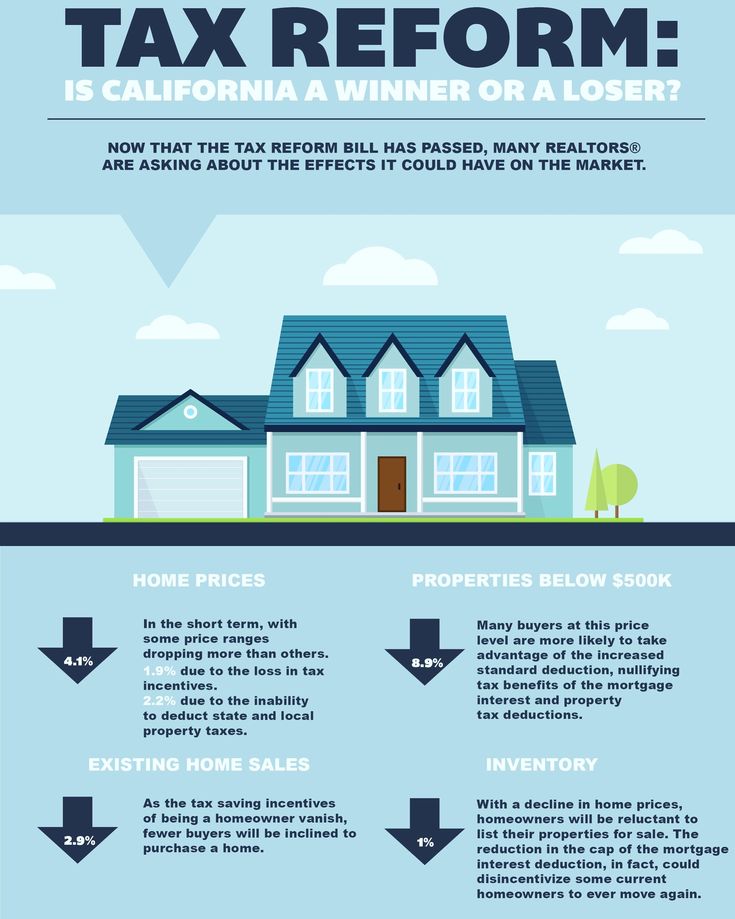
What does abort a baby mean
Abortion | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
beginning of content8-minute read
Listen
What is an abortion?
An abortion (or termination) is the medical process of ending a pregnancy so it does not result in the birth of a baby. Depending on how many weeks you have been pregnant, the pregnancy can be ended by taking medication or by having a surgical procedure.
An abortion is not the same as a miscarriage, where the pregnancy ends without medical intervention (although medical treatment may be needed after a miscarriage).
Why do women have abortions?
There are many reasons why a woman might choose to have an abortion. Deciding to have an abortion is a deeply personal choice and in many cases, a very difficult decision to make.
For example, the pregnancy may be unplanned and the woman’s personal circumstances might make it difficult or impossible to raise a child. These reasons could include financial considerations, being in an abusive relationship, where assault is involved, not being the right time, or the woman may not want to have a baby.
Some women may discover there is something wrong with their baby or that continuing with the pregnancy may put their own health at risk.
Whatever the reason a woman decides to terminate a pregnancy, the choice is hers to make.
When can I have an abortion?
There are 2 different types of abortion that you could have based on your stage of pregnancy. The earlier you talk to your doctor or clinic about having an abortion, the more choices you will have.
Surgical abortion
The most common type of abortion is a surgical procedure called a ‘suction curette’. This involves removing of the lining and the contents of the uterus by applying gentle suction to the inside of the uterus with a small plastic tube. Surgical abortion is a safe and straightforward day-surgery procedure most often performed in the first trimester (up to 14 weeks’ gestation).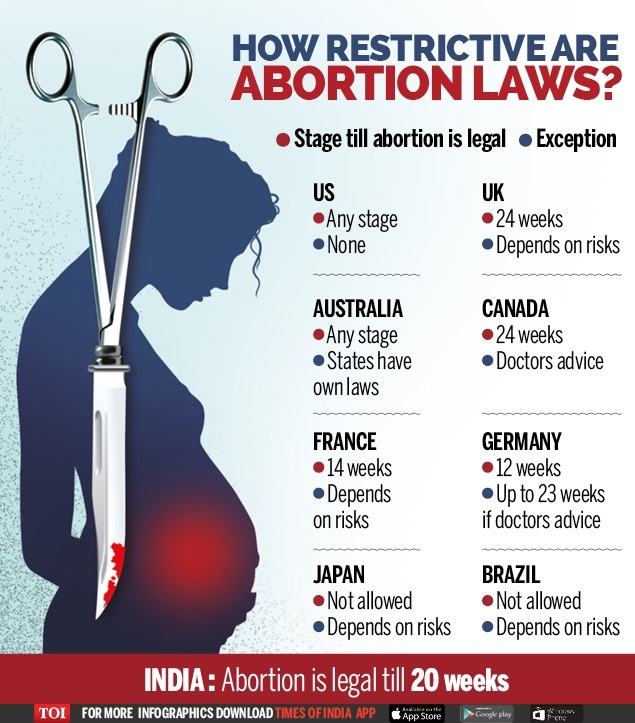 The procedure takes about 15 minutes, but you will need to be at the clinic or hospital for about 4 hours.
