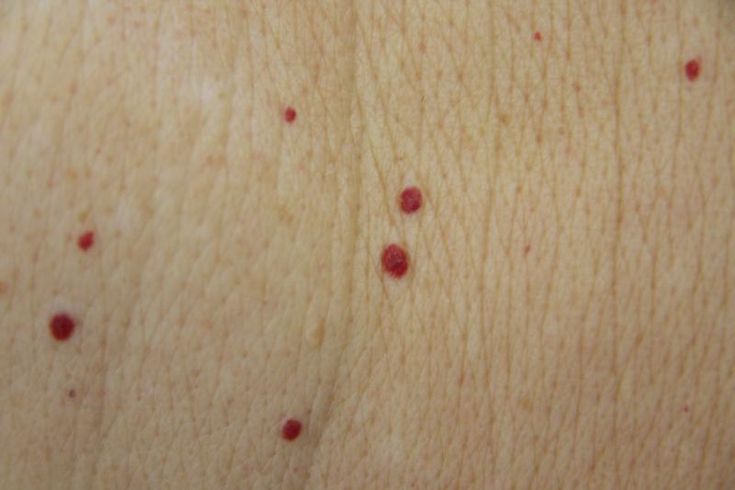
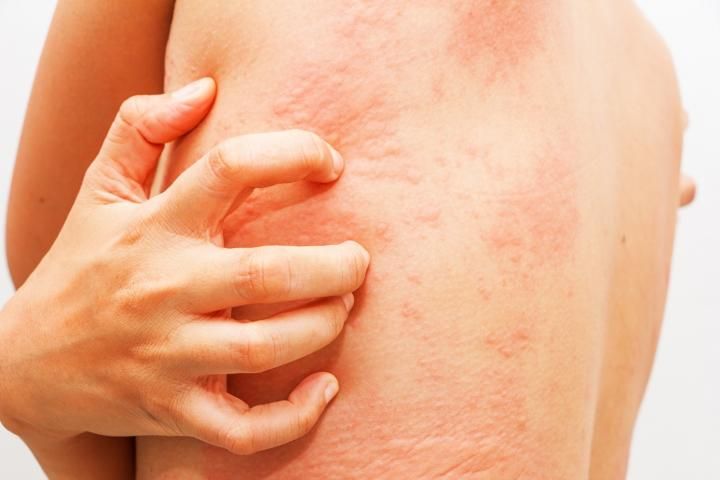
Red rash spots on legs
What Causes Red Spots on Legs?
Changes in your skin can be worrisome, especially if your symptoms include itchiness, discomfort, or pain.
And while red spots on your legs could be due to things like mild acne or a simple heat rash, other possible causes may warrant medical attention.
In this article, I’ll describe 12 possible causes of red spots on legs as well as treatment options and when to see a doctor. If you’ve developed a mild skin rash on your legs and you have no other symptoms, it’s OK to wait a few days to see if the rash will go away on its own.
However, if the spots persist for a few days, spread, become painful or infected, or if you develop any additional symptoms, contact your healthcare provider.
They can diagnose the rash and recommend the appropriate treatment plan.
Talk to a doctor online.
Start my visitPotential Causes of Red Spots on Legs
Some causes of red spots on legs clear up in a few days on their own, while other causes require medical attention.
Identifying what’s going on can help determine the most effective course of treatment.
Below are some of the common causes of red spots on legs.
Folliculitis
Folliculitis occurs when a fungal or bacterial infection (or even ingrown hairs) causes hair follicles to become inflamed or infected.
This can look like:
- Small red, itchy, or sore bumps
- White-headed pimples around hair follicles
- Tiny blister clusters around hair follicles
Mild cases of folliculitis can clear up on their own with basic self-care, including cleaning the affected area with antibacterial soap, using a warm compress, and applying soothing lotions to relieve itchy skin.
In other cases, your doctor may recommend using antibiotic or antifungal cream or shampoo.
If your folliculitis persists after a few days, contact a healthcare provider to discuss treatment options.
Psoriasis
Thick pink or red spots on the legs covered with white or silvery scales (called plaques) typically indicate psoriasis.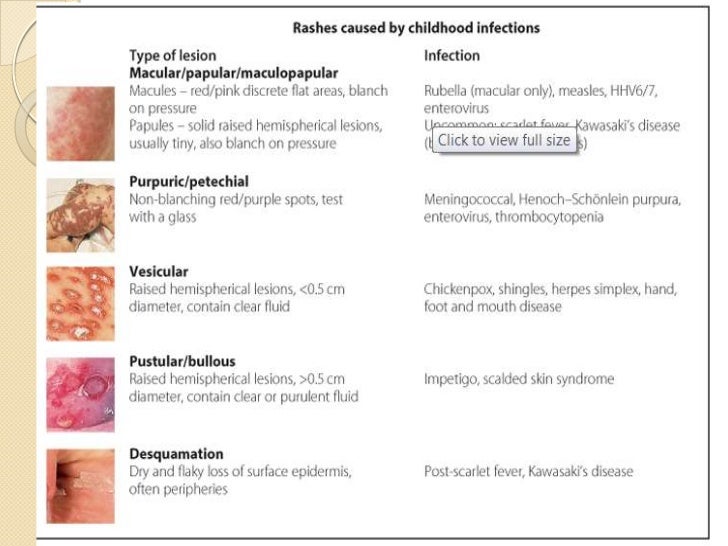
This chronic autoimmune disease tends to run in families.
While psoriasis most often affects only a few areas of skin, it can cover a larger area of the body.
The places most commonly affected by psoriasis are the:
- Elbows
- Knees
- Face, scalp, and inside of the mouth
- Fingernails and toenails
- Genitals
- Lower back
- Palms and feet
Steroid creams, moisturizers, and medicated lotions can treat psoriasis.
Eczema (atopic dermatitis)
Eczema (atopic dermatitis) causes dry, red, very itchy patches or spots that can appear on the hands, feet, neck, inside of elbows, legs, behind the knees, face, and elsewhere on the body.
Most times eczema is a chronic condition, with changes in severity from time to time.
There is no cure for eczema.
However, over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription creams can help alleviate symptoms.
Hives (urticaria)
Allergies to foods, medications, or insect bites, and exposure to heat, cold, or the sun can cause hives (urticaria) in some people.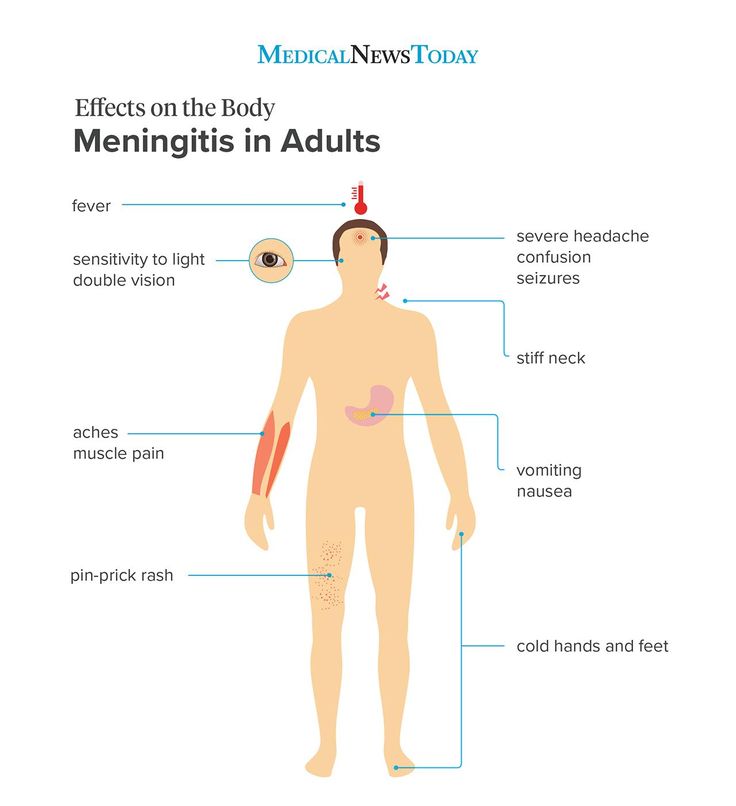
These uncomfortable, red, raised, itchy bumps come in a variety of shapes and sizes and can occur anywhere on the body.
