Uterine measurements during pregnancy
What It Is, Why It Matters, and How to Measure It
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
Reviewed by Dan Brennan, MD on October 25, 2021
In this Article
- What Is Fundal Height?
- What Does Fundal Height Tell You About Your Baby?
- How Do You Measure Fundal Height?
- What Should Your Fundal Height Be?
- What Can Impact Fundal Height?
- What Should You Do if You’re Concerned About Your Fundal Height?
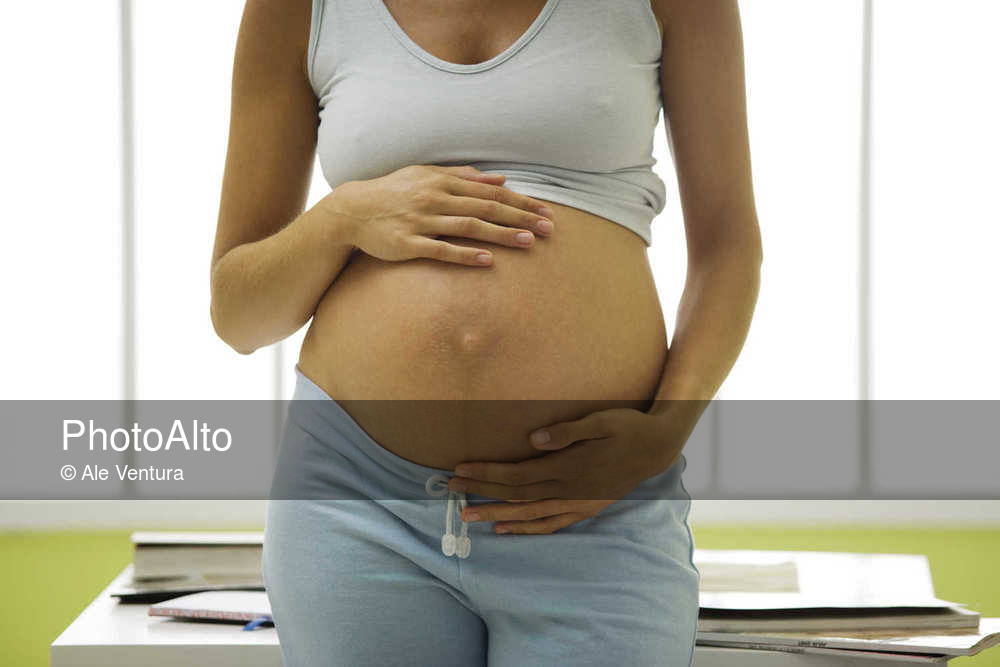
Choosing to have a baby can be a magical experience. But there are also many unknowns that come with pregnancy. You’re doing everything you can to care for your body and your unborn child, but you may wonder how to know if your baby is growing well in your uterus (womb).
Measuring fundal height is one way to keep track of your baby’s development while you’re pregnant.
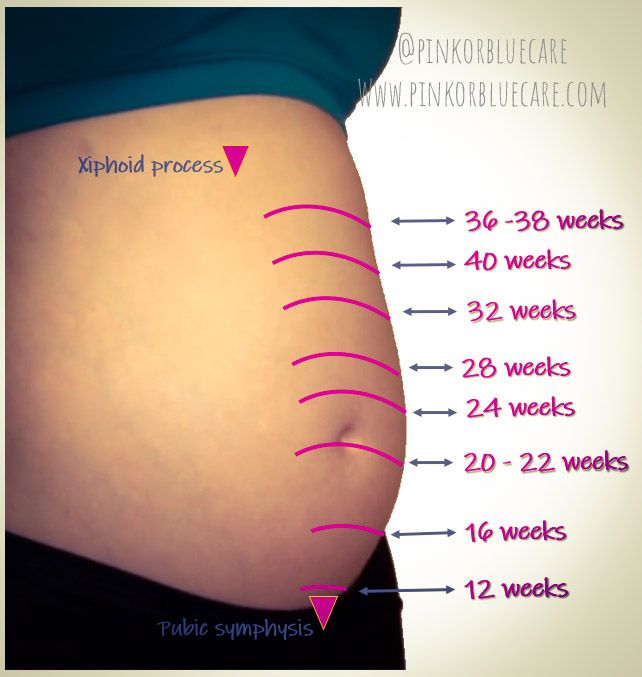
What Is Fundal Height?
It’s the distance from your pubic bone to the top of your uterus.
Measuring your fundal height is one test your doctor may do at your pregnancy check-ups. Other ways they may check on your baby’s health include checking your physical health, running labs on your body, listening to your baby’s heartbeat, checking how often your baby moves, and looking at your baby with an ultrasound.
Doctors combine all of these factors to give you the most accurate understanding of how well your baby is developing.
What Does Fundal Height Tell You About Your Baby?
Doctors use your fundal height measurement to test how well your baby is growing.
It’s one of many tests doctors use to measure your baby’s growth. Your fundal height is compared to your estimated pregnancy date to suggest whether your baby is growing on track.
If your fundal height isn’t what you expect it to be, it doesn’t automatically mean that there’s something wrong with your baby. But if your fundal height is on track, you may be able to rest a little easier knowing your baby is growing the way your doctors are expecting it to.
How Do You Measure Fundal Height?
Understand that even trained doctors can have a hard time measuring it accurately.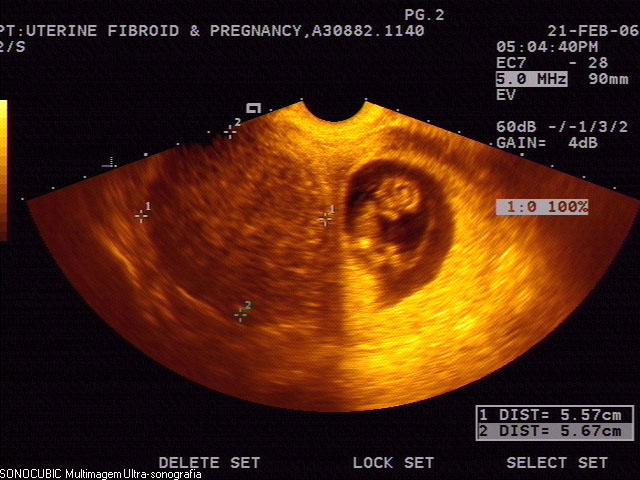 So, before you try measuring fundal height at home, have your doctor show you where your pubic bone is and how to locate the top of your uterus.
So, before you try measuring fundal height at home, have your doctor show you where your pubic bone is and how to locate the top of your uterus.
Once you know, here are the basic steps to follow.
- Empty your bladder first. Studies show that a full bladder can change fundal height measurements by several centimeters.
- Next, lay down on your back with your legs out in front of you. Using a tape measure that measures centimeters, place the zero marker at the top of the uterus.
- Move the tape measure vertically down your stomach and place the other end at the top of your pubic bone. This is your fundal height measurement.
What Should Your Fundal Height Be?
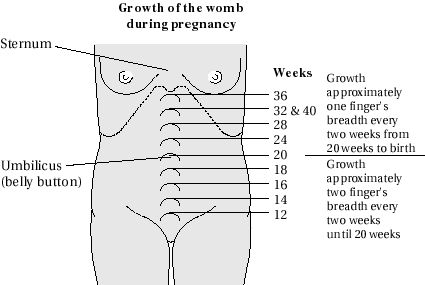
Starting at 24 weeks, your fundal height should be about the same number of centimeters as the number of weeks you’ve been pregnant.
Your fundal height may be off by up to 2 centimeters in either direction and still be considered normal.
So, for example, if you’re 30 weeks pregnant, a fundal height of 28 to 32 centimeters is considered to be a normal range.
What Can Impact Fundal Height?
There are a number of things that can affect it. Not all of these factors have to do with your baby. For example, your fundal height measurement may not be accurate if:
- You have a BMI of 30 or more.
- You have a history of uterine fibroids.
- Your bladder is full.
- You’re not lying on your back when you take the measurement.
There are other reasons your fundal height may be bigger or smaller than expected. If your fundal height is larger than expected, it may be because:
- You have too much amniotic fluid.
- You’re having more than one baby.
- Your baby is larger than expected.
If your fundal height is smaller than expected, it may be because:
- Your baby is smaller than expected.
- You don’t have enough amniotic fluid.
- Your baby’s growth is being restricted.
Your fundal height measurement may also be off if your pregnancy is further along, or less far along, than you thought. Your due date is an estimate based on the last day of your last period, so it can sometimes be inaccurate.
Your due date is an estimate based on the last day of your last period, so it can sometimes be inaccurate.
Doctors usually use the assumption that you have a standard 28-day period when making their due date predictions. Since periods and ovulation windows can vary, your doctor may have been off by a couple of weeks when first predicting your due date.
What Should You Do if You’re Concerned About Your Fundal Height?
If your fundal height isn’t measuring as expected, your doctor will need to do some follow-up tests to determine the root cause. These tests could include an ultrasound to get a better look at your baby or labs to test the health of your body.
An unusual fundal height measurement on its own is an indication that there’s something happening with your baby.
Once your doctor has figured out why your fundal height measurement is off, they can help you figure out what steps need to be taken next, if any, to help your baby grow at a healthy rate.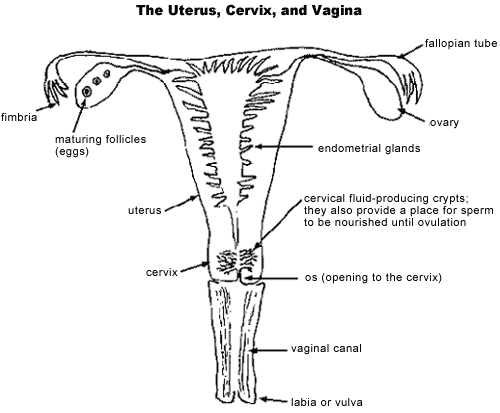
What It Is, Why It Matters, and How to Measure It
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
Reviewed by Dan Brennan, MD on October 25, 2021
In this Article
- What Is Fundal Height?
