Ultrasound timeline for pregnancy
Ultrasounds During Pregnancy: How Many and How Often?
Ultrasounds During Pregnancy: How Many and How Often? | BIDMC of Boston Skip to content SearchFind a Doctor
Search for doctors by name, specialty, hospital, or location.
Find a Doctor
For Patients
Call 1-800-667-5356, Monday-Friday, 8:30am-5:00pm or Find a Doctor
For Physicians
For help with specialty consultations, call 617-667-2020, Monday-Friday, 8:30am-5:00pm or refer to our ED
PatientSite
Manage your health care online.
PatientSite Login New User? Sign up now
Medical Records
Pay Hospital Bill
Now available: new PatientSite design and features for a simpler user experience.
Learn more.
Request an Appointment
If you are experiencing a medical emergency, call 911. Please do not use this form.
New Patients
Request
Current Patients
Schedule through PatientSite
Urgent Care
If this is an emergency, call 911 or visit the nearest emergency room.
Chelsea Urgent Care
Chestnut Hill Urgent Care
Dedham Urgent Care
Quincy Urgent Care
Walk-ins are welcome or reserve your spot online.
Close
Close Alert
ALERT
Learn more about our Visitor Policy and COVID-19 Resources.
BIDMC Contributor
SEPTEMBER 18, 2018
Back to All Articles
Ultrasounds are a regular part of prenatal medical care for most pregnant women, and also provide parents with their first glimpses of their developing baby. Although these photographs make for nice keepsakes, most women need very few scans, and medical guidelines firmly state that ultrasounds during pregnancy should be performed only when there is a valid medical indication.
Although these photographs make for nice keepsakes, most women need very few scans, and medical guidelines firmly state that ultrasounds during pregnancy should be performed only when there is a valid medical indication.
According to the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, there have been no reports of documented negative effects on the fetus from diagnostic ultrasound procedures. But, the ACOG discourages the use of ultrasounds for nonmedical purposes because while there are no confirmed biological effects caused by scans, there's always a possibility that some could be identified in the future.
"2D ultrasounds are the safest radiological modality offered to pregnant women, but as with everything, should be used in moderation," says Monica Mendiola, MD, a practicing physician in Women's Health at Beth Israel Deaconess HealthCare-Chelsea and an instructor in Obstetrics & Gynecology at Harvard Medical School.
Most healthy women receive two ultrasound scans during pregnancy.
"The first is, ideally, in the first trimester to confirm the due date, and the second is at 18-22 weeks to confirm normal anatomy and the sex of the baby," explains Mendiola. "As long as these ultrasounds are normal and mom's abdomen measures consistent with her gestation, then that is all most women need."
Mendiola notes that if there are any problems with these initial ultrasounds, or if there is a discrepancy in the fetus size along the way, a repeat ultrasound is warranted.
"Additionally, if moms have medical issues such as diabetes or hypertension, then they will also receive additional scans," she says.
Above content provided by Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. For advice about your medical care, consult your doctor.
View All Articles
What To Expect, Purpose & Results
Overview
What is an ultrasound in pregnancy?
A prenatal ultrasound (or sonogram) is a test during pregnancy that checks on the health and development of your baby.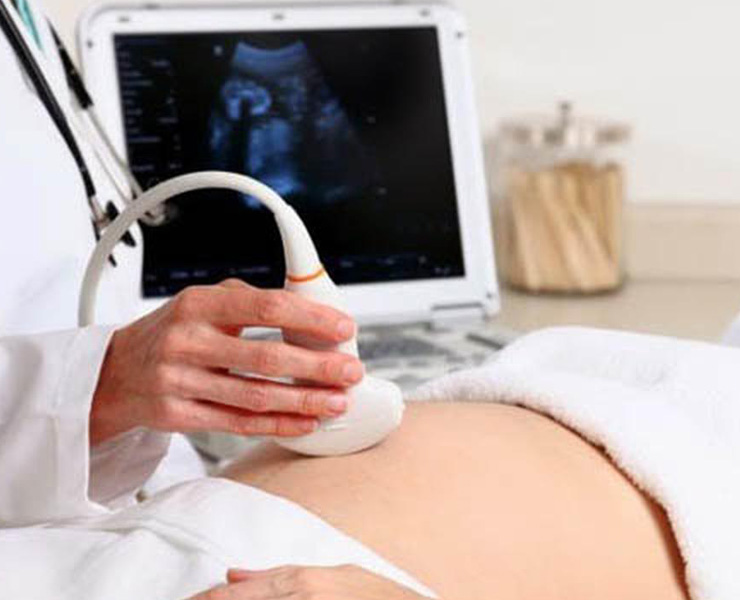 An obstetrician, nurse midwife or ultrasound technician (sonographer) performs ultrasounds during pregnancy for many reasons. Sometimes ultrasounds occur to check on your baby and make sure they’re growing properly. Other times your pregnancy care provider orders an ultrasound after they detect a problem.
An obstetrician, nurse midwife or ultrasound technician (sonographer) performs ultrasounds during pregnancy for many reasons. Sometimes ultrasounds occur to check on your baby and make sure they’re growing properly. Other times your pregnancy care provider orders an ultrasound after they detect a problem.
During an ultrasound, sound waves are sent through your abdomen or vagina by a device called a transducer. The sound waves bounce off structures inside your body, including your baby and your reproductive organs. Then, the sound waves transform into images that your provider can see on a screen. It doesn’t use radiation, like X-rays, to see your baby.
Even though prenatal ultrasounds are safe, you should only have them when it’s medically necessary. If there’s no reason for an ultrasound (for example, if you just want to see your baby), your insurance company might not pay for it.
Prenatal ultrasounds may be called fetal ultrasounds or pregnancy ultrasounds. Your provider will talk to you about when you can expect ultrasounds during pregnancy based on your health history.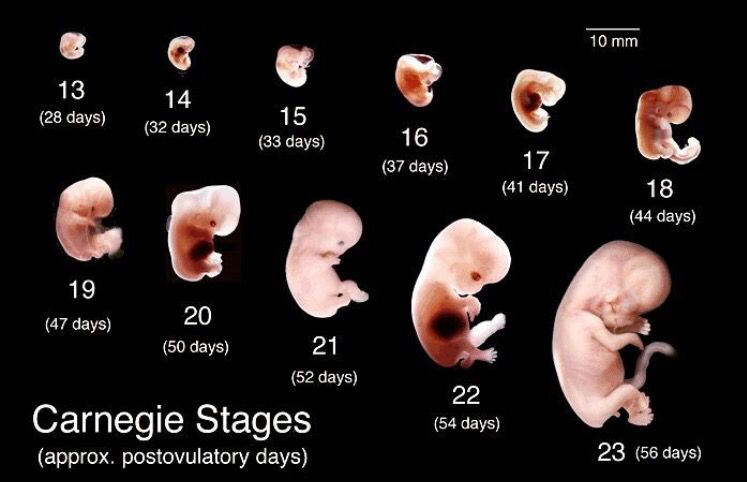
Why is a fetal ultrasound important during pregnancy?
