Last week pregnancy symptoms
37 Weeks Pregnant | Pregnancy
Your baby could come any day now – and this would not be considered early. Your baby is now "full term", which means that they're probably big enough, and mature enough, to survive in the outside world. However you still may have to wait another few weeks.
If you're carrying twins, then you will probably give birth this week. Twin pregnancies rarely go beyond 38 weeks. The Twins and Multiple Birth Association (TAMBA) has more information.
What's happening in my body?
Around 95% of babies will now be head down, facing their mother's back, which is the best position for labour. When the baby's head moves down into the pelvis, it's said to be "engaged". You might see your bump drop a bit when this happens.
If your baby's still in the bottom-down position (breech) don't worry, there's still time for them to turn. Some babies don't move into place until labour starts. When you're sitting down, try leaning forwards, with your hips above your knees. It's not a proven technique but many women say that it coaxes the baby into position and it certainly can't do any harm.
You might find that you're getting more vaginal discharge now and Braxton Hicks contractions. These are the "practice contractions", which can feel uncomfortable but should not be painful.
You could also be getting a sudden urge to spring clean. That's your "nesting" instinct kicking in. Just don't overdo it, you should try to rest as much as possible.
Talk to your midwife about group B strep
Group B strep is a common bacteria – up to 2 in 5 people have it living in their body. If you carry group B strep while you're pregnant, there's a small risk it could make your baby seriously ill. Most group B strep infections in newborn babies are preventable.
For more information talk to your midwife, or visit the Group B Strep Support website.
Look out for these signs:
1. The "show": you may see a sticky blob of mucus in your pants, which might be yellow or bloody. This is called a "show". This plug used to seal up your cervix and when it comes undone, this can be one of the first signs of labour. However, you may still have days, or even weeks to wait.
This is called a "show". This plug used to seal up your cervix and when it comes undone, this can be one of the first signs of labour. However, you may still have days, or even weeks to wait.
2. Your waters break (rupturing of the membranes): don't expect a massive gush like you see in films – it could just be a little "pop" and a trickle. The liquid should be clear. If it drips, then use a pad, not a tampon. Contact your midwife or doctor immediately if it's smelly or coloured.
3. Back pain: this is caused by your baby's head on your spine. When their head meets your sacrum (tailbone) it can be quite uncomfortable!
4. The urge to go to the toilet: this is caused by your baby's head pressing on your bladder or bowels. You may find that you wet or poo yourself. It's very common, so no need to be embarrassed.
5. Contractions or tightening around your bump: it hurts when your bump goes hard, and then the pain goes away when the muscles relax. It feels like period pains to start with or a heavy dragging feeling in your pelvis and legs. Then your contractions get longer, stronger and more frequent.
It feels like period pains to start with or a heavy dragging feeling in your pelvis and legs. Then your contractions get longer, stronger and more frequent.
When your contractions last for at least 60 seconds and come every 5 minutes, it's time to call your midwife or hospital. Phone straight away if:
- you're losing blood
- you're in too much pain
- you're worried that something's wrong
- your baby stops moving
3rd trimester pregnancy symptoms (at 37 weeks)
As your baby moves down into your pelvis, you may start to feel some relief from pregnancy symptoms such as heartburn, indigestion and needing to pee every 5 minutes.
Your pregnancy symptoms could include:
Your signs of pregnancy could also include:
- painless contractions around your bump, known as Braxton Hicks contractions
- sleeping problems (week 19 has information about feeling tired)
- stretch marks (read about stretch marks on week 17's page)
- swollen and bleeding gums (week 13 has information about gum health during pregnancy)
- pains on the side of your baby bump, caused by your expanding womb ("round ligament pains")
- piles (read about piles on week 22's page)
- headaches
- backache
- indigestion and heartburn (week 25 talks about digestive problems)
- bloating and constipation (read about bloating on week 16's page)
- leg cramps (week 20 explains how to deal with cramp)
- feeling hot
- dizziness
- swollen hands and feet
- urine infections
- vaginal infections (see week 15 for vaginal health)
- darkened skin on your face or brown patches – this is known as chloasma or the "mask of pregnancy"
- greasier, spotty skin
- thicker and shinier hair
You may also experience symptoms from earlier weeks, such as:
- mood swings (week 8's page has information on mood swings)
- morning sickness (read about dealing with morning sickness on week 6's page)
- weird pregnancy cravings (read about pregnancy cravings on week 5's page)
- a heightened sense of smell
- sore or leaky breasts (read about breast pain on week 14's page)
- a white milky pregnancy discharge from your vagina and light spotting (seek medical advice for any bleeding)
Read Tommy's guide to common pregnancy symptoms.
