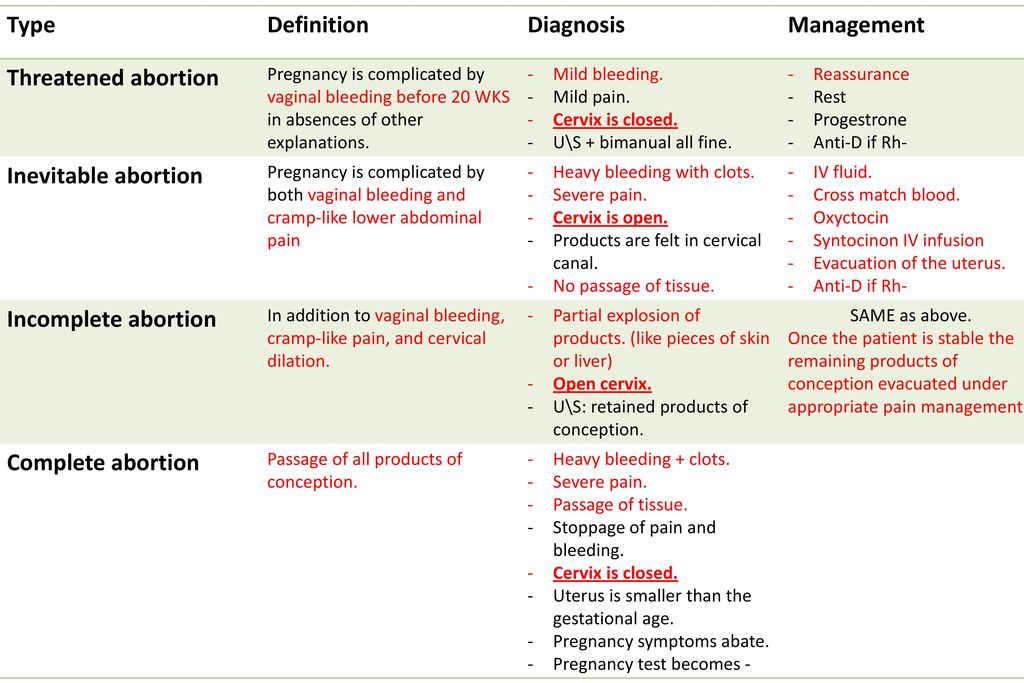
Symptoms of threatened miscarriage
Miscarriage - threatened: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
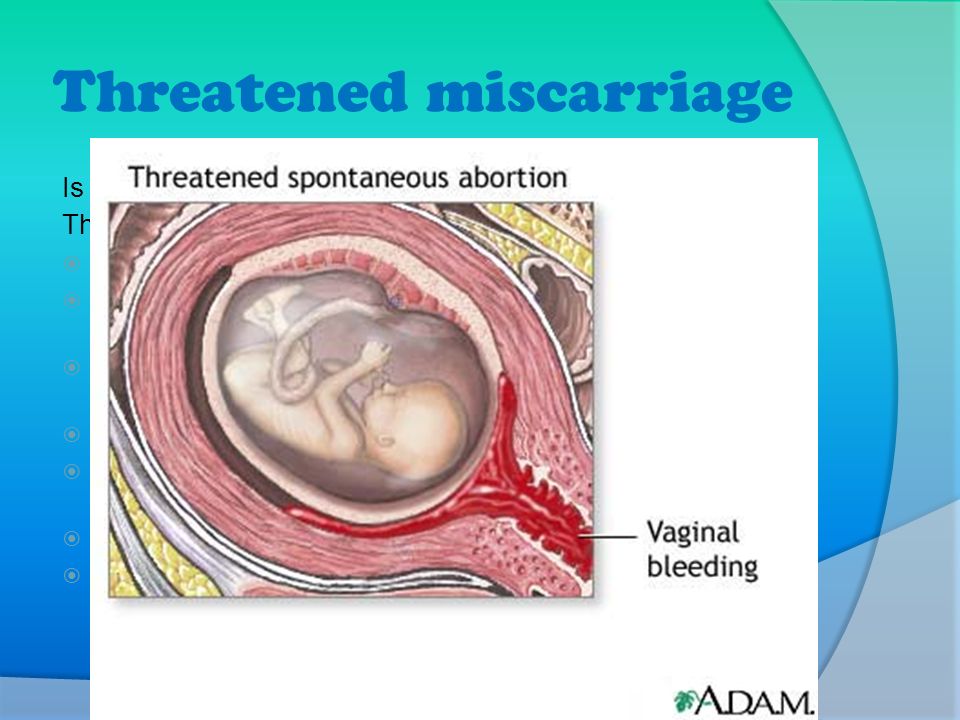
A threatened miscarriage is a condition that indicates the potential for a miscarriage or early pregnancy loss. It might take place before the 20th week of pregnancy.
Some pregnant women have some vaginal bleeding during the first 3 months of pregnancy. Bleeding may occur with or without abdominal cramps. When the symptoms indicate a miscarriage is possible, the condition is called a "threatened abortion." (This refers to a natural event that is not due to a medical or surgical abortion.)
Miscarriage is common. Small falls, injuries or stress during the first trimester of pregnancy can cause threatened miscarriage. It occurs in almost one half of all pregnancies. The chance of miscarriage is higher in older women. About one half of women who have bleeding in the first trimester will have a miscarriage.
