Food poisoning 36 weeks pregnant
What to Do, Causes, and Prevention
Food Poisoning When Pregnant: What to Do, Causes, and PreventionMedically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI — By Jesica Salyer on December 17, 2018
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:
- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness.
Overview
If you have food poisoning, it means you’ve consumed something that contains bacteria, a virus, or a toxin that’s causing your body to react negatively. Often characterized by vomiting, nausea, or diarrhea, food poisoning is an unpleasant experience for anyone.
During pregnancy, food poisoning can cause anxiety. In addition to feeling ill, you’re worried about the safety of your unborn child.
If you get food poisoning while pregnant, it can be dangerous. If you get food poisoning during pregnancy, it’s important to let your doctor know right away.
Food safety is an important issue for pregnant women, for good reason. In the worst cases, it can cause miscarriage, stillbirth, or premature delivery.
Pregnant women are more vulnerable to food poisoning because of changes to their metabolism and circulation. Here’s a look at the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for food poisoning during pregnancy.
Causes of food poisoning during pregnancy
According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), you’re prone to foodborne illnesses during pregnancy because your immune system is altered. This suppressed state of immunity is largely because your hormones are in flux.
During pregnancy, most of your energy goes toward your body’s prime mission of growing your baby. For this reason, pregnant women need to be careful about what they eat and how it’s prepared.
In addition, your baby’s immune system is underdeveloped. If you get food poisoning, it can be dangerous for them.
Symptoms of food poisoning during pregnancy
In addition to nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, common symptoms of food poisoning during pregnancy include:
- headache
- fever
- abdominal pain or discomfort
- dehydration
- bloody stool
With the constant changes your body experiences during pregnancy, it might be difficult to tell if symptoms such as nausea and vomiting are normal or if they’re caused by food poisoning.
Look for symptoms that present themselves suddenly or feel abnormal. If you’re unsure, it’s best to consult your doctor to rule out an infection or virus.
Types of food poisoning
The most common types of food poisoning include:
- norovirus
- listeria
- E. coli
- Salmonella
If left untreated, all of these can be dangerous during pregnancy.
If you think you have food poisoning from a foodborne illness, contact your doctor right away. If you think you’ve fallen ill after eating out, also contact your local health department. They can investigate if there’s a serious foodborne illness outbreak in your area.
Treatment of food poisoning during pregnancy
Dehydration is one of the most common complications of food poisoning. This is because of the diarrhea and vomiting that you’re experiencing.
To replenish lost fluids, it’s important to ramp up water consumption. If you’re throwing up, start by slowly drinking a sip of water until liquids are tolerated. Then build up slowly from there.
Then build up slowly from there.
Keep in mind that your body is comprised primarily of water. It’s the body’s master cleanser, flusher, and detoxifier. Keeping your fluid intake continuous will play a role in how quickly your body recovers from illness.
Water’s the most economical and universally effective way to help your body heal. Ideally, you want to consume clean, purified water from a trusted home filter or bottled source.
Let your doctor know if you become dehydrated. Severe dehydration during pregnancy might require hospitalization or an IV to issue fluids.
Complications of food poisoning during pregnancy
In addition to dehydration, food poisoning can also lead to other severe complications.
- Norovirus can lead to malnutrition in some rare cases.
- Listeria can cause long-term neurological development problems for your fetus.
- E. coli can cause blood vessel lining damage or kidney failure, often indicated by bloody stools.

- Salmonella has the potential to cause meningitis, reactive arthritis, and bacteremia.
In extreme cases, food poisoning can cause miscarriage or stillbirth.
For these reasons, it’s important to be careful about what you eat during pregnancy.
Preventing food poisoning during pregnancy
Food safety is important during pregnancy. To avoid getting sick, follow all of your doctor’s instructions for preparing food, and avoid foods that aren’t pregnancy-safe.
There are several precautions you can take in order to minimize your chances of experiencing food poisoning while pregnant.
Keep these pointers in mind when you’re preparing food.
Food safety tips
- Keep raw foods separate from ready-to-eat foods.
- Steer clear of raw or unpasteurized dairy.