- What Does Fundal Height Tell You About Your Baby?
- How Do You Measure Fundal Height?
- What Should Your Fundal Height Be?
- What Can Impact Fundal Height?
- What Should You Do if You’re Concerned About Your Fundal Height?
Choosing to have a baby can be a magical experience. But there are also many unknowns that come with pregnancy. You’re doing everything you can to care for your body and your unborn child, but you may wonder how to know if your baby is growing well in your uterus (womb).
Measuring fundal height is one way to keep track of your baby’s development while you’re pregnant.
What Is Fundal Height?
It’s the distance from your pubic bone to the top of your uterus.
Measuring your fundal height is one test your doctor may do at your pregnancy check-ups. Other ways they may check on your baby’s health include checking your physical health, running labs on your body, listening to your baby’s heartbeat, checking how often your baby moves, and looking at your baby with an ultrasound.
Doctors combine all of these factors to give you the most accurate understanding of how well your baby is developing.
What Does Fundal Height Tell You About Your Baby?
Doctors use your fundal height measurement to test how well your baby is growing.
It’s one of many tests doctors use to measure your baby’s growth. Your fundal height is compared to your estimated pregnancy date to suggest whether your baby is growing on track.
If your fundal height isn’t what you expect it to be, it doesn’t automatically mean that there’s something wrong with your baby. But if your fundal height is on track, you may be able to rest a little easier knowing your baby is growing the way your doctors are expecting it to.
How Do You Measure Fundal Height?
Understand that even trained doctors can have a hard time measuring it accurately. So, before you try measuring fundal height at home, have your doctor show you where your pubic bone is and how to locate the top of your uterus.
Once you know, here are the basic steps to follow.
- Empty your bladder first. Studies show that a full bladder can change fundal height measurements by several centimeters.
- Next, lay down on your back with your legs out in front of you. Using a tape measure that measures centimeters, place the zero marker at the top of the uterus.
- Move the tape measure vertically down your stomach and place the other end at the top of your pubic bone. This is your fundal height measurement.
What Should Your Fundal Height Be?
Starting at 24 weeks, your fundal height should be about the same number of centimeters as the number of weeks you’ve been pregnant.
Your fundal height may be off by up to 2 centimeters in either direction and still be considered normal.
So, for example, if you’re 30 weeks pregnant, a fundal height of 28 to 32 centimeters is considered to be a normal range.
What Can Impact Fundal Height?
There are a number of things that can affect it. Not all of these factors have to do with your baby. For example, your fundal height measurement may not be accurate if:
- You have a BMI of 30 or more.
- You have a history of uterine fibroids.
- Your bladder is full.
- You’re not lying on your back when you take the measurement.
There are other reasons your fundal height may be bigger or smaller than expected. If your fundal height is larger than expected, it may be because:
- You have too much amniotic fluid.
- You’re having more than one baby.
- Your baby is larger than expected.
If your fundal height is smaller than expected, it may be because:
- Your baby is smaller than expected.
- You don’t have enough amniotic fluid.

- Your baby’s growth is being restricted.
Your fundal height measurement may also be off if your pregnancy is further along, or less far along, than you thought. Your due date is an estimate based on the last day of your last period, so it can sometimes be inaccurate.
Doctors usually use the assumption that you have a standard 28-day period when making their due date predictions. Since periods and ovulation windows can vary, your doctor may have been off by a couple of weeks when first predicting your due date.
What Should You Do if You’re Concerned About Your Fundal Height?
If your fundal height isn’t measuring as expected, your doctor will need to do some follow-up tests to determine the root cause. These tests could include an ultrasound to get a better look at your baby or labs to test the health of your body.
An unusual fundal height measurement on its own is an indication that there’s something happening with your baby.
Once your doctor has figured out why your fundal height measurement is off, they can help you figure out what steps need to be taken next, if any, to help your baby grow at a healthy rate.
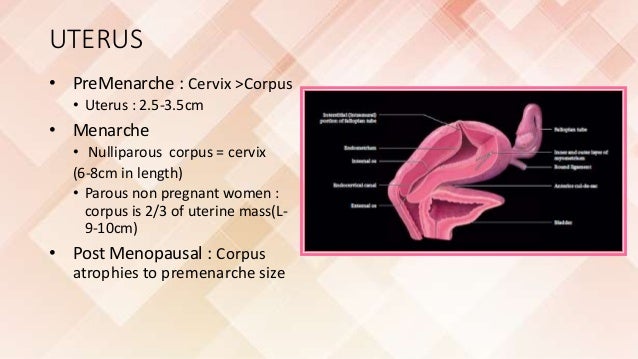
Normal size of the uterus - City Hospital No. 12, Barnaul: Articles
The size of women's uterus varies depending on age, hormonal status, pregnancy or abortion, aneurysms, etc. During the measurement, neighboring organs of the female genital system are also checked simultaneously. The difference in the size of the standard value accepted in the gynecological field indicates the existence of organs and abnormal growth.
How to determine the size of the uterus?
In gynecological treatment, we use the parameters of the uterus for clarification.
- Double Expedition - Vagina / laparoscopy method with both hands. This will be implemented when you consult with the gynecology department.
- Diagnosis material a-ultrasound (Echo). If the gynecological screening result is suspicious, it occurs during perinatal, after surgery, etc.

- The living body method is the sound cavity of the organs. Appointed on the basis of specific adaptation after postoperative surgery.
The most common method is pelvic ultrasonography.
The survey is conducted in two ways.
- Skill-in-Convex type ultrasound probe from the anterior abdominal wall.
- Ultrasonography Skil l-Insint a certain depth into the vagina through internal nodules.
The second option is considered more information.
Women's uterine size is normal
In tests on both sides, gynecologists evaluate the shape and mobility of training equipment, study the age of the ovaries and tubes, and detect the potential of new organisms (cysts, tumors, polyps). According to the test results, it is desirable that the average size of women at the age of childbirth is about 70 mm.
At the time of detection, a 7 cm mark is marked in the direction of the length of the uterine metal sheet, which is a 25 cm long metal instrument, to display the correct dimensions of the uterus.
Ultrasound diagnosis of the vagina provides the most detailed information about the health of the female reproductive system.
Judge ultrasonic waves.
- Size, shape, position of the uterus.
- Uterine wall thickness
- Length and thickness of the cervix.
- The structure of the body of the uterus is usually uniform (homogeneous).
- This is the state of the inner layer (endometrium) and the middle layer (muscle layer) of the organs.
- To obtain objective data, it is recommended that women of reproductive age perform ultrasound tests at 5–8 years of follicles during their menstrual cycle. This is due to the degree of mature follicles, changes in the size of the uterine body and the thickness of the endometrium for different cycles. The organs of the uterus increase during secretion, and the period of growth decreases.
- After menopause and after menopause, the ultrasound cycle is not determined. The diagnosis is appointed systematically or by the patient's complaint.

To measure the size of the uterus, it is necessary to estimate the length, width and thickness. Various default values are accepted per patient category.
Table 1: Normal parameters for girls and adolescent girls
The length, thickness and width of the uterus are 34-43 mm, 28-35 mm, 32-46 mm respectively and are normal for Virgos (before damage to the virgin shaft) .
Table 2: Estimation of uterine parameters for unintended women
For adult women who have terminated pregnancy and due to childbirth, the size of the reproductive organs is larger (compared to the fetus). The uterus, distributed in the perinatal period, does not decrease to the original limit after childbirth and remains slightly larger. Thereafter, each time the distribution is repeated, the parameters change in the upward direction.
Table 3: Ultrasonography of women for childbirth
Length (cm
Width (cm)
| Thickness (cm | Body | neck | |||
| body | neck | body | neck | body | neck |
2. 8-4.0 8-4.0 | |||||
| 4.5-5.5 | 2.8-3.8 | 3.4-4.4 | 2.4-3.2 | Second birth | 4.7-6.5 |
| 3.1-4.3 | |||||
| 5.0-6.0 | 2.9-3.9 | 3.7-4.9 | 2.5-3.5 | During pregnancy, women's sexual function and sexual systems usually change. | Regular examinations, including an ultrasound test for pregnant women, are scheduled three times. |
10 to 14 weeks -
20 to 24 weeks - with more
- 32 weeks to 34 weeks - run.
- If necessary, you can increase the number of ultrasonic checks.
- As mass increases, the torso of the uterus also increases. The length, width and weight of the organs increase. In addition to the standard parameters, the distance between the VDM (the height of the fundus of the uterus) during pregnancy, the distance from the wall of the uterus to the joints of the bones of the hip joint is assessed.
 This index reflects the size of the uterus and the compatibility of the pregnancy period.
This index reflects the size of the uterus and the compatibility of the pregnancy period.
Table 4: Perinatal index
Week of pregnancy
When you become pregnant, your cervix becomes smaller and firmer. As a result, it is necessary to prevent children from obstructing the movement of the child at birth.
