Pregnancy stuck in fallopian tube
Ectopic pregnancy - NHS
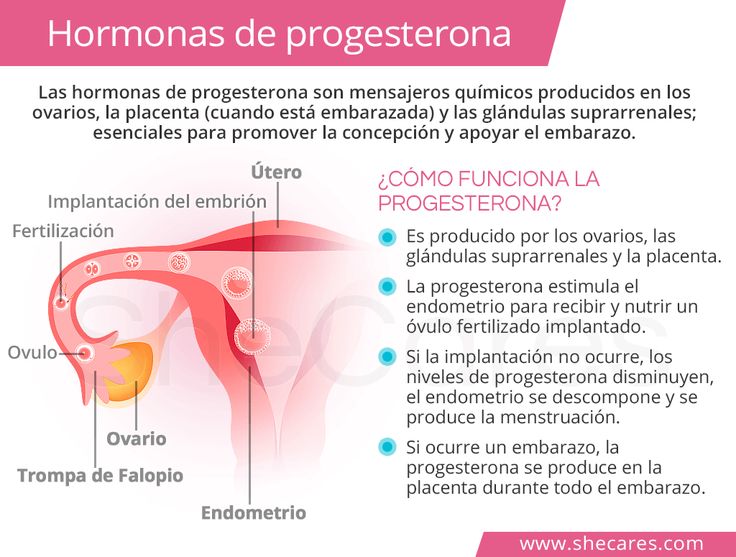
An ectopic pregnancy is when a fertilised egg implants itself outside of the womb, usually in one of the fallopian tubes.
The fallopian tubes are the tubes connecting the ovaries to the womb. If an egg gets stuck in them, it won't develop into a baby and your health may be at risk if the pregnancy continues.
Unfortunately, it's not possible to save the pregnancy. It usually has to be removed using medicine or an operation.
In the UK, around 1 in every 90 pregnancies is ectopic. This is around 11,000 pregnancies a year.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy doesn't always cause symptoms and may only be detected during a routine pregnancy scan.
If you do have symptoms, they tend to develop between the 4th and 12th week of pregnancy.
Symptoms can include a combination of:
- a missed period and other signs of pregnancy
- tummy pain low down on one side
- vaginal bleeding or a brown watery discharge
- pain in the tip of your shoulder
- discomfort when peeing or pooing
But these symptoms aren't necessarily a sign of a serious problem. They can sometimes be caused by other problems, such as a stomach bug.
Read more about the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy.
When to get medical advice
Contact your GP or call NHS 111 if you have a combination of any of the above symptoms and you might be pregnant – even if you haven't had a positive pregnancy test.
An ectopic pregnancy can be serious, so it's important to get advice right away.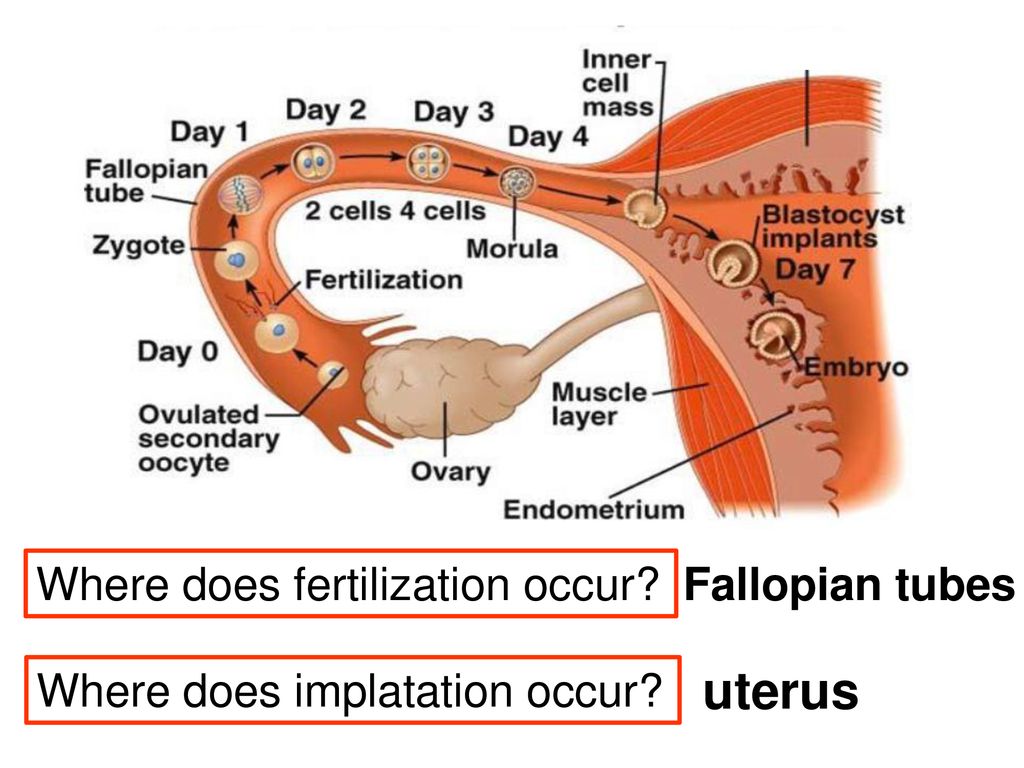
Your GP will ask about your symptoms and you'll usually need to do a pregnancy test to determine if you could have an ectopic pregnancy.
