Normal baby sleeping patterns
Baby sleep: what to expect at 2-12 months
Baby sleep needs
Babies need sleep to grow and develop well. But babies’ sleep needs vary, just as the sleep needs of older children and adults do. Your baby might be doing well with more or less sleep than other babies the same age.
Your baby’s mood and wellbeing is often a good guide to whether your baby is getting enough sleep. If your baby is:
- wakeful and grizzly, they might need more sleep
- wakeful and contented, they’re probably getting enough sleep.
How baby sleep changes from 2 to 12 months
As they get older, babies:
- sleep less in the daytime
- are awake for longer between naps
- have longer night-time sleeps and wake less at night
- need less sleep overall.
2-3 months: what to expect from baby sleep
At this age, babies sleep on and off during the day and night. Most babies sleep for 14-17 hours in every 24 hours.
Young babies sleep in cycles that last 50-60 minutes. In young babies, each cycle is made up of active sleep and quiet sleep. Babies move around and grunt during active sleep, and sleep deeply during quiet sleep.
At the end of each cycle, babies wake up for a little while. They might grizzle or cry. They might need help to settle for the next sleep cycle.
At 2-3 months, babies start developing night and day sleep patterns. This means they tend to start sleeping more during the night.
Around 3 months: what to expect from baby sleep
Babies keep developing night and day sleep patterns.
Their sleep cycles consist of:
- light sleep, when baby wakes easily
- deep sleep, when baby is sound asleep and very still
- dream sleep, when baby is dreaming.
Sleep cycles also get longer, which might mean less waking and resettling during sleep. At this age, some babies might regularly be having longer sleeps at night – for example, 4-5 hours.
Most babies still sleep for 14-17 hours in every 24 hours.
3-6 months: what to expect from baby sleep
At this age, most babies sleep for 12-15 hours every 24 hours.
Babies might start moving towards a pattern of 2-3 daytime sleeps of up to two hours each.
And night-time sleeps get longer at this age. For example, some babies might be having long sleeps of six hours at night by the time they’re six months old.
But you can expect that your baby will still wake at least once each night.
6-12 months: what to expect from baby sleep
Babies sleep less as they get older. By the time your baby is one year old, baby will probably sleep for 11-14 hours every 24 hours.
Sleep during the night
From about six months, most babies have their longest sleeps at night.
Most babies are ready for bed between 6 pm and 10 pm. They usually take less than 40 minutes to get to sleep, but some babies take longer.
At this age, baby sleep cycles are closer to those of grown-up sleep – which means less waking at night. So your baby might not wake you during the night, or waking might happen less often.
But many babies do wake during the night and need an adult to settle them back to sleep. Some babies do this 3-4 times a night.
Sleep during the day
At this age, most babies are still having 2-3 daytime naps that last for between 30 minutes and 2 hours.
6-12 months: other developments that affect sleep
From around six months, babies develop many new abilities that can affect their sleep or make them more difficult to settle:
- Babies learn to keep themselves awake, especially if something interesting is happening, or they’re in a place with a lot of light and noise.
- Settling difficulties can happen at the same time as crawling. You might notice your baby’s sleep habits changing when baby starts moving around more.

- Babies learn that things exist, even when they’re out of sight. Now that your baby knows you exist when you leave the bedroom, baby might call or cry out for you.
- Separation anxiety is when babies get upset because you’re not around. It might mean your baby doesn’t want to go to sleep and wakes up more often in the night. As babies mature they gradually overcome this worry.
6-12 months: night-time feeding
From around six months of age, if your baby is developing well, it’s OK to think about night weaning and phasing out night feeds. But if you’re comfortable with feeding your baby during the night, there’s no hurry to phase out night feeds.
You can choose what works best for you and your baby.
A rollover feed is a late feed somewhere between 10 pm and midnight. Some parents find that rollover feeds help babies sleep longer towards morning. If this works for you and your baby, it’s fine to give baby a rollover feed.
Concerns about baby sleep
If you’re concerned about your baby’s sleep, it can be a good idea to track your baby’s sleep for a week or so. This can help you get a clear picture of what’s going on.
This can help you get a clear picture of what’s going on.
