Pulling calf muscle while sleeping
Causes, Pain Relief & Prevention
Overview
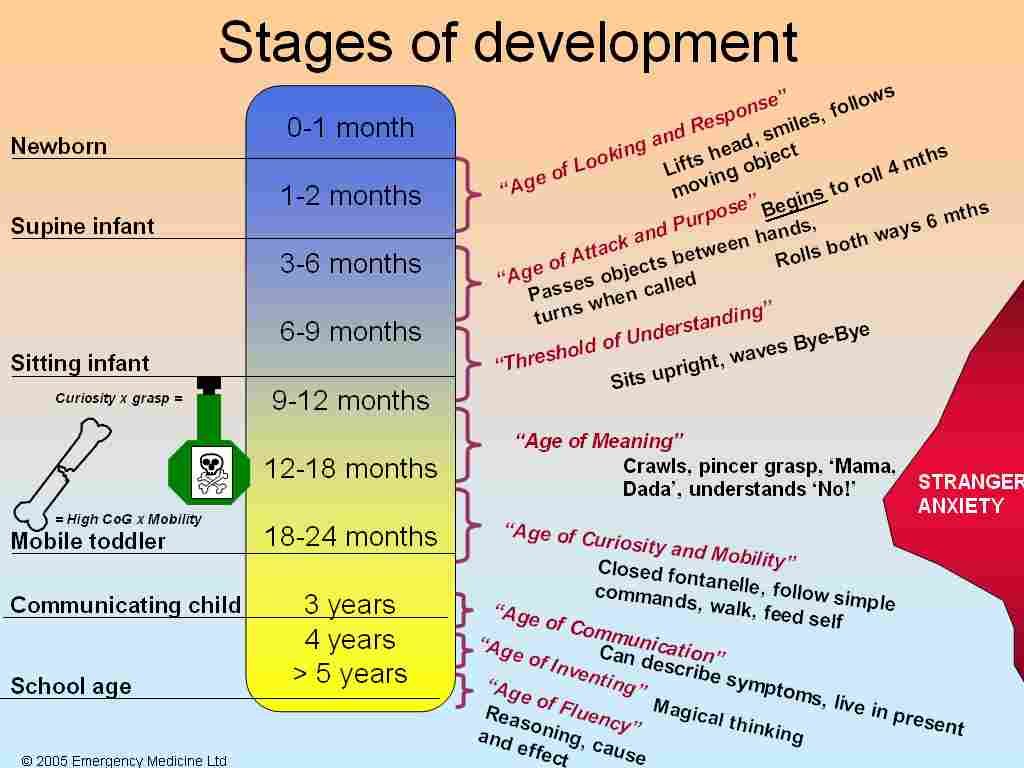
Leg Cramps at NightWhat are leg cramps?
Leg cramps are sudden, involuntary, intense muscle pains usually in your calf, foot or thigh. You might also know them as a “charley horse.” Sometimes the cramp may cause your leg to spasm – to tighten uncontrollably. Although painful to live with, cramps are generally harmless.
What does a leg cramp feel like?
A leg cramp feels like a clenched, contracted muscle tightened into a knot. It can be severely uncomfortable, painful or even unbearable. Your muscles in the area might hurt for hours after the cramp goes away.
How do I stop a leg cramp?
Try forcefully stretching the affected muscle (for example, stretch your calf muscle by flexing your foot upward). Jiggle your leg, massage it, or force yourself to walk. It might also help to apply ice or heat – use a heating pad or take a warm bath. (Read the “Management and Treatment” section for more tips. )
Unfortunately, there are no pills or injections that instantly relieve a leg cramp when it’s happening. There are, however, ways that may prevent the cramp from happening in the first place (see the “Prevention” section).
Can you get leg cramps at night?
Leg cramps at night happen when you’re not very active, or when you’re asleep. They may wake you up, make it harder for you to fall back asleep and leave you feeling sore all night. Yearly, monthly, weekly, nightly – the frequency of leg cramps depends on the person. Nocturnal leg cramps can happen to anyone at any age, but they happen most often to older adults. Of people over age 60, 33% will have a leg cramp at night at least once every two months. Nearly every adult age 50 and older will have them at least one time. Seven percent of children will, as well. Approximately 40% of pregnant women will experience leg cramps at night. The reason behind that is thought to be that the extra weight of pregnancy strains the muscles.
Three-quarters (75%) of all reported leg cramps happen at night.
How long do leg cramps last?
An instance of a leg cramp can last from several seconds to several minutes.
Who gets leg cramps?
The older you are, the more likely you are to have leg cramps. This is because your tendons (the tissues that connect your muscles to your bones) naturally shorten as you age. You’re also more likely to get them if you’re a woman. Up to 60% of adults get leg cramps at night, as do up to 40% of children and teenagers.
Are leg cramps a sign of something serious?
Leg cramps can sometimes be a symptom of a serious health condition. (See the “Symptoms and Causes” section.) If you are concerned that you have a serious health condition, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider and report your symptoms, including your leg cramps.
How common are leg cramps?
Leg cramps are very common and normal, especially at night.
What is the difference between leg cramps and Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)?
Although both nocturnal leg cramps (leg cramps at night) and restless legs syndrome tend to happen to you at night or when you’re at rest, restless legs syndrome doesn’t cause the severe pain. Restless legs syndrome is uncomfortable, but not agonizing. It’s a crawling sensation that makes you want to move your legs. When you do move, the restlessness stops, but there is still discomfort.
Restless legs syndrome is uncomfortable, but not agonizing. It’s a crawling sensation that makes you want to move your legs. When you do move, the restlessness stops, but there is still discomfort.
Symptoms and Causes
What causes leg cramps?
Some leg cramps happen for no known reason and they are called “idiopathic” cramps. “Secondary” leg cramps are a symptom or complication of a more serious health condition. The primary cause of idiopathic leg cramps is up for debate. Possible causes of them include:
- Involuntary nerve discharges.
- Restriction in the blood supply.
- Stress.
- Too much high-intensity exercise.
Women who are pregnant often have leg cramps during the day and at night.
Possible causes for leg cramps at night (nocturnal leg cramps) include:
- Sitting for long periods of time.
- Overusing the muscles.
- Standing or working on concrete floors.
- Sitting improperly.
Leg cramps are not likely to cause:
- Broken bones.

- Fainting.
- Nausea.
- Numbness.
What medications may cause leg cramps?
Drugs have side effects. It’s possible that a prescription you’re taking could be causing your leg cramps. In that case, work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the pros and cons of the medication vs. its side effects. It’s possible that your healthcare provider may be able to put you on a different medication that doesn’t have leg cramps as a side effect. Medicines that have leg cramps as a side effect include:
- Albuterol/Ipratropium (Combivent®).
- Conjugated estrogens.
- Clonazepam (Klonopin®).
- Diuretics.
- Gabapentin (Neurontin®).
- Naproxen (Naprosyn®).
- Pregabalin (Lyrica®)
- Statins.
