Pregnancy throwing up
Vomiting and morning sickness - NHS
Nausea and vomiting in pregnancy, often known as morning sickness, is very common in early pregnancy.
It can affect you at any time of the day or night or you may feel sick all day long.
Morning sickness is unpleasant, and can significantly affect your day-to-day life. But it usually clears up by weeks 16 to 20 of your pregnancy and does not put your baby at any increased risk.
There is a chance of developing a severe form of pregnancy sickness called hyperemesis gravidarum. This can be serious, and there's a chance you may not get enough fluids in your body (dehydration) or not get enough nutrients from your diet (malnourishment). You may need specialist treatment, sometimes in hospital.
Sometimes urinary tract infections (UTIs) can also cause nausea and vomiting. A UTI usually affects the bladder, but can spread to the kidneys.
Non-urgent advice: Call your midwife, GP or 111 if:
you're vomiting and:
- have very dark-coloured urine or have not had a pee in more than 8 hours
- are unable to keep food or fluids down for 24 hours
- feel severely weak, dizzy or faint when standing up
- have tummy (abdominal) pain
- have a high temperature
- vomit blood
- have lost weight
Treatments for morning sickness
Unfortunately, there's no hard and fast treatment that will work for everyone’s morning sickness. Every pregnancy will be different.
But there are some changes you can make to your diet and daily life to try to ease the symptoms.
If these do not work for you or you're having more severe symptoms, your doctor or midwife might recommend medicine.
Things you can try yourself
If your morning sickness is not too bad, your GP or midwife will initially recommend you try some lifestyle changes:
- get plenty of rest (tiredness can make nausea worse)
- avoid foods or smells that make you feel sick
- eat something like dry toast or a plain biscuit before you get out of bed
- eat small, frequent meals of plain foods that are high in carbohydrate and low in fat (such as bread, rice, crackers and pasta)
- eat cold foods rather than hot ones if the smell of hot meals makes you feel sick
- drink plenty of fluids, such as water (sipping them little and often may help prevent vomiting)
- eat foods or drinks containing ginger – there's some evidence ginger may help reduce nausea and vomiting (check with your pharmacist before taking ginger supplements during pregnancy)
- try acupressure – there's some evidence that putting pressure on your wrist, using a special band or bracelet on your forearm, may help relieve the symptoms
Find out more about vitamins and supplements in pregnancy
Anti-sickness medicine
If your nausea and vomiting is severe and does not improve after trying the above lifestyle changes, your GP may recommend a short-term course of an anti-sickness medicine, called an antiemetic, that's safe to use in pregnancy.
Often this will be a type of antihistamine, which are usually used to treat allergies but also work as medicines to stop sickness (antiemetic).
Antiemetics will usually be given as tablets for you to swallow.
But if you cannot keep these down, your doctor may suggest an injection or a type of medicine that's inserted into your bottom (suppository).
See your GP if you'd like to talk about getting anti-sickness medication.
Risk factors for morning sickness
It's thought hormonal changes in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy are probably one of the causes of morning sickness.
But you may be more at risk of it if:
- you're having twins or more
- you had severe sickness and vomiting in a previous pregnancy
- you tend to get motion sickness (for example, car sick)
- you have a history of migraine headaches
- morning sickness runs in the family
- you used to feel sick when taking contraceptives containing oestrogen
- it's your first pregnancy
- you're obese (your BMI is 30 or more)
- you're experiencing stress
Visit the pregnancy sickness support site for tips for you and your partner on dealing with morning sickness.
Find maternity services near you
Sign up for pregnancy emails
Sign up for Start4Life's weekly emails for expert advice, videos and tips on pregnancy, birth and beyond.
Video: how can I cope with morning sickness?
In this video, a midwife gives advice on how to deal with morning sickness during your pregnancy.
Media last reviewed: 25 January 2023
Media review due: 25 January 2026
Page last reviewed: 13 April 2021
Next review due: 13 April 2024
Severe vomiting in pregnancy - NHS
Sickness in pregnancy (sometimes called morning sickness) is common. Around 8 out of every 10 pregnant women feel sick (nausea), are sick (vomiting) or both during pregnancy. This does not just happen in the morning.
This does not just happen in the morning.
For most women, this improves or stops completely by around weeks 12 to 20, although for some women it can last longer.
