Red itchy rash stomach
Rash on Stomach: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Skin rashes can be uncomfortable, causing patches of itchy, irritated, red, and swollen skin.
Rashes can form on any part of the skin, including the stomach.
In some cases, it’s easy to identify the cause of your stomach rash, like when you accidentally come into contact with poison oak or poison ivy.
Other times, it can be harder to know where the rash originated.
There are many possible causes of a stomach rash and many are not cause for concern.
But they all have something in common: If you’ve got a rash on your stomach, you probably want it to be gone!
In this article, I’ll tell you about some of the most common potential causes of a stomach rash.
I’ll talk about their symptoms, including serious symptoms to watch out for, and how these rashes can be treated.
I’ll also tell you when to see a doctor.
Talk to a doctor online.
Start my visitWhat Causes a Rash on Your Stomach?
Not all stomach rashes are the same.
They may develop quickly, or spread over time. A rash may indicate anything from an allergic reaction to an underlying infection.
There are many possible causes of a stomach rash, which is why it’s important to speak to a provider when you’re unsure about what’s causing your symptoms.
Possible causes of a mild stomach rash include:
- Pregnancy: During the third trimester of pregnancy, an itchy rash can appear in the stretch marks on the stomach. This is called pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy, or PUPPP. This rash looks like little pink pimples or hives inside the stretch marks. The rash usually goes away within 1-2 weeks of delivering your baby. A PUPPP rash can be very itchy, but it shouldn’t cause complications for you or your baby.
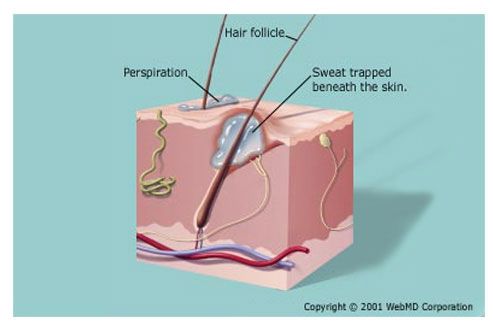
- Scabies: This pimple-like rash is caused by an infestation of skin mites. The human itch mite, or scabies mite, burrows into your skin and lays eggs. The resulting rash is very itchy, especially at night; the rash may also have scales.
 Scabies can be spread from one person to another via prolonged, skin-to-skin contact—institutions such as nursing homes and child care facilities are often the sites of scabies outbreaks. Scabies can be cured by a prescription scabicide—a product that kills the mites and their eggs.
Scabies can be spread from one person to another via prolonged, skin-to-skin contact—institutions such as nursing homes and child care facilities are often the sites of scabies outbreaks. Scabies can be cured by a prescription scabicide—a product that kills the mites and their eggs.
- Ringworm: This rash is not caused by a worm, as its name suggests. Ringworm is caused by a fungus, and it usually becomes a red, scaly rash in a circular—or ring-like—pattern. You can get ringworm from contact with another person who has a ringworm infection, or from an animal or object that has the fungus. Athlete’s foot and jock itch are types of ringworm. If you have it on your stomach, it’s possible that jock itch has spread up from your groin area to infect your stomach. Over-the-counter antifungal treatments can help; if they don’t, contact a doctor.
- Scarlet fever: Scarlet fever is caused by the same bacteria that causes strep throat.
 If your child has a sore throat and a rash, they may have contracted scarlet fever. The rash usually starts on the neck, armpits, or groin, but can spread to other parts of the body, including the stomach. The rash will feel like sandpaper. Scarlet fever is more common in children, but adults can get it, too. If you or your child has scarlet fever, you’ll need antibiotics to clear the infection.
If your child has a sore throat and a rash, they may have contracted scarlet fever. The rash usually starts on the neck, armpits, or groin, but can spread to other parts of the body, including the stomach. The rash will feel like sandpaper. Scarlet fever is more common in children, but adults can get it, too. If you or your child has scarlet fever, you’ll need antibiotics to clear the infection.
- Contact dermatitis: Contact dermatitis is a type of rash that can happen when your skin comes into contact with irritants, or if you have an allergic reaction to something you’ve touched. Symptoms of contact dermatitis include redness, itching, swelling and stinging of the skin. Other times, you may experience blistering or an oozy rash, like those caused by poison ivy, poison oak, and allergic reactions. Contact dermatitis is not contagious and cannot be spread through the fluid caused by blisters.
- Eczema: Eczema refers to several types of allergic skin conditions.
 Eczema rashes are often red, dry, and very itchy. They can appear on the face, hands, feet, inside of elbows, behind the knees, or on the stomach. Though experts don’t fully understand the connection, people with eczema are more likely to develop asthma or experience regular allergies. The severity of eczema may change over time, but it’s typically a chronic condition.
Eczema rashes are often red, dry, and very itchy. They can appear on the face, hands, feet, inside of elbows, behind the knees, or on the stomach. Though experts don’t fully understand the connection, people with eczema are more likely to develop asthma or experience regular allergies. The severity of eczema may change over time, but it’s typically a chronic condition.