They can also change size and location.
Hives tend to resolve after the allergic reaction ends and typically aren’t life-threatening.
Vasculitis
Vasculitis refers to the inflammation of the body’s blood vessels.
More than 20 different types of vasculitis can affect men and women of all ages.
Hypersensitivity vasculitis (HV), also called leukocytoclastic vasculitis, is an extreme reaction to a drug, infection, or foreign substance that can cause red spots on the skin, often found on the lower legs.
In most cases, stopping use of the drug or substance causing the reaction will clear the rash.
Otherwise, prescription medications can help control symptoms.
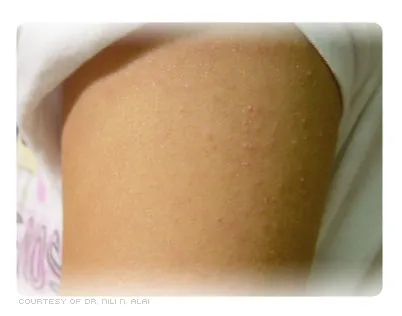
Keratosis pilaris
Keratin is a protein that makes up skin, hair, and nails.
If keratin builds up and plugs hair follicles, it causes keratosis pilaris.
This benign skin condition can look like small bumps or goosebumps on the skin and has a rough texture.
Keratosis pilaris more commonly affects people with very dry skin or eczema.
Moisturizers are usually sufficient to manage symptoms, otherwise, your provider may recommend a steroid cream to reduce redness.
Insect bites
Most insect bites are harmless, but they can sometimes cause pain, itchiness, or discomfort.
Fire ant bites and certain other insect bites can also cause red spots on the skin.
Using insect repellant and protective clothing can help prevent insect bites.
If bitten, topical or oral pain relievers, including ibuprofen (Advil) or lidocaine (Solarcaine), can help provide pain relief. Antihistamines and calamine lotion can help relieve itching.
Rosacea
Rosacea causes flushing and redness in the face.
Rarely, it causes red spots on the legs.
Most people can manage rosacea by identifying and avoiding triggers, wearing sunscreen, and, if necessary, taking prescription medication or using laser therapy.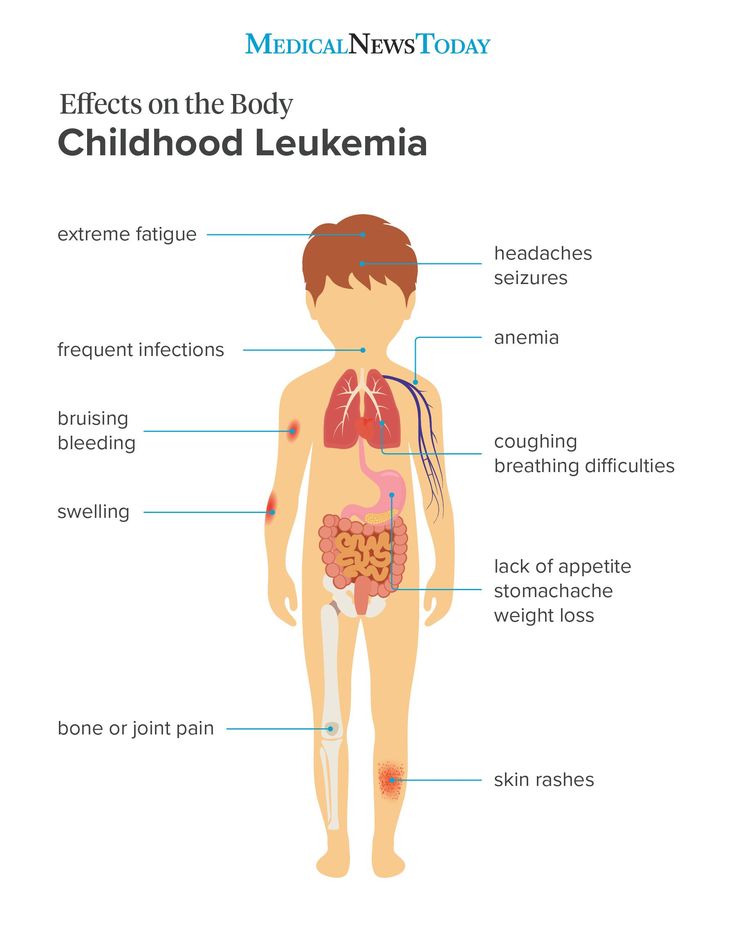
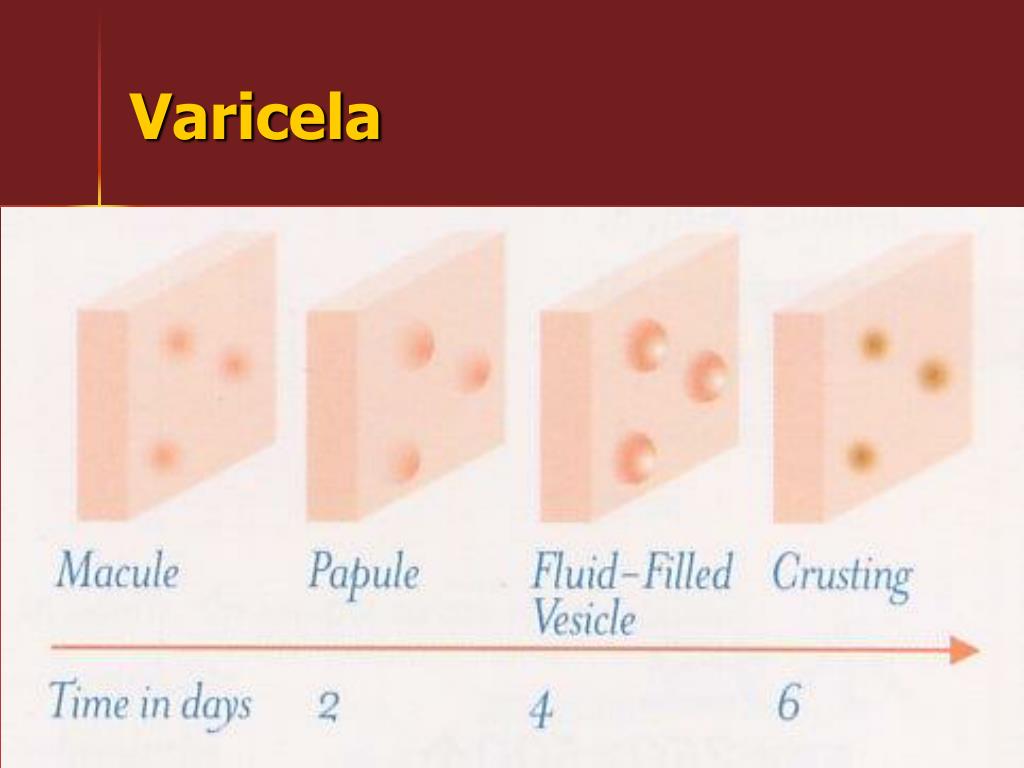
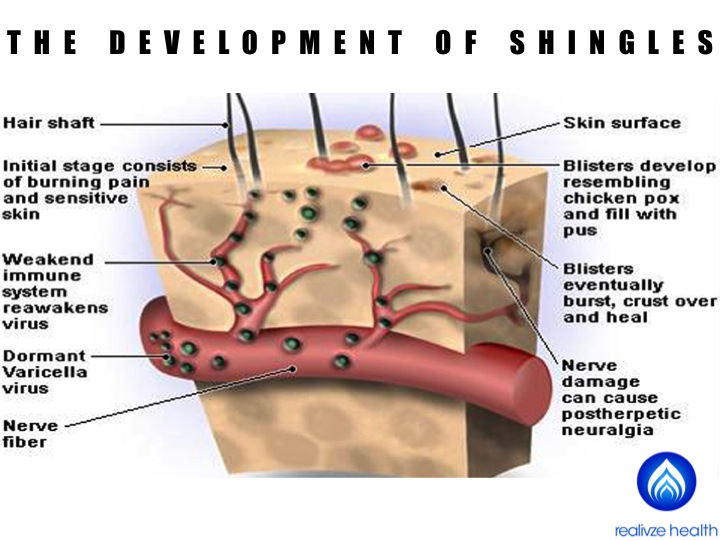
Chicken pox
Though it’s less common since the chicken pox vaccine became available in 1995, children and adults still get this highly contagious viral infection.