You can do this by drawing up a simple chart with columns for each day of the week. Divide the days into hourly blocks, and colour the intervals when your baby is asleep. Keep your chart for 5-7 days.
Once completed, the chart will tell you things like:
- when and how much sleep your baby is getting
- how many times your baby is waking during the night
- how long your baby is taking to settle after waking.
You can also record how you tried to resettle your baby and what worked or didn’t work.
Then you can compare the information in your chart with the general information about baby sleep needs above:
- How does your child compare to other babies the same age? If your baby is wakeful and grizzly and getting much less sleep than others, your baby might need more opportunities for sleep.
- How many times is your baby over six months old waking up during the night? If it’s 3-4 times a night or more, you might be feeling very tired.
 You might want to think about phasing out some of your baby’s sleep habits.
You might want to think about phasing out some of your baby’s sleep habits.
If you decide you need to see a professional for help with your baby’s sleep, take your chart with you.
If you’re concerned about your baby’s sleep, it’s a very good idea to see a child health professional for help. You could start by talking with your GP or child and family health nurse.
How baby sleep patterns affect grown-ups
Babies and grown-ups need sleep for wellbeing, but babies sleep differently from adults. Most parents of babies under six months of age get up in the night to feed and settle their babies. For many, this keeps going after six months.
Some parents are OK with getting up a lot at night as long as they have enough support and they can catch up on sleep at other times. For others, getting up in the night over the long term has a serious effect on them and their family lives.
The quality of your sleep can affect your health and your mood. Being exhausted can make it hard to give your baby positive attention during the day. And your relationship with your baby and the time and attention you give baby during the day can affect the quality and quantity of baby’s sleep.
And your relationship with your baby and the time and attention you give baby during the day can affect the quality and quantity of baby’s sleep.
So it’s important that you get some help if you’re not getting enough sleep. You could start by asking family or friends for help. And if you feel that lack of sleep is affecting you mentally or emotionally, it’s a very good idea to talk with your GP or another health professional.
There’s a strong link between baby sleep difficulties and symptoms of postnatal depression in women and postnatal depression in men. But the link isn’t there if parents of babies with sleep difficulties are getting enough sleep themselves.
Languages other than English
- Arabic (PDF: 471kb)
- Dari (PDF: 469kb)
- Karen (PDF: 298kb)
- Persian (PDF: 420kb)
- Simplified Chinese (PDF: 502kb)
- Vietnamese (PDF: 324kb)
Typical sleep behaviour (1) – newborns 0 to 3 months
Newborn sleep patterns and behaviours
Crying is the way babies communicate with you. In the first three months, newborns cry a lot because they need your help to feed, change or settle so they can get back to sleep. Although they seem to spend a lot of time sleeping (generally 12 to 16 hours in a 24-hour period), they do not have established sleep-wake rhythms like we do. These first three months are an important time for you and your baby to start to learn and understand each other.
In the first three months, newborns cry a lot because they need your help to feed, change or settle so they can get back to sleep. Although they seem to spend a lot of time sleeping (generally 12 to 16 hours in a 24-hour period), they do not have established sleep-wake rhythms like we do. These first three months are an important time for you and your baby to start to learn and understand each other.
Sometimes newborn babies cry for no apparent reason, even though you have helped to soothe them. This is normal – as long as your baby is growing, gaining weight and is happy at other times. However, if you are worried about your newborn’s crying, please talk to your maternal and child health nurse, doctor or phone the Maternal and Child Health Line on 13 22 29.
Newborn sleep rhythms
Newborns do not know the difference between day and night. They do not have established sleep–wake rhythms.
Newborns wake frequently during the night, often because they need to be fed or changed.
At around three months of age, they may start to learn the rhythm of day and night.
You can help your newborn learn to sleep more at night by exposing them to light and gently playing with them during the day. You can also provide a dim and quiet environment at night.
Newborn sleep cycles
We all have sleep cycles. These change as we develop and grow.
Newborns sleep in short bursts, known as sleep cycles. Sleep cycles are usually around 20 to 50 minutes long.
Sleep cycles consist of active sleep and quiet sleep. During active sleep, the newborn may move, groan, open their eyes, cry out or breathe noisily or irregularly. During quiet sleep, they will lie relatively still and their breathing will be more even.