Symptoms of a threatened miscarriage include:
- Vaginal bleeding during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy (last menstrual period was less than 20 weeks ago).
Vaginal bleeding occurs in almost all threatened miscarriages.
- Abdominal cramps may also occur. If abdominal cramps occur in the absence of significant bleeding, consult your health care provider to check for other problems besides threatened miscarriage.
Note: During a miscarriage, low back pain or abdominal pain (dull to sharp, constant to intermittent) can occur. Tissue or clot-like material may pass from the vagina.
Your provider may perform an abdominal or vaginal ultrasound to check the baby's development and heartbeat, and the amount of bleeding. A pelvic exam may also be done to check your cervix.
Blood tests done may include:
- Beta HCG (quantitative) test (pregnancy test) over a period of days or weeks to confirm whether the pregnancy is continuing
- Complete blood count (CBC) to determine the presence of anemia
- Progesterone level
- White blood count (WBC) with differential to rule out infection
Apart from controlling the blood loss, you may not need any particular treatment. If you are Rh Negative, then you may be given immune globulin. You may be told to avoid or restrict some activities. Not having sexual intercourse is often recommended until the warning signs have disappeared.
If you are Rh Negative, then you may be given immune globulin. You may be told to avoid or restrict some activities. Not having sexual intercourse is often recommended until the warning signs have disappeared.
Most women with a threatened miscarriage go on to have a normal pregnancy.
Women who have had two or more miscarriages in a row are more likely than other women to miscarry again.
Complications may include:
- Anemia from moderate to heavy blood loss, which may require a blood transfusion.
- Infection.
- Miscarriage.
- The health care provider will want to ensure that the symptoms are not due to an ectopic pregnancy. This is a potentially life-threatening complication.
If you know you are (or are likely to be) pregnant and you have any symptoms of threatened miscarriage, contact your prenatal provider right away.
Most miscarriages cannot be prevented. The most common cause of a miscarriage is a random genetic abnormality in the developing pregnancy.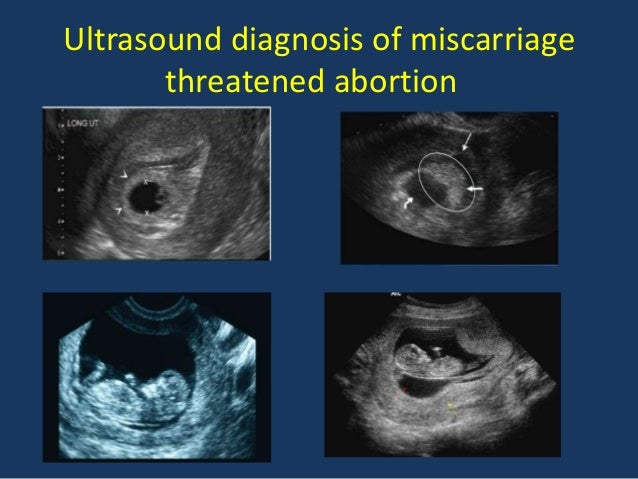 If you have two or more repeated miscarriages, you should consult a specialist to look for an underlying condition that is causing the problem. Women who get prenatal care have better pregnancy outcomes for themselves and their babies.
If you have two or more repeated miscarriages, you should consult a specialist to look for an underlying condition that is causing the problem. Women who get prenatal care have better pregnancy outcomes for themselves and their babies.
A healthy pregnancy is more likely when you avoid things that are harmful to your pregnancy, such as:
- Alcohol
- Infectious diseases
- High caffeine intake
- Recreational drugs
- X-rays
Taking a prenatal vitamin or folic acid supplement before becoming pregnant and throughout your pregnancy can lower your chance of miscarriage and improve the chance of delivering a healthy baby.
It is better to treat health problems before you get pregnant than to wait until you are already pregnant. Miscarriages caused by diseases that affect your whole body, such as high blood pressure, are rare. But you can prevent these miscarriages by detecting and treating the disease before becoming pregnant.
Other factors that can increase your risk for miscarriage include:
- Obesity
- Thyroid problems
- Uncontrolled diabetes
Threatened miscarriage; Threatened spontaneous abortion; Abortion - threatened; Threatened abortion; Early pregnancy loss; Spontaneous abortion
- Early pregnancy
- Threatened miscarriage
Keyhan S, Muasher L, Muasher SJ. Spontaneous abortion and recurrent pregnancy loss: etiology, diagnosis, treatment. In: Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 16.
Spontaneous abortion and recurrent pregnancy loss: etiology, diagnosis, treatment. In: Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 16.
Richards DS. Obstetric ultrasound: imaging, dating, growth, and anomaly. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 9.
Salhi BA, Nagrani S. Acute complications of pregnancy. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 178.
Updated by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Tests
A threatened abortion is vaginal bleeding that occurs in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy and is sometimes accompanied by abdominal cramps.
The condition is known as threatened abortion or threatened miscarriage because its symptoms indicate a miscarriage is possible.
Vaginal bleeding is fairly common among pregnant people. In a 2016 cohort, 24% of women experienced bleeding during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy. Of these women, 60% carried their pregnancy to term.
The exact cause of a threatened abortion usually isn’t known. But it’s more common among people who previously had a miscarriage.
Any vaginal bleeding during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy can be a symptom of a threatened abortion. Some people also have abdominal cramps or lower back pain.