You may be referred to a specialist early pregnancy clinic for further assessment, where an ultrasound scan and blood tests may be carried out to confirm the diagnosis.
Read more about ectopic pregnancy tests.
When to get emergency help
Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest accident and emergency (A&E) department immediately if you experience a combination of:
- a sharp, sudden and intense pain in your tummy
- feeling very dizzy or fainting
- feeling sick
- looking very pale
These symptoms could mean that your fallopian tube has split open (ruptured). This is very serious and surgery to repair the fallopian tube needs to be carried out as soon as possible.
This is very serious and surgery to repair the fallopian tube needs to be carried out as soon as possible.
A rupture can be life threatening, but fortunately they're uncommon and treatable, if dealt with quickly. Deaths from ruptures are extremely rare in the UK.
How an ectopic pregnancy is treated
There are 3 main treatments for an ectopic pregnancy:
- expectant management – you're carefully monitored and 1 of the treatments below is used if the fertilised egg doesn't dissolve by itself
- medicine – an injection of a powerful medicine called methotrexate is used to stop the pregnancy growing
- surgery – keyhole surgery (laparoscopy) is performed under general anaesthetic to remove the fertilised egg, usually along with the affected fallopian tube
You'll be told about the benefits and risks of each option. In many cases, a particular treatment will be recommended based on your symptoms and the results of the tests you have.
In many cases, a particular treatment will be recommended based on your symptoms and the results of the tests you have.
Some treatments may reduce your chances of being able to conceive naturally in the future, although most women will still be able to get pregnant. Talk to your doctor about this.
Read more about treating an ectopic pregnancy.
Help and support after an ectopic pregnancy
Losing a pregnancy can be devastating, and many women feel the same sense of grief as if they had lost a family member or partner.
It's not uncommon for these feelings to last several months, although they usually improve with time. Make sure you give yourself and your partner time to grieve.
If you or your partner are struggling to come to terms with your loss, you may benefit from professional support or counselling. Speak to your GP about this.
Speak to your GP about this.
Support groups for people who have been affected by loss of a pregnancy can also help.
These include:
- The Ectopic Pregnancy Trust
- Ectopic Pregnancy Foundation
- Miscarriage Association
- Cruse Bereavement Care
Read more about dealing with loss and find bereavement support services in your area.
Trying for another baby
You may want to try for another baby when you and your partner feel physically and emotionally ready.
You'll probably be advised to wait until you've had at least 2 periods after treatment before trying again to allow yourself to recover.
If you were treated with methotrexate, it's usually recommended that you wait at least 3 months because the medicine could harm your baby if you become pregnant during this time.
Most women who have had an ectopic pregnancy will be able to get pregnant again, even if they've had a fallopian tube removed. Occasionally, it may be necessary to use fertility treatment such as IVF.
The chances of having another ectopic pregnancy are higher if you've had one before, but the risk is still small.
If you do become pregnant again, it's a good idea to let your GP know as soon as possible so early scans can be carried out to check everything is OK.
What can cause an ectopic pregnancy?
In many cases, it's not clear why a woman has an ectopic pregnancy. Sometimes it happens when there's a problem with the fallopian tubes, such as them being narrow or blocked.
The following are all associated with an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy:
- pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) – inflammation of the female reproductive system, usually caused by a sexually transmitted infection (STI)
- previous ectopic pregnancy – the risk of having another ectopic pregnancy is around 10%
- previous surgery on your fallopian tubes – such as an unsuccessful female sterilisation procedure
- fertility treatment, such as IVF – taking medicine to stimulate ovulation (the release of an egg) can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy
- becoming pregnant while using an intrauterine device (IUD) or intrauterine system (IUS) for contraception – it's rare to get pregnant while using these, but if you do you're more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy
- smoking
- increasing age – the risk is highest for pregnant women aged over 35
You can't always prevent an ectopic pregnancy, but you can reduce your risk by using a condom when not trying for a baby to protect yourself against STIs, and by stopping smoking if you smoke.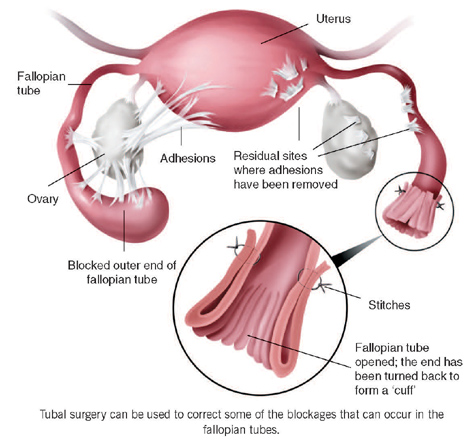
Page last reviewed: 23 August 2022
Next review due: 23 August 2025
Ectopic (Extrauterine) Pregnancy
Series Ectopic Pregnancy
Written by Shishira Sreenivas
What Is Ectopic Pregnancy?