- Zolpidem (Ambien®).
Others may include: Amoxicillin, bromocriptine (Parlodel), bupropion (Wellbutrin), celecoxib (Celebrex®), cetirizine (Zyrtec), chromium, cinacalcet (Sensipar), ciprofloxacin (Cipro), citalopram (Celexa), donepezil (Aricept), eszopiclone (Lunesta), fluoxetine (Prozac), IV iron sucrose, lansoprazole (Prevacid), levalbuterol, levothyroxine, metformin, niconitis acid, nifedipine, rivastigmine (Exelon), sertraline (Zoloft), telmisartan (Micardis), teriparatide (Forteo®) and teriparatide raloxifene (Evista®).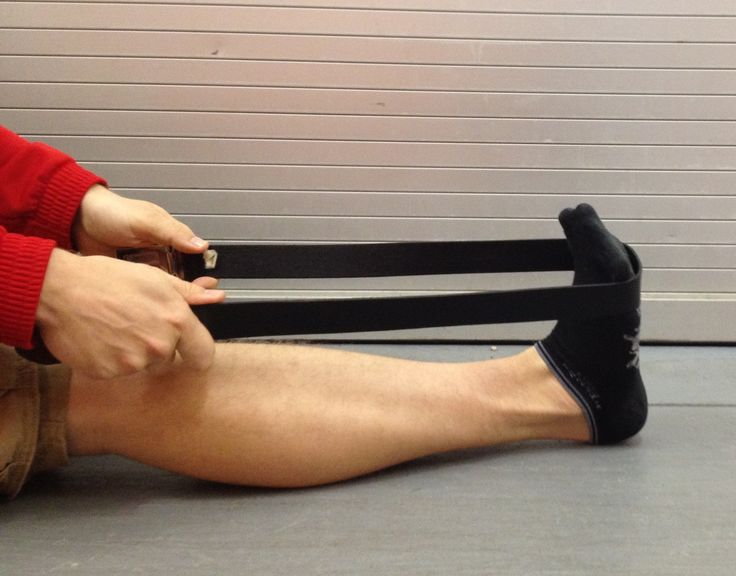
What medical problems can cause leg cramps?
Sometimes leg cramps happen to you for no reason, but other times they could possibly be a sign or symptom of a health condition. If you have any of the following conditions, it’s possible that your leg cramps are a result of that condition. Also keep in mind that if you don’t already know if you have any of these conditions, your leg cramps may be a sign that you do. Always consult your healthcare provider if you think your leg cramps are a symptom of a more serious medical condition.
Leg cramps can possibly be a sign of lifestyle choices such as:
- Alcoholism: An addiction to alcohol.
- Pregnancy.
- Dehydration: The lack of sufficient water in the body. (This sign is debated among experts.)
Leg cramps can also possibly be a sign of serious conditions including:
- ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/Lou Gehrig’s disease): Progressive neuromuscular disease.

- Cardiovascular disease: Heart conditions caused by blood clots or diseased blood vessels. Also, coronary artery disease: The narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries.
- Cirrhosis of the liver: Scarring of the liver.
- Diabetes: A disease that prevents your body from properly using the energy from the food you eat.
- Flat feet: The absence of the supportive arch in the foot.
- Hypokalemia: Low potassium levels in your blood.
- Kidney failure (hemodialysis): A condition in which one or both kidneys no longer work correctly.
- Osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease): The corrosion of the cartilage that protects your bones. Also, lumbar canal stenosis: A narrowing of the spinal canal in the lower back.
- Parkinson’s disease: A neurological movement disorder.
- Peripheral artery disease: Narrowing of the arteries.
 Also, peripheral neuropathy: Damage or dysfunction of one or more nerves.
Also, peripheral neuropathy: Damage or dysfunction of one or more nerves.
Cancer treatments like chemotherapy can cause nerve damage, which may cause leg cramps.
There are rumors that leg cramps can also be a sign of the following conditions. Fortunately, that is not the case. Leg cramps are unlikely to be a sign of:
- Labor (giving birth).
- Lung cancer.
- Menopause.
- Multiple sclerosis.
Leg cramps are not likely to be a sign of a deficiency in:
- Alanine transaminase.
- Albumin.
- Bilirubin.
- Calcium.
- Creatinine.
- Glucose.
- Magnesium.
- Zinc, vitamin B12 or vitamin D.
What are the warning signs that leg cramps are coming?
Unfortunately, leg cramps happen very suddenly. There are no warning signs. However, there are risk factors such as pregnancy and the use of medications that have leg cramps as a side effect.
Diagnosis and Tests
How are leg cramps diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will need to know your medical history, medications and a description of what you’re experiencing. Be specific. Report your symptoms to your healthcare provider and include the following information:
Be specific. Report your symptoms to your healthcare provider and include the following information:
- When the leg cramps started happening.
- What your pain feels like.
- When the cramps happen (at night, for example, or after vigorous exercise).
- How long the cramps last.
- Any other symptoms you’re experiencing.
Your healthcare provider will need to tell the difference between your leg cramps from other conditions that may resemble them:
- Claudication.
- Peripheral neuropathy.
- Myositis.
- Restless legs syndrome.
To distinguish those differences, your healthcare provider may:
- Check the palpation of pulses.
- Evaluate physical sensations such as pinpricks.
- Test deep tendon reflexes.
- Test the strength of your leg.
Do I need to have any testing done to diagnose my leg cramps?
Blood, urine and other routine tests are not helpful in diagnosing leg cramps but they may help identify previously undiagnosed medical conditions that have leg cramps as a symptom. For example, your healthcare provider will likely perform typical tests such as taking your blood pressure, and that can reveal cardiac and vascular risks.
For example, your healthcare provider will likely perform typical tests such as taking your blood pressure, and that can reveal cardiac and vascular risks.
What questions might my healthcare provider ask about my leg cramps?
To help your healthcare provider diagnose you, they may ask the following questions about your leg cramps:
- When do you experience the leg cramps?
- How often do your leg cramps occur?
- How would you describe your leg cramps?
- How long do the leg cramps last?
- What medications are you currently taking?
- What known medical conditions do you have?
- Are you concerned about medical conditions that may be causing your leg cramps?
- Are you having any symptoms of another medical condition?
Management and Treatment
What can I do to make leg cramps go away if they happen?
You want to get rid of a leg cramp the moment it strikes. You might be finishing up an exercise routine, or you might be awakened in the middle of the night. In moments like that there are, unfortunately, no magical injections that can instantly relieve your pain. However, there are eight steps to take to possibly get rid of a leg cramp:
In moments like that there are, unfortunately, no magical injections that can instantly relieve your pain. However, there are eight steps to take to possibly get rid of a leg cramp:
- Stretch. Straighten your leg and then flex it, pulling your toes towards your shin to stretch the muscles.
- Massage. Use your hands or a roller to massage the muscles.
- Stand. Get up. Press your feet against the floor.
- Walk. Wiggle your leg while you walk around.
