Signs that your egg has been fertilized
Early symptoms and when to take a pregnancy test
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
A pregnancy test can detect pregnancy before a woman misses her period, but some may notice symptoms even earlier than this.
The first sign of pregnancy is often a missed period, which happens around 15 days past ovulation (DPO). Some women may notice symptoms as early as 5 DPO, although they won’t know for certain that they are pregnant until much later.
Early signs and symptoms include implantation bleeding or cramps, which can occur 5–6 days after the sperm fertilizes the egg. Other early symptoms include breast tenderness and mood changes.
In this article, we look at the early signs and symptoms of pregnancy and discuss how soon women can get an accurate reading from a pregnancy test.
Women who are trying to conceive are often particularly sensitive to what is happening with their bodies as they are looking for symptoms of pregnancy.
Some women share anecdotes about their pregnancy symptoms as early as 4–5 DPO, while others report not noticing any changes to their body until much later.
Although signs are possible this early on, they are unlikely to appear this soon in the majority of people. Many of the early symptoms, such as breast tenderness or fatigue, are instead linked to hormonal changes during ovulation or menstruation.
Implantation may already have taken place at 5 DPO, or it may be about to happen soon. As a result, depending on the time of conception, it is possible for women to feel some symptoms of pregnancy this early on.
Pregnancy tests are not accurate at 5 DPO, but some women later find that their early symptoms were indeed due to pregnancy.
At 5 DPO, if the sperm has reached and fertilized the egg, the cells within the newly formed zygote begin multiplying to create a lump of cells called a blastocyst.
These cells continue to multiply as the blastocyst makes its way down the fallopian tubes and into the uterus.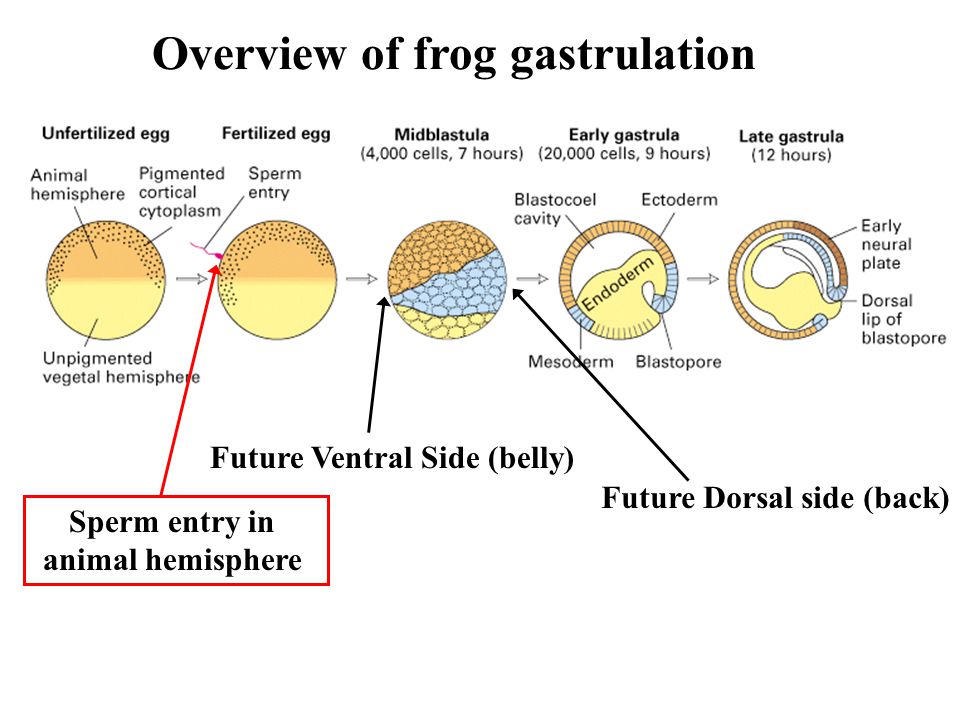
When the blastocyst reaches the uterine wall, it attaches itself to get access to nutrients through the blood. At 5 DPO, the blastocyst may either be traveling to the uterine wall or already connected to it.
If it is attached, the blastocyst has started its journey toward becoming a fetus, and pregnancy is underway.
The specific symptoms of pregnancy vary hugely from woman to woman. There is no “normal,” as each pregnancy is unique.
However, some of the earliest symptoms that women may notice tend to include the following:
Implantation cramping and bleeding
Women may experience cramps very early on in pregnancy. These are due to implantation, which is when the fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus.
Implantation cramps may occur a few days after ovulation, and many women say that they feel cramps around 5 DPO. These cramps may occur in the lower back, abdomen, or pelvis.
Around 25 percent of women may notice slight bleeding around the time of implantation. This is called implantation bleeding, and it tends to be lighter in color and flow than a menstrual bleed.
This is called implantation bleeding, and it tends to be lighter in color and flow than a menstrual bleed.
Raised basal body temperature
Many women keep track of their basal, or baseline, body temperature while trying to conceive because it changes throughout the menstrual cycle. The temperature increases after ovulation and may stay higher than usual until the period begins.
A basal body temperature that remains unusually high beyond the typical length of time may indicate pregnancy.
However, these signs are not unique to pregnancy and can be due to another hormonal or lifestyle factor.
Other early signs and when they happen
According to the National Institutes of Health, other early signs and symptoms of pregnancy may include:
- Breast tenderness. Hormone fluctuations may cause the breasts to swell, feel tender, and tingle or itch. Women may notice these symptoms as early as 1–2 weeks after conception.
- Fatigue.
 Changes in hormones, especially a steep rise in progesterone during the early stages of pregnancy, may make women feel sleepy throughout much of the day. Fatigue can occur as soon as 1 week after conception.
Changes in hormones, especially a steep rise in progesterone during the early stages of pregnancy, may make women feel sleepy throughout much of the day. Fatigue can occur as soon as 1 week after conception. - Headaches. Raised hormone levels may also trigger headaches early on in a pregnancy, although the stage at which they appear can vary.
- Food cravings. Many women find that they have very specific cravings during pregnancy, and these often begin early on.
- Food aversion. Just as women may crave particular tastes, they can begin to find other flavors repellant. The smell or taste of some foods may make them lose their appetite or feel nauseous.
- Urinating more frequently. The need to urinate more often is a sign of pregnancy in some women. It may be due to the increased levels of pregnancy hormones in the body, which increase blood flow in the kidneys and pelvic region.
- Mood swings.
 Significant mood swings may also be an early sign of pregnancy. Again, these can result from significant changes in hormone levels. Mood swings may begin a few weeks after conception.
Significant mood swings may also be an early sign of pregnancy. Again, these can result from significant changes in hormone levels. Mood swings may begin a few weeks after conception. - Morning sickness. Women may experience nausea and vomiting at any time throughout the day and as early as 2 weeks after conception.
