Diet plan for a pregnant women
Healthy diet during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Healthy diet during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content9-minute read
Listen
Why diet is important during pregnancy for you and your baby
Your diet during pregnancy helps to support your own wellbeing and supplies the nutrition your baby needs to develop and grow.
As a general guide, pregnant mothers need to eat a healthy diet, high in nutrients and low in sugar, salt and saturated fats.
It’s normal for a pregnant mother to gain weight — however, gaining too much or too little weight increases the risk of complications for you and your baby.
Healthy weight gain depends on a mother’s weight before pregnancy. Evidence supports using Body Mass Index (BMI) as a guide for how much weight gain is recommended during pregnancy.
A well balanced diet is usually enough to meet your nutritional needs during pregnancy. However, some foods contain higher concentrations of certain nutrients which are specifically recommended during pregnancy.
Folate, iron, iodine and vitamin D are nutrients needed to support a growing baby’s health and development and can prevent certain conditions. If you are planning a pregnancy, you should start taking a folic acid supplement at least one month before you fall pregnant and for 3 months after conception. Folic acid supplements have been proven to help protect against neural tube defects.
If you are considering taking or currently taking any supplements, please discuss this with your doctor or midwife, as doses can vary depending on your individual circumstance.
What is a 'balanced diet'?
A healthy, balanced diet includes a wide variety of nutritious foods from the five food groups. It’s also advisable to drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Wholegrains and cereals
- Vegetables and legumes/beans
- Lean meats and poultry, fish, eggs, tofu, nuts and seeds as well as legumes/beans
- Fruit
- Dairy foods including mostly reduced fat milk, cheese and yoghurt
Most of us have days when we eat well, and days where our intake of ‘treat’ foods may be higher. Pregnancy cravings can also make this harder to manage, especially when they’re for foods which are high in sugar, salt or fat.
Pregnancy cravings can also make this harder to manage, especially when they’re for foods which are high in sugar, salt or fat.
If you are suffering from morning sickness or severe vomiting during pregnancy, it is important to eat what you can at the time. You should contact you doctor or midwife if you are concerned.
What about pregnancy cravings?
It used to be thought that pregnancy food cravings were a sign of nutrient deficiencies in a pregnant mother’s diet; however, there is no evidence to support this link. Pregnancy can also cause changes in a mother’s tastes, and foods once found appealing can take on a completely different flavour. Food aversions can develop during pregnancy, due in part to hormonal influence.
Are there any foods I should avoid during pregnancy?
There are some foods which need to be avoided during pregnancy, due to their risk of carrying specific bacteria or parasites. An infection with listeria, salmonella or toxoplasmosis when pregnant can cause serious complications to your baby and increase the risk of pregnancy loss.
Some types of fish contain high levels of mercury, including shark/flake, marlin or broadbill/swordfish, orange roughy and catfish. Being selective about what type of fish to eat is important during pregnancy.
It’s also important to check ‘use-by’ dates and to make sure that food has been stored correctly. If in doubt about the safety of a particular food, the safest option is to not eat it.
Food and drink guide
Useful guide to food and drink during pregnancy
Do I need to prepare and cook food differently when I’m pregnant?
It’s important to be careful about food preparation and safety during pregnancy. Food poisoning is generally caused by contamination of food with certain bacteria or viruses. Sometimes it’s easier to suspect food has been contaminated because it smells ‘off’ or looks different to what it should. But it’s not always obvious that food may not be safe. When preparing food, you should always:
- defrost frozen meat, especially poultry, in the fridge or in the microwave
- wash your hands before preparing food and eating
- use different cutting boards for vegetables and meat
- wash benches, cutting boards and utensils with hot, soapy water
- change dishcloths frequently — if they smell, this is a sign of contamination
- cook food thoroughly and don’t eat raw or ‘rare’ meats or fish
- reheat foods to at least 60° Celsius and until it’s steaming hot
What can I drink during pregnancy?
The safest drinks during pregnancy are water and milk. Current evidence supports the recommendations that you should avoid drinking alcohol if you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy. Even small amounts can harm a baby’s development and may have lifelong effects.
Current evidence supports the recommendations that you should avoid drinking alcohol if you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy. Even small amounts can harm a baby’s development and may have lifelong effects.
Water and milk are considered to be safe to drink when pregnant. Low sugar soft drinks, small amounts of juice and soda or mineral water are also fine to drink. Likewise, small amounts of caffeine in tea and coffee are thought to be safe. During pregnancy and when breastfeeding, consuming up to 200 mgs/day is considered safe for a mother and her baby.
As a guide the approximate amounts of caffeine found in food and drinks are:
- 1 cup of instant coffee – 60mg
- 1 shot of espresso coffee – 100mg
- 1 cup of plunger coffee – 80mg
- 1 cup of tea – 30mg
- 375ml can of cola – 49mg
- 250ml can of energy drink – 80mg
- 100g bar of milk chocolate – 20mg
What foods should I limit during pregnancy?