- Thoroughly cook your raw meat. Use a meat thermometer if need be. Some harmful bacteria can’t survive at a high temperature.
- Avoid packaged meats as much as possible.

- Wash fruits and vegetables well before eating.
- Store perishable foods safely.
- Pay attention to expiration dates.
- Store foods in the freezer to retain optimum freshness.
- Opt to defrost foods instead of letting them sit out at room temperature.
Foods and beverages to avoid during pregnancy include:
- uncooked or raw meat, poultry, seafood, eggs
- unpasteurized fruit or vegetable juices
- unpasteurized dairy products
- spreads containing cheese or meat
- packaged meats
The takeaway
Getting rid of mild food poisoning symptoms can be a dreadful period of trial and error, especially during pregnancy. Talk to your doctor to decide what the best healing approach is for you.
Food poisoning can’t always be treated at home. Your doctor may recommend and prescribe medication.
More serious cases of food poisoning might require antibiotics. Listeria during pregnancy is commonly treated via hospitalization and administered IV antibiotics.
Last medically reviewed on December 18, 2018
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Health
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Bacteria and viruses. (n.d.).
foodsafety.gov/poisoning/causes/bacteriaviruses/index.html - How to stay safe from salmonella poisoning. (2018).
health.clevelandclinic.org/how-to-stay-safe-from-salmonella-poisoning/ - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2017). Food poisoning.
mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/food-poisoning/symptoms-causes/syc-20356230 - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2017). Pregnancy nutrition: Foods to avoid during pregnancy.
mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/pregnancy-nutrition/art-20043844 - What is foodborne illness? Food safety for moms to be. (2018).
fda.gov/Food/FoodborneIllnessContaminants/PeopleAtRisk/ucm083316.htm
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Dec 18, 2018
Written By
Jesica Salyer
Edited By
Nizam Khan (TechSpace)
Medically Reviewed By
Debra Sullivan, PhD, MSN, RN, CNE, COI
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI — By Jesica Salyer on December 17, 2018
related stories
Food Safety During Pregnancy
Top 9 Foods Most Likely to Cause Food Poisoning
What to Know About Dehydration
10 Signs and Symptoms of Food Poisoning
How Long Do Symptoms of Food Poisoning Last?
Read this next
Food Safety During Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Kimberly Dishman, MSN, WHNP-BC, RNC-OB
Some foods contain toxins that are harmful to pregnant women and their developing baby.
 Read more about these toxins and how to avoid them.
Read more about these toxins and how to avoid them.READ MORE
Top 9 Foods Most Likely to Cause Food Poisoning
By Daisy Coyle, APD
Food poisoning can cause unpleasant symptoms ranging from nausea to vomiting. These 9 high-risk foods are the most likely to cause food poisoning.
READ MORE
What to Know About Dehydration
Medically reviewed by Cynthia Taylor Chavoustie, MPAS, PA-C
Dehydration takes place when your body loses more fluid than you drink. The most common cause of water loss from the body is excessive sweating.
READ MORE
10 Signs and Symptoms of Food Poisoning
By Helen West, RD
Food poisoning is extremely common, but its symptoms and severity can vary, making it hard to identify. This article lists 10 symptoms of food…
READ MORE
How Long Do Symptoms of Food Poisoning Last?
Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph.
 D., MSN
D., MSNIf you have food poisoning, here's what you should know about the duration period, symptoms, and when to see your doctor.
READ MORE
Can I Still Eat It: How to Safely Store Meat
Medically reviewed by Natalie Butler, R.D., L.D.
How long you can keep that steak in the fridge? Is that can of tuna still good enough for your casserole? We’ve got you covered. From freezer and…
READ MORE
13 Foods to Eat When You’re Pregnant
By Adda Bjarnadottir, MS, RDN (Ice)
What you eat during pregnancy is important for your health, as well as the health of your baby. Here are 13 foods you should eat when you're pregnant.
READ MORE
11 Foods and Beverages to Avoid During Pregnancy - What Not to Eat
By Adda Bjarnadottir, MS, RDN (Ice)
Certain foods can be very harmful for pregnant women and their babies.