The procedure takes about 15 minutes, but you will need to be at the clinic or hospital for about 4 hours.
Medical abortion
A low-risk alternative to surgery used for terminating pregnancies earlier than 9 weeks (depending on the clinic) is a medication called mifepristone (RU486). It is sometimes called ‘the abortion pill’ and is the most widely known medication used for this procedure. Medical abortion is a 2-stage process. The first stage involves taking a tablet that blocks the hormone necessary for the pregnancy to continue. This is followed 36 to 48 hours later by a second medication that causes the contents of the uterus to be expelled.
What is a 'late-term' abortion?
A late-term or second trimester abortion is when a pregnancy is terminated after 14 weeks. The process is similar to a surgical abortion, but instead of suction, instruments are used to remove the fetus.
You may need to travel interstate to have a late-term abortion since states and territories have different laws on how late an abortion can be performed.
Is abortion legal in Australia?
Abortion law in Australia varies across states and territories. Abortion is legal in all states and territories under certain circumstances and when it is done by a registered medical professional.
In most states and territories, it is illegal to protest within 150m of a clinic or service that provides abortions.
ACT
Abortion is legal and must be performed by a medical professional.
New South Wales
Abortions can be performed at up to 22 weeks' gestation. After that, 2 doctors must approve the procedure.
Northern Territory
One doctor can approve and perform an abortion at up to 14 weeks. Between 14 and 23 weeks, a second doctor also needs to approve. After 23 weeks, an abortion can only be performed if the life of the woman is at risk.
Queensland
Abortions can be performed at up to 22 weeks. After 22 weeks, 2 doctors must approve the procedure.
South Australia
Abortions can be performed at up to 22 weeks and 6 days. Abortions performed after this time, must be approved by 2 doctors and only if they agree that the health or mental wellbeing of the woman is at risk, to save another fetus (multiple pregnancy) or the fetus has a serious abnormality.
Abortions performed after this time, must be approved by 2 doctors and only if they agree that the health or mental wellbeing of the woman is at risk, to save another fetus (multiple pregnancy) or the fetus has a serious abnormality.
Tasmania
Abortions can be performed at up to 16 weeks. After 16 weeks, 2 doctors must approve the procedure.
Victoria
Abortions can be performed at up to 24 weeks. After 24 weeks, 2 doctors must approve the procedure.
Western Australia
Abortions can be performed at up to 20 weeks. Termination after 20 weeks is very restricted.
How much does an abortion cost?
The cost of an abortion will depend on whether it is a medical or surgical abortion, how far along you are and whether you are using a public service or a private clinic.
Not all GPs can prescribe a medical abortion and not all chemists stock the medication required. Depending on where you live, you may need to go to an approved clinic or a hospital.
Hospitals and GPs may offer bulk billing or they may be partially covered by Medicare. For a private clinic, the consultation can cost several hundred dollars. The medication costs around $50, less if you have a healthcare card.
Surgical abortions cost around the same as a medical abortion, but this cost can vary depending on how many weeks along you are and whether you are a public or private patient.
Apart from the cost of the actual procedure, many women may need to travel to get an abortion. Termination services are not easily accessible in rural and remote areas and depending on the law in your state or territory, you may need to travel interstate to have an abortion.
Some clinics can offer medical abortion consultations via telehealth video call. Speak to your GP or clinic to find out if this option is available to you.
Can I get counselling before an abortion?
Yes, you can. Counselling is an important part of the decision making process when you are considering whether to have an abortion. You should understand all of your options and make the decision that is right for you.
You should understand all of your options and make the decision that is right for you.
Your doctor or clinic will talk to you about your choices and offer support services so you can talk to someone.
If you can, talk to family and friends, but you shouldn’t allow anyone else to pressure you. You should also make sure you seek advice and support from counselling services that will give you unbiased information and won’t try to talk you into making a decision that is not right for you.
When can I start contraception after an abortion?
After you’ve had an abortion, your normal menstrual cycle will resume. This means it’s possible for you to fall pregnant again. You should talk to your doctor or clinic about the best type of contraception to use.
How do I find an abortion clinic?
You can contact the Family Planning clinic in your state or territory. You can also use the Find a Health service or call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 to get help finding a service near you.
How is the 'morning after' pill different from an abortion?
Emergency contraception, sometimes called the ‘morning after pill’, can be taken up to 5 days after having unprotected sex. Unlike an abortion which ends a pregnancy, emergency contraception prevents a pregnancy from happening.
There are 2 types of medication available to prevent pregnancy in Australia. The levonorgestrel pill can be taken up to 72 hours (3 days) after unprotected sex. Ulipristal acetate (UPA) can be taken up to 120 hours (5 days) after unprotected sex. Both are available over the counter from a pharmacist without a prescription.
Australia has safe and supportive abortion and family planning clinics that can provide reliable advice.
To find these clinics, and for reliable, unbiased information about abortion in your state or territory, contact:
- Family Planning Alliance Australia
- MSI Australia
- Children by Choice (Queensland)
- 1800MyOptions (Victoria)
- NSW Pregnancy Options Helpline (1800 131 231)
You can also discuss your options with your doctor, or call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 to speak with a maternal child health nurse for information and support.