Some women also report feeling dizzy or wobbly early on in pregnancy, often when they get up after lying down. This symptom may be due to changes in the blood vessels carrying oxygen to the brain.
Some women cannot explain any specific symptoms or changes in their body, but they intuitively feel that something is different.
They might describe it as not feeling like themselves or feeling as though they are suddenly always a step behind. This may be a sign of fatigue and an indication of hormonal changes.
As tempting as it can be to take pregnancy tests early and often, it may not be helpful. At 5 DPO, there is no reliably accurate way to check for pregnancy.
Most tests check for a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which the placenta makes. This hormone starts building up in the body after implantation.
While implantation may occur early on in some women’s menstrual cycles, it does take time for the hormone to build up to a level in the blood that will make it detectable in a blood or urine test.
According to the American Pregnancy Association, blood tests for hCG levels should be accurate 11 days after conception, while it would be best to wait 12–14 days before taking a urine test.
Taking a pregnancy test too early may give inaccurate results. It is possible that a pregnant woman could still get a negative result if the level of hCG has not yet built up in her body.
A false positive is also possible, which is a positive result on a pregnancy test when the woman is not pregnant. This can happen when a woman performs the test incorrectly, has a chemical pregnancy, or is taking certain hormonal medications as part of fertility treatment.
When a woman thinks that she might be pregnant, she may wish to note any signs and symptoms and discuss them with a doctor. It will only be a few more days until the level of the pregnancy hormone hCG in the blood or urine is sufficient to allow an accurate reading on a pregnancy test.
Pregnancy tests are available for purchase online.
*Please note that pregnancy tests are not accurate at 5 DPO.
Implantation Signs and Symptoms: Bleeding, Cramps, and More
Implantation is an essential early stage in conception, when cells attaches to the uterine wall. Signs of implantation include bleeding, cramps, discharge, and breast tenderness, and these can be early signs of pregnancy.
We don’t know if we should blame Hollywood or the false reality of social media, but the phrase “getting pregnant” gets tossed around as if it’s a simple one-step process. But there are actually a ton of tiny, amazing things that need to happen in your body to result in pregnancy.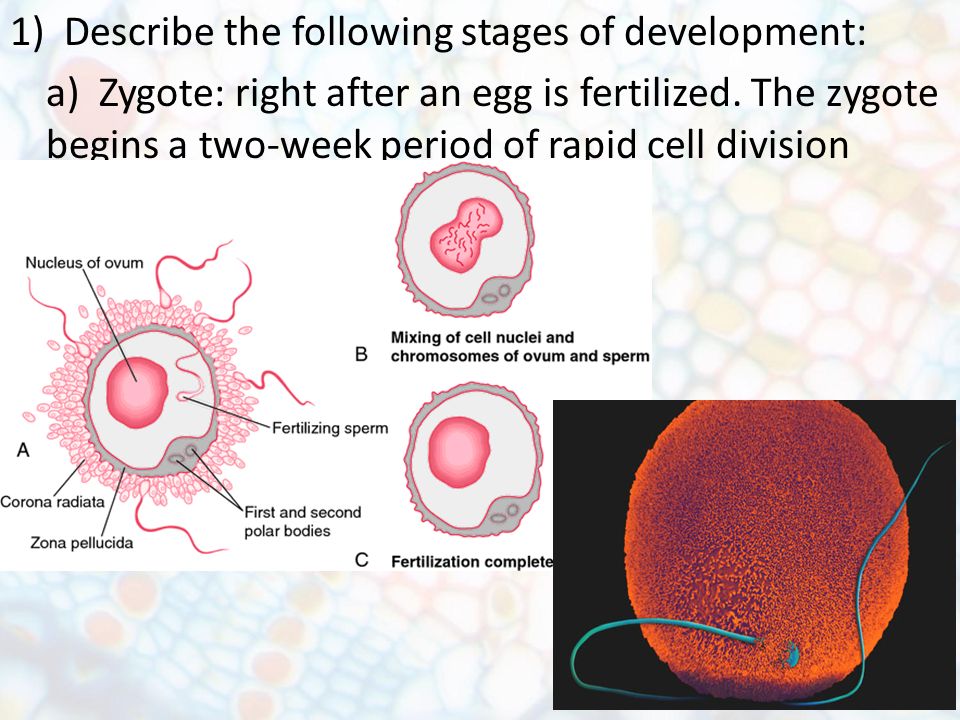
After the sperm and the egg join (conception), the combined cells start multiplying pretty quickly and moving through one of your fallopian tubes to your uterus. This cluster of rapidly growing cells is called a blastocyst.
Once in your uterus, this little bundle of cells has to attach, or implant, into your uterine wall. This step — known as implantation — triggers rising levels of all those fun pregnancy hormones (estrogen, progesterone, and hCG, or human chorionic gonadotropin).
If implantation doesn’t happen, your uterine lining is shed in your normal monthly period — a serious disappointment if you’re trying to get pregnant, but a reminder that your body is likely prepping for you to try again.
But if implantation does occur, your hormones — sometimes a nuisance, but doing their job — cause the placenta and the embryo (your future baby) to develop and your uterine lining to stay in place and support your pregnancy.
Implantation takes place anywhere between 6 and 12 days after you ovulate.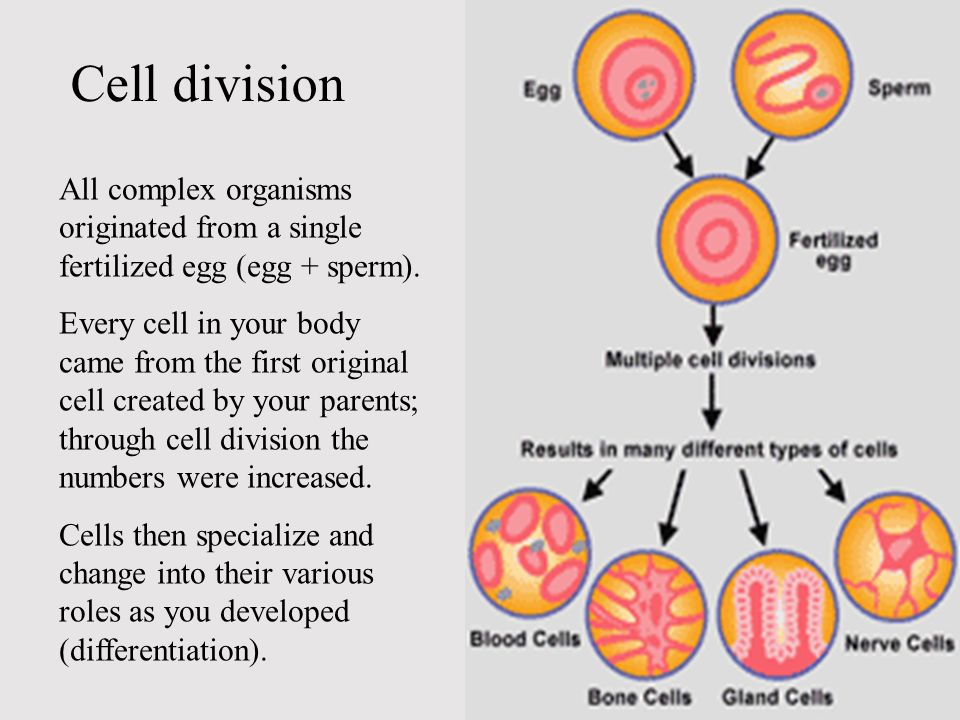 It most commonly occurs 8 to 9 days after conception. So the exact date of implantation can depend on when you ovulated, and whether conception occurred early or late in the ovulation window.