Chicken pox causes raised, itchy red bumps that, over time, become blister-like and eventually break open and then crust over. Fever, headache, and fatigue often occur as well.
These symptoms typically last 1-2 weeks and respond to home treatments such as calamine lotion, colloidal oatmeal baths, and OTC antihistamine and fever-reducing medication like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil).
Heat rash
Also called miliaria or prickly heat, heat rash occurs when blocked pores or sweat ducts trap sweat underneath the skin.
Adults, children, and babies can get heat rash.
Symptoms include red spots or bumps and itching or prickling.
Most heat rashes heal with cooling of the skin via methods such as spending time in air conditioning, taking a cool shower, and using cold compresses.
Acne
Acne is a common skin condition that occurs when excess oil, bacteria, and dead skin cells clog pores.
This leads to blemishes that can range in size from small whiteheads, blackheads, and red spots or bumps (pimples) to large, painful, cyst-like lumps under the skin.
While acne blemishes most commonly appear on the face, forehead, chest, upper back, and shoulders, they can also appear on the legs.
Treatment options vary depending on the type of acne, so it’s best to contact a doctor for customized acne care.
Skin cancer
In rare cases, unexplained bumps or spots on the legs or skin can be a sign of skin cancer.
There are three major types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Red spots on the legs could be a sign of BCC or an early form of skin cancer called Bowen’s disease.
Early detection is key to treating skin cancer, so if you notice abnormal growths or red spots on your legs that don’t go away within a week, follow up with a healthcare provider or dermatologist.
Treatment
Treatment for red spots on legs depends on the cause.
Some, such as psoriasis and eczema, may benefit from prescription lotions, ointments, and medications.
Others can be treated with over-the-counter (OTC) and home remedies.
OTC
OTC topical medications like hydrocortisone cream and calamine lotion may help alleviate itch and other symptoms caused by red spots on the skin.
And OTC pain relievers like ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol) may help with any pain.
Home remedies
Home remedies may alleviate some symptoms of certain causes of red spots and skin rashes.
For itchy skin in particular, applying a cool compress or adding baking soda, uncooked oatmeal, or colloidal oatmeal to a lukewarm bath may bring some relief.
Before trying any home remedy, consult a healthcare professional to determine if the therapy will make your specific symptoms better or worse.
Talk to a doctor online.
Start my visitWhen to See a Doctor
Many times, red spots on your legs isn’t cause for concern.
However, if they’re accompanied by severe symptoms or if they last for more than a week, contact a doctor.
They can help diagnose the cause of your symptoms and recommend a treatment plan.
How K Health Can Help
Did you know you can access online urgent care with K Health?
Check your symptoms, explore conditions and treatments, and if needed, text with a healthcare provider in minutes.
K Health’s AI-powered app is HIPAA compliant and is based on 20 years of clinical data.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes red spots on lower legs?
There are several possible causes of red spots on legs, including eczema (atopic dermatitis), hives (urticaria), insect bites, and heat rash. If you’re unsure what’s causing your symptoms, contact a medical provider.
What do leukemia spots look like?
Some people with acute promyelocytic leukemia develop small red dots under the skin (called petechiae) that are generally most noticeable on people with light skin tones. In people with darker skin tones, these spots may be darker or less noticeable.
Why am I getting spots on my legs?
Working with a healthcare professional is the best way to determine the exact cause of spots on your legs. Possible causes include eczema, hives, insect bites, heat rash, and more serious causes like skin cancer.
What causes little red spots on legs?
It can be difficult to discern what’s causing red spots on your legs. Possible causes include eczema, hives, insect bites, and heat rash. However, some causes can be more serious. If you’re unsure about what’s causing your symptoms, contact a medical provider.
Possible causes include eczema, hives, insect bites, and heat rash. However, some causes can be more serious. If you’re unsure about what’s causing your symptoms, contact a medical provider.
K Health articles are all written and reviewed by MDs, PhDs, NPs, or PharmDs and are for informational purposes only. This information does not constitute and should not be relied on for professional medical advice. Always talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of any treatment.
K Health has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references.
-
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia. (2020).
https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/acute-promyelocytic-leukemia/ -
Don’t Mistake These Skin Conditions for Acne.
 (2018).
(2018).
https://www.cedars-sinai.org/blog/skin-conditions-look-like-acne.html -
Heat Rash. (2020).
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-rash/symptoms-causes/syc-20373276 -
Hypersensitivity Vasculitis.
 (2021).
(2021).
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000874.htm -
Hypersensitivity Vasculitis (Leukocytoclastic). (2012).
https://www.vasculitisfoundation.org/education/forms/hypersensitivity-vasculitis/#1543688622801-0ff50ec0-074c -
Insect Bites and Stings.
 (2017).
(2017).
https://medlineplus.gov/insectbitesandstings.html -
Keratosis Pilaris. (2021).
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001462.htm -
Psoriasis.
 (2020).
(2020).
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/6866-psoriasis -
Rashes. (2016).
https://medlineplus.gov/rashes.html -
Rosacea.
 (2016).
(2016).
https://medlineplus.gov/rosacea.html -
Skin Cancer. (2020).
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/skin-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20377605 -
Vasculitis Care & Research.
 (n.d.).
(n.d.).
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/departments/orthopaedics-rheumatology/depts/vasculitis
Causes of Red Bumps and Spots on Legs
Red bumps on your legs may be caused by allergies, insect bites, and certain skin conditions. Occasionally, they may signify a more serious condition. On darker skin, such bumps may not appear red and may be harder to see.
In most instances, you shouldn’t panic if you spot red bumps on your legs. But red bumps can be itchy and annoying.
The chart below summarizes some of the most common causes of red bumps on your legs. Read on to learn more about each cause, how to recognize the symptoms, and how to treat the rash.
| If the red bumps… | Then it might be |
|---|---|
| do not itch or itch very little | keratosis pilaris |
| go away without treatment | folliculitis or hives |
| blister and ooze a clear fluid | eczema |
| turn white when you press them | hives |
| itch a lot | insect bites or eczema |
| have a scaly quality | eczema or psoriasis |
| are accompanied by night sweats and weight loss | vasculitis |
| are shiny and resemble open sores | skin cancer |
The following are images of conditions that may cause red bumps on the legs in different skin tones.
Do you have small red or dark bumps that resemble goosebumps on the fleshier areas of your thighs and arms? If they don’t itch or they itch very little, they may be keratosis pilaris.
Keratosis pilaris bumps may appear a few shades darker than your skin tone if you have black or brown skin. This is a common condition affecting approximately 50% to 80% of adolescents and 40% of adults.
It occurs when your pores are clogged with the protein keratin. Keratin is found in your skin, nails, and hair. You’re more likely to get keratosis pilaris if you have dry skin or eczema.
How it’s treated
Although the condition is harmless, you may want to talk with your doctor about using treatments such as medicated creams. Several over-the-counter (OTC) medicated creams are designed to help loosen and remove dead skin cells.
Look for products that contain ingredients such as:
- salicylic acid
- alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), such as lactic acid
- urea
Medicated creams may be especially beneficial when used with thick moisturizing creams. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution for this condition, but keeping your skin hydrated and moisturized should help. In severe cases, laser therapy may be used.
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution for this condition, but keeping your skin hydrated and moisturized should help. In severe cases, laser therapy may be used.
Folliculitis is typically caused by an infection in the hair follicles of the scalp or on areas of the body that have been shaved. It’s mostly caused by staph bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus). Folliculitis can also be caused by inflammation from ingrown hairs, viruses, or fungi.
It results in small red bumps or pimples on the skin, which you may know as razor burn or razor rash. These may appear the shade of your skin tone or darker if you have black or brown skin.