- Apply heat. Use a heating pad or take a warm bath.
- Apply cold. Wrap a bag of ice in a towel and apply it to the area.
- Pain killers. Take ibuprofen or acetaminophen to help with the pain.
- Elevate. Prop up your leg after the cramp starts to feel better.
What kinds of stretches help get rid of leg cramps?
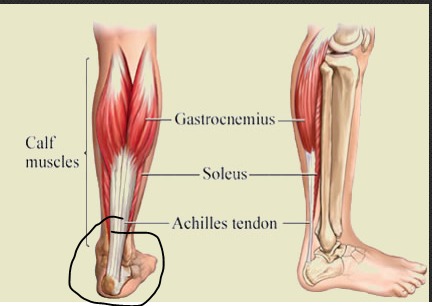
Try this if your cramp is in your calf muscle: While standing (or sitting with your leg unfolded before you), straighten your leg and lift your foot until your toes are pointing at your shin. Pull on your toes if you are able to reach them. You could also try walking around on your heels.
Pull on your toes if you are able to reach them. You could also try walking around on your heels.
What medicines may help with leg cramps?
At this time, there is no recommended medication that can prevent leg cramps 100% of the time. However, there are some prescription medications that show a little evidence of preventing leg cramps. Under your healthcare provider’s watchful eye, you might want to try the following:
- Carisoprodol (Soma®): A muscle relaxant.
- Diltiazem (Cartia XT®): A calcium-channel blocker.
- Orphenadrine (Norflex®): Treats muscle spasms and relieves pain and stiffness in muscles.
- Verapamil: A calciuim-channel blocker.
What vitamins may help with leg cramps?
No vitamin is likely to help with a leg cramp 100% of the time. However, some experts do recommend that you take a vitamin B12 complex.
Does quinine help with leg cramps?
Quinine was thought to show some promise with healing leg cramps, but it is no longer recommended..jpg) There are potentially life-threatening side effects: arrhythmias, thrombocytopenia and hypersensitivity reactions.
There are potentially life-threatening side effects: arrhythmias, thrombocytopenia and hypersensitivity reactions.
When should I get my leg cramps treated at the Emergency Department?
Go to the emergency department (ED) if a leg cramp lasts longer than 10 minutes or becomes unbearably painful. Also go if a leg cramp happens after you touch a substance that could be poisonous or infectious. For example, if you have a cut in your skin that touches dirt, you could get a bacterial infection like tetanus. Exposure to mercury, lead or other toxic substances should also be reason to go to the emergency department.
Is there a surgery that could help with my leg cramps?
At this time, surgery is not recommended as a cure for leg cramps.
Prevention
How can I reduce my risk of getting leg cramps?
Experts can’t promise that you’ll never have a leg cramp again, but there are some steps you can take that might reduce your risk!
- Make sure that you stay hydrated – drink six to eight glasses of water each day.
 Don’t drink as much alcohol and caffeine.
Don’t drink as much alcohol and caffeine. - Adjust how you sleep. Use pillows to keep your toes pointed upwards if you sleep on your back. If you lie on your front, try hanging your feet over the end of the bed. Both positions can keep you in a relaxed position.
- Gently stretch your leg muscles before you go to sleep.
- Keep blankets and sheets loose around your feet so that your toes are not distorted.
- Wear shoes that fit you well and support your feet.
- Perform frequent leg exercises.
- Stretch your muscles before and after you exercise.
- Experiment with mild exercise right before bed. Walk on the treadmill or ride a bicycle for a few minutes.
What kinds of stretches help prevent leg cramps?
Try the following to prevent leg cramps in your calves: Stand about three feet (one meter) away from a wall. Lean forward. Touch the wall with your arms outstretched while keeping your feet flat. Count to five before you stop, and do it over and over again for at least five minutes.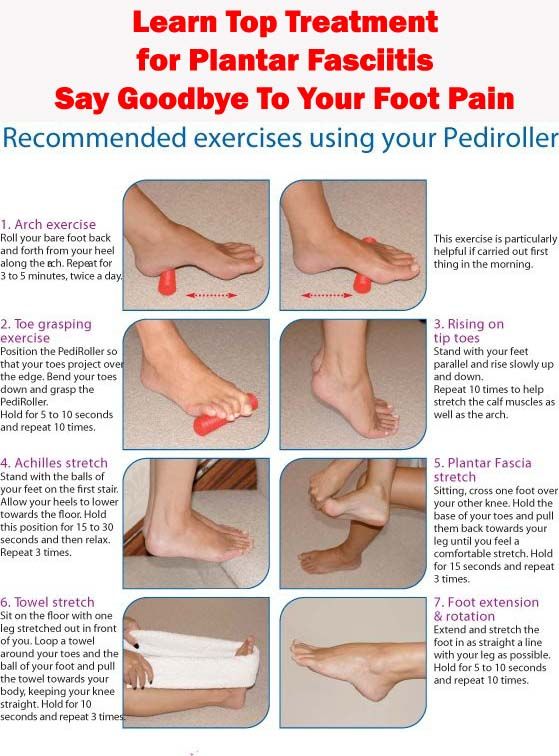 Repeat three times per day.
Repeat three times per day.
Outlook / Prognosis
Can leg cramps be cured?
Leg cramps don’t have a cure at this time. Fortunately, there are steps you can take to prevent leg cramps (see the “Prevention” section) and manage your leg cramps (see the “Management and Treatment” section).
Can leg cramps get worse?
The severity of a leg cramp is difficult if not impossible to predict. Some people see improvement with prevention and treatment plans, while others struggle. It is possible that your cramps will feel worse and happen more often as you age.
Living With
How do I take care of myself?Come up with a treatment plan with your healthcare provider that includes a prevention plan and an in-the-moment treatment plan. Ideas for a prevention plan include several activities you may want to do every day:
- Exercise: Do leg exercises during the day, and mild, brief walking or biking right before bed.
- Hydration: Drink eight glasses of water each day and avoid alcohol and caffeinated beverages.
- Medications and vitamins: Take all vitamins and medications (including muscle relaxants) exactly how they’re prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Prepare your bed space: Keep a heating pad and massage roller next to your bed.
- Shoes: Purchase supportive shoes.
- Sleeping position: Experiment with different positions to see if one works better than another. Keep your toes up if you’re on your back and hang your feet over the end of the bed if you lie on your front.
- Stretch: Stretch your legs before and after exercising, and right before you go to sleep.
Your in-the-moment treatment plan could include the eight steps mentioned in the Management and Treatment section:
- Stretch. Straighten your leg and then flex it, pulling your toes towards your shin to stretch the muscles (using a towel can assist).

- Massage. Use your hands or a roller to massage the muscles.
- Stand. Get up. Press your feet against the floor.
- Walk. Wiggle your leg while you walk around.
- Apply heat. Use a heating pad or take a warm bath.
- Apply cold. Wrap a bag of ice in a towel and apply it to the area.
- Pain killers. Take ibuprofen or acetaminophen to help with the pain.