Some pregnant women experience very bad nausea and vomiting. They might be sick many times a day and be unable to keep food or drink down, which can impact on their daily life.
This excessive nausea and vomiting is known as hyperemesis gravidarum (HG), and often needs hospital treatment.
Exactly how many pregnant women get HG is not known as some cases may go unreported, but it's thought to be around 1 to 3 in every 100.
If you are being sick frequently and cannot keep food down, tell your midwife or doctor, or contact the hospital as soon as possible. There is a risk you may become dehydrated, and your midwife or doctor can make sure you get the right treatment.
Symptoms of hyperemesis gravidarum
HG is much worse than the normal nausea and vomiting of pregnancy.
Signs and symptoms of HG include:
- prolonged and severe nausea and vomiting
- dehydration – symptoms include feeling thirsty, tired, dizzy or lightheaded, not peeing very much, and having dark yellow and strong-smelling pee
- weight loss
Unlike regular pregnancy sickness, HG may not get better by 16 to 20 weeks. It may not clear up completely until the baby is born, although some symptoms may improve at around 20 weeks.
See your GP or midwife if you have severe nausea and vomiting. Getting help early can help you avoid dehydration and weight loss.
There are other conditions that can cause nausea and vomiting, and your doctor will need to rule these out first.
See videos and written interviews of women talking about their experiences of hyperemesis gravidarum on the healthtalk website.
What causes hyperemesis gravidarum?
It's not known exactly what causes HG, or why some women get it and others do not. There is evidence that it is linked to the changing hormones in your body that occur during pregnancy.
There is some evidence that it runs in families, so if you have a mother or sister who has had HG in a pregnancy, you may be more likely to get it yourself.
If you have had HG in a previous pregnancy, you are more likely to get it in your next pregnancy than women who have never had it before, so it's worth planning in advance.
Treating hyperemesis gravidarum
There are medicines that can be used in pregnancy, including the first 12 weeks, to help improve the symptoms of HG. These include anti-sickness (anti-emetic) drugs, steroids, or a combination of these.
You may need to try different types of medicine until you find what works best for you.
You can visit the Bumps website to find out which medicines are safe to use in pregnancy.
If your nausea and vomiting cannot be controlled, you may need to be admitted to hospital. This is so doctors can assess your condition and give you the right treatment to protect the health of you and your baby.
Treatment can include intravenous fluids, which are given directly into a vein through a drip. If you have severe vomiting, the anti-sickness drugs may also need to be given into a vein or a muscle.
The charity Pregnancy Sickness Support has information and tips on coping with nausea and vomiting, including HG.
Will hyperemesis gravidarum harm my baby?
HG can make you feel very unwell, but it's unlikely to harm your baby if treated effectively.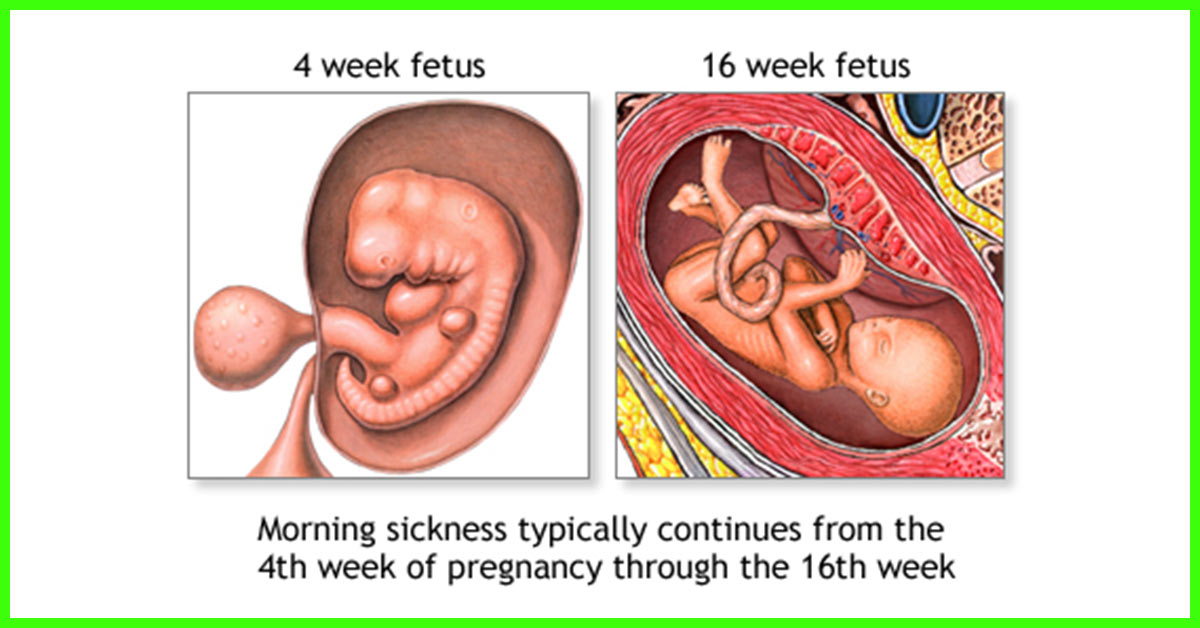
However, if it causes you to lose weight during pregnancy, there is an increased risk that your baby may be born smaller than expected (have a low birthweight).