What does my baby look like?
Your baby, or foetus, is around 48.6cm long from head to heel, and weighs about 2.9kg. That's approximately the length of 2 cucumbers and the weight of 14 baked potatoes.
Your baby will be trying out different facial expressions, such as frowning and smiling.This is random and not linked to sadness or happiness.
By now, you will hopefully know when your baby's active and when they're calmer.
Action stations
Read a little bit about postnatal depression and encourage your partner to do the same – either one of you could develop symptoms after the birth, although it's most likely to affect you.
More than 1 in 10 will develop this condition after they are pregnant - usually in the first year. Signs include low mood, lack of energy, sleeping problems and frightening thoughts. It's important to get help from your doctor or health visitor if either of you develop these symptoms.
This week you could also...
You may be on your maternity leave or about to stop work. Find out how much maternity leave and pay you're entitled to.
Find out how much maternity leave and pay you're entitled to.
It's a good time to tone up your pelvic floor muscles. Gentle pelvic floor exercises can help to prevent leakage when you laugh, sneeze or cough. Get the muscles going by pretending that you're having a wee and then stopping midflow.
To keep bones and muscles healthy, we need vitamin D. From late March/early April to the end of September, most people make enough vitamin D from sunlight on their skin. However, between October and early March, you should consider taking a daily vitamin D supplement because we cannot make enough from sunlight.
Some people should take a vitamin D supplement all year round, find out if this applies to you on the NHS website. You just need 10 micrograms (it's the same for grown-ups and kids). Check if you're entitled to free vitamins.
It's recommended that you do 150 minutes of exercise a week while pregnant. You could start off with just 10 minutes of daily exercise - perhaps take a brisk walk outside. Check out Sport England's #StayInWorkOut online exercises (scroll to the pregnancy section). Listen to your body and do what feels right for you.
Check out Sport England's #StayInWorkOut online exercises (scroll to the pregnancy section). Listen to your body and do what feels right for you.
There's no need to eat for 2. Now you're in the 3rd trimester, you may need an extra 200 calories a day, but that's not much. It's about the same as 2 slices of wholemeal toast and margarine.
Try to eat healthily, with plenty of fresh fruit and veg, and avoid processed, fatty and salty foods. You may be able to get free milk, fruit and veg through the Healthy Start scheme.
How are you today? If you're feeling anxious or low, then talk to your midwife or doctor who can point you in the right direction to get all the support that you need. You could also discuss your worries with your partner, friends and family.
You may be worried about your relationship, or money, or having somewhere permanent to live. Don't keep it to yourself. It's important, so ask for help if you need it.
Having another baby is probably the last thing on your mind.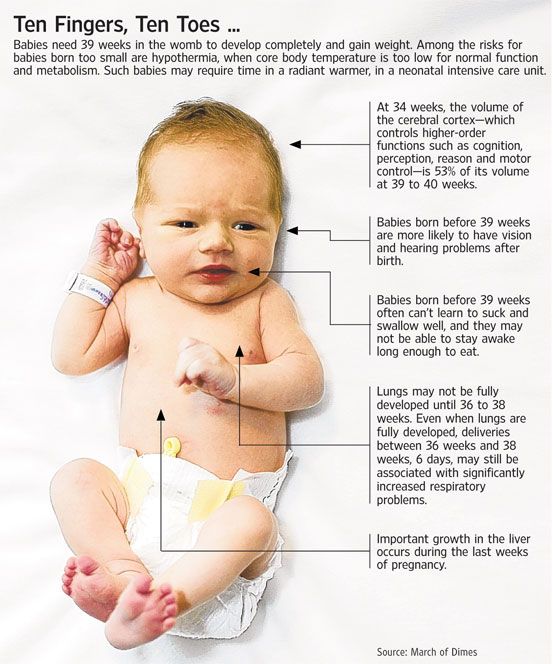 However, now is a good time to start planning what type of contraception you would like to use after your baby is born. Getting pregnant again could happen sooner than you realise and too short a gap between babies is known to cause problems. Talk to your GP or midwife to help you decide.
