Signs of a non viable pregnancy
Early Pregnancy Loss - familydoctor.org
What is early pregnancy loss?
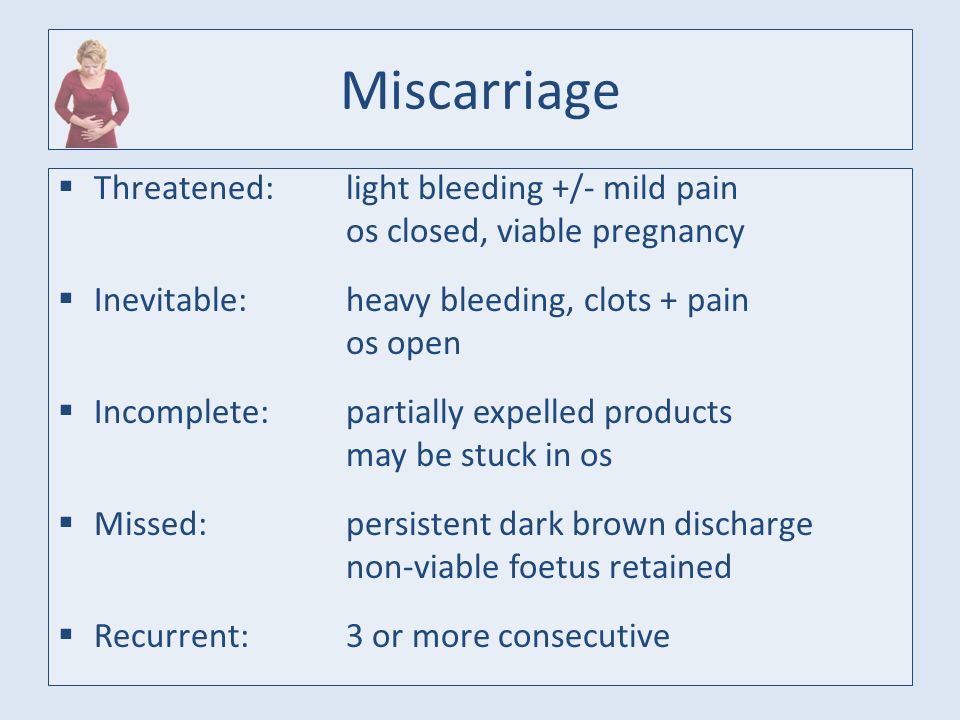
An early pregnancy loss is known as a miscarriage. This represents any pregnancy that ends on its own in the first 20 weeks of gestation. Experts estimate that 10% to 20% of known pregnancies end in miscarriage. There are several classifications of miscarriage:
- Complete – when the embryo and surrounding tissues have emptied out of the uterus. It typically involves cramping and bleeding. These resolve quickly, usually in a few days to a week.
- Incomplete or inevitable – when the cervix opens, and some tissue is expelled (released). The embryo or tissue may not completely leave the uterus. This can cause continued pain and bleeding.
- Missed – when the embryo has died, but it stays in the uterus. You may have no idea that it has happened. It is often discovered when pregnancy symptoms stop, or an ultrasound shows no heartbeat.
- Threatened – when you experience some bleeding and cramping, but the cervix remains closed. A miscarriage may or may not happen.
- Recurrent –when you have 3 or more miscarriages in your first trimester.
Other problems can also result in an early pregnancy loss:
- Chemical pregnancy – This is a very early miscarriage. It usually happens in the first few weeks after conception. Chromosomal abnormalities keep the embryo from developing normally. The tissue is passed from your uterus around the same time that you normally have your period. Many women don’t even know they are pregnant when they have a miscarriage from a chemical pregnancy.
- Blighted ovum –This is also called an embryonic pregnancy. It happens when the fertilized egg implants in the wall of the uterus, but a fetus never develops.
- Ectopic pregnancy –This is when the fertilized egg implants somewhere other than the uterus.
 Often, it implants in the fallopian tube. This can cause serious problems for the mother. Treatment — usually surgery — is needed right away to remove the tissue. This is never a viable pregnancy.