 This is a list of 11 foods and drinks that pregnant women should avoid.
This is a list of 11 foods and drinks that pregnant women should avoid. READ MORE
Do’s and Don’ts When a Loved One Is Experiencing a Stroke
Medically reviewed by Seunggu Han, M.D.
A stroke can be life-threatening, so it's important to act fast. If you think a loved one is having a stroke, here's what you should and shouldn't do.
READ MORE
Your Guide to a Pregnancy-Safe Skin Care Routine
When you're expecting, pregnancy-safe skin care can help ensure the health of you and your baby. We'll tell you what to avoid — and some good…
READ MORE
Food Poisoning During Pregnancy: What To Do
Written by Rachel Reiff Ellis
In this Article
- Types of Food Poisoning
- Symptoms of Food Poisoning During Pregnancy
- Home Remedies for Food Poisoning When Pregnant
- When to See a Doctor About Food Poisoning When Pregnant
- Complications of Food Poisoning When Pregnant
- Preventing Food Poisoning When Pregnant
It’s common to have morning sickness when you’re pregnant. But sometimes your symptoms might come from something else -- food poisoning.
But sometimes your symptoms might come from something else -- food poisoning.
How can you tell if it’s foodborne illness that’s making you sick? Once you know it is, how can you treat it safely when you have a baby on board?
Types of Food Poisoning
Your immune system is weaker than usual when you’re pregnant, so it’s harder for your body to fight off germs that might hitch a ride on food and make you feel bad.
You can get food poisoning when you eat foods contaminated with:
- Bacteria
- Parasites
- Viruses
- Certain chemicals
There are many types of food poisoning. Some are more common, and more dangerous, when you’re pregnant.
- Listeriosis. This comes from listeria bacteria. Pregnant women are 13 times more likely to get listeriosis than other people. It can lurk in ready-to-eat meats like hot dogs and cold cuts. Poultry, seafood, and dairy products can have it, too, especially if they’re not pasteurized.
 It can grow even on foods that are cold in the refrigerator.
It can grow even on foods that are cold in the refrigerator. - Escherichia coli (E. coli). This bacteria lives in your gut naturally. Still, you can get sick if you eat contaminated fruits and vegetables, raw or undercooked meats, or unpasteurized milk and fruit juices with certain types of E. coli.
- Salmonella. This bacteria causes something called salmonellosis. Most often, you get it from undercooked or raw eggs, meats, poultry, or unpasteurized foods. You can also get it if you eat food that has touched soil or animal poop infected with salmonella.
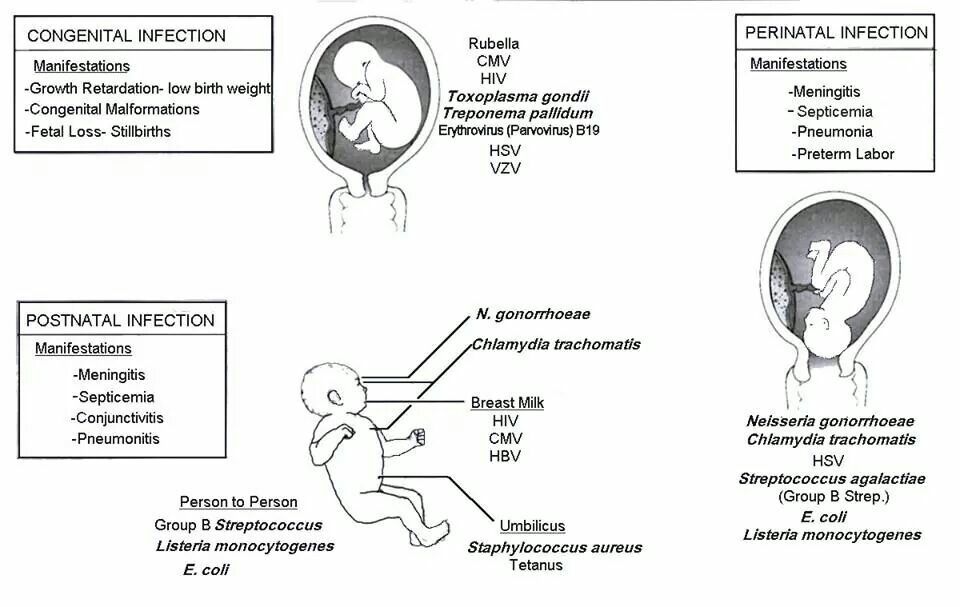
- Campylobacter. You get this bacteria mainly through contaminated chicken or unpasteurized foods.