Shaving, tight clothing, and combining heat and sweat are typical sources of folliculitis. Folliculitis can affect people of all ages, but certain factors may increase your risk. You may be at higher risk of this condition if you:
- have a condition that negatively affects your immune system, such as diabetes or HIV and AIDS
- use of antibiotics to treat acne
- use certain topical medications
- have skin that’s been damaged from hair removal techniques, such as shaving against the grain or waxing
- frequently sit hot tubs that aren’t well-maintained or sanitary
Folliculitis can be itchy and uncomfortable. However, it isn’t serious unless it progresses to a more severe type of infection. These severe infections may include boils, carbuncles, and cellulitis.
However, it isn’t serious unless it progresses to a more severe type of infection. These severe infections may include boils, carbuncles, and cellulitis.
How it’s treated
Folliculitis usually clears up on its own. If it lasts longer than 7 to 10 days or it worsens, you should see your doctor.
Antibiotics in the form of pills or creams are typically used to treat persistent or severe folliculitis that’s caused by bacteria. Viral, fungal, or parasitic folliculitis will require antiviral, antifungal, and antiparasitic medications, respectively.
If the cause is an underlying condition like HIV, a person will need to get treatment for the condition, such as antiretroviral medications.
If the red spots combine in patches and itch, you may have eczema. This can also appear dark brown, purple, or ashen gray on darker skin.
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition. Eczema may be dry and scaly, or it can blister and ooze a clear fluid. Eczema tends to flare up at times.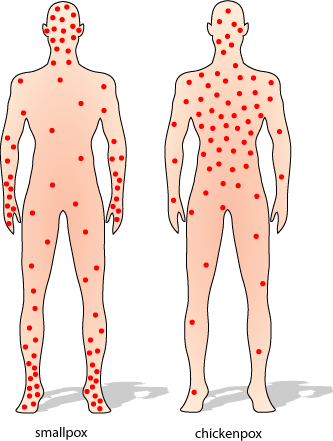 Common triggers include:
Common triggers include:
- soaps and detergents
- cleaning products
- perfumes
- cosmetics
- animal fur or dander
- wool
- sweat and heat
- cold, dry conditions
- stress
The cause of eczema is not fully understood, but there are some common patterns:
- Eczema often runs in families.
- You have a greater likelihood of getting eczema if you or a family member has asthma or seasonal allergies.
- Eczema is more common in urban areas with high levels of pollution and in colder climates.
- Children born to older mothers are more likely to have the condition.
Although people of all ages can have eczema, 85% to 95% of cases begin in children under age 5. Although several studies have gotten different results, it is also clear that many children continue to have eczema when they become adults.
Like most skin conditions, eczema can become infected. Additionally, if you have eczema, avoid being around people who have cold sores or chicken pox. Exposure to the viruses that cause these conditions puts you at risk of getting eczema herpeticum, a severe, rapidly spreading infection.
Exposure to the viruses that cause these conditions puts you at risk of getting eczema herpeticum, a severe, rapidly spreading infection.
How it’s treated
A number of medications are used to treat eczema, including antibiotics, antihistamines, and corticosteroids. Your doctor will help you find the medications that are most effective for you.
Regular use of non-medicated moisturizing creams and ointments is also usually recommended for the treatment and prevention of eczema flares. Your doctor will also work with you to identify and reduce your exposure to eczema triggers.
Approximately 20% of people will get hives in their lifetime. Hives, also called urticaria, are raised, itchy, red, or skin-tone welts. They turn white when you press their center. Hives can appear anywhere on the body, and people of all ages get them.
Hives are usually similar in color to your skin tone. Sometimes, they may be slightly lighter or darker, depending on what’s causing them. Because of this, hives on darker skin can be more difficult to identify.
Because of this, hives on darker skin can be more difficult to identify.
You can get hives in response to a wide range of triggers, such as:
- some foods
- medications
- pollen
- latex
- insects
- cold
- heat or the sun, in a condition known as solar urticaria
Hives are also associated with certain conditions, including:
- colds or other viral infections
- sinusitis, strep throat, or other bacterial infections
- mononucleosis
- hepatitis
- autoimmune diseases
Hives are generally not serious unless accompanied by a more systemic allergic reaction. Seek urgent medical attention if you have the following symptoms:
- trouble breathing or swallowing
- coughing
- wheezing
- dizziness
- abdominal pain or vomiting
- swelling of your face or tongue
How it’s treated
Hives often go away without treatment, except in cases of an allergic reaction. Antihistamines are the most commonly used medication for the treatment of hives.
Antihistamines are the most commonly used medication for the treatment of hives.
You may use prescription or OTC antihistamines for hives caused by an allergic reaction. For initial treatment, you’ll likely be recommended a non-sedating antihistamine. Examples include loratadine (Claritin), cetirizine (Zyrtec), and fexofenadine (Allegra).
If those medications don’t get rid of the hives, you’ll also add a sedating antihistamine at night. Examples include diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and the prescription medication hydroxyzine (Atarax).
In some cases, oral steroids may be prescribed. Injections of the steroid betamethasone (Celustone) might also be needed to treat hives.
If you have chronic hives, especially in cases of an undetermined cause, there are other treatments you can try, such as corticosteroids such as prednisone, immune suppressants like cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune), h3 blockers such as cimetidine (Tagamet HB), and others.
Your little red bumps may be bug bites — especially if they itch like the devil. Insect bites on darker skin may appear purple or dark brown.
Insect bites on darker skin may appear purple or dark brown.
Common culprits in the insect kingdom include:
Fire ants
Fire ant bites are actually stings, which may appear as raised clusters. These raised, red bumps sometimes contain pus. They may be accompanied by welts, followed by blisters.
How it’s treated
Treatment includes a variety of antihistamines, cold compresses, and pain medication.
Oral pain medications that may provide relief include acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin). A topical pain medication that can be used is lidocaine (Solarcaine).
Mosquitoes
Mosquito bites can be hard to the touch. They can occur as solo bumps, or you may see several in a cluster. They may or may not turn red.
How it’s treated
The itch from mosquito bites can be reduced with the topical use of witch hazel or hydrocortisone cream.
Fleas
Fleabites appear in multiple clusters, each with three or four red, raised bumps. There’s a lighter red circle around each bump. The bumps may bleed.
There’s a lighter red circle around each bump. The bumps may bleed.
If your bites fill with pus, you should have them checked by a doctor.
How it’s treated
Hydrocortisone creams and antihistamines are usually enough to reduce the itch.
Chiggers
Chigger bites result in small, red, itchy bumps, each with a bright red dot in the center. They can cause intense itching.
How it’s treated
Itching may be reduced with hydrocortisone creams.
Lice
Lice bites can occur on the head, in the pubic area, or on the body. The bites look like red or pink clusters. You may see eggs along with the bumps.
How it’s treatedReducing the lice infestation by combing out the eggs, and using topical creams designed for this purpose, will help to eliminate the bumps.
Bed bugs
Bed bug bites can look like red lines made up of dots, which may be flat or raised.
How it’s treatedThe itching can be reduced with hydrocortisone creams and antihistamines.
Scabies
Scabies leads to raised, red bumps, which may appear along wavy lines. The wavy lines are made by the burrowing insects.
How it’s treated
Treatment requires a scabicide cream such as permethrin (Eilimite). It kills scabies mites and their eggs.
General tips
The itching caused by most bug bites may be helped by:
- oral or topical corticosteroids
- a variety of OTC or prescription antihistamines, which may be taken orally or applied topically
- ice or cool compresses
- an application of calamine lotion
Remember that prevention, in the form of insect repellents and keeping your skin covered, is the most important step in keeping bloodthirsty critters away.
Psoriasis is a chronic condition that causes scaly red, purple, or gray patches to appear on the skin.
