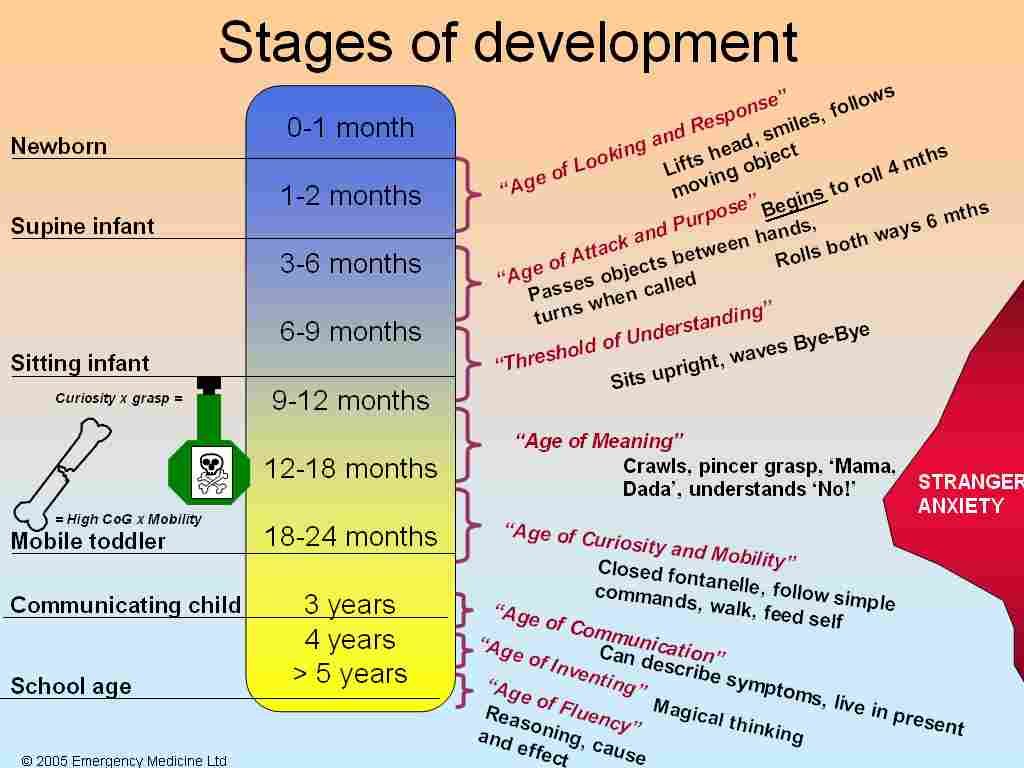
How to manage cluster feeding
Cluster feeding | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Cluster feeding | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
Key facts
- Cluster feeding is when your baby wants lots of short feeds over a few hours.
- Cluster feeding is very common, especially in the late afternoon or early evening.
- No one really knows why some babies cluster feed, but it may be a way for your body to boost your milk supply.
- If your baby cluster feeds, this does not mean that you don't have enough milk.
- Cluster feeding can be exhausting; it's a good idea to think of strategies to help you cope when your baby feeds frequently.
What is cluster feeding?
Cluster feeding is a time when your baby wants lots of short feeds over a few hours. It's normal and often happens in the early days of breastfeeding.
Cluster feeding is a normal behaviour for your baby. It's more common in the late afternoon or early evening, but it can happen anytime of the day.
It seems that some babies prefer to fill up on milk for a few hours then often have a longer sleep.
Why do some babies cluster feed?
There is no particular reason why some babies cluster feed. Some people believe it might boost your milk supply. If your baby wants more milk, then feeding more often will trigger your body to make it.
Is my baby cluster feeding?
If your baby is having a lot of short feeds close together over a few hours, you are cluster feeding.
If you are cluster feeding, you might also find that your baby:
- has short rests or sleeps between these feeds
- feeds for a few minutes then pulls off and on the breast
- cries and is fussy during this time
Common worries about cluster feeding
Cluster feeding can make you physically and emotionally drained. Many parents feel exhausted and frustrated. Some mothers say they feel like a failure, or that they lose confidence about being able to breastfeed.
Many parents feel exhausted and frustrated. Some mothers say they feel like a failure, or that they lose confidence about being able to breastfeed.
You might worry that you don't have enough milk because your baby takes a long time to settle. You might also think your breasts feel empty.
But there is always milk in your breasts. They are never completely empty.
What can I do to make cluster feeding easier?
The first thing to remember is that this is normal. Cluster feeding doesn't mean that you don't have enough milk.