Often, it implants in the fallopian tube. This can cause serious problems for the mother. Treatment — usually surgery — is needed right away to remove the tissue. This is never a viable pregnancy. - Molar pregnancy –This is a rare problem that starts with a genetic error during fertilization. This causes abnormal tissue to grow instead of an embryo. It is not a viable pregnancy. But it still causes regular pregnancy symptoms. These include a missed period, positive pregnancy test, and nausea.
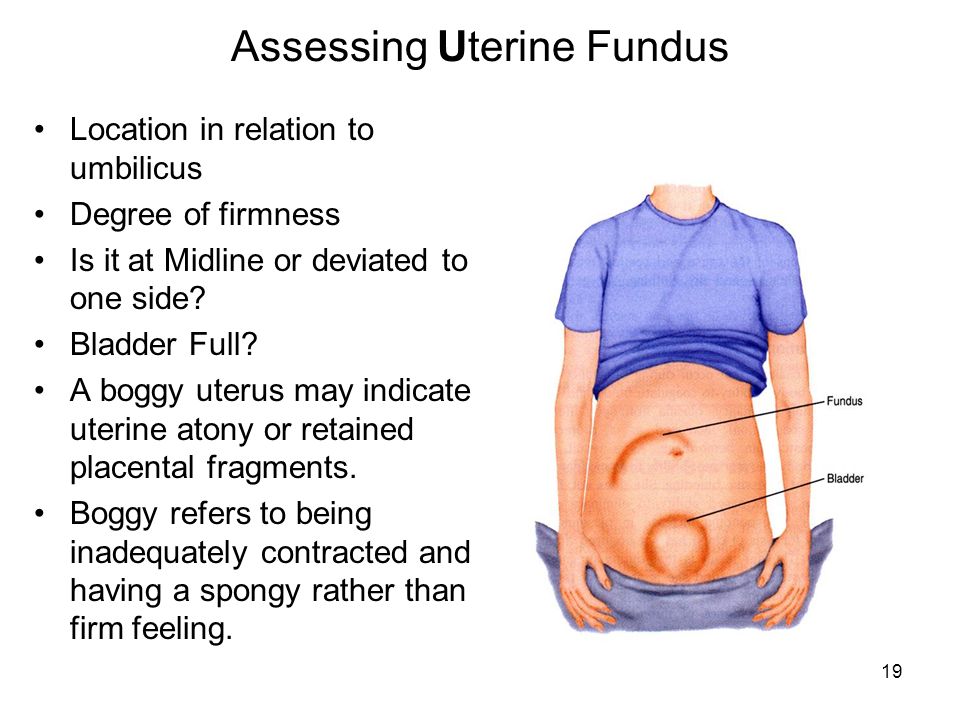
Symptoms of early pregnancy loss
The most common symptoms of miscarriage are bleeding and cramping. But they don’t necessarily mean you’re having a miscarriage. Up to one-third of pregnancies come with some bleeding early on. About half of those result in normal pregnancies. If you have any bleeding or cramping in your first trimester, call your doctor.
There are other common signs that indicate you may be having a miscarriage. If you experience any of these symptoms, call your doctor right away:
- Mild to severe back pain (worse than menstrual cramps)
- Weight loss
- White-pink mucus discharge from the vagina
- Contractions (painful, happening every 5 to 20 minutes)
- Tissue that looks like a clot passing from the vagina
- Sudden decrease in signs of pregnancy
What causes early pregnancy loss?
In some cases, the cause of your pregnancy loss is unknown. Often, it is a random problem with chromosomes that happens at conception. You might be afraid that you did something that caused your miscarriage. But things like working, exercising, having sex, or morning sickness do not cause miscarriage. Any kind of fall or blow is rarely to blame. The research on the effects of alcohol, tobacco, and caffeine is unclear. So, there is nothing you could have done to prevent it. It is not the result of anything you did or didn’t do. You should never blame yourself for a miscarriage.
Often, it is a random problem with chromosomes that happens at conception. You might be afraid that you did something that caused your miscarriage. But things like working, exercising, having sex, or morning sickness do not cause miscarriage. Any kind of fall or blow is rarely to blame. The research on the effects of alcohol, tobacco, and caffeine is unclear. So, there is nothing you could have done to prevent it. It is not the result of anything you did or didn’t do. You should never blame yourself for a miscarriage.