Table 5: Typical size of the cervix in the perinatal period
Total period of pregnancy in the cervix (maturity
16-20
| 25-28 | 32-36 | Normal length (mm) | 40-45 |
| 35-40 | 30-35 | A woman's life continues through menstruation, menstruation, menopause and postpartum. Changes in hormones begin when they are over 45 years of age. The functional capacity of the ovaries gradually decreases, the endometrium becomes thinner, and the detector and neck are deformed. The width and length of the uterus decrease by 10-25 mm due to menopause. | Table 6: Women's reproductive parameters after menopause |
Within 5-6 years from the date of menstruation
The thickness of the endometrium for menopause is one of the important indicators that represent the health of the uterus. Normally, the endometrium becomes thinner, and when it becomes thicker, it becomes a pathological condition of broken epithelium, and there is a risk of developing cancer.
Why is the uterus smaller?
Causes of deviations from the correct size
The main reason for the small size is the low formation of organs, that is, underdeveloped. Lesions also occur due to abnormal organ formation and ovarian dysfunction.
Create three times.
Anatomical abnormal development in the uterus (fetus), very common 30 mm.
If the length does not exceed 55 mm, childhood or infant.
- puberty.
- You can diagnose pathology with ultrasound and sound results.
- Why is the size bigger?
The baby may be abnormally large for an ultrasound diagnosis.
Shape varies (from pear type to spherical).
The growth of the body of the uterus is the length and width.
- Empty extension-.
- The ovaries are enlarged.
- Heterogeneous structure.
- The endometrium and the muscular layer of the uterus become thicker.
- The reason for the deviation is the existence of female reproductive hormones and tumors.
- The main diseases in which the rates increase are as follows.
Benon New creatures o-Fibroids.
Benon tumor on the wall of the uterus.
- Multiple cyst formation of a pair of glands-polycystic ovaries.
- Pelvis and neck, guided uterus.
- Malignant lesions in the perspective of the uterus in the epithelial layer (cancer).
- Endometrial tissue changes - adenomyosis.
- An increase in parameters may be due to an ectopic pregnancy.
- Preventive measures to improve women's health help to avoid pathological changes in the internal genital organs.
Regular preventive visits to the gynecologist and screening tests.
Contraceptive compliance ・Contraceptive compliance
- Adequate diet rich in fatty acids, vitamins A and E.
- regular sports activities - regular physical activity
- Amblation (exercises that work the muscles of the vagina and pelvic floor)
- weight control
- Seek medical attention if you experience pain, discomfort, or menstrual irregularities. Early diagnosis helps to avoid serious complications.
- Uterine fibroids are benign, hormone-dependent tumors arising from muscle and connective tissue. The disease affects women of all ages, but is more common in women of childbearing age. According to statistics, 1 in 4 women in the world are currently diagnosed with fibroids. They may be solitary, multiple, or localized and may be several centimeters long.
The size of fibroids is conveniently determined by specialists in proportion to the size of the uterus, which increases during pregnancy. Thus, the muscle
2-2.5 cm corresponds to the size of the uterus at 4-5 weeks of pregnancy.
Dimensions of uterine fibroids in weeks
5-6 cm-myoma corresponds to 10-12 weeks.
- 8 cm or more - Enlargement of the uterus corresponds to 12-15 weeks of pregnancy.
- In some patients, fibroids grow very quickly and press on nearby organs, while in some patients the nodules grow slowly and are detected by chance during routine examinations. Accelerated growth means that within a year the fibroids have grown to a size approaching the fifth week of pregnancy.
- Uterine fibroids at 4-5 weeks of age do not have characteristic symptoms, but as the formation grows, pains in the lower abdomen, irregular menstruation, and uterine bleeding appear. Prolonged bleeding can lead to anemia. Large fibrous nodes compress neighboring organs, causing constipation, frequent urination, and compression of the ureters, which can lead to obstruction of urine flow and severe kidney disease.
Fibroid nodes can also cause infertility, but if you do get pregnant, you have an increased risk of miscarriage, preterm labor, and complications during childbirth. A common complication is torsion of the calf muscle knots, which can necrotize and cause peritonitis if the blood supply is interrupted.
Clinical manifestations and complications
In submucosal fibroids, the uterus may become twisted and the fibroids may "grow" causing severe pain and bleeding. It is also necessary to take into account the risk of malignant tumors, and the degeneration of uterine fibroids into malignant tumors is observed in 2% of patients.
For patients with uterine fibroids up to 7-8 weeks in size and patients in menopause, conservative treatment is possible with regular dispensary observation and the use of hormonal agents. At the same time, drugs are prescribed to relieve symptoms such as bleeding, pain, and anemia. However, it should be borne in mind that it is impossible to get rid of this disease with drug therapy.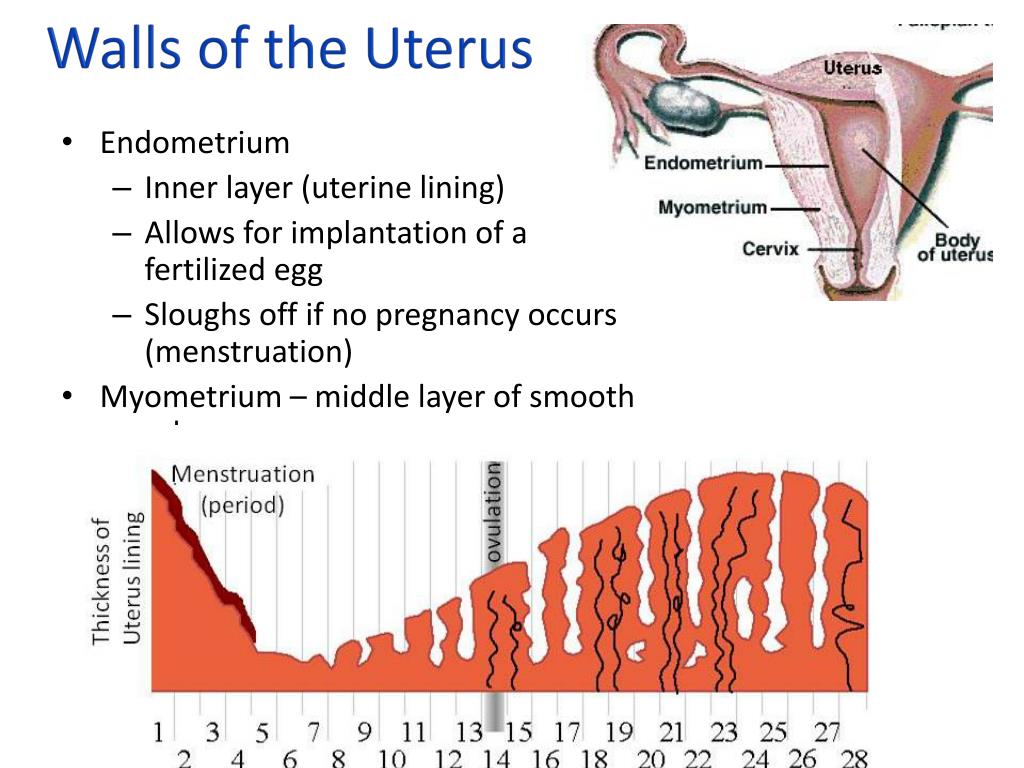 The only effective treatment is surgery.
The only effective treatment is surgery.
Uterine bleeding or menstrual irregularities.
Treatment for uterine fibroids
We actively develop nodes (4 to 5 weeks or more per year).
Indications for surgery
- Large fibroids, huge fibroids and uterine size for 11 weeks or more.
- Pain and syndrome
- Below normal values, understood nodules, atypical positions.
- Complications: anemia, necrosis, disorders in every organ, infertility, etc.
- Risk of being excluded
- To choose the treatment in your case, you can send a written consultation to my personal email address [email protected] [email protected], internal organs of the pelvis. Copy the explanation and show the age and main complaint. Thus, you should be able to respond more accurately to your situation.
- In a large European and American clinic, the "gold" standard for the treatment of uterine fibroids is recognized as the "uterine fibroids cavity", which sutures the uterus after removal of the nodes.
 Since there is a capsule around the nodules, the nodules can be removed with "External", but the uterine muscles around the capsule are not really damaged.
Since there is a capsule around the nodules, the nodules can be removed with "External", but the uterine muscles around the capsule are not really damaged.
The operation is performed laparoscopically, and after several small incisions that do not exceed 10 mm in the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. To eliminate the risk of exposure to complications (bleeding, the need for laparoscopic surgery, etc.), extermination of the fascia, which temporarily blocks the uterine artery and safely removes the large size. The technique has been developed.
Surgical treatment of fibroids
The blood vessels of the uterus are blocked during the operation and the principle is temporarily stopped. Thus, the node is removed in a "dry" working field. In addition to the lack of bleeding, the intermediate site looks perfect so you can compare the muscles as accurately as possible and effectively shorten the wound. In the future, the scar at the bottom will not be formed in action. At the last stage, the blood supply to the uterus will be fully restored.
At the last stage, the blood supply to the uterus will be fully restored.
Use the latest tools and devices (ultrasonic scissors, ligator devices, V-Rock (Covidien) system, latest generation, anti-personality, etc.). Surgery can be performed in a short time without transfusion, and recovery is much shorter than open access.
Thanks to the uterine supply organ, the fibroids, there is a greater chance that women who give birth later will become mothers. Patients who do not plan to become pregnant can maintain menstrual function until natural menopause so that they can talk about QOL at the same level.
