What does a negative blood type mean
Rh factor blood test - Mayo Clinic
Overview
Rh factor is an inherited protein found on the surface of red blood cells. If your blood has the protein, you're Rh positive. If your blood doesn't have the protein, you're Rh negative. The "+" or "–" you might see after your blood type refers to Rh positive or Rh negative.
Rh positive is much more common than Rh negative. Having an Rh negative blood type is not an illness, and it usually does not affect your health. But it can affect pregnancy. Your pregnancy needs special care if you're Rh negative and your baby is Rh positive. That's called Rh incompatibility. A baby can inherit the Rh factor from either parent.
Your health care provider will advise that you have a blood type and Rh factor screening test during your first prenatal visit. This will show whether you are Rh positive or Rh negative.
Products & Services
- Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th Edition
- Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy
- Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter — Digital Edition
Why it's done
During pregnancy, problems can happen if you're Rh negative and your baby is Rh positive. Usually, your blood doesn't mix with your baby's blood during pregnancy. However, a small amount of your baby's blood could come in contact with your blood when the baby is born. It can also happen if you have bleeding or trauma to your abdomen during pregnancy.
If you're Rh negative and your baby is Rh positive, your body might produce proteins called Rh antibodies if your blood and the baby's blood mix. Those antibodies aren't a problem during the first pregnancy. But problems can happen if you become pregnant again.
If your next baby is Rh positive, the Rh antibodies can cross the placenta and damage the baby's red blood cells. This could lead to life-threatening anemia, a condition in which red blood cells are destroyed faster than the baby's body can replace them. Red blood cells are needed to carry oxygen throughout the body.
If you're Rh negative, you might need to have another blood test — called an antibody screen — several times: during your first trimester, during week 28 of pregnancy and when your baby is born. Some people need the test more often.
Some people need the test more often.
That test is used to detect antibodies to Rh positive blood. If you haven't started to produce Rh antibodies, you'll likely need a shot (injection) of a blood product called Rh immune globulin. This prevents your body from producing Rh antibodies during your pregnancy.
If your baby is born Rh negative, you don't need any other treatment. If your baby is born Rh positive, you'll need another injection shortly after delivery.
If you're Rh negative and your baby might be or is Rh positive, your health care provider may recommend an Rh immune globulin injection after situations in which your blood could come into contact with the baby's blood, including:
- Miscarriage
- Ectopic pregnancy — when a fertilized eggs implants somewhere outside the uterus, usually in a fallopian tube
- Abortion
- Removal of a molar pregnancy — a noncancerous (benign) tumor that develops in the uterus
- Amniocentesis — a prenatal test in which a sample of the fluid that surrounds and protects a baby in the uterus (amniotic fluid) is removed for testing or treatment
- Chorionic villus sampling — a prenatal test in which a sample of the wispy projections that make up most of the placenta (chorionic villi) is removed for testing
- Cordocentesis — a prenatal test in which a sample of the baby's blood is removed from the umbilical cord for testing
- Bleeding during pregnancy
- Injury or other trauma to your abdomen during pregnancy
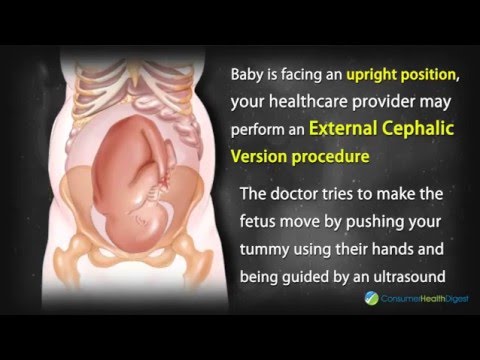
- The external manual rotation of a baby in a breech position — such as buttocks first — before labor
- Delivery
If the antibody screen shows that you're already producing antibodies, an injection of Rh immune globulin won't help.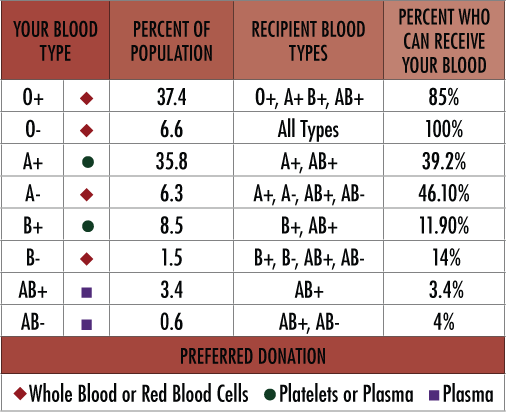 Your baby will be carefully monitored during your pregnancy. The baby might be given a blood transfusion through the umbilical cord during pregnancy or immediately after delivery if necessary.