- Elevate. Prop up your leg after the cramp starts to feel better.
See your healthcare provider if your leg cramps are unbearably painful, happen frequently or last for a long time. Also, talk to your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms in addition to leg cramps:
- Muscle cramps in other parts of your body.
- Significant pain.

- Swelling or numbness in the leg.
- Changes in the skin of your leg.
- Waking up over and over again with leg cramps.
- If your leg cramps are stopping you from getting enough sleep.
- If you have fluid abnormalities or electrolyte imbalances.
- See your healthcare provider immediately if you’re concerned that your leg cramps are a symptom of an underlying serious medical condition.
- Do you think that my leg cramps are a symptom of an underlying condition?
- Can you show me the best exercises I can do to stretch my muscles?
- Can you show me the best massage techniques I can use to help with my leg cramps?
- Is it safe for me to take medication for my leg cramps? Which medications should I take?
- Do you recommend that I see a physical therapist, sleep specialist, massage therapist, or other specialist?
- How can I help my child when they have a leg cramp?
- Should I keep an eye out for symptoms other than leg cramps that might indicate a more serious condition?
- How often should I come back to visit you about my leg cramps?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Leg cramps can be unpredictable and agonizing. They can affect your sleep, your exercise routine and your general quality of life. They’re common – very normal – and, fortunately, temporary, and there are steps you can take to manage them. Do your best to avoid risk factors, avoid medications with leg cramps as a side effect and take recommended preventative measures.
They can affect your sleep, your exercise routine and your general quality of life. They’re common – very normal – and, fortunately, temporary, and there are steps you can take to manage them. Do your best to avoid risk factors, avoid medications with leg cramps as a side effect and take recommended preventative measures.
If you’re concerned about the severity and duration of your leg cramps, or think that they may be caused by a serious condition, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider. Ask questions and voice your concerns. You don’t have to just “live with” leg cramps.
Causes, Pain Relief & Prevention
Overview
Leg Cramps at NightWhat are leg cramps?
Leg cramps are sudden, involuntary, intense muscle pains usually in your calf, foot or thigh. You might also know them as a “charley horse.” Sometimes the cramp may cause your leg to spasm – to tighten uncontrollably. Although painful to live with, cramps are generally harmless.
What does a leg cramp feel like?
A leg cramp feels like a clenched, contracted muscle tightened into a knot. It can be severely uncomfortable, painful or even unbearable. Your muscles in the area might hurt for hours after the cramp goes away.
It can be severely uncomfortable, painful or even unbearable. Your muscles in the area might hurt for hours after the cramp goes away.
How do I stop a leg cramp?
Try forcefully stretching the affected muscle (for example, stretch your calf muscle by flexing your foot upward). Jiggle your leg, massage it, or force yourself to walk. It might also help to apply ice or heat – use a heating pad or take a warm bath. (Read the “Management and Treatment” section for more tips.)
Unfortunately, there are no pills or injections that instantly relieve a leg cramp when it’s happening. There are, however, ways that may prevent the cramp from happening in the first place (see the “Prevention” section).
Can you get leg cramps at night?
Leg cramps at night happen when you’re not very active, or when you’re asleep. They may wake you up, make it harder for you to fall back asleep and leave you feeling sore all night. Yearly, monthly, weekly, nightly – the frequency of leg cramps depends on the person.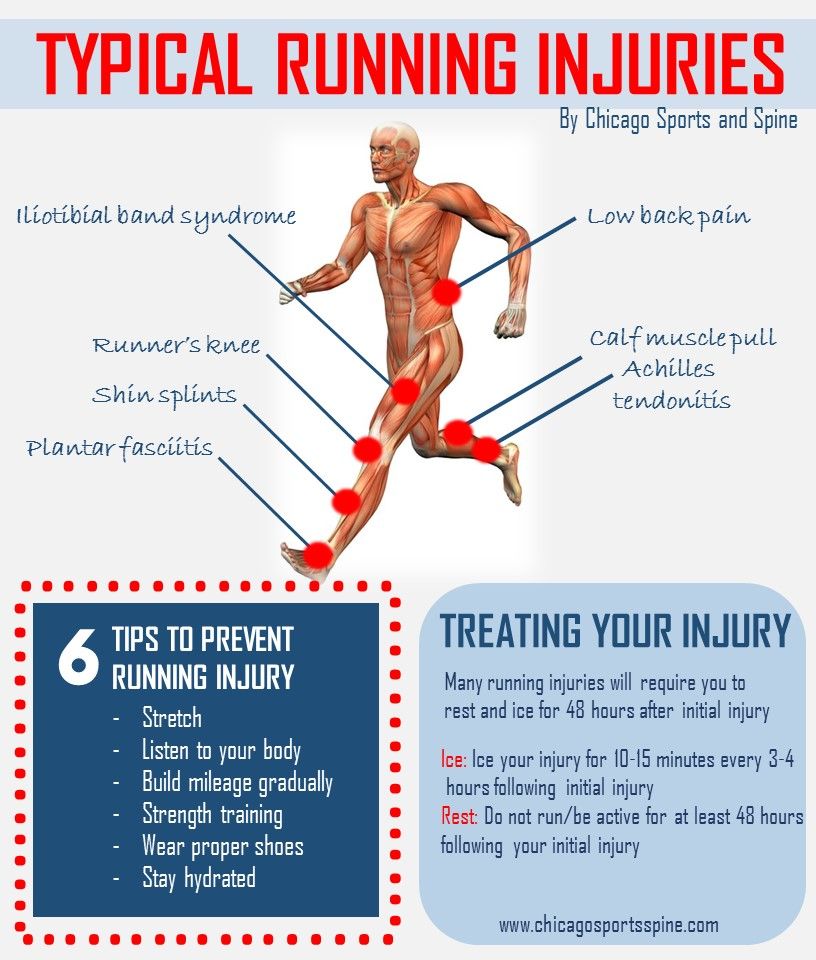 Nocturnal leg cramps can happen to anyone at any age, but they happen most often to older adults. Of people over age 60, 33% will have a leg cramp at night at least once every two months. Nearly every adult age 50 and older will have them at least one time. Seven percent of children will, as well. Approximately 40% of pregnant women will experience leg cramps at night. The reason behind that is thought to be that the extra weight of pregnancy strains the muscles.
Nocturnal leg cramps can happen to anyone at any age, but they happen most often to older adults. Of people over age 60, 33% will have a leg cramp at night at least once every two months. Nearly every adult age 50 and older will have them at least one time. Seven percent of children will, as well. Approximately 40% of pregnant women will experience leg cramps at night. The reason behind that is thought to be that the extra weight of pregnancy strains the muscles.
Three-quarters (75%) of all reported leg cramps happen at night.
How long do leg cramps last?
An instance of a leg cramp can last from several seconds to several minutes.
Who gets leg cramps?