If there are contraindications for organo-revision fibroid nucleus surgery, it is recommended to remove the uterus, leaving the cervix or accessories and neck. In this case, it is possible to maintain the state of the hormone, so that unusual results and due to a decrease in hormone levels can be avoided. By the way, root surgery is usually performed with laparoscopes and has many advantages.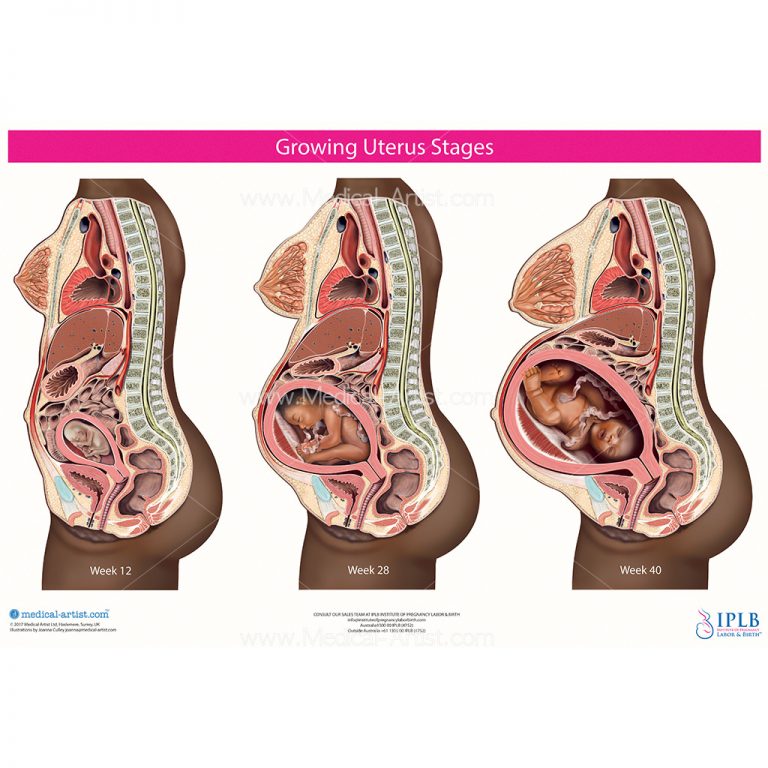
When choosing the method of intervention and quantity, you need to keep the approach to each patient. At present, I always try to perform organ-sparing surgery according to the methodology of a certain author, which is included in the standard of surgical treatment in an excellent clinic in France, Switzerland and Germany.
Professor Petitkov on the TV program "Doctor"
April 25, 2022.
And at one moment they removed me, and in myometrium there was a small fibroid, albeit a little. Also, when I did the video consultation, you took the exam and found him. You are, of course, a super-mega-class professional. You exuded a certain calmness and reliability. You are a very knowledgeable doctor and a wonderful person! ". Thanks a lot.
More information on uterine fibroids:
Patient testimonials
Apr 19 2022 11:02:00 Orkha
Hello Konstantin Viktorovich.
You will receive a letter from the patient. On March 11, 2022, I underwent surgery to remove a large multiple uterine fibroids (before 15 weeks of pregnancy). And in this letter I would like to share the history of my hospital, my thoughts and impressions.
And in this letter I would like to share the history of my hospital, my thoughts and impressions.
For me, it is rather mediocre. Honey time a year ago. The committee diagnosed her as a fibroid and recommended her removal. I am far from medicine, and I don’t have a doctor in my family, so I decided to read on my own what kind of animal such a “myoma” is and what treatment options are (try it). While searching, I immediately found information about my disease, the website of a Swiss university clinic and a video review of a patient with the same diagnosis as mine, who had successfully enucleated uterine fibroids. All saved in favorites. And now that this information has come to my attention, it will be good material for deepening communication with the doctor during the examination, which I am very glad about.
At first I didn't think of Moscow as a place for therapy. For those of us who live in the Far East, this is a very distant and dear existence. So, I digested what I read on the Internet and went to the gynecologist at the oncology dispensary of the city. The head of the department, who saw my documents and examined them, said that I would be hospitalized soon. What operation to do, to remove the uterus, are there any options? — Tell us about Professor K.V. Puchkov, how professional and trustworthy is he? I asked the director to read the article about uterine fibroids, which I opened on my smartphone on the main page https://www.puchkovk.ru/. It seemed interesting to me, and when reading the article, I emphasized several points. But when she called back, she said: “No, I can’t say anything about this expert. And at least just lie down with me tomorrow.” So we parted ways.
The head of the department, who saw my documents and examined them, said that I would be hospitalized soon. What operation to do, to remove the uterus, are there any options? — Tell us about Professor K.V. Puchkov, how professional and trustworthy is he? I asked the director to read the article about uterine fibroids, which I opened on my smartphone on the main page https://www.puchkovk.ru/. It seemed interesting to me, and when reading the article, I emphasized several points. But when she called back, she said: “No, I can’t say anything about this expert. And at least just lie down with me tomorrow.” So we parted ways.
At home I thought about the results of the consultation. I had to answer the difficult question of whether I was ready for the removal of the uterus. The doctor probably thinks that this is an amateurish reason, but my fibroids look like a wart on my finger, and when I asked him to remove it, for some reason he told me to cut off the entire finger. Stranger still, a radical surgical treatment was proposed, despite the fact that no damage was found in the internal organs, except for uterine fibroids, and the patient was healthy. The second thing that puzzled me is that I can have children. I can not say that now I am planning a pregnancy. However, I do not want to do irreversible actions with my body. No one knows what will happen to us tomorrow and how our life will change. Fatal mistakes can make you suffer, so I prefer to take the initiative and avoid mistakes. And in general, Konstantin Viktorovich, the skepticism sown in your article about the need for a hysterectomy is painfully conveyed.
The second thing that puzzled me is that I can have children. I can not say that now I am planning a pregnancy. However, I do not want to do irreversible actions with my body. No one knows what will happen to us tomorrow and how our life will change. Fatal mistakes can make you suffer, so I prefer to take the initiative and avoid mistakes. And in general, Konstantin Viktorovich, the skepticism sown in your article about the need for a hysterectomy is painfully conveyed.
I always had time to have my uterus removed, so I thought I shouldn't be impatient. I again searched for medical institutions and doctors related to my problem. This time I focused on the page of the Vladivostok medical center "Fefu". He spoke to Women's Health on the phone that the desire to perform a uterine fibroidectomy using bleeding organs was realistic. In my mind, he obnoxiously admitted that it was "difficult for me". “Is there any specialist who hears such requests?” - she said, - except Petikov K.V. ". Well, Konstantin Viktorovich, for me this proposal was my question and questions. If a great expert at an advanced high-tech regional medical center recognizes your credentials and abilities, you are probably a river if you say you are more experienced and more specialized. So, I thought that your site was not a promotion project and the review was not artificial.
Well, Konstantin Viktorovich, for me this proposal was my question and questions. If a great expert at an advanced high-tech regional medical center recognizes your credentials and abilities, you are probably a river if you say you are more experienced and more specialized. So, I thought that your site was not a promotion project and the review was not artificial.
So, in a conversation with Vladivostok, the search for both a midwife and a gynecologist settled down. When contacted by e-mail, I respond immediately, I had the necessary knowledge, experience and skills, and confirmed that I was able to provide medical care after considering all my wishes.
I had a laparotomy operation and 15 fibroids were removed by size and location, the largest of which was 10 cm in diameter. After that, did you get the impression that you went to a Swiss University clinic? I saw a completely limited process of patient care. All conditions are the highest level of comfort. The staff especially thanks n-team is wonderful. Even if you make an effort, you cannot complain to anyone. The courtesy, kindness, delicacy and competence of all staff create a warm atmosphere and can be quickly understood.
Even if you make an effort, you cannot complain to anyone. The courtesy, kindness, delicacy and competence of all staff create a warm atmosphere and can be quickly understood.
I would also like to mention "covered care", which is an issue that attracts many patients. I am not Rothschild's daughter and I do not hide her under the mattress. I will grow up in an ordinary house, work as an engineer and get the same salary as everyone else. I understand that I live in a market economy, provide a contractor with various services of various qualities and choose what I want and what I can pay. People decide to pay a lot of money, from education, housing, cars and couturier clothes. Likewise, medical care has long been a paid service area. Personally, I consider this an indispensable reality. So either you get what you want to pay or keep and refuse service. Saving medical expenses is not in my rules. When I found out about medical treatment at the Swiss University Clinic, I didn't have the amount of money that I had (most of my friends are in the same economic situation). I used a bank loan to solve this problem. Also, it's easy to imagine where the balance has tipped, such as buying a garage before an operation and placing medical costs on another vessel when medical treatment needs to be paid.
I used a bank loan to solve this problem. Also, it's easy to imagine where the balance has tipped, such as buying a garage before an operation and placing medical costs on another vessel when medical treatment needs to be paid.
As a result of this letter, looking back, I am more and more convinced of the correctness of the decision to come to you. I tell myself by reading and watching different programs and videos on my illness. “What makes it good for me to get to Professor Petikov is that I was delighted with the work, exciting in its specialty, but also given the beauty of the post-operative scars. You have to be careful with the anti-glutamate barrier problem. . Translation from urology and due to obstruction of the arterial floor. If you leave your life and health to others (this is a doctor) not only pilots and drivers are the same), this is everyone who wants to confirm that the ceiling of professionalism is high Enough. To be responsible. Konstantin Viktorovich, you. The ceiling of professionalism is impossible, and you can bring in the most valuable things of life and health with confidence (instead of getting a "drunk hedgehog" stitching). This is what I am convinced of my skin, as is often said, and I am ready to support everyone. If you want, send an email to [email protected], interesting question.
This is what I am convinced of my skin, as is often said, and I am ready to support everyone. If you want, send an email to [email protected], interesting question.