However, now is a good time to start planning what type of contraception you would like to use after your baby is born. Getting pregnant again could happen sooner than you realise and too short a gap between babies is known to cause problems. Talk to your GP or midwife to help you decide.
You and your family should follow the government and NHS guidance on coronavirus (COVID-19):
To find out about about COVID-19 and pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding, have a look at advice on the:
38 Weeks Pregnant | Pregnancy
What's happening in my body?
At your antenatal appointment, around now, your midwife or doctor will measure the size of your bump with a tape measure and check your blood pressure. They will also look for any protein in your urine that could indicate that you've got a dangerous condition called pre-eclampsia. This can happen in the 2nd half of pregnancy or after the baby is delivered.
They will also look for any protein in your urine that could indicate that you've got a dangerous condition called pre-eclampsia. This can happen in the 2nd half of pregnancy or after the baby is delivered.
If you're having a planned caesarean, otherwise known as an elective caesarean, then you'll probably be booked in when you're at least 39 weeks' pregnant. This is to give your baby's lungs the best chance of being fully developed.
You'll have a chat about what might happen if you go beyond 41 weeks. There could be risks for you or the baby, so you may be offered induction. This is where labour can be brought on artificially by putting a tablet or gel in your vagina. Around 1 in 5 labours are started this way.
5 tips for a happy home birth
Around 1 in 50 women in England have their babies at home, supported by a midwife. Here are some tips for a happy, healthy home birth.
-
Be organised and have everything put aside for the big day. That includes something to wear in labour, a nursing bra, breast pads, maternity pads, and new baby essentials.

-
Plan pain relief with your midwife. You may want to a TENS machine, a birthing ball and a birthing pool. You can arrange for your midwife to bring Entonox (gas and air) and pethidine on the day.
-
Put aside some towels and waterproof sheets – you'll need them to soak up the fluids.
-
Think about the atmosphere you'd like to create – will you burn scented candles and play your favourite music?
-
Have a bag packed just in case there are complications and you need to get to hospital in a hurry. Week 33 has advice on what to pack.
Flexibility is the key, whatever type of birth you choose. Ultimately your baby is the boss – and all everyone wants for you is a safe, peaceful delivery.
Baby sling safety
Many parents use a sling or baby carrier instead of a pram to keep their baby close to them. If you decide to use a sling, make sure you have learned how to use it safely, as a small number of deaths from suffocation have been linked to slings.
The Royal Society for the Prevention of Accidents (RoSPA) advises the safest slings are the ones that hold your baby solidly against your body, in an upright position. Make sure you can see your baby, that their face is not restricted, and their airways are always clear.
The T.I.C.K.S rule to keep your baby safe when wearing a sling or carrier is:
T – Tight
I – In view at all times
C – Close enough to kiss
K – Keep chin off the chest
S – Supported back
Read more about sling safety and the T.I.C.K.S rule on the RoSPA website.
3rd trimester pregnancy symptoms (at 38 weeks)
One new symptom this week could be frustration or even boredom. It really won't be long now, try to be patient!
Your signs of pregnancy could also include:
- painless contractions around your bump, known as Braxton Hicks contractions
- sleeping problems (week 19 has information about feeling tired)
- stretch marks (read about stretch marks on week 17's page)
- swollen and bleeding gums (week 13 has information about gum health during pregnancy)
- pains on the side of your baby bump, caused by your expanding womb ("round ligament pains")
- piles (read about piles on week 22's page)
- headaches
- backache
- indigestion and heartburn (week 25 talks about digestive problems)
- bloating and constipation (read about bloating on week 16's page)
- leg cramps (week 20 explains how to deal with cramp)
- feeling hot
- dizziness
- swollen hands and feet
- urine infections
- vaginal infections (see week 15 for vaginal health)
- darkened skin on your face or brown patches – this is known as chloasma or the "mask of pregnancy"
- greasier, spotty skin
- thicker and shinier hair
You may also experience symptoms from earlier weeks, such as:
- mood swings (week 8's page has information on mood swings)
- morning sickness (read about dealing with morning sickness on week 6's page)
- weird pregnancy cravings (read about pregnancy cravings on week 5's page)
- a heightened sense of smell
- sore or leaky breasts (read about breast pain on week 14's page)
- a white milky pregnancy discharge from your vagina and light spotting (seek medical advice for any bleeding)
Read Tommy's guide to common pregnancy symptoms.