It most commonly occurs 8 to 9 days after conception. So the exact date of implantation can depend on when you ovulated, and whether conception occurred early or late in the ovulation window.
When you’re hoping to get pregnant, it’s natural to be very aware of your body and notice every change, no matter how small.
Assuming a lack of symptoms means you’re not pregnant? Not so fast. Keep in mind that most women experience no signs at all of conception or implantation — and are still pregnant! — though some women do experience signs of implantation.
Let’s explore some symptoms you might notice if implantation has occurred, but keep our little disclaimer in mind:
Having the symptoms listed below doesn’t necessarily mean you’re pregnant — and having no symptoms doesn’t necessarily mean you’re not.
Bleeding
It’s actually a little unclear how common implantation bleeding is. Some sources claim that one-third of all women who become pregnant experience implantation bleeding, but this actually isn’t backed by peer-reviewed research. (Something on the internet that may not be true? Say it ain’t so!)
(Something on the internet that may not be true? Say it ain’t so!)
Here’s what we can tell you. Up to 25 percent of women experience bleeding or spotting in the first trimester — and implantation is one cause of first trimester bleeding.
This bleeding can be confusing, because it may happen around the time that your regular period would start. Most commonly though, it will occur a few days to a week before you expect your menstrual period.
There are other differences that can help you determine whether you are experiencing implantation bleeding or your period:
- implantation bleeding is most likely to be light pink or brown (as opposed to the bright or dark red of your period)
- implantation bleeding is more like spotting than an actual flow of blood
This spotting may occur once, or last for a few hours, or even up to three days. You may notice some pink or brown discharge when you wipe or on your underwear, but you won’t need a full pad or tampon — possibly not for many months!
Cramps
It’s no secret that early pregnancy causes a rapid shift of hormones. More specifically, implantation is a trigger for the hormone surge — that’s why you can’t get that second pink line on a home pregnancy test until after implantation.
More specifically, implantation is a trigger for the hormone surge — that’s why you can’t get that second pink line on a home pregnancy test until after implantation.
And the changing hormonal tide can also cause cramping. Furthermore, there’s a lot going on in your uterus as the fertilized egg implants and begins to grow.
While there’s no research indicating that implantation itself causes cramps, some women do feel abdominal tenderness, lower back pain, or cramping around the time of implantation. This may seem like a mild version of how you feel before your period starts.
Discharge
Let’s talk about what’s going on down there.
If you’ve been monitoring your cervical mucus, good work, future mama! Being aware of what’s going on with your body can be empowering when trying to conceive.
You may notice some cervical mucus changes around the time of implantation.
During ovulation, your cervical mucus will be clear, stretchy, and slippery (sort of like egg whites). You probably already know this as your green light to get your baby dance on.
You probably already know this as your green light to get your baby dance on.
After implantation occurs, your mucus might have a thicker, “gummier” texture and be clear or white in color.
And in the days of early pregnancy, rising progesterone and estrogen may cause your mucus to become even thicker, more profuse, and white or yellow in color.
We hate to say it, though: Cervical mucus can be affected by a number of things (hormones, stress, intercourse, pregnancy, implantation bleeding or your period, etc.) and may not be a reliable indicator of whether or not implantation has occurred.
Start tracking your cervical mucus while you’re not pregnant, and a more useful indicator may be how different it is from your norm during each stage of your cycle.
Bloating
Rising progesterone (which happens in early pregnancy) slows your digestive system down. This can make you feel bloated. But as so many of us know, this feeling can be a really common symptom of your period, too. Want to know why? Progesterone also rises when your period is imminent. Thanks, hormones.
Want to know why? Progesterone also rises when your period is imminent. Thanks, hormones.
Tender breasts
After implantation, levels of hCG, estrogen, and progesterone all increase rapidly. This can cause your boobs to feel very sore. (These hormones sure are multitaskers!) While many women experience breast swelling or tenderness before their periods, this is likely to be more noticeable than usual in very early pregnancy.
Nausea
Ah, arguably the most famous of the early pregnancy symptoms: nausea, aka “morning sickness” (though it can happen at any time of day).
Increased levels of progesterone following implantation can make you feel nauseous. But again, this most commonly occurs around 4 or 5 weeks of pregnancy (about the time you miss your period).
Progesterone slows down your digestion, which can contribute to nausea. Rising hCG levels and a more sensitive sense of smell can make the problem worse — so now might be a good time to avoid cooking liver and onions.
Headaches
While they’re good and necessary for a successful pregnancy, those wildly rising hormone levels (particularly progesterone) can also give you headaches following implantation.
Mood swings
Find yourself content and happy one minute, and weeping at a commercial on TV the next? Or excited to see your partner in the evening and then biting their head off over nothing? You may be experiencing mood swings.
Estrogen and progesterone, as well as hCG, increase very quickly following implantation. This can make you feel “off” or moodier than usual.
Implantation dip
While this sounds like some kind of weird appetizer, “implantation dip” refers to a one-day decrease in your basal body temperature that can occur as a result of implantation.
If you’ve been tracking your basal body temperature (BBT) to help identify your most fertile days, you likely already have a log of your daily BBT over the course of a few months.
Typically, a woman’s temperature is lower before ovulation, and then increases, and then drops again before her period starts.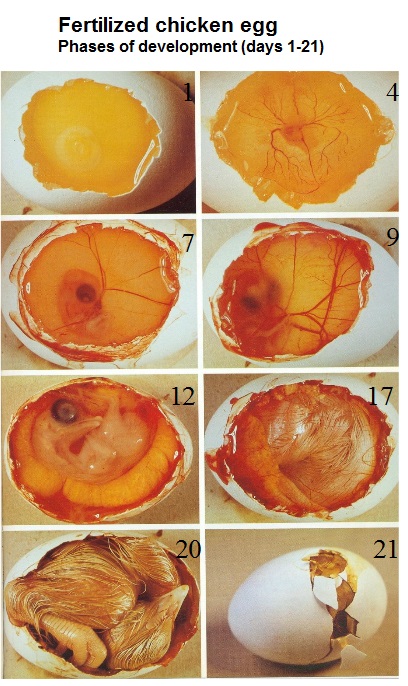 If you get pregnant, your temperature remains elevated.