Usually, a fertilized egg attaches itself to the lining in your uterus. But with an ectopic pregnancy (also called extrauterine pregnancy), the fertilized egg grows outside your uterus. This can include other areas like a fallopian tube, the ovaries, in your belly, or the lower part of your cervix, which is above the vagina. In more than 90% of cases, the egg attaches itself in a fallopian tube. This is called a tubal pregnancy.
Rates are hard to determine, but one study suggests that about 1 in 50 pregnancies in the U.S. are ectopic. As the fertilized egg grows, it can burst (rupture) and can cause life-threatening bleeding. If this happens, you will need medical care right away. If you don’t treat it, it can be deadly. In fact, ectopic pregnancies are the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the first trimester.
It’s important to note that the fertilized egg in an ectopic pregnancy is not “viable.” That means it’s impossible for the egg to survive and grow into a baby that can survive in or outside your body. It will always result in a pregnancy loss. That’s because the egg can’t get the blood supply and support it needs to grow outside of the uterus.
Ectopic Pregnancy Signs and Symptoms
Most of the time, an ectopic pregnancy happens within the first few weeks of pregnancy. You might not even know that you're pregnant and may not notice any problems.
Early signs of an ectopic pregnancy include:
- Light vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain
- Upset stomach and vomiting
- Sharp abdominal cramps
- Pain on one side of your body
- Dizziness or weakness
- Pain in your shoulder, neck, or rectum
An ectopic pregnancy can cause your fallopian tube to burst or rupture. Emergency symptoms include major pain, with or without severe bleeding.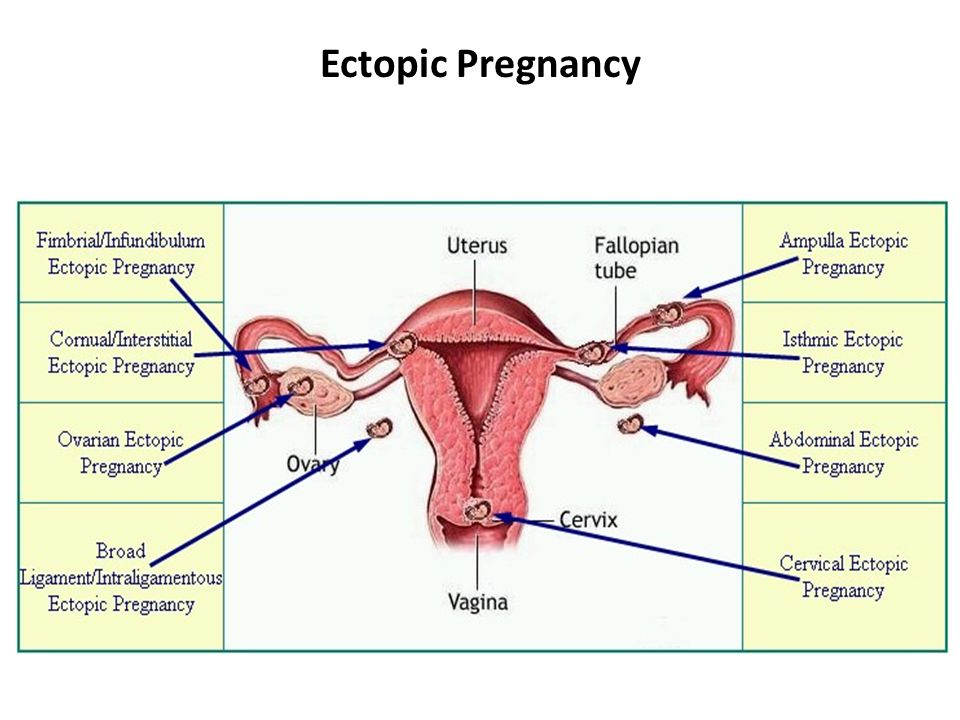 Call your doctor right away if you have heavy vaginal bleeding with lightheadedness, fainting, or shoulder pain, or if you have severe belly pain, especially on one side.
Call your doctor right away if you have heavy vaginal bleeding with lightheadedness, fainting, or shoulder pain, or if you have severe belly pain, especially on one side.
You might need to call 911 or head to the nearest hospital to have it treated right away.
Ectopic Pregnancy Causes and Risk Factors
You may never know why you have an ectopic pregnancy. One cause could be a damaged fallopian tube. It could keep the fertilized egg from getting into your uterus.
You’re more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy if you:
- Have pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Smoke cigarettes
- Are older than 35
- Have a sexually transmitted infection
- Have scarring from pelvic surgery
- Had a previous ectopic pregnancy
- Tried to have tubal ligation (tubes tied) or tubal ligation reversal
- Use fertility drugs
- Had fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF)
It could also happen if you become pregnant while you have an intrauterine device (IUD) for birth control.
Ectopic Pregnancy Complications
During an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg is wrapped in a structure that can grow for several weeks outside your uterus. But the structure usually bursts between 6 and 16 weeks. This can cause severe bleeding. If the bleeding isn’t stopped, your body might start to shut down due to the blood loss (hemorrhagic shock), and the odds of dying from it increases. If it’s treated before it bursts, it rarely results in death.
If the structure does burst, it may damage the fallopian tube it was attached to. Your doctor might remove the fallopian tube during the surgery. But you have two fallopian tubes. If your other fallopian tube is healthy, you should still be able to get pregnant. But if your other fallopian tube is damaged or not there, you may have fertility issues. In this case, talk to your doctor about other ways to get pregnant, like IVF (in vitro fertilization).
Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosis
Your doctor will probably do tests that include a pregnancy test and a pelvic exam. They might give you an ultrasound to look at your uterus and fallopian tubes.
They might give you an ultrasound to look at your uterus and fallopian tubes.
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
Because a fertilized egg can’t survive outside a uterus, your doctor will need to take it out, so you don’t have serious health problems. They’ll use one of two methods: medication or surgery.
Medication. If your fallopian tube hasn’t ruptured and your pregnancy isn’t far along, your doctor can give you a shot of methotrexate (Trexall). You only need one dose of the injection. It stops the fertilized egg from growing. Your body will absorb the egg in about 4-6 weeks. With this treatment, there’s no need to remove the fallopian tube.
Before you can take methotrexate, your doctor will need to run a few blood tests to measure your hCG levels (human chorionic gonadotropin). It’s the hormone your body produces when it detects a pregnancy. You won’t be able to take methotrexate if you’re breastfeeding or have certain health problems.
Once you get the shot, the doctor will check your hCG levels during follow-up appointments.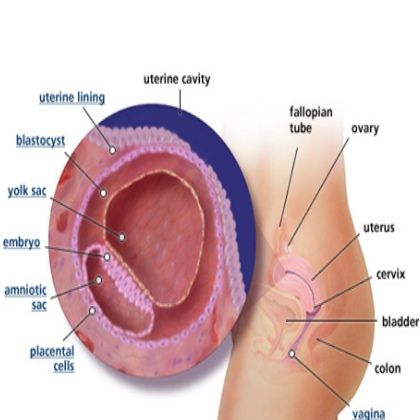 If your levels don’t drop after the first dose, you might need a second dose of the same medication. You’ll need to follow up until your blood no longer has hCG.
If your levels don’t drop after the first dose, you might need a second dose of the same medication. You’ll need to follow up until your blood no longer has hCG.
It’s important to note that taking methotrexate is not the same as having a medical abortion, as you could get if you had a “viable” pregnancy in which the fertilized egg attaches inside the uterus. For a medical abortion, you need a combination of two prescription drugs: mifepristone and misoprostol.
The methotrexate that you take during an ectopic pregnancy before the egg bursts is medically necessary. It can lower your risk of dying or other serious complications.
Surgery. In other cases, you’ll need surgery. The most common is laparoscopy. Your doctor will make very small cuts in your lower belly and insert a thin, flexible tube called a laparoscope to remove the ectopic pregnancy. If your fallopian tube is damaged, they may have to remove it as well. If you’re bleeding a lot or your doctor suspects that your fallopian tube is ruptured, you might need emergency surgery with a larger cut. This is called a laparotomy.
This is called a laparotomy.
Surgery side effects can include:
- Pain
- Fatigue
- Bleeding
- Infection
Whether you take methotrexate or have surgery, you may feel tired for a few weeks and have some discomfort in your belly. You may continue to have pregnancy-like symptoms for a bit. It might take a few period cycles before you feel back to normal.
After an Ectopic Pregnancy
It might be hard for you to have a typical pregnancy afterward. Consider talking to a fertility specialist, especially if you had a fallopian tube removed.
And talk to your doctor about how long to wait before trying again. Some experts suggest giving yourself at least 3 months so your body has time to heal.
An ectopic pregnancy raises your risk of having another one. If you think you’re having another pregnancy, be mindful of the changes in your body. Check with your doctor, and they can confirm it and take the necessary steps.
An ectopic pregnancy can take a toll on your mental health, too.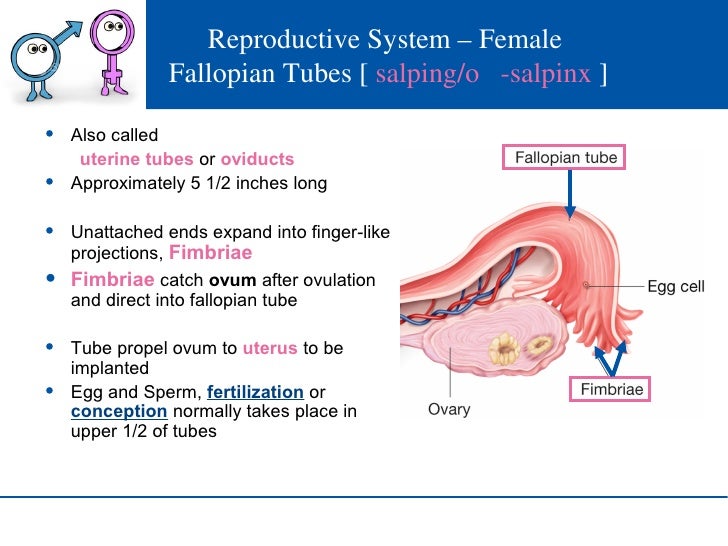 Don’t hesitate to reach out to mental health experts like a licensed counselor or therapist.
Don’t hesitate to reach out to mental health experts like a licensed counselor or therapist.
There’s no way to prevent an ectopic pregnancy. But you can lower your odds with certain lifestyle choices.
You can:
- Use a condom when you have sex. This can lower your risk for PID and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Quit smoking.