To make cluster feeding easier you can:
- relax and follow your baby's lead
- feed to their need
- look forward to a sleepy, settled baby after feeding
- try to rest in the early part of the day to prepare
- drink lots of water
- make sure you eat well — don't miss meals
- get as much family and partner support as you can
Things to look out for
Cluster feeding is a normal part of a baby's feeding routine. Talk to your nurse, midwife or doctor if your baby:
Talk to your nurse, midwife or doctor if your baby:
- is not gaining weight
- is not producing wet and dirty nappies
- is not settling after they have finished feeding
Where can I go for help and advice about breastfeeding?
For advice and support contact:
- a lactation consultant
- your family health nurse
- Pregnancy Birth Baby on 1800 882 436
- the Australian Breastfeeding Association Helpline on 1800 686 268
Speak to a maternal child health nurse. Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. This is a free service, and is available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Australian Breastfeeding Association (Cluster feeding and fussy babies), Royal Australian College of General Practitioners (RACGP) (Infant and toddler nutrition), Royal Children’s Hospital (RCH) (Breastfeeding)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: May 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Breastfeeding your baby
Need more information?
Cluster feeding | Australian Breastfeeding Association
Baby feeds all evening? Witching hour, empty breasts, unsettled baby. It's usually all normal.
Read more on Australian Breastfeeding Association website
Is it really low supply? | Australian Breastfeeding Association
Fussy or crying baby? Soft breasts? Baby cluster feeding? Can't pump milk? It can be hard to know what’s going on.
Read more on Australian Breastfeeding Association website
Breastfeeding your baby
Breastfeeding is the most natural way to feed your baby, providing all the nutrition your baby needs during the first six months of life and a loving bond with your baby.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Breastfeeding Tips and Videos | Tresillian
Find videos and top breastfeeding tips to answer your questions, including how long to breastfeed, milk supply tips, and weaning your baby.
Read more on Tresillian website
Why do some mums stop breastfeeding before 6 months?
Most new parents know 'breast is best', but while more than 9 out of 10 babies are breastfed at birth, few mums are breastfeeding exclusively 5 months later.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
How to increase breast milk supply
Find out what causes low breast milk supply, what is normal and how to boost breast milk production.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
A day in the life of a newborn
Most babies will start to settle into a daily pattern of sleeping, feeding and playing, whether you follow what your newborn does or establish a simple routine.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
What to Expect and Tips for Managing It
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission Here’s our process.
If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission Here’s our process.
Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:
- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness.
Read more about our vetting process.Was this helpful?
Cluster feeding, or frequent feedings with only short breaks between, can be typical newborn behavior. Certain practices, such as staying hydrated and planning ahead, may help you manage it.
Cluster feeding is when a baby suddenly starts eating much more frequently — in clusters — for a period of time. It usually lasts a couple of hours at a time and differs from your baby’s usual eating behavior.
Cluster feeding is normal baby behavior, seen primarily in breastfeeding newborns in the first few weeks. It doesn’t necessarily mean there’s anything wrong with your baby or your milk supply.
Read on to learn more about cluster feeding and how to manage it.
Cluster feeding can be hard to identify because newborns rarely have a predictable eating or sleeping schedule.