40th week of pregnancy - what happens at the fortieth week of pregnancy: nausea, discharge, signs of labor
WHAT HAPPENS
There is very little space in the uterus now, so do not be surprised if the number of movements is reduced. Be sure to listen to every movement of the baby: both excessive activity and complete cessation are not very good signs. Normally, at 40 weeks of pregnancy, in 12 hours you should feel about 10 movements.
Like the mother, the baby is preparing for the birth. In order for the process of childbirth to go smoothly, the hormones adrenaline and norepinephrine are produced in the tiny body, which should reduce pain during the passage of the fetus through the birth canal.
By the 39th - 40th week of pregnancy, the baby's blood circulation is established, the digestive system is actively functioning, processing the amniotic fluid and dead skin cells. The meconium formed from them will leave the intestines of the child only after birth. The bones of the skull are still flexible, so that the fetus can pass through the birth canal unhindered.
The bones of the skull are still flexible, so that the fetus can pass through the birth canal unhindered.
The 40th week of pregnancy should be the final one, but in practice, only a few women give birth at the expected time. So be patient and wait, continuing to lead a normal life. In any case, very soon you will hug your baby.
YOUR WELL FEELING
If you have not yet had signs of childbirth, they may appear at the 40th week of pregnancy.
- Lowering of the abdomen. The baby in the uterus moves down and presses the head against the pelvic floor. Due to this, heartburn disappears in the expectant mother and it becomes much easier for her to breathe. But due to the strong pressure on the bladder, pregnant women at this time are forced to go to the toilet more often;
- Disorders of the food system. Approximately 24 to 48 hours before the onset of labor, stool liquefaction may occur;
- Loss of appetite;
- Weight loss.
 Before childbirth, body weight may decrease by 1 - 2 kg;
Before childbirth, body weight may decrease by 1 - 2 kg; - Mucus plug outlet. During 40 weeks of pregnancy, the cork closed the entrance to the cervix, protecting the baby from infections. Her separation (you will learn about this from lumps of mucus on panties) frees the birth canal for the child;
- Amniotic fluid discharge. Amniotic fluid is poured out immediately before childbirth. Most often it is transparent, but if meconium particles have got into it, the color may be yellowish or greenish;
- Painful and false contractions at 40 weeks. Primiparous women can confuse training contractions with real ones, especially since by the time of 39-40 weeks of pregnancy, false uterine contractions are also accompanied by pain and are repeated more often than in previous periods. To understand exactly what kind of contractions you have, change the position of the body during muscle contractions. Lie down or, conversely, stand up, walk around the room, then sit on a chair.
 If the contractions have stopped, then this is not childbirth.
If the contractions have stopped, then this is not childbirth.
RISK FACTORS
The main danger of 40 weeks of pregnancy is rapid delivery. A baby can be born very quickly, especially in multiparous women. Therefore, it is better to go to the hospital in advance, about a week before the expected date of birth. And if you live near a hospital, avoid long trips and tiring shopping trips.
At the 40th week of pregnancy, it is necessary to monitor the nature of the discharge. If they have changed their smell, color and texture (for example, they have become purulent or curdled), this indicates an infectious disease that requires immediate treatment. The presence of pathogenic microbes in the vagina creates a risk of infection of the child.
As at any time, anemia is dangerous at 39-40 weeks of gestation, due to which the level of oxygen in the tissues decreases. Low hemoglobin provokes fetal hypoxia, and the expectant mother faces an increased risk of developing late toxicosis and complications in childbirth.
Possible signs of anemia during pregnancy:
- Dry skin;
- Brittle nails and hair;
- Feeling weak and easily fatigued;
- Paleness of skin and mucous membranes;
- Insomnia;
- Headaches;
- Feeling of impending fainting;
- Arrhythmia and bradycardia;
- Constipation;
- Presence of taste perversions.
Anemia is treated with iron supplements and a special diet.
MEDICAL SUPERVISION
At the 40th week of pregnancy, you will have another trip to the doctor, where the usual procedures will be carried out: measuring blood pressure, weighing, determining the height of the fundus of the uterus and, of course, listening to the baby's heartbeat.
