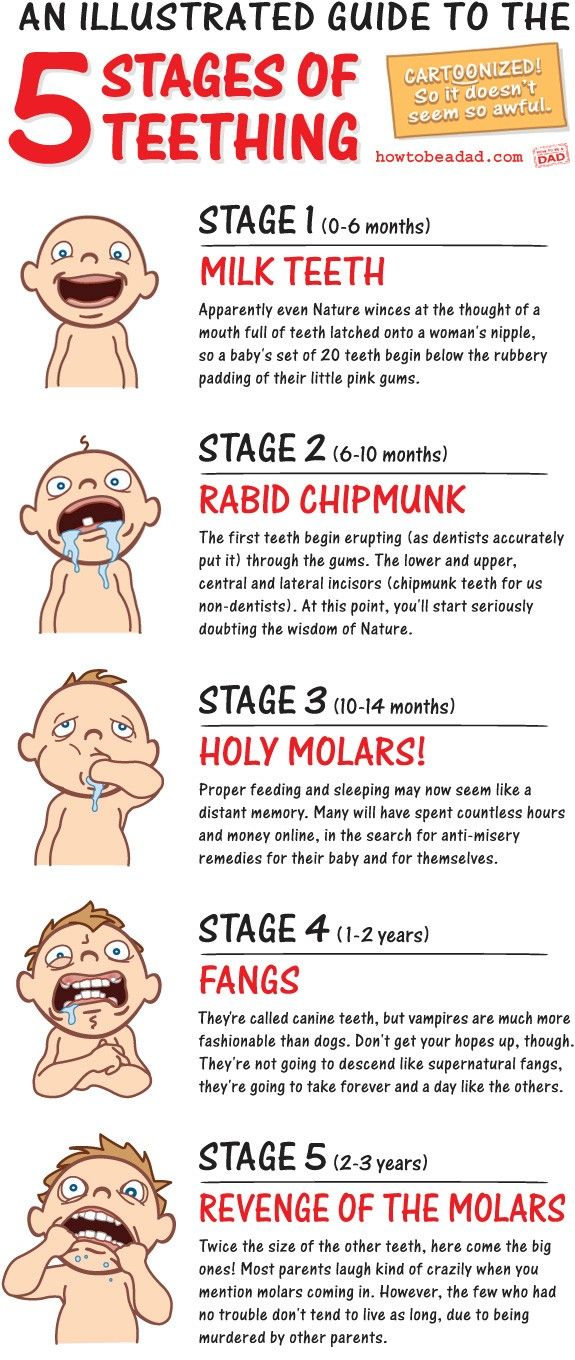 Before you know it, they’ll (hopefully!) be brushing their teeth on their own.
Before you know it, they’ll (hopefully!) be brushing their teeth on their own.
teething. How to understand that a child's first teeth are starting to cut
Teething is a difficult process not only for a child, but also for parents. Usually the baby is naughty, cries a lot, sleeps badly. It’s really hard for him and you can’t get angry at the crumbs. We need to help him!
Dry milk drink "Baby milk" Valio Baby 3 NutriValio for feeding children over 12 months Read more
When do teething start? This usually happens at the age of 6-8 months, however, there is no strict “should” in this matter. All organisms develop according to their own schedule. The first incisors (always the central lower ones) may appear at 4-5 months, and it happens that the baby begins to acquire teeth only after 10 months, closer to a year. A very important role in this matter is played by heredity (on the mother’s side), the baby’s nutrition (whether he gets enough calcium with breast milk or artificial mixtures), climatic conditions (pediatricians have noticed that in hot climates, babies teeth erupt earlier). There is an opinion that gender also matters - boys are often late in comparison with girls.
There is an opinion that gender also matters - boys are often late in comparison with girls.
How do you know if a child is teething?
The symptoms are as follows:
- swollen and reddened gums
- profuse salivation
- sour breath
- feeling unwell, moodiness, restless sleep
The baby begins to pull any objects into his mouth. This increases the risk of gastrointestinal disorders. Be especially attentive to the cleanliness of toys and other things that the baby can reach to scratch inflamed gums. Remove from the child's field of vision small things that he can choke on. Often, when a baby is teething, his temperature rises. As a rule, it does not exceed 38 ° C and passes in 1-2 days. If this does not happen, consult a doctor, perhaps the matter is not at all in the teeth. Especially if during this period a runny nose also began. Such colds must be treated.