One form of psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, is characterized by small reddish or pinkish spots that may also have a scaly quality. Spots are likely to occur on the trunk and limbs.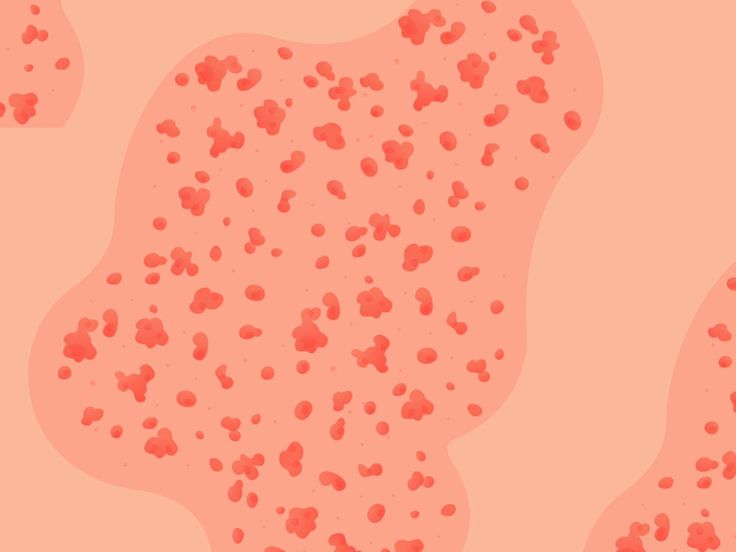 Guttate psoriasis is the second most common type of psoriasis, following plaque psoriasis. It may cause hundreds of spots to occur at one time.
Guttate psoriasis is the second most common type of psoriasis, following plaque psoriasis. It may cause hundreds of spots to occur at one time.
Triggers or risk factors for guttate psoriasis include:
- tonsillitis
- strep throat or other strep infections
- upper respiratory infection
- skin injury
- medications, such as beta-blockers or antimalarial drugs
- high levels of stress
How it’s treated
Topical ointments, such as corticosteroids, can effectively reduce outbreaks. But if the bumps are very widespread, they may also be cumbersome to apply. Other treatments can include:
- phototherapy, which may be combined with a light-sensitizing medication such as psoralen in ultraviolet light therapy
- methotrexate
- immunosuppressants like cyclosporine
- biologics
There are several different types of skin cancer. These include basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and Bowen’s disease. Skin cancer is typically caused by unprotected, chronic exposure to the sun.
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common form of skin cancer. BCCs are abnormal growths that form in the skin’s basal cell layer. They often appear as one small and shiny red bump, and they can look like an open sore. They may also appear as brown or glossy black bumps on darker skin.
How it’s treated
BCCs must be removed surgically.
Bowen’s disease
Bowen’s disease is an early form of skin cancer. It appears on the surface of the skin and is also referred to as squamous cell carcinoma in situ. It resembles a reddish, scaly patch, which may ooze, crust over, or itch.
In addition to sun exposure, Bowen’s disease may be caused by exposure to arsenic or human papillomavirus 16 (HPV 16). HPV 16 is the virus associated with cervical cancer.
How it’s treated
Patches caused by Bowen’s disease must also be removed surgically.
Vasculitis is a condition that causes inflammation of the blood vessels.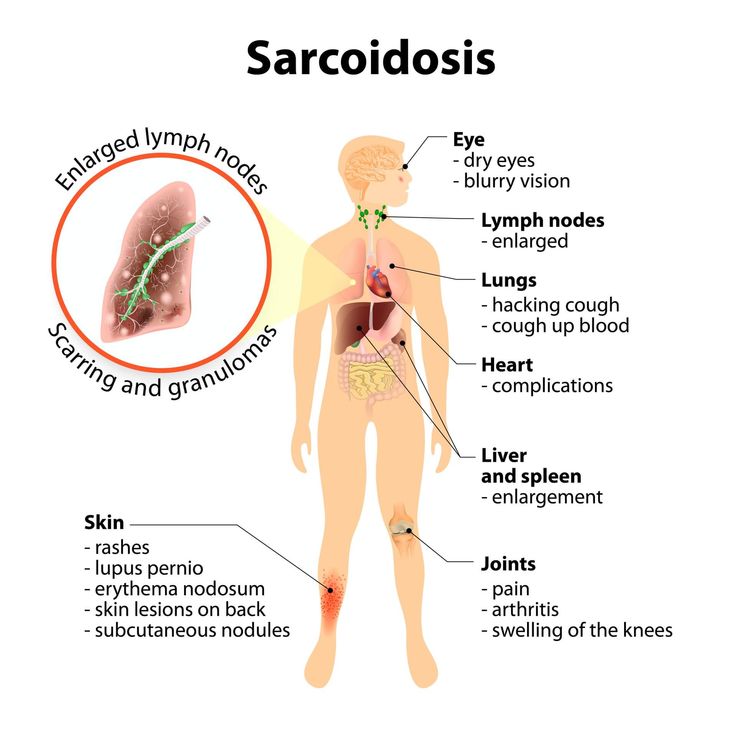 This decrease in the flow of blood results in a wide range of symptoms, including:
This decrease in the flow of blood results in a wide range of symptoms, including:
- aches and pains
- weight loss
- night sweats
- rashes
There are many types of vasculitis, most of which are rare. Some of them have red skin, purple, or dark bumps as a symptom, including:
Hypersensitivity vasculitis
Hypersensitivity vasculitis is also known as allergic vasculitis. It’s marked by red spots on the skin, which often appear on the lower legs.
An outbreak may be triggered by infection or adverse reaction to medications such as antibiotics, antiseizure drugs, and gout medications.
How it’s treatedIn most cases, no treatment is required. Some people may be prescribed anti-inflammatory medications or corticosteroids to help with joint pain.
Kawasaki disease
Kawasaki disease, or mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome, is most often seen in children under 5 years of age. Symptoms include skin rash, swollen tongue, red eyes, and fever. Its cause is unknown.
Its cause is unknown.
How it’s treated
This condition can become dangerous if not caught and treated early. Treatment usually consists of intravenous immunoglobulin.
If you have an outbreak of red bumps on your legs, you’ll want to eliminate their itch and their physical presence. There are a number of at-home remedies you can try, including:
- Aloe vera gel: Aloe vera is known to soothe inflamed skin. You can purchase this commercially or cut open the plant and use the sticky substance inside its leaves.
- Apple cider vinegar and white vinegar: When applied topically, either type of vinegar can help to soothe itchy skin.
- Calamine lotion or menthol: These can be applied topically on the bumps.
- Oatmeal: Oatmeal contains chemicals called avenanthramides that reduce itching and inflammation. They also block the action of histamines — the chemicals in your body that cause allergic reactions.
 Try oatmeal compresses, ointments, or bath treatments. Treatments that use colloidal oatmeal are soothing for irritated or itchy skin.
Try oatmeal compresses, ointments, or bath treatments. Treatments that use colloidal oatmeal are soothing for irritated or itchy skin.
The presence of little red bumps on your legs isn’t necessarily a matter of concern. If you experience itching or discomfort, your doctor can determine the cause and recommend the best treatment.
However, skin conditions carry the risk of becoming more serious infections. It’s important to treat your rash as recommended by your doctor and keep an eye out for signs of infection, such as pain, fever, blisters, or increasing redness, streaking, and swelling around the bumps.
Rash in a child on the body, legs, back
We treat children according to the principles of evidence-based medicine: we choose only those diagnostic and treatment methods that have proven their effectiveness. We will never prescribe unnecessary examinations and medicines!
Make an appointment via WhatsApp
Prices Doctors
The first children's clinic of evidence-based medicine in Moscow
No unnecessary examinations and medicines! We will prescribe only what has proven effective and will help your child.
Treatment according to world standards
We treat children with the same quality as in the best medical centers in the world.
The best team of doctors in Fantasy!
Pediatricians and subspecialists Fantasy - highly experienced doctors, members of professional societies. Doctors constantly improve their qualifications, undergo internships abroad.
Ultimate treatment safety
We made pediatric medicine safe! All our staff work according to the most stringent international standards JCI
We have fun, like visiting best friends
Game room, cheerful animator, gifts after the reception. We try to make friends with the child and do everything to make the little patient feel comfortable with us.
You can make an appointment by calling or by filling out the form on the site
Other Pediatric services
- Pediatrician's consultation
- Child Health Management Program
Frequent calls
- Acute bronchiolitis in children: diagnosis and treatment
- SARS
- Angina streptococcal tonsillitis
- Frequently ill child
- Intestinal infections
- Pneumonia (pneumonia) in children
- Colic
- Feeding problems
- Prolonged cough in a child: diagnosis and treatment
- Acute bronchitis in children: diagnosis and treatment
- Pneumonia (pneumonia) in children: diagnosis and treatment
- False croup in a child
- Coxsackie virus in a child
- The child was bitten by a tick! What to do?