- Avoid using a vaginal douche. Studies show that using a douche can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Next In Ectopic Pregnancy Series:
SymptomsEctopic pregnancy - Family clinic
24 July 2016 Gynecology
This is the settling and development of the fetal egg outside the uterus. It poses a great danger to the life of a pregnant woman. A fertilized egg can graft on the ovaries, peritoneum, omentum and other abdominal organs, but most often in the tubes (99%).
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
Unfortunately, this pathology is quite common.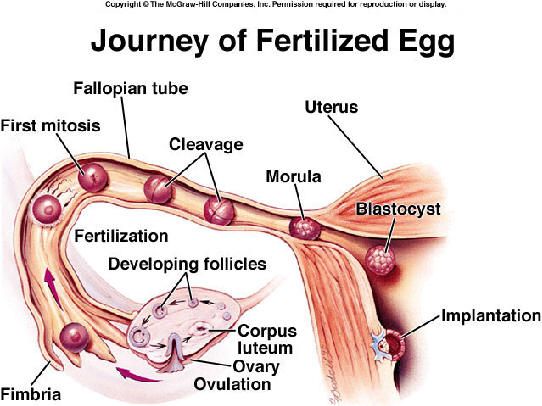 During the operation, the couple had to take the fetal egg from anywhere: from the fallopian tubes, ovaries, even from the abdominal cavity. But more often than others, there is still a tubal pregnancy. Why does the attachment of a fertilized egg occur outside the uterus? What makes it go astray and begin to develop in an unintended place? As a rule, the fallopian tubes are to blame, unable to perform their functions. nine0003
During the operation, the couple had to take the fetal egg from anywhere: from the fallopian tubes, ovaries, even from the abdominal cavity. But more often than others, there is still a tubal pregnancy. Why does the attachment of a fertilized egg occur outside the uterus? What makes it go astray and begin to develop in an unintended place? As a rule, the fallopian tubes are to blame, unable to perform their functions. nine0003
Clinical experience shows that ectopic pregnancy is almost always preceded by inflammatory or infectious diseases of the genitals, abortion, difficult childbirth, complicated by the inflammatory process. In this case, the mucous membrane of the fallopian tubes swells, its folds stick together, the tubes are deformed and lose their ability to contract normally. Infantilism also predisposes to ectopic pregnancy.
With this disease, the tubes are excessively elongated, tortuous, their lumen is narrowed, they contract weakly.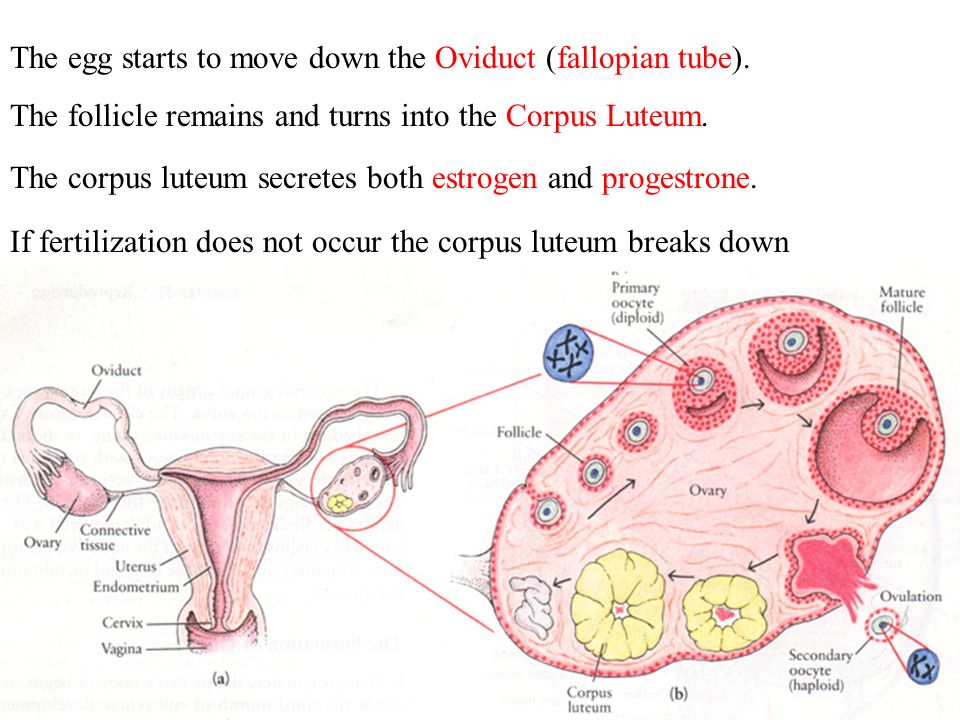 A healthy tube must contract actively in order to move the egg into the uterus. Moreover, this must be done within strictly defined deadlines, otherwise delay is fraught with disaster. After all, a fertilized egg develops and at a certain stage, villi appear in it, which need to gain a foothold and begin to receive a stable blood supply. If by this time the fetal egg has not been delivered to the uterus, it attaches anywhere, to the wall of the fallopian tube, for example, and begins to grow, unaware that this is the most inappropriate place for the development of the fetus. nine0003