Your baby may be cluster feeding if:
- they’re a few days or weeks old
- they’re showing their usual hunger signs or won’t stop crying until they’re fed
- they want to eat constantly or they eat very frequently for short sessions each time
- nothing else seems wrong and they’re content when eating
- they still have regular wet and dirty diapers
Cluster feeding is more common in the evenings.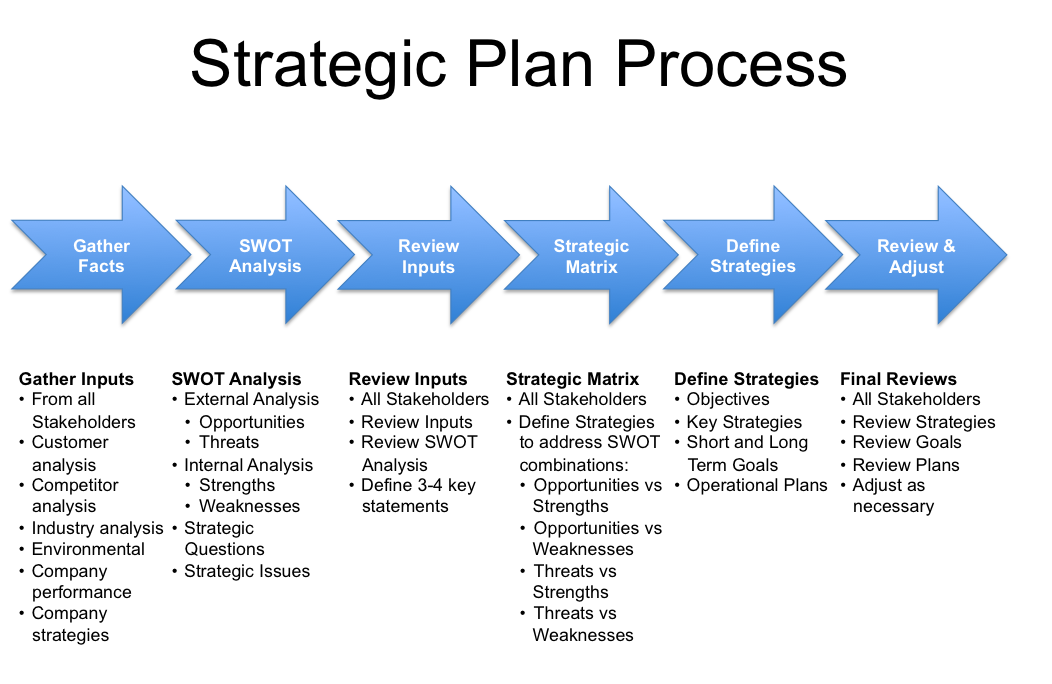 With an older infant, though, there may be several days in a row when they eat a lot more than usual throughout the entire day. This may be due to growth spurts or teething.
With an older infant, though, there may be several days in a row when they eat a lot more than usual throughout the entire day. This may be due to growth spurts or teething.
What’s a normal baby feeding schedule?
Every baby is different, but a typical feeding session for a baby that isn’t cluster feeding can range from 10 to 30 minutes. Experts advise to feed your newborn baby an average of at least 8 to 12 times in 24 hours. Your baby may show hunger signs and need to eat more frequently.
Frequent feeding may help:
- prevent jaundice
- promote healthy weight gain in babies
- mothers develop a milk supply
Cluster feeding vs. colic
If your baby is fussier than usual, you might wonder if they have colic. Colic is similar to cluster feeding in that it can come on suddenly and often occurs in the evening.
A baby with colic usually can’t be soothed with nursing or formula. However, a cluster feeding baby will be soothed during nursing sessions.
Colic is defined as at least three hours of crying for at least three days a week, at least three weeks in a row. It affects 10 to 40 percent of all babies worldwide. There’s no difference in risk between male or female babies, nor between breastfed or formula-fed babies.
Colic symptoms include:
- crying that sounds more like screaming
- face and body that appears tense or contorted
- crying at a predictable time each day, often in the evenings
- crying that peaks at six weeks and usually passes by 3 months old
Researchers don’t fully understand why babies cluster feed, but there are many unproven theories. Cluster feeding probably meets a combination of needs that your baby has at this developmental stage.
Heather Turgeon, MFT, a psychotherapist and author of The Happy Sleeper, says, “cluster feeding is likely a way for babies, who have maturing nervous systems, to regulate. It could also be a way to store up on food for the night.
“What we do know about breastfeeding is that it’s a supply and demand system. When little babies want to feed, that’s a good sign that we should let them, because trying to schedule or space feedings out doesn’t give that supply and demand system the right feedback.
“So while we can have theories about why they cluster feed, what matters is that we let them do it — that’s the way to establish and maintain mom’s milk supply.”
Cluster feeding can be exhausting and you may hear people stressing the importance of a schedule for baby, but cluster feeding is a normal part of the development of many babies.
Is cluster feeding a sign of low milk supply?
More frequent eating shouldn’t cause worry about your milk supply. A doctor can easily tell you if your baby is getting enough milk based on their weight gain.
Tracking a young baby’s wet diapers can also help you tell if they’re getting enough milk. Below are the average number of wet diapers per day, based on baby’s age:
| Age | Average wet diapers per day |
|---|---|
| Newborn | 1 to 2 |
| 4 to 5 days old | 6 to 8 |
| 1 to 2 months | 4 to 6 |
If you’re ever concerned about your baby’s eating, ask your pediatrician and meet with a lactation consultant. Babies who struggle to gain weight or seem frustrated while eating may not be getting enough milk.
Babies who struggle to gain weight or seem frustrated while eating may not be getting enough milk.