It is a part of normal sleep cycles for newborns to wake between sleep cycles. As they get older, they will learn to settle themselves and fall back to sleep.
Settling your newborn
A newborn’s ability to settle themselves between sleep cycles is called self-settling. Different babies have different temperaments, personalities and self-settling abilities.
Different babies have different temperaments, personalities and self-settling abilities.
You can help your newborn to settle by:
- Putting them in their cot when they are tired, but still awake
- recognising and responding to tired signs
- using a gentle, positive and consistent routine, such as feed, play, sleep
- using different techniques to settle your baby
It is important to create positive sleep associations for your newborn. Some settling techniques may be hard to keep doing for the long term, such as holding your baby until they fall asleep. These can create a negative sleep association for your newborn, resulting in them needing to be held to fall asleep. You need to decide what is right for you and your family.
Feeding your newborn
Newborns need regular feeding, so they usually sleep in short periods.
The first three months are an important time for both you and your baby to learn how to feed and to develop a routine together.
Being breastfed or formula fed does not impact on the age at which your baby will sleep through the night.
Using a sleep routine that prioritises your newborn’s feeding needs, rather than trying to establish a strict sleeping routine is important.
Newborns communicate by crying
The average newborn cries and fusses almost three hours a day until around 3 to 6 months of age. Some newborns cry more than this.
Newborns are usually the most unsettled during their first three months. They also have their longest periods of crying during this time.
A lot of this crying and fussing tends to happen in the late afternoon and evening.
Crying is a newborn’s main way of communicating, you should respond calmly and consistently.
Sometimes, there is no clear reason why a newborn is crying. They may not stop crying even though you try to help them settle.
From approximately two weeks to three to four months of age, newborns go through a stage of increased crying, which peaks around 6 to 8 weeks of age.
The crying may be difficult to soothe. If you need to take a break, place your newborn in their cot or another safe place and take a break for a few minutes. Your self-care is important.
This is a completely normal part of newborn development. There is no need for concern, as long as your baby is growing, gaining weight and is happy at other times.
However, if you are worried about your newborn’s crying, please talk to your maternal and child health nurse, doctor or phone the Maternal and Child Health Line on 13 22 29.
This fact sheet is available for download in the following community languages:
- Arabic - صحيفة المعلومات 1، سلوك النوم المعتاد: المواليد الجدد 0-3 أشهر
- Burmese - အချက်အလက်မှတ်တမ်း 1 - အိပ်စက်ခြင်းအပြုအမူ - မွေးကင်းစကလေးငယ်များ 0-3 လ
- Dari - ورقۀ معلوماتی 1: رفتار خاص خواب: نوزادان 0 تا 3 ماه
- Khmer - សន្លឹកព័ត៌មានទី១៖ ឥរិយាបទគេងជាធម្មតា៖ ទារកទើបនឹងកើតអាយុ០-៣ខែ
- Persian - برگه اطلاع رسانی 1: رفتار معمول خواب: نوزادان 0 تا 3 ماهه
- Punjabi - ਤੱਥ ਸ਼ੀਟ 1: ਨੀਂਦ ਦੇ ਖਾਸ ਵਿਵਹਾਰ: ਨਵਜੰਮੇ 0-3 ਮਹੀਨੇ
- Simplified Chinese - 信息说明书1:典型睡眠行为:0–3个月新生儿
- Simplified English - Typical sleep behaviour (1) – newborns 0 to 3 months
- Spanish - Hoja informativa 1: Conducta habitual del sueño en bebés de 0 a 3 meses
- Vietnamese - Tờ thông tin 1: Hành vi ngủ đặc trưng - trẻ sơ sinh từ 0 đến 3 tháng tuổi
A full list of all our sleep behaviour fact sheets available in community languages can be found here.
Maternal and child health nurse visits are important
Victorian parents have free access to the Maternal and Child Health Service, which is a great support after your baby is born.
Specially trained maternal and child health will work with your family to help you care for your child until they are ready to start school.
As part of this service, you will visit a maternal and child health nurse in your local area at 10 key ages and stages in your child’s development. These visits are important because they you an opportunity to identify and address any issues and concerns early in your child’s development.