How is early pregnancy loss diagnosed?
Your doctor will start by asking you questions about your symptoms and when they started. They will do a physical exam. Your doctor might do an ultrasound. This can reveal if the embryo is still growing, and it can check for a heartbeat. They may also order blood tests. These can measure pregnancy hormone levels. This can give your doctor an idea if you are losing the pregnancy.
Can early pregnancy loss be prevented or avoided?
There is no conclusive research that says there is anything you can do to prevent a miscarriage. You didn’t cause it, so you couldn’t have prevented it.
You didn’t cause it, so you couldn’t have prevented it.
Risk factors
Patients who are pregnant and who have had a miscarriage are at greater risk of having another one. Your risk also increases as you get older. You are at highest risk when you are age 35 or older. Some medical conditions also increase your risk. These include:
- Diabetes.
- Thyroid disease.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Problems with the immune system.
Even if you have one of these conditions, you can’t do anything to avoid having a miscarriage. Many patients who are pregnant and have these health conditions have healthy pregnancies.
Early pregnancy loss treatment
There are two main types of treatment for miscarriage: non-surgical and surgical.
Non-surgical
In many cases, your body passes all of the pregnancy tissue naturally. This could take a few days up to a few weeks. No treatment is needed. If it is taking a long time, your doctor can give you medicine that can help pass the tissue.
The process of passing the tissue can involve heavy bleeding, cramping pain, diarrhea, and nausea. Your doctor may give you pain medicine to help ease your symptoms. If you are in your first trimester, the tissue will be small. It will look like a blood clot. It will not look like a baby.
Your doctor may do an ultrasound or blood tests after you are finished with the miscarriage. This will confirm that the miscarriage is complete, and no tissue remains.
Surgical
Surgical treatment is usually done if there are complications with your miscarriage.
Complications could include:
- An infection
- Heavy bleeding
- Any condition that keeps pregnancy tissue inside your uterus
Common surgical treatments include:
- Vacuum aspiration.In this procedure, a thin tube is inserted into your uterus. It is connected to a suction device. The pregnancy tissue is suctioned out of your body. The procedure is done under local anesthesia.
 Your doctor can perform it in his or her office.
Your doctor can perform it in his or her office. - Dilation and curettage (D&C).This procedure opens the cervix and uses an instrument to remove the pregnancy tissue. It is usually done under regional or general anesthesia. Your doctor will perform it in a hospital or surgery center.
After treatment, your doctor may recommend you not put anything into your vagina for a few weeks. This includes using tampons and having sex. This helps prevent infection. Signs of infection include:
- Heavy bleeding
- Fever
- Chills
- Severe pain
Call your doctor right away if you have any of these symptoms.
Living with early pregnancy loss
Everyone handles loss differently. Some patients who are pregnant may have trouble coping with the feelings that can go along with miscarriage. If you are very upset or feel like you need help, there are resources available. Talk to your doctor. They may be able to refer you to a local support group. There are also national resources you can access, such as SHARE: Pregnancy and Infant Loss Support. It lists local support groups and offers online resources that could help you.
There are also national resources you can access, such as SHARE: Pregnancy and Infant Loss Support. It lists local support groups and offers online resources that could help you.
Questions to ask your doctor
- I’m having symptoms of miscarriage. What are the chances that I will miscarry?
- How will I know what caused my early pregnancy loss?
- Is there an advantage to letting the tissue pass naturally over having a D&C?
- Will a miscarriage affect my ability to get pregnant again?
- How long should I wait after an early pregnancy loss to try to get pregnant again?
Resources
National Institutes of Health, MedlinePlus: Miscarriage
National Institute of Child Health and Human Development: Pregnancy Loss
SHARE: Pregnancy and Infant Loss Support
A Determined Look into Non-Viable Pregnancy: Heartbreak and The Way Forward
I won’t lie to you, mama. This topic is HARD. Non-viable pregnancy is sometimes a blessing but ALWAYS a tragedy.
Growing a little one is such a special thing, and you don’t need me to tell you: losing a pregnancy is one of the hardest things in the world to handle.