The older you are, the more likely you are to have leg cramps. This is because your tendons (the tissues that connect your muscles to your bones) naturally shorten as you age. You’re also more likely to get them if you’re a woman. Up to 60% of adults get leg cramps at night, as do up to 40% of children and teenagers.
Are leg cramps a sign of something serious?
Leg cramps can sometimes be a symptom of a serious health condition. (See the “Symptoms and Causes” section.) If you are concerned that you have a serious health condition, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider and report your symptoms, including your leg cramps.
How common are leg cramps?
Leg cramps are very common and normal, especially at night.
What is the difference between leg cramps and Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)?
Although both nocturnal leg cramps (leg cramps at night) and restless legs syndrome tend to happen to you at night or when you’re at rest, restless legs syndrome doesn’t cause the severe pain. Restless legs syndrome is uncomfortable, but not agonizing. It’s a crawling sensation that makes you want to move your legs. When you do move, the restlessness stops, but there is still discomfort.
Symptoms and Causes
What causes leg cramps?
Some leg cramps happen for no known reason and they are called “idiopathic” cramps. “Secondary” leg cramps are a symptom or complication of a more serious health condition. The primary cause of idiopathic leg cramps is up for debate. Possible causes of them include:
“Secondary” leg cramps are a symptom or complication of a more serious health condition. The primary cause of idiopathic leg cramps is up for debate. Possible causes of them include:
- Involuntary nerve discharges.
- Restriction in the blood supply.
- Stress.
- Too much high-intensity exercise.
Women who are pregnant often have leg cramps during the day and at night.
Possible causes for leg cramps at night (nocturnal leg cramps) include:
- Sitting for long periods of time.
- Overusing the muscles.
- Standing or working on concrete floors.
- Sitting improperly.
Leg cramps are not likely to cause:
- Broken bones.
- Fainting.
- Nausea.
- Numbness.
What medications may cause leg cramps?
Drugs have side effects. It’s possible that a prescription you’re taking could be causing your leg cramps. In that case, work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the pros and cons of the medication vs. its side effects. It’s possible that your healthcare provider may be able to put you on a different medication that doesn’t have leg cramps as a side effect. Medicines that have leg cramps as a side effect include:
its side effects. It’s possible that your healthcare provider may be able to put you on a different medication that doesn’t have leg cramps as a side effect. Medicines that have leg cramps as a side effect include:
- Albuterol/Ipratropium (Combivent®).
- Conjugated estrogens.
- Clonazepam (Klonopin®).
- Diuretics.
- Gabapentin (Neurontin®).
- Naproxen (Naprosyn®).
- Pregabalin (Lyrica®)
- Statins.
- Zolpidem (Ambien®).
Others may include: Amoxicillin, bromocriptine (Parlodel), bupropion (Wellbutrin), celecoxib (Celebrex®), cetirizine (Zyrtec), chromium, cinacalcet (Sensipar), ciprofloxacin (Cipro), citalopram (Celexa), donepezil (Aricept), eszopiclone (Lunesta), fluoxetine (Prozac), IV iron sucrose, lansoprazole (Prevacid), levalbuterol, levothyroxine, metformin, niconitis acid, nifedipine, rivastigmine (Exelon), sertraline (Zoloft), telmisartan (Micardis), teriparatide (Forteo®) and teriparatide raloxifene (Evista®).
What medical problems can cause leg cramps?
Sometimes leg cramps happen to you for no reason, but other times they could possibly be a sign or symptom of a health condition. If you have any of the following conditions, it’s possible that your leg cramps are a result of that condition. Also keep in mind that if you don’t already know if you have any of these conditions, your leg cramps may be a sign that you do. Always consult your healthcare provider if you think your leg cramps are a symptom of a more serious medical condition.
Leg cramps can possibly be a sign of lifestyle choices such as:
- Alcoholism: An addiction to alcohol.
- Pregnancy.
- Dehydration: The lack of sufficient water in the body. (This sign is debated among experts.)
Leg cramps can also possibly be a sign of serious conditions including:
- ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/Lou Gehrig’s disease): Progressive neuromuscular disease.
- Cardiovascular disease: Heart conditions caused by blood clots or diseased blood vessels. Also, coronary artery disease: The narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries.
- Cirrhosis of the liver: Scarring of the liver.
- Diabetes: A disease that prevents your body from properly using the energy from the food you eat.
- Flat feet: The absence of the supportive arch in the foot.
- Hypokalemia: Low potassium levels in your blood.
- Kidney failure (hemodialysis): A condition in which one or both kidneys no longer work correctly.
- Osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease): The corrosion of the cartilage that protects your bones. Also, lumbar canal stenosis: A narrowing of the spinal canal in the lower back.
- Parkinson’s disease: A neurological movement disorder.
- Peripheral artery disease: Narrowing of the arteries.
.jpg) Also, peripheral neuropathy: Damage or dysfunction of one or more nerves.
Also, peripheral neuropathy: Damage or dysfunction of one or more nerves.
Cancer treatments like chemotherapy can cause nerve damage, which may cause leg cramps.
There are rumors that leg cramps can also be a sign of the following conditions. Fortunately, that is not the case. Leg cramps are unlikely to be a sign of:
- Labor (giving birth).
- Lung cancer.
- Menopause.
- Multiple sclerosis.
Leg cramps are not likely to be a sign of a deficiency in:
- Alanine transaminase.
- Albumin.
- Bilirubin.
- Calcium.
- Creatinine.
- Glucose.
- Magnesium.
- Zinc, vitamin B12 or vitamin D.
What are the warning signs that leg cramps are coming?
Unfortunately, leg cramps happen very suddenly. There are no warning signs. However, there are risk factors such as pregnancy and the use of medications that have leg cramps as a side effect.
Diagnosis and Tests
How are leg cramps diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will need to know your medical history, medications and a description of what you’re experiencing. Be specific. Report your symptoms to your healthcare provider and include the following information:
Be specific. Report your symptoms to your healthcare provider and include the following information:
- When the leg cramps started happening.
- What your pain feels like.
- When the cramps happen (at night, for example, or after vigorous exercise).
- How long the cramps last.
- Any other symptoms you’re experiencing.
Your healthcare provider will need to tell the difference between your leg cramps from other conditions that may resemble them:
- Claudication.
- Peripheral neuropathy.
- Myositis.
- Restless legs syndrome.
To distinguish those differences, your healthcare provider may:
- Check the palpation of pulses.
- Evaluate physical sensations such as pinpricks.
- Test deep tendon reflexes.
- Test the strength of your leg.
Do I need to have any testing done to diagnose my leg cramps?
Blood, urine and other routine tests are not helpful in diagnosing leg cramps but they may help identify previously undiagnosed medical conditions that have leg cramps as a symptom. For example, your healthcare provider will likely perform typical tests such as taking your blood pressure, and that can reveal cardiac and vascular risks.
For example, your healthcare provider will likely perform typical tests such as taking your blood pressure, and that can reveal cardiac and vascular risks.
What questions might my healthcare provider ask about my leg cramps?