Your baby will be carefully monitored during your pregnancy. The baby might be given a blood transfusion through the umbilical cord during pregnancy or immediately after delivery if necessary.
| Mother's Rh factor | Father's Rh factor | Baby's Rh factor | Precautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rh positive | Rh positive | Rh positive | None |
| Rh negative | Rh negative | Rh negative | None |
| Rh positive | Rh negative | Could be Rh positive or Rh negative | None |
| Rh negative | Rh positive | Could be Rh positive or Rh negative | Rh immune globulin injections |
What you can expect
An Rh factor test is a basic blood test. The blood sample usually is taken during the first prenatal visit and sent to a lab for testing. No special preparation is necessary.
The blood sample usually is taken during the first prenatal visit and sent to a lab for testing. No special preparation is necessary.
Results
If you're Rh positive, you don't need to do anything.
If you're Rh negative and your baby is Rh positive, your body could make antibodies that might be harmful during another pregnancy. Take these steps:
- If you have vaginal bleeding any time during pregnancy, contact your health care provider right away.
- Talk with your health care provider about scheduling an Rh immune globulin injection during your pregnancy.
- Remind your health care team during labor that you're Rh negative.
By Mayo Clinic Staff
Related
Products & Services
Blood Types Explained - A, B, AB and O
How Blood Type Is Determined And Why You Need To Know
Blood types are determined by the presence or absence of certain antigens – substances that can trigger an immune response if they are foreign to the body. Since some antigens can trigger a patient's immune system to attack the transfused blood, safe blood transfusions depend on careful blood typing and cross-matching. Do you know what blood type is safe for you if you need a transfusion?
Since some antigens can trigger a patient's immune system to attack the transfused blood, safe blood transfusions depend on careful blood typing and cross-matching. Do you know what blood type is safe for you if you need a transfusion?
Discover what blood types are compatible with yours.
Get our guide to find out.
Download Guide
There are four major blood groups determined by the presence or absence of two antigens, A and B, on the surface of red blood cells. In addition to the A and B antigens, there is a protein called the Rh factor, which can be either present (+) or absent (–), creating the 8 most common blood types (A+, A-, B+, B-, O+, O-, AB+, AB-).
",xd="",yd="
",zd="",Ad='
There are very specific ways in which blood types must be matched for a safe transfusion. The right blood transfusion can mean the difference between life and death. Use the interactive graphic below to learn more about matching blood types for transfusions.
Also, Rh-negative blood is given to Rh-negative patients, and Rh-positive or Rh-negative blood may be given to Rh-positive patients. The rules for plasma are the reverse.
- The universal red cell donor has Type O negative blood.
- The universal plasma donor has Type AB blood.
There are more than 600 other known antigens, the presence or absence of which creates "rare blood types." Certain blood types are unique to specific ethnic or racial groups. That’s why an African-American blood donation may be the best hope for the needs of patients with sickle cell disease, many of whom are of African descent. Learn about blood and diversity.
Universal donors are those with an O negative blood type. Why? O negative blood can be used in transfusions for any blood type.
Type O is routinely in short supply and in high demand by hospitals – both because it is the most common blood type and because type O negative blood is the universal blood type needed for emergency transfusions and for immune deficient infants.
Approximately 45 percent of Caucasians are type O (positive or negative), but 51 percent of African-Americans and 57 percent of Hispanics are type O. Minority and diverse populations, therefore, play a critical role in meeting the constant need for blood.
Types O negative and O positive are in high demand. Only 7% of the population are O negative. However, the need for O negative blood is the highest because it is used most often during emergencies. The need for O+ is high because it is the most frequently occurring blood type (37% of the population).
The universal red cell donor has Type O negative blood. The universal plasma donor has Type AB blood. For more about plasma donation, visit the plasma donation facts.
Nearly 16 million blood components are transfused each year in the U.S."
What is your blood type? Donate and find out.
Schedule Your Appointment
There are more than 600 other known antigens, the presence or absence of which creates "rare blood types. " Your blood type is considered rare if you lack antigens that 99% of the people are positive for. If you somehow lack an antigen that 99.99% are positive for, your blood type is extremely rare.
" Your blood type is considered rare if you lack antigens that 99% of the people are positive for. If you somehow lack an antigen that 99.99% are positive for, your blood type is extremely rare.
It’s inherited. Like eye color, blood type is passed genetically from your parents. Whether your blood group is type A, B, AB or O is based on the blood types of your mother and father.
View all child parent pairings
* Note: If you have questions about paternity testing or about blood group inheritance, your primary care physician should be able to provide you with an appropriate referral. Testing difficulties can cause exceptions to the above patterns. ABO blood typing is not sufficient to prove or disprove paternity or maternity.