It’s my belief that knowing all there is to know in advance, or at least having the information from a source that gets you and feels for you, will help you to work through the worries or heartbreak that accompanies such a tough thing.
Table Of Contents
- Our Objective Regarding Non-Viable Pregnancy
- What is a Non-Viable Pregnancy?
- Determining Viability in Pregnancy
- Symptoms of a Non-Viable Pregnancy: What to Look For
- The Causes of a Non-Viable Pregnancy
- Non-Viable Pregnancy Options
- Making It Through a Non-Viable Pregnancy
Get more support from the @mommy.labornurse Instagram community!Join over 530k mamas for tips and solidarity on all things pregnancy, birth, and postpartum!
Our Objective Regarding Non-Viable PregnancyAs a labor and delivery nurse, you can guess that I’ve seen every shade of non-viable pregnancy. I’m here to tell you, they are all hard. If you experience or have experienced a non-viable pregnancy, it can feel like no one understands.
I’m here to tell you, they are all hard. If you experience or have experienced a non-viable pregnancy, it can feel like no one understands.
But I’m with you, lady. As are millions of women before and beside you.
Your medical staff, the people you pass on the street, those somber-eyed ladies in black and white photos–we are all touched by this unique form of tragedy in one way or another at some point in our lives, even if we never know it.
So let’s take some time to review it all; it’s not always something to fear or something to dwell on, but knowledge and understanding can sometimes be our greatest hope. I firmly believe that context always provides a wider platform for acceptance and RECOVERY.
What Should You Do With This Information?If you are NOT working through a non-viable pregnancy at this time and are simply hoping to be well-informed, it’s my hope that I give you everything you need to feel good about your options–all without increasing your FEAR. Life’s too short for that, mama.
Life’s too short for that, mama.
That said, be sure to ask about the pregnancy viability milestones your provider uses, as their information and how they relate that to you is going to more important than any other resource.
If, on the other hand, you are currently experiencing or are in danger of having a non-viable or at-risk pregnancy, my heart goes out to you–as does my hand.
I’ll be taking you through the definitions, causes, and treatment options necessary to cover ALL YOUR BASES.
I hope we’ll be able to examine non-viable pregnancy treatments together to ensure you have everything you need to make the best choices in what is easily a crucible for the best of us.
What is a Non-Viable Pregnancy?There’s a little push and pull when it comes to the definition of a non-viable pregnancy.
The reason for this is that there are legal implications if a radiologist or a practitioner uses a term like “non-viable pregnancy” or “non-viable fetus” outside of a very specific range of time.
It’s typically safer for medical staff to refer to it as a failed pregnancy.
This makes for pretty stale reading, but suffice it to say that we’re talking about a fetus that cannot be carried to term.
Because it’s simpler for our needs, we’ll stick to non-viable, but remember that your OB or radiologist might go a different way, mama.
If it becomes important to know the difference, your care provider will help you understand.
What Does Viability Mean Regarding Pregnancy?If non-viable means the baby can’t be carried to term, it follows that viability is the consideration of whether or not that little seed can actually grow into a plant.
Viability is determined by a lot of things, including:
- How and where the zygote (little baby bubble) attaches to the uterine wall
- What kind of conditions exist in the womb
- What kind of data mom and dad put into the sperm and egg that connected
In broader terms, “viable” means “capable of working successfully” or “feasible”. In biological terms, it’s more about being capable of surviving or living successfully, particularly in specific environmental conditions.
In biological terms, it’s more about being capable of surviving or living successfully, particularly in specific environmental conditions.
The viability of a pregnancy looks a little different depending on what term you’re in. As you can imagine, a lot goes into losing viability as a zygote.
That little seed pod needs very different conditions than a fully formed and growing embryo; even further still are the requirements for a legit fetus or an actual baby.
You can probably guess, but it’s a much more dangerous world for a tiny little zygote or an embryo than it is for a fetus or a baby.
The result is that you’re much more likely to have a failed pregnancy in the first trimester (the first 0-13 weeks of pregnancy).