An ultrasound is one of the few ways your pregnancy care provider can see and hear your baby. It can help them determine how far along you are in pregnancy, if your baby is growing properly or if there are any potential problems with the pregnancy. Ultrasounds may occur at any time in pregnancy depending on what your provider is looking for.
What can be detected in a pregnancy ultrasound?
A prenatal ultrasound does two things:
- Evaluates the overall health, growth and development of the fetus.
- Detects certain complications and medical conditions related to pregnancy.
In most pregnancies, ultrasounds are positive experiences and pregnancy care providers don’t find any problems. However, there are times this isn’t the case and your provider detects birth disorders or other problems with the pregnancy.
Reasons why your provider performs a prenatal ultrasound are to:
- Confirm you’re pregnant.
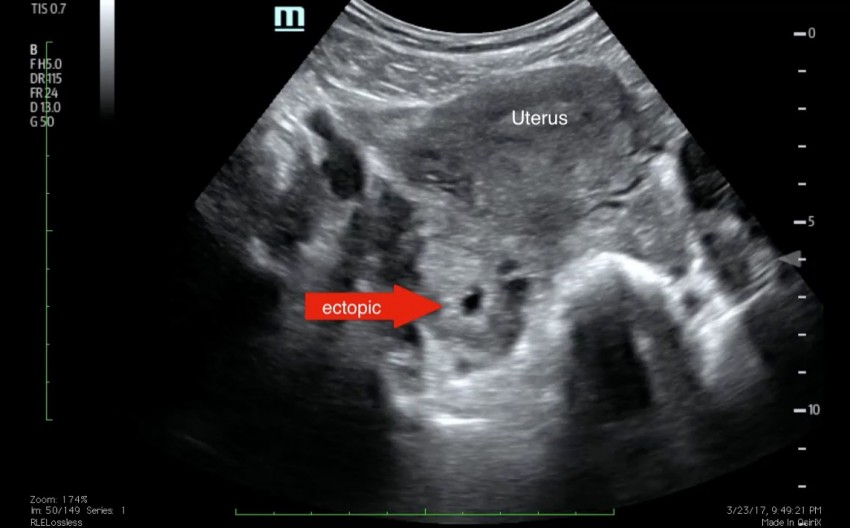
- Check for ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancy, miscarriage or other early pregnancy complications.
- Determine your baby’s gestational age and due date.
- Check your baby’s growth, movement and heart rate.
- Look for multiple babies (twins, triplets or more).
- Examine your pelvic organs like your uterus, ovaries and cervix.
- Examine how much amniotic fluid you have.
- Check the location of the placenta.
- Check your baby’s position in your uterus.
- Detect problems with your baby’s organs, muscles or bones.
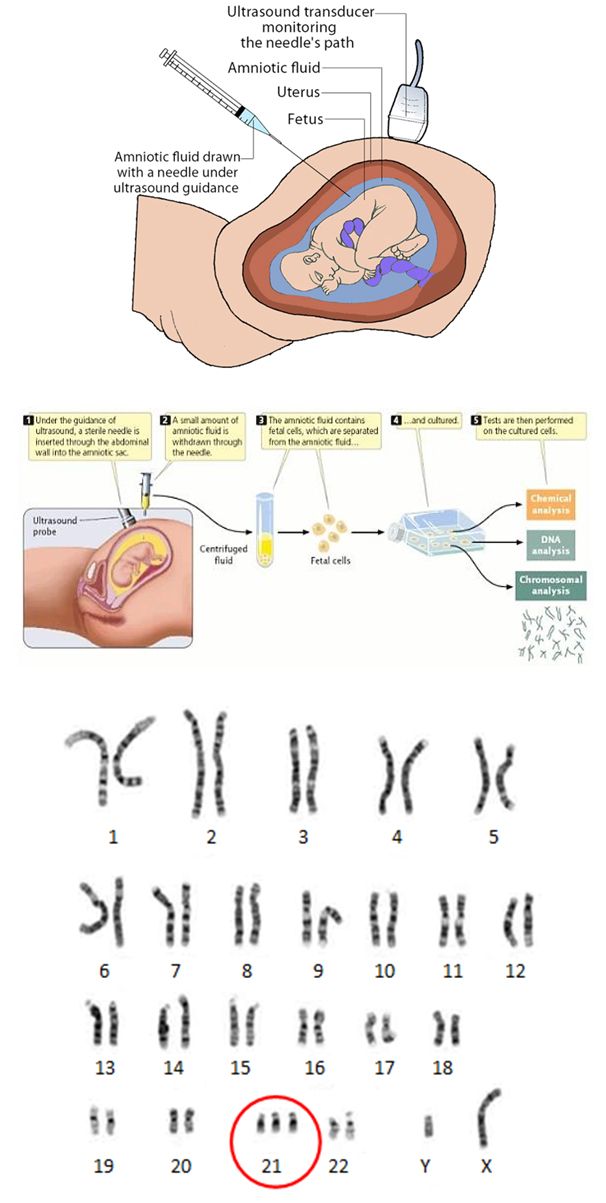
Ultrasound is also an important tool to help providers screen for congenital conditions (conditions your baby is born with). A screening is a type of test that determines if your baby is more likely to have a specific health condition. Your provider also uses ultrasound to guide the needle during certain diagnostic procedures in pregnancy like amniocentesis or CVS (chorionic villus sampling).
An ultrasound is also part of a biophysical profile (BPP), a test that combines ultrasound with a nonstress test to evaluate if your baby is getting enough oxygen.
How many ultrasounds do you have during your pregnancy?
Most pregnant people have one or two ultrasounds during pregnancy. However, the number and timing vary depending on your pregnancy care provider and if you have any health conditions. If your pregnancy is high risk or if your provider suspects you or your baby has a health condition, they may suggest more frequent ultrasounds.
When do you have your first prenatal ultrasound?
The timing of your first ultrasound varies depending on your provider. Some people have an early ultrasound (also called a first-trimester ultrasound or dating ultrasound). This can happen as early as seven to eight weeks of pregnancy. Providers do an early ultrasound through your vagina (transvaginal ultrasound). Early ultrasounds do the following:
- Confirm pregnancy (by detecting a heartbeat).
- Check for multiple fetuses.
- Measure the size of the fetus.
- Help confirm gestational age and due date.