During a regular miscarriage, people often experience dull or sharp pain in the abdomen and lower back. They may also pass tissue with clot-like material from the vagina.
Call your doctor or obstetrician immediately if you’re pregnant and experiencing these symptoms.
The actual cause of a threatened abortion isn’t always known. Still, certain factors may increase your risk of having one. These include:
These include:
- a bacterial or viral infection during pregnancy
- trauma to the abdomen
- advanced parental age (over age 35)
- exposure to certain medications or chemicals
Other risk factors for a threatened abortion include obesity, unmanaged diabetes, and unmanaged thyroid disease. If you’re overweight, have diabetes, or have thyroid disease, speak with your doctor about ways to stay healthy during pregnancy.
You should also tell your doctor about any medications or supplements you take. Some may be unsafe to use during pregnancy.
Your doctor will perform a pelvic exam if a threatened abortion is suspected. During a pelvic exam, your doctor will examine your reproductive organs, including your vagina, cervix, and uterus.
They’ll look for the source of your bleeding and determine whether the amniotic sac has ruptured. The pelvic exam will take only a few minutes to complete.
An ultrasound will monitor the heartbeat and development of the fetus. It can also help determine the amount of bleeding. A transvaginal ultrasound, or an ultrasound that uses a vaginal probe, is typically more accurate than an abdominal ultrasound in early pregnancy.
It can also help determine the amount of bleeding. A transvaginal ultrasound, or an ultrasound that uses a vaginal probe, is typically more accurate than an abdominal ultrasound in early pregnancy.
During a transvaginal ultrasound, your doctor will insert an ultrasound probe about 2 or 3 inches into your vagina. The probe uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of your reproductive organs, allowing your doctor to see them in more detail.
Blood tests, including a complete blood count, may also be performed to check for abnormal hormone levels. Specifically, these tests will measure the levels of hormones in your blood called human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) and progesterone.
HCG is a hormone that your body produces during pregnancy, and progesterone is a hormone that supports a pregnancy. Atypical levels of either hormone may indicate a problem.
A miscarriage often can’t be prevented. In some cases, though, your doctor may suggest ways to lower your risk of having a miscarriage.
As you recover, your doctor may tell you to avoid certain activities. Bed rest and avoiding sexual intercourse may be suggested until your symptoms go away. However, there is no research to back up these suggestions.
Your doctor will also treat conditions that increase the risk of complications during pregnancy, such as diabetes or hypothyroidism.
Your doctor may also want to give you a progesterone injection to increase hormone levels. Your doctor will also administer Rh immunoglobulin if you have Rh-negative blood and your developing fetus has Rh-positive blood. This stops your body from creating antibodies against your child’s blood.
Many people who experience a threatened abortion go on to deliver healthy babies. This is more likely if your cervix isn’t already dilated and the fetus is still securely attached to the wall of your uterus. If you have atypical hormone levels, hormone therapy can often help you carry the baby to term.
Approximately 50% of people who experience a threatened abortion don’t have a miscarriage. Most people who do miscarry will go on to have successful pregnancies in the future. But you should see your doctor to discuss possible causes if you’ve experienced two or more miscarriages in a row.
Most people who do miscarry will go on to have successful pregnancies in the future. But you should see your doctor to discuss possible causes if you’ve experienced two or more miscarriages in a row.
For some people, a threatened abortion is a very stressful experience and can lead to anxiety and depression. It’s important to talk with your doctor if you’re experiencing symptoms of either condition following a threatened abortion or miscarriage. They can help you get the treatment you need.
Your doctor may also know about local support groups where you can discuss your experience and concerns with others who can relate to what you’re experiencing.
It’s difficult to prevent a miscarriage, but certain behaviors can help support a healthy pregnancy. These include:
- avoiding drinking alcohol
- avoiding smoking cigarettes
- not using illegal drugs
- minimizing consumption of caffeine
- avoiding certain foods that can make you ill and harm your fetus
- avoiding exposure to toxic chemicals or harsh cleaning solutions
- promptly treating any viral or bacterial infections that occur
- taking prenatal vitamins, such as folic acid
- exercising at least 2 hours a week
You can also maintain a healthy pregnancy by getting early, comprehensive prenatal care.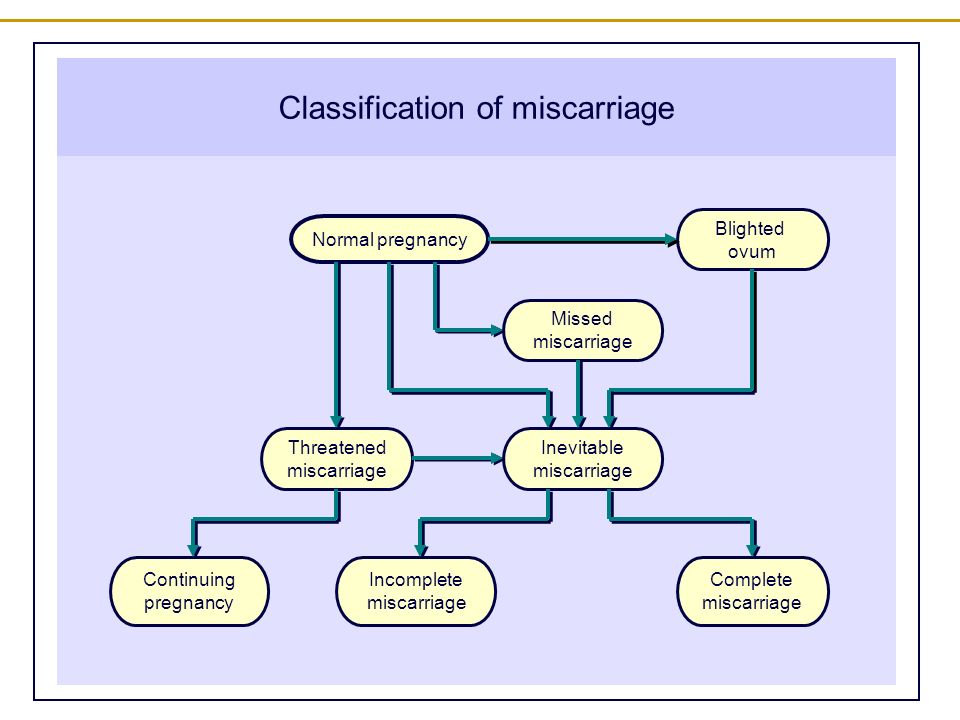 Receiving prompt prenatal care makes it possible for your doctor to detect and treat any potential health problems early in the pregnancy. This will prevent complications and help ensure the delivery of a healthy baby.