Other reasons for nighttime fussiness
Some babies just tend to get fussier in the evenings. Reasons may include:
- being overtired or overstimulated
- missing parents who’ve been at work or away all day
- needing to be burped if they’ve been eating a lot
Cluster feeding has both positive and negative effects.
Benefits
- Baby may sleep longer after cluster feeding.
- It may help to increase your milk supply.
- It may help babies emotionally and neurologically regulate.
- It can increase your skin-to-skin time with baby, which has benefits for both mom and baby.
Risks
- It can increase nipple soreness.
- It’s unpredictable.
- It can be exhausting, both physically and emotionally.
- It often takes time away from other family or household needs in the evening.
While cluster feeding is a normal, brief behavior, it can still be taxing on the whole family. Here are some tips for taking care of yourself, your family, and your baby during cluster feedings:
- Keep a large bottle of water and snacks near your nursing area to stay hydrated and nourished during cluster feeds.
- Set up a nursing area in front of the TV so you can watch something during cluster feedings. Or use the time to listen to audiobooks or podcasts. Keep chargers within reach.
- Change breastfeeding positions often so you don’t get sore.
- Use the downtime to call a friend. Since you’ll want to keep your hands free to hold and aid your baby, consider using earbuds.
- Sit on the couch or floor while you feed baby so you can read or play with older kids at the same time.
- Have a basket of special toys for older siblings that they only play with when the baby is nursing.
- Practice nursing your baby while they’re in a baby carrier so you can potentially walk around while they feed.
- Plan ahead. If baby usually starts cluster feeding around 7 p.m., plan to use the restroom, eat, and get comfortable before then.
- Hand off the baby to your partner or a close friend whenever you can to get a short break. This also allows for other people to have time with them.
- Talk with your partner about expectations and plan for how you’ll handle evening chores if the baby starts to cluster feed.
- Let friends help cook or do housework, or, if possible, consider hiring a housekeeper for the first few weeks postpartum.
Cluster feeding isn’t a sign that you need to supplement with formula. If you’re nursing and need a break, you or someone else can offer a bottle of breastmilk.
You’ll still need to pump at this time in order to keep up your milk supply at pace with the baby’s eating, however.
There are many tricks other than feeding you can try to soothe a fussy baby. Some babies may be soothed by the same method every time. For other babies, what worked yesterday, or even earlier in the same day, may no longer work. Feel free to experiment with these or other ideas:
Feel free to experiment with these or other ideas:
- Wrap baby in a swaddle to help recreate the experiences from the womb.
- Offer a pacifier.
- Hold baby as you slowly walk or rock.
- Dim the lights and reduce other stimuli, such as loud noises.
- Use white noise, either from a white noise machine or cell phone app, or from a fan, gently running water, or even a vacuum. You can also create your own white noise by holding your baby upright on your chest and humming in low tones.
- Hold them in different positions. They may be fussy because they’re uncomfortable or want a change of scenery.
- Sing peaceful songs, recite poems, or speak to baby in a soft, gentle voice.
It’s important to go to your baby’s recommended checkups or wellness visits so the doctor can keep track of growth and development. These visits are more frequent when your baby is first born, when tracking weight gain is vital.
Your doctor will tell you if they suspect your baby isn’t getting enough milk or if they aren’t gaining enough weight. More frequent feedings, fussiness, or breasts not feeling full don’t necessarily mean your baby isn’t getting enough milk.
More frequent feedings, fussiness, or breasts not feeling full don’t necessarily mean your baby isn’t getting enough milk.
Always call your pediatrician if your baby seems very sick, lethargic, or has trouble breathing.
Cluster feeding is normal baby behavior and can happen any time, though it’s most common with newborns and in the evenings. Researchers don’t totally understand why it happens, but it’s not a sign that there’s anything wrong.
You may need to reset your expectations for these periods but cluster feeding isn’t permanent and will pass eventually.
Breastfeeding in the first month: what to expect
Not sure how to establish lactation and increase milk production? If you need help, support, or just want to know what to expect, read our first month breastfeeding advice
Share this information
The first weeks of breastfeeding are a very stressful period. If at times you feel like you can't handle it, know that you are not alone. Feeding your baby all day long is completely natural and helps produce breast milk, but can be quite tiring at times. Be patient, think about yourself and remember: after the first month, when milk production stabilizes, it will become easier.
Feeding your baby all day long is completely natural and helps produce breast milk, but can be quite tiring at times. Be patient, think about yourself and remember: after the first month, when milk production stabilizes, it will become easier.
How often should a baby be breastfed?