Make Your Appointment
About Blood Types - Blood Center
When a doctor talks about your blood type, he usually means two things: your ABO blood type and your Rh (rhesus factor).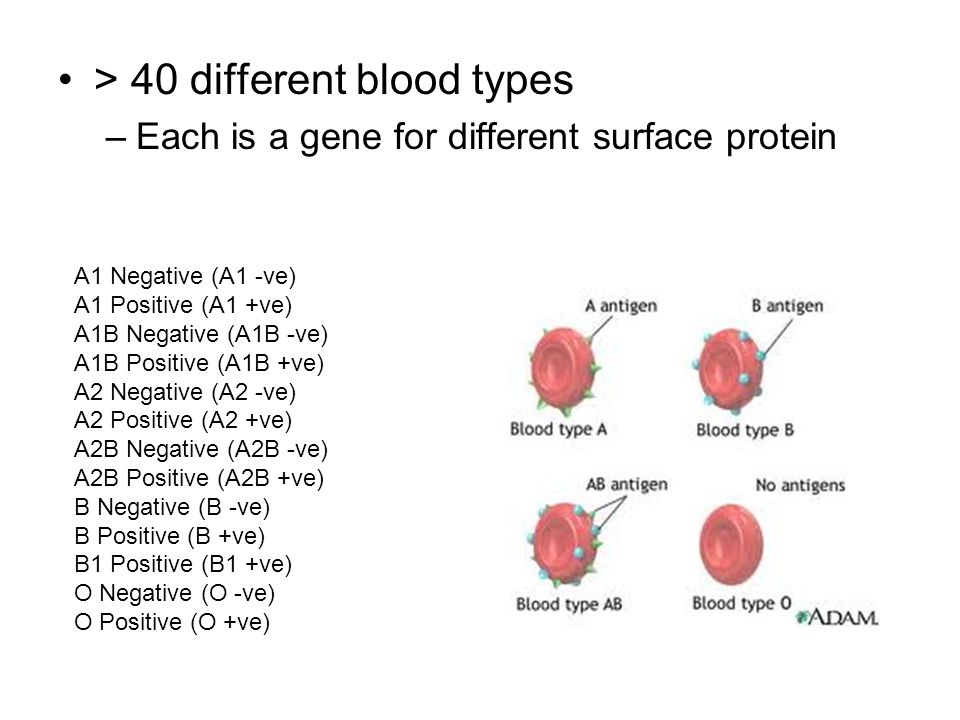
A person's blood group is determined by antigens found on his red blood cells. An antigen is a structure on the surface of a cell. If it is foreign to the body, then the human defense system will react to it. Therefore, it is necessary to take into account blood groups when transfusing: the donor's blood group is determined at the Blood Center, and the patient's blood group is determined before transfusion.
AB0 system
The most important is the ABO blood group system, according to which blood is divided into groups A, B, O and AB. It is determined by two antigens located on the surface of red blood cells:
- group A - only antigen A is present on the surface of erythrocytes
- group B - only antigen B is present on the surface of erythrocytes
- group AB - both A and B antigens are present on the surface of erythrocytes
- group O - on the surface of erythrocytes there is neither antigen A nor antigen B.

If a person has blood type A, B or 0, then in his blood plasma there are also antibodies that destroy those antigens that the person himself does not have. Examples: If you have type A blood, then you cannot be transfused with type B blood, because in this case there are antibodies in your blood that fight against B antigens. If you have blood type 0, then your blood contains antibodies that fight like against antigens A and against antigens B.
If a person has blood type AB, then he does not have such antibodies, so he can be transfused with blood of any group. Therefore, the carrier of the AB blood group can be called universal patient.
A carrier of blood type 0 with a negative Rh factor, in turn, is called a universal donor, , since his red blood cells are suitable for all patients.
Rhesus (Rh ) accessory
Rh factor (Rh) can be positive (+) and negative (-).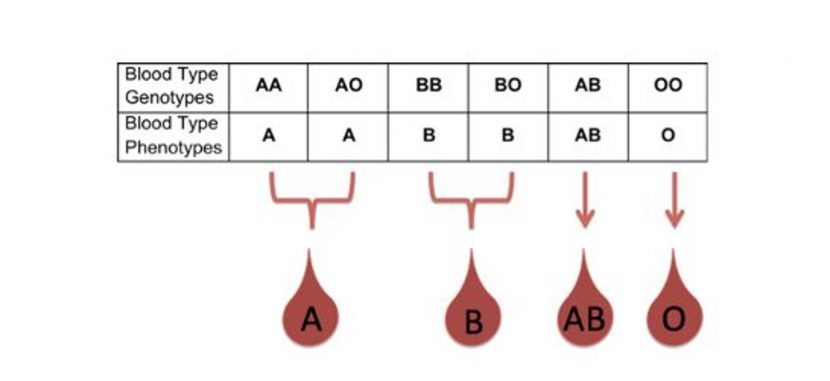 It depends on the presence of the D antigen on the surface of the red blood cells. If the D antigen is present, the person is considered Rh-positive, and if the D antigen is absent, then the person is Rh-negative.