Receiving prompt prenatal care makes it possible for your doctor to detect and treat any potential health problems early in the pregnancy. This will prevent complications and help ensure the delivery of a healthy baby.
Treatment of threatened miscarriage in clinic
Sign up
+7 812 6100061 Russia, St. Petersburg, Kirochnaya st., 64
22222222222222222222222222222222
The term “threatened miscarriage” refers to a condition in which a woman may lose a child for up to 22 weeks. When the gestational age passes the mark of 22 weeks, the threat may also arise, but here we are talking about premature birth. There is another concept - unaccounted for pregnancy loss, when the gestation of the fetus is interrupted already in the second or third week, and the woman herself does not notice this. Approximately 30% of pregnancies, according to statistics, are interrupted in this way - the so-called "reset" of natural errors occurs, that is, initially non-viable embryos stop developing.
What causes the threat?
There are quite a lot of factors that cause the threat of termination of pregnancy. The main ones are:
- Hormonal changes . Of course, in itself, a change in hormonal levels during pregnancy is considered normal, but in some cases it can be unfavorable. The most serious problem is the lack of the hormone progesterone, since it is he who does not allow the uterus to randomly contract, which means it prevents spontaneous miscarriage. Progesterone deficiency occurs due to dysfunction of the corpus luteum, disorders in the thyroid gland or pituitary gland. The situation is also considered dangerous when, at a normal level of progesterone, the level of the male hormone androgen is elevated.
- Genetic disorders . Usually it is this factor that provokes miscarriages in the first weeks of gestation. Due to the mutation of the chromosomes, the normal development of the child becomes impossible, the woman's body itself rejects the fetus, thus preventing the birth of a child with severe health disorders, unviable.
 The immunity of a pregnant woman can also cause a threat of miscarriage - it reacts to the child as if it were a foreign body and rejects it. In such situations, future parents should definitely consult a geneticist.
The immunity of a pregnant woman can also cause a threat of miscarriage - it reacts to the child as if it were a foreign body and rejects it. In such situations, future parents should definitely consult a geneticist. - STI (predominantly sexually transmitted infections): chlamydia, herpes, cytomegalovirus, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis. These diseases are very unfavorable for the child and the pregnant woman. In the fetus, they can cause serious developmental disorders, prevent the correct laying of internal organs at the first stage, their further growth and performance of functions.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases (influenza, acute respiratory viral infections, hepatitis, rubella, tonsillitis, pneumonia, etc.) can also lead to abortion due to fever, oxygen starvation, intoxication of the body. During pregnancy, you need to communicate with patients as little as possible, avoid crowded places.
- Diseases of the genital organs : fibroids, endometriosis, developmental anomalies, consequences of trauma, adhesions - all this often prevents the development and normal growth of the fetus.
 Therefore, the expectant mother throughout the pregnancy should be observed and examined in specialized clinics by experienced specialists.
Therefore, the expectant mother throughout the pregnancy should be observed and examined in specialized clinics by experienced specialists. - Stressful situations . No wonder doctors recommend expectant mothers to monitor their psychological state. Sometimes this factor can become a trigger for a miscarriage. Do not take the events happening around you to heart at any stage of pregnancy.
- Invasive examination , i.e. amniotic fluid sampling for further research in the genetic laboratory, as well as cordocentesis, i.e. blood sampling from the umbilical vein of the baby. Such examinations are prescribed, for example, when there are serious suspicions that the fetus has chromosomal abnormalities, genetic diseases.
- Injuries, falls, overwork of a woman during pregnancy.
- Alcohol, tobacco smoking, etc.
- Thrombophilia - bleeding disorder, increased likelihood of blood clots.
- Rh conflict .
 In situations where the mother's blood is Rh negative and the father's blood is positive, the child may develop a positive Rh. Then the mother's body begins to produce antibodies that fight (as they "seem") with a foreign body.
In situations where the mother's blood is Rh negative and the father's blood is positive, the child may develop a positive Rh. Then the mother's body begins to produce antibodies that fight (as they "seem") with a foreign body.