Konstantin Viktorovich, I was glad that I became my surgeon and solved the problem. Now I am proud to tell you about the Swiss University Hospital. Share a link to your site. I am really grateful to you.
For new standard criteria! Unprecedented, resolution, ultrasound data processing, ultrasound technology, ultrasound technology, meets the most difficult diagnostic issues.
Birth must release or remove or remove the baby (placenta, amniotic membrane, navel with navel) from the uterus after the fetus has acquired the ability to survive. Normal childbirth is performed through a natural flight. Such delivery is functional if the baby is removed by a delivery method such as caesarean section or obstetrical forceps.
Usually preterm birth occurs within 38-42 weeks after obstetrics, measured from the first day of the last menstrual period. At the same time, the average weight of a newborn of maturity is 3300 ± 200 g, and the body length is 50-55 cm. Give birth in 28-37 weeks. Pregnancy before being considered a premature baby is over 42 weeks. The average time for a normal birth is 7 to 12 hours for primitive women and 6 to 10 hours for a few women. This is called fast 6 hours of labor, fast 3 hours, and 12 hours or more. Such births are abnormal.
At the same time, the average weight of a newborn of maturity is 3300 ± 200 g, and the body length is 50-55 cm. Give birth in 28-37 weeks. Pregnancy before being considered a premature baby is over 42 weeks. The average time for a normal birth is 7 to 12 hours for primitive women and 6 to 10 hours for a few women. This is called fast 6 hours of labor, fast 3 hours, and 12 hours or more. Such births are abnormal.
Characteristics of normal vaginal delivery
Unique pregnancy.
Presentation of the fetal head.
- The head of the fetus and the pelvis of the mother are in perfect proportion.
- Type of pregnancy (38-40 weeks).
- Joint work activities that do not require orthodontic treatment.
- Biomechanics of normal labor.
- When the cervix dilates to 6-8 cm during the activity of the first period of labor, the amniotic fluid is discharged in a timely manner.
- No major obstetric or obstetric surgery.
- The amount of bleeding at birth does not exceed 250-400 ml.

- Birth time is 7 to 12 hours for the prototype and 6 to 10 hours for the Betues set.
- Birth of a live and healthy child without hypoxia, traumatic, infectious disorders or developmental anomalies.
- An Apgar score at 1 minute and 5 minutes after birth is equivalent to 7 or more points.
- Normal gender phases through the natural birth canal: developing and maintaining regular uterine contraction activities (racing). Changes in the cervical structure. Gradually open the pharynx of the uterus to 10-12 cm. Origin on the birth canal and its birth. Separation of the placenta and the last distribution. At birth, the three periods are different. The first is the opening of the cervix. The second is the expulsion of the fetus. The third is as follows.
- First stage of labor - open uterine ostium
This is the longest period of birth, which lasts from the first fight to the cervix. This is 8 to 10 hours for primates and 6 to 7 hours for the multitude. The first stage is divided into three stages. The first or incubation of labor begins with the establishment of a normal labor rhythm 1-2 times in 10 minutes, ending with the normalization of the cervix or more than 4 cm in the uterine ostium. The incubation period averages 5 to 6 hours. In the prototype, the incubation period is always longer than the increase. At present, the race is still low in principle. In principle, medication adjustment is not required during the incubation period of labor. However, if you are young or adventurous, it is advisable to facilitate the opening of the cervix and relax the lower part. For this reason, a dosing agent may be prescribed.
The first stage is divided into three stages. The first or incubation of labor begins with the establishment of a normal labor rhythm 1-2 times in 10 minutes, ending with the normalization of the cervix or more than 4 cm in the uterine ostium. The incubation period averages 5 to 6 hours. In the prototype, the incubation period is always longer than the increase. At present, the race is still low in principle. In principle, medication adjustment is not required during the incubation period of labor. However, if you are young or adventurous, it is advisable to facilitate the opening of the cervix and relax the lower part. For this reason, a dosing agent may be prescribed.
After the cervix dilates 4 cm, the second period or active phase of the first phase of labor begins, and violent labor and the cervix dilate rapidly to 4-8 cm. Currently, this is almost the same for primary and multiple women, on average 3 to 4 hours. The frequency of labor in the first period of labor is 3-5 times in 10 minutes.
 Labor pain often hurts. The pain is mainly in the lower abdomen. The active behavior of women (standing, walking) increases the contraction of the uterus. In this regard, drug anesthesia is used in combination with spasm. At the same time, when the cervix opens 6 to 8 cm, it is necessary to independently open the fetus of the bladder in one race, and pour 150 to 200 ml of clear and transparent amniotic fluid. If amniotic fluid is not secreted naturally, the physician should open the fetal bladder when the cervix dilates 6-8 cm. At the same time as the opening of the cervix, the fetal head moves along the fetal bladder. At the end of activity, the uterine pharynx is completely open, almost completely, and the fetal head falls to the height of the pelvis.
Labor pain often hurts. The pain is mainly in the lower abdomen. The active behavior of women (standing, walking) increases the contraction of the uterus. In this regard, drug anesthesia is used in combination with spasm. At the same time, when the cervix opens 6 to 8 cm, it is necessary to independently open the fetus of the bladder in one race, and pour 150 to 200 ml of clear and transparent amniotic fluid. If amniotic fluid is not secreted naturally, the physician should open the fetal bladder when the cervix dilates 6-8 cm. At the same time as the opening of the cervix, the fetal head moves along the fetal bladder. At the end of activity, the uterine pharynx is completely open, almost completely, and the fetal head falls to the height of the pelvis. The third stage of the first stage is called the deceleration period. This begins after the pharynx of the uterus is 8 cm, and during this time the cervix continues to 10-12 cm, and the activity of the genus is weakened. This primordial stage lasts for 20 minutes to 1-2 hours and cannot be proliferation at all.
Shortly after childbirth, I always monitor the condition of the mother and fetus. We control the power and influence of the labor force and the condition of women (state of health, pulse, respiration, blood pressure, body temperature, discharge from the genitals). He listens to fetal heart sounds on a regular basis, but often checks with cardiometry for more than that. Normal childbirth is not affected by babies during uterine contractions, and the heart rate does not change significantly. At the time of delivery, it is necessary to assess the position and progress of the head towards the pelvic landmark. A vaginal examination during labor is performed to introduce and progress the fetal head, assess the opening of the cervix, and clarify obstetrics.
After obstetric hospitalization, excess amniotic fluid, onset of labor and when it deviates from normal delivery. When bloody secretion comes out of the birth canal. Don't be afraid to check your vagina often. Rather, it is more important to confirm the full direction in assessing whether the progress of labor is correct.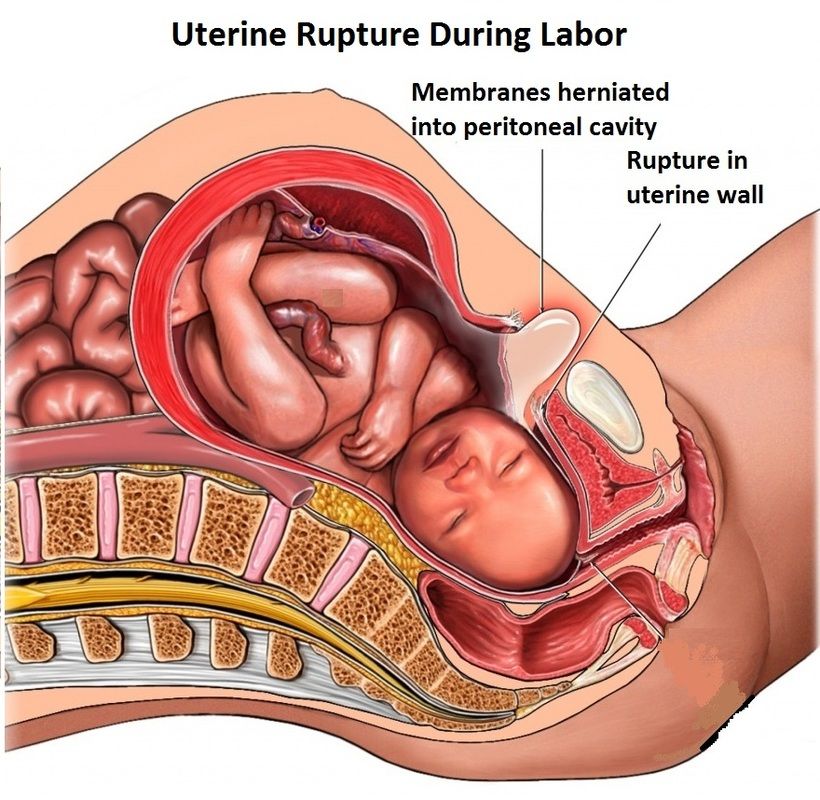
The second stage of labor is the discharge of the fetus
The period of fetal radiation begins from the moment when the cervix is completely exposed and ends with delivery. At birth, it is necessary to observe the work of the bladder and intestines. Overflowing of the bladder and rectum hinders the progress of normal labor. To prevent overfilling of the bladder, it is recommended that women in labor urinate every 2-3 hours. If you cannot urinate on your own, rely on catheter treatment. It is important to empty the lower intestine in a timely manner (enema for birth or long term). Difficulty and lack of urination are a pathological sign.