It depends on the presence of the D antigen on the surface of the red blood cells. If the D antigen is present, the person is considered Rh-positive, and if the D antigen is absent, then the person is Rh-negative.
If a person is Rh negative, contact with Rh positive blood (for example, during pregnancy or blood transfusion) may form antibodies. These antibodies can cause pregnancy problems in an Rh-negative woman if she is carrying an Rh-positive baby.
In addition to the ABO and Rh systems, about thirty more blood group systems have been discovered to date. Clinically, the most important of these are the Kell, Kidd and Duffy systems. According to the Kell system, donor blood is also examined.
How is the blood type determined?
To determine the blood type, it is mixed with a reagent containing known antibodies.
Three drops of blood taken from one person are applied to the base: the anti-A test reagent is added to one drop, the anti-B test reagent to the other, and the anti-D test reagent to the third, i.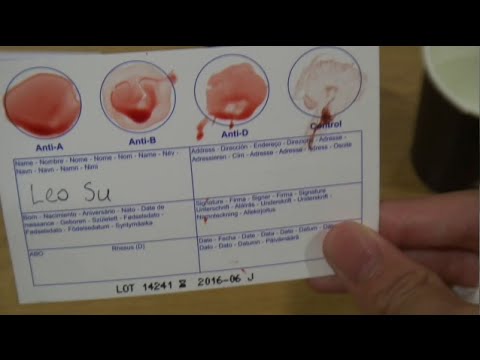 e. Rh test reagent. If blood clots form in the first drop, i.e. erythrocytes stick together (agglutination), then the person has antigen A. If erythrocytes do not stick together in another drop, therefore the person does not have antigen B; and if agglutination occurs in the third drop, then this indicates a positive Rh factor. In this example, the donor has blood type A and is Rh positive.
e. Rh test reagent. If blood clots form in the first drop, i.e. erythrocytes stick together (agglutination), then the person has antigen A. If erythrocytes do not stick together in another drop, therefore the person does not have antigen B; and if agglutination occurs in the third drop, then this indicates a positive Rh factor. In this example, the donor has blood type A and is Rh positive.
Donor and recipient blood group compatibility is extremely important, otherwise the recipient may have dangerous reactions to the blood transfusion.
Inheritance of blood groups
A person inherits from his father and from his mother to the same extent. Therefore, the hereditary substance has a double structure: one part from the mother and the other from the father. Speaking about the inheritance of blood groups, it must be borne in mind that:
- Most of our genes exist in two copies
- Each parent gives (based on a random selection) one of these copies to their children
- Genes occur in different versions (alleles)
- Some versions of the gene are stronger than others
| ABO system | System Rh | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In the AB0 system, antigens are presented in three versions A, B and 0.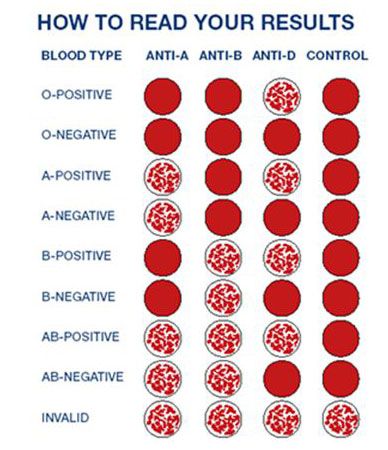 Given that the hereditary substance consists of two parts, six different combinations can occur: Given that the hereditary substance consists of two parts, six different combinations can occur:
The stronger part appears, both equally or a combination. In the AB0 system, genes A and B are stronger than 0, which affects the formation of the blood group as follows:
Example: The mother has a combination of A0 genes in hereditary substance, and her blood type is A (at the same time, she is a carrier of the blood type 0 gene, and there is a possibility that she will pass it on to her child).
| In the Rh system, things are somewhat simpler, since there are only two options: the D antigen is either present (Rh positive) or absent (Rh negative). A positive Rh factor dominates a negative one.
Example: if the mother has Rh positive blood, and there is a hidden negative version, that is, the allele (+/-), and the father has exactly the same combination, and they both pass the negative allele, then two Rh-positive parents can have a child with a negative Rh factor.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
How is blood type inherited? - American Medical Clinic
Blood consists of a liquid part - plasma and various blood cells (shaped elements). Plasma contains proteins, minerals. The formed elements of blood are erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets. The volume of blood is 6-8% of body weight - about 5 liters. Blood performs a number of important functions: transports oxygen, carbon dioxide and nutrients; distributes heat throughout the body; provides water-salt exchange; delivers hormones and other regulatory substances to various organs; has a protective (immune) function.
Differences between people in terms of blood types are differences in the composition of certain antigens and antibodies.