Babies are born with a small stomach that grows rapidly with increasing milk production: in the first week it is no larger than an apricot, and after two weeks it is already the size of a large chicken egg. 1.2 Let the child eat as much as he wants and when he wants. This will help him quickly regain the weight lost after birth and grow and develop further.
“Be prepared to feed every two to three hours throughout the day. At night, the intervals between feedings can be longer: three to four or even five hours, says Cathy Garbin, a recognized international expert on breastfeeding. Some eat quickly and are satiated in 15 minutes, while others take an entire hour to feed. Do not compare your breastfeeding regimen with that of other mothers - it is very likely that there will be nothing in common between them.
Do not compare your breastfeeding regimen with that of other mothers - it is very likely that there will be nothing in common between them.
At each feed, give your baby a full meal from one breast and then offer a second one, but don't worry if the baby doesn't take it. When the baby is full, he lets go of his chest and at the same time looks relaxed and satisfied - so much so that he can immediately fall asleep. The next time you feed, start on the other breast. You can monitor the order of the mammary glands during feeding using a special application.
Why does the child always ask for a breast?
The first month is usually the hardest time to breastfeed. But do not think that because the baby is constantly hungry and asks for a breast almost every 45 minutes, then you do not have enough milk.
In the first month, the baby needs to eat frequently to start and stimulate the mother's milk production. It lays the foundation for a stable milk supply in the future. 3
3
In addition, we must not forget that the child needs almost constant contact with the mother. The bright light and noise of the surrounding world at first frighten the baby, and only by clinging to his mother, he can calm down.
Sarah, mother of three from the UK, confirms: “Crying is not always a sign of hunger. Sometimes my kids just wanted me to be around and begged for breasts to calm them down. Use a sling. Place the cradle next to the bed. Don't look at the clock. Take advantage of every opportunity to relax. Forget about cleaning. Let those around you take care of you. And not three days, but six weeks at least! Hug your baby, enjoy the comfort - and trust your body."
Do I need to feed my baby on a schedule?
Your baby is still too young for a strict daily routine, so
forget about breastfeeding schedules and focus on his needs.
“Volumes have been written about how to feed a baby on a schedule, but babies don't read or understand books,” Cathy says. - All children are different. Some people can eat on a schedule, but most can't. Most often, over time, the child develops his own schedule.
- All children are different. Some people can eat on a schedule, but most can't. Most often, over time, the child develops his own schedule.
Some mothers report that their babies are fine with scheduled feedings, but they are probably just the few babies who would eat every four hours anyway. Adults rarely eat and drink the same foods at the same time of day - so why do we expect this from toddlers?
Offer your baby the breast at the first sign of hunger. Crying is already the last stage, so be attentive to early signs: the baby licks his lips, opens his mouth, sucks his fist, turns his head with his mouth open - looking for the breast. 4
What is a "milk flush"?
At the beginning of each feed, a hungry baby actively sucks on the nipple,
thereby stimulating the milk flow reflex - the movement of milk through the milk ducts. 5
“Nipple stimulation triggers the release of the hormone oxytocin,” explains Cathy. “Oxytocin is distributed throughout the body and causes the muscles around the milk-producing glands to contract and the milk ducts to dilate. This stimulates the flow of milk.
If the flushing reflex fails, milk will not come out. This is a hormonal response, and under stress it may not work at all or work poorly. Therefore, it is so important that you feel comfortable and calm when feeding.
“Studies show that each mother has a different rhythm of hot flashes during one feed,” Kathy continues, “Oxytocin is a short-acting hormone, it breaks down in just 30-40 seconds after formation. Milk begins to flow, the baby eats, the effect of oxytocin ends, but then a new rush of milk occurs, the baby continues to suckle the breast, and this process is repeated cyclically. That is why, during feeding, the child periodically stops and rests - this is how nature intended.
The flow of milk may be accompanied by a strong sensation of movement or tingling in the chest, although 21% of mothers, according to surveys, do not feel anything at all. 5 Cathy explains: “Many women only feel the first rush of milk. If you do not feel hot flashes, do not worry: since the child eats normally, most likely, you simply do not understand that they are.
How do you know if a baby is getting enough milk?
Since it is impossible to track how much milk a baby eats while breastfeeding, mothers sometimes worry that the baby is malnourished. Trust your child and your body.