Sources:
Children By Choice (Australian abortion law and practice), NSW Health (Pregnancy options), Family Planning NSW (Unplanned pregnancy: Abortion), MSI Australia (Medical abortion), MSI Australia (Surgical abortion)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: March 2021
Back To Top
Related pages
- Making decisions about unplanned pregnancies
- Abortion - surgical and medical options
- Counselling before and after an abortion
Need more information?
Abortion - surgical and medical options
An abortion is when a pregnancy is terminated. If you decide to have an abortion, there are 2 options available - surgical or medical.
If you decide to have an abortion, there are 2 options available - surgical or medical.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Abortion Australia | MSI Australia
Abortion in Australia, also known as termination of pregnancy, is a safe and standard medical procedure.
Read more on MSI Australia website
Counselling before and after an abortion
Counselling before and after an abortion can help you to feel supported and empowered to make the right decision for you.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Medication Abortion Clinic Melbourne | Medication Abortion Cost | Abortion Melbourne support - Sexual Health Victoria
FPV provide medication abortion services, advice and support within their Melbourne CBD and Box Hill clinics
Read more on Sexual Health Victoria website
Abortion Counseling Service | MSI Australia
MSI Australia provides free decision-based abortion counseling services to women seeking a termination of pregnancy.
Read more on MSI Australia website
Unplanned Pregnancy: Abortion | Family Planning NSW
This fact sheet is for women who are experiencing an unplanned pregnancy and want information about abortion. Abortion is when a pregnancy is terminated (ended).
Read more on Family Planning Australia website
Abortion | Women's Health Victoria
Read more on Women's Health Victoria website
Episode #28: Abortion - Sexual Health Victoria
Sexual Health Victoria (formally Family Planning Victoria) focuses on reproductive and sexual health care, education and advocacy. Our vision is to improve ever
Read more on Sexual Health Victoria website
Teleabortion | MSI Australia
Teleabortion is a safe and private way to have a medical abortion, in the privacy of your own home with the support of registered nurses over the phone.
Read more on MSI Australia website
The Differences Between MTOP and STOP | MSI Australia
The decision to have an abortion can be challenging, and choosing which type of procedure (MTOP or STOP) can add to the confusion. Read on for more info.
Read more on MSI Australia website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKHealthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Abortion | Definition, Procedure, Laws, & Facts
- Key People:
- Harry A. Blackmun Norma McCorvey Warren E. Burger Madame Restell
- Related Topics:
- dilatation and curettage early abortion late abortion hysterotomy dilatation and evacuation
See all related content →
Mar. 10, 2023, 8:37 PM ET (AP)
Texas women sued for wrongful death after aiding in abortion
Three women in Texas are being sued for wrongful death by a man who claims they helped his now-ex-wife obtain medication for an abortion
Mar. 10, 2023, 11:19 AM ET (AP)
10, 2023, 11:19 AM ET (AP)
Florida abortion ban could have impact beyond the state
A stricter abortion ban under consideration for Florida could have practical implications for women throughout the South and political implications for Gov. Ron DeSantis
Mar. 9, 2023, 4:16 PM ET (AP)
Missouri voters could restore abortion rights in 2024
Missouri voters could decide whether to restore abortion rights if proposed constitutional amendments make it on the 2024 ballot
Mar. 8, 2023, 7:57 PM ET (AP)
California to end Walgreens contract after abortion dispute
California Gov. Gavin Newsom is withdrawing a $54 million contract with Walgreens
Mar. 7, 2023, 6:01 PM ET (AP)
Women sue Texas over abortion ban, say it risked their lives
Five women who said they were denied abortions even when pregnancy endangered their lives are suing Texas over its abortion ban
Top Questions
What is an abortion?
An abortion is the expulsion of a fetus from the uterus before it has reached the stage of viability (in human beings, usually about the 20th week of gestation).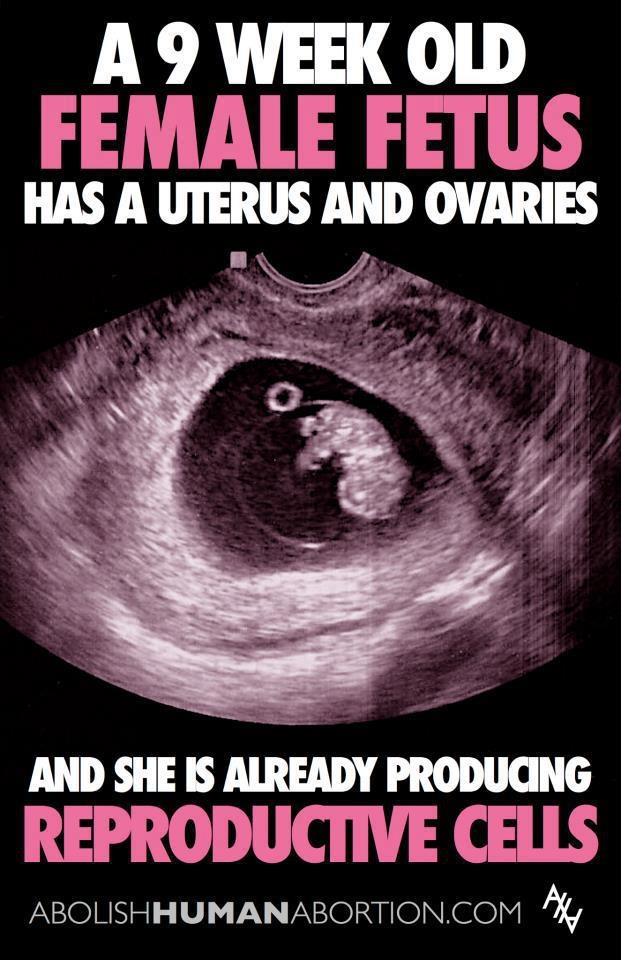
Should abortion be legal?
