Wetting the bed pregnancy symptom
Causes, Management Tips, and More
Pregnancy Incontinence: Causes, Management Tips, and MoreMedically reviewed by Michael Weber, M.D. — By Ashley Marcin on February 22, 2017
What is pregnancy incontinence?
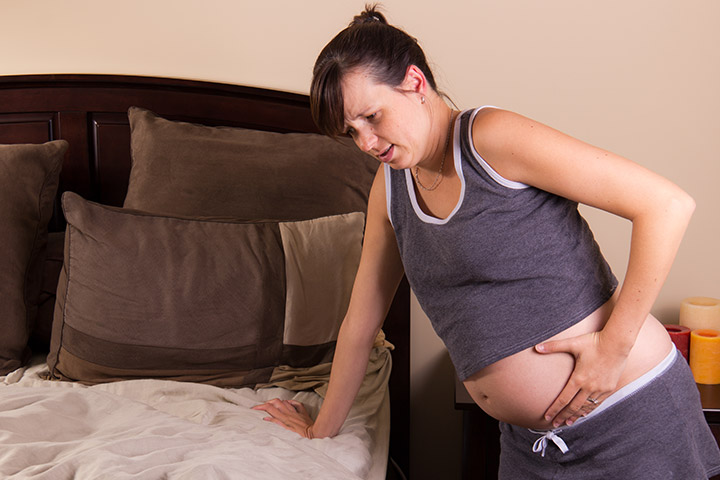
Frequent urination is one of the earliest signs of pregnancy. Leaking urine, or incontinence, is also a common symptom during and after pregnancy. About 54.3 percent of pregnant women report negative effects on their quality of life, including travel and emotional areas. Symptoms can increase as the baby grows and last a few weeks after birth.
There are several types of urinary incontinence:
- stress incontinence: loss of urine due to physical pressure on the bladder
- urgency incontinence: loss of urine due to an urgent need to urinate, commonly caused by bladder contractions
- mixed incontinence: a combination of stress and urgency incontinence
- transient incontinence: temporary loss of urine due to a medication or a temporary condition, such as a urinary tract infection or constipation
Learn more about why you may have incontinence during or after pregnancy, what it means for you and baby, and how you can cope.
Is it urine or amniotic fluid?
Q:
How can I know if I’m leaking urine or amniotic fluid?
Anonymous patient
A:
Short of going to the hospital to test the fluid, you can check how the fluid leaks. If it’s appearing intermittently and in smaller amounts, it’s probably urine. Most of the time when amniotic fluid leaks, it comes in much larger amounts (often described as a “gush”) and persists continuously. The presence of a white waxy or dark green substance is also indicative of amniotic fluid.
Michael Weber, MD
Answers represent the opinions of our medical experts. All content is strictly informational and should not be considered medical advice.
What causes pregnancy incontinence?
Your bladder sits right above your pelvic bones and is supported by your pelvic floor. It relaxes and fills with urine throughout the day while the sphincter keeps the organ closed until you can use the bathroom. During pregnancy and childbirth, your pelvic floor muscles are put to the test.
During pregnancy and childbirth, your pelvic floor muscles are put to the test.
Common causes of pregnancy incontinence include:
Pressure: You may leak when you cough, sneeze, exercise, or laugh. These physical movements put extra pressure on your bladder, which causes stress incontinence. Your baby also puts extra pressure on your bladder as they grow bigger.
Hormones: Changing hormones can affect the lining of your bladder and urethra.
Medical conditions: Some medical causes for incontinence include diabetes, multiple sclerosis, anxiety medications, or a stroke in the past.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Between 30 to 40 percent of women who didn’t treat their UTI completely will develop symptoms during pregnancy. Incontinence is a symptom of UTI.
What are the treatment options for pregnancy incontinence?
The first lines of treatment for pregnancy incontinence are lifestyle changes and bladder management. Here are some tips for managing your bladder:
Here are some tips for managing your bladder:
Do Kegels: Kegel exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor. They’re a safe and effective exercise before, during, and after pregnancy. To do a Kegel, focus on the muscles you use to hold in urine. Squeeze them for ten seconds before relaxing. Aim to do five sets of these exercises per day. Learning how to relax your pelvic floor may help during and after labor.
Create a bladder diary: Jot down when you notice the most leaks so you can plan your trips. This is also the first step to bladder retraining. Bladder retraining is about re-teaching your bladder to hold more urine by extending time between trips.
Avoid carbonated or caffeinated drinks: Avoid carbonated drinks, coffee, or tea. These beverages may make you feel like you need to use the bathroom more often. Try drinking more water or decaffeinated drinks.
Avoid drinking at night: Limit your beverages in the evening to avoid frequent trips to the bathroom and leaking at night.
Eat a high-fiber diet: Eat foods that are high in fiber to avoid constipation, which puts added stress on your pelvic floor.
Maintain a healthy weight: Extra weight, especially around your abdomen, increases pressure over your bladder. Losing weight after labor can also help with incontinence after pregnancy.
Read more: Natural remedies for an overactive bladder »
Discuss any big changes with your doctor to make sure you’re doing what’s best for yourself and your baby. While medication and surgery are also options for incontinence, you may want to wait until after your pregnancy.