- Norovirus. This is the main cause of foodborne illness in the U.S. The virus spreads easily through contaminated food and drinks.
Symptoms of Food Poisoning During Pregnancy
It can be tricky to know when food poisoning is to blame for your sickness.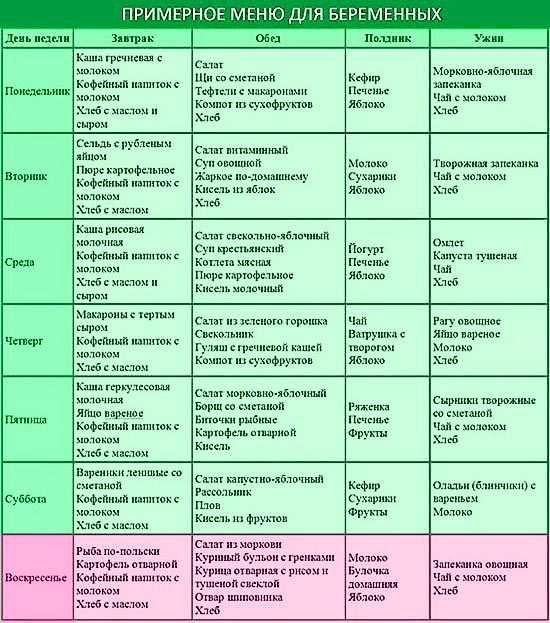 Sometimes, germs from food can make you sick right away. Other times, they hang around in your body for days or even weeks before you have symptoms.
Sometimes, germs from food can make you sick right away. Other times, they hang around in your body for days or even weeks before you have symptoms.
Usually, it causes:
It can be tricky to know when food poisoning is to blame for your sickness. Sometimes, germs from food can make you sick right away. Other times, they hang around in your body for days or even weeks before you have symptoms.
Usually, it causes:
- Stomach pain
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramps
- Dehydration
Often, food poisoning can feel like the flu, because you might have fever, headache, and body aches along with your other things.
- Stomach pain
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramps
Often, food poisoning can feel like the flu, because you might have fever, headache, and body aches along with your other things.
Home Remedies for Food Poisoning When Pregnant
When you’re pregnant, it’s more than just your health you’re protecting. Some bouts of food poisoning can pose problems for your baby, whose immune system isn’t strong enough yet to fight off germs.
Some bouts of food poisoning can pose problems for your baby, whose immune system isn’t strong enough yet to fight off germs.
When you start having symptoms that seem like food poisoning, call your doctor right away. They can help you figure out if it is food poisoning, and if so, what may have caused it.
You may be able to handle your symptoms at home with your doctor’s guidance. However, if you're vomiting and having diarrhea, you may need treatment at the doctor’s office or even a hospital. Don’t take any over-the-counter medications without talking to your doctor first.
If your case is mild enough to treat at home, work on rest and rehydration. Get fluids however you can: ice chips, small sips of water or clear liquids, or by drinking a sports drink with electrolytes in it. Wait until you’re sure your vomiting is over before you try to eat. Take your first foods slowly, and stick with bland, non-greasy foods.
When to See a Doctor About Food Poisoning When Pregnant
Your food poisoning needs professional treatment if you’re having:
- Signs of dehydration like excessive thirst, dry lips, little to no urine, or dizziness
- Vomiting or diarrhea that won’t stop
- Severe pain in your abdomen
- A fever higher than 101 F
- Blood or pus in your stool
- Black or tarry stool
Call your doctor right away if you have one or more of these problems. They’ll do tests on your blood or stool to find out what's making you sick. You may need treatment with antibiotics. They’ll also want to be sure your body has enough fluids. You may need an IV to help your body rehydrate.