Online payment
Documents online
Online services
reasons for the appearance of spots on the legs, head, hands
Publication: 09/13/2022 Change: 09/19/2022
Many doctors consider the skin to be an indicator of health, as it signals the onset of pathological processes within the body. Therefore, even such a common symptom as red spots indicates various diseases. Possible causes include skin diseases, allergic reactions, infectious pathologies or autoimmune processes. However, in some cases, red spots on the skin can be a cosmetic defect, which is why it is so important to understand the causes of the appearance and choose the right method of treatment.
Therefore, even such a common symptom as red spots indicates various diseases. Possible causes include skin diseases, allergic reactions, infectious pathologies or autoimmune processes. However, in some cases, red spots on the skin can be a cosmetic defect, which is why it is so important to understand the causes of the appearance and choose the right method of treatment.
Author:
Ibraev Anatoly Tomasovich
Head of the Department of Cosmetology and Laser Technologies. Dermatologist-cosmetologist Work experience: 16 yearsImportant!
The information in this article should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. For staging correct diagnosis and treatment should always consult a doctor.
Types of red spots on the skin
A macula or macula is a localized discoloration of the skin that is either inflammatory or non-inflammatory in nature:
- Inflammatory (vascular) formations appear as a result of the expansion of the blood vessels of the papillary dermis.
 In this case, bright red or red-bluish rashes appear, which may lighten with time. Spots of small diameter (up to 20-25 mm) are called roseola, in other cases we are talking about erythema. If all skin integuments are included in the pathological process, erythroderma occurs.
In this case, bright red or red-bluish rashes appear, which may lighten with time. Spots of small diameter (up to 20-25 mm) are called roseola, in other cases we are talking about erythema. If all skin integuments are included in the pathological process, erythroderma occurs. - As a result of hemorrhages, hemorrhagic spots appear. Initially they have a purple-red tint, but over time they turn yellow and disappear. The appearance of such formations is preceded by tissue injury.
- Non-inflammatory spots are the result of hemorrhage, disturbances in the content of melanin in cells or the introduction of dyes into the skin. In some cases (for example, with vasodilation) they can also have a red or red-cyanotic tint.
A cosmetic defect in the form of red spots occurs in people of any gender and age, often spots are found even in infants. At the same time, such rashes have a different appearance: they differ not only in shape, size and quantity, but also in shade. Conventionally, red spots are divided into the following groups:
Conventionally, red spots are divided into the following groups:
- flat and convex;
- swollen (inflamed) and not inflamed;
- smooth and rough;
- wet and dry;
- with a clear outline and blurry;
- dark purplish or reddish (pink).
The localization of spots also differs. In rare cases, they appear on almost all parts of the body. More often you can find an option when the rashes are concentrated on a separate area: face, neck, arms, back, genitals.
Symptoms and causes
We have already noted that there are a huge number of possible reasons for the appearance of such formations. More often we are talking about the development of skin or infectious diseases, but sometimes spots are the result of mental disorders or other malfunctions in the body. The following factors can provoke the appearance of rashes:0003
- Diseases of the heart or blood vessels.
- Allergic reactions.
- Autoimmune pathologies.
- Dermatological diseases.
- Dysfunction of internal organs.
- Parasitic and bacterial infections.
- Some insect bites.
- Oncological diseases.
- Malnutrition, disturbances in the digestive tract.
- Poor ecological situation in the place of residence.
- Frequent stress and anxiety.
Because there are many causes for red rashes, symptoms will vary from case to case. Spots can be all over the body or only in certain areas, itching, burning or peeling are additionally manifested, but sometimes they may not be. It is impossible to talk about the presence of a single clinical picture, so a separate diagnosis will be required.
If we talk about the most common conditions that provoke the appearance of red spots, then it is worth highlighting the following pathologies:
Allergy . The external manifestation of this problem is itchy reddish spots of various sizes and shapes. Their appearance is accompanied by swelling and peeling of the skin. Some patients experience general malaise, weakness, chills. As a rule, symptoms appear immediately after contact with the allergen: they can be certain products, cosmetics, medicines, plants. In rare cases, the appearance of rashes is associated with exposure to low temperatures.
Their appearance is accompanied by swelling and peeling of the skin. Some patients experience general malaise, weakness, chills. As a rule, symptoms appear immediately after contact with the allergen: they can be certain products, cosmetics, medicines, plants. In rare cases, the appearance of rashes is associated with exposure to low temperatures.
Allergies often show up as pink spots where skin contacts clothing, which may indicate the use of inappropriate detergent or personal care products.
Rubella . Red small spots on the skin can be the result of rubella measles. They occur throughout the body, but the maximum localization is noted on the back, face and neck. As a rule, the formations disappear within a few days, but only with treatment.
Scarlet fever . This infectious disease is caused by group A streptococcus. One of the symptoms of the disease is small spots all over the body, the size of which does not exceed a few millimeters. Rashes appear after the onset of a sore throat, more often located on the lower abdomen or in the groin area. The skin appears reddened and inflamed.
Rashes appear after the onset of a sore throat, more often located on the lower abdomen or in the groin area. The skin appears reddened and inflamed.
Pityriasis rosea Gibert . This pathology is most often encountered by patients with weakened immunity. For this reason, the risk of disease in spring and autumn increases significantly. Lichen may appear as pink, reddish or crimson spots up to 5 cm in diameter. Outwardly, such formations resemble plaques. First, one spot appears, after 5–7 days, others, smaller in size, are found near it. At the same time, peeling of the skin may appear, less often - swelling of the tissues is observed.
Erythema . This condition is characterized by reddening of the skin, which occurs after the activation of blood circulation and the expansion of capillaries. As a rule, this is the result of heavy physical exertion or excitement. Often, redness is observed on the face after massage, peeling or masks. The spots are relatively large, but do not require treatment, as they quickly disappear on their own.
Less common is persistent erythema characterized by extensive areas of redness resembling bruising or bruising. Such a problem can lead to the development of rosacea, therefore, it requires an examination and consultation with a dermatologist.
Urticaria . A fairly common cause of skin rashes, which is often characterized by a long course. Under the urticaria understand a whole group of diseases that lead to the formation of angioedema and blisters. Urticaria can result from medications, certain foods, and supplements. In rare cases, pathology occurs as a result of infections.
Chickenpox . Chickenpox is infectious and can be dangerous to health. This pathology is complicated by pustular lesions, stomatitis and conjunctivitis, in rare cases, damage to internal organs and the brain occurs.
Chickenpox is one of the common causes of red spots on the skin. As a rule, the rashes are small, localized throughout the body. Further, bubbles up to 5 mm in diameter are formed, which after 2–3 days become covered with a dry crust.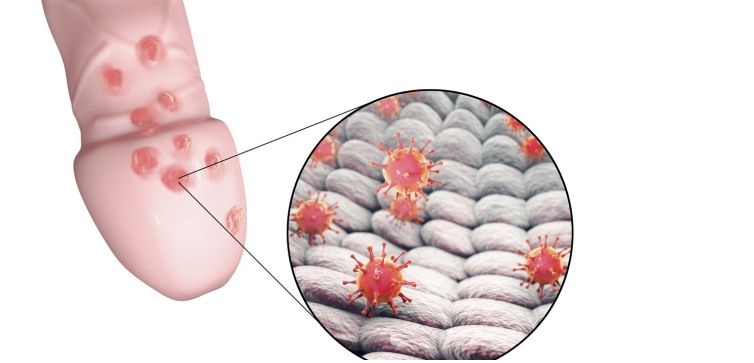 Both spots and vesicles can be present on the skin at the same time.
Both spots and vesicles can be present on the skin at the same time.
Ringworm . This is a pathology of fungal origin, which is known in dermatology under the term "microsporia". The causative agent of pathology is a fungus of the genus Microsporum, which parasitizes in the stratum corneum of the epidermis. It is because of it that the skin is covered with rounded spots that have a non-uniform color: the center is lighter, while the edges of the formation may have a bright red tint. As a rule, rashes are found on the head, arms and legs.