Tips for preventing UTIs
Do
- drink plenty of water, up to eight glasses per day
- urinate before and after having sex
- wipe from front to back after urination
- wear cotton fabrics and loose fitting clothes when possible
- change your underwear each day
Contact your doctor if you think you have a UTI. An untreated UTI can lead to a kidney infection, which may also cause early labor and a low birth weight.
An untreated UTI can lead to a kidney infection, which may also cause early labor and a low birth weight.
Don’t
- engage in intercourse while you have a UTI
- drink beverages that irritate the bladder, like fruit juices, caffeine, alcohol, and sugar
- hold your urine for long periods of time
- use strong soaps, douches, sprays, or powders
- wear the same underwear for more than a day
Treatment for a UTI involves antibiotics for three to seven days. This treatment is safe for your baby. Call your doctor if you have side effects, such as a fever, chills, or cramps, after taking your medication.
Are some women more at risk for pregnancy incontinence?
Women who already have an overactive bladder or urgency incontinence will likely have symptoms that continue or worsen during pregnancy.
Other risk factors include:
- older age
- being overweight
- having previous vaginal delivery
- having previous pelvic surgery
- smoking, which leads to chronic coughing
Causes after childbirth
Giving birth can contribute to incontinence after pregnancy. During vaginal delivery, muscles and nerves may be injured. A long labor or prolonged pushing can increase the likelihood of damage to nerves as well. The American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recognizes that cesarean delivery reduces incontinence during the first year. However, the benefits go away two to five years after delivery.
During vaginal delivery, muscles and nerves may be injured. A long labor or prolonged pushing can increase the likelihood of damage to nerves as well. The American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recognizes that cesarean delivery reduces incontinence during the first year. However, the benefits go away two to five years after delivery.
How is pregnancy incontinence diagnosed?
Tell your doctor if you’re experiencing incontinence. In some cases, it may be a UTI and you may need antibiotics. If you’re near the end of your pregnancy, you may also confuse leaking urine with leaking amniotic fluid. It’s best to check with your doctor so you know the exact cause.
If signs of labor and infection are cleared, your doctor may perform other tests. A bladder scan using ultrasound can help see if your bladder is emptying the whole way. A bladder stress test allows your doctor to see if you have leaking when you cough or bend down.
If your doctor suspects you have a UTI, they will likely ask for a urine sample for lab testing. This may require you go to your hospital’s lab instead of your usual office. Your doctor may also perform special tests to check if the fluid you’re leaking is from your water breaking.
This may require you go to your hospital’s lab instead of your usual office. Your doctor may also perform special tests to check if the fluid you’re leaking is from your water breaking.
Does incontinence go away after the baby is born?
Some women’s incontinence symptoms go away in the days or weeks after their baby is born. For others, the leaking continues or may get worse. However, incontinence can be managed with first line treatments such as Kegels, bladder retraining, weight loss, and exercise.
Speak with your doctor about your concerns, especially if lifestyle changes don’t work or you’re still experiencing incontinence six or more weeks after delivery. You may want to consider other treatments such as medications and surgery after your pregnancy.
Read more: Female urinary stress incontinence treatments »
How can you prevent pregnancy incontinence?
Remember: Pregnancy incontinence is a common condition, especially as your belly grows or after your delivery. The good news is that the tips listed above are effective ways to manage incontinence.
The good news is that the tips listed above are effective ways to manage incontinence.
Keep reading: Prenatal care: Urinary frequency and urgency »
Last medically reviewed on February 22, 2017
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Health
How we vetted this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Bladder control problems in women (Urinary incontinence). (2016, July)
niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/bladder-control-problems-women - Committee opinion. (2015)
acog.org/Resources-And-Publications/Committee-Opinions/Committee-on-Obstetric-Practice/Cesarean-Delivery-on-Maternal-Request - Hooton, T.
 M. (2016, April 29). Urinary tract infections and asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy
M. (2016, April 29). Urinary tract infections and asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy
uptodate.com/contents/urinary-tract-infections-and-asymptomatic-bacteriuria-in-pregnancy - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2014, September 16). Stress incontinence: Risk factors
mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/stress-incontinence/basics/risk-factors/con-20027722 - Poise. (n.d.). How can I identify if I have pregnancy incontinence? Retrieved from
poise.com.au/facts-and-support/pregnancy-incontinence/how-can-i-identify-if-i-have-pregnancy-incontinence/ - Pregnancy, childbirth, & bladder control. (2016, February 2)
my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/pregnancy-childbirth-bladder-control - Sangsawang, B., & Sangsawang, N. (2013). Stress urinary incontinence in pregnant women: A review of prevalence, pathophysiology, and treatment. International Urogynecology Journal, 24(6), 901-912
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3671107/ - Urinary tract infection during pregnancy.
 (2015, August)
(2015, August)
americanpregnancy.org/pregnancy-complications/urinary-tract-infections-during-pregnancy/
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Feb 22, 2017
By
Ashley Marcin
Edited By
Austin Anaya
Medically Reviewed By
Michael Weber, MD
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Michael Weber, M.D. — By Ashley Marcin on February 22, 2017
related stories
Overflow Incontinence: What Is It and How Is It Treated?