Processed foods tend to be high in sugar, fat and salt.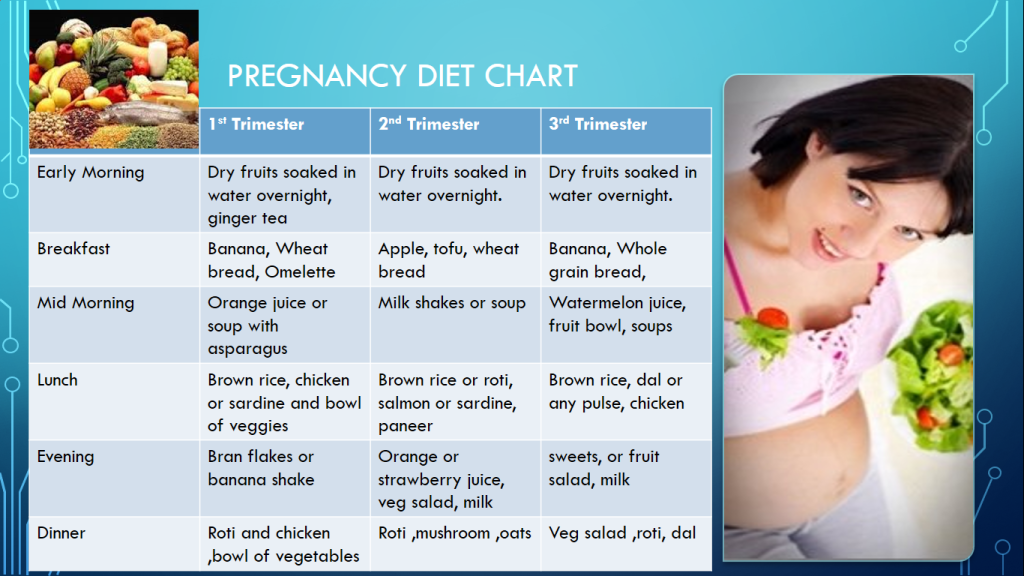 Although they can taste good and are often convenient, they don’t meet the daily requirements for nutrition. The Australian Dietary Guidelines recommend that during pregnancy, you should limit the amount of foods that contain saturated fat, added salt and sugars as well as alcohol.
Although they can taste good and are often convenient, they don’t meet the daily requirements for nutrition. The Australian Dietary Guidelines recommend that during pregnancy, you should limit the amount of foods that contain saturated fat, added salt and sugars as well as alcohol.
During pregnancy, you will have extra energy requirements and needs more serves from the five food groups. It’s important to understand that the ‘serving size’ doesn’t change, but instead the variety of food and serves per day increases to meet the mother and baby’s needs.
| Food group | Serves per day |
|---|---|
| Vegetables and legumes/beans | 5 |
| Fruit | 2 |
| Grains and cereals, mostly wholegrain and/or high fibre cereals | 8 |
| Lean meat/fish/poultry/eggs/tofu/nuts | 3. 5 5 |
| Milk/dairy foods | 3.5 |
Speak with your maternity care provider. If necessary, they can refer you to a dietician who specialises in pregnancy eating support.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Australian Government Department of Health (Alcohol during pregnancy and breastfeeding), Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ) (Folic acid/folate and pregnancy), NSW Food Authority (Foods to eat or avoid when pregnant), Eat for Health (Healthy eating during your pregnancy poster), Queensland Health (Healthy eating for gestational diabetes mellitus), Eat For Health (Healthy Eating When You’re Pregnant or Breastfeeding), Eat For Health (Australian Guide to Healthy Eating), The Royal Women's Hospital (Food & nutrition in pregnancy)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: April 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Food preparation and safety
- Food cravings during pregnancy
- Alcohol and pregnancy
- Guide to food and drink during pregnancy
- Foods to avoid when pregnant
- Vitamins and supplements during pregnancy
- Appetite changes and food aversions during pregnancy
Need more information?
Pregnancy health & wellbeing | Raising Children Network
Pregnant? Here’s all you need to stay healthy during pregnancy, including tips for healthy diet and lifestyle and a guide to pregnancy health care.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Having a healthy pregnancy
Having a healthy pregnancy means following a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, knowing what to avoid and making sure your vaccinations are up to date.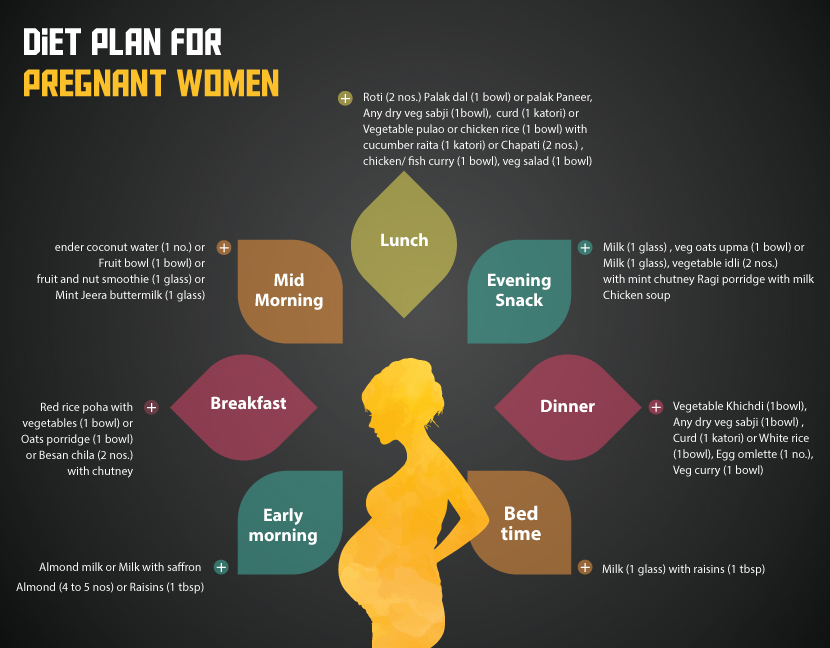 Find out more here.