After a rush of milk, the baby usually begins to suckle more slowly. Some mothers clearly hear how the baby swallows, others do not notice it. But one way or another, the child himself will show when he is full - just watch carefully. Many babies make two or three approaches to the breast at one feeding. 6
“When a child has had enough, it is noticeable almost immediately: a kind of “milk intoxication” sets in. The baby is relaxed and makes it clear with his whole body that he is completely full, says Katie, “Diapers are another great way to assess whether the baby is getting enough milk. During this period, a breastfed baby should have at least five wet diapers a day and at least two portions of soft yellow stool, and often more. ”
From one month until weaning at six months of age, a baby's stool (if exclusively breastfed) should look the same every day: yellow, grainy, loose, and watery.
When is the child's birth weight restored?
Most newborns lose weight in the first few days of life. This is normal and should not be cause for concern. As a rule, weight is reduced by 5-7%, although some may lose up to 10%. One way or another, by 10–14 days, almost all newborns regain their birth weight. In the first three to four months, the minimum expected weight gain is an average of 150 grams per week. But one week the child may gain weight faster, and the next slower, so it is necessary that the attending physician monitor the health and growth of the baby constantly. 7.8
At the slightest doubt or signs of dehydration, such as
dark urine, no stool for more than 24 hours, retraction of the fontanel (soft spot on the head), yellowing of the skin, drowsiness, lethargy, lack of appetite (ability to four to six hours without feeding), you should immediately consult a doctor. 7
What is "cluster feeding"?
When a baby asks to breastfeed very often for several hours, this is called cluster feeding. 6 The peak often occurs in the evening between 18:00 and 22:00, just when many babies are especially restless and need close contact with their mother. Most often, mothers complain about this in the period from two to nine weeks after childbirth. This is perfectly normal and common behavior as long as the baby is otherwise healthy, eating well, gaining weight normally, and appears content throughout the day. 9
Cluster feeding can be caused by a sharp jump in the development of the body - during this period the baby especially needs love, comfort and a sense of security. The growing brain of a child is so excited that it can be difficult for him to turn off, or it just scares the baby. 9 If a child is overworked, it is often difficult for him or her to calm down on his own, and adult help is needed. And breastfeeding is the best way to calm the baby, because breast milk is not only food, but also pain reliever and a source of happiness hormones. 10
“Nobody told me about cluster feeding, so for the first 10 days I just went crazy with worry - I was sure that my milk was not enough for the baby,” recalls Camille, a mother from Australia, “It was a very difficult period . I was advised to pump and supplement until I finally contacted the Australian Breastfeeding Association. There they explained to me what was happening: it turned out that it was not about milk at all.
Remember, this is temporary. Try to prepare dinner for yourself in the afternoon, when the baby is fast asleep, so that in the evening, when he begins to often breastfeed, you have the opportunity to quickly warm up the food and have a snack. If you are not alone, arrange to carry and rock the baby in turns so that you have the opportunity to rest. If you have no one to turn to for help and you feel that your strength is leaving you, put the baby in the crib and rest for a few minutes, and then pick it up again.
Ask your partner, family and friends to help you with household chores, cooking and caring for older children if you have any. If possible, hire an au pair. Get as much rest as possible, eat well and drink plenty of water.
“My daughter slept a lot during the day, but from 23:00 to 5:00 the cluster feeding period began, which was very tiring,” recalls Jenal, a mother from the USA, “My husband tried his best to make life easier for me - washed, cleaned, cooked, changed diapers, let me sleep at every opportunity and never tired of assuring me that we were doing well.
If you are concerned about the frequency of breastfeeding, it is worth contacting a specialist. “Check with a lactation consultant or doctor to see if this is indicative of any problems,” recommends Cathy. “Resist the temptation to supplement your baby with formula (unless recommended by your doctor) until you find the cause. It may not be a matter of limited milk production at all - it may be that the child is inefficiently sucking it.
When will breastfeeding become easier?
This early stage is very special and does not last long. Although sometimes it seems that there will be no end to it, rest assured: it will get easier soon! By the end of the first month, breast milk production will stabilize, and the baby will become stronger and learn to suckle better. 2.3 Any problems with latch on by this time will most likely be resolved and the body will be able to produce milk more efficiently so inflammation and leakage of milk will begin to subside.
“The first four to six weeks are the hardest, but then things start to get better,” Cathy assures. It just needs to be experienced!”
The longer breastfeeding continues, the more benefits it brings, from saving on formula and improving sleep quality 11–13 to boosting your baby's immune system 14 and reducing your risk of certain cancers. 15
“When you feel like you're pushing yourself, try to go from feed to feed and day to day,” says Hannah, a UK mom. “I was sure I wouldn’t make it to eight weeks. And now I have been breastfeeding for almost 17 weeks, and I dare say it is very easy.”