The existence of blood groups became known only at the beginning of the last century, in 1900-1902, when the Austrian scientist Karl Landsteiner found that when the blood of two different people is mixed, in some cases, red blood cells stick together, in others they do not.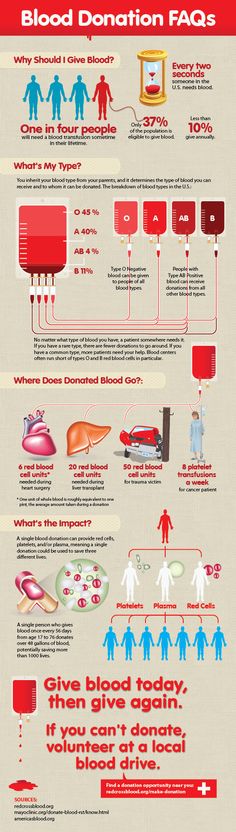 This means that not everyone has the same blood, and there are compatible and incompatible blood types. This discovery was of great importance, as it suggested a way to safely transfuse blood: you just need to determine its compatibility.
This means that not everyone has the same blood, and there are compatible and incompatible blood types. This discovery was of great importance, as it suggested a way to safely transfuse blood: you just need to determine its compatibility.
More than 20 years later, it became known that blood types are inherited and that inheritance occurs in strict accordance with the laws of genetics.
Any hereditary trait is controlled by at least a couple of genes, one of which the child receives from the mother, the other from the father. And in this case, too, parents pass on to the child not a “ready-made” blood type, but one gene responsible for its formation. It depends on the interaction of these genes what kind of blood type the child will have: the same as that of the father, the same as that of the mother, or as a result of a combination of genes, a third variant will arise.
Studying the structure of red blood cells, Landsteiner discovered special substances. He divided them into two categories, A and B, highlighting the third, where he took the cells in which they were not. Later, his students discovered erythrocytes containing A- and B-type markers at the same time.
Later, his students discovered erythrocytes containing A- and B-type markers at the same time.
As a result of research, a system of division into blood groups arose, which was called ABO (read a, b, zero), in which four groups are distinguished. We are still using this system.
- I (0) - blood group is characterized by the absence of antigens A and B;
- II (A) - is established in the presence of antigen A;
- III (B) - is established in the presence of antigens B;
- IV (AB) - is established in the presence of antigens A and B.
Group I is called zero and is designated as 00, which indicates the presence of two identical genes that determined the sign of the group - one zero was received from the father, the other from the mother.
If a child has I blood type, this means that both the father and mother necessarily have gene 0, but it does not mean at all that they also have group I, since their second genes could be different.
The gene of group II is denoted by the letter A. And if a child receives such a gene from both parents, then, of course, he will have blood group II (AA). But he will have the same group and if he receives gene 0 from one of the parents, and A from the other, since gene 0 has one feature - it cannot manifest itself in the presence of gene A.
The gene of the III blood group is denoted by the letter B. This group is also formed in those who received from their parents two identical BB genes or two different ones - B and 0, because gene 0 does not manifest itself in this combination either.
What happens if a child inherits gene A from one parent and gene B from the other? In relation to each other, they are tolerant, one does not suppress the other, and their combination leads to the appearance of a new sign - blood group IV (AB).
Table of inheritance of the blood type of the child depending on the blood types of the father and mother
| Mom + Dad | Child's blood group: Options (in %) | |||
| I + I | I (100%) | - | - | - |
| I + II | I (50%) | II (50%) | - | - |
| I + III | I (50%) | - | III (50%) | - |
| I + IV | - | II (50%) | III (50%) | - |
| II + II | I (25%) | II (75%) | - | - |
| II + III | I (25%) | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| II + IV | - | II (50%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| III + III | I (25%) | - | III (75%) | - |
| III + IV | - | II (25%) | III (50%) | IV (25%) |
| IV + IV | - | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (50%) |
Rh inheritance
The birth of a child with a negative Rh factor in a family with Rh-positive parents causes deep bewilderment at best, distrust at worst.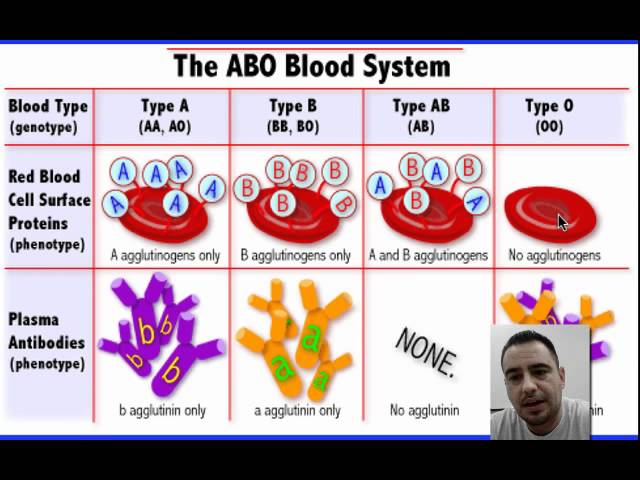 Reproaches and doubts about the fidelity of the spouse. Oddly enough, there is nothing exceptional in this situation. There is a simple explanation for such a delicate problem.