If you get pregnant, your temperature remains elevated.
Simple, right? Except there’s something else.
Some women seem to experience a one-day drop in temperature around the time of implantation. This is different than the drop in temperature that means your period is coming — in the case of an imminent period, your temperature would stay low.
In the case of implantation dip, your temp drops for one day and then goes back up. It’s thought that this might be due to a rise in estrogen, but it’s not entirely understood.
According to an analysis of more than 100,000 BBT charts from the popular app Fertility Friend, 75 percent of pregnant women using the app did not experience an implantation dip. Additionally, a dip was noted on approximately 11 percent of the charts of women who were not pregnant.
But it’s pretty interesting that 23 percent of app users who turned out to be pregnant did have a so-called implantation dip.
This isn’t a peer-reviewed, medically conducted study.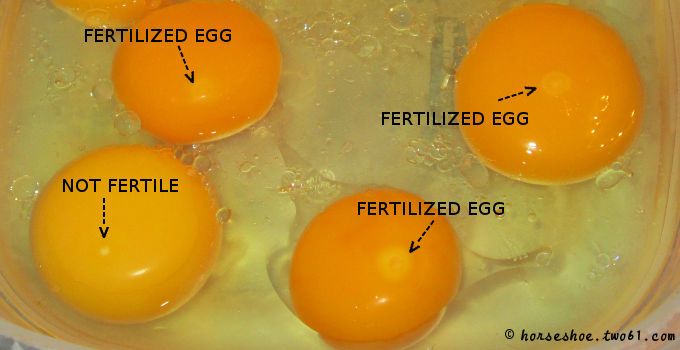 (We wish it were — when will researchers get on this?) But it may be helpful when it comes to interpreting your BBT chart. An implantation dip is more likely if you’re pregnant than if you’re not, but you can absolutely still be pregnant without a dip.
(We wish it were — when will researchers get on this?) But it may be helpful when it comes to interpreting your BBT chart. An implantation dip is more likely if you’re pregnant than if you’re not, but you can absolutely still be pregnant without a dip.
Trying to get pregnant can be both an exciting and nerve-wracking time. The days and months of your cycle can feel like forever when you’re waiting for a baby, and it’s easy to notice every tiny change in your body and wonder if it means you’re pregnant. This isn’t bad — knowledge is empowering — and in fact, it’s a very normal thing to do.
Some women do notice signs and symptoms that implantation has occurred. Signs may include light bleeding, cramping, nausea, bloating, sore breasts, headaches, mood swings, and possibly a change in basal body temperature.
But — and here’s the frustrating part — many of these signs are very similar to PMS. Additionally, most women experience no signs of implantation at all and are in fact pregnant.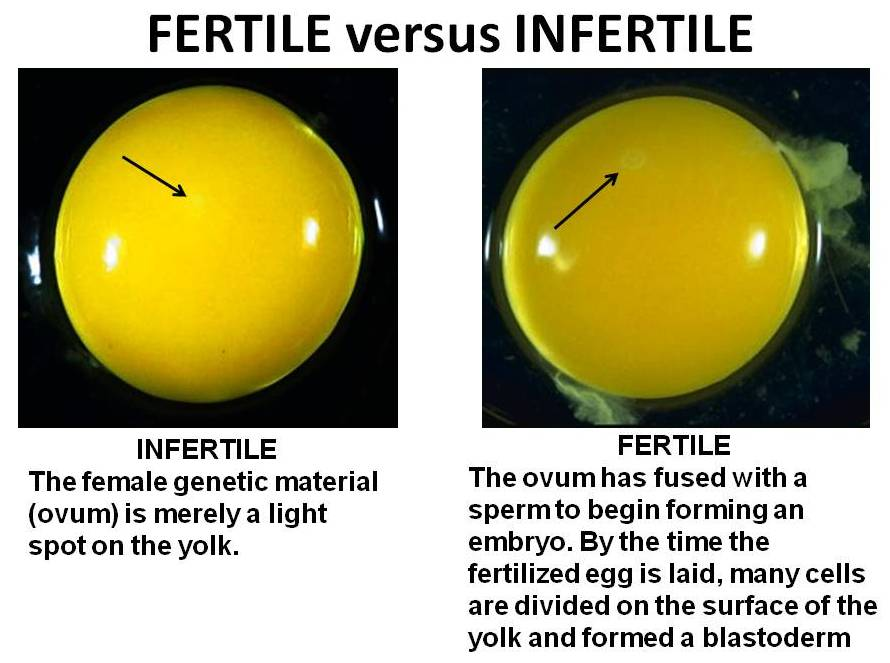
The best way to know for sure if you’re pregnant is to take an at-home pregnancy test or call your doctor. (Keep in mind that even if you have implantation symptoms, it takes a few days for enough hCG to build up to turn a test positive.)
The “two week wait” — the time between ovulation and when you can usually get a positive pregnancy test — can test all your patience. Keep paying attention to you and your body, find some activities you particularly enjoy to take your mind off the wait, and know that you’re going to be an amazing parent.
Signs and features of embryo implantation in the uterus | Reproduction and IVF Center
The birth of a new life is a truly miraculous event. After all, so many things must happen at the right time and in the right place for the fertilization of the egg to occur, that one can only be surprised at the foresight of nature. The embryo will face a very important test - its implantation (introduction) into the uterus. What it is, how and on what day it happens, what sensations it causes - all this needs to be known not only to pregnant women, but also to women who are just planning a pregnancy, including with the help of IVF.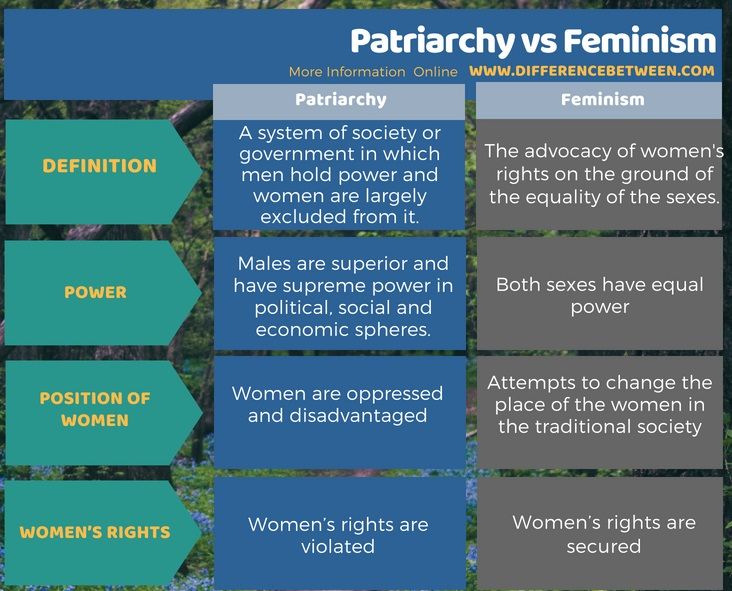
A fertilized egg, protected by a special membrane formed around it by a spermatozoon, begins its movement from the fallopian tubes without ceasing to divide. At the same time, she, now called morula, secretes a special enzyme trypsin, which signals the uterus to prepare a “landing site”. In order for the implantation of the embryo into the uterus to proceed safely, an intact and normally functioning endometrium is required, as well as a favorable hormonal background in the woman's body and, in particular, the production of progesterone in the required amount. This hormone will continue to maintain pregnancy until the placenta is formed.