What You Need to Know About Urge Incontinence
What Causes Peeing While Coughing?
Stress Incontinence
What Is a Nurse Midwife and How to Tell If They Are Right for You
Read this next
Overflow Incontinence: What Is It and How Is It Treated?
Medically reviewed by Harshil Matta, DO
Overflow incontinence occurs when your bladder doesn't completely empty when you urinate.
 Learn why this happens and how it's managed.
Learn why this happens and how it's managed.READ MORE
What You Need to Know About Urge Incontinence
Medically reviewed by Stacy Sampson, D.O.
Urge incontinence occurs when you have a sudden urge to urinate and can’t hold the urine in. Discover causes, home remedies, and more here.
READ MORE
What Causes Peeing While Coughing?
Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph.D., MSN
Having urine leak while you cough is a medical condition known as stress urinary incontinence. Learn more about what causes it.
READ MORE
Stress Incontinence
Medically reviewed by Graham Rogers, M.D.
Stress incontinence is the inability to control your urge to urinate. Read more on how to treat this serious and embarrassing disorder.

READ MORE
What Is a Nurse Midwife and How to Tell If They Are Right for You
Medically reviewed by Meredith Wallis, MS, APRN, CNM, IBCLC
A nurse midwife is a nurse with education, training, and certification to provide prenatal, delivery, and women's care.
READ MORE
Your 6-Week Ultrasound: What to Expect
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
We'll tell you all about the 6-week ultrasound, including why your doctor may have ordered it, what the risks are, and what it means if no heartbeat…
READ MORE
Does Swaddling Increase the Risk of SIDS?
Medically reviewed by Mia Armstrong, MD
Is swaddling safe, or is it a risk factor for SIDS? Here's what the most recent research says.
READ MORE
How to Relieve and Prevent Hip Pain During Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Holly Ernst, PA-C
Hip pain is a common complication of pregnancy.
 Here are stretches, other home remedies, causes, and what you can do to prevent it.
Here are stretches, other home remedies, causes, and what you can do to prevent it. READ MORE
Antidepressants in Pregnancy Aren't Linked to Increased Neurological Issues in Children
A cohort study of antidepressant use in pregnancy found that the rate of neurological disorders in children born to those who took antidepressant…
READ MORE
These Guided Pregnancy Journals Will Help You Document All the Feels
Medically reviewed by Meredith Wallis, MS, APRN, CNM, IBCLC
The pregnancy and postpartum periods are full of emotions (rightfully so!), and these pregnancy journals are a great place to document it all.
READ MORE
Frequent Urination During Pregnancy | Pampers
You may be wondering whether peeing a lot is a sign of pregnancy or whether this urge to pee so often will ever go away. Frequent urination is a common early pregnancy symptom, but it can also reappear later on during pregnancy as your uterus and baby grow, putting pressure on your bladder. Although it can definitely be annoying, in most cases, it's nothing to worry about. Read on to find out what causes frequent urination during pregnancy, get some tips to help you manage it, and learn the signs that indicate it may be linked to another condition, like a urinary tract infection.
Frequent urination is a common early pregnancy symptom, but it can also reappear later on during pregnancy as your uterus and baby grow, putting pressure on your bladder. Although it can definitely be annoying, in most cases, it's nothing to worry about. Read on to find out what causes frequent urination during pregnancy, get some tips to help you manage it, and learn the signs that indicate it may be linked to another condition, like a urinary tract infection.
What Causes Frequent Urination During Pregnancy?
What makes you need to pee more is often the increased amount of blood in your body. To process this blood flow, your kidneys need to produce extra fluids, which then end up in your bladder. Although peeing often during pregnancy is annoying, it's also a normal and common pregnancy symptom. Here are some frequently asked questions about this symptom:
What is considered frequent urination in pregnancy? There's no set number of visits to the bathroom – it's simply needing to go more often than you usually would.

When does frequent urination start during pregnancy? How soon it may start differs for each woman, but you may find yourself needing to pee more often from around six to eight weeks of pregnancy.
Will I need to pee this often the whole pregnancy? It may ease up for a while after you enter the second trimester, but you may find the increased urge to pee returns later on, as your growing baby places more pressure on your bladder. Toward the end of the third trimester, when your baby “drops," the extra pressure on your pelvis and bladder might have you rushing to pee even more frequently.
How often should you pee? Whenever you have to! It's better not to hold it in.
Tips to Manage Peeing Often While Pregnant
You can't really avoid more frequent urination, and you really wouldn't want to, as it's a natural consequence of drinking lots of fluids to stay well hydrated and healthy during pregnancy. Here are some tips that might help make your life easier:
Here are some tips that might help make your life easier:
Lean forward when you pee so that you properly empty your bladder
To prevent increased urination at night, try not to drink too much water just before going to bed
Avoid beverages and foods containing caffeine, which can make you need to pee more often. (Read our article to find out more about what not to eat or drink while you're pregnant.)
Practice Kegel exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles, as this can help prevent leaking when you cough, sneeze, or laugh, both before and after giving birth. (If you do find yourself peeing when you sneeze, consider wearing a panty liner.)