What symptoms indicate a threatened abortion?
Pain . A woman may feel pain in the lower abdomen, in the lumbar region. Sometimes the pain gives to the side on the right or left. The nature of the pain is varied - pulling, stabbing, cutting. Also, the pain can be cramping in nature and does not depend on whether the woman is sitting, standing or lying. After sleep or rest, the pain does not go away, remains the same or even increases.
Emergence of secretions . Anxiety is caused by bleeding. They can be scarce, spotting, then developing into heavy bleeding. In cases where a woman goes to the doctor immediately, having discovered small bloody discharge, there are quite a lot of chances to keep the pregnancy and eliminate the threat. Excessive bleeding almost always leads to the loss of the fetus, moreover, it becomes a threat to the life and health (in particular, to the reproductive function) of the woman herself.
Excessive bleeding almost always leads to the loss of the fetus, moreover, it becomes a threat to the life and health (in particular, to the reproductive function) of the woman herself.
Increased uterine tone . This condition can be observed constantly or it can occur periodically. A woman usually feels the tone herself when the uterus tenses, contracts. With such a symptom, it is imperative to consult a doctor, especially if the tone is accompanied by pain or bleeding.
How can a threatened miscarriage be suspected on ultrasound?
Ultrasound reveals only indirect signs of a threat, but they are also very important for diagnosing a pathological condition:
- Uterine tone. A condition where the tone is localized only along the anterior or posterior wall of the uterus should not cause serious concern, but only cause more careful monitoring of the pregnant woman. This condition may be transient and disappear without pain or abnormal discharge.
 The full tone of the uterus (hypertonicity), that is, when it all tenses up (“hardens”), already requires treatment.
The full tone of the uterus (hypertonicity), that is, when it all tenses up (“hardens”), already requires treatment. - Fetal palpitations. Fetal heart rate can be determined as early as 5 weeks of gestation. For a period of 8 weeks or more, a heart rate of 120-160 beats per minute is considered normal. The deviation of the heart rate value up or down should alert the doctor.
- Chorionic hyperplasia. The placenta develops from the chorion. Accordingly, its underdevelopment will lead to the fact that the placenta will not be able to fully nourish the fetus.
- Retrochorial (extramenopausal) hematoma. When the fetal egg partially exfoliates from the chorion, damage to the vessels and outflow of blood occurs. Thus, a hematoma is formed, the further development of which leads to termination of pregnancy. Timely detection of such a pathology and proper treatment will help maintain pregnancy. Usually, a hematoma is detected at the first ultrasound screening, while the woman herself may not notice any pain or discomfort.

- Reducing the length of the cervix with an enlarged internal os.
What treatment is given to a woman when a threatened miscarriage is detected?
Numerous studies in the field of gynecology and genetics suggest that a threatened pregnancy up to 12 weeks should not be maintained at all costs. As mentioned earlier, at such a short time, a woman's body often rejects embryos with genetic pathologies.
The doctor assesses the patient's condition, prescribes an early ultrasound, prescribes treatment. Then it remains only to wait for a positive outcome, but at the same time be prepared for the fact that it will not come to childbirth. Even if a miscarriage has occurred, you should not despair and talk about a serious pathology of the reproductive system. You will need to prepare for the next pregnancy, undergo additional examinations, possibly hormonal or other therapy - as prescribed by the doctor.
At later stages, the treatment of the threat of abortion is carried out in a hospital - day or full. A woman may be prescribed droppers, injections, physiotherapy and other procedures, depending on the symptoms and ultrasound indications.
A woman may be prescribed droppers, injections, physiotherapy and other procedures, depending on the symptoms and ultrasound indications.
What is the treatment for the threat in the early stages - 3-12 weeks?
Usually, at such short terms, with the threat of termination of pregnancy, the following measures will be required to prevent it:
- Correction of the mode of life. Sometimes this means bed rest, sometimes it just means limiting physical activity. Doctors often write sick leave for pregnant women, as the stress, stress and anxiety associated with work only exacerbate the situation.
- Sexual abstinence.
- Prescription of sedative (sedative) drugs. Usually, women are prescribed valerian, motherwort tincture and other relatively safe drugs.
- Administration of drugs aimed at regulating stools (for example, glycerin suppositories).
- Administration of preparations containing magnesium. They have a calming effect and normalize bowel function.
- Hormone therapy. Women are often prescribed drugs Duphaston or Utrozhestan (contain progesterone). Especially such medicines are necessary if during the period of pregnancy planning there were menstrual irregularities, miscarriages occurred earlier, infertility treatment was carried out, and so on. The dosage, frequency and duration of taking the drugs are determined by the doctor on an individual basis.
Also, a woman whose pregnancy is in danger undoubtedly needs the psychological support of loved ones.
Treatment of threatened pregnancy in the second trimester
All of the above prescriptions can be maintained in the second trimester. You can supplement the treatment with the following:
- Magnesia therapy. Women are often prescribed magnesia in the form of droppers with a slow introduction in order to relieve uterine tension. This therapy is safe, its effectiveness has long been proven. In addition to a relaxing effect on the uterus, magnesium contributes to the prevention or removal of edema.