Some providers perform your first ultrasound closer to 12 weeks of pregnancy.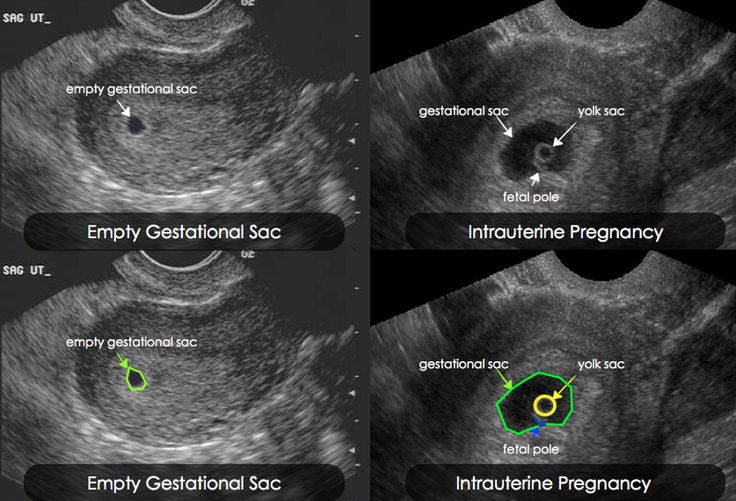
20-week ultrasound (anatomy scan)
You can expect an ultrasound around 18 to 20 weeks in pregnancy. This is known as the anatomy ultrasound or 20-week ultrasound. During this ultrasound, your pregnancy care provider can see your baby’s sex (if your baby is in a good position for viewing their genitals), detect birth disorders like cleft palate or find serious conditions related to your baby’s brain, heart, bones or kidneys. If your pregnancy is progressing well and with no complications, your 20-week ultrasound may be your last ultrasound during pregnancy. However, if your provider detects a problem during your 20-week ultrasound, they may order additional ultrasounds.
How soon can you see a baby on an ultrasound?
Pregnancy care providers can detect an embryo on an ultrasound as early as six weeks into the pregnancy. An embryo develops into a fetus around the eighth week of pregnancy.
If your last menstrual period isn’t accurate, it’s possible that it may be too early to detect a fetal heart rate.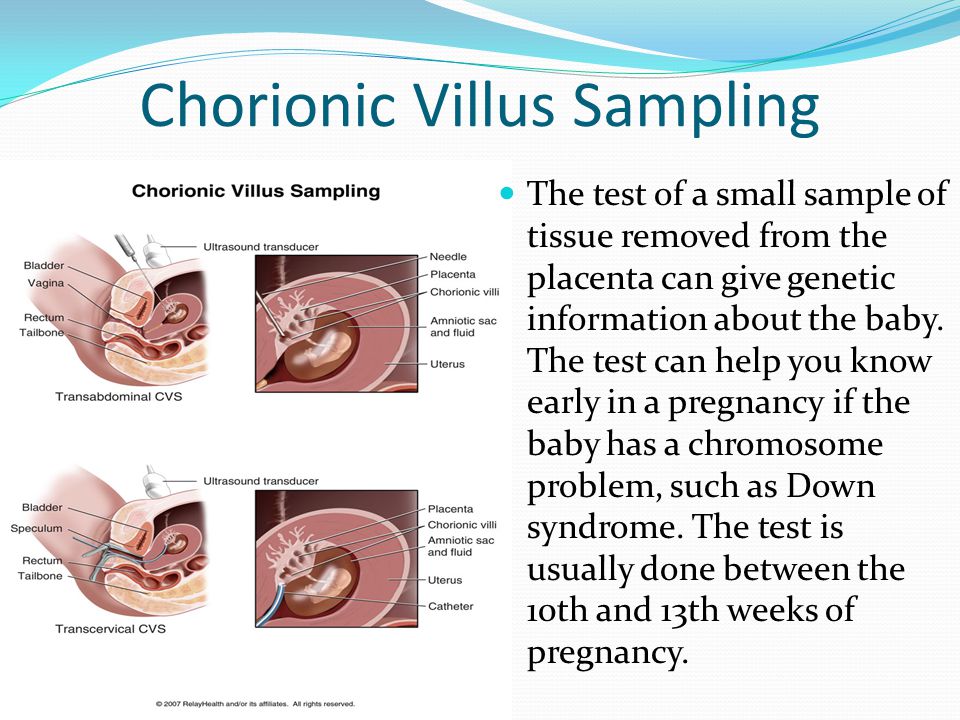
Which ultrasound is most important during pregnancy?
All ultrasounds during pregnancy are important. Your pregnancy care provider uses ultrasound to tell them important information about your pregnancy.
Test Details
What are the two main types of pregnancy ultrasounds?
The two main types of pregnancy ultrasound are transvaginal ultrasound and abdominal ultrasound. Both use the same technology to produce images of your baby. Your pregnancy care provider performs a transvaginal ultrasound by placing a wand-like device inside your vagina. They perform an abdominal ultrasound by placing a device on the skin of your belly.
Transvaginal ultrasound
During a transvaginal ultrasound, your pregnancy care provider places a device inside your vaginal canal (similar to how you place a tampon). In early pregnancy, this ultrasound helps to detect a fetal heartbeat or determine how far along you are in your pregnancy (gestational age). Images from a transvaginal ultrasound are clearer in early pregnancy as compared to abdominal ultrasound.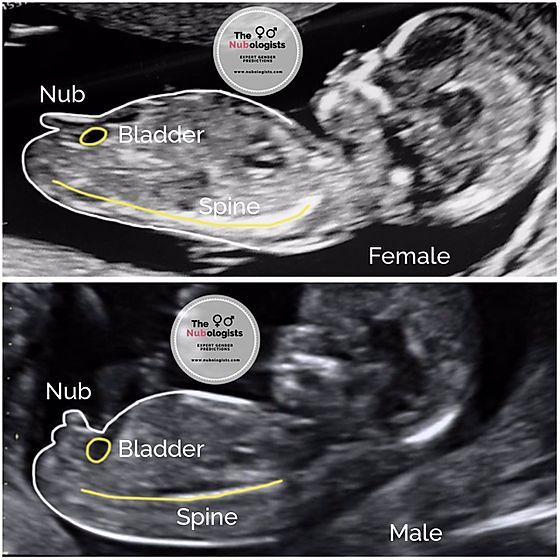
Abdominal ultrasound
Your pregnancy care provider performs an abdominal ultrasound by placing a transducer directly on your skin. Then, they move the transducer around your belly (abdomen) to capture images of your baby. Sometimes slight pressure has to be applied to get the best views. Providers use abdominal ultrasounds after about 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Traditional ultrasounds are 2D. More advanced technologies like 3D or 4D ultrasound can create better images. This is helpful when your provider needs to see your baby’s face or organs in greater detail. Not all providers have 3D or 4D ultrasound equipment or specialized training to conduct this type of ultrasound.
Your provider may recommend other types of ultrasounds. Examples of additional ultrasounds are:
- Doppler ultrasound: This type of ultrasound checks how your baby’s blood flows through its blood vessels. Most Doppler ultrasounds occur later in pregnancy.
- Fetal echocardiogram: This type of ultrasound looks at your baby’s heart size, shape, function and structure.