And in order to monitor the work of the kidneys, you will need to pass urine for analysis. If the date of delivery, which was set by the doctor, has passed, you may be prescribed a Doppler ultrasound. This study makes it possible to assess the blood flow of the fetus, blood circulation in the placenta and uterine vessels, and also to determine whether the baby receives enough oxygen and necessary substances. Another study, sometimes prescribed at 40 weeks of gestation, is cardiotocography, thanks to which the specialist will be able to exclude intrauterine hypoxia.
This study makes it possible to assess the blood flow of the fetus, blood circulation in the placenta and uterine vessels, and also to determine whether the baby receives enough oxygen and necessary substances. Another study, sometimes prescribed at 40 weeks of gestation, is cardiotocography, thanks to which the specialist will be able to exclude intrauterine hypoxia.
RECOMMENDATIONS
In the time remaining before the birth, try to relax properly, because after the birth of the child this is unlikely to work. It is very important to remain calm now, because your emotional state greatly affects the baby. Tune in to the upcoming birth and think only about the good.
At the 39th - 40th week of pregnancy, you should not experiment with nutrition. Eat foods high in protein and carbohydrates. They will help to accumulate strength and stock up on energy that you will need during childbirth. Don't forget about vitamins. Now the body needs vitamin K (it is found in spinach, in all types of cabbage, in asparagus, herbs, plums and prunes). This element improves blood clotting, which is very important for childbirth. You also need vitamin A, which is found in yellow, red and orange vegetables and fruits, beef liver, egg yolks and full-fat dairy products. Its lack can lead to a lack of baby weight. And at 39– At 40 weeks pregnant, you need B vitamins: they ensure not only the proper development of the fetus, but also the well-being of the mother. Their most valuable source is dry brewer's yeast, but they can be used only after consulting a doctor. Also, B vitamins are present in oatmeal, millet, meat, fish, eggs, legumes and dairy products.
This element improves blood clotting, which is very important for childbirth. You also need vitamin A, which is found in yellow, red and orange vegetables and fruits, beef liver, egg yolks and full-fat dairy products. Its lack can lead to a lack of baby weight. And at 39– At 40 weeks pregnant, you need B vitamins: they ensure not only the proper development of the fetus, but also the well-being of the mother. Their most valuable source is dry brewer's yeast, but they can be used only after consulting a doctor. Also, B vitamins are present in oatmeal, millet, meat, fish, eggs, legumes and dairy products.
If at 40 weeks of pregnancy you feel the onset of contractions, do not rush to go to the hospital. Before childbirth, you should replenish energy reserves, and for this you can drink sweet tea, jelly or compote, eat a little low-fat cottage cheese or yogurt. As soon as the duration of the contractions reaches 1 minute, and the interval between them is 5-7 minutes, go to the hospital.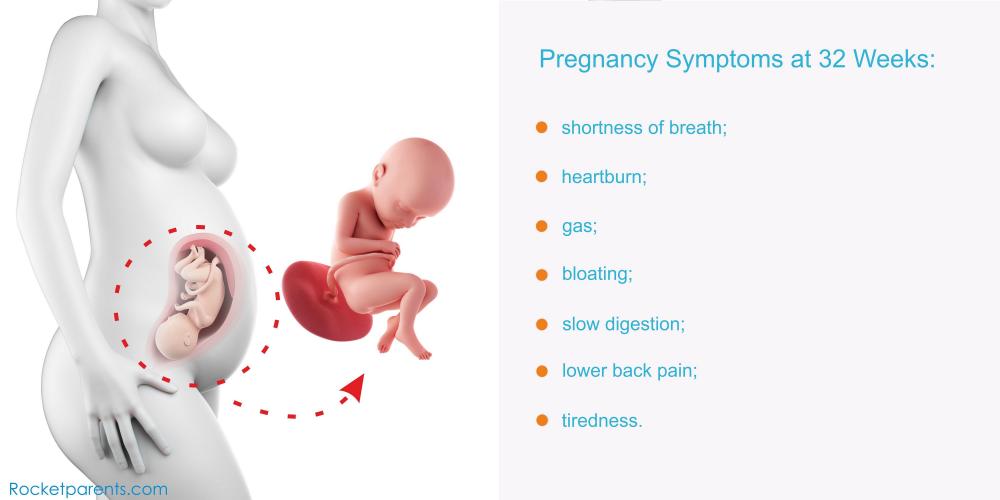
Many future parents are interested in the question of whether it is harmful to have sex at the 39th - 40th week of pregnancy. In the absence of contraindications, this is not prohibited. And in some cases, sexual intercourse is even recommended as a means of preparing for childbirth. The semen contains the hormone prostaglandin, which softens the cervix, and the orgasm experienced by a woman stimulates the onset of contractions.