A healthy tube must contract actively in order to move the egg into the uterus. Moreover, this must be done within strictly defined deadlines, otherwise delay is fraught with disaster. After all, a fertilized egg develops and at a certain stage, villi appear in it, which need to gain a foothold and begin to receive a stable blood supply. If by this time the fetal egg has not been delivered to the uterus, it attaches anywhere, to the wall of the fallopian tube, for example, and begins to grow, unaware that this is the most inappropriate place for the development of the fetus. nine0003
After all, the lumen of the pipe is in its different sections from 1 mm to 1.5 cm, and a thin and delicate machine is not capable of stretching like a uterus. Therefore, approximately on the 4th-6th week, the chorionic villi “gnaw through” the wall, the tube breaks - and bleeding occurs into the abdominal cavity, accompanied by a sharp cramping pain in the lower abdomen, a feeling of lightheadedness, dizziness, and often loss of consciousness.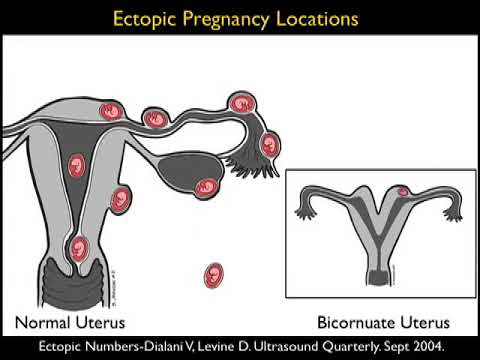
If a large vessel is damaged, massive blood loss threatens the woman with death, and only an emergency operation can save her. Sometimes events develop according to a slightly modified "scenario". It is not the tube that breaks, but the wall of the fetal egg, which is then expelled into the abdominal cavity. There is a so-called tubal abortion, also accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes vomiting and dark brown bloody discharge from the vagina. After a while, the pain subsides and the woman begins to reassure herself that everything will be fine. No, it won't! And in this case, surgical intervention is necessary, otherwise peritonitis, a purulent inflammation of the peritoneum, may develop. nine0003
Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy
Are there any special signs by which a woman herself can guess about an ectopic pregnancy? Alas, there are no special signs. A catastrophe (ruptures, bleeding) sometimes comes like a bolt from the blue: almost nothing bothers, except for a slight aching pain in the lower abdomen and spotting .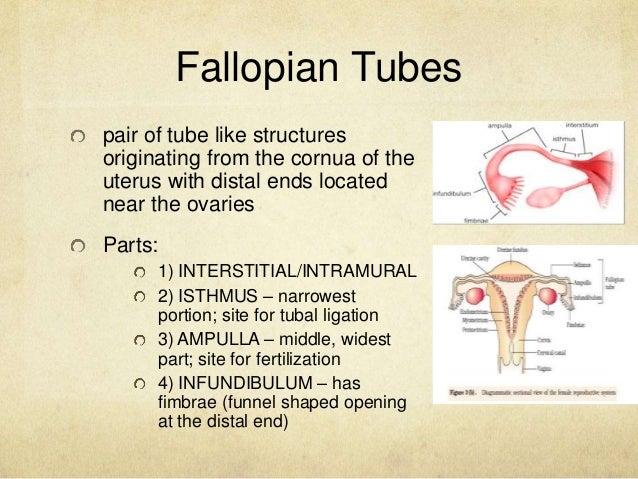 ..
..
And suddenly! But more often, an ectopic pregnancy is disguised as a normal one: the same delay in menstruation, the mammary glands are also engorged, sometimes there is slight nausea, taste and olfactory sensations are distorted. Therefore, a woman cannot independently recognize an ectopic pregnancy, but she certainly can prevent trouble without bringing the matter to bleeding, pain, loss of consciousness. How? nine0003
Yes, you just need to go to the antenatal clinic on the 4-7th day after the delay in menstruation. And there the experts will determine what it is connected with. Modern diagnostic methods, including ultrasound, allow you to establish pregnancy in the early stages. It is especially desirable to undergo an ultrasound examination for those who have a delay in menstruation accompanied by spotting bloody discharge.