If your urine is dark yellow or orange, this may be a sign of dehydration − try to increase your fluid intake until your urine is back to a normal pale yellow
If you're heading out the door, or you know you're going into a long meeting, consider one more dash to the toilet beforehand.
 You can also try to scout out where the nearest bathroom so you're not caught off guard.
You can also try to scout out where the nearest bathroom so you're not caught off guard.
Can Pregnancy Peeing Be a Sign of a Problem?
More frequent urination is usually a normal pregnancy symptom. However, sometimes it can be a sign of a medical condition that may require treatment by your healthcare provider. These conditions include:
Urinary tract infection (UTI). Many women wonder whether frequent urination is part of pregnancy or a UTI. If it's a UTI, you may notice a painful, burning sensation while peeing, have a fever, notice cloudy urine, or see blood in the toilet. You may also feel the strong urge to pee, but then only a few drops will come out. Pregnant women face an increased risk of UTI from week 6 to week 24, because the growing uterus can place pressure on the urinary tract, increasing the chance of bacterial infections. If you suspect you have a UTI, consult your healthcare provider, as this infection requires treatment – often antibiotics.

Gestational diabetes. Frequent urination can sometimes be a sign of gestational diabetes, generally a temporary form of diabetes that affects a small percentage of moms-to-be. Healthcare providers usually test for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. If gestational diabetes is treated, then the baby's health isn't adversely impacted, and the diabetes will usually go away after you give birth. If you notice symptoms like frequent urination combined with persistent thirst, nausea, or fatigue, consult your healthcare provider.
Frequent urination during early pregnancy is common and usually nothing to worry about. Although it may feel as if you are peeing all the time, keep in mind that it may ease up for a time, before returning later on. Once your baby is born, your urge to pee more often should go away, and you'll only have your newborn's pee to worry about!
Early pregnancy | Shchelkovsky perinatal center
Pregnancy is a wonderful period! However, the changes taking place in the body at this time can greatly frighten you. The phenomena characteristic of pregnancy are different for all women, and will not necessarily be repeated during each subsequent gestation. Let's analyze the most common symptoms, their causes and possible methods of correction.
The phenomena characteristic of pregnancy are different for all women, and will not necessarily be repeated during each subsequent gestation. Let's analyze the most common symptoms, their causes and possible methods of correction.
1. Frequent urination.
Frequent, painless (!) urge to urinate is one of the signs of pregnancy. This is due to increased secretion of progesterone (pregnancy hormone), changes in metabolism and pressure from the growing uterus on the bladder.
Be sure to see a doctor if:
- painful urination (this may be a sign of an infection)
- urine of strange color (stained with blood, brown)
- the amount of urine excreted per day is much less than the liquid drunk per day
Life hack! Under no circumstances should fluid intake be restricted! To alleviate the condition and reduce the frequent urge to urinate, it is necessary to exclude products that have a diuretic effect: tea, coffee, zucchini, watermelon; as well as salty, spicy and fried foods. It is better to drink water or juice. Wear comfortable cotton underwear that does not squeeze the lower abdomen.
It is better to drink water or juice. Wear comfortable cotton underwear that does not squeeze the lower abdomen.
2. Nausea, vomiting, heartburn, increased susceptibility to smells.
Nausea is one of the common symptoms of early pregnancy. The range of issues related to nausea and vomiting during pregnancy is quite wide. From "it's good, I don't even feel sick" (with relief), "I don't feel sick, what's wrong with me?" (with anxiety) to "when will this nausea pass" (with hope). Indeed, these symptoms are not at all a mandatory accompaniment of gestation, they can manifest at 7-8 weeks and last up to 12-14 weeks. The duration of this condition can sometimes be delayed, but rarely persists throughout pregnancy.
Life hack! For nausea, eat before feeling hungry. Solid, non-hot food and drinks at a cool temperature are best. With heartburn, you should eat small portions of food and often, and most importantly, sit, stand or walk for at least 30 minutes after eating, but do not lie down.
You should definitely consult a doctor if:
- vomiting occurs even after drinking water
- vomiting is exhausting, accompanied by dizziness, weakness
- dryness, jaundice and flaking of the skin appear
- Nausea and vomiting interfere with proper nutrition, accompanied by weight loss
To reduce nausea and vomiting in the morning, try eating something before you get out of bed. It can be a cracker, a cookie, a piece of hard cheese. And salty food is preferable to sweet. You can have a snack in the same way at night when you get up to go to the toilet. Do not lie down immediately after eating, this will only increase nausea. Vitamins for pregnant women with nausea should be taken in the evening after meals. Cool water with lemon, ginger, mint tea, or ginger or mint candies can alleviate the condition. It is necessary to exclude those foods, drinks and smells that are unpleasant to you. Brushing your teeth and rinsing your mouth often can also reduce nausea.