To help your healthcare provider diagnose you, they may ask the following questions about your leg cramps:
- When do you experience the leg cramps?
- How often do your leg cramps occur?
- How would you describe your leg cramps?
- How long do the leg cramps last?
- What medications are you currently taking?
- What known medical conditions do you have?
- Are you concerned about medical conditions that may be causing your leg cramps?
- Are you having any symptoms of another medical condition?
Management and Treatment
What can I do to make leg cramps go away if they happen?
You want to get rid of a leg cramp the moment it strikes. You might be finishing up an exercise routine, or you might be awakened in the middle of the night. In moments like that there are, unfortunately, no magical injections that can instantly relieve your pain. However, there are eight steps to take to possibly get rid of a leg cramp:
In moments like that there are, unfortunately, no magical injections that can instantly relieve your pain. However, there are eight steps to take to possibly get rid of a leg cramp:
- Stretch. Straighten your leg and then flex it, pulling your toes towards your shin to stretch the muscles.
- Massage. Use your hands or a roller to massage the muscles.
- Stand. Get up. Press your feet against the floor.
- Walk. Wiggle your leg while you walk around.
- Apply heat. Use a heating pad or take a warm bath.
- Apply cold. Wrap a bag of ice in a towel and apply it to the area.
- Pain killers. Take ibuprofen or acetaminophen to help with the pain.
- Elevate. Prop up your leg after the cramp starts to feel better.
What kinds of stretches help get rid of leg cramps?
Try this if your cramp is in your calf muscle: While standing (or sitting with your leg unfolded before you), straighten your leg and lift your foot until your toes are pointing at your shin. Pull on your toes if you are able to reach them. You could also try walking around on your heels.
Pull on your toes if you are able to reach them. You could also try walking around on your heels.
What medicines may help with leg cramps?
At this time, there is no recommended medication that can prevent leg cramps 100% of the time. However, there are some prescription medications that show a little evidence of preventing leg cramps. Under your healthcare provider’s watchful eye, you might want to try the following:
- Carisoprodol (Soma®): A muscle relaxant.
- Diltiazem (Cartia XT®): A calcium-channel blocker.
- Orphenadrine (Norflex®): Treats muscle spasms and relieves pain and stiffness in muscles.
- Verapamil: A calciuim-channel blocker.
What vitamins may help with leg cramps?
No vitamin is likely to help with a leg cramp 100% of the time. However, some experts do recommend that you take a vitamin B12 complex.
Does quinine help with leg cramps?
Quinine was thought to show some promise with healing leg cramps, but it is no longer recommended. There are potentially life-threatening side effects: arrhythmias, thrombocytopenia and hypersensitivity reactions.
There are potentially life-threatening side effects: arrhythmias, thrombocytopenia and hypersensitivity reactions.
When should I get my leg cramps treated at the Emergency Department?
Go to the emergency department (ED) if a leg cramp lasts longer than 10 minutes or becomes unbearably painful. Also go if a leg cramp happens after you touch a substance that could be poisonous or infectious. For example, if you have a cut in your skin that touches dirt, you could get a bacterial infection like tetanus. Exposure to mercury, lead or other toxic substances should also be reason to go to the emergency department.
Is there a surgery that could help with my leg cramps?
At this time, surgery is not recommended as a cure for leg cramps.
Prevention
How can I reduce my risk of getting leg cramps?
Experts can’t promise that you’ll never have a leg cramp again, but there are some steps you can take that might reduce your risk!
- Make sure that you stay hydrated – drink six to eight glasses of water each day.
 Don’t drink as much alcohol and caffeine.
Don’t drink as much alcohol and caffeine. - Adjust how you sleep. Use pillows to keep your toes pointed upwards if you sleep on your back. If you lie on your front, try hanging your feet over the end of the bed. Both positions can keep you in a relaxed position.
- Gently stretch your leg muscles before you go to sleep.
- Keep blankets and sheets loose around your feet so that your toes are not distorted.
- Wear shoes that fit you well and support your feet.
- Perform frequent leg exercises.
- Stretch your muscles before and after you exercise.
- Experiment with mild exercise right before bed. Walk on the treadmill or ride a bicycle for a few minutes.
What kinds of stretches help prevent leg cramps?
Try the following to prevent leg cramps in your calves: Stand about three feet (one meter) away from a wall. Lean forward. Touch the wall with your arms outstretched while keeping your feet flat. Count to five before you stop, and do it over and over again for at least five minutes. Repeat three times per day.
Repeat three times per day.
Outlook / Prognosis
Can leg cramps be cured?
Leg cramps don’t have a cure at this time. Fortunately, there are steps you can take to prevent leg cramps (see the “Prevention” section) and manage your leg cramps (see the “Management and Treatment” section).
Can leg cramps get worse?
The severity of a leg cramp is difficult if not impossible to predict. Some people see improvement with prevention and treatment plans, while others struggle. It is possible that your cramps will feel worse and happen more often as you age.
Living With
How do I take care of myself?Come up with a treatment plan with your healthcare provider that includes a prevention plan and an in-the-moment treatment plan. Ideas for a prevention plan include several activities you may want to do every day:
- Exercise: Do leg exercises during the day, and mild, brief walking or biking right before bed.

- Hydration: Drink eight glasses of water each day and avoid alcohol and caffeinated beverages.
- Medications and vitamins: Take all vitamins and medications (including muscle relaxants) exactly how they’re prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Prepare your bed space: Keep a heating pad and massage roller next to your bed.
- Shoes: Purchase supportive shoes.
- Sleeping position: Experiment with different positions to see if one works better than another. Keep your toes up if you’re on your back and hang your feet over the end of the bed if you lie on your front.
- Stretch: Stretch your legs before and after exercising, and right before you go to sleep.
Your in-the-moment treatment plan could include the eight steps mentioned in the Management and Treatment section:
- Stretch. Straighten your leg and then flex it, pulling your toes towards your shin to stretch the muscles (using a towel can assist).

- Massage. Use your hands or a roller to massage the muscles.
- Stand. Get up. Press your feet against the floor.
- Walk. Wiggle your leg while you walk around.
- Apply heat. Use a heating pad or take a warm bath.
- Apply cold. Wrap a bag of ice in a towel and apply it to the area.
- Pain killers. Take ibuprofen or acetaminophen to help with the pain.
- Elevate. Prop up your leg after the cramp starts to feel better.
See your healthcare provider if your leg cramps are unbearably painful, happen frequently or last for a long time. Also, talk to your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms in addition to leg cramps:
- Muscle cramps in other parts of your body.
- Significant pain.
.jpg)
- Swelling or numbness in the leg.
- Changes in the skin of your leg.
- Waking up over and over again with leg cramps.
- If your leg cramps are stopping you from getting enough sleep.
- If you have fluid abnormalities or electrolyte imbalances.
- See your healthcare provider immediately if you’re concerned that your leg cramps are a symptom of an underlying serious medical condition.
- Do you think that my leg cramps are a symptom of an underlying condition?