Pregnancy and childbirthNinth month of pregnancy: changes in the female body and fetal development by week
Newborn careDowry for a newborn
What do you need to have at home for discharge, what stroller and crib to choose, and what equipment to buy?
Pregnancy and childbirthWhat to take with you to the hospital
Pregnancy and childbirthPsychology of pregnancy and motherhood
Positive attitude and overcoming fears during pregnancy, psychological hygiene and well-being of a woman.
How to Prepare for Pregnancy
How to properly organize your life before childbirth and how to choose a maternity hospital.
Communication with a childHow to prepare for the birth of a baby?
How to build a relationship between an older and younger child and what you need to be prepared for.
Breast-feedingAll About Breastfeeding
Let's dispel the most popular misconceptions about breastfeeding.
37-40 weeks of pregnancy
37th week of pregnancy for a baby
At 37 weeks of gestation, the baby is approximately 48 cm tall and weighs 2,600 g. facial features, pronounced cartilage tissue. The accumulation of subcutaneous fat at this stage of pregnancy makes the outline of the body softer and more rounded. The skin of the child is gradually smoothed out, it is no longer as pink as in the previous weeks of intrauterine development, the integument gradually brightens. The body of the baby is still abundantly covered with grease, but the amount of fluff is noticeably reduced, fluff hair remains only on the shoulders and back, in some babies they disappear almost completely.
facial features, pronounced cartilage tissue. The accumulation of subcutaneous fat at this stage of pregnancy makes the outline of the body softer and more rounded. The skin of the child is gradually smoothed out, it is no longer as pink as in the previous weeks of intrauterine development, the integument gradually brightens. The body of the baby is still abundantly covered with grease, but the amount of fluff is noticeably reduced, fluff hair remains only on the shoulders and back, in some babies they disappear almost completely.
Fat accumulation continues this week. It reaches a maximum of 15% of the total body weight of the child. It is difficult to overestimate the importance of adipose tissue for newborns, it is it that protects the child from overheating or hypothermia, since the baby's thermoregulation system after childbirth is still not sufficiently formed and continues to develop in the first months of a small person's life.
At this time, not only the volume of subcutaneous fat increases, but muscles and skeleton also develop intensively. The child constantly moves arms and legs. These unique workouts help increase muscle mass. Also, the baby makes rhythmic respiratory movements that strengthen the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm, and prepare the respiratory organs for childbirth.
The child constantly moves arms and legs. These unique workouts help increase muscle mass. Also, the baby makes rhythmic respiratory movements that strengthen the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm, and prepare the respiratory organs for childbirth.
Pregnant woman at 37 weeks
As the due date approaches, pregnant women begin to notice the appearance of their precursors, that is, certain signs, changes that occur under the influence of hormones. The body of a woman is preparing to give birth to a child, progesterone gives way to the dominant role of the birth hormone estrogen, the state of health of a pregnant woman changes.
From the 37th week, expectant mothers can observe the following changes:
- slight weight loss;
- abdominal shrinkage;
- the appearance of training or "false" contractions and the increase in their intensity;
- discharge of mucus from the cervix.
The nature of the stool changes, it becomes looser, aching pains in the lower back of varying intensity may appear, the fundus of the uterus descends. A woman notes some signs on her own, others are observed by a gynecologist during a routine examination.
A woman notes some signs on her own, others are observed by a gynecologist during a routine examination.
Harbingers do not appear in all women. Some expectant mothers notice only some of the above symptoms, while others observe signs of an impending birth not two or three weeks before their date, but just a few hours. Both the appearance of precursors at the 37th week and their absence are a variant of the norm and depend on the individual characteristics of the woman's body.
This week the woman's body is intensified preparation for the birth of a child. If the fetus is located correctly, head down, it gradually descends, goes to the lower part of the uterus, presses to the body and bends the limbs, intuitively taking the most comfortable position for passing the birth canal. The consequence of the movement of the fetus is the omission of the bottom of the uterus. The abdomen drops, the pressure on the diaphragm significantly decreases, the pregnant woman can breathe easily, the shortness of breath that haunted her in previous weeks disappears. The pressure on the stomach also decreases, heartburn disappears, a feeling of heaviness after eating and other unpleasant sensations. Moving the baby can put pressure on the bowels and bladder. A pregnant woman at this time often experiences the urge to urinate, may suffer from frequent loose stools. The reason for frequent bowel movements is not only the mechanical effect of the uterus on it, but also an increase in the content of estrogens in the body, hormones that contribute to the excretion of fluid. At the 37th week, the expectant mother can empty her intestines up to 3-4 times a day and at the same time observe a significant liquefaction of feces.