3. Pain or cramps in the lower abdomen, constipation, pain in the lumbar region.
The simplest and most easily controlled cause of pain is delayed and incomplete bowel movements. An increase in the concentration of progesterone relaxes the smooth muscles, which are located not only in the uterus, but also in other hollow organs. In this case, the correction of the diet and the restoration of the passage of feces will help. If the measures are ineffective, the doctor may prescribe safe drugs for you. A special type of pain that occurs during exclusivity in pregnant women is pain in the round ligament of the uterus. This acute, rather intense pain occurs, as a rule, on the one hand with a sharp change in body position (for example, when getting up from a chair or leaving a car). This pain occurs due to stretching, and then a sharp contraction, like a spring, of the round uterine ligaments. The pain quickly passes if you immediately take a comfortable position and does not require special treatment.
You should definitely consult a doctor if:
- pain is accompanied by spotting bloody discharge from the external genitalia
- increasing duration and intensity of pain
- abdominal pain accompanied by dizziness, fever, loss of consciousness
Life hack! To normalize bowel movements, eat more vegetables and fruits, drink water and move more during the day. Try to eat often and in small portions.
4. Enlargement and soreness of the mammary glands.
Hormonal restructuring of the body during gestation is accompanied, among other things, by an increase in the size of the mammary glands and an increase in their sensitivity. By the end of the first trimester, the soreness usually disappears, no additional methods of treatment are needed.
Life hack! Choose comfortable supportive underwear (it should not leave marks on the skin at the end of the day). You may need a larger size or a sports bra. Pain in the mammary glands is relieved by a warm shower at the end of the day.
You may need a larger size or a sports bra. Pain in the mammary glands is relieved by a warm shower at the end of the day.
You should definitely see a doctor if:
- the pain is intense
- mammary glands are very dense with redness and body temperature is increased
- discharge from the nipples appears (purulent, bloody)
5. Increased body temperature.
In early pregnancy, an increase in body temperature to 37.5 ° C is not necessary, but is possible due to the peculiarities of the action of progesterone. Because of this, it is difficult for pregnant women to endure stuffy, hot rooms. Self-medication is dangerous: an attempt to bring down the temperature even with a seemingly harmless folk method - tea with raspberries - can mask the true cause of hyperthermia and delay the diagnosis. Due to the increased body temperature, pregnant women should dress in layers and avoid stuffy and hot rooms and spaces so that they can always “adjust” their temperature on their own.
- temperature above 37.5 °C
- along with fever, any pain occurs
- runny nose, cough, body aches appear
6. Nasal congestion, difficulty breathing, nosebleeds.
These symptoms can be explained by the individual reaction of the vascular system to the increase in blood volume that occurs during pregnancy. Another possible reason is dry air in the room, the operation of central heating batteries.
Life hack! The easiest way to deal with nasal congestion is to use a humidifier. If you don't have one, you can put a damp towel on the battery - less effective, but better than nothing. It is possible to use sprays with sea salt, but you need to carefully read the instructions and especially the "Indications" section, it should contain information about the safety of the product during pregnancy.
You should definitely see a doctor if:
- symptoms of a cold occur
- nasal congestion accompanied by ear congestion
- These symptoms appeared after exposure to the allergen known to you
7. Blood pressure fluctuations.
Blood pressure fluctuations.
An ideal option for the course of any pregnancy is the stability of the blood pressure throughout the gestation. However, this is extremely rare. A small (up to 10 units) increase in pressure from the usual reference may be due to an increase in the load on the cardiovascular system as a result of changes in body weight, hormonal changes, and uterine pressure on the vessels. Normal pressure: systolic below 130 mm Hg, diastolic no more than 85 mm Hg. Blood pressure in the range of 130-139/ 85–89 mm Hg considered high to be normal. High numbers are often observed in patients of older reproductive age, suffering from diabetes mellitus and kidney disease, obesity, etc. However, it is imperative to tell the doctor about all these concomitant pathological conditions at the first appointment and, if necessary, consult a neurologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist and other related specialists . Reasonable physical activity, adherence to sleep and wakefulness, a balanced diet, and the rejection of coffee and strong tea allow you to keep pressure within limits. Of the completely exotic for our days, but no less significant - the prevention of stress.
Of the completely exotic for our days, but no less significant - the prevention of stress.
Life hack! If you first discovered that you have high normal pressure, repeat the measurement after 15 minutes. If the pressure remains elevated, see a doctor.
Be sure to see a doctor if:
- your blood pressure is above 140/90 mmHg.
- pressure increased by more than 10 mm Hg. relative to your regular
- an increase in the pressure indicator is accompanied by edema, the appearance of "flies" before the eyes
NB! You should also pay attention to lowering blood pressure. Numbers less than 90/60 mmHg - an excuse to see a doctor.
Life hack! Keep a blood pressure diary, especially if you are prone to hypertension. Show your diary to your doctor at every appointment.
8. Heaviness and pain in the legs.
Heaviness and pain in the legs, especially in the evening, are frequent companions of pregnancy. There is an explanation for the occurrence of symptoms: an increase in load due to growing weight and a shift in the center of gravity of the body.
There is an explanation for the occurrence of symptoms: an increase in load due to growing weight and a shift in the center of gravity of the body.
Life hack! Ask your partner/husband to give you a foot massage, relax with your limbs elevated (not too much!) A therapeutic pedicure, dousing the legs with cool water, a contrast shower, a cream or gel for legs with cooling components (menthol, essential oils), as well as compression stockings or stockings of the lightest degree of compression will help.