Visits take place:
- following discharge from hospital (home visit)
- two weeks
- four weeks
- eight weeks
- four months
- eight months
- one year
- 18 months
- two years
- three and a half years
Families can access the service at other times by telephone or through a centre visit.
Where to get help
- Your local maternal and child health service
- Your GP (doctor)
- Maternal and Child Health Line Tel: 13 22 29 – available 24 hours a day for the cost of a local call throughout Victoria
- Mercy O’Connell Family Centre Tel. (03) 8416 7600
- Queen Elizabeth Centre (QEC) Tel. (03) 9549 2777
- Tweddle Child and Family Health Service Tel. (03) 9689 1577
- Aboriginal Health Service (VAHS) Tel. 03 9419 3000
- Parentline Tel. 13 22 89
- Translating and Interpreting Service (TIS National) Tel. 131 450 – available (24 hours, 7 days a week) for callers who speak other languages
- National Relay Service (24 hours a day, every day) – Speak and listen Tel: 1300 555 727, TTY Tel: 133 677, SMS relay Tel: 0423 677 767. Captioned, internet and video relay calls are also available through this service.
- NURSE-ON-CALL Tel. 1300 60 60 24 – for expert health advice 24 hours a day, 7 daysa week
Children's Clinical Medical Center of Chita
Sadly, pediatricians are increasingly stating the fact that modern children do not get enough sleep. And the lack of sleep in a child is much more dangerous than the lack of sleep in an adult. Children who sleep significantly less than normal grow more slowly and develop worse than their peers. This is easily explained.
And the lack of sleep in a child is much more dangerous than the lack of sleep in an adult. Children who sleep significantly less than normal grow more slowly and develop worse than their peers. This is easily explained.
First, growth hormones are produced during sleep.
Secondly, a good sound sleep contributes to a better memorization of previously received information.
Thirdly, general weakness due to lack of sleep makes it difficult to fully assimilate information.
In addition, the immune system is weakened in children with little sleep and the likelihood of developing diseases of the cardiovascular system increases. Sleep-deprived children become nervous, absent-minded, fussy. This applies to all children, regardless of their age: Babies and teenagers alike should sleep well.
Parents are obligated to provide their child with adequate and healthy sleep.
For children, as for adults, the normal amount of sleep is individual.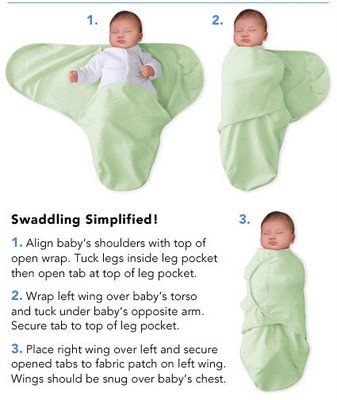 Some kids sleep more, some less. The figures given by doctors are an average. In general, they should strive for. These figures reflect the total amount of sleep per day, that is, taking into account both night sleep and daytime sleep.
Some kids sleep more, some less. The figures given by doctors are an average. In general, they should strive for. These figures reflect the total amount of sleep per day, that is, taking into account both night sleep and daytime sleep.
- Newborn baby sleeps an average of 18-22 hours a day.
- Baby from 1 to 3 months old sleeps 18-20 hours.
- A 3-4 month old baby can sleep 17-18 hours.
- A 5-6 month old baby must sleep at least 16 hours.
- Baby 7 to 12 months old sleeps 14 to 16 hours a day.
- A child from 1 to 1.5 years old must sleep at least 10-11 hours at night and 3-4 hours during the day. In general, at least 14 hours a day.
- A child from one and a half to 2 years old must sleep at least 10-11 hours at night and 2-3 hours during the day. In general, at least 13 hours a day.
- Child 2 to 3 years old must sleep at least 10-11 hours at night and 2-2. 5 hours during the day. In general, at least 12.5 hours a day.
5 hours during the day. In general, at least 12.5 hours a day.
- Children 3-4 years old should sleep at least 10 hours at night and 2 hours during the day. In general, at least 12 hours a day.
- Children 5 to 7 years old should sleep at least 9-10 hours at night and 1.5-2 hours during the day. In general, at least 10.5-11 hours a day.