Find out more here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy and Healthy Eating
It’s especially important to eat healthy food during pregnancy and while breast feeding.
Read more on Healthy Eating Active Living NSW website
Pregnancy healthy eating in pictures | Raising Children Network
Healthy eating for pregnancy means lots of fruit, vegetables and foods with calcium, protein and iron. Avoid sugary, fatty foods, and drink plenty of water.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Pregnancy: illustrated guides | Raising Children Network
Parenting in pictures provides step-by-step guides to pregnancy topics such as healthy eating, pelvic floor exercises and more.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Appetite changes and food aversions during pregnancy
It’s common to experience food cravings or a food aversion during pregnancy. Find out how to ensure you continue to eat healthily if this affects you.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Healthy eating when you’re pregnant or breastfeeding | Eat For Health
Eating well during pregnancy and while breastfeeding has health benefits for you and your baby.
Read more on NHMRC – National Health and Medical Research Council website
Gi and Pregnancy | GI Foundation
Home / Gi Health Benefits / Gi and Pregnancy Gi and Pregnancy Following a healthy low Gi diet during pregnancy helps protect your child’s future health and improves health and wellbeing for lifelong benefits
Read more on Glycemic Index Foundation website
Pregnancy and diet - Better Health Channel
Good nutrition during pregnancy can help to keep you and your developing baby healthy.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Male fertility and conception- tips for getting pregnant by improving sperm health
Male fertility is vital for conception and a healthy pregnancy. Couples trying to get pregnant need to pay attention to factors which increase the chances of infertility in men. In addition to a healthy diet and regular exercise, treating sexual problems and avoiding recreational drugs helps boost male fertility.
Read more on Parenthub website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.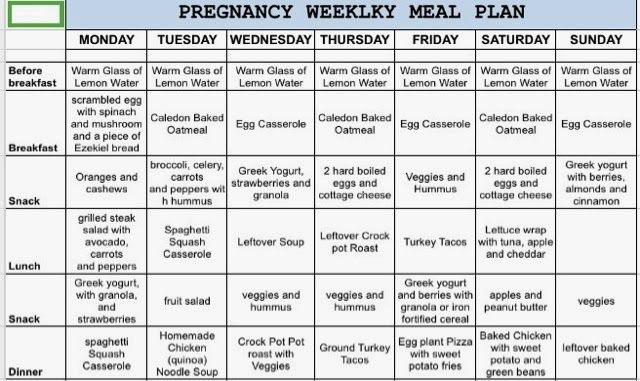
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
A Pregnant Woman's Daily Diet
Written by Elizabeth Somer, MA, RD
At no other time in life is nutrition as important as before, during, and following pregnancy. On the other hand, women can still eat foods that come in a box or a bag, eat out several times a week, or order pizza to go as long as they also follow a few simple eating-for-two dietary guidelines.
A Pregnant Woman Should Include in Their Daily Diet at Least:
- Five servings of fresh fruits and vegetables (including at least one serving of a dark orange vegetable, two servings of dark green leafy vegetables, and one serving of citrus fruit)
- Six servings of enriched, whole-grain breads and cereals. Three servings of nonfat or low-fat milk or milk products
- Two to three servings of extra-lean meats, chicken without the skin, fish, or cooked dried beans and peas
- Eight glasses of water
The guidelines for eating well for a healthy pregnancy are simple and easy to follow. When, where, and how much they eat is flexible, and often is governed by necessity. A pregnant woman in their first trimester might choose a snack for breakfast and a large evening meal if they suffer from morning sickness, but select a larger breakfast and a light evening meal in the last trimester when heartburn is more of a problem. Avoid or limit caffeine (such as coffee, tea, and colas) and avoid alcohol and tobacco. Since no safe limit has been established for alcohol, abstinence is a woman's best bet.
Since no safe limit has been established for alcohol, abstinence is a woman's best bet.
A Weighty Issue
If a woman does not gain enough weight, their baby also won't gain enough weight, which places the newborn at high risk for health problems. Optimal weight gains of 25 to 35 pounds in a slender woman helps ensure a healthy-sized baby. Underweight women should gain more weight, or approximately 28 to 40 pounds. Overweight women should not attempt to use pregnancy as a way to use up extra body fat, since stored body fat is not the stuff from which babies are made. A modest weight gain of between 12 to 25 pounds is recommended for these women.
Further weight gain beyond recommended amounts will not make bigger or healthier babies. It will make regaining a desirable figure more difficult after delivery. The secret is to pace the gain, with weight gain increasing from very little in the first trimester to as much as a pound a week in the last two months of pregnancy.
Folic Acid: It's a Must
Nutrition experts agree that the best place for the mother-to-be to get all the essential nutrients, including ample amounts of vitamins and minerals, is from their diet. The trick is getting enough. For example, the MRC Vitamin Study at the Medical College of St. Bartholomew's Hospital in London found that women taking folic acid supplements around conception had significantly lower risks for giving birth to babies with neural tube defects (NTD), a type of birth defect where the embryonic neural tube that forms the future brain and spinal column fails to close properly.
Luckily, in 1996 the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a regulation requiring that all enriched grain products, including breads and pasta, be supplemented with folic acid. Every woman during the childbearing years should make sure they get at least 400 micrograms of folic acid from food or supplements.