- Indomethacin rectal suppositories. Contraindications - gastric or duodenal ulcer, colitis, gastritis, thrombocytopenia. Contraindications associated with the state of the fetus - intrauterine growth retardation, anomaly in the development of the kidneys, inflammation of the chorion, heart defects, oligohydramnios, uneven blood supply (with twins).
- Suturing the cervix in cases where its length deviates from the standard.
- Appointment of antispasmodics (no-shpa, rectal suppositories with papaverine).
Effective treatment and removal of the threat of termination of pregnancy does not mean that the observation of a woman can be transferred to the usual mode. It is necessary to maintain close attention to her condition and, at the slightest suspicion of a new threat, promptly take action. In many ways, the success of pregnancy depends on the woman herself, on how carefully she listens to her own body and to the advice of a doctor.
Sometimes the threat persists throughout pregnancy. Often this happens after IVF or artificial insemination. But the possibilities of modern medicine make it possible to maintain such pregnancies - women give birth to healthy children, although they have to experience a lot of difficulties.
Often this happens after IVF or artificial insemination. But the possibilities of modern medicine make it possible to maintain such pregnancies - women give birth to healthy children, although they have to experience a lot of difficulties.
As you can see, the treatment of a threat can be very different, and when prescribing a doctor, it is important to take into account all the individual characteristics of the woman's condition and the development of the fetus. Specialists of the Genesis Reproduction Center in St. Petersburg have been helping women successfully conceive for many years and keep their patients' pregnancies under threat. But first of all, we do everything to prevent the threat - we conduct examinations, prescribe the optimal dosage of vitamins, give recommendations on adjusting the diet, and so on.
Possible consequences of a threatened abortion
Statistics show that 50% of women at least once during their pregnancy faced the threat of abortion, and not every case ended sadly. If we talk about the consequences of the threat to the fetus, it is worth highlighting the following:
If we talk about the consequences of the threat to the fetus, it is worth highlighting the following:
- Fetal hypoxia (oxygen starvation). Acute and prolonged hypoxia can adversely affect the development of the child's brain, cause cerebral palsy and other serious pathologies.
- Slow fetal growth (according to ultrasound, the number of weeks of gestation does not match the number of obstetric weeks).
- Fetal infection in utero.
As a rule, if a woman follows the recommendations of the attending physician, undergoes scheduled and unscheduled ultrasound screenings, this helps to maintain the pregnancy and prevent any pathologies in the baby.
Every woman during pregnancy should first of all think about herself and the child, and not about work, household chores, shopping and the like. Proper nutrition, calmness, outdoor walks, positive emotions are all prerequisites for a successful pregnancy and the birth of a healthy baby.
Make an appointment
Surname, name, patronymic*Phone*Pregnancy: Terrible word THREAT! Let's save ourselves!
Our today's conversation will touch upon recommendations for a pregnant woman who is faced with such a complication of pregnancy as a threatened miscarriage.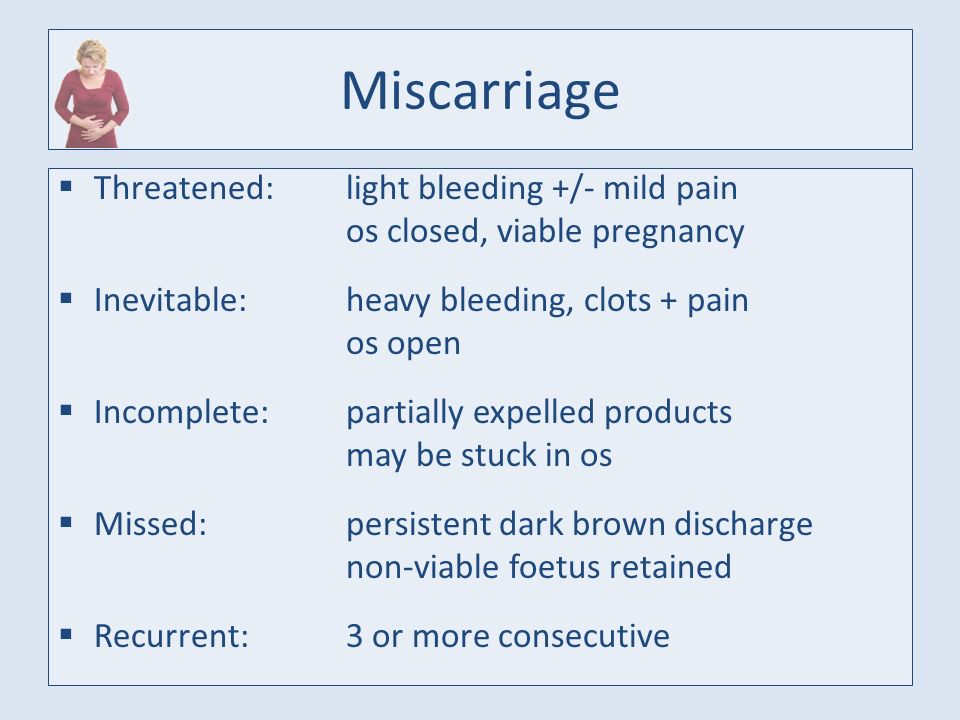
Pregnancy is a physiological process for the female body. If a woman is young (18-30 years old) and healthy, then, as a rule, pregnancy proceeds without complications. Recently, in the world and in our country, there has been a sharp deterioration in the health of women of reproductive age.