- Pupils of elementary school may not sleep during the day. At night, they should sleep at least 9 hours, preferably 10 hours.
- Adolescent needs at least 9 hours of sleep per night.
- high school students should sleep an average of 8 hours per night.
In order for the child to get enough sleep, it is necessary to follow the regimen and put him to bed at the same time. This is especially true for night sleep. Make it a rule to put the child to bed, for example, at 21 o'clock. And never deviate from this rule. Let there be guests in the house, let the child become interested in the game, let the parents have things to do - everything should be postponed for the sake of the child's sleep. If he gets used to going to bed at the same time, nothing will prevent him from relaxing in time and wanting to sleep. No game will seem more attractive to him than a fresh warm bed and a cozy pillow.
If he gets used to going to bed at the same time, nothing will prevent him from relaxing in time and wanting to sleep. No game will seem more attractive to him than a fresh warm bed and a cozy pillow.
2. Preparation for sleep, relaxation, rituals.
In order for the child to fall asleep easily and quickly, already an hour or two before bedtime, he must be in a calm atmosphere. Noisy games, difficult puzzles, intellectual tasks, homework preparation, computer games, watching noisy long movies and cartoons, listening to loud music, etc. - all this should end an hour or two before going to bed. The kid at this time can calmly play with toys or listen to a fairy tale read by his mother. An older child can read by himself, chat with his parents, watch a calm movie. Yes, and not so much time will be left for quiet leisure, because direct preparation for sleep will require a lot of time. It is necessary to take a shower, brush your teeth, straighten the bed, change into pajamas, drink some water, etc. The same actions performed day after day before going to bed become a kind of ritual, the performance of which also helps the child tune in to sleep. And this, in turn, contributes to faster and deeper falling asleep and, as a result, better rest. If, for example, a few sips of water before bedtime suddenly become a habit, do not try to wean your child from it. Let this be your ritual helper. If a child is used to parents reading a fairy tale to him, then he needs to read, regardless of employment.
The same actions performed day after day before going to bed become a kind of ritual, the performance of which also helps the child tune in to sleep. And this, in turn, contributes to faster and deeper falling asleep and, as a result, better rest. If, for example, a few sips of water before bedtime suddenly become a habit, do not try to wean your child from it. Let this be your ritual helper. If a child is used to parents reading a fairy tale to him, then he needs to read, regardless of employment.
3. Lightness in the stomach.
The last meal should be 2 hours before bedtime (this does not apply to infants and children who are breastfed). Shortly before bedtime, a child can drink a cup of tea with 1-2 cookies or a glass of kefir, but not with a high-calorie sandwich. Firstly, with ease in the body falls asleep more soundly. Secondly, dense high-calorie snacks before bedtime are bad for the stomach.
4. Comfortable atmosphere in the room.
The room must be well ventilated before putting the child to bed. If the room is dry, after airing it is worth turning on the humidifier and bringing the humidity level to an acceptable level. When the child goes to bed, you need to turn off the light, you can leave a dim nightlight if the baby asks for it. In no case should children be put to bed with the TV turned on or a flickering computer monitor. However, it is impossible to turn on the TV, the overhead light and the sound of the computer speakers even after the child falls asleep. Light noises and light may not wake him up, but they will make the child's sleep superficial, because of this, the body will not get proper rest. If this happens consistently, the child will show signs of sleep deprivation. That is, he seems to be sleeping as much as necessary, but still does not get enough sleep. The reason is the lack of conditions. The room where the child sleeps should be fresh, dark and quiet.
If the room is dry, after airing it is worth turning on the humidifier and bringing the humidity level to an acceptable level. When the child goes to bed, you need to turn off the light, you can leave a dim nightlight if the baby asks for it. In no case should children be put to bed with the TV turned on or a flickering computer monitor. However, it is impossible to turn on the TV, the overhead light and the sound of the computer speakers even after the child falls asleep. Light noises and light may not wake him up, but they will make the child's sleep superficial, because of this, the body will not get proper rest. If this happens consistently, the child will show signs of sleep deprivation. That is, he seems to be sleeping as much as necessary, but still does not get enough sleep. The reason is the lack of conditions. The room where the child sleeps should be fresh, dark and quiet.