If you don’t feel like going to the clinic, buy any test indicator for early diagnosis of pregnancy at the pharmacy.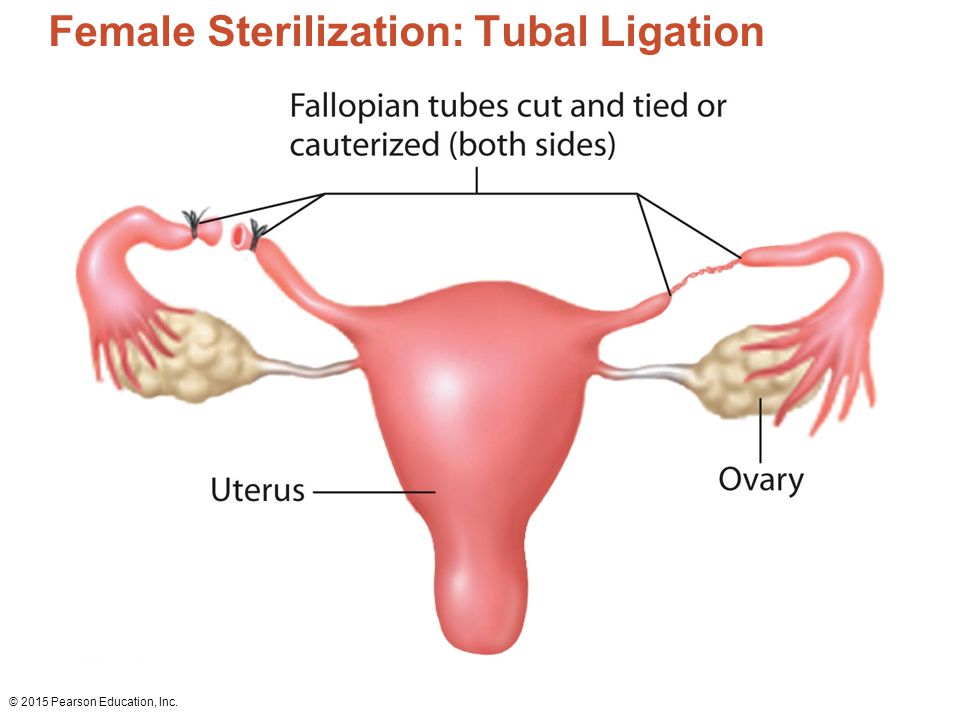 There are a lot of them, and it’s easy to use them (the instructions indicate how). With the help of the indicator, you can make sure that the pregnancy has occurred, but only a specialist can determine what kind of pregnancy it is - normal or pathological. At the slightest suspicion of an ectopic pregnancy, the doctor suggests that the woman go to the hospital. nine0003
There are a lot of them, and it’s easy to use them (the instructions indicate how). With the help of the indicator, you can make sure that the pregnancy has occurred, but only a specialist can determine what kind of pregnancy it is - normal or pathological. At the slightest suspicion of an ectopic pregnancy, the doctor suggests that the woman go to the hospital. nine0003
Do not refuse: only in a specialized institution equipped with modern equipment, you can conduct the necessary studies and make an accurate diagnosis, determine where the embryo was implanted - in the uterus or outside it. Please note: the sooner an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed, the more gentle ways doctors will be able to terminate it.
If the pathology is detected when the receptacle of the fetal egg is still intact, a laparoscopic, low-traumatic method is used. The surgeon inserts the instrument through a small incision in the skin; he sees the operating field and the manipulations themselves on the monitor (the laparoscope is equipped with an optical system). With such an intervention, the surrounding organs and tissues are practically not injured, there is no severe bleeding, the risk of adhesions and scarring is much less. Deaths are rare. nine0003
With such an intervention, the surrounding organs and tissues are practically not injured, there is no severe bleeding, the risk of adhesions and scarring is much less. Deaths are rare. nine0003
Sometimes, with the help of a laparoscope, it is possible to simply "suck" the fetal egg in much the same way as a mini-abortion is done. It is important that during such operations the tube is preserved, it continues to function, and after a while the woman, after undergoing a course of treatment, can become pregnant again.
← All articles
Ectopic Pregnancy: Symptoms and Treatment
Ectopic Pregnancy: Symptoms and Treatment - ilaya(044) 204 40 40 •(044) 284 00 00 nine0003
Office
Make an appointment
Ectopic pregnancy — is a pathology in which a fertilized egg is attached not in the uterus, but in the fallopian tubes, ovary, cervix or abdominal cavity.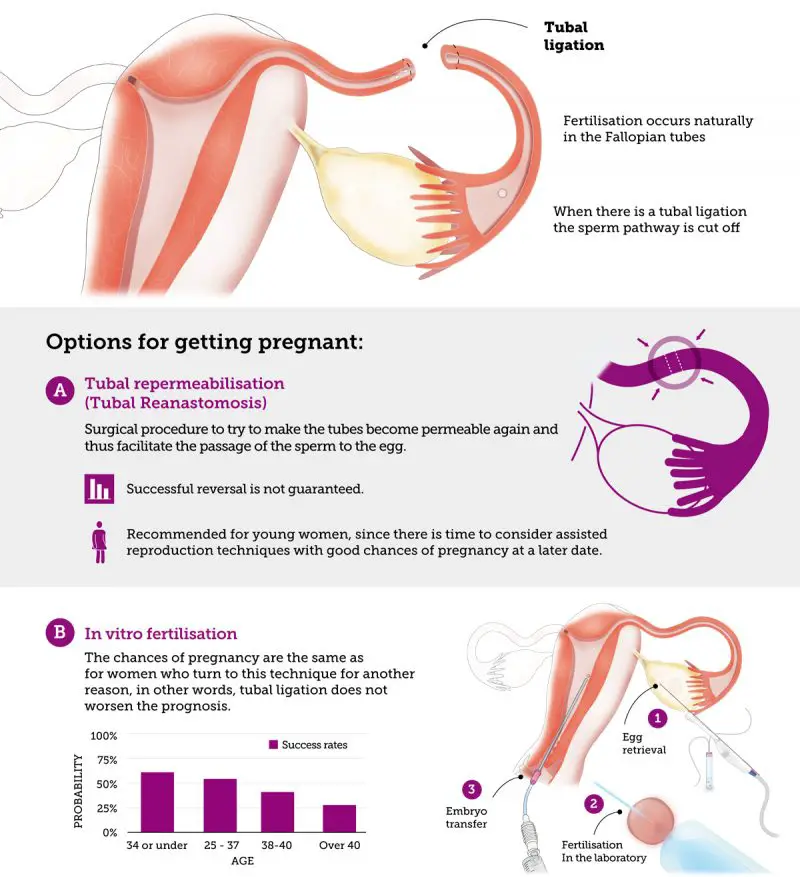 Previously, such a complication ended most often with the removal of the affected organ.