Whether abortion should be legal in the U.S. is heavily debated. Some argue that abortion is a safe medical procedure that protects lives and that bans endanger healthcare for those not seeking abortions. While others argue that abortion is murder and legalizing the procedure promotes a culture in which life is disposable. For more on the abortion debate ProCon.org.
Summary
Read a brief summary of this topic
abortion, the expulsion of a fetus from the uterus before it has reached the stage of viability (in human beings, usually about the 20th week of gestation). An abortion may occur spontaneously, in which case it is also called a miscarriage, or it may be brought on purposefully, in which case it is often called an induced abortion.
Spontaneous abortions, or miscarriages, occur for many reasons, including disease, trauma, genetic defect, or biochemical incompatibility of mother and fetus. Occasionally a fetus dies in the uterus but fails to be expelled, a condition termed a missed abortion.
Occasionally a fetus dies in the uterus but fails to be expelled, a condition termed a missed abortion.
More From Britannica
pregnancy: Abortion
Induced abortions may be performed for reasons that fall into four general categories: to preserve the life or physical or mental well-being of the mother; to prevent the completion of a pregnancy that has resulted from rape or incest; to prevent the birth of a child with serious deformity, mental deficiency, or genetic abnormality; or to prevent a birth for social or economic reasons (such as the extreme youth of the pregnant female or the sorely strained resources of the family unit). By some definitions, abortions that are performed to preserve the well-being of the female or in cases of rape or incest are therapeutic, or justifiable, abortions.
Numerous medical techniques exist for performing abortions. During the first trimester (up to about 12 weeks after conception), endometrial aspiration, suction, or curettage may be used to remove the contents of the uterus. In endometrial aspiration, a thin, flexible tube is inserted up the cervical canal (the neck of the womb) and then sucks out the lining of the uterus (the endometrium) by means of an electric pump.
In endometrial aspiration, a thin, flexible tube is inserted up the cervical canal (the neck of the womb) and then sucks out the lining of the uterus (the endometrium) by means of an electric pump.
In the related but slightly more onerous procedure known as dilatation and evacuation (also called suction curettage, or vacuum curettage), the cervical canal is enlarged by the insertion of a series of metal dilators while the patient is under anesthesia, after which a rigid suction tube is inserted into the uterus to evacuate its contents. When, in place of suction, a thin metal tool called a curette is used to scrape (rather than vacuum out) the contents of the uterus, the procedure is called dilatation and curettage. When combined with dilatation, both evacuation and curettage can be used up to about the 16th week of pregnancy.
From 12 to 19 weeks the injection of a saline solution may be used to trigger uterine contractions; alternatively, the administration of prostaglandins by injection, suppository, or other method may be used to induce contractions, but these substances may cause severe side effects. Hysterotomy, the surgical removal of the uterine contents, may be used during the second trimester or later. In general, the more advanced the pregnancy, the greater the risk to the female of mortality or serious complications following an abortion.
Hysterotomy, the surgical removal of the uterine contents, may be used during the second trimester or later. In general, the more advanced the pregnancy, the greater the risk to the female of mortality or serious complications following an abortion.
Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content. Subscribe Now
In the late 20th century a new method of induced abortion was discovered that uses the drug RU 486 (mifepristone), an artificial steroid that is closely related to the contraceptive hormone norethnidrone. RU 486 works by blocking the action of the hormone progesterone, which is needed to support the development of a fertilized egg. When ingested within weeks of conception, RU 486 effectively triggers the menstrual cycle and flushes the fertilized egg out of the uterus. RU-486 is typically used in combination with another drug, misoprostol, which softens the cervix and induces uterine contractions. By 2020 the two-drug combination, commonly referred to as a “medication abortion” or the “abortion pill,” accounted for more than half of all abortions in the United States.