Complications of pregnancy can be divided into 3 groups for a better understanding of the reader (these are not standards).
- Firstly, the complications associated with the pregnancy itself, if it were not for this condition, then there would be no complication - the threat of abortion (the threat of premature birth).
- Secondly, these are complications associated with a disease (for example, rubella) that occurred during pregnancy.
- Thirdly, these are complications that arose in a woman who suffered from a particular disease before pregnancy (perhaps the first exacerbation of this disease is associated with pregnancy).
The most unpleasant psychological and physical complications are threatened miscarriage . If this happens in the early stages, then the term is used, the threat of termination of pregnancy ", if in the later stages (after 28 weeks), then " the threat of premature birth.
If this happens in the early stages, then the term is used, the threat of termination of pregnancy ", if in the later stages (after 28 weeks), then " the threat of premature birth.
What to do if there is a threat of termination of pregnancy
In some countries, including Russia, it is customary to keep a pregnancy of any term; accordingly, if a woman notes spotting during pregnancy, then she immediately should see a doctor during the daytime or seek help from the emergency team at night. But the question of the expediency of maintaining pregnancy with the onset of bleeding up to 12 weeks remains open, because. it is known that 70-80% of pregnancies terminated during this period are associated with chromosomal pathologies, sometimes incompatible with life. Those. It can be said that the body itself corrects its mistakes.
Reasons for termination of pregnancy
Termination of pregnancy may also be associated with cervical incompetence . Those. its upper part may not be tightly closed, i.e. unable to play the role of a "castle". This condition may be caused by trauma during previous births or during abortions ( even if it was a single ). In this case, treatment is carried out in a hospital, and in the future, pregnancy is observed by an outpatient doctor. A woman can be stitched on the cervix if such a diagnosis is made at 16-20 weeks or a special retaining ring is placed if complaints appear later than this period. The suture or ring is removed at the time of the onset of labor, i.e. with the appearance of regular contractions or the outflow of amniotic fluid. However, this procedure can be performed two weeks before the expected date of birth.
Those. its upper part may not be tightly closed, i.e. unable to play the role of a "castle". This condition may be caused by trauma during previous births or during abortions ( even if it was a single ). In this case, treatment is carried out in a hospital, and in the future, pregnancy is observed by an outpatient doctor. A woman can be stitched on the cervix if such a diagnosis is made at 16-20 weeks or a special retaining ring is placed if complaints appear later than this period. The suture or ring is removed at the time of the onset of labor, i.e. with the appearance of regular contractions or the outflow of amniotic fluid. However, this procedure can be performed two weeks before the expected date of birth.
Termination of pregnancy may be associated with the hormonal status of a woman , therefore hormones play a leading role in the treatment of this complication. In order to clarify the diagnosis in the antenatal clinic, they can take the so-called “threat smear” (this is not a 100% confirmation of the diagnosis). Of course, hormones play one of the main roles in the regulation of pregnancy. The problem of treatment of miscarriage is very complex and multifaceted. I repeat that in our country it is customary to preserve early pregnancy. For this purpose, hormone therapy is used, based on the physiological and pathogenetic processes of the onset and development of pregnancy. A woman diagnosed with threatened miscarriage or threatened miscarriage is admitted to the hospital for appropriate therapy in severe condition, or may be observed on an outpatient basis and given hormonal therapy, as in inpatient treatment.
Of course, hormones play one of the main roles in the regulation of pregnancy. The problem of treatment of miscarriage is very complex and multifaceted. I repeat that in our country it is customary to preserve early pregnancy. For this purpose, hormone therapy is used, based on the physiological and pathogenetic processes of the onset and development of pregnancy. A woman diagnosed with threatened miscarriage or threatened miscarriage is admitted to the hospital for appropriate therapy in severe condition, or may be observed on an outpatient basis and given hormonal therapy, as in inpatient treatment.
Symptoms of a threatened miscarriage
As for the threat of preterm labor, the first symptoms may not be bloody discharge, but simply heavy discharge (sometimes a woman thinks that she has urinary incontinence). This may be a signal that the integrity of the fetal bladder is broken. Of course, in this case, you should immediately consult a doctor. If it is daytime, then a doctor of antenatal clinic is enough. At night, it is better to call an ambulance or get to the maternity hospital on your own.
If it is daytime, then a doctor of antenatal clinic is enough. At night, it is better to call an ambulance or get to the maternity hospital on your own.
In later pregnancy there may also be spotting . The reason for them may be a low-lying placenta and constant uterine contractions (uterine tone). It is the tone of the uterus that can cause placental abruption and, accordingly, bleeding. Contacting a doctor should be in the same mode as described above.