 Your provider may use it if they suspect your baby has a congenital heart condition, if you had another child that had a heart condition or if you have certain health conditions that warrant taking a closer look at the heart.
Your provider may use it if they suspect your baby has a congenital heart condition, if you had another child that had a heart condition or if you have certain health conditions that warrant taking a closer look at the heart.
How do I prepare for the test?
There’s no special preparation for an ultrasound. Some pregnancy care providers ask that you come with a full bladder and don’t use the restroom before the test. This helps them view your baby better on the ultrasound. You can bring a support person, but bringing children is discouraged as this is an important test that requires complete focus.
You may be asked to change into a hospital gown, but this isn’t usually required for abdominal ultrasounds. If your provider is performing a transvaginal ultrasound in your first trimester, you’ll put on a hospital gown or undress from the waist down.
What should I expect during a prenatal ultrasound?
You’ll lie on a padded examining table during the test. Most ultrasounds occur in a dimly lit room, which helps your ultrasound technician (or sonographer) see the screen. Your sonographer applies a small amount of water-soluble gel to the skin of your belly. The gel doesn’t harm your skin or stain your clothes, but it may feel cold. This gel helps transmit sound waves more efficiently.
Most ultrasounds occur in a dimly lit room, which helps your ultrasound technician (or sonographer) see the screen. Your sonographer applies a small amount of water-soluble gel to the skin of your belly. The gel doesn’t harm your skin or stain your clothes, but it may feel cold. This gel helps transmit sound waves more efficiently.
Next, the sonographer places a transducer on the skin of your abdomen. The transducer sends sound waves into your body, which reflect off internal structures, including your baby. The sound waves that reflect back create pictures on a screen. Your sonographer uses these images to take important measurements such as your baby’s head circumference and length. You may see them making lines on the screen or clicking a button to “freeze” certain angles.
There’s virtually no discomfort during a prenatal ultrasound. You may feel mild discomfort if you have to pee. The ultrasound test takes about 30 minutes to complete.
If you have a transvaginal ultrasound, the process is only different in that the transducer is inside your vagina and not on your belly.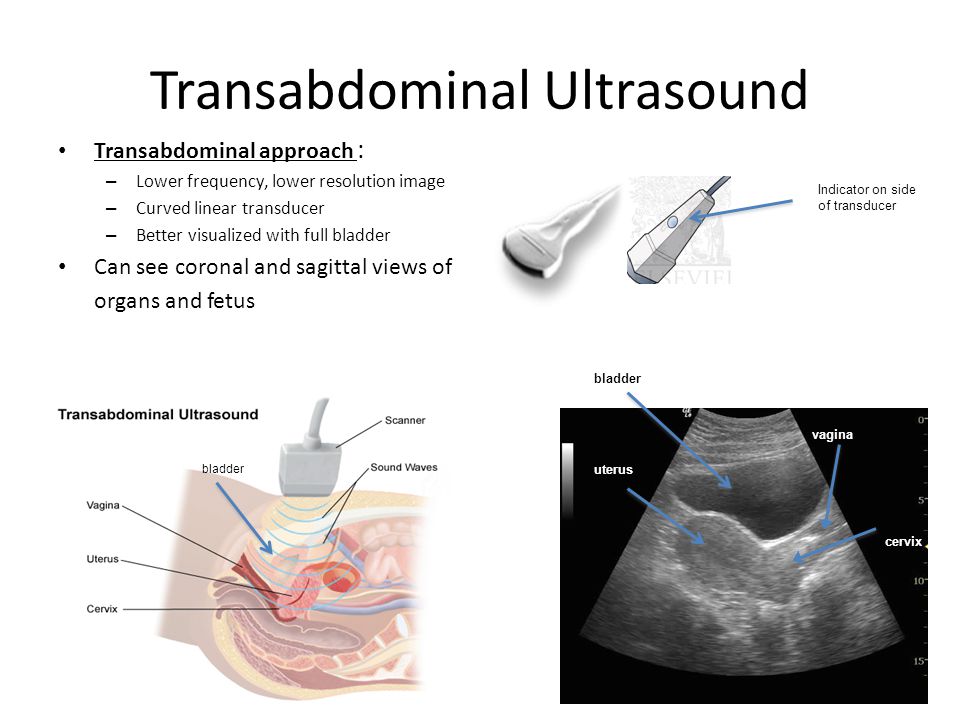
What should I expect after a pregnancy ultrasound?
If you had an abdominal ultrasound, your sonographer wipes the gel off your belly. They may print off some ultrasound pictures for you to take home with you.
In most cases, your sonographer won’t discuss the results of your test with you. If your obstetrician performs your ultrasound, they may discuss what they see as they go along.
If a sonographer performs your ultrasound, an obstetrician will look at the images, then discuss their findings with you at your next appointment. Most practices schedule your appointment right after your ultrasound so you get your results the same day.
What are the risks of prenatal ultrasounds?
Studies have shown ultrasounds are safe during pregnancy. There are no harmful side effects to you or your baby.
Is it safe to do an ultrasound every month during pregnancy?
While ultrasounds are safe for you and your baby, most major medical associations recommend that pregnancy care providers should only do ultrasounds when the tests are medically necessary.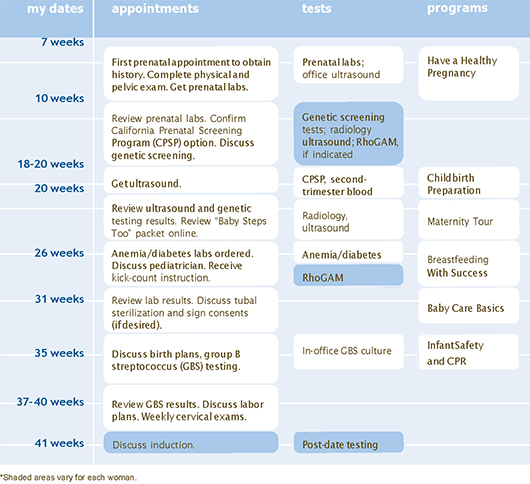 If your ultrasounds are normal and your pregnancy is uncomplicated or low risk, repeat ultrasounds aren’t necessary.
If your ultrasounds are normal and your pregnancy is uncomplicated or low risk, repeat ultrasounds aren’t necessary.
Results and Follow-Up
What results do you get on a pregnancy ultrasound?
Your ultrasound results will be normal or abnormal. A normal result means your pregnancy care provider didn’t find any problems and that your baby is growing and developing normally. An abnormal result means your provider noticed something irregular. If they do, your provider will order additional ultrasounds or diagnostic tests to determine if something is wrong.
Occasionally, the ultrasound is incomplete if there’s difficulty seeing all the structures needed for that particular ultrasound. Your baby’s position or movement sometimes makes it difficult to see everything your provider needs to see. If this is the case, you’ll need a repeat ultrasound and they’ll try again.