- Psoriasis: The stomach is a common area for a psoriasis flare up. Psoriasis is a chronic skin disorder that causes thick pink or red patches on the skin, often covered with white or silvery scales called plaques. Psoriasis is caused by an immune disorder, and is often an inherited condition.
- Impetigo: Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection that is more commonly found on infants and young children. The main symptoms of impetigo are reddish sores that ooze. These sores usually form around the nose and mouth, though they can form elsewhere on the body, including the stomach.
 Antibiotic ointment or cream prescribed by a provider is required to treat the infection.
Antibiotic ointment or cream prescribed by a provider is required to treat the infection.
Possible causes of a more serious stomach rash include:
- Allergies to food or medication: Allergic reactions to medications can happen when a substance that you’re allergic to comes in contact with your skin or enters the body through the mouth. Some allergic skin reactions can be mild, while others may be more life-threatening. If you or a loved one is experiencing a severe allergic reaction, reach out to a provider or seek emergency care immediately.
- Lyme disease: Lyme disease is extremely common in the United States and is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected ticks. Symptoms include fever, headache, fatigue, and a characteristic skin rash called erythema migrans (EM). The appearance of an EM rash can vary widely. It is generally described as target-like. It usually begins as a small bump or redness at the site of the bite and then gradually expands, sometimes reaching up to 12 inches in diameter.

- Kawasaki disease: Kawasaki disease (KD) is an extremely rare but serious disease that primarily affects children five years and younger. As few as 20 children in 100,000 in the United States have this condition. Though the exact cause of KD is unknown, it can cause fever for longer than five days, rash, swelling of the hands and feet, irritation and redness of the whites of the eyes, swollen lymph glands in the neck, and irritation and inflammation of the mouth, lips, and throat. Post-COVID multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), is a rare condition that occurs about one month after an infection with COVID-19 and can cause similar or identical symptoms. This may be seen in children up to 17 years old.
- Viral infection: Multiple viruses can also produce a rash. Viral rashes often come with additional viral symptoms, such as fever, diarrhea, runny nose, cough, or sore throat. Your healthcare provider can often recognize a viral rash based on its appearance and your other symptoms.
Symptoms of a Stomach Rash
A stomach rash can cause a wide array of symptoms, depending on the type of rash present.
Generally, a rash involves a change in the color, feeling, or texture of your skin.
Some symptoms you may experience with a stomach rash include:
- Dry, red, itchy skin
- Small blisters or bumps
- Thick, pink or red patches on the skin
- White or silvery scales on the skin
- Painful patches of skin
- General itchiness
Serious symptoms
Sometimes, a stomach rash can be a sign of a more serious condition.
In those cases, there may be additional symptoms present, like:
- Fever
- Chills
- Joint pain or stiffness
- Change in consciousness (including unresponsiveness or fainting)
- Purple-colored rash
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Sudden swelling of the face, lips, or tongue
- Tightness in the throat
- Symptoms that do not improve despite treatment
If you or a loved one experiences any of the above symptoms, seek emergency care as soon as possible.
What are the Treatments for a Stomach Rash?
The appropriate treatment for a skin rash depends on the cause of your symptoms.
Speak to a provider to determine which treatment option, if any, is right for you.
Prescription medications
Some skin rashes, including psoriasis and eczema, may be treated with prescription lotions, ointments, and/or oral or injectable medications.
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications
In many cases, over-the-counter (OTC) medications like hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion can help to soothe your rash, no matter the cause.
Other OTC medications, like ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol), may help to alleviate pain associated with your rash. Antihistamines like loratadine (Claritin), cetirizine (Zyrtec), and diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can be helpful in treating rashes and itching.
Home remedies
Before resorting to home remedies, consult with a healthcare professional to determine whether certain home remedies will make your symptoms better or worse.
If your provider says they are safe, home remedies can help soothe the discomfort and pain caused by some skin rashes.
A cool bath with baking soda, uncooked oatmeal, or colloidal oatmeal can help soothe the itching caused with chickenpox, poison ivy, and poison oak.
Stomach Rash Prevention
Not all stomach rashes are preventable.
However, there are some things you can do to prevent certain stomach rashes, including:
- Practice good personal hygiene to help prevent against viral infection, including washing hands thoroughly
- Avoid perfumed soaps and laundry detergents
- Moisturize your skin with a fragrance-free moisturizer, especially in dry and colder temperatures
- Get vaccinated whenever eligible, including the rubella and chickenpox vaccines
Talk to a doctor online.
Start my visitWhen to See a Doctor
If you’ve developed a mild rash and are not experiencing any other symptoms, it’s OK to try some over-the-counter treatments and to wait a few days to see if your rash will go away on its own.
If the rash persists for a few days, spreads, becomes painful or infected, or you develop a fever, your rash may indicate a medical condition that requires treatment.
If you experience severe symptoms, or if signs of a new rash don’t go away on their own within one week, reach out to your provider.
How K Health Can Help
Did you know you can access online urgent care with K Health?