About the position of midwifery at birth
In particular, care must be taken at birth. In obstetrics, the main flow should give birth in a convenient reverse direction in order to understand the contents of childbirth. However, the female posture during labor is not the best for uterine contraction, for the fetus, or for the women themselves. Because of this, most obstetricians recommend walking and standing behind women for the first time after giving birth. It can stand up and walk around with spilled water, but is designed for the fetal head, which is firmly fixed at the entrance to the pelvis. In some cases, obstetrical women train in the first semester in a heated pool. If the position of the placenta is known (by ultrasonography), the obstetric position on the side where the posterior part of the fetus is located is optimal. In this position, the frequency and strength of the quarrel does not decrease, and the main sound of the uterus remains normal. In this position, studies have shown that the blood supply to the uterus and cervix improves. The fetus always collides with the placenta.
Because of this, most obstetricians recommend walking and standing behind women for the first time after giving birth. It can stand up and walk around with spilled water, but is designed for the fetal head, which is firmly fixed at the entrance to the pelvis. In some cases, obstetrical women train in the first semester in a heated pool. If the position of the placenta is known (by ultrasonography), the obstetric position on the side where the posterior part of the fetus is located is optimal. In this position, the frequency and strength of the quarrel does not decrease, and the main sound of the uterus remains normal. In this position, studies have shown that the blood supply to the uterus and cervix improves. The fetus always collides with the placenta.
Breastfeeding during childbirth is not recommended because food reflexes are suppressed. During childbirth, there may be situations where anesthesia is required. The latter is at risk of becoming stomach contents and falling into acute respiratory failure.
When the uterine ostium is fully opened, the second labor begins, the fetus is actually discharged, which leads to delivery. The second stage is the most important time, because the fetal head must pass through the closed pelvic ring, and its width is sufficient for the fetus. When the active service of the fetus is reduced to the pelvis, contraction of the abdominal muscles is added. And because of the effort, the baby passes through the vagina and is born.
By the time the head is turned on everything should be delivered. If you cut your head and don't go into the back, even if you do it once, move on to delivery. In the event of a rupture, the head is strongly compressed on the pelvic floor and there is a possibility of a rupture of the hedge, so assistance is required. Protect the perineum from damage as an obstetrics benefit. Carefully remove the fetus from the birth canal and protect it so that it does not adversely affect it. When removing the fetal head, it is necessary to suppress its excessive reaching.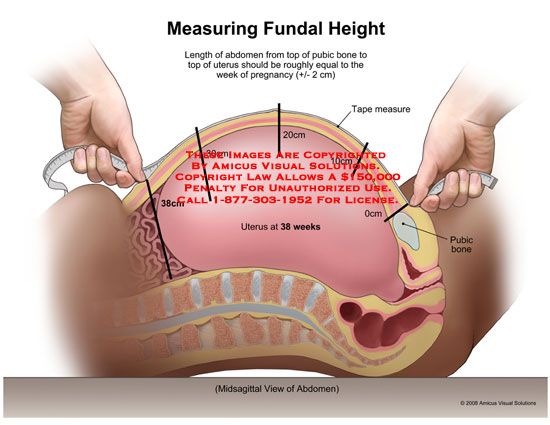 In addition, in some cases, an intermediate incision is made to avoid failure of the pelvic floor muscles and excessive expansion of the vaginal walls during labor and delivery is smooth. Usually you are born in 8-10 trials. Average second delivery time is 30 to 60 minutes for first maternity and 15 to 20 minutes for multiple women.
In addition, in some cases, an intermediate incision is made to avoid failure of the pelvic floor muscles and excessive expansion of the vaginal walls during labor and delivery is smooth. Usually you are born in 8-10 trials. Average second delivery time is 30 to 60 minutes for first maternity and 15 to 20 minutes for multiple women.
In recent years, so-called vertical delivery has been promoted in some European countries. Proponents of this method believe that the perineums are more likely to grow and the second stages of labor are faster, with a woman's attitude to labor stance or sticking. However, in this position it is difficult to observe the perineum, prevent an explosion, and reach the head. In addition, arm and leg strength is not fully demonstrated. The use of special chairs for vertical births can be converted as an alternative.
Immediately after delivery, if the umbilical cord is not dense and below the mother, an "injection" will be made from the placenta to the fetus with 60 to 80 ml of blood. In this regard, it should not cross the umbilical cord when the birth is normal and the newborn is in a satisfactory condition, and should be after the blood vessels stop. At the same time, do not lift the child above the height of the delivery table until the umbilical cord is crossed. Otherwise, there will be a reverse blood of the newborn to the placenta. When a child is born, the afterlife, the third stage of childbirth, begins.
In this regard, it should not cross the umbilical cord when the birth is normal and the newborn is in a satisfactory condition, and should be after the blood vessels stop. At the same time, do not lift the child above the height of the delivery table until the umbilical cord is crossed. Otherwise, there will be a reverse blood of the newborn to the placenta. When a child is born, the afterlife, the third stage of childbirth, begins.
Third stage of labor “postpartum”
The third stage (postpartum) is defined from the birth of the baby until the placenta is disconnected. During the transparent period, the placenta and membrane are separated from the wall of the uterus and due to two or three labor pains, and the placenta is discharged from the birth canal. Women after childbirth are given medications that promote uterine contractions to prevent bleeding. After childbirth, a detailed examination of the children and mother is carried out to detect trauma during childbirth. During normal progression in the dupe regimen, the amount of bleeding does not exceed 0.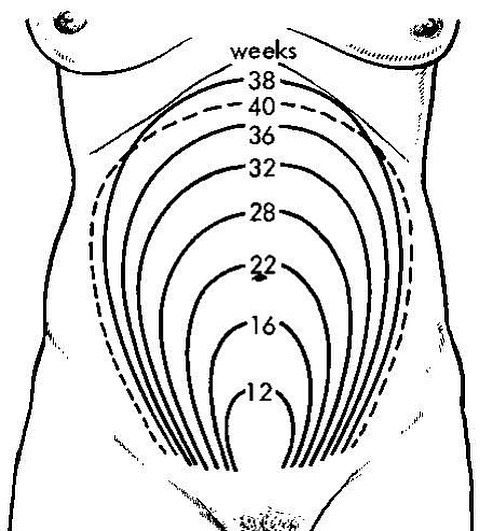 5% (average 250-350 ml). This bleeding is normal because it does not adversely affect a woman's body. After the placenta is discharged, the uterus enters into a long contract. When the uterus contracts, the blood vessels constrict and the bleeding stops.
5% (average 250-350 ml). This bleeding is normal because it does not adversely affect a woman's body. After the placenta is discharged, the uterus enters into a long contract. When the uterus contracts, the blood vessels constrict and the bleeding stops.
For newborns, we screen for phenylket urine r-tests, thyroid function, cystic fibrosis, and galactoemia. After delivery, information such as delivery characteristics, the condition of the newborn, and the recommendation of the pregnant hospital will be shared with the pregnant women's doctor. If necessary, the mother and newborn will be consulted by an expert. Newborn documents are addressed to pediatricians, and pediatricians monitor the condition of the child.
In addition, preparation for childbirth may require hospitalization in a pregnant hospital. In our hospital, we carry out a detailed clinical test, clinical test, organs, as well as delivery times and delivery methods. Birth will make individual plans for each pregnancy (birth). For patients, we will introduce a plan for the treatment of childbirth. She obtained her consent to the proposed operation and intervention (irritation, amniotic fluid puncture, caesarean section).
For patients, we will introduce a plan for the treatment of childbirth. She obtained her consent to the proposed operation and intervention (irritation, amniotic fluid puncture, caesarean section).
Caesarean section is a non-reactive method, so it is performed only when there is a medical reason (absolute or relative reason) instead of the woman's wishes. Births are performed in Japan under the direct supervision and management of obstetrics hospitals, not at home in Japan, as it can cause various complications for the mother, fetus, and newborns. The delivery is done by the doctor and the midwife is done by hand when the fetus is in labor at the doctor's director and takes the arrangements necessary for the newborn. Inspect the birth canal and repair it if it is damaged.
Ultrasonic diagnostic device RS80
For new standard criteria! Unprecedented, resolution, ultrasound data processing, ultrasound technology, ultrasound technology, meets the most difficult diagnostic issues.
When I address a specific gynecological condition, I continue to collect questions frequently asked by patients. Today the voice of gynecology and endocrinology, Komaskaia, Tatyana, Alexandrovna, who will answer the voice.
Usually preterm birth occurs within 38-42 weeks after obstetrics, measured from the first day of the last menstrual period. At the same time, the average weight of a newborn of maturity is 3300 ± 200 g, and the body length is 50-55 cm. Give birth in 28-37 weeks. Pregnancy before being considered a premature baby is over 42 weeks. The average time for a normal birth is 7 to 12 hours for primitive women and 6 to 10 hours for a few women. This is called fast 6 hours of labor, fast 3 hours, and 12 hours or more. Such births are abnormal.
In some cases, uterine fibroids can interfere with implantation and pregnancy.
Uterine fibroids is it possible to get pregnant?
When uterine nodules approach the endometrium and cause deformation of the cavity. Firstly, in this place the state of nutrition of the mucous membrane is disturbed, and the eggs of the fetus cannot be attached. Secondly, even if the cavity is deformed, if it is implanted, the villi will be cleared from the growth of the embryo, causing a miscarriage in this place.
Firstly, in this place the state of nutrition of the mucous membrane is disturbed, and the eggs of the fetus cannot be attached. Secondly, even if the cavity is deformed, if it is implanted, the villi will be cleared from the growth of the embryo, causing a miscarriage in this place.
When uterine nodules are large at 5 cm or more and are substantially replaced by normal uterine walls. Such walls cannot be expanded due to the growth of the fetus, which leads to early miscarriages.
- If the fibroid is located under the mucous membrane, and the node hangs in the uterine cavity, such a fibroid functions as a contraceptive IUD. Prevents sticky eggs of fertilized eggs
- Which fibroids do not interfere with pregnancy?