On what day does the embryo implantation take place?
Approximately on the 3rd-4th day, the ovum reaches the uterine mucosa and, having got rid of the membrane, begins implantation, which lasts up to 40 hours. During this time, the embryo, or rather, the part called the trophoblast, is introduced into the endometrium, “attaches” to the capillaries and continues its development. In the future, the trophoblast will turn into a placenta and will protect and feed the baby, and the endometrium will provide it with all the necessary nutrients.
In the future, the trophoblast will turn into a placenta and will protect and feed the baby, and the endometrium will provide it with all the necessary nutrients.
In some cases, the journey of the egg from the fallopian tubes can last longer than the specified time - about 10 days. This phenomenon is called late implantation.
Signs of implantation
A pregnant woman does not experience any special sensations during embryo implantation. Only in rare cases, the expectant mother may notice irritability, tearfulness, discomfort in the lower abdomen, a metallic taste in the mouth and mild nausea. Doctors consider these signs not directly related to the implantation of the fetal egg itself and write it down to the account of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin). This hormone begins to be produced in the body of a pregnant woman just after the introduction of the embryo into the endometrium.
In some women, bleeding will be a sign that the embryo has implanted in the uterus. Unlike menstruation, they are very scarce, almost imperceptible to a woman and quickly passing. These secretions appear when the egg is introduced into the uterine mucosa and destroys the walls of the capillaries. But if they are plentiful and accompanied by pain, you should immediately consult a doctor, because miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis and some other serious diseases can manifest themselves in this way.
Unlike menstruation, they are very scarce, almost imperceptible to a woman and quickly passing. These secretions appear when the egg is introduced into the uterine mucosa and destroys the walls of the capillaries. But if they are plentiful and accompanied by pain, you should immediately consult a doctor, because miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis and some other serious diseases can manifest themselves in this way.
It is also possible to calculate the day of embryo implantation in the uterus by measuring basal body temperature. This will be evidenced by its slight decrease and subsequent increase. This method will reliably report the fact of pregnancy even in the case of late implantation. Basal temperature is measured in the morning in the rectum. And if the expectant mother, planning pregnancy in advance, measures the basal temperature every day, she can calculate both the day of ovulation and the implantation of the embryo in the uterus, which will indicate the successful onset of a long-awaited pregnancy.
Not every fertilized egg implants in the uterus
Sometimes implantation does not occur after fertilization. This happens, for example, with genetic abnormalities or the absence of an embryo in a fetal egg. We can say that natural selection is carried out in this way. Implantation of the embryo into the uterus may not occur even if the outer membrane of the morula is too strong or if there are violations in the endometrium itself. However, sometimes the “test” itself can go wrong and a healthy embryo fails to implant. Conversely, a fetal egg with genetic abnormalities will be able to easily attach to the endometrium.
Most often, such a genetic "marriage" will end in a spontaneous miscarriage in the early stages. It also happens that the fetal egg is not attached to the wall of the uterus, but, for example, in the fallopian tubes. Then they talk about an ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy, which will be manifested by bloody discharge, pain in the lower abdomen, general poor health. In no case should you ignore this condition and wait for everything to go away by itself. You should immediately consult a doctor to prevent dangerous complications.
In no case should you ignore this condition and wait for everything to go away by itself. You should immediately consult a doctor to prevent dangerous complications.
The fact of the introduction of the egg into the wall of the uterus and its normal development can be confirmed by a gynecologist during an examination, starting from the 5-7th week of pregnancy. The fact is that by this time the genitals undergo some changes that are detected by specialists during a vaginal examination. Also, ultrasound helps to make an accurate diagnosis, determining the heartbeat of the fetus, even in the early stages of pregnancy. Sometimes with late implantation, ultrasound will not determine the presence of an embryo in the uterus. In this case, the examination must be repeated after seven days, when the fetal egg will most likely be noticeable.
Implantation of an embryo during IVF
When for some reason it is not possible to conceive or bear a child for a long time, in vitro fertilization (IVF) is possible, which has recently become increasingly popular. However, even this method does not always work, and after artificial insemination, pregnancy failure is possible. This can happen for many reasons: genetic abnormalities of the embryo, hormonal disorders of the mother, her age and general health. But women who dream of a child should not despair. In the clinic "IVF Center" in Petrozavodsk, an artificial implantation of the embryo into the uterus is performed even with unsuccessful attempts in other clinics.
However, even this method does not always work, and after artificial insemination, pregnancy failure is possible. This can happen for many reasons: genetic abnormalities of the embryo, hormonal disorders of the mother, her age and general health. But women who dream of a child should not despair. In the clinic "IVF Center" in Petrozavodsk, an artificial implantation of the embryo into the uterus is performed even with unsuccessful attempts in other clinics.
It should be understood that IVF is a whole complex of examinations and treatment aimed at successful IVF - implantation of the embryo into the uterus and further pregnancy.
In vitro fertilization is performed in several stages:
- Ovulation stimulation with drugs
- Egg and sperm retrieval
- Selection of the required "material"
- Artificial insemination
- Embryo transfer and implantation in the uterine cavity.
An artificially implanted embryo needs some time to adapt to the new environment, so the day of implantation will occur later than with natural insemination. To increase the likelihood of a successful "transplantation", the clinic's specialists implant two embryos. In the future, it is necessary to create favorable conditions for the expectant mother in order to protect her from spontaneous miscarriage and other complications. A woman should avoid excessive physical activity, stress. You need to get more rest, eat healthy food and avoid contact with infectious patients. Also, in the early stages, you can not take a hot shower, exclude sexual intercourse, do not overcool and spend more time in the fresh air, but without a long walk.
To increase the likelihood of a successful "transplantation", the clinic's specialists implant two embryos. In the future, it is necessary to create favorable conditions for the expectant mother in order to protect her from spontaneous miscarriage and other complications. A woman should avoid excessive physical activity, stress. You need to get more rest, eat healthy food and avoid contact with infectious patients. Also, in the early stages, you can not take a hot shower, exclude sexual intercourse, do not overcool and spend more time in the fresh air, but without a long walk.