Check your symptoms, explore conditions and treatments, and if needed, text with a healthcare provider in minutes.
K Health’s AI-powered app is HIPAA compliant and is based on 20 years of clinical data.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a rash on the stomach mean?
There are several possible causes of a stomach rash, many of which are not cause for concern. However, if you’re unsure about what’s causing your stomach rash, seek help from a medical professional in case you need prescription treatment.
However, if you’re unsure about what’s causing your stomach rash, seek help from a medical professional in case you need prescription treatment.
What does a stress rash look like on the stomach?
Rashes are a possible side effect of psychological stress. Rashes can include dry or sore skin, itchy patches on the skin, scaly skin, and other types of rashes.
How do you treat a rash on your stomach?
Most rashes will start to get better within a week. Depending on the type of rash you have, your provider may also recommend an over-the-counter or prescription treatment. If your rash does not improve within a week, or if you experience any severe symptoms, reach out to your provider for more information.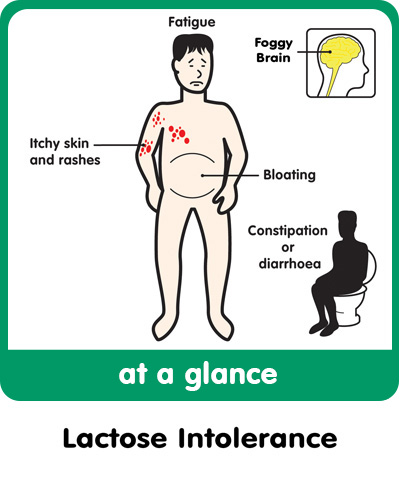
What does a virus rash look like?
Some viral rashes look like pink dots on the skin, while others may look lacy or like tiny blisters. Certain viral rashes are also more common in the summertime. Viral rashes often come with additional viral symptoms, such as fever, diarrhea, runny nose, cough, or sore throat.
K Health articles are all written and reviewed by MDs, PhDs, NPs, or PharmDs and are for informational purposes only. This information does not constitute and should not be relied on for professional medical advice. Always talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of any treatment.
K Health has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references.
-
Pruritic Urticarial Papules And Plaques Of Pregnancy.
 (2021).
(2021).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539700/ -
Scabies Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs). (2020).
https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/scabies/gen_info/faqs.html -
Scarlet Fever: All You Need to Know.
 (2021).
(2021).
https://www.cdc.gov/groupastrep/diseases-public/scarlet-fever.html -
Association of psychological stress with skin symptoms among medical students. (2018).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5885122/ -
Cutaneous signs in COVID‐19 patients: A review.
 (2020).
(2020).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7273098/ -
Kawasaki Disease. (2020).
https://www.cdc.gov/kawasaki/about.html -
Lyme Disease.
 (2021).
(2021).
https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/index.html -
Rashes. (2016).
https://medlineplus.gov/rashes.html -
Rosacea.
 (2016).
(2016).
https://medlineplus.gov/rosacea.html -
Rubella. (2019).
https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/rubella
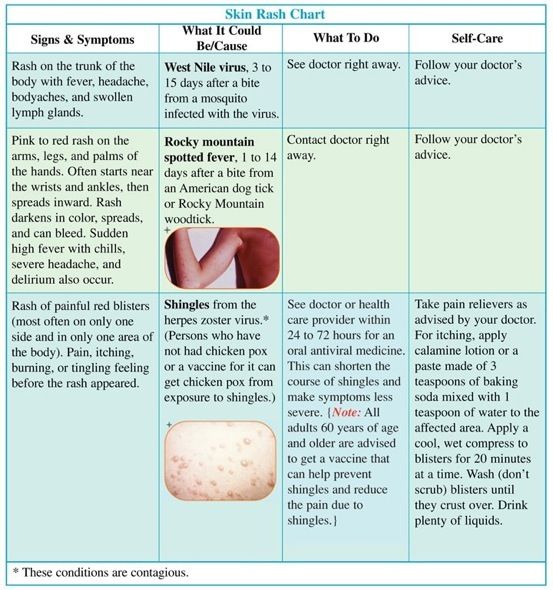
22 Common Skin Rashes, Pictures, Causes & Treatment
Rashes have a variety of causes, from bites to chickenpox to serious conditions like drug allergies.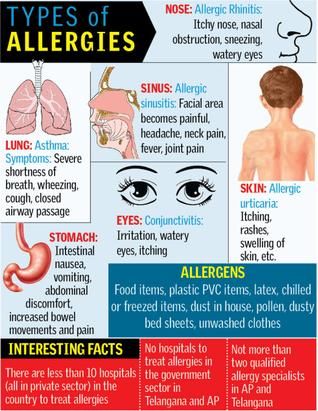 Seek medical attention if home remedies do not help or if you also have symptoms such as fever or dizziness.
Seek medical attention if home remedies do not help or if you also have symptoms such as fever or dizziness.
A rash is any area of irritated or swollen skin on your body. Rashes are often itchy and painful and can appear differently on different skin tones. While they are often described as red, on darker skin tones they may be purple, gray, or white.