The pressure on the stomach also decreases, heartburn disappears, a feeling of heaviness after eating and other unpleasant sensations. Moving the baby can put pressure on the bowels and bladder. A pregnant woman at this time often experiences the urge to urinate, may suffer from frequent loose stools. The reason for frequent bowel movements is not only the mechanical effect of the uterus on it, but also an increase in the content of estrogens in the body, hormones that contribute to the excretion of fluid. At the 37th week, the expectant mother can empty her intestines up to 3-4 times a day and at the same time observe a significant liquefaction of feces.
38th week of pregnancy: the development of the future baby
At the 38th week, the fetus is fully formed, so childbirth at this time is no longer dangerous for both the mother and the baby. The weight of the fetus is about 3 kg, but this indicator can vary significantly for different babies, the weight depends on the individual characteristics of the mother and child, the structural features of the body and other factors. The body length of a newborn is approximately 50 cm.
The body length of a newborn is approximately 50 cm.
All organs and systems at 38 weeks of age are characterized by physiological and morphological maturity, they are fully ready for work. At this time, the child prepares for childbirth, makes respiratory movements and prepares the intercostal muscles for breathing. The tissues of the lungs are bathed in amniotic fluid, which helps maintain the right level of surfactant that coats the baby's lungs from the inside. All elements of the respiratory system are ready for use. With the first breath after birth, the alveoli begin to transfer oxygen from the air to the blood, gas exchange occurs, the respiratory and circulatory systems begin to work intensively.
Pregnant woman
The body of a pregnant woman continues to actively prepare for the birth of a baby, the estrogen content rapidly increases, and the progesterone level decreases significantly. A change in the hormonal background contributes to the softening of the tissues of the birth canal and cervix. Throughout pregnancy, the lumen of the cervical canal is closed by a plug of thick mucus, which protects the baby from infection, and the uterine cavity protects against the penetration of microorganisms dangerous to health. In the last weeks of pregnancy, the consistency of the mucus changes, it becomes more liquid and begins to gradually flow out. In some women, mucus leaves gradually, while in other women in labor at the same time. The discharge resembles colorless egg white in its consistency and appearance. Sometimes the mucus is colored pinkish, brown or yellow. The discharge of the cork is painless, a woman may experience a slight feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen. More abundant vaginal discharge than during the entire pregnancy can signal the passage of the cork.
Throughout pregnancy, the lumen of the cervical canal is closed by a plug of thick mucus, which protects the baby from infection, and the uterine cavity protects against the penetration of microorganisms dangerous to health. In the last weeks of pregnancy, the consistency of the mucus changes, it becomes more liquid and begins to gradually flow out. In some women, mucus leaves gradually, while in other women in labor at the same time. The discharge resembles colorless egg white in its consistency and appearance. Sometimes the mucus is colored pinkish, brown or yellow. The discharge of the cork is painless, a woman may experience a slight feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen. More abundant vaginal discharge than during the entire pregnancy can signal the passage of the cork.
A woman should carefully monitor the color and volume of discharge, since too much colorless discharge may indicate not only the cork has come off, but also be one of the symptoms of amniotic fluid leakage. Indicator pads and amnio tests or test strips will help determine the cause of the discharge. Pads are sold in many pharmacies and can be easily used at home. If amniotic fluid leakage is confirmed, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Indicator pads and amnio tests or test strips will help determine the cause of the discharge. Pads are sold in many pharmacies and can be easily used at home. If amniotic fluid leakage is confirmed, you should immediately consult a doctor.
After the mucus plug has passed, you should stop visiting the pool and swimming in open water, as the risk of infection of the child increases significantly. It is also necessary to exclude sexual contact.
39th week of pregnancy: what happens to the fetus?