- Can you show me the best exercises I can do to stretch my muscles?
- Can you show me the best massage techniques I can use to help with my leg cramps?
- Is it safe for me to take medication for my leg cramps? Which medications should I take?
- Do you recommend that I see a physical therapist, sleep specialist, massage therapist, or other specialist?
- How can I help my child when they have a leg cramp?
- Should I keep an eye out for symptoms other than leg cramps that might indicate a more serious condition?
- How often should I come back to visit you about my leg cramps?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Leg cramps can be unpredictable and agonizing. They can affect your sleep, your exercise routine and your general quality of life. They’re common – very normal – and, fortunately, temporary, and there are steps you can take to manage them. Do your best to avoid risk factors, avoid medications with leg cramps as a side effect and take recommended preventative measures.
They can affect your sleep, your exercise routine and your general quality of life. They’re common – very normal – and, fortunately, temporary, and there are steps you can take to manage them. Do your best to avoid risk factors, avoid medications with leg cramps as a side effect and take recommended preventative measures.
If you’re concerned about the severity and duration of your leg cramps, or think that they may be caused by a serious condition, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider. Ask questions and voice your concerns. You don’t have to just “live with” leg cramps.
Night cramps: causes and remedies
Neurology
A sharp burning pain in the calf muscles is familiar to almost everyone. Pain can be strong or weak, but it usually lasts only a few seconds. If the pain was severe, then after night cramps for another 1-3 days, pain in the legs during movement may disturb.
As a rule, nocturnal cramps affect only the calf muscles. In some cases, it can reduce fingers, foot, thigh. In fact, a cramp is a muscle contraction that occurs involuntarily and is accompanied by burning pain. At the same time, the muscles become hard. This problem is usually faced by people in middle and older age, but it is possible to experience convulsions in childhood.
In some cases, it can reduce fingers, foot, thigh. In fact, a cramp is a muscle contraction that occurs involuntarily and is accompanied by burning pain. At the same time, the muscles become hard. This problem is usually faced by people in middle and older age, but it is possible to experience convulsions in childhood.
Causes of leg cramps at night:
1. Lack of certain substances: calcium, potassium, magnesium. This problem usually occurs in people who drink a lot of fluids or sweat a lot during the day. Together with excess fluid, the necessary elements are also removed from the body. In addition, during pregnancy, a woman gives all the necessary substances to the developing fetus, which also provokes a lack of potassium, calcium and magnesium in the body.
2. Too much caffeine in the diet, smoking.
3. Lack of vitamin D, which contributes to better absorption of calcium by the body. A lack of calcium can cause this unpleasant phenomenon. Vitamin D is produced by the body through exposure to sunlight. In places where the sun is rare, for example, in the north, people often face a lack of this vitamin.
In places where the sun is rare, for example, in the north, people often face a lack of this vitamin.
4. An excess of cortisol, which is produced during periods of depression and stress. Cortisol is a hormone that inhibits the absorption of calcium from food, and also increases its excretion with the help of the kidneys.
5. Curvature of the foot due to injury, flat feet.
6. Taking medicines for heartburn, gastritis, intestinal disorders also interferes with the normal absorption of trace elements from food intake, which results in night cramps.
7. The presence of a disease such as varicose veins.
8. Protein intake for muscle building. An excess of protein in the diet leads to ketosis, which becomes the main cause of calcium excretion from the body.
What to do in case of cramps in the calves:
1. As soon as the pain makes itself felt, you need to grab your toes with your hands and pull them towards you, hold your fingers in this position for about a minute. Then slightly relax your legs and pull your toes again.
Then slightly relax your legs and pull your toes again.
2. Pinch the muscle with your fingers to relax it a little.
3. Massage the muscle with a warming ointment.
4. If the pain is not very severe, get out of bed and walk barefoot on the cool floor.
5. Raise your legs on a soft pillow to start the outflow of blood.
To avoid problems in the future, you need to take a full-fledged vitamin complex, enrich your diet with seafood, dairy products, fresh herbs, and fruits. If convulsions at night have become a frequent occurrence, then you should consult a doctor.
Other articles on this topic
Epilepsy. Symptoms, causes, treatment of epilepsy
In ancient times, epilepsy was considered some kind of mystical disease, as if epileptics had a special gift. But in fact, everything is much more prosaic and sadder - epilepsy is a chronic disease.
Neurology
Insomnia: causes and prevention
Insomnia (insomnia) is a process of sleep disturbance, in which its duration and quality decrease. With insomnia, sleep disturbance factors have been observed for quite a long time.
With insomnia, sleep disturbance factors have been observed for quite a long time.
Neurology
Dementia: causes, symptoms and prevention
People of any age can get dementia. The main reason is hypertension with changes in blood pressure, atherosclerosis of the brain. Often, dementia causes Alzheimer's disease.
Neurology
Cramps in the calf: causes, treatment and prevention
"Cramps in the legs" is an everyday description of painful muscle spasms and cramps in the lower extremities. In some cases, spasms are not accompanied by pain, but only rapid rhythmic muscle contractions are observed. Muscles twitch chaotically, either contracting or relaxing.
Leg cramps develop as a result of various diseases and conditions, from electrolyte disorders to neurological disorders and hormonal imbalances. Therapists, neurologists, endocrinologists, phlebologists, etc. are engaged in the diagnosis and treatment of the causes of leg cramps (spasms themselves are not a disease), etc. It all depends on the nature of the problem.
are engaged in the diagnosis and treatment of the causes of leg cramps (spasms themselves are not a disease), etc. It all depends on the nature of the problem.
Causes of cramps
Involuntary muscle contractions (cramps in the legs) are a symptom of various diseases and pathological conditions. In healthy people, painful spasms occur against the background of excessive physical exertion, uncomfortable body position, unsuccessful movement, but in such cases, convulsions do not recur. In diseases, a repetition of episodes is possible, as well as an increase in symptoms.
Crampy syndrome
Crampy develops against a background of a number of diseases (avitaminosis, liver cirrhosis, neurological disorders, etc.), hypothermia, intense physical exertion. The exact reasons are unknown.