How you might feel
The nausea and vomiting of HG can impact your life at a time when you were expecting to be enjoying pregnancy and looking forward to the birth of your baby.
It can affect you both emotionally and physically. The symptoms can be hard to cope with. Without treatment HG may also lead to further health complications, such as depression or tears in your oesophagus.
Severe sickness can be exhausting and stop you doing everyday tasks, such as going to work or even getting out of bed.
In addition to feeling very unwell and tired, you might also feel:
- anxious about going out or being too far from home in case you need to vomit
- isolated because you do not know anyone who understands what it's like to have HG
- confused as to why this is happening to you
- unsure about how to cope with the rest of the pregnancy if you continue to feel very ill
If you feel any of these, do not keep it to yourself. Talk to your midwife or doctor, and explain the impact HG is having on your life and how it is making you feel. You could also talk to a partner, family members and friends if you want to.
Talk to your midwife or doctor, and explain the impact HG is having on your life and how it is making you feel. You could also talk to a partner, family members and friends if you want to.
If you want to talk to someone who has been through HG, you can contact Pregnancy Sickness Support's help section. They have a support network across the UK and can put you in touch with someone who has had HG.
Bear in mind that HG is much worse than regular pregnancy sickness. It is not the result of anything you have or have not done, and you do need treatment and support.
Another pregnancy
If you have had HG before, it's likely you will get it again in another pregnancy.
If you decide on another pregnancy, it can help to plan ahead, such as arranging child care so you can get plenty of rest.
You could try doing things that helped last time.
Talk to your doctor about starting medicine early.
Blood clots and hyperemesis gravidarum
Because HG can cause dehydration, there's also an increased risk of having a blood clot (deep vein thrombosis), although this is rare.
If you are dehydrated and immobile, there is treatment that you can be given to prevent blood clots.
Read more about how to prevent deep vein thrombosis.
Pregnancy - from the first days
With the onset of pregnancy, a woman's body immediately begins to rebuild in work and prepare for bearing a baby. After all, a young mother has a journey of 40 weeks, when she will carry a baby in herself, and her body will create all the most favorable conditions for this, provide the baby not only with a small, cozy apartment, but also with nutrition and oxygen. A woman who has received a long-awaited pregnancy treats all changes in her body with special attention, listens to every new sensation!
And how should a woman feel at the very beginning of pregnancy?
The first sign of an "interesting" situation, of course, menstruation that did not start on time . Already on the first day of delay, you can do a urinary pregnancy test, with a high probability it will show the true result. More informative and important for an obstetrician-gynecologist will be the value of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin, determined by the blood of a pregnant woman, this is a hormone that is produced by the future placenta, it appears in the woman's body from the first hours of pregnancy and actively increases in the future. By the amount of this hormone, the doctor will judge the gestational age, the absence of pathological conditions and the developmental norms of this pregnancy and will guide you on the most optimal terms for ultrasound examination.
Already on the first day of delay, you can do a urinary pregnancy test, with a high probability it will show the true result. More informative and important for an obstetrician-gynecologist will be the value of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin, determined by the blood of a pregnant woman, this is a hormone that is produced by the future placenta, it appears in the woman's body from the first hours of pregnancy and actively increases in the future. By the amount of this hormone, the doctor will judge the gestational age, the absence of pathological conditions and the developmental norms of this pregnancy and will guide you on the most optimal terms for ultrasound examination.