Pityriasis versicolor . Another type of infectious disease that leads to damage to the upper layers of the skin. However, this form of the disease is not contagious and rarely leads to serious consequences, but it is characterized by fairly large lesions. Pathology occurs as a result of some autoimmune disorders, excessive sweating, hormonal problems, etc.
Eczema . This inflammatory skin disease has an allergic nature, but the causes and prerequisites for its development are still not fully understood. Often the disease is called "weeping lichen" due to the presence of characteristic symptoms.
Often the disease is called "weeping lichen" due to the presence of characteristic symptoms.
Initially, inflamed areas appear on the skin in the form of red spots, which gradually merge into a separate affected area. After that, characteristic nodules with a bright red color and clear boundaries are formed. Bubbles quickly open, which leads to the appearance of point erosions, which are replaced by crusts and peeling.
Photodermatitis . The reason for the development of such a pathology is the increased sensitivity of the epidermis to ultraviolet radiation. As a result, persistent redness of the skin appears, which can be accompanied by itching, burning, and even blisters. Often there are large red spots on the skin. It should be noted that the symptoms of the condition are very similar to a number of dermatological diseases (for example, in many patients, photodermatitis has all the signs of systemic lupus erythematosus), which complicates the diagnostic process.
Important!
The information in this article should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. For staging correct diagnosis and treatment should always consult a doctor.
Psoriasis . One of the most common dermatological diseases is psoriasis. Pathology has an autoimmune origin, the causes of its development can be infectious, psychosomatic, hereditary or mixed.
Characteristic raised spots with a smooth surface appear on the skin. After a few days, they become covered with white scales, itching occurs. Many patients note dryness and flaking of the skin, and cracks and blisters are also found in advanced cases.
Atopic dermatitis . This chronic inflammatory disease is confused with eczema, although there are a number of differences between the pathologies. AtD is characterized by the appearance of red spots with peeling on various parts of the body. Most often, rashes are localized on the bend of the elbow and knee joints, neck and face.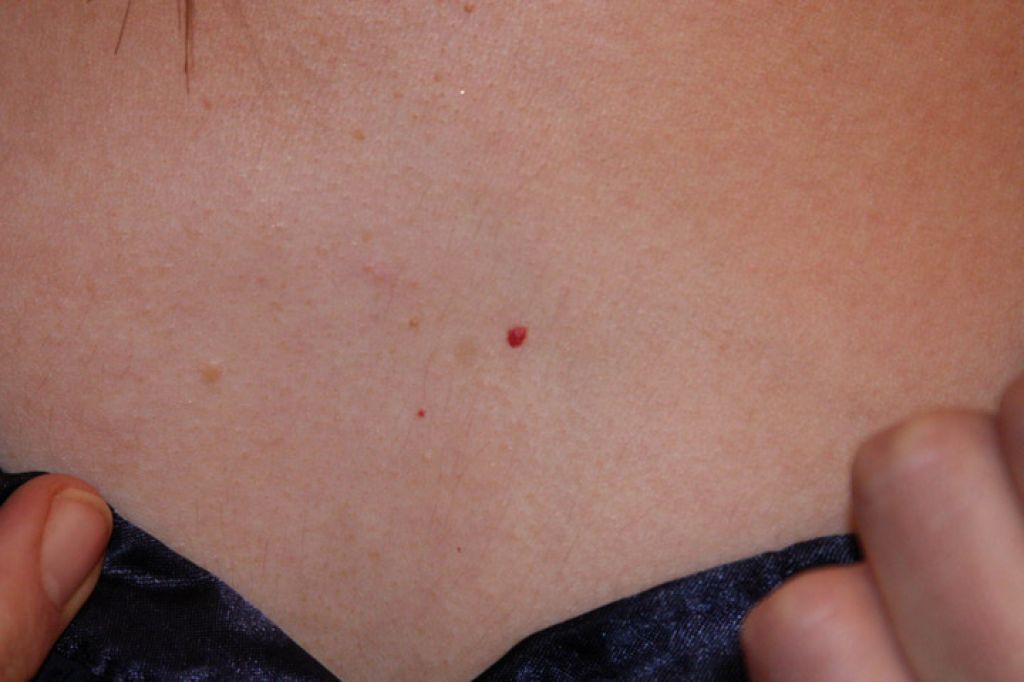
As a rule, pathology occurs in childhood and a whole complex of factors (both external and genetic) contributes to its appearance. In half of the cases, atopic dermatitis disappears over time, in the remaining patients it persists and recurs throughout life.
Helminthiases . One of the causes of red rashes is exposure to toxic substances that are released during the life of parasites. The size and location of the formations vary depending on the degree of intoxication of the body. As a rule, a rash appears first, which is accompanied by itching and skin irritation. In the future, purulent boils may appear.
Fungal mycosis . A fairly serious disease, a malignant lymphoid lesion, which is characterized by the appearance of red dry plaques (that is, large-sized elements that rise above the surface of the skin). Outwardly, the formations resemble eczema, but have a rounded shape and clear boundaries.
Hyperhidrosis . An unobvious cause of red round spots on the skin is hyperhidrosis.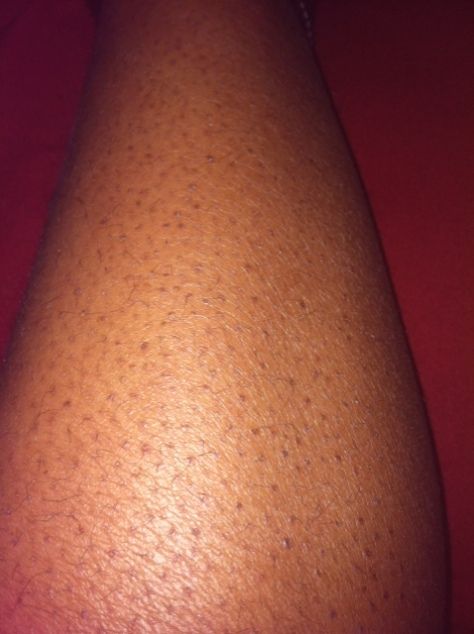 This is a functional disorder of sweating, characterized by the release of an increased amount of sweat. As a result of this, redness appears in the armpits and in other areas that are affected by the pathology.
This is a functional disorder of sweating, characterized by the release of an increased amount of sweat. As a result of this, redness appears in the armpits and in other areas that are affected by the pathology.
Emotional experiences . As a result of psychological disorders and excitement, characteristic redness periodically appears on the neck and face. This problem is the result of depression, emotional overload, chronic lack of sleep. In rare cases, the problem is accompanied by itching, swelling and peeling.
Diagnostic methods
In the event that a red spot appears on the skin that does not go away within a few days or changes its shape / appearance, it is better to seek the advice of a dermatologist. Such a measure will not be superfluous, as it will identify the causes of rashes and exclude serious pathologies. The presence of the following symptoms should alert:
- Itching or burning.
- Peeling of the skin.
- Increased size or number of spots.
- Soreness on pressure.
- Swelling, weeping.
- The beginning of the inflammatory process.
To determine the nature and characteristics of the formations, the doctor performs an examination using a dermatoscope. Of key importance is the collection of anamnesis, clarification of symptoms, identification of concomitant diseases. After the examination, the specialist appoints the patient a number of additional studies, among which may be:
- Complete blood count.
- Urinalysis.
- Microscopic examination of skin scrapings.
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
- ECG, etc.
If necessary, the patient is assigned a consultation with other specialists: for example, a therapist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, etc. As a result of such an examination, it will be possible to identify comorbidities and determine which diseases provoked red spots on the skin.