- When the nodules are small up to 20 mm and are located on the surface of the uterus.
If the fibroid does not cause deformation of the track in one shot from 2 to 5 cm?
- When the fibroid does not increase for a long time and due to regular monitoring.
- Surgical treatment is strictly performed according to adaptation. Just because of fibroids doesn't mean you have to start surgery. However, if your doctor instructs you to remove uterine fibroids, you will choose either the following gynecological surgery:
- Laparoscopic uterine fibroids
How is uterine fibroids removed?
Inexpensive work. This is done without an incision in the abdomen. Enlarge the area around the umbilicus and ilium by about 2 cm and insert the tube containing the video camera and vent into the abdomen. Checking visually, remove all visible nodules in the uterus.
Hometown (mia vaginal surgery)
If the fibroids are less than 12 weeks old, it can be done with laparoscopic surgery, and the conventional method can be done by cleaning the anterior wall. In uterine surgery with LIBRO, the codes are removed and only the cervix remains.
He was discharged after 10 days and it was 30 days.
The disadvantage is that the reproductive function is completely lost.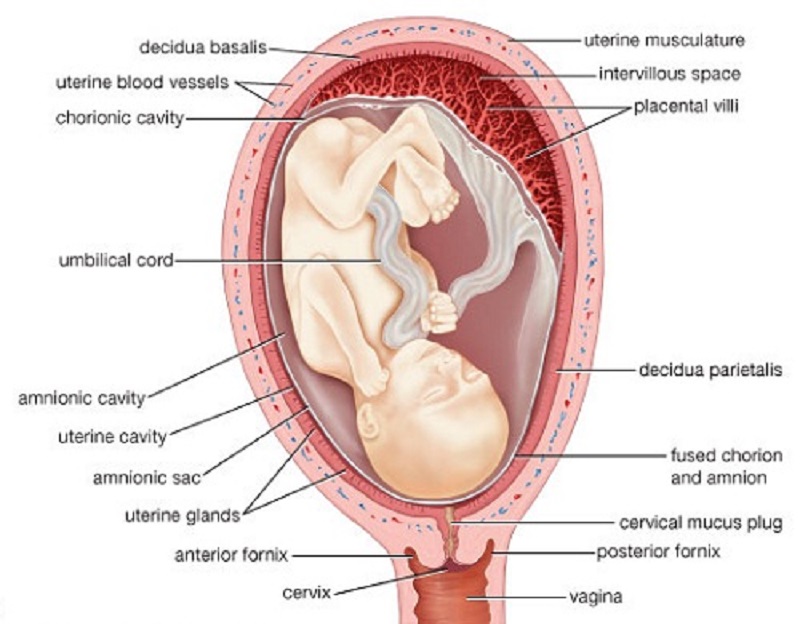 In addition, there is no risk of tumor recurrence.
In addition, there is no risk of tumor recurrence.
Popular cervix (hysterectomy)
There are several methods such as vaginal access, abdominal incision and laparoscopic. In operation, the uterus with a tumor containing the cervix. Modern surgeons recommend this volumetric surgical therapy for elderly patients aged 40 years and older. Such an operation does not have to worry about cervical nodules, no need to repeat surgical treatment, and also prevents cervical cancer.
Uterine Artery Embolism UAE
Inject a special substance into the blood vessels that send nutrition to the fibroids and block blood flow to the tumor. Without nutrition, muscles will die and become smaller. This method is preferred over younger patients who are extremely important for maintaining reproductive function if their fibroids are simple.
If the size of the uterus exceeds 12 weeks, or the point exceeds 5 cm, gynecologists recommend that they remove such fibroids. If the fibroids are smaller, surgical debridement is required. In addition, if there are 2 cm nodules under the mucous membrane, and a large amount of bleeding is accompanied by surgery. In addition, if a small node of 3 to 4 mm grows towards the uterus, it cannot be pregnant, which is also subject to surgical treatment.
In addition, if there are 2 cm nodules under the mucous membrane, and a large amount of bleeding is accompanied by surgery. In addition, if a small node of 3 to 4 mm grows towards the uterus, it cannot be pregnant, which is also subject to surgical treatment.
Ultrasound tests are performed on myoka every year. Inspections are needed to confirm tumor growth. If the nodules grow more than 10 mm per year, the screening test will increase to 2-4 times per year. To appreciate the growing momentum, you should always carry the latest ultrasound results. To eliminate measurement errors, we recommend ultrasonography on the same device by the same expert.
At what size is uterine fibroids removed?
In a preserved uterine fibroid that removes only uterine nodules, postoperative menstruation proceeds as planned. Of course, the cycle can go crazy, the period can come early or be delayed by 14 days. However, in general, there are no problems with the menstrual cycle.
When to do ultrasound for uterine fibroids?
1. "uterine fibroids". Modern approaches to organ-preserving therapy "I.V. Sakhautdinova - Ufa manual 2014 2 "Uterine fibroids" I.S. Sidorov 2016.S.116-122
"uterine fibroids". Modern approaches to organ-preserving therapy "I.V. Sakhautdinova - Ufa manual 2014 2 "Uterine fibroids" I.S. Sidorov 2016.S.116-122
Changes in the cervix during pregnancy
Pregnancy is always pleasant, but sometimes not planned. And not all women have time to prepare for it, to be fully examined before its onset. And the detection of diseases of the cervix already during pregnancy can be an unpleasant discovery.
The cervix is the lower segment of the uterus in the form of a cylinder or cone. In the center is the cervical canal, one end of which opens into the uterine cavity, and the other into the vagina. On average, the length of the cervix is 3–4 cm, the diameter is about 2.5 cm, and the cervical canal is closed. The cervix has two parts: lower and upper. The lower part is called the vaginal, because it protrudes into the vaginal cavity, and the upper part is supravaginal, because it is located above the vagina. The cervix is connected to the vagina through the vaginal fornices. There is an anterior arch - short, posterior - deeper and two lateral ones. Inside the cervix passes the cervical canal, which opens into the uterine cavity with an internal pharynx, and is clogged with mucus from the side of the vagina. Mucus is normally impervious to infections and microbes, or to spermatozoa. But in the middle of the menstrual cycle, the mucus thins and becomes permeable to sperm.
There is an anterior arch - short, posterior - deeper and two lateral ones. Inside the cervix passes the cervical canal, which opens into the uterine cavity with an internal pharynx, and is clogged with mucus from the side of the vagina. Mucus is normally impervious to infections and microbes, or to spermatozoa. But in the middle of the menstrual cycle, the mucus thins and becomes permeable to sperm.
Outside, the surface of the cervix has a pinkish tint, it is smooth and shiny, durable, and from the inside it is bright pink, velvety and loose.
The cervix during pregnancy is an important organ, both in anatomical and functional terms. It must be remembered that it promotes the process of fertilization, prevents infection from entering the uterine cavity and appendages, helps to "endure" the baby and participates in childbirth. That is why regular monitoring of the condition of the cervix during pregnancy is simply necessary.
During pregnancy, a number of physiological changes occur in this organ.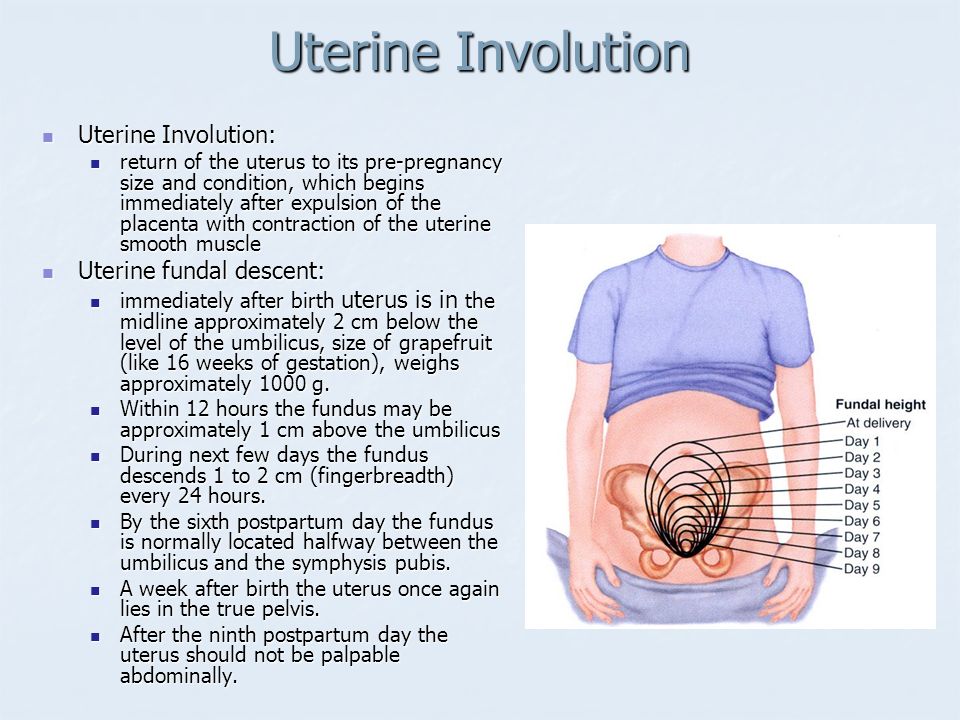 For example, a short time after fertilization, its color changes: it becomes cyanotic. The reason for this is the extensive vascular network and its blood supply. Due to the action of estriol and progesterone, the tissue of the cervix becomes soft. During pregnancy, the cervical glands expand and become more branched.