There are many different causes of rashes. Here’s a list of 22 potential causes with pictures.
Warning: graphic images ahead.
Fleabites
Share on PinterestFlea bites of the lower leg causing red bumps and scabbing. Angela Hampton Picture Library / Alamy Stock Photo
- usually located in clusters on the lower legs and feet
- itchy, small red bumps on lighter skin tones, and more plum-like in color on darker skin tones
- symptoms begin immediately after being bitten
Read the full article on fleabites.
Fifth disease
Share on PinterestFifth disease is a viral illness caused by parvovirus, which can cause a ‘slapped cheek’ rash. Kardelen Yang?n Via Wikipedia
Kardelen Yang?n Via Wikipedia
- symptoms include headache, fatigue, low fever, sore throat, runny nose, diarrhea, and nausea
- children are more likely than adults to experience a rash
- round, bright red rash on the cheeks, but it may be less noticeable on darker skin tones
- usually after the face rash, a lacy-patterned rash may appear on the arms, legs, and upper body and might be more visible after a hot shower or bath
Read the full article on fifth disease.
Rosacea
Share on PinterestWeinkle, A. P., Doktor, V., & Emer, J. (2015). Update on the management of rosacea. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, 8, 159177. https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S58940
- chronic (long-term) skin disease that goes through cycles of fading and relapse
- relapses may be triggered by spicy foods, alcoholic beverages, sunlight, stress, and the intestinal bacteria Helicobacter pylori
- the four subtypes of rosacea encompass a wide variety of symptoms
- common symptoms include facial flushing, raised red bumps, facial redness, skin dryness, and skin sensitivity
- on darker skin tones, brown or yellowish-brown bumps may appear, and the rash can have a dusky coloration
Read the full article on rosacea.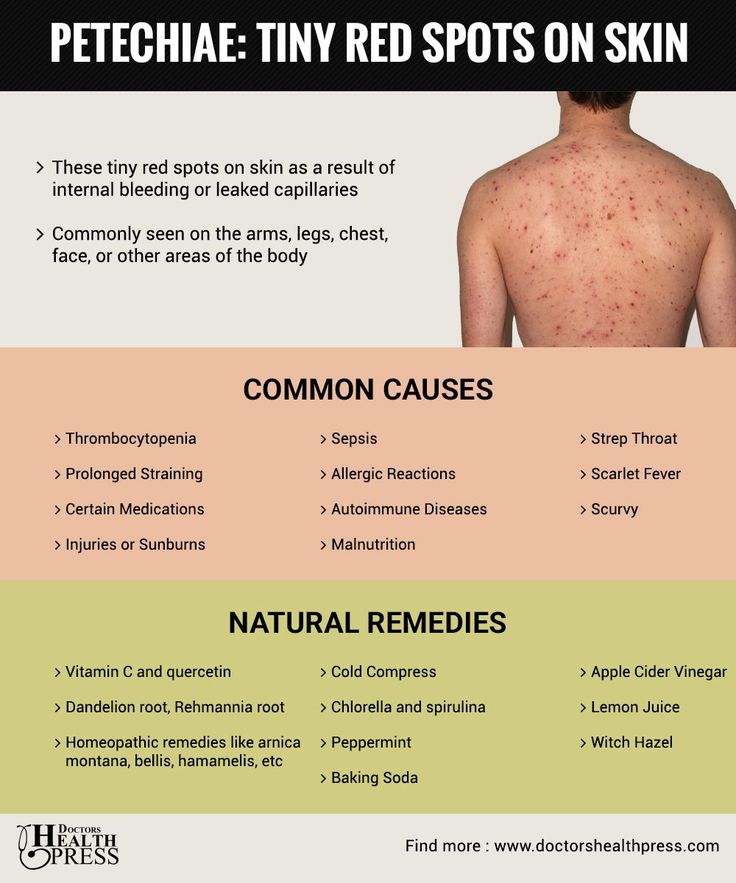
Impetigo
Share on PinterestThis image also depicts impetigo on dark skin. Photography courtesy of Grook Da Oger/Wikimedia
- most common in children 2 to 5 years old, but can happen at any age
- often located in the area around the mouth, chin, and nose
- irritating rash and fluid-filled blisters that pop easily and form a honey-colored crust
- can also appear brown, purple, or gray on darker skin tones
Read the full article on impetigo.
Ringworm
Share on PinterestRingworm on the face of a child. BSIP SA / Alamy Stock Photo
- itchy, circular scaly patches with raised borders
- on lighter skin tones, the patches can appear pink or red
- on darker skin tones, the patches can appear gray or brown
- skin in the middle of the ring appears clearer, and the edges of the ring may spread outward
Read the full article on ringworm.
Contact dermatitis
Share on PinterestContact dermatitis of the arm. vvoe/Shutterstock
- appears hours to days after contact with an allergen
- has visible borders and typically appears where your skin touched the irritating substance
- on lighter skin tones, it can appear red
- on darker skin tones, it may be less noticeable
- may have blisters that weep, ooze, or become crusty
- typically itchy, scaly, or raw
Read the full article on contact dermatitis.