Sleep is very important for a child's normal growth and brain development, and regular lack of sleep can lead to serious illnesses. Create the conditions for your baby to fall asleep and carefully make sure that nothing interferes with his full sleep.
Create the conditions for your baby to fall asleep and carefully make sure that nothing interferes with his full sleep.
Baby sleep mode
All parents dream of their baby sleeping well. And not only because they themselves need to snatch a piece of time for rest, but also because healthy sleep is vital for the normal functioning of the child's body.
A newborn and a child in a year or two sleep differently. The total duration of sleep in the first months of life is 16-20 hours a day, gradually decreasing to 12 hours at the age of five and up to 10 hours at the older age. However, with age, not only the duration of sleep changes, but also its rhythm. In young children, REM sleep with dreams predominates over slow-wave, deep sleep.
By about eight months, the proportion of REM sleep decreases and is about 20-25% of the total sleep duration, which corresponds to the sleep rhythm of an adult.
A child is born with an unformed circadian rhythm, and quite often even during pregnancy the baby slept or was awake contrary to his mother. A newborn usually sleeps no more than an hour and a half in a row - that's how long the sleep-wake cycle takes him. At the age of two to eight weeks, this cycle is extended to 4 hours.
Sleeping through the night without waking up, most children will learn before the age of one. At the age of two, children finally form a well-established daily rhythm, but it becomes more difficult to put the child to sleep.
Here are some average norms for the duration of daytime and nighttime sleep for children of different ages: hours;

It is important to note here that all children, of course, are individual and do not necessarily fit into the framework of these average parameters. Do not wake the child unless absolutely necessary, fearing that he will oversleep an extra hour. However, it should not be forgotten that compliance with the sleep regimen has a beneficial effect on the physical and psychological development of the child.
In order for the child to sleep well, certain conditions must be observed. Firstly, the bed and the room in which the child sleeps should be clean and cool, the air should not be too dry. Secondly, the child should not be prevented from falling asleep by extraneous sounds, it is advisable to turn off or dim the light. And, thirdly, before going to bed, the child should not be overfed, but not hungry, otherwise the discomfort in the stomach will prevent him from falling asleep.
Before going to bed, it is better not to play active games with the child - nervous excitement will not soon allow him to fall asleep peacefully. A warm bath soothes a child before bedtime, especially if you add a few drops of lavender essential oil to it. Lullabies should not be neglected - this daily ritual gives the baby a feeling of comfort and stability, calms him down.
A warm bath soothes a child before bedtime, especially if you add a few drops of lavender essential oil to it. Lullabies should not be neglected - this daily ritual gives the baby a feeling of comfort and stability, calms him down.
Several factors can interfere with a child's normal, healthy sleep. If the baby is hungry, thirsty or feels wet, he wakes up. If the baby is hot or, on the contrary, too cold, he can also wake up.
Intestinal colic can interfere with children's sleep, especially in the first months.
Colic is associated with the immaturity of the baby's digestive system: gases accumulate in the intestines and press on its walls, causing pain. Usually colic disappears by 2 months, but can last up to 4-5 months. Special medications, such as Espumizana, a vent tube, dill water, will help soothe the pain. Before using any means, you need to consult a pediatrician.
Erupting teeth cause pain to the child, which, of course, causes disturbances in the usual sleep pattern. To make the baby sleep more peacefully, you can give him special rings filled with gel before going to bed. Such rings are cooled in the refrigerator, after which they are given to the child.
To make the baby sleep more peacefully, you can give him special rings filled with gel before going to bed. Such rings are cooled in the refrigerator, after which they are given to the child.
Night terrors may appear in a child around 2 years of age and greatly interfere with his restful sleep. However, rare nightmares are not necessarily a sign of pathology; on the contrary, children who have never had nightmares are an exception to the rule. If nightmares become frequent, the same nightmare repeats (this can be judged by the description given by the child himself), then it is better to contact a psychologist.
Sometimes the child wakes up at night, but not completely, and in less than a minute he falls asleep again. Such "awakenings" should not frighten parents. Therefore, it is not necessary, having heard the slightest sound from the child’s crib, immediately run to him, grab him in his arms - perhaps it is precisely from the actions of the parents that the child will wake up completely and become capricious.