Previously, such a complication ended most often with the removal of the affected organ.
But today, much more gentle methods of treatment are used, which allow a woman to maintain the integrity of the reproductive system and become a mother in the future. It should be noted that the success of treatment depends on how quickly the pathology was detected, so every woman needs to know the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy. nine0003
Symptoms of the disease
Tubal ectopic pregnancy (when a fertilized egg attaches in the fallopian tube) is the most common type of pathology, occurs in 98%. As the fertilized egg grows, the fallopian tube begins to stretch and eventually burst. In this case, the woman experiences severe pain in the left or right side (depending on where the fetal egg is attached).
The pain is mild at first, gradually increases and becomes constant. Such pains begin to bother at 5-6 weeks of pregnancy, if implantation occurred in the narrow part of the tube, and at 8 weeks with implantation in the wide (ampulla) part of the fallopian tube. nine0003
nine0003
Bleeding occurs when the fetal egg is attached to the cervix, as this area is rich in blood vessels. Bleeding can also be with a tubal ectopic pregnancy, when the fallopian tube is damaged. State of shock If there was a large blood loss, a woman may lose consciousness, her blood pressure drops, her pulse becomes frequent and weak, her skin is pale.
Why does an ectopic pregnancy occur? If movement through the tubes is difficult, the egg is attached in the tube itself. Poor patency of the pipes may be the result of previous diseases:
• genital infections;
• inflammation of the female genital organs, eg inflammation of the appendages;
• endometriosis;
• adhesive processes as a result of surgeries.
Poor tubal patency can also be a congenital pathology. Other reasons may be:
• hormone therapy;
• heredity;
• use of an intrauterine device as a method of contraception;
• tumors;
• induced abortions
Women over 34 are also at risk.
Methods of treatment of the disease
The treatment consists in the removal of the fetal egg, which is fixed in the “wrong” place. During the operation, part of the tube or the entire tube is removed, depending on how badly it is affected.
The operation can be performed using the standard method (laparotomy) or the newer laparoscopy method. During laparotomy, an incision is made on the abdomen, while laparoscopy is performed using micro-instruments and the incision is minimal. nine0003
The second method is much more gentle as it avoids complications such as adhesive disease and infections. In addition, the patient recovers much faster with this method of surgery. Treatment does not end there, it depends on the severity of the consequences of the pathology. If a woman has lost a lot of blood, solutions are injected intravenously to make up for the loss of blood elements.
Treatment of inflammation and infections of the genital organs is mandatory, often both partners need to be treated. As a rule, after the operation, a woman is prescribed contraceptive therapy. nine0003
As a rule, after the operation, a woman is prescribed contraceptive therapy. nine0003
Complications of the disease
An ectopic pregnancy can result in infertility, which occurs on average in 30% of cases. Blood loss and temporary oxygen starvation of organs can affect their function in the future.
How to prevent disease
To reduce the risk, it is important to treat inflammation of the female genital organs and dysfunction of the female reproductive system in time.
If you are planning a pregnancy, it is important to get tested for genital infections even before conception in order to treat them in time. The father-to-be should also be tested. If an ectopic pregnancy has already occurred, it is important to receive full treatment to reduce the risk in the future. nine0003
Careful attention to your body is the task of every woman, and this task is even more important if a woman plans to become a mother in the future. Trust your instincts and at the slightest suspicion consult a doctor.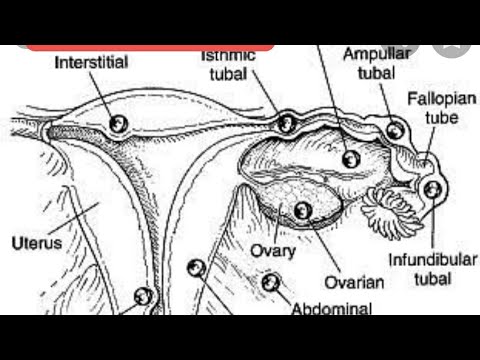 At the ilaya medical clinic, you can make an appointment with a gynecologist. Our highly qualified specialists will conduct a thorough diagnosis and treatment.
At the ilaya medical clinic, you can make an appointment with a gynecologist. Our highly qualified specialists will conduct a thorough diagnosis and treatment.
VIDEO DIRECTIONS
Mon. – Fri. 08:00 – 20:00
Sat. 08:00 - 16:00
Appointment
With the privacy policy of A.A. PARTNERS" is familiarized (on) and agrees (on).
I, in accordance with the Law of Ukraine "On the Protection of Personal Data", give consent to A.A. PARTNERS" for the processing of my personal personal data in the ways and terms determined by the legislation of Ukraine, namely: Last name, first name, patronymic, phone number, e-mail, which confirm my identification using the electronic information and analytical system of A.A. PARTNERS for the purpose of ordering and providing healthcare services.