Breast engorgement and enlargement. Gradually appearing symptom. If a woman has examined her breasts during the last year, was examined by a mammologist, underwent an ultrasound examination of the mammary glands, and received a conclusion from the doctor - she is healthy, there is nothing to worry about! The mammary glands enter a new phase of development and prepare for the upcoming feeding of the child. If the mammary glands have not been examined for more than a year, it is recommended to undergo an ultrasound scan to exclude possible pathology, especially since the obstetrician-gynecologist will need this examination to register for pregnancy.
If the mammary glands have not been examined for more than a year, it is recommended to undergo an ultrasound scan to exclude possible pathology, especially since the obstetrician-gynecologist will need this examination to register for pregnancy.
Drawing pains in the lower abdomen. May be normal only if they occur no more than 1-2 times a day, and go away on their own after a few minutes. In other cases, pain in the lower abdomen, of course, is not an indicator of a pathological or complicated course of pregnancy, but it is still necessary to consult a doctor. The gynecologist will determine the cause of the pain and give recommendations on the regimen, permissible loads and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
Nausea and vomiting. Not the most pleasant, but almost inevitable signs of pregnancy. If nausea occurs predominantly in the morning, try to fight it with food. Before going to bed, prepare for yourself a piece of an apple or a banana, you can have a cracker or a biscuit cookie, even a cracker will do. In the morning after waking up, without getting out of bed, enjoy the "piece" waiting for you, very often this is what saves you from an attack of morning sickness. A small spoonful of honey helps. Drink more liquids, mineral water, juices, tea. Ginger tea fights toxicosis well. Eat small meals. At least 5-7 times a day. Food should not be fatty or spicy. Avoid stuffy rooms. Walk outdoors more. Daytime naps are recommended. If vomiting occurs, especially more than 1-2 times a day, you should consult a doctor. Additional examination and more serious treatment may be required.
In the morning after waking up, without getting out of bed, enjoy the "piece" waiting for you, very often this is what saves you from an attack of morning sickness. A small spoonful of honey helps. Drink more liquids, mineral water, juices, tea. Ginger tea fights toxicosis well. Eat small meals. At least 5-7 times a day. Food should not be fatty or spicy. Avoid stuffy rooms. Walk outdoors more. Daytime naps are recommended. If vomiting occurs, especially more than 1-2 times a day, you should consult a doctor. Additional examination and more serious treatment may be required.
Discharge from the genital tract becomes more profuse during pregnancy. Normally, this is a clear, odorless mucous discharge. If there is “something wrong” in the discharge, it is better to consult a doctor. They will take a swab from you to determine the degree of purity of the vagina, see why the discharge has changed its character, and whether it needs treatment. Since during pregnancy the woman's body is in an immunosuppressive state, that is, the mother's immunity is reduced, inflammatory changes in the vagina may occur, which during pregnancy is very important to treat in a timely manner.
If you are concerned about bloody or brown discharge from the genital tract, you should not panic, but you must definitely consult a doctor on the same day. This may be one of the signs of a threatened abortion, so you should not self-medicate or resort to expectant tactics. It is necessary to establish the cause of the discharge and start treatment on time.
Drowsiness, periodic lethargy, increased fatigue, mood swings are also normal signs of a developing pregnancy.
During pregnancy, a woman should enjoy her position, and if something bothers you, even if it looks like a trifle to someone, it is better to consult a doctor. They will examine you, conduct the necessary examinations, explain how to behave and what medications to take. Pregnancy is not at all the time when you need to be independent. Always be in touch with your doctor, then nothing will go out of your attention. The pregnancy will go well, and after 40 weeks, your baby will thank you for your care of him with his birth!
Be healthy!