Whether and to what extent induced abortions should be permitted, encouraged, or severely repressed is a social issue that has divided theologians, philosophers, and legislators for centuries. Abortion was apparently a common and socially accepted method of family limitation in the Greco-Roman world. Although Christian theologians early and vehemently condemned abortion, the application of severe criminal sanctions to deter its practice became common only in the 19th century. In the 20th century such sanctions were modified in one way or another in various countries, beginning with the Soviet Union in 1920, with Scandinavian countries in the 1930s, and with Japan and several eastern European countries in the 1950s. In some countries the unavailability of birth control devices was a factor in the acceptance of abortion. In the late 20th century China used abortion on a large scale as part of its population control policy. In the early 21st century some jurisdictions with large Roman Catholic populations, such as Portugal and Mexico City, decriminalized abortion despite strong opposition from the church, while others, such as Nicaragua, increased restrictions on it.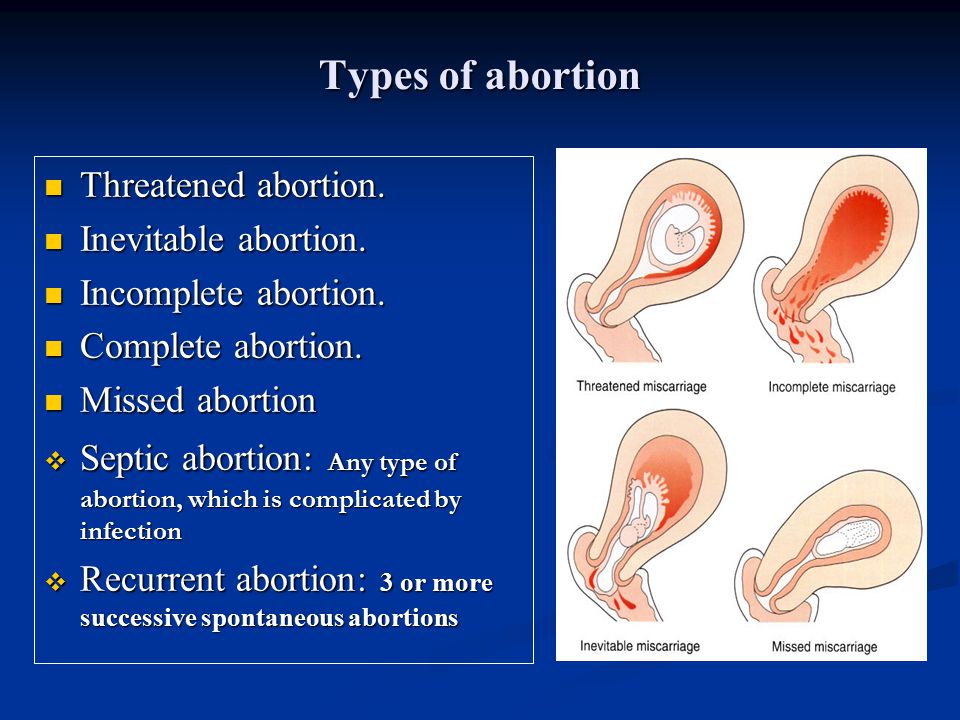
A broad social movement for the relaxation or elimination of restrictions on the performance of abortions resulted in the passing of liberalized legislation in several states in the United States during the 1960s. The U.S. Supreme Court ruled in Roe v. Wade (1973) that unduly restrictive state regulation of abortion was unconstitutional, in effect legalizing abortion for any reason for women in the first three months of pregnancy. A countermovement for the restoration of strict control over the circumstances under which abortions might be permitted soon sprang up, and the issue became entangled in social and political conflict. In rulings in 1989 (Webster v. Reproductive Health Services) and 1992 (Planned Parenthood v. Casey), a more conservative Supreme Court upheld the legality of new state restrictions on abortion, though it proved unwilling to overturn Roe v. Wade itself. In 2007 the Court also upheld a federal ban on a rarely used abortion method known as intact dilation and evacuation.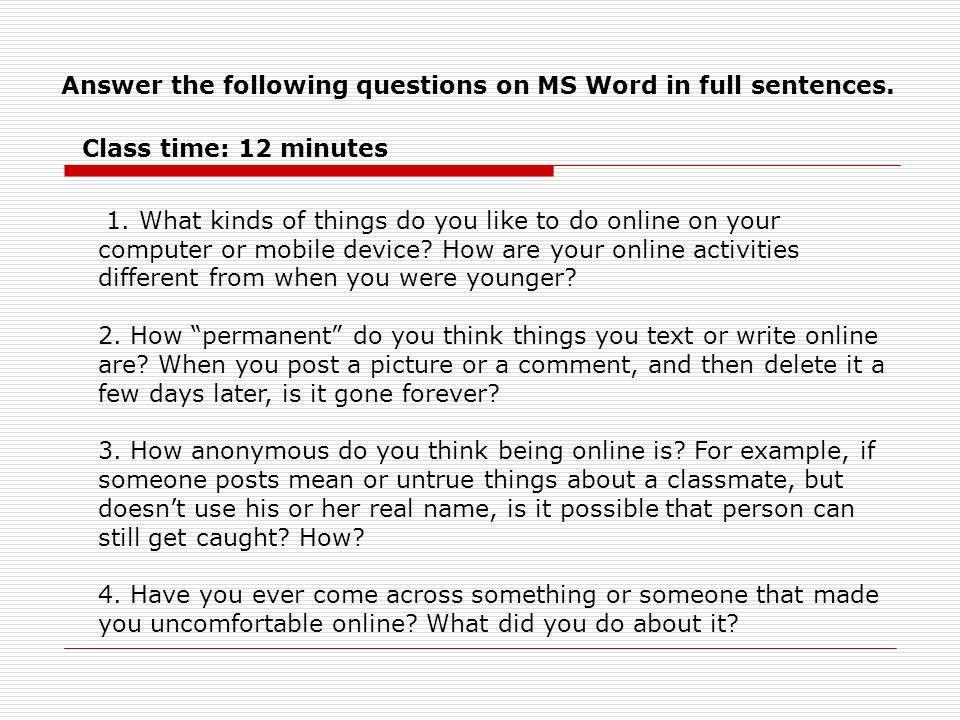 In a later ruling, Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization (2022), the Court overturned both Roe and Casey, holding that there is no constitutional right to abortion.