The disease is accompanied by short-term muscle spasms in the calves. The intensity of convulsions in the lower extremities is different, the pain syndrome is pronounced.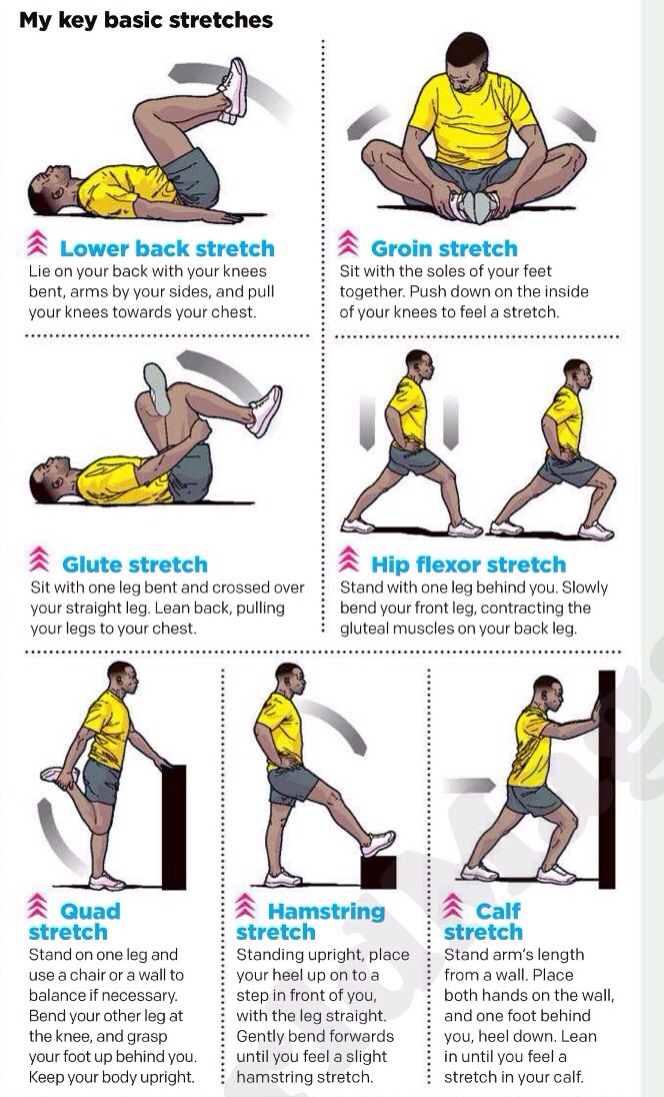 Most of the attacks occur at night.
Most of the attacks occur at night.
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of the pathology, as well as stopping the symptom. Doctors prescribe vitamins, minerals, anti-inflammatory drugs.
Flat feet
In flat feet, spasms of the lower extremities develop in response to uneven load distribution. Legs cramp during activity, less often at rest.
Spasms develop suddenly. Muscle contractions last from a few seconds to several minutes. After the attack, severe discomfort persists.
Treatment - orthopedic. The task is to achieve the correct distribution of the load on the lower limbs. Rarely resort to surgical correction.
Vascular diseases
Spasms (painful contractions) affecting the calf muscles occur in response to hypoxia and impaired energy metabolism in tissues. Seizures also develop as a result of such pathologies:
- varicose disease;
- endarteritis;
- atherosclerosis;
- thrombosis.
The clinical picture is complemented by sensations of heaviness and pressure in the legs. The phlebologist is engaged in the treatment of such conditions. Its task is to restore blood flow, venous-lymphatic outflow, eliminate inflammation, etc.
Endocrine diseases
Leg cramps are typical for thyroid pathologies (hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, hypoparathyroidism, diabetes mellitus). Diabetes insipidus can be an indirect cause, since the patient loses a lot of fluid, and with it, electrolytes.
The clinical presentation depends on the cause of the seizures. Treatment is the task of the endocrinologist. It is carried out with the help of medications, replacement therapy is also indicated. According to the situation, surgical treatment is carried out (tumors, tissue injuries).
Fluid and electrolyte disorders
Cramps (painful contractions in the legs) may be a symptom of a deficiency or excess of potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium. Seizures occur spontaneously and often recur. Seizures develop at night and last up to several minutes.
Seizures occur spontaneously and often recur. Seizures develop at night and last up to several minutes.
Treatment is the work of a therapist or other specialist (depending on the cause of the disorder). Restoration of electrolyte balance is carried out with the help of drugs, a therapeutic diet.
Hypovitaminosis
Most often, leg cramps develop in response to a lack of vitamins B1, B2, B6, D. Hypovitaminosis is accompanied by additional symptoms: reduced sensitivity of the lower extremities, burning in the legs, insomnia, dry skin, decreased vision, immunity. It all depends on the specific pathology.
Treatment is the work of the therapist. It is necessary to eliminate the primary disease, restore the level of vitamins and minerals in the body.
Intoxication
Convulsions are possible in case of poisoning with salts of heavy metals, vapors of volatile substances. Most often suffer laboratory workers, employees of hazardous enterprises. Intoxication occurs when using poisonous plants: belladonna, fly agaric, ergot. However, drugs are more often to blame. Painful muscle spasms develop as a side effect of certain medications.
Intoxication occurs when using poisonous plants: belladonna, fly agaric, ergot. However, drugs are more often to blame. Painful muscle spasms develop as a side effect of certain medications.
Spasms occur after the influence of a substance on the body. Muscle contractions can be persistent - it can be difficult to remove them even in a hospital setting. Treatment - detoxification with drugs, observation. Many poisonings are life-threatening.
Pathologies of pregnancy
Muscle cramps may occur in pregnant women. Often cramps of the calf muscles develop as a result of hypovitaminosis, electrolyte imbalance. There are more threatening conditions: inferior vena cava syndrome, eclampsia.
Patients with recurrent muscle spasms are managed by OB/GYNs. They figure out why the problem has developed, prescribe treatment.
Other causes
There are other factors that cause cramps in the legs. Other causes of calf spasms include:
- alcohol intoxication;
- high body temperature;
- tumors of the central nervous system and endocrine system;
- jumps in blood pressure;
- traumatic brain injury;
- infections;
- dehydration;
- heat stroke.
This also includes leg injuries. Less commonly, the symptom occurs due to anemia.
Night cramps in the legs
Spasms at night develop with varicose veins, lack of trace elements, vitamins. They also occur with intense physical exertion, wearing uncomfortable shoes. There are more serious causes of night cramps. For example, epilepsy. To put an end to the question, you need to undergo an examination.
Why does the calf cramps - doctors should understand. The reasons are not always obvious. It is possible to understand why a symptom developed only after a thorough diagnosis. Diagnosis is by sighting or exclusion.
First aid for cramps in the legs
First aid is aimed at relieving an attack. To get rid of cramps, you need to:
- raise your legs above the level of your head;
- pull the toe up;
- if it doesn't help, do a light massage of the calves and feet.
Actions to be repeated until improvement. After stabilization of the condition, it is worth taking a warm bath and moving around a little.
After stabilization of the condition, it is worth taking a warm bath and moving around a little.
Diagnosis
The doctor evaluates complaints, collects anamnesis, prescribes general and biochemical blood and urine tests, if necessary, performs a toxicological test. An important role is played by instrumental research methods for establishing the cause of spasms: electromyography, EEG, ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities, MRI of the brain, organs of the endocrine system, etc.
Treatment
Treatment can be conservative or surgical. Surgical methods are used in rare cases.
Conservative therapy
Conservative treatment includes medication, physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy. Relieve an attack, there is little tension in the muscles during convulsions. If nothing is done about the cause of the symptom, a relapse is likely. Attacks can be repeated and become more frequent. Medicines are selected individually.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment is possible with flat feet, varicose veins, vascular diseases, tumors.