There are some limitations to ultrasounds, so your provider may not find certain abnormalities until after birth.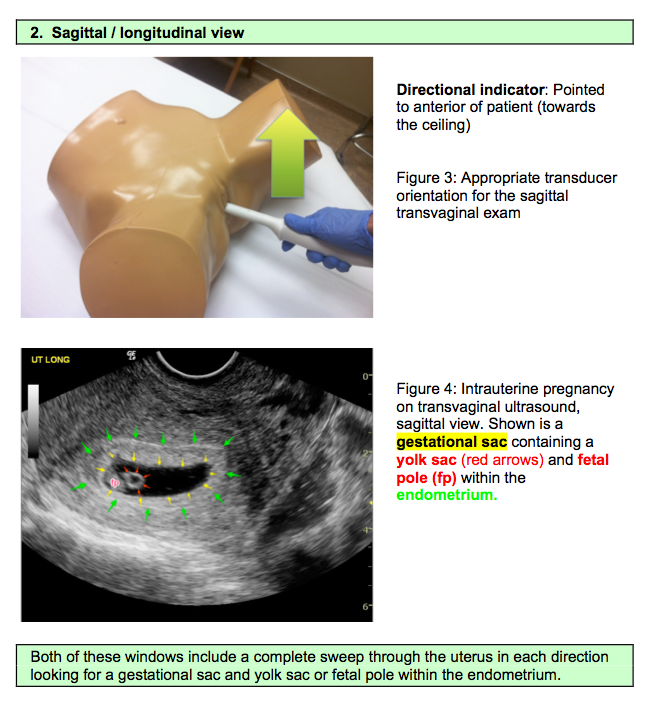
What are reasons you need more ultrasounds during pregnancy?
There are several reasons your pregnancy care provider may order additional ultrasounds during your pregnancy. Some of these reasons include:
- Problems with your ovaries, uterus, cervix or other pelvic organs.
- Your baby is measuring small for their gestational age or your provider suspects IUGR (intrauterine growth restriction).
- Problems with the placenta like placenta previa or placental abruption.
- You’re pregnant with twins, triplets or more.
- Your baby is breech.
- You have too much amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios).
- You have too little amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios).
- You have a condition like gestational diabetes or preeclampsia.
- Your baby has a congenital disorder.
Normal results on pregnancy ultrasounds can vary. Generally, a normal result means your baby appears healthy and your provider didn’t find any issues.
Why do some pregnancy providers schedule ultrasounds differently?
The number of ultrasounds you’ll have and when you have them can vary between providers. Every practice operates differently and some providers do things differently based on your health history or symptoms.
Every practice operates differently and some providers do things differently based on your health history or symptoms.
When does a pregnancy ultrasound determine sex?
Your baby’s sex isn’t visible on an ultrasound until about 18 to 20 weeks. Be sure to tell your pregnancy care provider whether or not you want to know the sex of your baby before your ultrasound.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
An ultrasound during pregnancy can be both exciting and terrifying. Your pregnancy care provider uses ultrasound to get a better idea of how your baby is growing and developing. There are different types of ultrasounds, and the exact timing may vary depending on your provider. Most pregnant people have two ultrasounds — one in the first trimester and one in the second trimester. However, if there’s a potential complication or medical reason for more ultrasounds, your provider will order more as a precaution. Talk to your provider about the ultrasound schedule during pregnancy and what you can expect.
Ultrasound during pregnancy - terms, indications, advantages of ultrasound examination (screening) of expert class
Terms of ultrasound during pregnancy
Indications for ultrasound during pregnancy
Advantages of ultrasound of expert class
Expert-class ultrasound during pregnancy - peace of mind for the expectant mother.
Every mother is familiar with the state when the joy of pregnancy is mixed with anxiety: what about the baby? How does it develop? Is he well? nine0003
Timing of ultrasound during pregnancy
Ultrasound is included in the list of recommended screenings for expectant mothers. Pregnant women are advised to undergo ultrasound three times: in the first trimester - for a period of 9-11 weeks, in the second - from the 17th to the 22nd week, and in the third - at the 32-33rd week.
Ultrasound allows the doctor to visualize the fetus, perform fetometry (measurements of body structure) and determine if the baby is healthy. In addition, in the second half of pregnancy, the doctor can determine the sex of the child (unless, of course, the position of the fetus allows it to be considered). nine0009
In addition, in the second half of pregnancy, the doctor can determine the sex of the child (unless, of course, the position of the fetus allows it to be considered). nine0009
Indications for ultrasound during pregnancy
An expert ultrasound can be performed as prescribed by a doctor or at the request of the expectant mother. Doctors will recommend that you get an expert grade ultrasound if:
- If you have experienced a missed pregnancy, miscarriage, premature birth.
- You had an infectious disease in early pregnancy or just before conception.
- If you were treated during pregnancy with drugs that may affect the fetus. nine0028
- If you or the child's father is over 35 years old.
- If you or the child's father have relatives with genetic diseases.
- If you already have a child with genetic diseases.
- If you and the child's father are relatives.
Benefits of Expert Grade Ultrasound
Despite the fact that many future parents really want to know who the stork brought them, the task of ultrasound is much more serious - to study the structure of the fetus and give the doctor information about his state of health and possible deviations from the norm.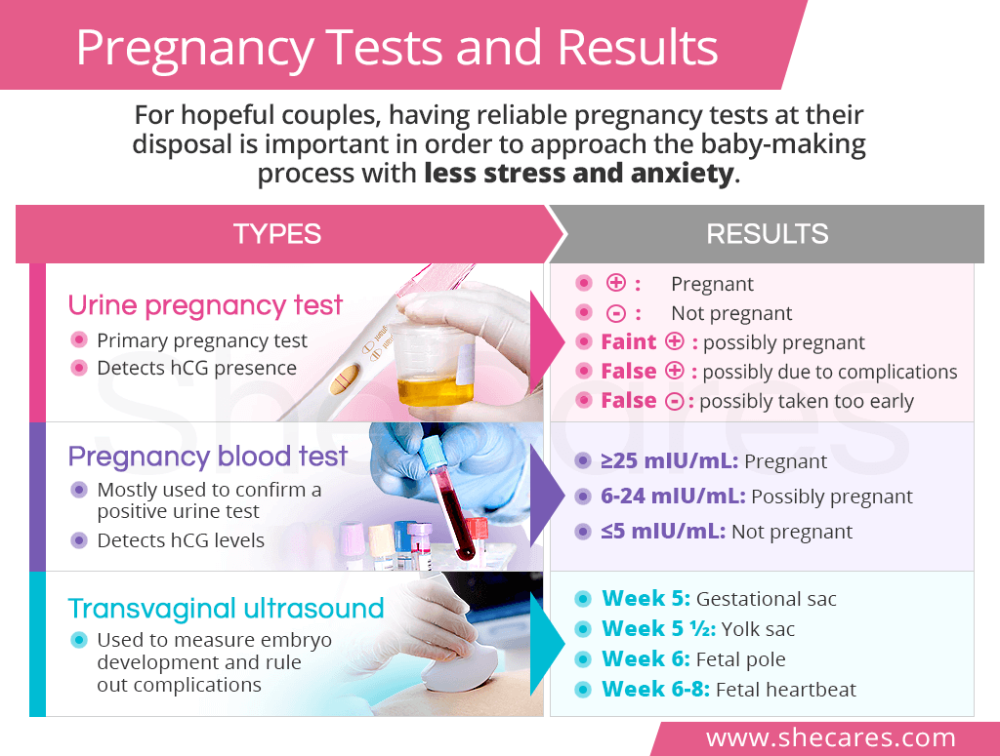 nine0003
nine0003
Expert-level ultrasound is a complete and detailed screening. The doctor examines the fetus in detail and gives an opinion on each organ - from how many fingers and toes, to the structure of the facial bones.