In a later ruling, Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization (2022), the Court overturned both Roe and Casey, holding that there is no constitutional right to abortion.
The public debate of the issue has demonstrated the enormous difficulties experienced by political institutions in grappling with the complex and ambiguous ethical problems raised by the question of abortion. Opponents of abortion, or of abortion for any reason other than to save the life of the mother, argue that there is no rational basis for distinguishing the fetus from a newborn infant; each is totally dependent and potentially a member of society, and each possesses a degree of humanity. Proponents of liberalized regulation of abortion hold that only a woman herself, rather than the state, has the right to manage her pregnancy and that the alternative to legal, medically supervised abortion is illegal and demonstrably dangerous, if not deadly, abortion.
The Editors of Encyclopaedia BritannicaThis article was most recently revised and updated by Brian Duignan.
Termination of pregnancy from the point of view of a medical psychologist
A modern woman is very different from her great-grandmother. The main difference is the possibility of reproductive choice, which our ancestors did not have.
The priorities of contemporaries are arranged differently, career, desire for personal growth, travel. The whole world is open to a woman today, and the birth of a child does not always fit into her plans.
It often happens that pregnancy just happens at the wrong time. Lack of material base, education, work, loneliness often push a woman to terminate a pregnancy.
According to statistics, there are more than 55 million abortions worldwide. More than half a million is made in Russia. Despite the fact that with the development of medicine, mortality from abortions in clinical settings is minimized, such cases do occur. 30% of maternal deaths in Russia are associated with abortion.
Abortion is the only operation that does not cure diseases and is contrary to the very nature of a woman. This is an interruption of the natural process. No matter how long, and no matter what method it is produced, it never passes without a trace for the physical and psychological health of a woman. Often women do not think about the real dangers of abortion and consider it a means of contraception.
This is an interruption of the natural process. No matter how long, and no matter what method it is produced, it never passes without a trace for the physical and psychological health of a woman. Often women do not think about the real dangers of abortion and consider it a means of contraception.
Abortion translated from Latin - abortus - "miscarriage".
Can only be performed in a specialized medical clinic with a license, exclusively by a specialist doctor. Every woman has the right to independently decide on the issue of motherhood, which is enshrined in federal law No. 323 "On the fundamentals of protecting the health of citizens in the Russian Federation"
Three methods of artificial termination of pregnancy are used. The most common of these is the "scraping" method, today WHO has recognized it as obsolete. In second place is the vacuum aspiration method or mini-abortion and medical abortion.
The most common method of abortion "curettage" can cause great complications already during the operation. Such an abortion is performed almost blindly, and artificial opening of the uterus can result in her injury. This abortion can cause severe bleeding, and the most serious consequence of such an abortion may be the removal of the uterus.
Such an abortion is performed almost blindly, and artificial opening of the uterus can result in her injury. This abortion can cause severe bleeding, and the most serious consequence of such an abortion may be the removal of the uterus.
This termination of pregnancy is carried out under anesthesia, therefore, it is necessary to remember the possible consequences of the use of anesthesia. In addition to the risk of an allergic reaction, there may be a heart rhythm failure, respiratory failure, a violation of the functions of the liver and other internal organs.
Vacuum aspiration is a less traumatic way for a woman to terminate a pregnancy, but the risk of anesthesia remains.
Medical abortion is performed for up to 9 weeks, on an outpatient basis and up to 12 weeks in an inpatient setting, requires virtually no anesthesia. But it also deals a significant blow to the hormonal system of a woman. Uterine bleeding may also occur or the abortion will be incomplete. In this case, vacuum extraction and treatment will be required.
During and after an abortion, various complications are possible.
Early complications of abortion
- profuse bleeding,
- rupture of the uterine walls,
- filling of the uterine cavity with blood,
- the occurrence of painful contractions,
- incomplete removal of the dead fetus.
There are later consequences of abortion. They can appear in the first weeks after the abortion.
- sepsis,
- metroendometritis (inflammatory processes on the mucosa and muscles of the uterus),
- adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages).
Long-term complications of abortion may occur even several years after the abortion. Each abortion undermines the health of a woman and never goes completely without a trace.
- menstrual disorders,
- amenorrhea,
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes,
- endometriosis,
- inflammation of the genital organs,
- difficulties in conception and pregnancy,
- ectopic pregnancy,
- miscarriage,
- premature birth and complications in them,
- infertility,
- increased risk of breast cancer,
- increased risk of developing uterine tumors.
In case of termination of the first pregnancy, the body can change the “carrying program” of the pregnancy to the “miscarriage program”. And the subsequent, already desired pregnancy will end in spontaneous abortion at an early stage. The body will launch a new program, and the pregnancy will not be saved.
A woman going for an abortion does not think about the fact that she may be forever deprived of the happy opportunity to become a mother. Termination of pregnancy cannot go unnoticed by the whole organism as a whole. First of all, it affects the menstrual cycle and the work of the ovaries. But, in addition to the ovaries, there is a violation in the work of such organs as the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland. There comes an imbalance of hormonal, immune, renal and hepatic functions, regulation of blood pressure, blood volume. The woman becomes irritable, sleep worsens, fatigue increases. That is, there is an "ideal state" for the penetration of any infection that provokes the development of infectious and inflammatory diseases.
Very often, when deciding to have an abortion, a woman is aware of the possible consequences for her body, but does not want to know about the consequences for her psyche.