Allergic eczema
Share on PinterestDmitriy SIMAKOV/Getty Images
- may resemble a burn
- often found on hands and forearms
- skin is itchy, scaly, or raw
- may have blisters that weep, ooze, or become crusty
- on lighter skin tones, it can appear red
- on darker skin tones, it can cause darker brown, purple, or gray patches
Read the full article on allergic eczema.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease
Share on PinterestHand-foot-and-mouth disease MidgleyDJ at en.wikipedia, CC BY-SA 3. 0, via Wikimedia Commons
- usually affects children under age 5
- painful, red blisters in the mouth and on the tongue and gums
- flat or raised red spots located on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
- on darker skin tones, it can be skin-colored or grayish-brown
- spots may also appear on the buttocks or genital area
Read the full article on hand, foot, and mouth disease.
Diaper rash
Share on Pinterest
- located on areas that have contact with a diaper
- skin looks red, wet, and slightly lighter or darker than typical skin color
- may be warm to the touch
Read the full article on diaper rash.
Eczema
Share on PinterestBenislav/Shuttertstock
- dry, rough, flaky, inflamed, and irritated skin
- affected areas may be red and itchy
- hair loss may occur in the area with the rash
- on darker skin tones, it can appear as darker brown or gray patches
Read the full article on eczema.
Psoriasis
Share on PinterestPsoriasis is an inflammatory skin condition that causes dry, scaly plaques on the skin. It is immune system mediated, and genetics likely also play a role. Vitek2808/Shutterstock
- scaly, silvery, sharply defined skin patches
- on darker skin tones, it may look darker than the surrounding skin or it might appear purple
- commonly located on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back
- may be itchy or asymptomatic
Read the full article on psoriasis.
Chickenpox
Share on PinterestChild with chickenpox Grook da oger, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
- clusters of itchy, red, fluid-filled blisters in various stages of healing all over the body
- on darker skin tones, it can be red, the same as the natural skin tone, or a little darker; scabs can appear gray
- rash is accompanied by fever, body aches, sore throat, and loss of appetite
- remains contagious until all blisters have crusted over
Read the full article on chickenpox.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Share on Pinterestbutterfly rash.SLE systemic lupus erythematosus
- an autoimmune disease that displays a wide variety of symptoms and affects many body systems and organs
- a wide array of skin and mucous membrane symptoms that range from rashes to ulcers
- classic butterfly-shaped face rash that crosses from cheek to cheek over the nose
- can appear bright red on lighter skin tones
- on darker skin tones, it may appear red, brown, or darker than the original skin color
- rashes may appear or get worse with sun exposure
Read the full article on systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Share on Pinterestchatuphot/Shutterstock
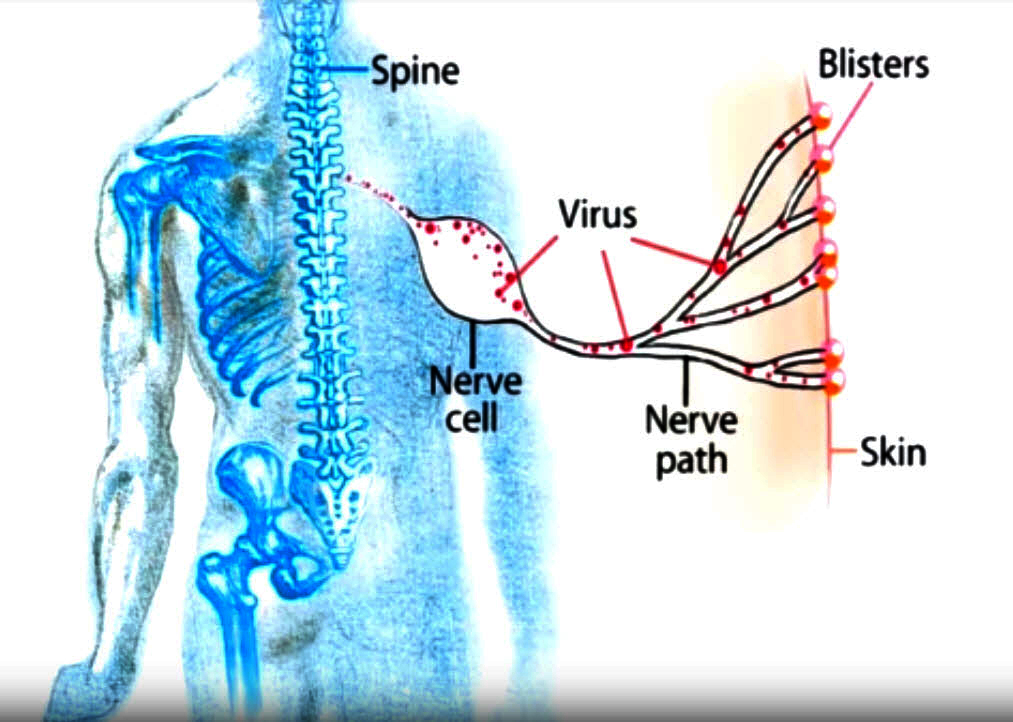
- painful rash that may burn, tingle, or itch, even if there are no blisters present
- clusters of fluid-filled blisters that break easily and weep fluid
- rash emerges in a band-like pattern that appears most commonly on the torso, but may occur on other parts of the body, including the face
- may be accompanied by low fever, chills, headache, or fatigue
Read the full article on shingles.