Differential diagnosis is important at this stage, since sometimes rashes in various pathologies can be identical.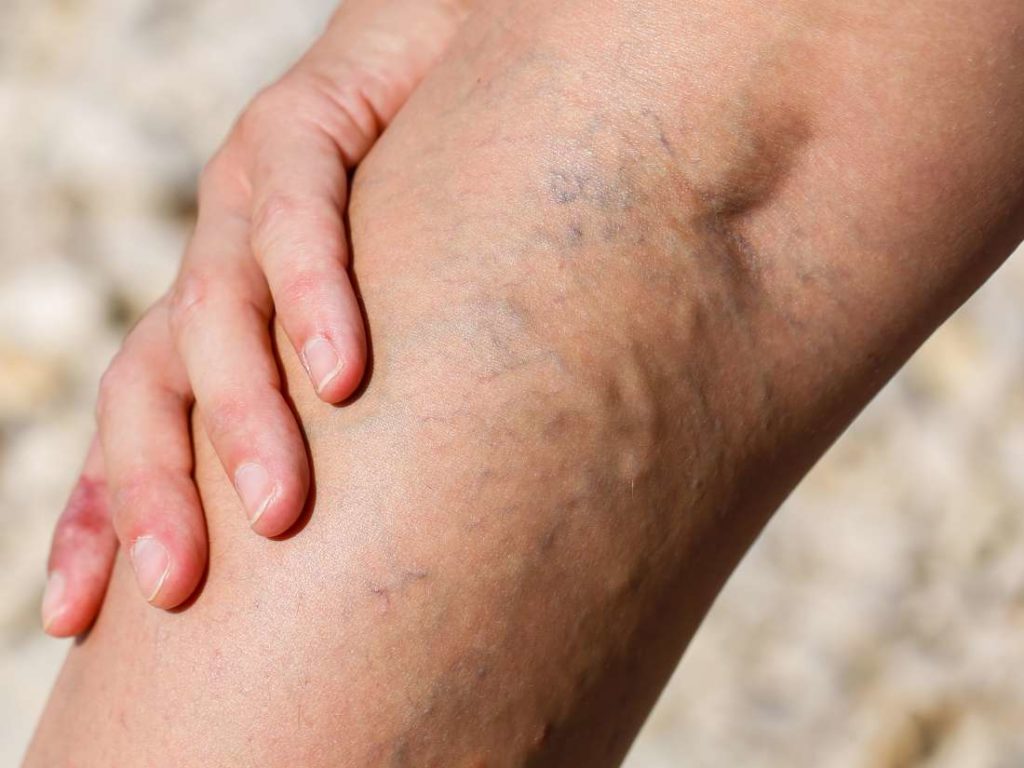 That is why it is required to exclude the presence of other diseases and allergic reactions.
That is why it is required to exclude the presence of other diseases and allergic reactions.
Already during the examination, the doctor may suspect the presence of a particular pathology. The existing symptoms and the appearance of the spots are taken into account. For example:
- Red rashes that look like mosquito bites but without itching or pain are often the result of stress or anxiety. In rare cases, this may be a manifestation of an allergy or pink lichen Zhibera.
- Spots combined with soreness or itching may indicate the presence of autoimmune diseases, urticaria or psoriasis.
- A rash that looks like a burn is often a manifestation of atopic dermatitis. They may be accompanied by itching (especially at night).
- Red sores or plaques along the hairline may be a symptom of seborrheic dermatitis.
- Small spots all over the body indicate the presence of measles, chickenpox or lichen. Also, such symptoms occur in some patients with coronavirus.

- Red rough spots on the skin of the hands indicate a lack of certain vitamins and microelements in the body. In most cases, you can compensate for their lack by changing the diet.
Methods of treatment
The treatment of the problem is individual, since when drawing up the scheme, the doctor takes into account the patient's state of health, the identified pathologies and the presence of symptoms. An integrated approach is always used for the treatment of spots, which includes various conservative methods:
- Medical therapy.
- Local therapy (treatment of the skin).
- Physiotherapy procedures.
Radical removal procedures are required in rare cases. During treatment, the patient may need to adjust the diet and avoid interaction with allergens. At the same time, in most cases, the use of traditional medicine is unacceptable, since they aggravate the course of the disease and lead to the development of a chronic process.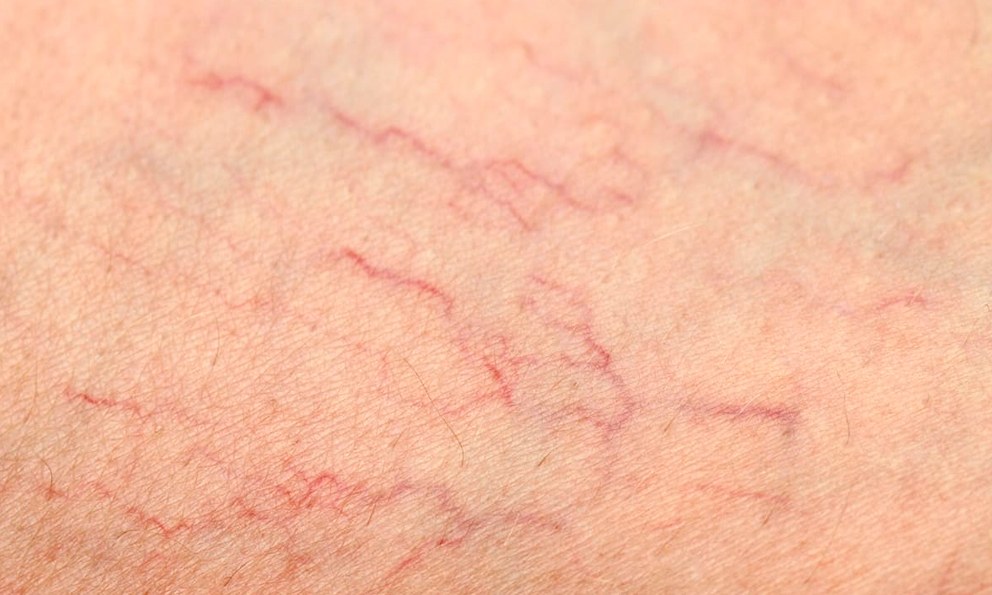
Different groups of drugs are used for drug therapy. Most often it is:
- Antihistamines . With a severe allergic reaction or exacerbation of eczema.
- Antibiotics . To combat the infectious nature of different types of red spots on the skin.
- Glucocorticosteroids . Hormonal agents to relieve inflammation.
- Tranquilizers . Used to relieve severe itching.
- Diuretics . Drugs to eliminate puffiness.
- Enterosorbents . To remove the products of intoxication from the intestines.
- B vitamins . They are used to normalize the functioning of the nervous system.
As for the radical methods of treatment, they include electrocoagulation, laser removal and cryosurgery (exposure to liquid nitrogen). Such procedures are used in cases where conservative treatment did not bring relief to the patient or cosmetic defects remained after the therapy.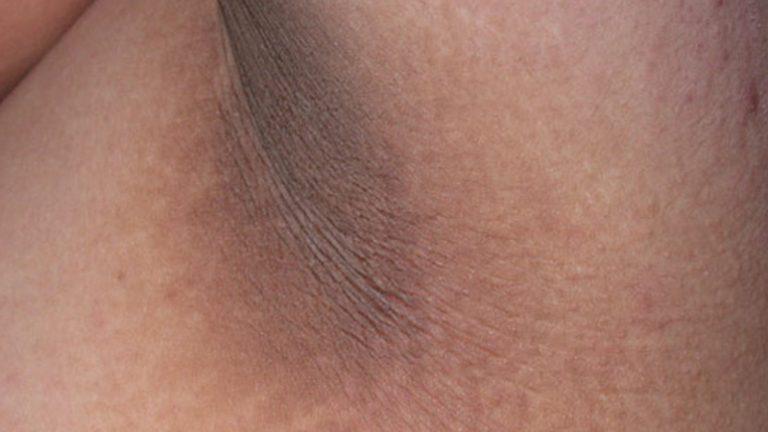
If we talk about the prevention of red spots, then there are no universal recommendations, since it is always necessary to take into account the cause of the pathology. In order to reduce the likelihood of rashes, it is best to exclude contact with stray animals, refuse products that cause allergies, and regularly undergo preventive examinations with doctors. This will allow early detection of any disturbances in the functioning of the immune system and prevent possible diseases of the internal organs.
Literature
- Karavaeva TA, Korolkova TN Psychological mechanisms and psychosomatic correlations in various dermatoses // Clinical dermatology and venereology. - 2018. - V. 17, No. 5. - S. 7–16.
- Kubanova AA Analysis of the incidence of diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue in the Russian Federation for the period 2003–2016.