Reproaches and doubts about the fidelity of the spouse. Oddly enough, there is nothing exceptional in this situation. There is a simple explanation for such a delicate problem.
The Rh factor is an antigen (protein) found on the surface of red blood cells (erythrocytes). It was discovered at 1919 g in the blood of monkeys, and later in humans. Approximately 80-85% of people have it and are accordingly Rh-positive. Those who do not have it (the remaining 15%) are Rh-negative. It is also taken into account in blood transfusion.
These indicators are denoted by the Latin letters Rh with a plus or minus sign, respectively.
The inheritance of blood type and Rh factor occur independently of each other. If both parents are Rh positive, the child will be positive. If both parents are negative. - the child inherits more often - negative. If one of the parents is Rh-positive and the other is Rh-negative, then the probability of the baby's Rh-affiliation is determined by 50% to 50%.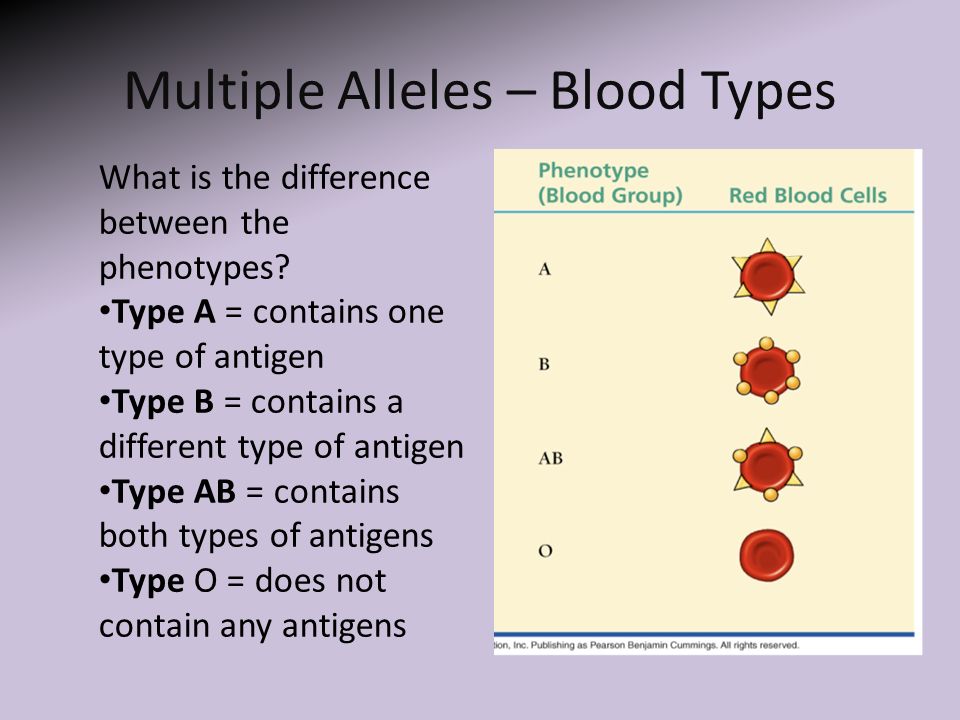 There is a possibility of Rhesus inheritance after several generations (the case when the father and mother have a positive Rh, and the born child has a negative Rh). Therefore, when planning a family, parental compatibility studies are mandatory - it is necessary to determine blood groups and blood rhesus. Women with Rh-negative blood are at risk.
There is a possibility of Rhesus inheritance after several generations (the case when the father and mother have a positive Rh, and the born child has a negative Rh). Therefore, when planning a family, parental compatibility studies are mandatory - it is necessary to determine blood groups and blood rhesus. Women with Rh-negative blood are at risk.