Differences Between a Non-Viable Pregnancy and a MiscarriageA miscarriage is defined as the spontaneous loss of a fetus BEFORE 20 weeks of development.
Loss of the fetus after that would be considered a “stillbirth“.
There are a lot of similarities and correlations between a non-viable pregnancy and a miscarriage, mama. They overlap a lot, actually.
The reason for this is that miscarriage falls under the UMBRELLA of what we consider non-viable pregnancy.
But a non-viable pregnancy doesn’t have to be a miscarriage. Things like genetic issues may leave the zygote or fetus alive but with a low or null chance to survive beyond the womb.
Can You Have a Non-Viable Pregnancy Without MiscarriageYes, you CAN absolutely have a non-viable pregnancy but no miscarriage. The products of conception may have to be removed surgically if the pregnancy is non-viable.
Related: Everything You Need to Know About Pelvic Pain During Pregnancy (Right Now!)
Determining Viability in PregnancyAs you can imagine, mama, a lot goes into determining whether or not a zygote, embryo, or fetus presents a viable pregnancy.
Because of the drastic nature of a non-viable pregnancy, it is very important for your health care provider to be as certain as possible before declaring the pregnancy non-viable.
Symptoms of a Non-Viable Pregnancy: What to Look ForIf you have excessive bleeding and cramping, it’s always a good idea to see your care provider as soon as possible.
Severe abdominal pain can be a strong indicator that something is wrong.
Also watch out for severe headaches (particularly with blurred vision), convulsions of any kind, a fever accompanied by extreme weakness or fast/labored breathing–they can all be indicators that something is wrong with your pregnancy.
You can read more details about when to call your doctor during pregnancy which might help!
Determining Whether or Not Your Pregnancy May Be Non-ViableAs with testing for the pregnancy itself, measurements of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) along with an early ultrasound can help in diagnosing the potential for complications.
Keep in mind that these methods aren’t 100% conclusive, though–this is important to note because a failed diagnosis could be catastrophic.
For this reason, and I hope your practitioner agrees, the investigation of viability should come to a screeching halt when the practitioner asks themselves “Is there a chance of viability”.
Diagnostic criteria for a non-viable pregnancy in the first trimester are imperfect enough that your doc should always be erring on the side of caution.
Ultimately, the consequences of your doctor giving you a false positive result (saying the pregnancy is non-viable when it’s not) blow the consequences of a false negative WAY out of the water.
Believing a pregnancy IS viable when it’s actually NOT may result in a slight delay in the correct treatment (and possibly a little more disappointment, if that’s possible), while the opposite can lead to birth defects and even CAUSING a non-viable pregnancy when a bit of waiting might have put your worries to bed for good.
Ultimately, there is no silver bullet amount of hCG that can tell us whether or not a pregnancy is non-viable.
There’s a lot of overlap between different conditions and the amount of hCG present in the body at any given time.
Can a Non-Viable Pregnancy be MisdiagnosedWe’ve covered it a bit here, but there is EVERY POSSIBILITY that a doctor may misdiagnose a non-viable pregnancy.
Technology has progressed a lot with the advent of things like the transvaginal probe, but we are still limited to what we can test for in the chemistry.
The Causes of a Non-Viable PregnancyThe various causes of a non-viable pregnancy range from significant defects preventing there from ever being a fetus to infections that erode the environment in which the fetus grows.
Some of these are pretty small potatoes, mama. But some of them can be really serious if left untreated.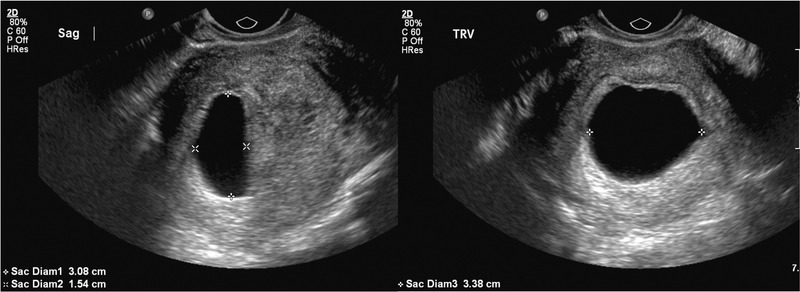
Anembryonic Gestation is a condition where the gestational sac forms but no embryo grows within it. They used to call this a blighted ovum, but the term isn’t as widely used today. Some believe that it can be due to chromosomal abnormalities.