They’ll do tests on your blood or stool to find out what's making you sick. You may need treatment with antibiotics. They’ll also want to be sure your body has enough fluids. You may need an IV to help your body rehydrate.
Complications of Food Poisoning When Pregnant
Certain kinds of food poisoning are very dangerous for your unborn baby.
If you get listeriosis , you may have no symptoms at all. However, you can pass it on to your baby. That can cause serious health problems like:
- Paralysis
- Blindness
- Seizures
- Issues with the brain, heart, or kidneys
At worst case, listeriosis can cause preterm labor, low birthweight, and even miscarriage or stillbirth.
Salmonellosis can also pass to your baby and put them at risk of serious complications like meningitis.
Campylobacter can cause miscarriage if you get it early in your pregnancy. It’s also very dangerous if you have it at the time you give birth and pass it to your newborn. Infection in a new baby can be life-threatening.
Infection in a new baby can be life-threatening.
For you, the most common complication from food poisoning in general is dehydration. Some foodborne illnesses, especially E. coli, can also cause kidney damage.
Preventing Food Poisoning When Pregnant
You can protect yourself from many kinds of food poisoning, whether you’re pregnant or not, by being careful about what you eat and how you handle it.
Safe food handling tips:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before and after you touch food.
- Don’t let raw meat come in contact with anything you’ll eat raw, like produce, or food that’s already prepared.
- Keep perishable foods refrigerated or frozen.
- Clean fruits and vegetables before you eat or cook them.
- Wash utensils and food prep surfaces after you use them.
- Cook food to a high enough temperature to kill germs.
- Refrigerate leftovers right away. Don’t eat food that’s been sitting out or that has expired.

Certain foods should be off the menu until after your baby is born. Don’t eat or drink:
- Unpasteurized dairy products, like raw milk and some brands of soft cheese
- Raw or undercooked meat, poultry, fish, or shellfish
- Runny or raw eggs, or things that contain them, like cookie dough and homemade eggnog. Pasteurized raw eggs are OK.
- Hot dogs or deli meat, unless heated to 165 degrees
- Refrigerated patés or meat spreads. Jarred or canned are OK.
- Premade chicken, ham, or seafood salads from a deli
- Smoked fish, unless it came from a can or you cook it
- Unpasteurized juice or cider
- Sprouts
Also pay attention to food recalls. Companies have to tell the public if they find out something they’ve sold is making people sick.
90,000 food poisoning during pregnancy in the early and later stages, treatmentComplain
Updated
Content:
What causes
Danger for mother and child
Clinical manifestations
that includes diagnostics
How to cope with poisoning
Pregnant women carefully monitor their diet. But the appearance and taste of food does not always allow you to recognize low-quality or contaminated products. When pathogenic microorganisms enter the digestive tract, poisoning occurs, which poses a danger to the mother and fetus of varying severity; in severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary for treatment. nine0005
But the appearance and taste of food does not always allow you to recognize low-quality or contaminated products. When pathogenic microorganisms enter the digestive tract, poisoning occurs, which poses a danger to the mother and fetus of varying severity; in severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary for treatment. nine0005
Pregnancy poisoning accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea
What causes poisoning
Food poisoning is an acute disease that is associated with the consumption of foods with various types of toxins. The latter can be of biological and non-biological origin. Main types of toxins:
- microbial toxins;
- natural poisons of animals, plants or fungi; nine0034
- chemicals.
Most often, during pregnancy, poisoning develops when using low-quality products. Signs of an infectious process occur when food is contaminated with staphylococci, proteus, clostridia, toxigenic types of Escherichia coli, salmonella. Sometimes dysentery, cholera, shigellosis are diagnosed.
Sometimes dysentery, cholera, shigellosis are diagnosed.
For a clinical picture of poisoning to appear, microbes must multiply on foods and release their toxins. This is accompanied by the appearance of gas bubbles, an unpleasant odor or a change in color. This quality of food is usually repulsive. But symptoms in a pregnant woman can also appear after a normal-looking meal. nine0005
Microbes secrete several types of toxins. In staphylococci, a thermostable type is synthesized, which is not destroyed by boiling or heat treatment. Toxin can penetrate into food from an abscess on the skin of the hands of a food production worker.