Cellulitis
Share on PinterestCellulitis of the lower legs. TisforThan/Shutterstock
This condition is considered a medical emergency. Urgent care is required.
- caused by bacteria or fungi entering through a crack or cut in the skin
- tends to be red or pink
- it may appear less obvious on darker skin tones and can also look brown, gray, or purple
- painful, swollen skin with or without oozing that spreads quickly
- hot and tender to the touch
- might be a sign of serious infection requiring medical attention
Read the full article on cellulitis.
Drug allergy
Share on Pinterest
This condition is considered a medical emergency. Urgent care is required.
- mild to severe itchy, red rash may occur days to weeks after taking a drug
- severe drug allergies can be life threatening, and symptoms include rash, blisters, hives, racing heart, swelling, itching, and difficulty breathing
- other symptoms include fever, stomach upset, and tiny purple or red dots on the skin
Read the full article on drug allergies.
Scabies
Share on PinterestScabies is an itchy skin infestation with mites. Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
- symptoms may take 2 to 5 weeks to appear
- extremely itchy rash with small bumps that may be scaly
- raised, white, or flesh-toned lines
Read the full article on scabies.
Measles
Share on PinterestMeasles on the torso of a child phichet chaiyabin/Shutterstock
- symptoms include fever, sore throat, red watery eyes, loss of appetite, cough, and runny nose
- depending on skin tone, the rash may be red, skin-colored, or darker than the natural skin color
- the rash spreads from the face down the body 3 to 5 days after first symptoms appear
- tiny white spots with bluish-white centers on a red background can appear inside the mouth
Read the full article on measles.
Tick bite
Share on PinterestAitor Diago/Getty Images
- painless and causes only minor signs and symptoms, such as a change in skin color, swelling, or a sore on the skin
- rash, burning sensation, or blisters
- difficulty breathing, which requires immediate medical attention
- the tick often remains attached to the skin for a long time
- bites rarely appear in groups
- may look like a target, circular, expanding — 70 to 80 percent of people with Lyme disease will have this rash
Read the full article on tick bites.
Seborrheic eczema
Share on PinterestZay Nyi Nyi/Shutterstock
- yellow or white scaly patches that flake off
- affected areas may be red — though they may appear faint on darker skin tones —, itchy, greasy, yellowish or white patches
- hair loss may occur in the rash area
Read the full article on seborrheic eczema.
Scarlet fever
Share on PinterestChild with scarlet fever rash and rosy cheeks badobadop, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
- occurs at the same time as or right after a strep throat infection
- rash is made up of tiny bumps that make it feel like “sandpaper”
- bright red tongue
- people with lighter skin tones can have a bright red rash all over the body (but not on the palms of your hands and soles of your feet)
- on people with darker skin tones, it may be more difficult to see the rash, but their skin will have a sandpaper-like texture
Read the full article on scarlet fever.
Kawasaki disease
Share on Pinterest
This condition is considered a medical emergency. Urgent care is required.
- usually affects children under age 5
- red cracked lips, swollen tongue (strawberry tongue), high fever, swollen red palms and soles of the feet, swollen lymph nodes, bloodshot eyes
- can be harder to recognize on darker skin tones
- may cause severe heart problems
Read the full article on Kawasaki disease.
Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is one of the most common causes of rashes. This type of rash occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with a foreign substance that causes an adverse reaction, leading to a rash. The resulting rash may be itchy, red, or inflamed.
Possible causes of contact dermatitis include:
- beauty products
- soaps
- laundry detergent
- dyes in clothing
- chemicals in rubber, elastic, or latex
- poisonous plants, such as poison oak, poison ivy, or poison sumac
Medications
Taking medications may also cause rashes. They can form as a result of:
- an allergic reaction to the medication
- a side effect of the medication
- photosensitivity from the medication
Other causes
Other possible causes of rashes include the following:
- A rash can sometimes develop in the area of a bug bite, such as a fleabite. Tick bites are of particular concern because they can transmit disease.
- Atopic dermatitis, the most common form of eczema, is a rash that may be more common in people with asthma or allergies. The rash is often reddish, though it can be skin-colored or darker on people with darker skin tones. It can be itchy with a scaly texture.
- Psoriasis is a common skin condition that can cause a scaly, itchy, red, or purplish rash to form along the scalp, elbows, and joints.
- Seborrheic eczema is a type of eczema that most often affects the scalp and causes redness, scaly patches, and dandruff. It can also occur on the ears, brows, or nose. When babies have it, it’s known as cradle cap.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease that can trigger a rash on the cheeks and nose. This rash is known as a “butterfly,” or malar, rash.