A positive Rh factor in a woman and a negative one in a man do not represent any cause for concern. If a woman has Rh-negative blood, and her husband has Rh-positive blood, then Rh conflict may develop during pregnancy, so a woman is recommended to do a blood test for antibodies to the Rh factor before pregnancy. The fact is that if a woman has undergone a surgical operation (including abortion) or a blood transfusion before pregnancy, or if the pregnancy is not the first, then there is a possibility of formation of specific antibodies in her blood. In a Rh-negative woman with a Rh-positive fetus, immune complications (hemolytic disease of the newborn, etc.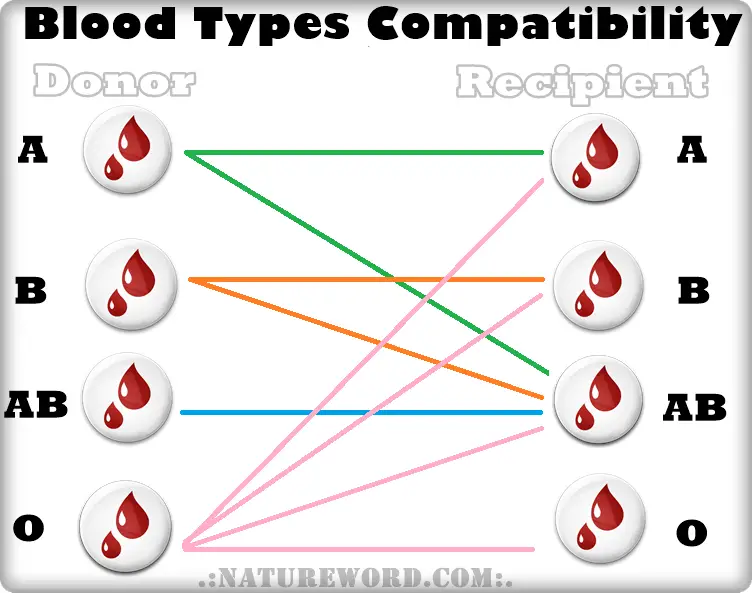 ) are possible, and especially from the second or third pregnancy. To prevent complications, anti-Rhesus gamma globulin is administered. It is necessary to regularly examine the blood for Rh antibodies in dynamics.
) are possible, and especially from the second or third pregnancy. To prevent complications, anti-Rhesus gamma globulin is administered. It is necessary to regularly examine the blood for Rh antibodies in dynamics.
Character inheritance
For centuries, parents only wondered what their child would be like. Today there is an opportunity to look into the beautiful far away. Thanks to ultrasound, you can find out the sex and some features of the anatomy and physiology of the baby.
Genetics allows you to determine the likely color of the eyes and hair, and even the presence of an ear for music in a baby. All these traits are inherited according to the laws of Mendel and are divided into dominant and recessive. The dominant gene is indicated by a capital letter of the Latin alphabet, and in its presence, the recessive gene, as a rule, does not show its properties. The recessive gene is indicated by a capital letter of the Latin alphabet. If, for some trait, an organism contains two identical genes (two recessive or two dominant), then it is called homozygous for this trait. If the organism contains one dominant and one recessive gene, then it is called heterozygous for this trait, and at the same time, those properties of the trait that are encoded by the dominant gene are manifested.
If the organism contains one dominant and one recessive gene, then it is called heterozygous for this trait, and at the same time, those properties of the trait that are encoded by the dominant gene are manifested.
For example,
A is a dominant gene that determines brown eye color
a - recessive gene that determines the blue color of the eyes
Possible variants of the genotype:
AA - homozygous, brown eyes
Aa - heterozygote, brown eyes
aa - homozygous, blue eyes
Brown eyes, hair with small curls, and even the ability to roll the tongue into a tube are dominant signs. Most likely, the child will inherit them.
Unfortunately, the dominant features also include a tendency to early baldness and graying, myopia and a gap between the front teeth.
Gray and blue eyes, straight hair, fair skin, mediocre ear for music are considered recessive. These symptoms are less likely to occur.
Blood type and risk of certain diseases
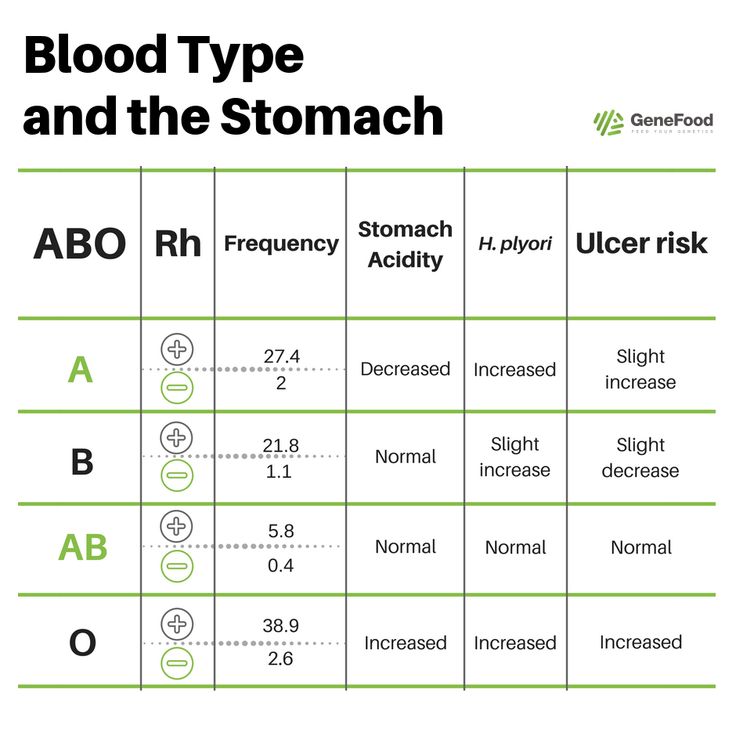
There is a pattern between blood type and the risk of developing certain diseases (predisposition).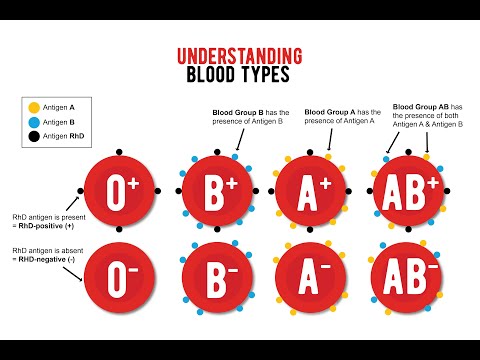 Australian scientists have found that people with blood type 0 (I) are much less likely to suffer from schizophrenia. People with type B (III) blood have a higher risk than others of a severe disease of the nervous system - Parkinson's disease. Of course, the blood type itself does not mean that a person will necessarily suffer from a "characteristic" disease for her. There are many factors involved, and blood type is just one of them.