#PROMO_BLOCK#
How to help a child?
1. Massage your baby's gums. This can be done with a finger (necessarily cleanly washed) or a special massager in the form of a thimble with bristles (you can buy it at a pharmacy).
Massage your baby's gums. This can be done with a finger (necessarily cleanly washed) or a special massager in the form of a thimble with bristles (you can buy it at a pharmacy).
2. Buy a teether. It can be plastic or silicone, solid or water-filled. Place the teether in the refrigerator before giving it to your child. The cold will soothe itchy gums.
3. Let your baby nibble on a piece of apple, baby biscuits, or biscuits. However, be sure to keep the baby in sight, he may choke.
4. With a very painful experience of growing teeth, turn to pharmaceuticals. There are special gels that relieve pain. However, they do not last long, as the medicine is quickly washed off with saliva. Do not use such products often - they can cause an allergic reaction.
5. Breastfeed your baby as often as possible. Breast milk is a natural pain reliever for a baby.
Be affectionate with the child, take him in your arms more often, kiss, soothe. Distract with games. Try not to get angry or irritated. The baby is very sensitive to your mood and emotional state. At the end of the article, we want to reassure parents that teething in children is not always painful. Often, adults learn about the baby's first tooth only when they hear a knock on a spoon.
Distract with games. Try not to get angry or irritated. The baby is very sensitive to your mood and emotional state. At the end of the article, we want to reassure parents that teething in children is not always painful. Often, adults learn about the baby's first tooth only when they hear a knock on a spoon.
3.38 24
Care and development3-6 monthsShare:
You might be interested
Author: Reetta Tikanmäki
Palm oil in baby food
Infant milk formulas are made from cow's milk.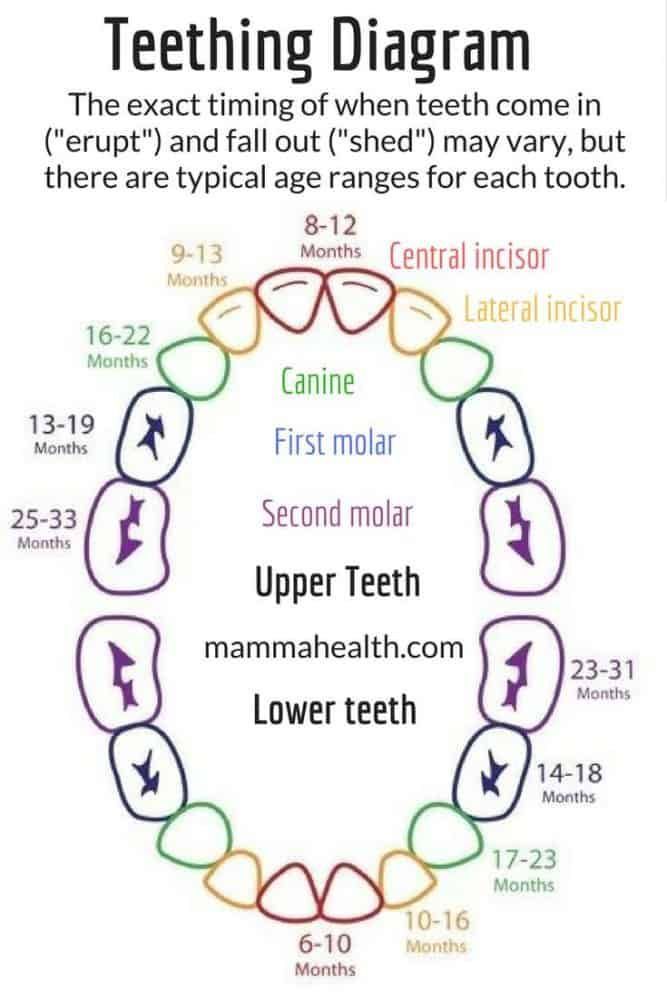 However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
Read
Author: Ivargizova Oksana
How to choose milk formula for a baby
Breast milk is the best food for a newborn baby. It contains all the necessary nutritional components that fully meet the needs of the child and are necessary for his healthy and harmonious development.