- Rosacea is a chronic skin condition of unknown cause. There are several types of rosacea, but all are characterized by redness and rash on the face.
- Ringworm is a fungal infection that causes a distinctive ring-shaped rash. The same fungus that causes ringworm on the body and the scalp also causes jock itch and athlete’s foot.
- Diaper rash is a common skin irritation in infants and toddlers. It can be associated with prolonged exposure to a wet diaper.
- Scabies is an infestation by tiny mites that live on and burrow into your skin. It causes a bumpy, itchy rash.
- Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of the skin. It usually appears as a red, swollen area that is painful and tender to the touch. If left untreated, the infection causing the cellulitis can spread and become life threatening.
Causes of rashes in children
Children are particularly prone to rashes that develop as a result of illnesses:
- Chickenpox is caused by a virus, and the rash is characterized by small itchy bumps and blisters that form all over the body.
- Measles is a viral respiratory infection that causes a widespread rash consisting of itchy, red bumps.
- Scarlet fever is an infection due to group A Streptococcus bacteria that produces a toxin, causing a bright red or skin-tone-colored, sandpaper-like rash.
- Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a viral infection that can cause red lesions on the mouth and a rash on the hands and feet.
- Fifth disease is a viral infection that causes a red, flat rash on the torso, arms, and legs.
- Kawasaki disease is a rare but serious illness that triggers a rash and fever in the early stages and can lead to heart complications.
- Impetigo is a contagious bacterial infection that causes an itchy, crusty rash and yellow, fluid-filled sores on the affected area, such as the face, neck, or hands.
You can treat most contact rashes, but it depends on the cause. Follow these guidelines to help ease discomfort and speed up the healing process:
- Use mild, gentle cleansers instead of scented bar soaps.
- Use warm water instead of hot water for washing your skin and hair.
- Pat the rash dry instead of rubbing it.
- Let the rash breathe. If it’s possible, avoid covering it with clothing.
- Stop using new cosmetics or lotions that may have triggered the rash.
- Apply unscented moisturizing lotion to areas affected by eczema.
- Avoid scratching the rash because doing so can make it worse and could lead to infection.
- Apply an over-the-counter (OTC) hydrocortisone cream to the affected area if the rash is very itchy and causing discomfort. Calamine lotion can also help relieve rashes from chickenpox, poison ivy, or poison oak.
- Take an oatmeal bath. This can soothe the itchiness associated with rashes from eczema or psoriasis. Here’s how to make an oatmeal bath.
- Wash your hair and scalp regularly with dandruff shampoo if you have dandruff along with a rash. Medicated dandruff shampoo is commonly available at drugstores, but your doctor can prescribe stronger types if you need them.
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications
Talk with a healthcare professional, who may recommend OTC medication like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to treat mild pain associated with the rash.
Avoid taking these medications for an extended period because they can have side effects. Ask a healthcare professional how long it’s safe for you to take them. You may not be able to take them if you have liver or kidney disease or a history of stomach ulcers.
Call a healthcare professional if the rash doesn’t go away with home remedies. You should also contact them if you’re experiencing other symptoms in addition to your rash and you suspect you have an illness.
If you don’t already have a physician, you can use the Healthline FindCare tool to find a professional near you.
Go to the hospital immediately if you experience a rash along with any of the following symptoms:
- increasing pain or discoloration in the rash area
- tightness or itchiness in the throat
- difficulty breathing
- swelling of the face or limbs
- fever of 100.
4°F (38°C) or higher
- confusion
- dizziness
- severe head or neck pain
- repeated vomiting or diarrhea
Contact a healthcare professional if you have a rash as well as other systemic symptoms, including:
- joint pain
- a sore throat
- red streaks or tender areas near the rash
- a recent tick bite or animal bite
Your healthcare professional will perform a physical exam and inspect your rash. Expect to answer questions about your:
- rash
- medical history
- diet
- recent use of products or medications
- hygiene
Your healthcare professional may also:
- take your temperature
- order tests, such as an allergy test or complete blood count
- perform a skin biopsy, which involves taking a small sample of skin tissue for analysis
- refer you to a specialist, such as a dermatologist, for further evaluation
Your healthcare professional may also prescribe medication or medicated lotion to relieve your rash. Most people can treat their rashes effectively with medical treatments and home care.
Follow these tips if you have a rash:
- Use home remedies to soothe mild contact rashes.
- Identify potential triggers for the rash and avoid them as much as possible.
- Call a healthcare professional if the rash doesn’t go away with home treatments. You should also contact them if you’re experiencing other symptoms in addition to your rash and you suspect you have an illness.
- Carefully follow any treatments your doctor prescribes. Speak with a healthcare professional if your rash persists or gets worse despite treatment.
Healthline and our partners may receive a portion of revenues if you make a purchase using a link above.
Read the article in Spanish.
Allergic rash - urticaria | Symptoms
Drugs, contrast agents (used in imaging studies such as computed tomography)
Signs: Allergic rash that begins within 48 hours after using the drug.