Chemical PregnancyA chemical pregnancy is when an egg gets fertilized but never attaches to the uterus. Chances are that you’ll never know you had one of these, honey, so don’t lose sleep over it.
Ectopic PregnancyAn ectopic pregnancy is when a fertilized egg implants inside of a fallopian tube or some other cavity, rather than inside the uterus. This one can actually be really dangerous if left untreated too long.
Molar PregnancyA molar pregnancy occurs when an already non-viable egg attaches to the uterine wall. Because the egg already can’t become a fetus for one reason or another, it grows into a non-cancerous mass instead.
A septic abortion occurs when an infection takes hold in the placenta. This septic infection can transfer to the uterus and pelvis, potentially damaging organs nearby and even further away if left untreated.
Genetic / Congenital DefectsA genetic or congenital defect is an error in the DNA (or “code”) that comprises the substance of mommy or daddy.
These defects may be specific to a single specimen of sperm or ovum, or they can be substantial defects that affect all or most of a potential parent’s stuff.
Extremely Premature LaborThis one is what it is, mama. Premature labor short of about 24 weeks will be considered non-viable, as the fetus is insufficiently developed for survival outside of mom.
Non-Viable Pregnancy OptionsWhat options a mama has when the fetus is determined non-viable vary significantly depending on why the pregnancy is non-viable.
As always, the best recommendations are going to come directly from your care provider.
Hopefully, though, you can walk into that conversation armed to the teeth with the information necessary to ask the right questions and walk away fully satisfied by the outcome. Or at least as satisfied as can be under such circumstances.
First and foremost, you want to manage your expectations. If you know the little one is not viable, it’s important to frame your feelings and thoughts in a way that allows you to work through this difficult time.
If you suspect your pregnancy is not viable, be sure to walk in with hope but be prepared for the possibility of the worst news.
Management Options for a Non-Viable PregnancyYour doctor will have a very strong set of early pregnancy loss guidelines they follow.
When in doubt–if they aren’t entirely sure the pregnancy is non-viable, they will typically offer expectant management, which is a fancy way of saying “let’s do nothing and see what happens”.
That might sound messy, and even risky in some of the scenarios we worked through earlier.
What this recommendation DOES do for us is give a chance for a false positive to be determined false. Because some of this is a bit like educated guesswork, there’s always a chance that the pregnancy may be viable when the circumstances suggest otherwise.
But What Does That Mean For YOU?It’s a little bit of a waiting game.
Beyond that, there are medical treatments with medicine that can ensure your non-viable pregnancy will come to an end without much more effort and agony on your part.
In the worst case, a doctor may sometimes recommend surgical evacuation of the products of your non-viable pregnancy. It’s hard and drawn-out by comparison, but your doctor will know best if this is necessary.
Making It Through a Non-Viable PregnancyObviously, mama, this is the last place any of us want to be.
Losing a pregnancy, even early on, can be incredibly difficult for the strongest of us.
The most important thing you can do for yourself is trust in the science, trust in the people, and trust in the fact that these things happen for a reason–biologically speaking.
With the rare exception of something like an infection, you can basically assume that if your pregnancy becomes non-viable, that fetus would likely not have had much of a life given the complications that feed into most or all of these situations.
That’s small consolation if you’ve been there. Trust me, I get it. Your medical staff feels it too. We never get into the business to deal with the non-viable ones–but it’s worth all the tears in the world to be there for mamas like you in such a tough time.
As with anything, be sure to seek solace in the arms of loved ones and know that you have support.
With the right social interaction and a proper mindset, you stand a great chance of working through a non-viable pregnancy.
With a heavy heart, happy future-making, mama.
Treatment of non-progressing pregnancy | Krasnaya Gorka
Obstetrics and gynecology
List of services
Non-developing (frozen) pregnancy is a pathological symptom complex, including:
- fetal failure;
- pathological inertia of the myometrium;
- disorders in the hemostasis system.