The Post-Pregnancy Diet
Whether a woman breastfeeds or not, the secret to post-pregnancy nutrition is to gradually regain a desirable figure, while maintaining or restocking nutrient stores. In addition, since some babies are planned and others are surprises, it's never too late to start nourishing the next baby by continuing to eat a diet based on fresh fruits and vegetables, nonfat milk products, whole grains, and protein-rich beans and meats.
In addition, since some babies are planned and others are surprises, it's never too late to start nourishing the next baby by continuing to eat a diet based on fresh fruits and vegetables, nonfat milk products, whole grains, and protein-rich beans and meats.
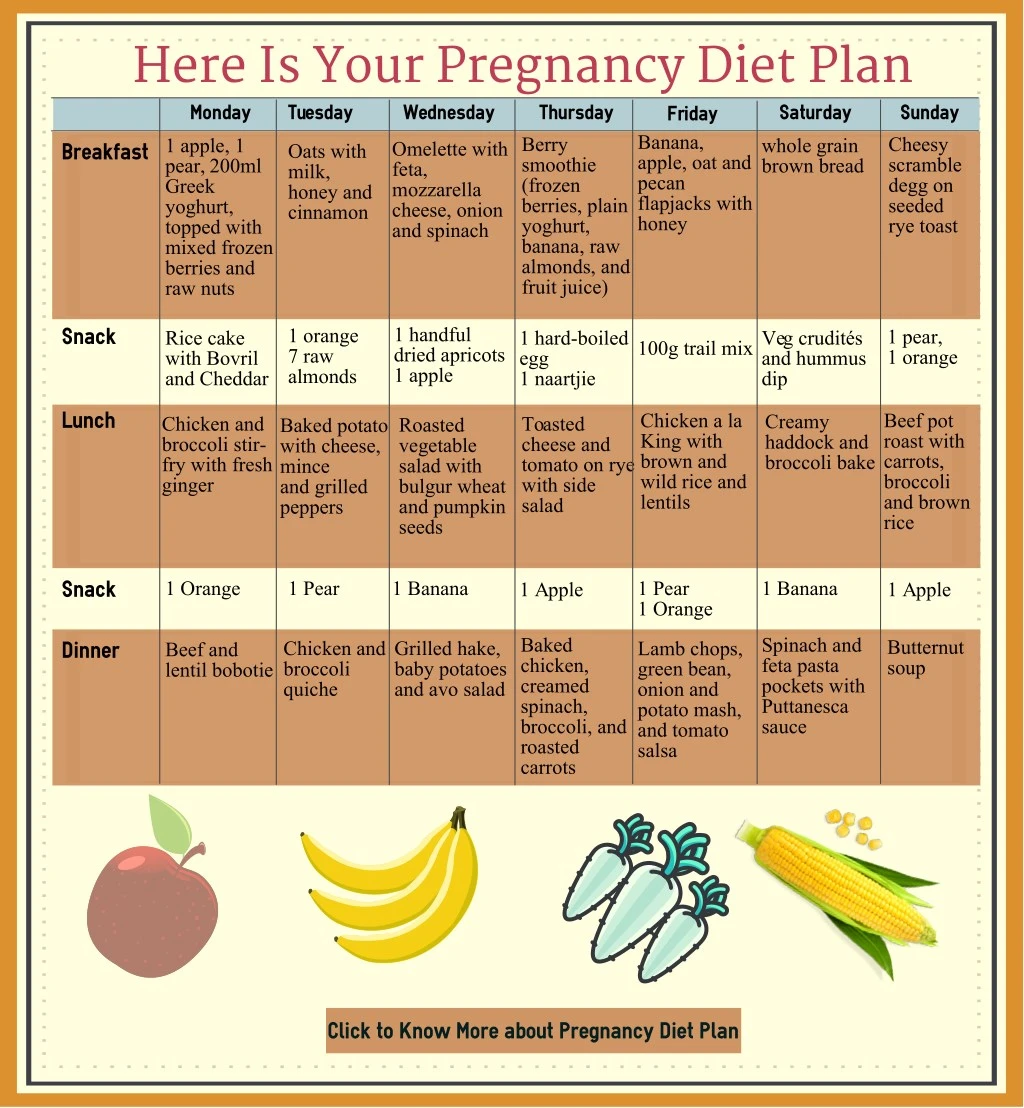
Diet for pregnant women for weight loss
While expecting a baby, a woman experiences not only hormonal and physical changes in her body. It is important for her to rebuild some eating habits in favor of more correct ones. When carrying a fetus, the consumption of valuable vitamins and trace elements increases, so you need to replenish their reserves all the time. Let's talk about what a pregnant woman's diet can be and how to make nutrition complete.
Website editor
Tags:
diets
protein diet
diet table
How to lose weight during pregnancy
Diet for pregnant women
If you follow the rules of nutrition during pregnancy, the diet will keep the weight normal and will not harm the baby. Here are the basic principles of the diet for expectant mothers and draw up an approximate menu.
Here are the basic principles of the diet for expectant mothers and draw up an approximate menu.
Contents of the article
Diet during pregnancy must solve a large number of problems. First, you need to provide your body and the developing body of the child with all the necessary substances. Secondly, to minimize the symptoms of toxicosis, reduce the burden on the liver and stomach. And, thirdly, to avoid excessive weight gain in the expectant mother. We tell you what a safe diet for pregnant women consists of for weight loss.
Is it safe to lose weight during pregnancy?
Pregnant women are generally not advised to lose weight or follow a strict diet during pregnancy. But as part of a balanced diet, the expectant mother can safely lose a few pounds during the first trimester. The main thing is to stick to a healthy diet and avoid fatty and sugary foods. Only in this case, after giving birth, you will quickly return to your previous shape.