Artificial termination of pregnancy is contrary to the very nature of man. The body does not know if it is carrying a wanted or unwanted pregnancy. The “program of childbearing” laid down in the woman strives to preserve the pregnancy. No matter how the pregnancy is terminated, it is unnatural for the woman's body.
Abortion causes not only physical but also psychological damage to a woman's body. After an abortion, a woman often experiences mental discomfort. 60% of women develop post-abortion syndrome - PAS. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the moral and ethical harm of abortion. Even those who do not believe in God consider this procedure a sin and experience pangs of conscience and guilt.
What is PAS - a set of mental consequences and illnesses that can result from an abortion.
PAS can occur immediately after an abortion and manifest itself in the form of such experiences as a feeling of emptiness, loss, grief. Often women feel guilty, become irritable, aggressive. Anxiety and depressive disorders can often develop.
Abortion is the strongest stress for a woman's psyche. In fact, this is the death of a child, even if not yet born. This feeling is reinforced by the fact that the woman herself made the choice in favor of an abortion.
Every woman who terminates a pregnancy feels guilty. Abortion is generally condemned by society, condemnation from the staff, misunderstanding of loved ones, articles and videos on the Internet only increase the feeling of guilt. After an abortion, a woman is left alone with herself. As a rule, she always understands that all the reasons why she refused to give birth (except for medical reasons) are better called excuses.
When pregnancy comes, a woman feels something inside herself, she feels that this is her child, she can imagine how he will grow and develop, what he would become when he was born. She subconsciously feels that he wanted to be born, but she did not give it to him.
She subconsciously feels that he wanted to be born, but she did not give it to him.
Conditions such as panic and helplessness accompany PAS during the first time after an abortion. After a perfect abortion, there remains a deep feeling that everything, nothing can be returned, no one will help. Relatives often do not know how to behave, and the phrases “you will still give birth”, “now is not the best time for children”, “where would you live with him” and others cause only anger and irritation.
A woman has many questions to which there are no answers. How to be further? Do you speak to loved ones? How will your relationship with your husband develop? How will this affect children? Will I still be able to get pregnant and give birth? What “punishment” will I bear for my sin?
When you decide to have an abortion and sign your consent, no one gives you a list of answers to these questions.
Aggression, irritability, anger, "hardening", intolerance. These qualities can manifest themselves both in the first days after an abortion, and after a fairly long time. Sometimes women talk about how they cannot communicate with pregnant women and feel annoyed when they meet strangers on the street. Some say that even commercials showing small children have become unpleasant to them. All this often leads to the fact that a woman is fenced off from the environment, reduces communication with loved ones to a minimum.
Sometimes women talk about how they cannot communicate with pregnant women and feel annoyed when they meet strangers on the street. Some say that even commercials showing small children have become unpleasant to them. All this often leads to the fact that a woman is fenced off from the environment, reduces communication with loved ones to a minimum.
Violation of relationships in a couple up to physical and psychological disgust. Abortion will forever stand in the relationship between a man and a woman. Guilt may be the third in such a pair for many years. The future of an aborted couple is often in doubt.
An unplanned pregnancy is not the fault of only the woman or only the man. Very often, partners begin to mutually blame each other for what happened. A woman often blames a man for pushing her to have an abortion. Many couples break up after an abortion. Many women say that after an abortion it is difficult to physically let a man near them. Libido decreases, it becomes more difficult for a woman to achieve orgasm, in rare cases anorgasmia, frigidity, vaginismus develop.
Negative attitudes towards people and life events in general can persist for a long time after an abortion. Even after a few years, a woman may feel guilty about having an abortion, for example, carrying a desired pregnancy. Because she saved this child, but did not allow the previous one to be born. Some admit that when they become pregnant and give birth to a child after an abortion, instead of warm feelings, they sometimes experience irritation and anger.
The hormonal system is the basis of the woman's psyche. When pregnancy occurs, it is rebuilt so that a woman can bear and give birth to a child. If the pregnancy is terminated, serious disturbances occur in the hormonal system, the woman loses the ability to control her own emotions and feelings.
Endless mood changes, depression, conflicts, insomnia, breaking of consciousness and the existing model of perception of the world - all these are the mental consequences of abortion.
According to the law, every pregnant woman has the right to make her own decision: to give birth or not. But, before deciding to take such a step, every woman should weigh everything well and think it over, because the consequences of an abortion can appear even many years after the operation itself.
But, before deciding to take such a step, every woman should weigh everything well and think it over, because the consequences of an abortion can appear even many years after the operation itself.
Abortion will not solve your financial or housing problems.
Abortion will not solve family problems.
Abortion will not make you happier.
Abortion is always a choice against life.
Think, maybe this child will become your joy and support in the future.
(c) Yulia Afanasyeva. Leading psychologist GBUZ "UMRD"
Give life
Abortion is the only operation, the purpose of which is not to cure the disease. On the contrary, abortion is used to prevent a natural process. And no matter how long it would be possible to have an abortion, no matter what method would be used, abortion rarely passes without a trace for a woman's health. The number of abortions in our country is growing every year. Often women do not think about the real harm of abortion. But the consequences after an abortion can manifest themselves, if not immediately, then after some time, even after many years.
But the consequences after an abortion can manifest themselves, if not immediately, then after some time, even after many years.