At 39 weeks, the baby weighs 3100-3500 g and is 50-52 cm tall. Height and weight are very relative and can vary significantly. The baby is rapidly preparing for the most important test of his life - birth, which requires endurance and considerable effort. During this period of pregnancy, the size and weight of the child's adrenal glands, that is, the glands of the endocrine system, which are responsible for the reaction of the human body to stress factors, increase. It is the hormones adrenaline and norepinephrine produced by the adrenal glands that help the child quickly adapt to new temperature conditions, tactile, sound and light impulses.
All the senses of the baby are developed at 39 weeks. Within a few moments after birth, the baby can focus his eyes, he reacts to bright light and moving objects, many scientists claim that newborns distinguish colors, see the faces of parents and doctors. The hearing of the baby in the last weeks of fetal life is also fully developed; after birth, he reacts to loud sounds and noise. A newborn baby is able to determine the main shades of taste, recognize sour, bitter, sweet and salty.
In the womb, the baby is in an aquatic environment that minimizes contact. Immediately after birth, the baby experiences many tactile sensations, unlike intrauterine life, he feels the touch of his mother's hands and diapers, towels, dressings and other materials. Babies especially like the touch of skin to skin, so in a modern maternity hospital, newborns must be laid out on their mother's stomach even before cutting the umbilical cord. The child adapts to the new environment more easily, feels protected. Laying out a child has not only a psychological aspect, since it contributes to the colonization of microorganisms from the mother's skin to the skin and mucous membranes of the baby, and increases its immunity.
Laying out a child has not only a psychological aspect, since it contributes to the colonization of microorganisms from the mother's skin to the skin and mucous membranes of the baby, and increases its immunity.
Pregnant woman
In the last weeks of pregnancy, the expectant mother strives to prepare her apartment or house as much as possible for the arrival of a new family member. Scientists call this sign of impending birth the nesting syndrome. Many women observe signs of the syndrome from the thirtieth week of pregnancy, however, nesting reaches its maximum point at the 39-40th week. Pregnant women tend to do general cleaning and repairs, re-paste the wallpaper and purchase a lot of new things that, in their opinion, are simply necessary in the house. After giving birth, many purchases are puzzling. The reason for this behavior is an increase in the level of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the body. These hormones are produced by the adrenal glands, they are necessary not only for the woman, but also for the baby to prepare for the upcoming birth.
40th week of pregnancy: how does the baby develop?
40 weeks - term pregnancy. The weight of a child who was born at such a period ranges from 2,600 g to 4,400 g, and his body length is 48-53 cm. These indicators are very arbitrary, since miniature babies weighing 2,600 g and real heroes are born at 40 weeks, whose body weight approaches 5,000 g. The length of the newborns can also vary from 45 to 55 cm.
Most women give birth exactly at 40 weeks. At this time, the baby is completely ready for birth, it meets all the parameters of a full-term baby. Before childbirth, the child closely presses the arms and legs to the body, bends the head as much as possible and presses against the exit from the uterus. This position allows you to make it possible to pass the birth canal with the narrowest part of the skull. In the course of labor, with each contraction, the child gradually moves down, he does not move in a straight line, but makes helical-translational movements, as if screwing into the mother's birth canal. During the progress of the newborn, the complete descent of his head, the cervix fully opens. This is followed by attempts, that is, contractions of the uterus, which advance the child through the birth canal. Gradually, the head of the baby is shown, and after it - his torso. Childbirth is a complex mechanism that is aimed not only at the safe passage of the birth canal by the child, protecting him from accidental injuries due to increased pressure, but also at preventing ruptures of the woman's soft tissues.
During the progress of the newborn, the complete descent of his head, the cervix fully opens. This is followed by attempts, that is, contractions of the uterus, which advance the child through the birth canal. Gradually, the head of the baby is shown, and after it - his torso. Childbirth is a complex mechanism that is aimed not only at the safe passage of the birth canal by the child, protecting him from accidental injuries due to increased pressure, but also at preventing ruptures of the woman's soft tissues.
Pregnant woman
The long wait for meeting her unborn child is coming to an end, and the 40th week of pregnancy is the last for most women. Every day, the anxiety of the expectant mother increases, a long wait affects the mood and well-being. Women strive to have a baby as soon as possible so that pregnancy and painful contractions are a thing of the past. Every pregnant woman dreams of meeting a baby, wants to hug him to her chest and stroke the delicate head.
Many women, especially primiparas, are afraid that labor will begin unnoticed, but such cases are extremely rare.