Pustular skin lesions are most often associated with staphylococcal infection. Therefore, people involved in cooking and food production are prohibited from working with damage to the skin of their hands.
nine0049The following factors contribute to the spread of foodborne infections:
- violation of sanitary and hygienic norms;
- prolonged storage of food without a refrigerator or in the open air;
- presence in the premises of insect vectors of infection - flies, cockroaches;
- wrong conditions of sale;
- storage or recycling of expired food.

Less often, intoxication occurs in a pregnant woman when poisonous plants, mushrooms are used in food. The danger is represented by mushrooms collected independently in the forest, among which it is not always possible to recognize poisonous ones. For poisoning, it is enough for only one inedible to hide among the edible ones. But toxic substances can also be present in good mushrooms if they are old or were picked in the wrong place. nine0005
Chemical poisoning can occur through accidental or intentional ingestion of chemicals. These may be:
- alcohol and its analogues;
- narcotic substances;
- medicines.
Mushrooms and chemicals lead to toxic liver damage, which is very dangerous for pregnant women and can be fatal.
Mushrooms can cause serious poisoning with vomiting
Danger condition for mother and child
Depending on the type of pathogen and its amount in the body, poisoning during pregnancy can occur in three forms:
- mild;
- medium;
- heavy.

Vomiting and diarrhea are the main signs of intoxication. They lead to the loss of a large amount of fluid and trace elements. The severity of dehydration is determined by the frequency and abundance of diarrhea. The following degrees of dehydration are distinguished:
- 1 st. - a woman loses up to 3% of body weight;
- 2 tbsp. – loss of 4–6% of the mass;
- 3 tbsp. – weight loss by 7–9%;
- 4 tbsp. – Weight has decreased by 10% or more.
Dehydration occurs due to the loss of fluid from the blood plasma and tissues. In pregnant women, this leads to an increase in blood clotting, the risk of thrombosis, placental abruption and fetal hypoxia. Toxic substances are also able to cross the placenta to the fetus. In the early stages, while the chorion is not formed, toxins can have a damaging effect on the tissues of the embryo or lead to miscarriage. nine0005
For a pregnant woman, damage to liver cells and the development of hepatitis are dangerous.
This condition often leads to severe liver failure, which ends in clouding of consciousness and coma. Violation of the balance of electrolytes in the blood becomes a trigger in the development of convulsive syndrome.
A pregnant woman becomes weak, her temperature rises
Clinical manifestations
The first symptoms of poisoning appear 2-24 hours after eating poor-quality food. Pathology can occur in the form of damage to several parts of the digestive tract:
- acute gastritis - infection of the stomach;
- gastroenteritis - affection of the stomach and small intestine;
- colitis - involvement of the colon;
- Enterocolitis is a lesion of the small and large intestine.
Sometimes the entire digestive tract is involved in the infectious process.
Poisoning during pregnancy begins with symptoms of acute gastritis. A woman feels pain in the stomach, a feeling of heaviness, belching may appear.
The feeling of nausea ends with vomiting, accompanied by weakness, chills. With mild intoxication, body temperature rises. After involvement in the inflammatory process of the small intestine, abdominal pain becomes more pronounced, cutting. nine0005
Poison diarrhea is easy to distinguish from normal loose stools. It is characterized by:
- high frequency, more than 5 times a day;
- offensive smell;
- particles of undigested food;
- gas bubbles or foam;
- a large amount of liquid.
Pathological impurities - blood and mucus - appear in severe infectious lesions of the intestines with salmonella, shigella, dysenteric bacillus. nine0005
Severe intoxication is accompanied by high body temperature, which can rise above 38°C. In some cases, a sign of a serious condition is the absence of fever with a decrease in temperature below 36 °.