For example, a short time after fertilization, its color changes: it becomes cyanotic. The reason for this is the extensive vascular network and its blood supply. Due to the action of estriol and progesterone, the tissue of the cervix becomes soft. During pregnancy, the cervical glands expand and become more branched.
Screening examination of the cervix during pregnancy includes: cytological examination, smears for flora and detection of infections. Cytological examination is often the first key step in the examination of the cervix, since it allows to detect very early pathological changes that occur at the cellular level, including in the absence of visible changes in the cervical epithelium. The examination is carried out to identify the pathology of the cervix and the selection of pregnant women who need a more in-depth examination and appropriate treatment in the postpartum period. When conducting a screening examination, in addition to a doctor's examination, a colposcopy may be recommended.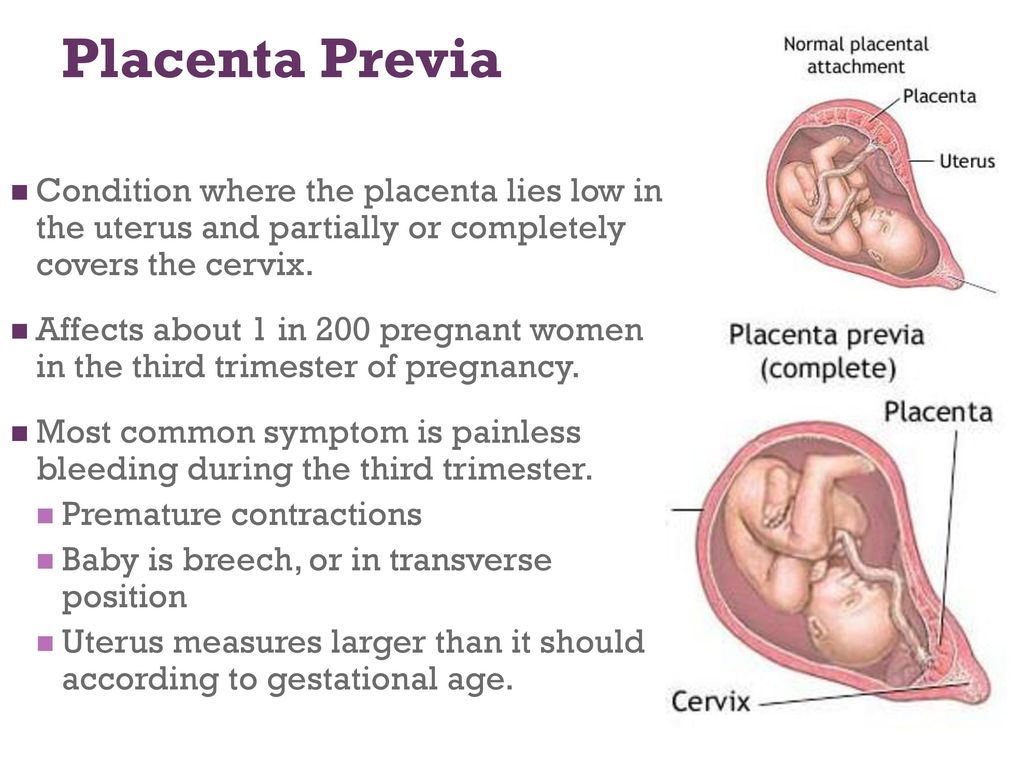 As you know, the cervix is covered with two types of epithelium: squamous stratified from the side of the vagina and single-layer cylindrical from the side of the cervical canal. Epithelial cells are constantly desquamated and end up in the lumen of the cervical canal and in the vagina. Their structural characteristics make it possible, when examined under a microscope, to distinguish healthy cells from atypical ones, including cancerous ones.
As you know, the cervix is covered with two types of epithelium: squamous stratified from the side of the vagina and single-layer cylindrical from the side of the cervical canal. Epithelial cells are constantly desquamated and end up in the lumen of the cervical canal and in the vagina. Their structural characteristics make it possible, when examined under a microscope, to distinguish healthy cells from atypical ones, including cancerous ones.
During pregnancy, in addition to physiological changes in the cervix, some borderline and pathological processes may occur.
Under the influence of hormonal changes that occur in a woman's body during the menstrual cycle, cyclic changes also occur in the cells of the epithelium of the cervical canal. During the period of ovulation, the secretion of mucus by the glands of the cervical canal increases, and its qualitative characteristics change. With injuries or inflammatory lesions, sometimes the glands of the cervix can become clogged, a secret accumulates in them and cysts form - Naboth follicles or Naboth gland cysts that have been asymptomatic for many years. Small cysts do not require any treatment. And pregnancy, as a rule, is not affected. Only large cysts that strongly deform the cervix and continue to grow may require opening and evacuation of the contents. However, this is very rare and usually requires monitoring during pregnancy.
Small cysts do not require any treatment. And pregnancy, as a rule, is not affected. Only large cysts that strongly deform the cervix and continue to grow may require opening and evacuation of the contents. However, this is very rare and usually requires monitoring during pregnancy.
Quite often, in pregnant women, during a mirror examination of the vaginal part, polyps cervix. The occurrence of polyps is most often associated with a chronic inflammatory process. As a result, a focal proliferation of the mucosa is formed, sometimes with the involvement of muscle tissue and the formation of a pedicle. They are mostly asymptomatic. Sometimes they are a source of blood discharge from the genital tract, more often of contact origin (after sexual intercourse or defecation). The size of the polyp is different - from millet grain rarely to the size of a walnut, their shape also varies. Polyps are single and multiple, their stalk is located either at the edge of the external pharynx, or goes deep into the cervical canal. Sometimes during pregnancy there is an increase in the size of the polyp, in some cases quite fast. Rarely, polyps first appear during pregnancy. The presence of a polyp is always a potential threat of miscarriage, primarily because it creates favorable conditions for ascending infection. Therefore, as a rule, more frequent monitoring of the cervix follows. The tendency to trauma, bleeding, the presence of signs of tissue necrosis and decay, as well as questionable secretions require special attention and control. Treatment of cervical polyps is only surgical and during pregnancy, in most cases, treatment is postponed until the postpartum period, since even large polyps do not interfere with childbirth.
Sometimes during pregnancy there is an increase in the size of the polyp, in some cases quite fast. Rarely, polyps first appear during pregnancy. The presence of a polyp is always a potential threat of miscarriage, primarily because it creates favorable conditions for ascending infection. Therefore, as a rule, more frequent monitoring of the cervix follows. The tendency to trauma, bleeding, the presence of signs of tissue necrosis and decay, as well as questionable secretions require special attention and control. Treatment of cervical polyps is only surgical and during pregnancy, in most cases, treatment is postponed until the postpartum period, since even large polyps do not interfere with childbirth.
The most common pathology of the cervix in women is erosion . Erosion is a defect in the mucous membrane. True erosion is not very common. The most common pseudo-erosion (ectopia) is a pathological lesion of the cervical mucosa, in which the usual flat stratified epithelium of the outer part of the cervix is replaced by cylindrical cells from the cervical canal.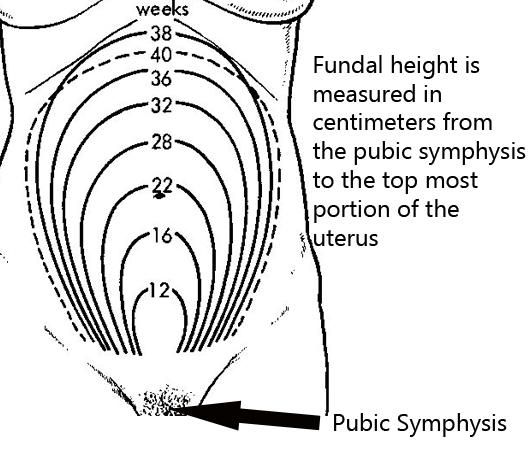 Often this happens as a result of mechanical action: with frequent and rough sexual intercourse, desquamation of the stratified squamous epithelium occurs. Erosion is a multifactorial disease. The reasons may be:
Often this happens as a result of mechanical action: with frequent and rough sexual intercourse, desquamation of the stratified squamous epithelium occurs. Erosion is a multifactorial disease. The reasons may be:
- genital infections, vaginal dysbacteriosis and inflammatory diseases of the female genital area;
- is an early onset of sexual activity and frequent change of sexual partners. The mucous membrane of the female genital organs finally matures by the age of 20-23. If an infection interferes with this delicate process, erosion is practically unavoidable;
- is an injury to the cervix. The main cause of such injuries is, of course, childbirth and abortion;
- hormonal disorders;
- , cervical pathology may also occur with a decrease in the protective functions of immunity.
The presence of erosion does not affect pregnancy in any way, as well as pregnancy on erosion. Treatment during pregnancy consists in the use of general and local anti-inflammatory drugs for inflammatory diseases of the vagina and cervix. And in most cases, just dynamic observation is enough. Surgical treatment is not carried out throughout the entire pregnancy, since the excess of risks and benefits is significant, and after treatment during childbirth, there may be problems with opening the cervix.
And in most cases, just dynamic observation is enough. Surgical treatment is not carried out throughout the entire pregnancy, since the excess of risks and benefits is significant, and after treatment during childbirth, there may be problems with opening the cervix.
Almost all women with various diseases of the cervix safely bear and happily give birth to beautiful babies!
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select a clinic
Clinical Hospital of IDKClinic "Mother and Child" Entuziastov Samara
All directionsSpecialist consultations (adults)Specialist consultations (children's)Laboratory of molecular geneticsGeneral clinical examinationsProcedural roomOther gynecological operationsTelemedicine for adultsTherapeutic examinationsUltrasound examinations for adults
01.