How long does pregnancy last: signs, terms and stages of fetal development
https://ria. ru/20210125/beremennost-1594527284.html
ru/20210125/beremennost-1594527284.html
How long does pregnancy last: signs, terms and stages of fetal development
How long does pregnancy last: signs, terms and stages of fetal development - RIA Novosti, 01/25/2021
How long does pregnancy last: signs, terms and stages of fetal development
Pregnancy is the period when the formation and development of the fetus in the mother's body. About signs and duration - in the material of RIA Novosti. RIA Novosti, 01/25/2021
2021-01-25T18: 38
2021-01-25T18: 38
2021-01-25T18: 38
Health-Society
Pregnancy
Women
/HTML/Head/Meta [@name = Name = Name = Name = Name = Name = Name. 'og:title']/@content
/html/head/meta[@name='og:description']/@content
https://cdnn21.img.ria.ru/images/156254/97/
MOSCOW, January 25 - RIA Novosti. Pregnancy is a period when the formation and development of the fetus in the mother's body. About the signs and duration - in the material of RIA Novosti. Signs of pregnancy After conception, anatomical, physiological and hormonal changes occur in the body of a woman. There are a number of signals that may indicate pregnancy. Among the presumptive signs can be distinguished: - vomiting and nausea; - drowsiness; - aversion to certain smells; - frequent mood swings; - tearfulness; - dizziness. Also, a woman may experience frequent urination, an increase in the mammary glands. The most obvious indicator is the cessation of menstruation. Most often, pharmacy tests are used to determine pregnancy. Although they are reliable, they do not provide complete information. “A pregnancy test is one of the likely signs,” added Svetlana Ivanova. - He can tell that the patient is pregnant, but at the same time, he will not show whether this is a uterine or ectopic pregnancy. This can only be determined by ultrasound.” How many weeks does a woman's pregnancy last? The expert answered the question about the pregnancy rate in weeks. According to her, pregnancy lasts 40 weeks, that is, ten obstetric months or nine calendar.
Signs of pregnancy After conception, anatomical, physiological and hormonal changes occur in the body of a woman. There are a number of signals that may indicate pregnancy. Among the presumptive signs can be distinguished: - vomiting and nausea; - drowsiness; - aversion to certain smells; - frequent mood swings; - tearfulness; - dizziness. Also, a woman may experience frequent urination, an increase in the mammary glands. The most obvious indicator is the cessation of menstruation. Most often, pharmacy tests are used to determine pregnancy. Although they are reliable, they do not provide complete information. “A pregnancy test is one of the likely signs,” added Svetlana Ivanova. - He can tell that the patient is pregnant, but at the same time, he will not show whether this is a uterine or ectopic pregnancy. This can only be determined by ultrasound.” How many weeks does a woman's pregnancy last? The expert answered the question about the pregnancy rate in weeks. According to her, pregnancy lasts 40 weeks, that is, ten obstetric months or nine calendar. Embryonic periodFrom the moment of fertilization, the embryonic period lasts until the tenth week of the obstetric period. At this time, the formation and development of the fetus in the mother's body begins. In particular, germ layers are formed in the embryo first, then tissues, organs and the placenta. During this period, the fetus increases to three centimeters, but it still does not resemble a baby, but only over time acquires the appropriate features. The fetal period The fetal period lasts from the 11th week of the obstetric period and ends with childbirth. At this time, the active growth of the fetus occurs, its proportions change, all organ systems begin to develop. In addition, the fetus begins to move in the womb. Physiological changes in the mother-fetus system Since the onset of pregnancy, two closely interconnected systems are formed. Firstly, maternal, which provides the fetus with everything necessary, and, secondly, the functional system of the fetus. Significant changes take place in the mother's body.
Embryonic periodFrom the moment of fertilization, the embryonic period lasts until the tenth week of the obstetric period. At this time, the formation and development of the fetus in the mother's body begins. In particular, germ layers are formed in the embryo first, then tissues, organs and the placenta. During this period, the fetus increases to three centimeters, but it still does not resemble a baby, but only over time acquires the appropriate features. The fetal period The fetal period lasts from the 11th week of the obstetric period and ends with childbirth. At this time, the active growth of the fetus occurs, its proportions change, all organ systems begin to develop. In addition, the fetus begins to move in the womb. Physiological changes in the mother-fetus system Since the onset of pregnancy, two closely interconnected systems are formed. Firstly, maternal, which provides the fetus with everything necessary, and, secondly, the functional system of the fetus. Significant changes take place in the mother's body. During pregnancy, a woman needs to receive vitamins, as the need for them increases. Therefore, the body needs one and a half times more zinc, iodine, vitamins B6 and B12. Lack of vitamins can affect the duration of pregnancy.
During pregnancy, a woman needs to receive vitamins, as the need for them increases. Therefore, the body needs one and a half times more zinc, iodine, vitamins B6 and B12. Lack of vitamins can affect the duration of pregnancy.