Other criteria for a severe course of poisoning are:
- pronounced weakness, loss of strength;
- dryness of mucous membranes and skin;
- blue extremities;
- severe muscle and joint pain; nine0034
- rapid breathing;
- muffled heart sounds, but severe tachycardia;
- lowering blood pressure;
- vomiting more than 15 times a day;
- diarrhea more than 20 times a day;
- severe abdominal pain;
- convulsions.
In a mild form of pathology, it lasts 1-3 days. It can be cured at home. But in severe cases with signs of dehydration, the pregnant woman needs hospitalization in the infectious diseases department. If there is a suspicion of poisoning with mushrooms or chemicals, the woman is hospitalized in the toxicology or intensive care unit. nine0005
What diagnostics include
At the first stage of diagnosis, complaints about the condition, frequency of diarrhea, vomiting are evaluated. A connection is established with the use of substandard products or hazardous substances. By the nature of the stool, the doctor can determine the level of damage to the digestive tract and suspect dangerous infections.
Stool culture is performed to determine the type of pathogen. It is important to do this before starting antibiotics. The search for the following infections is mandatory:
- dysentery;
- salmonellosis;
- escherichiosis;
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- yersiniosis.

In an unfavorable epidemic situation, feces are examined for cholera and rotaviruses.
A biochemical blood test is required to determine blood electrolytes, assess liver function. Additionally, serological tests, abdominal ultrasound, examination of vomit or washings can be used. If fever persists for several days during treatment, blood cultures are performed. nine0005
For food poisoning, blood tests are done
How to deal with poisoning
What to do with toxic infection depends on the condition of the woman. With a slight malaise, vomiting less than 5 times a day, you can try to cope with the disease on your own. For treatment on the first day, it is necessary to completely refuse food and consume a large amount of fluid to replenish its balance. Water will bring little benefit, you need to make up for the loss of ions. This is helped by special solutions of salts for rehydration, which are sold in a pharmacy in the form of a powder.
It must be dissolved in clean water and drunk as often as possible during the day. nine0005
Dried fruit compote can also be prepared. It contains a lot of potassium, which helps restore the work of the heart and muscles.
What can be eaten from the second day of illness:
- viscous cereals;
- lean pureed meat;
- dry white bread;
- low-fat kefir.
Exclude from the diet fresh vegetables and fruits, fatty, fried and any other dishes that can injure the mucous membrane. Women who are in hospital are assigned table No. 4 according to Pevzner. nine0005
Do not use loperamide for diarrhea, imodium. These drugs inhibit peristalsis and contribute to the retention of toxic substances in the body.
Severe dehydration requires fluid and electrolyte replenishment, which cannot be done orally. The woman is hospitalized.
Poisoning is dangerous for pregnant women, it can lead to fetal hypoxia in the later stages, severe dehydration.
Therefore, the expectant mother needs to carefully monitor her diet and not eat suspicious foods. nine0005
Read more: how to get rid of constipation during pregnancy
* The information provided cannot be used for self-diagnosis, treatment determination and does not replace a visit to a doctor!
HeadingHealth
Why intravenous magnesia is prescribed during pregnancy
An orthopedist told why pregnant women develop flat feet
Live in the moment and make it so beautiful that it is worth remembering
Comments
' + '
' +tooltips[tooltip][0] + '
' +'' +tooltips[tooltip][1] +'' + '
' + 'Learn and participate
Baby.ru clubs are a treasure trove of useful information
Winter holidays: what to choose? Is there an alternative to school? Speech development of children: when to start? nine0005
Poisoning during pregnancy: what to do?
No one is safe from food poisoning, but it is especially unpleasant if it happened during pregnancy and the expectant mother does not know what to do to protect the baby from its consequences.
Most often, such a nuisance as food poisoning overtakes during the summer heat and on holidays. In the first case, food spoils due to violation of storage conditions, which become more difficult to observe at this time. In the second case, cooked in abundance, festive food spoils due to long storage. nine0005
If poisoning has already occurred, then it is necessary to help the body overcome the food poisoning that has penetrated into it. Intoxication usually occurs with nausea, vomiting, hyperthermia and diarrhea. This condition poses a certain danger to the child and needs immediate elimination.