You should always see a doctor if:
- one or both legs are very swollen or discolored
- previously diagnosed varicose veins, family history of thrombosis
9. Skin changes.
During pregnancy, you may notice dark spots on your skin. Especially often such darkening (hyperpigmentation) is observed in the nipple area, along the white line of the abdomen. Stretch marks (stretch marks) may appear on the skin of the abdomen and thighs. These are normal signs and do not require any treatment. In most cases, skin color will return to normal after breastfeeding ends, and stretch marks will shrink and fade. Itching can be associated with stretching of the skin, especially in the abdomen and mammary glands. This symptom occurs infrequently and is usually successfully stopped by the use of special products to moisturize and soften the skin. By the way, these same remedies usually help in the fight against stretch marks.
These are normal signs and do not require any treatment. In most cases, skin color will return to normal after breastfeeding ends, and stretch marks will shrink and fade. Itching can be associated with stretching of the skin, especially in the abdomen and mammary glands. This symptom occurs infrequently and is usually successfully stopped by the use of special products to moisturize and soften the skin. By the way, these same remedies usually help in the fight against stretch marks.
Life hack! Oils and moisturizing creams to increase skin elasticity, contrast showers, massage with a hard brush will help reduce the likelihood of skin changes.
You should definitely consult a doctor if:
- along with itching there are areas of redness, spots, peeling
- itching increases
10. Bleeding gums.
Changes in the characteristics of blood circulation in the body of a pregnant woman can cause bleeding gums. The appearance of minor blood impurities during brushing your teeth, when eating solid foods (for example, an apple) is acceptable. However, the key provision is "insignificant". If you find it difficult to assess your own condition, consult a specialist.
The appearance of minor blood impurities during brushing your teeth, when eating solid foods (for example, an apple) is acceptable. However, the key provision is "insignificant". If you find it difficult to assess your own condition, consult a specialist.
You should definitely consult a doctor if:
- you have loose teeth, sore gums, bad breath
- bleeding in the gum area increases
11. Fatigue, mood instability.
Tearfulness, lack of strength, forgetfulness, distraction, the whole palette of feelings "here and now"... The list can be continued, and there is only one explanation for this - pregnancy. The most common early symptom is severe fatigue. There is no universal recipe, just as there is no single picture of these states. The main recommendation for all pregnant women is to rest often, relax and even sleep during the day. Most importantly, you need to remember: pregnancy is not a disease, but a great time to prepare for motherhood.
The first signs of pregnancy in the early stages - how to determine whether conception has occurred?
Table of contents:
- General information
- First signs of pregnancy
- Minor signs of pregnancy
- Signs of pregnancy while breastfeeding
- Types of pregnancy diagnostics
Not every woman realizes that the long-awaited pregnancy has already begun. Indeed, the first signs of the birth of a new life can easily be mistaken for the harbingers of menstruation. How to determine pregnancy in the early stages and prepare for the thought that you will have a baby? In this article, we will give an answer to this question.
General information
Some women quickly realize that they are about to become a mother, others do not notice any changes in their condition for a long time. But if you listen to yourself, it will not be difficult for you to recognize the first signs of pregnancy even before the test shows the coveted two strips. This will allow you to see a doctor as soon as possible in order to undergo the necessary examination and ensure peace of mind for the next nine months.
This will allow you to see a doctor as soon as possible in order to undergo the necessary examination and ensure peace of mind for the next nine months.
After how many days can you find out about pregnancy?
In the very first days after conception, the body will not give you any specific signals. Signs of pregnancy in the early stages can be observed no earlier than the 8-10th day from the moment of fertilization of the egg, when the embryo attaches to the wall of the uterus and the pregnancy hormone, chorionic gonadotropin, begins to enter the mother's body. How noticeable they appear depends on the body's sensitivity to hormonal changes. On the 20th day of embryo development (coincides with the first days of delayed menstruation), most women usually guess about their condition.
Important! Standard rapid tests determine the content of human chorionic gonadotropin in the urine at the 3-4th week of pregnancy, i.e. 1-2 weeks after fertilization 1 .
During this period, it is extremely important that the body receives all the necessary vitamins and minerals for the development of the baby. Therefore, as soon as you begin to suspect that you are expecting a baby, start taking special vitamin and mineral complexes. This is important because the formation of all organs and systems of the embryo occurs from the very first weeks.
The first signs of pregnancy
After fertilization of the egg and its transition from the fallopian tube to the uterine cavity, a series of hormonal changes occur in the woman's body, which rather quickly make themselves felt in the form of the first signs of pregnancy in the early stages1.
Breast enlargement and tenderness
A few days after the expected date of menstruation:
- breasts swell,
- nipple halo widens and darkens,
- bumps on the halo, the so-called tubercles of Montgomery, increase in size.
If swollen breasts cause discomfort and pain during sleep, try wearing a padded bra without wires at night.
Important! The mammary glands are designed in such a way that they do not have muscles that could prevent the skin from stretching, therefore, during pregnancy and lactation, it is necessary to wear a supportive bra and change it in accordance with breast growth to avoid squeezing.