The doctor will not only examine the fetus, but also measure certain parameters. If the results of fetometry deviate from the norm for a given gestational age, this may be a marker of such genetic diseases as:
- Patau syndrome; nine0028
- Edwards syndrome;
- Down syndrome;
- De Lange syndrome;
- Smith-Opitz syndrome;
- triploid set of chromosomes.
In addition, ultrasound allows you to:
- identify possible pathologies of CNS development;
- determine the position of the fetus;
- to study the condition of the placenta and the volume of amniotic fluid;
- diagnose cord entanglement; nine0028
- to detect intrauterine growth retardation of the baby.

Ultrasound examination can detect up to 90% of visible developmental pathologies .
The data obtained during ultrasound allows parents to decide whether to continue or terminate the pregnancy, prepare for the characteristics of the baby and possible difficulties in his upbringing. For doctors, ultrasound screening of pregnant women allows them to choose the tactics of childbirth and prepare in a timely manner to provide assistance to a baby with developmental disabilities. nine0003
Full fetal screening on an expert-class ultrasound machine is the key to the confidence and peace of mind of the expectant mother. And when mom is calm - it's good for the baby!
The author of the article:
Grigoryan Syuzanna Vovaevna
obstetrician-gynecologist, Head of the gynecological department
work experience 4 years
reviews leave feedback
Clinic
m. Sukharevskaya
Sukharevskaya
Reviews
Services
- Title
- Council of Medical Specialists4725
- Appointment, consultation with a specialist doctor PhD 3000
Health articles
All articlesAllergologistGastroenterologistHematologistGynecologistDermatologistImmunologistInfectionistCardiologistENT doctor (otolaryngologist)MammologistNeurologistNephrologistOncologistOphthalmologistProctologistPsychotherapistPulmonologistRheumatologistTraumatologistTrichologistUrologistPhlebologistSurgeonEndocrinologist nine05 years. Red Gates. AvtozavodskayaPharmacy. Glades. Sukharevskaya. st. Academician Yangelam. Frunzenskaya ZelenogradDmitrieva Olga Nikolaevna
Chief physician of "Polyclinika.ru" on Frunzenskaya, neurologist, ENMG specialist
reviews
Clinic
m.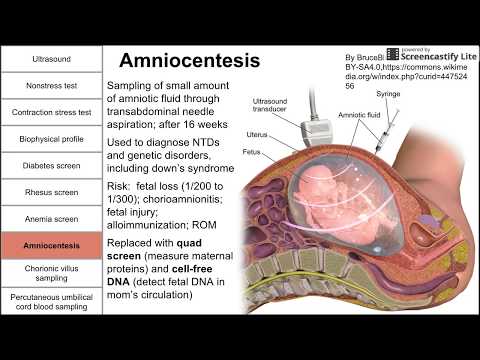 Frunzenskaya
Frunzenskaya
Stolbova Tatyana Sergeevna
Chief physician of "Polyclinika.ru" on the street. 1905, therapist, gastroenterologist
reviews
Clinic
m. Street 1905 Goda
Yuliy Sergeevich Gromov
Head physician of "Polyclinic.ru" on Sukharevskaya, surgeon
reviews nine0003
Clinic
m. Sukharevskaya
Agarkova Elena Valentinovna
Head physician "Polyclinika.ru" in Zelenograd, gastroenterologist
reviews
Clinic
Zelenograd
Aydinov Gennady Ivanovich Academician Yangel, therapist
reviews
Clinic
m. st. Academician Yangel
st. Academician Yangel
Godulyan Aleksey Viktorovich
chief doctor of "Polyclinika.ru" at Krasnye Vorota, endocrinologist, KMN
reviews
Clinic
m. Red Gate
Kupriyanova Olga Sergeevna
Head doctor "Polyclinika.ru" on Avtozavodskaya, general practitioner
reviews
Clinic
m. Avtozavodskaya
Sumina Evgenia Yuryevna
Chief physician of "Polyanka.ru" in Polyanka, neurologist
reviews nine0003
Clinic
m. Polyanka
Tolstikova Anna Pavlovna
Chief physician of "Polyclinic.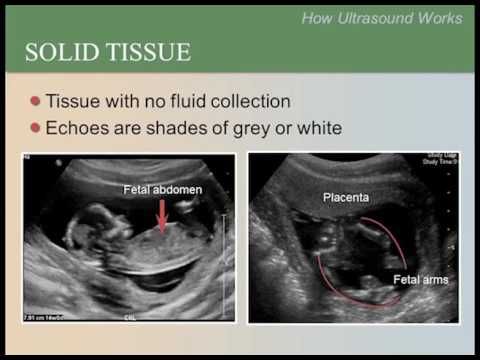 ru" on Taganskaya, general practitioner
ru" on Taganskaya, general practitioner
reviews
Clinic
m. Taganskaya
Shishkina Svetlana Valerievna
Medical Director
reviews
Clinic
01/600
When to do the first ultrasound during pregnancy - “happy days” for screening of the 1st trimester
The world of a modern woman is always full of important events, meetings and an endless series of pre-planned tasks. When pregnancy occurs, many planned events can be moved from “expected” to “impossible” or simply postponed indefinitely. It is quite difficult to worry in advance and reschedule an important event at the most appropriate time, because planning events against the backdrop of pregnancy is a very difficult science.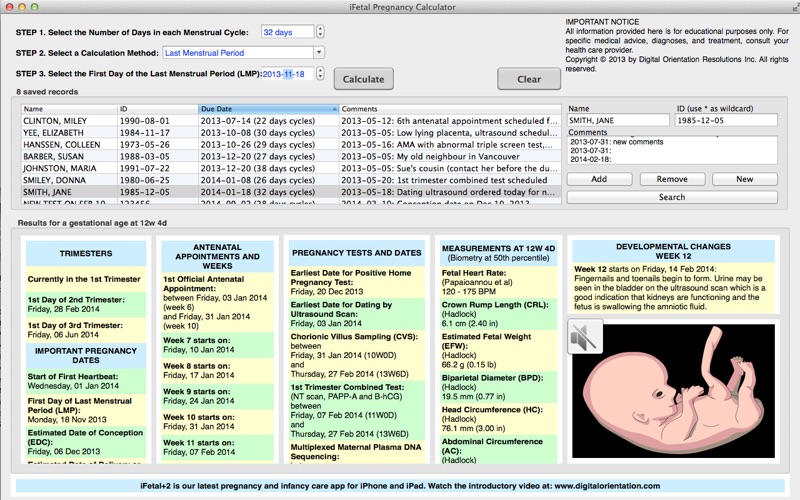 nine0003
nine0003
Therefore, when pregnancy occurs, it is advisable to draw up at least an approximate “life plan for 9 months”. For example, it is known that maternity leave is most often preceded by unspent regular leave, and registration for pregnancy is preceded by the fact that a pregnancy has occurred and is developing normally.