Non-developing pregnancy is one of the scenarios for the development of events in the diagnosis of miscarriage. Another scenario of miscarriage is spontaneous miscarriage.
Modern clinical practice allows, based on the results of ultrasound, to diagnose two types of non-developing pregnancy: anembryony (the absence of an embryo in the fetal egg) and the death of the embryo.
Two options for the origin of anembryony are considered: either the embryo did not form initially, or its development stopped at the earliest stages (no later than the 5th week of gestation). If a fetal egg without an embryo is visualized in a patient in the uterine cavity with ultrasound, either a short period of developing pregnancy or anembryony should be assumed.
They say about the death of the fetus when at first it developed normally, but for some reason died. With a recent death, the embryo and fetal egg have the usual shapes and sizes, but there are no signs of fetal life. This condition may not be accompanied by clinical symptoms of threatened abortion.
This condition may not be accompanied by clinical symptoms of threatened abortion.
The death of the embryo is not always accompanied by a rapid spontaneous miscarriage. Dystrophic and necrobiotic changes in the cellular and tissue elements of the fetal egg, combined with myometrium unreactivity, often become the reason why the dead fetal egg lingers in the uterine cavity for a long time. In these cases, we are talking about a non-developing pregnancy, which is distinguished from the concept of "spontaneous abortion" precisely by the absence of independent emptying of the uterine cavity.
Harmony in intimate relationships Harmony in the family.
For various reasons, a man's sexual life may decline. However, do not attribute everything to age and physiology. Men are too proud to seek help on their own, but they really need it. Yes, and any intimate problems in men can be corrected.
Learn more
Risk factors
According to the American Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, early pregnancy loss is most strongly associated with two risk factors:
- older and late reproductive age of the mother;
- a large number of previous miscarriages.

Thus, the risk of spontaneous abortion in women aged 20-24 years is 8.9%, 24-30 years old - up to 17%, 30-40 years old - up to 40%, and at the age of 45 years - already 75% or more.
The more episodes of miscarriage, the worse the prognosis for subsequent conception: the risk of recurrent miscarriage after a single gestational loss is comparable to the general population, but after two losses it reaches 29%, after three - 33%. In addition, reproductive opportunities are reduced by chronic diseases of the mother - both gynecological and extragenital:
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- poorly compensated diabetes mellitus;
- chronic kidney disease;
- systemic lupus erythematosus, antiphospholipid syndrome and other systemic connective tissue diseases;
- Uncompensated thyroid diseases;
- Severe arterial hypertension.
- Another risk factor is reproductive health disorders of the sexual partner.
In the genesis of spontaneous abortions, mutagenic and teratogenic factors can also play a certain role, but it is difficult to quantify them. These include a number of relatively manageable ones, such as:
- smoking;
- alcohol dependence;
- cocaine addiction;
- intake of high doses of caffeine;
- low body mass index.
Uncontrollable risk factors include: late reproductive age of the pregnant woman and/or her partner; stressful situations.