Read the resource Breastfeeding Beyond the First Month: What to Expect
Literature
1 Naveed M et al. An autopsy study of relationship between perinatal stomach capacity and birth weight. Indian J Gastroenterol .1992;11(4):156-158. - Navid M. et al., Association between prenatal gastric volume and birth weight. Autopsy. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1992;11(4):156-158.
2 Neville MC et al. Studies in human lactation: milk volumes in lactating women during the onset of lactation and full lactation .Am J Clinl Nutr . 1988;48(6):1375-1386. at the beginning and at the peak of lactation." Am F Clean Nutr. 1988;48(6):1375-1386.
3 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. J Obstet , Gynecol , & Neonatal Nurs . 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
4 Australian Breastfeeding Feeding cues ; 2017 Sep [ cited 2018 Feb ]. - Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet], Feed Ready Signals; September 2017 [cited February 2018]
5 Kent JC et al. Response of breasts to different stimulation patterns of an electric breast pump. J Human Lact . 2003;19(2):179-186. - Kent J.S. et al., Breast Response to Different Types of Electric Breast Pump Stimulation. J Human Lact (Journal of the International Association of Lactation Consultants). 2003;19(2):179-186.
6) Kent JC et al . Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
7 Lawrence RA, Lawrence RM. Breastfeeding: A guide for the medical profession. 7th ed. Maryland Heights MO, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. 1128 p . - Lawrence R.A., Lawrence R.M., "Breastfeeding: A guide for healthcare professionals." Seventh edition. Publisher Maryland Heights , Missouri, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. P. 1128.
8 World Health Organization. [Internet]. Child growth standards; 2018 [cited 2018 Feb] - World Health Organization. [Internet]. Child Growth Standards 2018 [cited February 2018].
9 Australian Breastfeeding Association . [ Internet ]. Cluster feeding and fussing babies ; Dec 2017 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet], Cluster Feeding and Screaming Babies; December 2017 [cited February 2018].
10 Moberg KU, Prime DK. Oxytocin effects in mothers and infants during breastfeeding. Infant . 2013;9(6):201-206.- Moberg K, Prime DK, "Oxytocin effects on mother and child during breastfeeding". Infant. 2013;9(6):201-206.
11 U.S. Department of Health & Human Services [Internet]. Surgeon General Breastfeeding factsheet; 2011 Jan 20 [cited 2017 Feb] - Department of Health and Human Services [Internet], "Breastfeeding Facts from the Chief Medical Officer", Jan 20, 2011 [cited Feb 2017]
12 Kendall-Tackett K et al. The effect of feeding method on sleep duration, maternal well-being, and postpartum depression. clinical lactation. 2011;1;2(2):22-26. - Kendall-Tuckett, K. et al., "Influence of feeding pattern on sleep duration, maternal well-being and the development of postpartum depression." Clinical Lactation. 2011;2(2):22-26.
13 Brown A, Harries V. Infant sleep and night feeding patterns during later infancy: Association with breastfeeding frequency, daytime complementary food intake, and infant weight. Breast Med . 2015;10(5):246-252. - Brown A., Harris W., "Night feedings and infant sleep in the first year of life and their association with feeding frequency, daytime supplementation, and infant weight." Brest Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(5):246-252.
14 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl immunology. 2013;2(4). - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4):e3.
15 Li DP et al. Breastfeeding and ovarian cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev . 2014;15(12):4829-4837. - Lee D.P. et al., "Breastfeeding and the risk of ovarian cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies." Asia Pas J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(12):4829-4837.
The child began to breastfeed more often. What is cluster feeding?
This is the period in a baby's life when he begins to breastfeed more often. For example, if yesterday your child ate an average of once every two hours, and today he requires a breast every half an hour or an hour, we are talking about cluster or group feeding. This is a temporary change in the feeding regime, however, parents are unlikely to be happy with such changes and may think that they are doing something wrong. We hasten to reassure you: cluster feeding is normal.
This usually happens within the first 28 days of a baby's life. As David Hill, Fellow of the American Academy of Pediatrics, says, the first "attack" of cluster feeding usually occurs on the 10-12th day of life, and then repeats in the region of three months. But in general, cluster feedings are typical for the entire first half of a baby's life.
Most often, cluster feedings occur in the late afternoon, when the child is tired of external stimuli and wants to calm down and fall asleep. Cluster feedings often accompany growth and developmental spurts. Sometimes they can last all day.