Read
Show all
When does a baby's first teeth erupt?
All babies teething according to their own individual program: for some, this process begins earlier, for others later. As practice shows, the first tooth in most children appears at the age of 6 to 8.5 months, and by the year every healthy child has at least one milk tooth in his mouth.
At the age of three or four months, teeth preparing for eruption begin to actively declare themselves: the baby becomes capricious, cries, tries to bite everything that gets into his hands.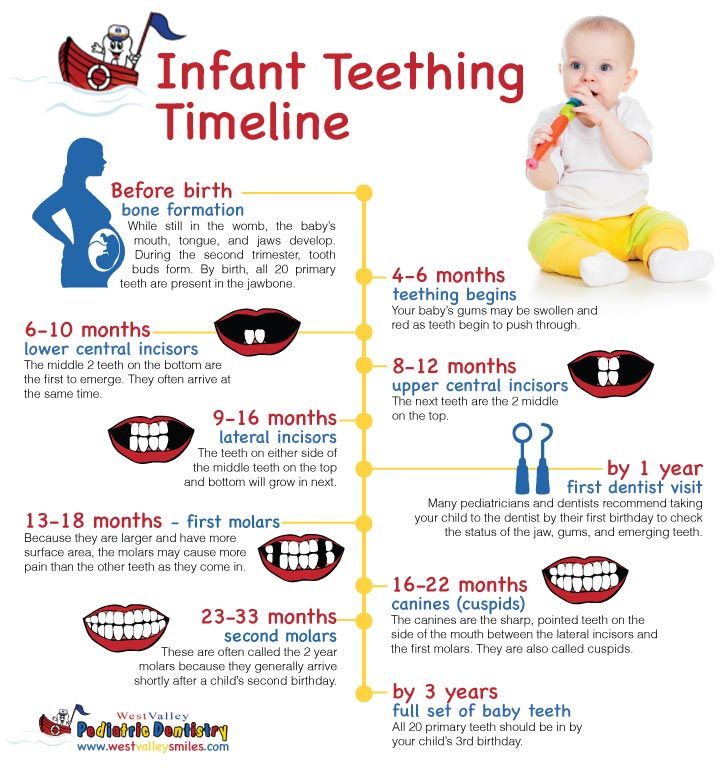
The first to appear are usually the two lower, centrally located teeth (lower central incisors or "ones"). Then - the central upper incisors, after which, by about ten months, the upper "twos", or lateral upper incisors, erupt. By eleven to twelve months, the lateral incisors can also be seen on the lower jaw. Thus, ideally, a one-year-old child is the proud owner of eight milk teeth.
By about sixteen months, many babies already have first molars on the bottom and top. Fangs ("threes") appear at the top and bottom later, in the eighteenth - twenty-second month of a child's life. The second upper and lower molars erupt at the age of 24-33 months. But again, it should be remembered that this process is individual and the order of teething may also be different.
Teeth often grow in pairs: two, and sometimes four at the same time. In girls, for the most part, teeth erupt earlier than in boys. By the age of 2.5-3 years, a complete set of twenty fully erupted teeth can be found in a baby.
Alertness must be shown if a child who is almost a year old does not have a single tooth. In principle, some children may have a congenital feature in the form of late teething, but you should not draw any conclusions on your own, you should definitely consult with a qualified specialist who, if necessary, will prescribe additional examinations.
Causes of late teething in children:
- hereditary predisposition, which is a variant of the norm and can be traced in other blood relatives;
- decreased thyroid function;
- rickets;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- violations of enzymatic (fermentation) metabolism;
- pituitary insufficiency;
- lack of calcium in the child's body;
- genetically determined diseases.
For the baby himself, the process of teething can proceed in different ways. Some children practically do not experience discomfort, others suffer from pain, their sleep is disturbed, their appetite worsens, their temperature rises (up to 38-39 ° C), salivation increases, nasal congestion, wet cough (due to profuse salivation), constipation or, conversely, , increased stool.