2021
RIA Novosti
1
5
4.7
9000
7 495 645-6601
FSUE MIA "Today"
https: // xn- xn- -c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn--p1ai/awards/
News
en-RU
https://ria.ru/docs/about/copyright.html
https://xn--c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn--p1ai /
RIA Novosti
1
5
4.7
96
7 495 645-6601
FSUE MIA "Russia Today"
https: //xn--c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn-p1ai/Awards/
1920 1920 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000
true
1920
1440
true
https://cdnn21.img.ria.ru/images/156254/97/1562549717_169:0:2900:2048_1920x0_80_0_0_15b447eb01248969392bfdc3b7477518.![]() jpg
jpg
1920
1920
true
RIA Novosti
1
5
4.7
9000 9000
7 495 645-6601
FSUE MIA Russia Today
https: //xn--c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn- P1AI/Awards/
RIA Novosti
1
5
4.7
9000
7 495 645-6601
FSUI MIA Russia Today
https :// xn--c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn--p1ai/awards/
health - society, pregnancy, women
Health - society, pregnancy, women
MOSCOW, January 25 - RIA Novosti . Pregnancy is a period when the formation and development of the fetus in the mother's body. About signs and duration - in the material of RIA Novosti.
Signs of pregnancy
After conception, anatomical, physiological and hormonal changes occur in a woman's body. There are a number of signals that may indicate pregnancy. Among the presumptive signs can be identified:
30 December 2020, 15:04
Pregnancy test: when and how to do it to get the correct result
- vomiting and nausea;
- drowsiness;
- aversion to certain smells;
- frequent mood swings;
- tearfulness;
- dizziness.![]()
Also, a woman may experience frequent urination, enlargement of the mammary glands. The most obvious indicator is the cessation of menstruation.
“Probable signs include an increase in the uterus,” Svetlana Ivanova, a teacher of obstetrics and gynecology of the highest category, told RIA Novosti. - When the doctor examines the patient, he can see the blueness of the vaginal cervix and the vagina itself. In general, the size of the uterus, shape and consistency changes.
Most often, pharmacy tests are used to determine pregnancy. Although they are reliable, they do not provide complete information.
“A pregnancy test is one of the likely signs,” added Svetlana Ivanova. - He can tell that the patient is pregnant, but at the same time, he will not show whether this is a uterine or ectopic pregnancy. This can only be determined by ultrasound.
July 3, 2020, 02:53
The gynecologist named the ideal age for the birth of the first child
How many weeks does a woman's pregnancy last
The expert answered the question about the pregnancy rate in weeks. According to her, the pregnancy lasts 40 weeks, that is, ten obstetric months or nine calendar months.
According to her, the pregnancy lasts 40 weeks, that is, ten obstetric months or nine calendar months.
“In general, her term is 280 days, counting from the first day of the last menstruation,” added Svetlana Ivanova. - It is believed that timely delivery occurs from the 37th week to the 42nd. Childbirth before 37 weeks is considered premature, after the 42nd week - belated. Both are deviations from the norm.”
Embryonic period
From the moment of fertilization, the embryonic period lasts until the tenth week of the obstetric period. At this time, the formation and development of the fetus in the mother's body begins. In particular, germ layers are formed in the embryo first, then tissues, organs and the placenta. During this period, the fetus increases to three centimeters, but it still does not resemble a baby, but only over time acquires the appropriate features.
January 19, 2021, 20:07
What you need to take with you to the hospital for the child and mother: a list for 2021
Fetal period
The fetal period starts from the 11th week of the obstetric period and ends with childbirth. At this time, the active growth of the fetus occurs, its proportions change, all organ systems begin to develop. In addition, the fetus begins to move in the womb.
At this time, the active growth of the fetus occurs, its proportions change, all organ systems begin to develop. In addition, the fetus begins to move in the womb.
Physiological changes in the mother-fetus system
From the moment of pregnancy, two closely interconnected systems are formed. Firstly, maternal, which provides the fetus with everything necessary, and, secondly, the functional system of the fetus. Significant changes take place in the mother's body.
“The level of progesterone, the main hormone responsible for gestation, increases, while estrogen decreases,” the expert explains. - They are responsible for the tone of the uterus. If there are too many hormones, a miscarriage may occur. During pregnancy, the heart, as well as the kidneys, work with increased stress. They excrete the urine of the mother and fetus. The thyroid and parathyroid glands increase in size, calcium production is disrupted, so pregnant women often experience brittle nails, hair loss, and teeth can crumble.