Causes
Food poisoning (FTI) is a group of diseases of various origins that occurs after eating foods containing a large number of toxins and pathogens. The infection gets on products by contact, while products infected with staphylococcus do not change either smell or taste. nine0005
The most dangerous are protein products, which are more susceptible to contamination by pathogens.
These are, first of all:
- dairy products;
- meat and sausages;
- salads with mayonnaise;
- canned fish and meat;
- cakes and pastries with cream.
The mechanism of development of toxic infection is very diverse and depends on the type of pathogen and the toxins it releases. Maternal IPT can cause serious fetal harm. It can affect the metabolism, disrupt the circulatory and cardiac activity of the baby. General dehydration of the mother due to profuse vomiting and diarrhea contributes to the leaching of minerals and vitamins from the body, as a result of which the child feels a lack of them. Of course, the most formidable complication of poisoning for a future mother is a miscarriage or premature delivery. nine0005
Signs
Signs of poisoning in pregnant women do not differ from those in ordinary people and are expressed in nausea, repeated vomiting and sharp cramping pains in the abdomen.
In addition, there may be:
- spasms and heaviness in the epigastric region;
- increased flatulence;
- abdominal discomfort;
- appetite disturbance; increased heart rate;
- pallor; weak pulse;
- rapid pressure drop; nine0034
- fever;
- disturbed general state of health, weakness;
- headache and chills.

The onset is acute, the disease lasts about 1-3 days and is relatively easily tolerated. Poisoning during pregnancy is more severe, may be accompanied by severe toxicosis. Based on the combination of signs, epidemiological and laboratory data, the doctor can determine the pathogen and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
How to treat? nine0029
Early treatment
To cleanse the body of toxins, gastric lavage with water or 2% soda solution is prescribed as an emergency measure. To do this, take cool boiled water. In case of food poisoning, you need to take about a liter of water, and then induce vomiting. After some time, the treatment should be repeated. The procedure is carried out under medical supervision with pressure measurement. To prevent abortion, Magnesia, Papaverine are used.
At the same time, one should not forget that gastric lavage should not be done if there is a threat of bleeding and miscarriage, such treatment can cause placental abruption.
In such cases, it is necessary to wait for the emptying of the stomach and take sorbents (activated carbon, Enterodez, Polysorbilact). nine0005
In case of food poisoning, you should replenish the loss of moisture and drink at least 2.5 liters of water per day. In order not to induce vomiting, water should be drunk little by little, but often. It is preferable to make electrolyte solutions instead of water to restore the water-salt balance, such as Regidron or Electrolyte. It is not necessary for diarrhea to use drugs that slow down the work of the intestines: this will delay the removal of toxins and microorganisms from the body, which is strictly prohibited during gestation. To combat toxins, a suspension of activated carbon should be made in the amount of 60 grams per 0.5 liter of water and taken during the day. nine0005
Treatment includes fasting diet: light chicken broth, croutons, sweet tea.
After the vomiting has stopped, it is necessary to replenish the loss of fluid and gradually expand the menu.
Starvation is unacceptable when carrying a child. After the recovery of the pregnant woman, it is advisable to take a vitamin-mineral complex. With a mild course of the disease, antibiotics are not prescribed.
Treatment at the end of pregnancy
It is necessary to treat food poisoning in the later stages with the use of diet, sorbents, and plenty of fluids. At the 37th week of pregnancy, Magnesia is no longer prescribed. According to indications, injections of drugs that improve placental circulation are made. nine0005
Severe food poisoning at the end of pregnancy can lead to the following complications:
- fetal malnutrition;
- placental abruption;
- threatened preterm labor;
- fetal hypoxia;
- placental insufficiency.
Such disorders develop only when intoxication is combined with pathology of pregnancy. In general, the consequences of a small poisoning are usually not severe.
Prevention
To prevent foodborne illness, pregnant women should not eat the following foods:
- expired;
- stored in violation of temperature conditions and separate storage;
- broken packaging;
- acquired from unhealthy people;
- exotic, brought from afar;
- unwashed fruits and vegetables;
- purchased at spontaneous markets;
- undercooked meat products.