Diet for pregnant women - general recommendations
There is a diet for pregnant women for the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimesters to reduce weight, but due to the competent construction of the diet, and not a complete rejection of food. We will talk about the nutritional features at each stage of fetal development. However, there are general rules that should be observed during the entire course of pregnancy.
- Eat 5-6 times a day in small portions.
- The last meal should be no later than 3 hours before bedtime.
- Avoid alcohol, fried, smoked, coffee and fast food.
- Consume a diet predominantly of fruits, nuts, vegetable broths, cereals, lean fish.
- Take vitamin complexes.
Pregnancy Diet - 1st Trimester
In the first trimester of pregnancy, the fetus is formed from the embryo, the brain and internal organs begin to develop. During this period, you need to approach the preparation of the diet most seriously.
During this period, you need to approach the preparation of the diet most seriously.
The body of the future mother should receive enough protein and folic acid. And a diet for pregnant women should take into account such important points. These substances are rich in foods such as lean meat and eggs, legumes, lettuce, whole grain bread, cheese, cottage cheese, celery, cabbage, liver, apples.
Diet menu for the 1st trimester of pregnancy
Our great-grandmothers' favorite saying that it's time to eat for two should encourage you to eat better, better, not more. Adjust your diet so as not to harm yourself or your child. In the early stages, a diet for pregnant women is especially important, so be sure to consult a doctor. He will be able to suggest which products to add and which should be excluded.
Monday
- Breakfast: buckwheat with yogurt, apple juice with celery.

- Second breakfast: cottage cheese.
- Lunch: vegetable soup, wholemeal bread.
- Afternoon snack: peach.
- Dinner: salad with salmon and avocado.
- Late dinner: berry juice.
Tuesday
- Breakfast: cottage cheese with berries, tea.
- Second breakfast: dry biscuits, freshly squeezed juice.
- Lunch: pumpkin puree soup.
- Snack: apples.
- Dinner: steamed turkey meatball.
- Late dinner: yogurt.
Wednesday
- Breakfast: oatmeal with milk.
- Second breakfast: bread with butter.
- Lunch: fish soup.
- Snack: cottage cheese with low-fat sour cream.
- Dinner: liver, buckwheat.
- Late dinner: seaweed salad.
Thursday
- Breakfast: sugar-free granola with milk.

- Second breakfast: yogurt.
- Lunch: weak meat broth with egg.
- Snack: vegetable salad.
- Dinner: stewed cabbage, rice.
- Late dinner: fruit drink.
Friday
- Breakfast: bread with tomatoes and cream cheese.
- Second breakfast: pear.
- Lunch: pasta with meat hedgehog.
- Snack: almonds.
- Dinner: baked potatoes with herbs and butter.
- Before going to bed: herbal tea, fermented baked milk.
Saturday
- Breakfast: cottage cheese pancakes 5%, green tea.
- Second breakfast: prunes.
- Lunch: chicken soup, bread.
- Snack: cabbage and carrot salad.
- Dinner: cucumber and tomato salad.
- Late dinner: a glass of milk.
Sunday
- Breakfast: millet porridge, juice.

- Second breakfast: orange.
- Lunch: vegetable soup with tomatoes, peppers and Brussels sprouts.
- Snack: pear.
- Dinner: steamed fish cake and vegetables.
- Late dinner: kefir.
Diet for Pregnancy - 2nd Trimester
In the second trimester of pregnancy (from 13 to 28 weeks), pay attention to vitamin D and calcium (they are absorbed only in conjunction). Include dairy products, spinach, eggs, sea fish, cod liver, butter in your diet. Pregnant women may experience swelling, so the diet for every day should include a decrease in the amount of salt consumed.
Get into the habit of regular walks in the fresh air, even during the cold season. Consume potentially allergenic foods with caution: citrus fruits, red berries, nuts. In the second trimester, the load on the liver of a pregnant woman increases, so exclude fatty and fried foods.
Diet for pregnant women - 3rd trimester
During this period (from 28 weeks to the end of the 40th), the baby grows more actively than in the previous two. Mom puts on weight more noticeably, the body prepares for childbirth. The diet of a pregnant woman in the 3rd trimester involves a menu with a restriction of simple carbohydrates. This does not mean that the diet should be aimed at losing weight and losing weight. It's more about a balanced diet.
Mom puts on weight more noticeably, the body prepares for childbirth. The diet of a pregnant woman in the 3rd trimester involves a menu with a restriction of simple carbohydrates. This does not mean that the diet should be aimed at losing weight and losing weight. It's more about a balanced diet.
During pregnancy, strict restrictions should be avoided, and even more so, you should not starve yourself. Just like in the second trimester, watch your calcium intake. To exclude edema, fatigue and toxicosis, try to give up fatty meat.
Protein Diet for Pregnancy
Following the principles of this diet helps to return to its former shape almost immediately after childbirth. The protein diet for pregnant women is based on the main rule - the daily protein intake should be 120 grams. However, in addition to protein foods, a future mother can consume up to 400 grams of carbohydrates per day.
It is also important to consider what not to eat during pregnancy. Banned are chocolates, cakes, sugar, white bread and fast food. There are other basic rules:
Banned are chocolates, cakes, sugar, white bread and fast food. There are other basic rules:
- Distribute food throughout the day. The optimal number of meals is 5 times a day. Five meals a day includes three main meals and two light snacks.
- Keep breaks between meals at 3.5 hours.