Nausea
This is not a sure sign of pregnancy, as nausea can also be caused by digestive problems. But in combination with other symptoms, nausea often signals that you will have a baby. In the first trimester, this is an absolutely normal, albeit unpleasant, manifestation of your new condition.
Nausea is more often mild and occurs only in the morning, but if it continues throughout the day and is accompanied by vomiting, then a doctor should be consulted.
A few simple tips will help you overcome the attacks that often overshadow the first weeks of pregnancy.
- If you feel sick in the morning, drink plenty of fluids. Before you get out of bed, you can eat low-fat yogurt - this will make you feel better.
 Avoid long breaks between meals, as even increased salivation when you are hungry can cause nausea. Salty crackers and biscuits are good snacks.
Avoid long breaks between meals, as even increased salivation when you are hungry can cause nausea. Salty crackers and biscuits are good snacks. - Eliminate coffee with milk, sweets and fried foods.
- Eat more often, but in small portions.
B vitamins and vitamin D can help reduce morning sickness. Add more whole grains, wholemeal bread, beef liver, cheese, dairy products and nuts, cabbage, apples to your diet. In addition, vitamin-mineral complexes specially designed for taking in the 1st trimester can replenish the reserves of these components.
Urination frequency
In the very first weeks of pregnancy, many women experience frequent urination. This is due to the increased production of the hCG hormone. Especially often the urge to go to the toilet disturbs at night.
Carefully monitor your condition, drink more fluids to make up for its losses. During this period, mineral water without gas, green tea, fruit drinks, compotes, juices half diluted with water are useful. They will not only replenish the volume of fluid, but also help reduce the severity of nausea.
They will not only replenish the volume of fluid, but also help reduce the severity of nausea.
Hypersensitivity to smells
If you feel sick from morning coffee, perfume, or any other strong smell, you may be pregnant. Some women note an increased sensitivity to smells and a sharp change in taste preferences as one of the first signs of pregnancy even before the delay in menstruation in the early stages. Do not rush to get rid of perfume, the aroma of which has become unbearable: after the baby is born, the old aromas and tastes will again become pleasant to you.
To reduce nausea caused by smells, spend more time outdoors and walk more. While at home, ventilate the room for 5-10 minutes every two hours. Access to fresh air will help reduce discomfort.
Drowsiness and fatigue
Decrease in blood pressure at the beginning of pregnancy and more intense metabolic processes in the body often provoke severe fatigue. A balanced diet and walks in the fresh air will help to improve the general condition.
Important! If in the early stages you are haunted by dizziness, we can talk about anemia, that is, a lack of iron, or changes in blood pressure. It is necessary to consult a doctor.
To reduce the risk of anemia, it is necessary to eat foods containing iron: red meat, offal (beef liver, heart). In order for iron to be better absorbed from food, it is worth adding foods rich in vitamin C to the diet: fresh vegetables, citrus fruits, garden greens. Meat dishes, complemented by vegetable salad, are a great option. Special vitamin-mineral complexes for pregnant women with the inclusion of iron will help replenish stocks. They contain the necessary daily dose of this mineral.
Delayed menstruation
One of the most reliable signs of pregnancy. After menstruation stops, because the endometrium creates optimal conditions for the development of the child. However, cycle disorders can also be associated with stress, diseases of the reproductive organs and hormonal disruptions.
Important! About a week after conception, small spotting is possible, which accompanies the attachment of a fertilized egg in the uterus. Doctors call this phenomenon implantation bleeding. It is also considered one of the early signs of pregnancy.
Important! From the very first days you learn about pregnancy, you need to start taking folic acid. The active form of this substance is metafolin. When ingested, metafolin is 100% absorbed and helps the proper development of the baby's heart and brain.
Secondary signs of pregnancy
In addition to direct, there are indirect signs of pregnancy that will help confirm your guesses. They also shouldn't cause you concern.
Heaviness in the lower abdomen
The uterus is preparing to receive its new inhabitant, therefore the blood circulation in it increases, which is accompanied by characteristic sensations in the pelvic region.
Increased appetite
At the beginning of pregnancy, the body consumes more energy - no wonder you are constantly hungry. However, bouts of hunger attack just before the onset of menstruation, stress can also be the cause. In any case, you should not lean on fast food, sweets and starchy foods, especially if the suspicion of pregnancy is confirmed.
However, bouts of hunger attack just before the onset of menstruation, stress can also be the cause. In any case, you should not lean on fast food, sweets and starchy foods, especially if the suspicion of pregnancy is confirmed.
Diversify your diet with fresh fruits and vegetables, protein products (fish, chicken). An excellent snack between meals can be nuts, dried fruits, dairy products (cottage cheese, yogurt). They saturate well without giving an excess of calories.
Insomnia
It happens that as a result of hormonal and psychological changes, the expectant mother hardly falls asleep and often wakes up at night. Try to compensate for the lack of sleep by resting in the afternoon at least on weekends, before going to bed, take a walk in the fresh air and ventilate the bedroom for at least 10-15 minutes.