Emotional and physical stimuli (stress and anxiety, cold, exercise, skin pressure, heat, sunlight, sweating)
Signs: Allergic rash, which usually begins within seconds or minutes after contact with an irritant; an allergic rash that starts within 4 to 6 hours and affects only the area of skin where pressure has been applied, or an allergic rash that only affects the area of skin exposed to sunlight.
Food (food allergens)
Signs: Allergic rash that starts within minutes or hours of consumption.
Infections (bacterial, parasitic, viral)
Signs: Fever, chills, and fatigue. Specific infection symptoms, particularly for parasitic infections, recent travel to a developing country.
Insect bites or burns
Signs: Allergic rash that starts within seconds or minutes of an insect bite or burn.
Serum sickness
Signs: Allergic rash that begins within 7 to 10 days after an injection of a blood product (as in a transfusion), a drug derived from the blood of animals (used to treat venomous snake and spider bites). May be accompanied by fever, joint pain, swollen lymph nodes, and abdominal pain.
Contact allergens (latex, animal saliva or dander, dust, pollen or mold)
Signs: An allergic rash that begins within minutes or hours of contact.
Transfusion reactions
Signs: Allergic rash that usually starts within minutes of a blood product transfusion.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Signs: Various symptoms depending on the autoimmune disease. With systemic lupus erythematosus, symptoms may include fever, fatigue, headache, joint pain and swelling, pain when breathing, and mouth ulcers.
Sjögren's syndrome
Signs: Dry eyes and dry mouth.
Urticarial vasculitis
Signs: An allergic rash that may be painful but not itchy. Usually lasts more than 24 hours. Does not whiten (brighten) when pressure is applied. May be accompanied by the formation of small blisters and red-violet spots (purpura).
Cancer (digestive or lung or lymphoma)
Signs: Weight loss, night sweats, abdominal pain, cough (sometimes with blood), jaundice, swollen lymph nodes, or a combination of these symptoms.
Chronic idiopathic allergic rash
Signs: Allergic rash that occurs almost daily and itching that lasts for 6 weeks with no apparent cause.
Endocrine disorders (thyroid disease or elevated progesterone)
Signs: For thyroid disorders: difficulty in tolerating heat or cold, slow or fast heart rate, and shaking (tremor) or slowness. Occurs in women who take birth control pills, undergo hormone therapy, or who have an allergic rash that appears before the onset of the menstrual period and disappears after it ends.
Mastocytosis
Signs: Small red bumps that turn into an allergic rash when touched. Sometimes abdominal pain, mild flushing, and recurring headaches.
Skin manifestations of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
If, when dealing with complaints of skin problems, a dermatologist advises you to consult a gastroenterologist, do not be surprised. His recommendation is for good reason, especially if the skin conditions are accompanied by abdominal pain and other digestive disturbances such as bloating, diarrhea, or constipation.
The skin is the largest organ in the body and has important protective functions. In addition, it is an indicator of what is happening inside the body and in particular the state of the gastrointestinal tract. Most skin problems do not occur on their own, but are the result of disease or malnutrition. Unlike other organs, we can easily check the health of the skin, so the appearance of skin problems is an occasion to contact a specialist and check your health.
The skin and organs of the gastrointestinal tract are closely related, they have a common origin and perform protective functions in the body, which include the formation of immunity and interaction with microflora. Skin problems can develop as a result of a violation of the functions of the digestive organs, and accompany the course of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract lead to a violation of the absorption of substances necessary for the body with the development of their deficiency, which affects the condition of the skin. Such a violation can be caused by celiac disease, lactase deficiency, chronic pancreatitis, liver and gallbladder diseases, atrophic gastritis, infectious and parasitic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Most often, deterioration of the skin condition causes malabsorption of vitamins and minerals in the intestines.
External manifestations of vitamin and mineral deficiency:
- dryness, pallor and peeling of the skin;
- eruptions resembling acne, pustular lesions of the skin;
- pruritus;
- discoloration of the skin - redness, pigmentation disorder;
- hemorrhages, gingivitis, stomatitis, poorly healing wounds;
- dryness, dullness, hair loss;
- brittleness, striation of nails;
Infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori , is known to cause chronic gastritis and peptic ulcer disease. But in addition to its main role, this bacterium can participate in the development of skin diseases accompanied by a rash or rosacea (redness, expansion of small and superficial vessels of the skin of the face with the formation of eruptive elements).
The presence in the body of other intruders - worms can also cause skin problems, most often it is a rash like urticaria.
Skin manifestations of diseases of the digestive tract are varied, and it is difficult to independently identify the cause of their appearance. Therefore, if any skin lesion appears, it is necessary to consult a doctor to exclude diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In gastroenterological practice, the condition of the skin also plays an important role in assessing the activity of the disease and prescribing effective treatment.
In addition to the health of the digestive tract, nutrition significantly affects the condition of the skin. Therefore, along with the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, you need to make sure that you get enough of the nutrients your body needs: micro- and macronutrients.