The first weeks and months of a baby's life are a difficult time for him, because he is constantly growing and developing, accepting new conditions of life outside the womb, adapting to the outside world. To do this, he needs not only to get food regularly, but also to calm down, because this big world is such a complicated thing.
Sucking and being at the mother's breast is a natural need for the baby, so he uses cluster feedings not only to eat, but also to get close contact with the mother. So don't get mad at him, he really needs it. And do not listen to those who say that "that way he will make a dummy out of you." Won't. Listen to yourself and the child, you are doing everything right.
The good news is that there is evidence that this behavior of the child precedes a longer sleep (we are talking about four to five hours). Why, it's a whole chasm of uninterrupted sleep when you have a newborn!
Yes, indeed, cluster feedings can exhaust a mother. But, as the same Hill says, they are important for her, especially if they occur at the initial stage of motherhood. The fact is that by frequent application, the baby stimulates the production of milk, thus helping the mother to quickly establish full lactation.
Of course, the baby needs maternal care and warmth, skin-to-skin contact, but you should not forget about yourself during this exhausting period of group feeding! More precisely, it is strictly forbidden, otherwise you risk bringing yourself to emotional exhaustion. Here's what can be done.
Do not blame yourself and the child. He is all right, all babies have such days, and you are doing everything right - offering him what he needs most of all now.
Do not forget to drink and eat , because your body is now intensively establishing lactation, which means it consumes a large amount of energy. Eat well and don't limit yourself to kuro-buckwheat.
Sleep between feeds . Facebook and Instagram can wait. Especially if cluster feedings caught you at night, and the baby wakes up every hour. Yes, it will seem to you that it is easier not to sleep at all than to spend time on short sleep sessions, but this is not so.
Connect partner . Yes, you may think that this is rather pointless, because he does not have breasts with milk. But he can carry the baby in his arms while you drink tea or spend time in the shower - during this period it is important to give yourself a little respite.
Don't listen to the "experts" . You will definitely be advised to put the child down and "let him scream" or do something else so that "God forbid, spoil him." But you shouldn't do that. We now know more about children and their needs than ever before. So: cluster feedings will not spoil your baby. He really needs them. In any case, more than senseless motion sickness, attempts to distract and hiss are more necessary.
It is believed that one episode of grouped feedings should not exceed two days, and the application itself should not exceed an hour. If the baby “hangs” on the chest for an hour and this has been happening for two days, you need to contact a lactation consultant or a pediatrician you trust.
We asked Daria Utkina, a doula and mother-and-child care consultant, to talk about cluster feeding.
Not all babies go through this period, but most do. It seems to me that knowing in itself that this is a physiological norm, and not an epic fail in becoming a milk fairy, already gives a lot of peace of mind. Often women worry that the reason for cluster feedings is the notorious “not enough milk”, although the child has just enough of everything.
Speaking of support, it's very cool when there are people nearby who also know that cluster feeding is a variant of the norm and you don't have to fight with it. Because even a confident and informed mother will be disturbed by the constant background anxiety of relatives. And if this is the first baby and everything is still completely new, then any comments on the topic “something is not working out for you”, “something is wrong with the child” will fall into the most vulnerable point.
Evening time can also be planned in advance, taking into account the baby hanging on the chest. Arrange with a partner to come to the beginning of vigils, call a postpartum doula or a friend / mother / anyone to be around.
On the contrary, it helps some women to break the stereotype about crazy evenings at home, pack the baby in a sling where he can feed non-stop, and go out into the world.
Well, adjust expectations all the time. Cluster feedings become a problem when the idea sits in your head that a baby usually eats at least once an hour, or even every three hours. And when everything happens differently, it makes you reconsider your ideas not only about babies, but also about your life with them.
Many of my clients find it helpful to remind themselves of "one thing a day." Especially for those who are accustomed to work tirelessly and assumed that while the baby was sleeping and eating, it would be possible to continue almost in the same rhythm.
Plus, sometimes it happens that cluster feedings are just situations where a child for some reason (inefficient attachment, a short bridle, for example) has to be on the breast all the time to get the right amount of milk. In this case, it would be good to call a consultant on breastfeeding and find out what is the reason.
During cluster feedings, the mother has a huge responsibility, and she can feel overwhelmed, exhausted and disappointed. Obviously, dads can't offer to help feed their baby, but there are some important ways they can help moms.
- Get up with your mother. This is really important, she will not feel so lonely if the partner tries to cheer her up during feeding (and at the same time not fall asleep next to her).
- Bathe, walk, entertain the child (and also his brothers and sisters).