Important! Never take sleeping pills without consulting your doctor. There are many ways to improve sleep without drugs. A warm (not hot) shower or bath, reading a book, relaxing music helps. At least an hour before bedtime, you must stop using gadgets and watching TV: they overload the nervous system. Warm milk with a spoonful of honey before bed will help you fall asleep.
At least an hour before bedtime, you must stop using gadgets and watching TV: they overload the nervous system. Warm milk with a spoonful of honey before bed will help you fall asleep.
Constipation
During pregnancy, the increased production of progesterone relaxes the intestinal muscles, making digestion difficult. Include high-fiber foods in the menu in reasonable quantities: whole grain bread, fruits, vegetables.
Magnesium helps regulate bowel function, and it is also involved in the transmission of nerve impulses and muscle function. Magnesium is found in grains and nuts, dark chocolate, legumes, leafy vegetables and dairy products. To provide the body with a daily dose of magnesium will help to take a specialized vitamin and mineral complex for pregnant women.
Magnesium not only regulates bowel function, but has a sedative, anti-stress effect and is important for the prevention of increased uterine tone.
Headache
Due to the same hormones , the expectant mother feels a headache in the early stages, which can also be one of the signs of pregnancy. It is necessary to consult a doctor in order not to miss arterial hypertension.
It is necessary to consult a doctor in order not to miss arterial hypertension.
Make it a rule from the very beginning of pregnancy to regularly measure the pressure twice a day: in the morning, just waking up, before breakfast and hygiene procedures, and in the evening, at about 19-20 hours, after a 15-minute rest.
Irritability
Many pregnant women complain of emotional instability and mood swings in the early stages. When you find out the good news about the addition to the family, warn your loved ones that your whims had a very good reason.
Pimples
If you forgot about rashes on your skin after you got out of adolescence, then during pregnancy you will probably have to remember: pimples can reappear on the face and again under the influence of hormones. Be patient, over time, the condition of the skin will return to normal.
It is important during this period to pay attention to face and body care. The immune system is being rebuilt to protect not only you, but also the baby, so choose hypoallergenic care products. They do not contain dyes and fragrances that can irritate the skin.
They do not contain dyes and fragrances that can irritate the skin.
Pigmentation on the abdomen
The appearance of a dark strip running from the navel to the lower abdomen is also included in the list of signs of early pregnancy.
Tingling in the groin
Under the influence of the hormone estrogen, the ligaments become more elastic so that the stomach can further increase in volume without hindrance. This process can respond with mild discomfort in the groin area.
Leg cramps
If you have calf cramps, this indicates a change in metabolism and, in combination with other symptoms of pregnancy, signals your condition.
Consult your doctor, he will select a set of measures that will relieve you of cramps, and tell you about the measures to prevent varicose veins during pregnancy. Wear shoes with low heels, do foot baths with alternating cool and warm water, a light massage of the calf muscles and feet.
Thrush
An increase in vaginal secretions is normal during pregnancy. But if the discharge has become liquid and has acquired a gray-white color with an unpleasant odor, or, conversely, has become cheesy, flaky or purulent, be sure to consult your doctor. In these cases, the risk of infectious complications, including infection of the fetus, increases.
But if the discharge has become liquid and has acquired a gray-white color with an unpleasant odor, or, conversely, has become cheesy, flaky or purulent, be sure to consult your doctor. In these cases, the risk of infectious complications, including infection of the fetus, increases.
Signs of pregnancy while breastfeeding
The myth that a nursing mother cannot get pregnant is one of the most persistent. If the birth of another child is not in your plans, do not forget to use reliable methods of contraception. Your doctor will help you choose a contraceptive. If you are preparing to give your baby a brother or sister, it is not at all necessary to stop breastfeeding. Breastfeeding is also possible during pregnancy if your doctor allows it. It is important that you get all the minerals and vitamins you need. Pay attention to the sufficient intake of iodine: it helps in the formation of the brain and thyroid gland of the baby.
Why pregnancy diagnosis is important
The sooner you find out that you are pregnant, the sooner you will be registered at the antenatal clinic and meet with doctors who will exclude the risk of ectopic pregnancy, hereditary and genetic diseases of the fetus, and will also provide all the necessary information about how to behave during pregnancy. They will tell you the rules of nutrition and recommend taking special vitamin and mineral complexes for the proper formation of organs and the development of the baby, they will warn you about what changes will happen to you during this period, and indicate the timing of screening examinations that allow you to assess the course of pregnancy and fetal development.
They will tell you the rules of nutrition and recommend taking special vitamin and mineral complexes for the proper formation of organs and the development of the baby, they will warn you about what changes will happen to you during this period, and indicate the timing of screening examinations that allow you to assess the course of pregnancy and fetal development.
Types of pregnancy diagnostics
Pregnancy test
The level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) increases gradually, so a standard rapid pregnancy test will give a reliable result only two weeks after conception.
Blood test
A laboratory blood test for hCG will give reliable information starting from the 7th day after the fertilization of the egg.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound will confirm pregnancy no earlier than 3-4 weeks after fertilization.
Gynecological examination
By examining the condition of the uterus, the gynecologist will also be able to diagnose pregnancy after egg implantation.