The sensations during implantation and during pregnancy itself do not differ from those during natural insemination. Their difference lies only in the greater susceptibility to various complications of those women who have undergone artificial insemination. Prenatal infections, placental insufficiency, detection of congenital malformations, immune conflict between mother and child can lie in wait for pregnant women after IVF.
The management of pregnant women after in vitro fertilization is more stringent and includes receiving hormonal drugs in larger than usual doses; enhanced vitamin therapy; taking metabolic drugs; prevention and timely treatment of infectious diseases and increased attention of the attending physician. But even with such intensive therapy, there is a risk of complications and miscarriage. Often the consequence of artificial insemination is multiple pregnancy, which can also become a problem for the mother. However, with the competent management of the clinic's specialists, strict adherence to their recommendations and a positive attitude, pregnancy after IVF will proceed quite well and will be resolved by the birth of a long-awaited baby.
If you have any problems with childbearing, you can contact the IVF Center in Petrozavodsk. Our specialists will determine the reason for the absence of the desired pregnancy and select the best treatment for you. You will surely be able to experience the joy of motherhood!
Signs of ovulation
A Harvard University study found that women who drank three glasses of apple juice every day were 15% more likely to develop type II diabetes. In the case of orange juice, the likelihood of illness increases by 25%, plus there is a risk of obesity.
In the case of orange juice, the likelihood of illness increases by 25%, plus there is a risk of obesity.
OVULATION (from lat. ovum - egg) - release of a mature egg capable of fertilization from the ovarian follicle into the abdominal cavity; stage of the menstrual cycle (ovarian cycle). Ovulation in women of childbearing age occurs periodically (every 21-35 days). Periodicity ovulation is regulated by neurohumoral mechanisms, mainly gonadotropic hormones of the anterior pituitary gland and ovarian follicular hormone. Ovulation contributes to the accumulation of follicular fluid and thinning of the ovarian tissue located above the protruding pole of the follicle. Constant rhythm for every woman ovulation undergoes changes within 3 months after an abortion, within a year after childbirth, and also after 40 years, when the body is preparing for the premenopausal period. Stops ovulation with the onset of pregnancy and after the extinction of menstrual function. Establishing the term ovulation is important when choosing the most effective time for fertilization, artificial insemination and in vitro fertilization.
Establishing the term ovulation is important when choosing the most effective time for fertilization, artificial insemination and in vitro fertilization.
Signs of ovulation
Subjective signs of ovulation may be short-term pain in the lower abdomen. objective signs of ovulation are an increase in mucous discharge from the vagina and a decrease in rectal (basal) temperature on the day of ovulation with its increase the next day, an increase in the content of progesterone in the blood plasma, etc. Violation of ovulation is due to dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system and can be caused by inflammation of the genitals, dysfunction of the adrenal cortex or thyroid gland, systemic diseases, tumors of the pituitary and hypothalamus, stressful situations. Absence ovulation at childbearing age (anovulation) is manifested by a violation of the rhythm of menstruation by the type of oligomenorrhea (menstruation lasting 1-2 days), amenorrhea, dysfunctional uterine bleeding.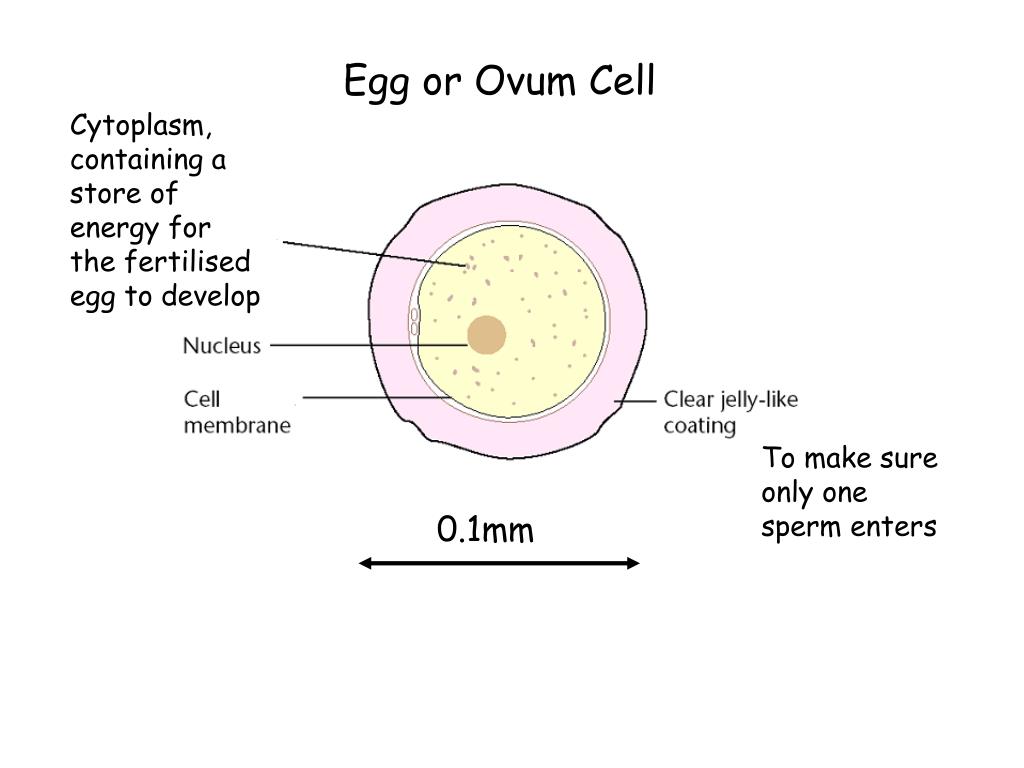 Lack of ovulation (anovulation) is always the cause of a woman's infertility. Methods for restoring ovulation are determined by the cause that caused anovulation, and require an appointment with a gynecologist and special treatment.
Lack of ovulation (anovulation) is always the cause of a woman's infertility. Methods for restoring ovulation are determined by the cause that caused anovulation, and require an appointment with a gynecologist and special treatment.
Some women experience the peak of sexual excitability in 9 days0064 ovulation . However, the use of a physiological method of contraception against pregnancy, based on sexual abstinence during ovulation , is especially difficult for young spouses, whose frequency of sexual intercourse reaches a fairly high level. In addition, with strong love excitement and nervous stress, additional ovulation can occur (especially with episodic, irregular intercourse), and then not one, but two eggs mature in one menstrual cycle. This should be remembered when choosing one or another method of contraception.
As soon as every healthy girl aged 11-15 starts menstruating, which is an indicator of her body's readiness for childbearing, then there are problems associated with counting the days of the menstrual cycle and the legitimate question why menstruation does not occur, or vice versa, why does not occur long-awaited pregnancy.