Why abortion is dangerous.
Artificial termination of pregnancy is contrary to the very nature of man. The body cannot determine whether a woman's pregnancy is desirable or undesirable. And any interference in the process of reproduction can be perceived in its own way. Abortion during the first pregnancy is especially dangerous (read more about this below). The “default” mechanism of pregnancy and birth is undergoing a critical change. The body does not know how the cervix opens ahead of schedule, why the fetus is removed in an unnatural way. Therefore, no matter how traumatic the operation would be, the harm of abortion will be present. After all, abortion encroaches on the most important function of the female body - childbearing.
More than half of infertile women have lost the ability to reproduce precisely "thanks" to abortion. This could be due to the fact that complications arose during or after the abortion. Abortion could also result in traumatism of the internal genital organs. The risk of infertility is highest in girls who decide to have an abortion during their first pregnancy. According to statistics, 50% of cases of tubal infertility are caused by abortions.
Abortion could also result in traumatism of the internal genital organs. The risk of infertility is highest in girls who decide to have an abortion during their first pregnancy. According to statistics, 50% of cases of tubal infertility are caused by abortions.
About the dangers of abortion and about all the complications that arise during and after an abortion, read in this article.
Complications during abortion.
The most common method of abortion - curettage of the fetus from the uterus - even during the operation can cause great complications. Abortion of this type takes place almost blindly and by touch. Even the most experienced specialist will have to act literally by the “sticking method”, since the vaginal cavity, cervix and fetus are not visually presented to him. The surgeon's hands will guide the instruments inwards in order to find, dissect and pull out the fetus. In the process, many of the internal genital organs can be harmed.
First, the artificial opening of the uterus can result in her injury. Ruptures will occur very easily with careless impact on the cervix, because its cavity is very tender and elastic. The muscles of the pregnant uterus are very tender and soft, so scraping the fetus from its walls can be accompanied by its unintentional injury. The consequences of abortion in the worst case with serious damage to the uterus - immediate surgical removal of the uterus.
Ruptures will occur very easily with careless impact on the cervix, because its cavity is very tender and elastic. The muscles of the pregnant uterus are very tender and soft, so scraping the fetus from its walls can be accompanied by its unintentional injury. The consequences of abortion in the worst case with serious damage to the uterus - immediate surgical removal of the uterus.
We should also mention the individual tolerance of anesthesia by the body. Sometimes a woman under anesthesia has a heart rhythm failure, impaired liver function and the respiratory system. There is a possibility of allergic shock during anesthesia. Possible damage to blood vessels can lead to significant blood loss.
Consequences of abortion after surgery.
Abortion can lead to the following consequences - Inflammatory processes of the internal genital organs. Occurs due to infection during surgery. If the fallopian tubes have undergone inflammation, then in the future there is a risk of an ectopic pregnancy, which will also end in an abortion. Infertility. Occurs after an abortion due to obstruction of the fallopian tubes. Damage to the cervix can lead to a weakening of its tone, and this is fraught with miscarriages and premature births. Failure of the menstrual cycle. This happens due to scarring of the uterine mucosa. As a result, painful and heavy bleeding during menstruation. Mental disorders. Women who have had an abortion may experience guilt, fear, and depression. Twitch frequent mood swings, causeless tears, irritability. This is a consequence of the failure of the internal organs, heart rhythm disturbances, etc. The adverse effects of abortion are not uncommon.
However, there is a special risk group that is especially at risk after an abortion:
-
Women with 2 or more abortions;
-
Women with inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
-
Women having surgical abortion in their first pregnancy;
-
Women who have had ovarian or uterine surgery;
The most terrible consequence of an abortion is the inability to give birth to a healthy child. Abortion (vacuum abortion) increases the chance of an ectopic pregnancy, pathology of the placenta and the fetus itself. After the first abortion, the threat of miscarriage is 1/4 of all cases, the second abortion increases this figure to 1/3. subsequent abortions not only increase the risk of unsuccessful pregnancy by up to 50%, but also give rise to the threat of breast cancer, tumors of the uterus and cervix.
Complications of medical abortion.
Medical abortion is an early term abortion. It is carried out by taking special drugs that should expel the fetus with bleeding. Medical abortion is effective in 98% of cases. In other cases, an ultrasound scan will reveal that either the pregnancy has not been terminated, or other complications have arisen. Abortion will need to be completed surgically, which is fraught with all the above consequences of abortion.
First abortion in a nulliparous woman. Consequences.
Abortion carries a risk to women's health. But abortion during the first pregnancy is of particular danger. Why is abortion dangerous for a nulliparous woman? The statistics are horrendous. 75 women out of a hundred who are diagnosed with infertility had an abortion during their first pregnancy. The most common complications of abortion during the first pregnancy:
"Primary miscarriage" This means that the body has memorized the scenario of the first pregnancy and in the future tries to follow it.
Impossible gestation. The cervix, which was opened for the first time by artificial intervention, loses its tone and elasticity, which affects the ability of a woman to bear a child.
Failure of the menstrual cycle. The first abortion can disrupt the work of the endocrine glands. The hormonal background will deviate from the norm. Menses become irregular. Hormone failure also affects mental health, can lead to obesity and sexual pathology. Possible damage to the walls of the uterus, infection with an infection (both during the first and second abortions and subsequent ones).