Many events will now depend on how the new life develops. So, when a multiple pregnancy is diagnosed, not only the estimated due date will change, but maternity leave will come 14 days earlier, and the beginning of unspent leave will move with it. Therefore, one of the first steps in the event of a desired pregnancy is the passage of an ultrasound examination (ultrasound). Scientific and technological progress is rapidly changing the whole world, including the state of the prenatal ultrasound diagnostic service. Opportunities are changing, and with them the timing of the passage of research, which I would like to dwell on in more detail. nine0003
When to do an ultrasound during pregnancy
In 2012, in St. Petersburg, the regulation “Decree of the Health Committee of the Government of St. Petersburg No. 39-r”1 came into force. Based on the above document, for a full-fledged ultrasound screening, it is desirable to undergo a study in “... the first trimester: 11 + 0-13 + 6 weeks; 18+0-20+6 weeks; and 32+0-34+6 weeks of pregnancy.” However, these terms apply only to uncomplicated singleton pregnancies. At the same time, early registration is limited to up to 12 weeks of pregnancy with the ensuing consequences (payment of a lump-sum allowance to women registered in medical institutions in the early stages of pregnancy, clause 2-c of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 15, 2001 N 727 (as amended on 04.09.2012).
Petersburg, the regulation “Decree of the Health Committee of the Government of St. Petersburg No. 39-r”1 came into force. Based on the above document, for a full-fledged ultrasound screening, it is desirable to undergo a study in “... the first trimester: 11 + 0-13 + 6 weeks; 18+0-20+6 weeks; and 32+0-34+6 weeks of pregnancy.” However, these terms apply only to uncomplicated singleton pregnancies. At the same time, early registration is limited to up to 12 weeks of pregnancy with the ensuing consequences (payment of a lump-sum allowance to women registered in medical institutions in the early stages of pregnancy, clause 2-c of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 15, 2001 N 727 (as amended on 04.09.2012).
Therefore, at 11 weeks pregnant can be registered when ascertaining the fact of a developing pregnancy , for which ultrasound "... in the first trimester" is recommended. Most doctors recommend doing it at the terms 7-8 weeks of pregnancy , because it is at this time that the heartbeat of the developing embryo is always determined as a sign of the physiological development of pregnancy.
The next obligatory steps in the ultrasound are screening. The entire pregnancy is divided into three periods (trimesters) and ultrasound plays an important role in each. nine0003
What is the diagnostic window for ultrasound during pregnancy
The first screening test is carried out from 11 weeks 0 days of pregnancy to 13 weeks 6 days of pregnancy. These limits are adopted for the timely detection of pathological conditions that determine the prognosis for the health of the fetus. Theoretically, any pregnant woman can apply for an ultrasound both at the beginning of the eleventh and at the end of the thirteenth week - the entire period is screening. However, among doctors who have dedicated their lives to prenatal ultrasound diagnostics, there is an opinion about the most preferable period in each screening period - the so-called " diagnostic window" or "happy days" .
Terms of fetal ultrasound examination
| Legally regulated period (order KZ SPb No. 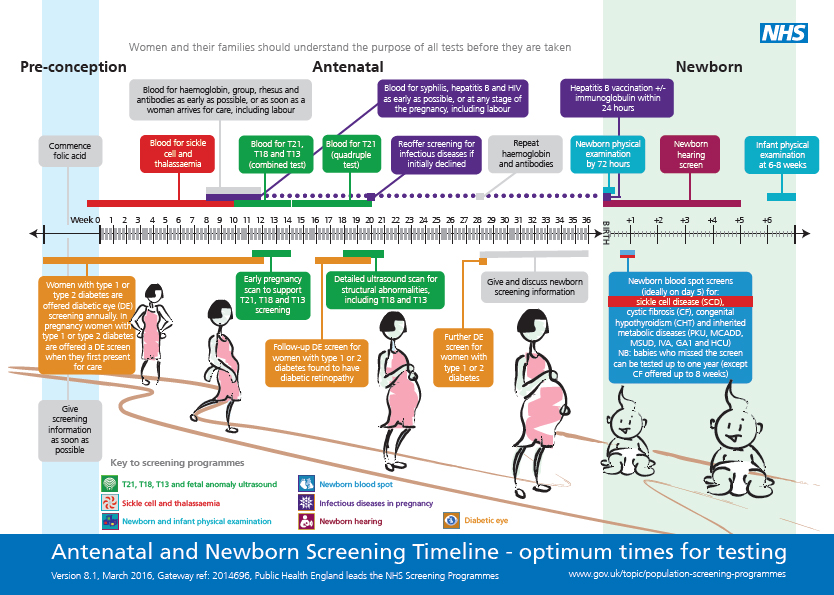 39-r dated 02/01/12) 39-r dated 02/01/12) | Optimal timing/happy days |
| - | 7-8 |
| 11 weeks 0 days – 13 weeks 6 days | 12 weeks 2 days - 12 weeks 4 days |
| 18 weeks 0 days – 20 weeks 6 days | 20 weeks 0 days - 20 weeks 6 days |
| 32 weeks 0 days – 34 weeks 6 days | 32 weeks 0 days - 33 weeks 3 days |
1st trimester diagnostic window
For the first screening test, these days include the interval from 12 weeks to 12 weeks. 2 days to 12 weeks 4 days . It is in this interval that the fetus has already grown enough to evaluate the smallest organs (eye lenses, heart), and the probability of ascertaining the most important morphological changes is significantly higher than at 11 weeks 0 days. On the other hand, each day lived by the baby increases not only the height and weight of the body, but the quality of the picture on the ultrasound machine.
On the other hand, each day lived by the baby increases not only the height and weight of the body, but the quality of the picture on the ultrasound machine.