Special mention should be made of ectopic pregnancy . This condition can also be associated with the threat of termination, only the consequences of the termination of an ectopic pregnancy can adversely affect the woman's health. An ectopic pregnancy is a condition in which a fertilized egg attaches itself outside the uterine cavity. This place is most often tubes, but an ectopic pregnancy can also be found directly in the ovary or in the abdominal cavity.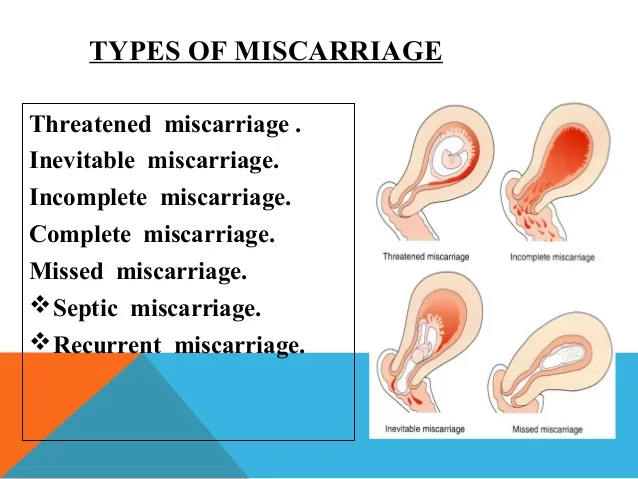 The diagnosis of "ectopic pregnancy" requires immediate surgical intervention. The scope of the operation and operative approach (cavitary or laparoscopic) can only be decided in a hospital setting and depends on many factors, including complications that have arisen at the time of admission to the hospital. Very often, an ectopic pregnancy occurs when there is a malfunction of the villi that are in the tubes and push the fertilized egg into the uterine cavity. It is impossible to predict this state. However, it can occur most often in chronic inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs.
The diagnosis of "ectopic pregnancy" requires immediate surgical intervention. The scope of the operation and operative approach (cavitary or laparoscopic) can only be decided in a hospital setting and depends on many factors, including complications that have arisen at the time of admission to the hospital. Very often, an ectopic pregnancy occurs when there is a malfunction of the villi that are in the tubes and push the fertilized egg into the uterine cavity. It is impossible to predict this state. However, it can occur most often in chronic inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs.
What to do in case of termination of pregnancy
If the pregnancy could not be maintained, then the question arises of the reasons for this situation. After what happened, an examination is necessary, which will include an examination of both spouses. It is necessary to obtain the results of a histological examination and consult a geneticist .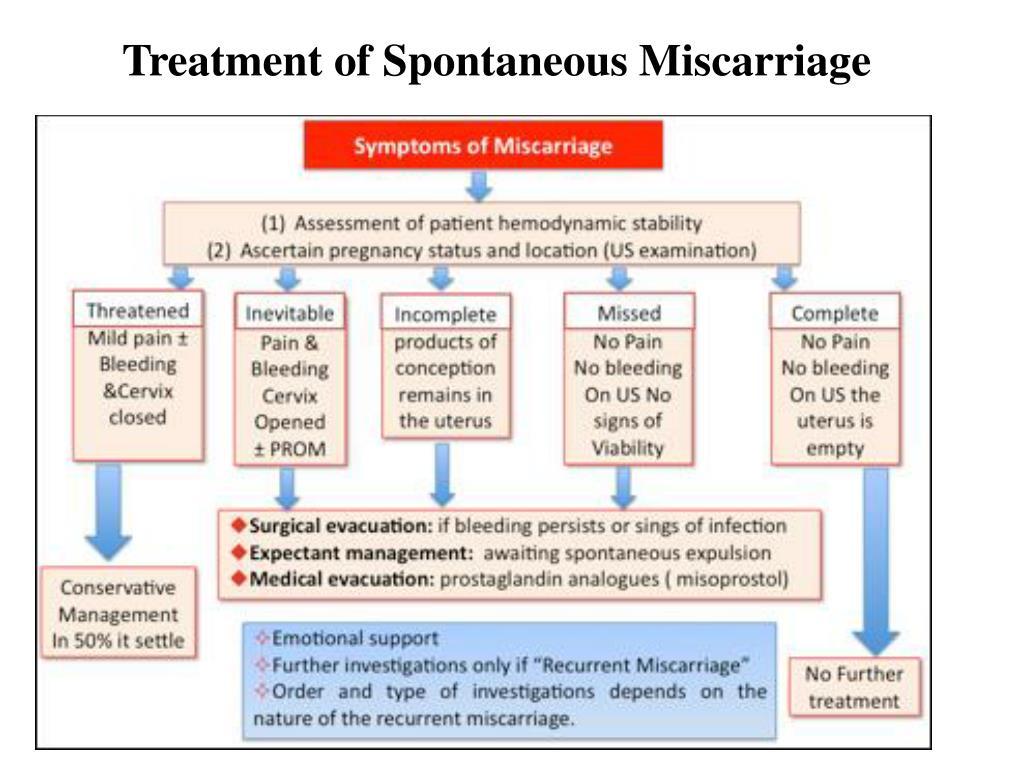 A woman will be examined by a gynecologist for infections or hormonal disorders, a man needs to consult a urologist (andrologist) for the same examination.
A woman will be examined by a gynecologist for infections or hormonal disorders, a man needs to consult a urologist (andrologist) for the same examination.
Sometimes it is very difficult to find the cause, but this is not a reason to despair. Subsequent pregnancies can pass without complications, and the first unsuccessful attempt is quickly forgotten. With a successful examination , it is recommended to plan the next pregnancy in 4-6 months .
Everything that we have talked about should draw attention to the health of a pregnant woman and help her orient herself in the event of a particular situation. A desired pregnancy is a joyful state for a woman and her family. The task of the doctor is to prevent and, as far as possible, solve the problem with a positive result.
Doctors of the Fetal Medicine Center are one of the leading specialists in prenatal diagnostics, candidates of medical sciences, doctors of the highest categories with a narrow specialization and extensive experience in prenatal medicine.