- Drink enough water per day, but in small portions during the day, not at night.
Benefits of a protein diet for pregnant women
- You eat a varied diet and don't feel hungry because protein takes a long time to digest.
- You eat enough protein, which is an important micronutrient for the body.
- You don't completely eliminate carbohydrates. The diet includes fruits, vegetables and grains. The only thing you cut out of your life is fast-digesting carbohydrates like white bread and sweets. Simple carbohydrates just negatively affect the digestion of pregnant women and lead to constipation.
 As a rule, these are empty calories with no nutritional value.
As a rule, these are empty calories with no nutritional value.
The cons of a protein diet for pregnant women for weight loss
- The protein diet may not suit you, as it does not adjust much depending on the trimester. Before starting a diet, you should consult a doctor.
- As part of the diet for pregnant women, general recommendations are given for each day, which you adhere to, missing individual indicators.
- Some sources state that in the first trimester it is necessary to consume 60-90 grams of protein per day, and from the 5th month of pregnancy - increase the daily rate to 120 grams. To determine the optimal amount, contact your doctor.
It should be noted that in excess of protein can overload the body and lead to undesirable consequences. It provokes increased work of the kidneys, necessary for the removal of their decay products. Lack of fiber and an excess of proteins - let it lead to stomach problems in the form of bloating, heaviness, heartburn, and so on.
Daily protein diet menu for pregnant women - 1st trimester
- Breakfast: oatmeal and dried fruits (literally a few pieces) and rosehip broth.
- Snack: any fruit, medium-fat cottage cheese no more than 100 grams and 1 tablespoon of curdled milk.
- Lunch: chicken broth soup, steamed vegetables up to 200 grams and 1 piece of lean fish for a couple.
- Snack: natural yogurt (1 cup) and an apple.
- Dinner: Mixed vegetable omelette and a slice of whole grain bread.
Daily protein diet menu for pregnant women - 2nd trimester
- Breakfast: whole grain bread slice, hard boiled egg and green tea.
- Snack: 1 glass of fermented baked milk and a small banana.
- Lunch: broccoli soup, rice with chicken (200 grams), grated carrot salad with sour cream
- Snack: a handful of hazelnuts and 5 pieces of dried apricots.

- Dinner: fresh vegetable salad and a handful of cottage cheese.
- Snack: a glass of low-fat yogurt.
Daily protein diet menu for pregnant women - 3rd trimester
- Breakfast: rice milk porridge with dried fruits, raisins and fruit drink.
- Snack: diet syrniki with oatmeal and pear.
- Lunch: fresh cabbage soup and grilled fish with vegetable stew (medium portions).
- Snack: 1 cup yogurt, a slice of whole grain bread, an apple.
- Dinner: fresh vegetable salad and steamed turkey with 50 grams of buckwheat.
- Snack: low-fat kefir 1 cup.
Diet number 9 for pregnant women
Diet (table) number 9 for pregnant women with diabetes provides for fractional meals with a break between meals of 2.5 hours. This mode will avoid spikes in blood sugar. One serving should not exceed 150 g. It is based on the recommendations of the Soviet gastroenterologist Pevzner.
When following table number 9, it is necessary to limit the amount of carbohydrates to 200-300 g per day. Two meals should be rich in protein. The total caloric content of the diet should not exceed 2500 kcal. At its core, diet number 9for pregnant women with gestational diabetes is somewhat similar to the principle of nutrition, in which protein predominates. Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) manifests itself during the period of bearing a child and is limited by the duration of pregnancy, that is, sugar rises only in these months.
When following the Pregnancy Diet 9, sugar and simple carbohydrates should be excluded from the diet. Limit your intake of pasta, starchy vegetables and legumes, fried foods, fatty foods, smoked foods, and salt.
Diet table number 9in case of diabetes, pregnant women are obliged to exclude sugar and simple carbohydrates: even from 100 g of pasta, the glucose level can jump up to 8 units. Now the woman's body is under tremendous stress: hormones block insulin, and the pancreas must produce more of it than in any other state.
Now the woman's body is under tremendous stress: hormones block insulin, and the pancreas must produce more of it than in any other state.
High blood sugar can affect both the mother's well-being and the baby's health. Diet table number 9 for gestational diabetes in pregnant women takes into account the preparation of a balanced menu that helps to cope with unpleasant symptoms. We recommend regular visits to the doctor during pregnancy so that he can track the dynamics of the baby's development and adjust therapeutic nutrition for diabetes.
It is not worth neglecting the doctor's recommendations, because diabetes during pregnancy can harm both the mother and the child. In rare cases, the disease can lead to miscarriage.
Diet table number 9 for GDM in pregnant women is also suitable for weight loss, because you control the amount of carbohydrates and reduce sugar in the diet. What do you need to know about the power plan? We share the basic principles of the 9th table.
Keep a food diary
To lose weight and improve your health, you need to control the percentage of carbohydrates and sugar in the diet. The easiest way to do this is with a diary. Write down every meal regularly so that the doctor can adjust the menu based on the results of the tests. If the sugar level jumps sharply, the specialist will know what is the reason.
Control carbohydrates
Diet table number 9 for pregnant women is a menu for every day with a minimum amount of carbohydrate foods. If they are present, they should be evenly distributed throughout the day. This way you avoid sudden spikes in blood sugar after eating. Doctors recommend reducing portions to small and medium and do not forget about healthy snacks.