 This makes a woman think and wait all the time, be in the dark about what happens to her every month. And so every month for decades
This makes a woman think and wait all the time, be in the dark about what happens to her every month. And so every month for decades Length of menstruation and cycle
Ideal menstruation lasts 3-5 days and repeats every 28 days. However, for some women, this cycle takes 19 days or even less, while for others it lasts from 35 to 45 days, which is a feature of their body, and not a violation of menstrual function. The duration of menstruation also, depending on the organism, can vary within a week. All this should not cause alarm in a woman, but a delay of more than two months, called opsometry or more than six months - amenorrhea, should alert the woman and make sure to find out the cause with a gynecologist.
Length of menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a complex physiological process that continues in women up to 45-55 years. It is regulated by the so-called sex centers located in the middle part of the diencephalon - the hypothalamus.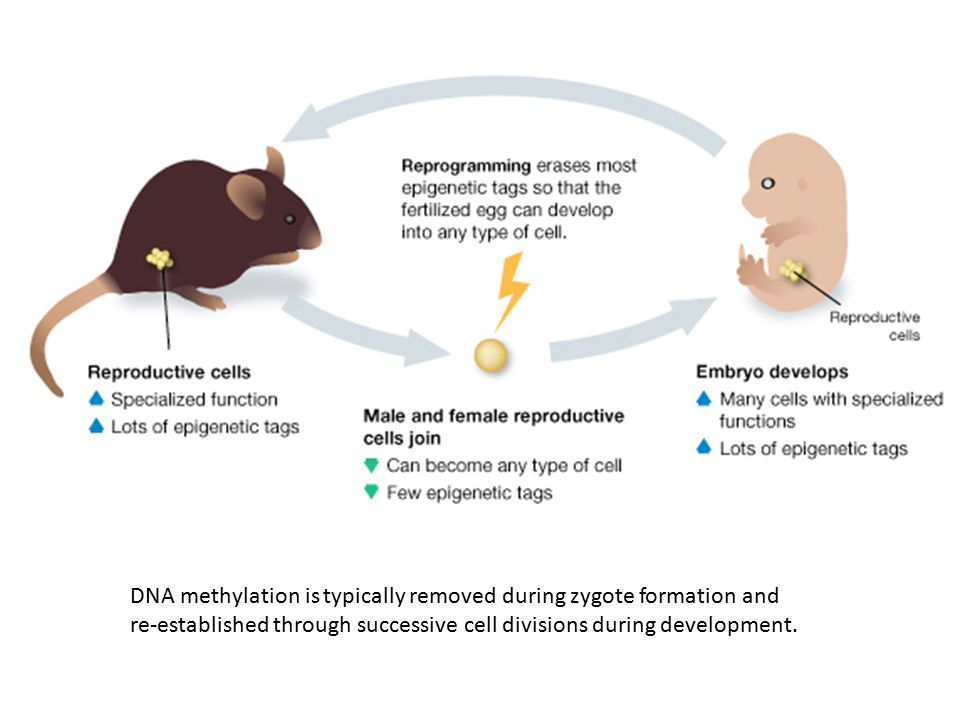 The changes that occur during the menstrual cycle are most pronounced in the uterus and ovaries. In the ovary, under the influence of hormones produced by the ovarian follicles, partly by the adrenal cortex and testes, the main follicle, which contains the egg, grows and matures. The mature follicle ruptures and the egg, together with the follicular fluid, enters the abdominal cavity, and then into the fallopian tube. The process of rupture of the follicle and the release of a mature (suitable for fertilization) egg from its cavity is called ovulation , which, with a 28-day cycle, occurs most often between the 13th and 15th days.
The changes that occur during the menstrual cycle are most pronounced in the uterus and ovaries. In the ovary, under the influence of hormones produced by the ovarian follicles, partly by the adrenal cortex and testes, the main follicle, which contains the egg, grows and matures. The mature follicle ruptures and the egg, together with the follicular fluid, enters the abdominal cavity, and then into the fallopian tube. The process of rupture of the follicle and the release of a mature (suitable for fertilization) egg from its cavity is called ovulation , which, with a 28-day cycle, occurs most often between the 13th and 15th days.
Corpus luteum, estrogen, progesterone
A corpus luteum forms at the site of the ruptured follicle. These morphological changes in the ovary are accompanied by the release of sex steroid hormones - estrogens and progesterone. Estrogens are secreted by the maturing follicle, and progesterone by the corpus luteum.
The release of estrogen has two maxima - during ovulation and during the period of maximum activity of the corpus luteum. So, for example, if the normal estrogen content is about 10 µg/l, then during ovulation it is about 50 µg/l, and during pregnancy, especially towards the end of it, the estrogen content in the blood increases to 70-80 µg/l per due to a sharp increase in the biosynthesis of estrogens in the placenta.
Together with progesterone, estrogens promote the implantation (introduction) of a fertilized egg, maintain pregnancy and promote childbirth. Estrogens play an important role in the regulation of many biochemical processes, are involved in carbohydrate metabolism, lipid distribution, stimulate the synthesis of amino acids, nucleic acids and proteins. Estrogens contribute to the deposition of calcium in bone tissue, delay the release of sodium, potassium, phosphorus and water from the body, that is, increase their concentration both in the blood and in electrolytes (urine, saliva, nasal secretions, tears) of the body.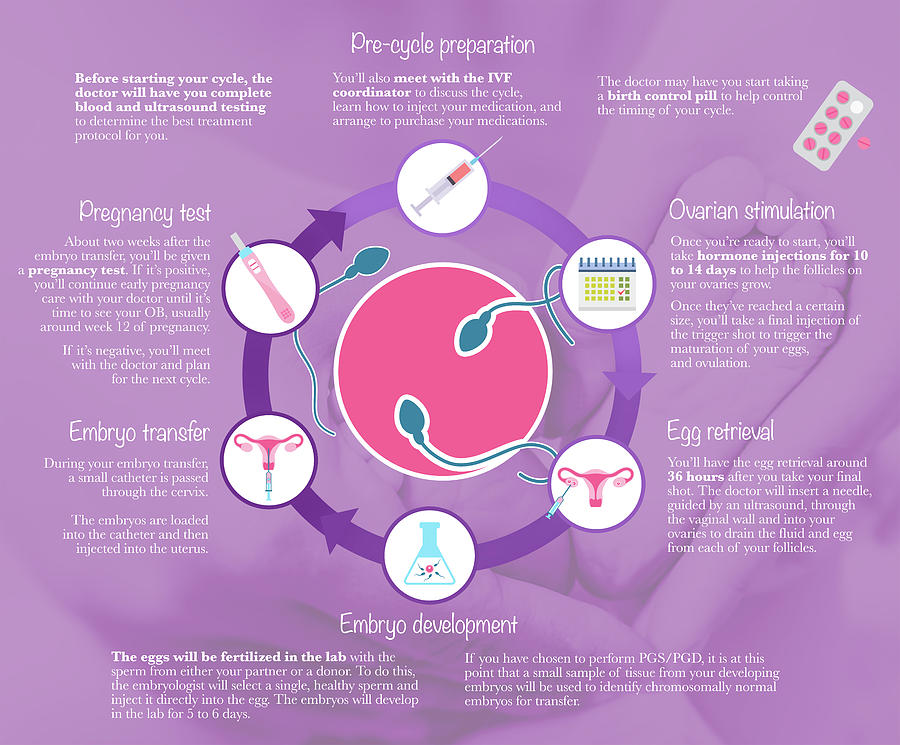
The secretion of estrogens is controlled by the anterior pituitary gland and its genadotropic hormones: follicle-stimulating (FSH) and luteinizing (LH).