Australian scientists have found that people with blood type 0 (I) are much less likely to suffer from schizophrenia. People with type B (III) blood have a higher risk than others of a severe disease of the nervous system - Parkinson's disease. Of course, the blood type itself does not mean that a person will necessarily suffer from a "characteristic" disease for her. There are many factors involved, and blood type is just one of them.
Blood type and human character
Blood type 0 (I). Energetic, sociable, good health, strong will. Striving for leadership. Fussy, ambitious.
Blood group A (II). Diligent and committed. They love harmony and order. Their weakness is stubbornness.
Blood group B (III). Delicate, impressionable, calm. Increased demands on themselves and others. Individualists. Easy to adapt to everything. Powerful and creative personalities.
Blood group AB (IV). Emotions and feelings take precedence over common sense and calculation.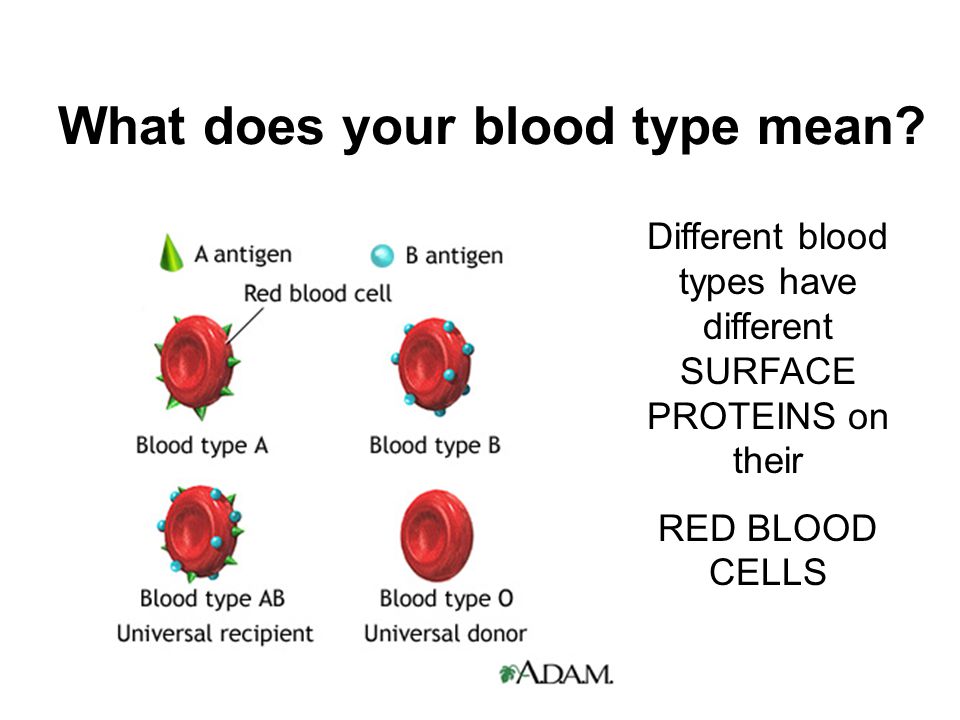
 The father's blood type has the designation 0, and in his hereditary substance there is a combination of genes 00. Accordingly, he can only pass 0 to the child, i.e. absence of antigens. Thus, their child may have an A (A0) or 0 (00) blood type.
The father's blood type has the designation 0, and in his hereditary substance there is a combination of genes 00. Accordingly, he can only pass 0 to the child, i.e. absence of antigens. Thus, their child may have an A (A0) or 0 (00) blood type.