Bet on foods with a low glycemic index
A diet for high sugar in a pregnant woman necessarily includes foods that do not cause large drops in blood glucose levels. Choose healthy, low-GI carbohydrate foods such as vegetables, beans, low-fat dairy, berries, and whole grain snacks.
Choose healthy, low-GI carbohydrate foods such as vegetables, beans, low-fat dairy, berries, and whole grain snacks.
Include lean proteins such as tofu, chicken, fish, and eggs, as well as healthy fats in your diet. The list includes nuts, avocados and olive oil.
Keep yourself away from foods that are low in nutrients. Sweets, sugary drinks, ice cream and fast food - these foods are prohibited for diabetics. And no compromises, because you need to think not about momentary pleasures, but about the health of both of you.
In order for the diet table No. 9 for pregnant women to be suitable for weight loss (under the supervision of a doctor), you need to follow other important rules:
- Control your daily calories. It is calculated from the individual characteristics of the body (35 kcal per 1 kilogram of mother's weight), but does not exceed 2000 calories per day. Half of the diet is healthy carbohydrate meals, 20% is protein foods, and the rest is unsaturated fats.

- Do not exceed the allowed daily allowance of salt - 12 grams.
- Drink the required amount of water, at least 2 liters.
- Eat small meals up to 6-7 times a day. Try to maintain a pause between meals at 2 hours.
- Replace sugar with sweeteners.
- Steam or simmer food. Fried foods are completely excluded. Meat and vegetables can be baked.
- Smoked and fried foods are prohibited.
- Priority is given to foods high in fiber.
If you are on a diet for pregnant women with diabetes and are overweight, be sure to keep an eye on the increase. Get on the scale every week and periodically take urine and blood tests. Of course, don't forget your home blood glucose meter. People with diabetes should definitely have a device in their first aid kit.
Diet 9 table for pregnant women - menu
Monday
- Breakfast: vegetable salad, porridge, boiled egg.

- Second breakfast: kissel.
- Lunch: liver with puree, chicken broth, juice.
- Afternoon snack: peach.
- Dinner: chicken breast, cabbage salad with carrots.
- Late dinner: curdled milk.
Tuesday
- Breakfast: cottage cheese, oatmeal, vegetable juice.
- Second breakfast: kefir.
- Lunch: boiled salmon, buckwheat, lean cabbage soup.
- Snack: apple.
- Dinner: boiled egg, vinaigrette.
- Late supper: fermented baked milk.
Wednesday
- Breakfast: chicory drink, yogurt, barley porridge.
- Second breakfast: milk.
- Lunch: baked turkey, vegetarian borscht, fruit.
- Snack: orange.
- Dinner: steamed fish cake, vegetables.
- Late dinner: kefir.
Thursday
- Breakfast: millet porridge, cottage cheese, tea.
- Second breakfast: kefir.
- Lunch: boiled chicken, soup, compote.
- Snack: jelly.
- Dinner: cabbage rolls, boiled meat.
- Late dinner: curdled milk.
Friday
- Breakfast: boiled egg, vegetable salad.
- Second breakfast: vegetable juice.
- Lunch: boiled veal, stewed cabbage, soup.
- Snack: pear.
- Dinner: boiled fish, vegetable casserole.
- Late dinner: yogurt.
Saturday
- Breakfast: buckwheat porridge with yogurt.
- Second breakfast: kissel.
- Lunch: stewed rabbit, baked potatoes, fish soup.
- Snack: kefir.
- Dinner: barley, boiled fish.
- Late dinner: apple.
Sunday
- Breakfast: buckwheat, boiled egg.
- Second breakfast: an apple.

- Lunch: rice, steamed beef cutlets, mushroom soup.
- Afternoon snack: fermented baked milk.
- Dinner: mashed potatoes with fish, vegetables.
- Late dinner: curdled milk.
Consult your doctor regularly, do not hesitate to ask questions about pregnancy - there can be no trifles in such a topic. Try to follow a healthy lifestyle. Eliminate harmful foods from the diet and add healthy foods to the menu based on the recommendations of experts.
Diet for pregnant women to lose weight - tips from a nutritionist: video
youtube
Click to watch Nutrition for pregnant women is of particular importance. Before pregnancy, not many of us think about what is healthy and proper nutrition. From the very moment when a woman finds out about her “interesting position”, the realization comes that now you need to “eat for two”. And this does not mean at all that the menu for a pregnant woman should contain more calories and, accordingly, food. This means that proper nutrition during pregnancy leads to the correct development of the fetus in terms of anatomy and physiology.
This means that proper nutrition during pregnancy leads to the correct development of the fetus in terms of anatomy and physiology.
Numerous research data have shown that malnutrition during pregnancy can not only lead to anatomical underdevelopment of the fetus, but can also affect the future cognitive abilities, memory and other developmental features of the baby.
Surprisingly, malnutrition during pregnancy is one of the underlying factors in the development of obesity. Even at the intrauterine level, the child turns on a gene that ensures the maximum absorption of all nutrients from any, even a limited, amount of food. In the future, even if the child's nutrition is sufficient, his body will still try to "accumulate" calories "with a margin."
In addition, malnutrition of a pregnant woman can cause problems in the future:
• with the psychomotor development of the child;
• with the immune system;
• with the endocrine system;
• with metabolism;
• lead to impaired memory, attention and even behavior of the child.
For this and other reasons, a balanced diet is a very important component, along with the psycho-emotional state. The diet of pregnant women should be carefully thought out and conscious so that the child from the moment of conception to the very birth develops as harmoniously and correctly as possible.