Under the influence of estrogens in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, called folliculin, regeneration occurs in the uterus, that is, the restoration and growth of its mucous membrane - the endometrium, the growth of glands that stretch in length and become convoluted. The mucous membrane of the uterus thickens 4-5 times. In the glands of the cervix, the secretion of mucous secretion increases, the cervical canal expands, and becomes easily passable for spermatozoa. In the mammary glands, the epithelium grows inside the milk ducts.
In the second phase, called luteal (from the Latin word luteus - yellow), under the influence of progesterone, the intensity of metabolic processes in the body decreases. The growth of the mucous membrane of the body of the uterus stops, it becomes loose, edematous, a secret appears in the glands, which creates favorable conditions for attaching a fertilized egg to the mucous membrane and developing the embryo.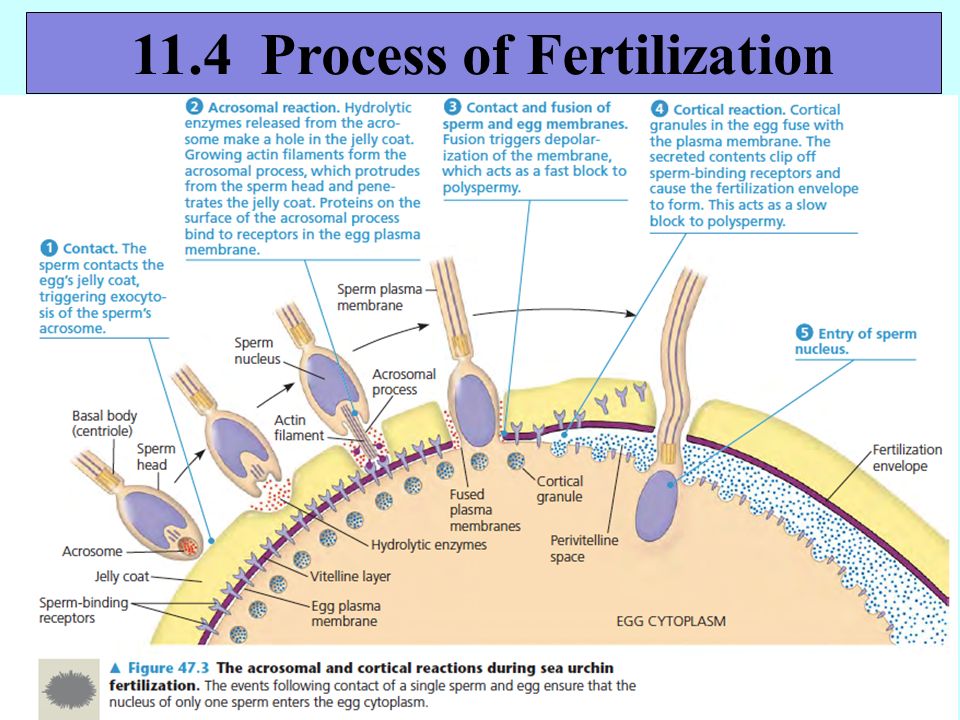 The glands stop secreting mucus, the cervical canal closes. In the mammary glands, from the overgrown epithelium of the end sections of the milk ducts, alveoli arise, capable of producing and secreting milk.
The glands stop secreting mucus, the cervical canal closes. In the mammary glands, from the overgrown epithelium of the end sections of the milk ducts, alveoli arise, capable of producing and secreting milk.
If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum dies, the functional layer of the endometrium is rejected, and menstruation occurs. Monthly bleeding varies from three to seven days, the amount of blood lost is from 40 to 150 g.
It should be noted that different women have a noticeable difference in the timing of ovulation . And even for the same woman, the exact timing of the onset fluctuates in different months. In some women, cycles are characterized by exceptional irregularity. In other cases, cycles may be longer or shorter than the average - 14 days. In rare cases, it happens that in women with a very short cycle ovulation occurs around the end of the period of menstrual bleeding, but still, in most cases, ovulation occurs quite regularly.
If, for one reason or another, ovulation does not occur, the endometrial layer in the uterus is thrown out during menstruation. If the fusion of the egg and sperm has occurred, then the cytoplasm of the egg begins to vibrate very strongly, as if the egg is experiencing an orgasm. Sperm penetration is the final stages of egg maturation. All that remains of a spermatozoon is its nucleus, where 23 chromosomes are densely packed (half the set of a normal cell). The sperm nucleus is now rapidly approaching the egg nucleus, which also contains 23 chromosomes. The two cores are slowly touching. Their shells dissolve and they merge, as a result of which they are divided into pairs and form 46 chromosomes. Of the 23 chromosomes of the sperm, 22 are completely analogous to the chromosomes of the egg. They determine all the physical characteristics of a person except gender. In the remaining pair from the egg there is always an X chromosome, and from the sperm there can be an X or Y chromosome. Thus, if there are 2 XX chromosomes in this set, then a girl will be born, if XY, then a boy.
Thus, if there are 2 XX chromosomes in this set, then a girl will be born, if XY, then a boy.
Studies conducted at the National Institute of Environmental Medical Problems (North Carolina) showed that not only the actual conception of a child, but also its gender depends on the time of conception in relation to the time of ovulation .
The probability of conception is maximum on day of ovulation and is estimated at about 33%. A high probability is also noted on the day before ovulation - 31%, two days before it - 27%. Five days before ovulation the probability of conception is estimated to be 10% four days before ovulation - 14% and three days - 16%. Six days before ovulation and the day after ovulation, the probability of conception during sexual intercourse is very small.
Considering that the average “lifespan” of spermatozoa is 2-3 days (in rare cases it reaches 5-7 days), and the female egg remains viable for about 12-24 hours, then the maximum duration of the “dangerous” period is 6- 9days and the “dangerous” period corresponds to the phase of slow rise (6-7 days) and rapid decline (1-2 days) before and after the day of ovulation , respectively.