According to various authors, the frequency of congenital pathology reaches 5%, and for patients in this group it is especially important to identify the problem at an early stage. In such special cases, it may be necessary to expand the range of diagnostic procedures, including prenatal karyotyping (obtaining samples of fetal tissue or amniotic structures in order to determine its karyotype). It takes time to carry out these procedures, from preparing the necessary tests for a pregnant woman, ending with directly invasive diagnostics and obtaining results about the health of the fetus. nine0003
In some cases, the established disease of the fetus raises the question of the impossibility of prolonging the pregnancy. According to the current legislation of the Russian Federation, the procedure for medical termination of pregnancy by the decision of the woman can be performed ". .. no later than the end of the twelfth week of pregnancy", but "... not earlier than 48 hours from the moment the woman applied to the medical organization for artificial termination of pregnancy" (clause 3.1, clause 3-b of article 56. Federal Law No. 323 of November 21, 2012)2. In other words, if a patient goes for an ultrasound scan at 12 weeks 5 days, if a serious pathology is detected, she is no longer sent for an artificial medical abortion, but for an abortion, which is a more complex and traumatic procedure. Therefore, when asked about the best rock for the first screening, almost any practitioner will answer: "up to 12 weeks 4 days" .
.. no later than the end of the twelfth week of pregnancy", but "... not earlier than 48 hours from the moment the woman applied to the medical organization for artificial termination of pregnancy" (clause 3.1, clause 3-b of article 56. Federal Law No. 323 of November 21, 2012)2. In other words, if a patient goes for an ultrasound scan at 12 weeks 5 days, if a serious pathology is detected, she is no longer sent for an artificial medical abortion, but for an abortion, which is a more complex and traumatic procedure. Therefore, when asked about the best rock for the first screening, almost any practitioner will answer: "up to 12 weeks 4 days" .
Diagnostic window in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy
The second screening period occurs at 18 weeks. 0 days and ends at 20 weeks 6 days pregnant . "Lucky days" is considered the entire twentieth week: 20 weeks. 0 days - 20 weeks 6 days .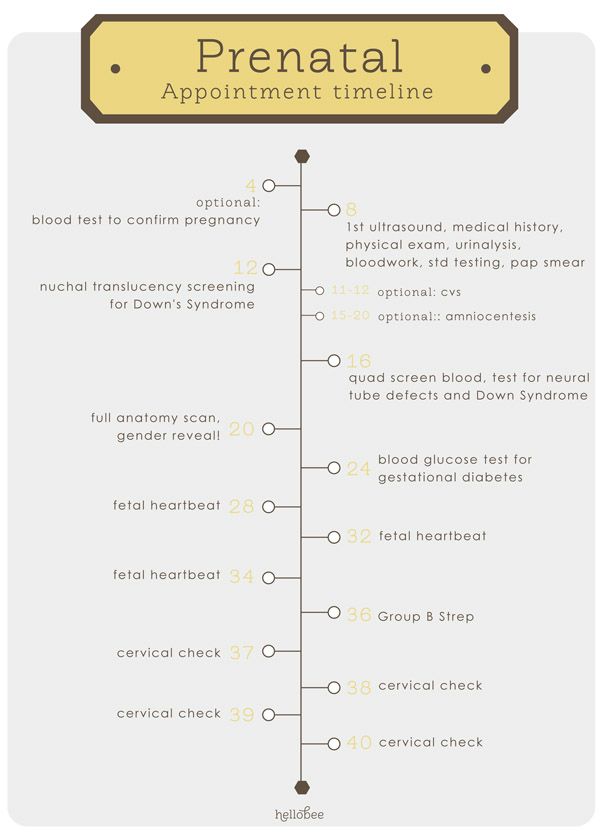 Not all the subtleties of the architectonics of the main organs can be considered so successfully, especially in pregnant women with increased body weight at 18 weeks of pregnancy. If so-called "markers of chromosomal problems" are detected, it may be necessary to perform prenatal karyotyping (obtaining fetal blood or amniotic fluid), which may take some time. nine0003
Not all the subtleties of the architectonics of the main organs can be considered so successfully, especially in pregnant women with increased body weight at 18 weeks of pregnancy. If so-called "markers of chromosomal problems" are detected, it may be necessary to perform prenatal karyotyping (obtaining fetal blood or amniotic fluid), which may take some time. nine0003
The collection of the material itself takes several minutes, but the preparation of the pregnant woman (examination, obtaining the results of blood and urine tests, etc.), transporting the material to the laboratory, examination and obtaining the results can take several days. If serious deviations in the state of health of the fetus are detected, in order to resolve the issue of further management tactics, the pregnant woman is sent to undergo a prenatal consultation consisting of an ultrasound doctor, a specialist in the field to which the identified disease belongs (for example, a surgeon, neurosurgeon, cardiologist, etc. ) . nine0003
) . nine0003
Prior to the new regulation, the second screening period ranged from 18-22 weeks, even earlier than 18-24 weeks of pregnancy. According to WHO recommendations, the fetus becomes viable from the 22nd week of pregnancy, therefore, before this period it is very important to obtain all possible information about its condition and form a prognosis for health and later life. That is why now there is a restriction regulated by law, so that if serious problems with the health of the fetus are detected, all additional diagnostic procedures should be carried out in a timely manner and, if necessary, terminate the pregnancy without violating the Legislation of the Russian Federation2. nine0003
Diagnostic window in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy
The third screening period (32 weeks 0 days - 34 weeks 6 days of pregnancy) has two main objectives: the exclusion of congenital malformations with late manifestation and assessment of the fetal condition. Issuance of a referral for the passage of the third ultrasound along with maternity leave of 30 weeks. 0 days of pregnancy potentiates untimely early appeal of pregnant women for the third screening ultrasound before the period of 32 weeks 0 days, which in turn may require a second planned ultrasound in the "scheduled time". A later turnout (after 34 weeks) reduces the quality of the ultrasound picture obtained by changing the relationship between the amount of amniotic fluid and the volume of the fetal body towards the latter. Therefore " happy days" of the third trimester can be considered the period 32 weeks 0 days - 33 weeks 3 days of pregnancy .
Issuance of a referral for the passage of the third ultrasound along with maternity leave of 30 weeks. 0 days of pregnancy potentiates untimely early appeal of pregnant women for the third screening ultrasound before the period of 32 weeks 0 days, which in turn may require a second planned ultrasound in the "scheduled time". A later turnout (after 34 weeks) reduces the quality of the ultrasound picture obtained by changing the relationship between the amount of amniotic fluid and the volume of the fetal body towards the latter. Therefore " happy days" of the third trimester can be considered the period 32 weeks 0 days - 33 weeks 3 days of pregnancy .
Unscheduled ultrasound at any stage is required, as a rule, only in case of complicated pregnancy, therefore, it is prescribed only according to indications and is performed regardless of the gestational age.
Notes: 1 - Order of the Health Committee of the Government of St.