Pregnancy menu: what will be useful?
The dietary menu for pregnant women should include a full range of vitamins, nutrients and minerals. In addition, such a menu should include immunonutrients and micronutrients. What is it and what is the significance of these substances in the formation of the fetus?
The main task of micronutrients is the direct protection of the fetus from any adverse external influences. These impacts include both environmental factors and exposure to various chemicals that are abundant in the environment. Micronutrients are involved in almost all biochemical processes in the body of the mother and fetus.
Immunonutrients are chemicals that have a direct impact on the formation of a child's immunity, the ability of his body to resist various bacterial, viral and other attacks of pathogens. These substances include amino acids, probiotics, nucleotides, fatty acids and some other elements.
Not only the lack of such elements in the future mother's diet is dangerous, but also their excess. For example, vitamin A is useful for the formation of the organs of vision in the fetus, but in large doses this vitamin can be toxic and lead to the development of intrauterine pathologies. For this reason, it is better to choose a menu for every day during pregnancy, taking into account the recommendations of a specialist leading your pregnancy. Any "amateur", in this case, it is better to exclude.
Early pregnancy nutrition
In the early stages of pregnancy, experts say, the energy needs of a woman practically do not change. It is not necessary at this time to drastically change your lifestyle and diet. If your diet was balanced, then you can stick to it throughout the first trimester.
If your diet was balanced, then you can stick to it throughout the first trimester.
Attention should be paid to ensure that the diet includes:
• fresh seasonal vegetables and fruits;
• greens;
• berries;
• horse crops.
Numerous studies have found that early pregnancy menus often exclude this particular food group. These products are recommended to be consumed raw or with minimal heat treatment. When choosing a diet, it is worth considering the history in terms of the presence of allergies in the mother and a predisposition to the development of diabetes.
The norm of sugar consumption per day in the menu for pregnant women is no more than 60 gr. If you cannot do without sweets, and you also need to avoid foods that cause allergic reactions, it is recommended to include foods such as:
• jams and jams without sugar;
• chocolate without sugar;
• dark chocolate with a cocoa content of at least 70%;
• peanut butter without sugar, etc.
Contrary to popular belief, such products have not only beneficial properties for the body, but also excellent organoleptic characteristics. Foods that are low in sugar or do not contain sugar at all have a taste and aroma that are in no way inferior to similar products with sugar.
Otherwise, the menu for pregnant women in the 1st trimester should not differ from the usual. For the formation of the fetus in the early stages, "building materials" in high doses are not needed. Thus, all the calories that a woman receives are spent at the same rate as usual. Increasing the amount of food and its calorie content can lead to overweight and will not benefit the child at all.
So, what should pregnant women eat in the early stages? The same as usual, including a large amount of fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs and berries. Vegetables and fruits should be typical for your region, you should not give preference to exotic and new products for you. Dishes for pregnant women should be as simple and familiar as possible, there is no need to invent something new. Eat what you want most, but don't overeat.
Eat what you want most, but don't overeat.
Proper nutrition for pregnant women in the 2nd trimester
In the second half of pregnancy, there is an active growth of the fetus, as well as various changes in the organs of the woman's reproductive system themselves. It is during this period that the need for nutrients and microelements for the normal physiological development of the fetus may increase.
A sample menu during pregnancy should be such that the pregnant woman receives all groups of the following foods:
• Dairy products, including whole milk and lactic acid products. The approximate volume of this product group should be 500 ml.
• Meat and poultry. The total amount of meat products should not be less than 170 gr. In the second trimester of pregnancy, 250 grams of any, but better - dietary, meat - this is the norm.
• Fish and seafood. It is enough to eat 70 grams daily.
• Cereals and bakery products in limited quantities. This group of products is simply necessary to prevent such problems in the gastrointestinal tract as constipation and bloating, which women often suffer from during the period of bearing a child.
This group of products is simply necessary to prevent such problems in the gastrointestinal tract as constipation and bloating, which women often suffer from during the period of bearing a child.
• Vegetables, fruits and berries, as well as juices. Total quantity - up to 1000
• Sugar and confectionery. Preference should be given to marmalade, marshmallows, marshmallows and jams on a natural basis, as well as products with low or no sugar content.
• Fats. Dishes for expectant mothers are best cooked in butter. The amount of vegetable fats should not exceed 15 g per day.
In the second trimester, a large load falls on the liver and kidneys. The menu for pregnant women in the 2nd trimester should exclude a large number of any salty foods, smoked meats and excess fluids. You need to focus on the fact that a woman should normally gain no more than 300 grams per week, and for the entire pregnancy - no more than 10-12 kg. If you are gaining more, then the diet should be reconsidered.
Nutrition during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester: menus and recommendations
The diet for pregnant women in the third trimester also has its own characteristics. The menu for the 3rd trimester should include products that stimulate lactation. First of all, these are dairy and lactic acid products, such as kefir, milk, fermented baked milk, cheese and cottage cheese.
Breakfast for pregnant women should be 30-40% of the total diet. You can have oatmeal, a few slices of cheese, yogurt and tea for breakfast. It is good to use herbal teas, which not only have high taste, but also have the following properties:
• anti-inflammatory;
• immunostimulating;
• normalizing metabolism;
• restoring the optimal water-salt balance and other useful properties.
Herbal tea may contain chamomile, rose hips, berries or fruits, calendula, string, twigs and leaves of useful plants. For a woman during childbearing, in general, green and herbal teas are much more beneficial than black teas and their blends.