Doctors attending:
-
Trishkin Alexey Gennadievich
Head department of ART, obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductive specialist, gynecologist-endocrinologist, ultrasound diagnostician, Head of the Department of New Reproductive Technologies, KemSU, Associate Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences
-
Bochkarnikova Hasmik Gerbertovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductologist, gynecologist-endocrinologist, ultrasound specialist
-
Zueva Galina Pavlovna
Deputy chief physician for medical work Krasnaya Gorka on Yuzhny, obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductive specialist, gynecologist-endocrinologist, ultrasound doctor, head of the RAHR department, associate professor of the Department of New Reproductive Technologies, KemSU, Candidate of Medical Sciences
-
Grigorieva Olesya Vladimirovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductologist, ultrasound specialist
-
Kuzmina Tatyana Sergeevna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductologist, ultrasound specialist
Make an appointment
Name
Phone number
Question
I visit the clinic for the first time
I have a map
Choose a doctorKaryakina L. S. Barashov A. Yu. Drozdik O. V. Ivanova A. V. Shamin M. V. Valshin T. Yu. O. Luneva E. V. Soloviev V. B. Neverova Yu. N. Zhivotovsky A. S. Bykova Yu. . A. Lobanova O. G. Pomeshkin E. V. Bushmakin A. D. Maruev M. B. Lesnikov A. I. Bezdenezhnykh A. V. Surtsev K. S. Shlegel E. G. Piskunov A. S. Grigorieva O V. Volodina S. S. Izmestiev K. V. Kuzmina T. S. Kurganova L. V. Pritchina S. S. Zueva G. P. Stepanova O. V. Burkov A. N. Barashova L. P. Stopicheva S L. Shipitsyna O. A. Golitenko E. Yu.0003
S. Barashov A. Yu. Drozdik O. V. Ivanova A. V. Shamin M. V. Valshin T. Yu. O. Luneva E. V. Soloviev V. B. Neverova Yu. N. Zhivotovsky A. S. Bykova Yu. . A. Lobanova O. G. Pomeshkin E. V. Bushmakin A. D. Maruev M. B. Lesnikov A. I. Bezdenezhnykh A. V. Surtsev K. S. Shlegel E. G. Piskunov A. S. Grigorieva O V. Volodina S. S. Izmestiev K. V. Kuzmina T. S. Kurganova L. V. Pritchina S. S. Zueva G. P. Stepanova O. V. Burkov A. N. Barashova L. P. Stopicheva S L. Shipitsyna O. A. Golitenko E. Yu.0003
Choose a clinic on Suvorova on Dvuzhilny
I agree to the processing of personal data
What is a missed pregnancy - Maternity Hospital "Leleka"
A missed pregnancy is the cessation of embryo development in the uterus of a pregnant woman, which ends in miscarriage and termination of pregnancy. This happens quite often: about one in five women has experienced a missed pregnancy.
According to statistics, approximately 80% of cases of pregnancy failure occur in the early stages of pregnancy. Perhaps this figure is even higher: after all, a delay in menstruation of several days is not considered a serious problem. When heavy periods begin after a delay, a woman may not even suspect that she was pregnant.
But even if pregnancy is already known for sure, in the early stages it can freeze and lead to auto-abortion. During this period, the laying and basic formation of all the vital organs of the child takes place. In some women, the body is very sensitive to any factors that can lead to fetal abnormalities, and reacts to them in this way.
In the second and third trimesters, pregnancy freezes much less frequently, but it does happen. With a timely visit to the doctor, a woman can receive the necessary assistance so that the interrupted pregnancy does not lead to further infertility. Fortunately, due to the development of medicine in recent years, this is more than possible.
Causes of miscarriage
A large proportion of miscarriages are due to genetic disorders and fetal anomalies. Alas, this is part of the mechanism of natural selection: non-viable organisms die in the bud. Neither the woman herself nor the known methods of evidence-based medicine can somehow influence this mechanism.
Among other causes of fetal fading in the early stages:
- polycystic ovaries;
- intoxication of the body with various substances - alcohol, dangerous chemical compounds, waste products of bacteria during infection;
- inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- other inflammatory diseases;
- serious illness of the mother, eg diabetes;
- TORCH infections;
- history of multiple abortions;
- severe stress;
- excessive physical activity, overwork.
In the second and third semesters, for the fading of the fetus, serious reasons are needed. Social factors cannot be ruled out - stress, overwork, drug use and large doses of alcohol. But the main factors are serious malformations in the fetus and severe illness of the mother.
Social factors cannot be ruled out - stress, overwork, drug use and large doses of alcohol. But the main factors are serious malformations in the fetus and severe illness of the mother.
Read in our media center: "What is oxidative stress." Find out why oxidative stress occurs in the body, why it is dangerous and how to resist it.
Symptoms of missed pregnancy
Signs of missed pregnancy differ at different stages. So, if this happened in the first weeks of pregnancy, a woman may not feel anything at all. And in the later stages, the first sign of fading - the child stops moving. In general, the signs are as follows:
- pulling pain in the lower abdomen;
- dark spotting;
- sharp relief of toxicosis;
- absence of fetal heartbeat on examination by a doctor;
- stabilization or decrease in the level of gonadotropin - "pregnancy hormone";
- worsening of health, fever, nausea when an abortion has begun.