Problems with the placenta in pregnancy
What complications can affect the placenta?
Complications that can affect the placenta during pregnancy or childbirth include:
- low-lying placenta and placenta praevia
- retained placenta – when part of the placenta remains in the womb after giving birth
- placental abruption – when the placenta starts to come away from the wall of the womb
These complications aren't common.
Low-lying placenta and placenta praevia
As your pregnancy progresses, your womb expands and this affects the placenta's position. The area where the placenta is attached usually stretches upwards, away from your cervix.
If the placenta stays low in your womb, near to or covering your cervix, it may block the baby's way out.
This is called low-lying placenta if the placenta is less than 2cm from the cervix, or placenta praevia if the placenta is completely covering the cervix.
Placenta praevia, where the cervix is completely covered at the end of pregnancy, affects about 1 in every 200 births.
The position of your placenta will be recorded at your 18- to 21-week ultrasound scan.
If your placenta is significantly low, you'll be offered an extra ultrasound scan later in your pregnancy (usually at about 32 weeks) to check its position again.
For 9 in every 10 women, the placenta will have moved into the upper part of the womb by this point.
If the placenta is still low in your womb, there's a higher chance that you could bleed during your pregnancy or during your baby's birth. This bleeding can be very heavy and put you and your baby at risk.
You may be advised to come into hospital at the end of your pregnancy so emergency treatment (such as a blood transfusion) can be given very quickly if you bleed.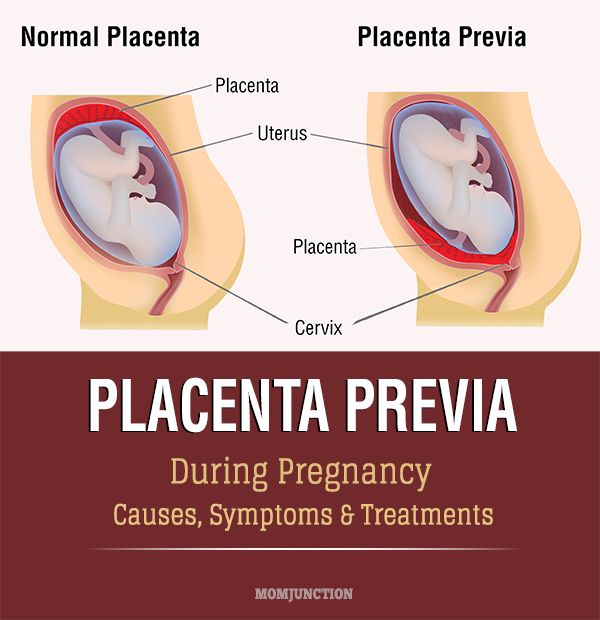
If the placenta is near or covering the cervix, your baby can't be delivered through the vagina, so a caesarean section will be recommended.
A low-lying placenta can be associated with painless, bright red bleeding from the vagina during the last 3 months of pregnancy. If this happens to you, contact your midwife or GP immediately.
Retained placenta
After your baby's born, part of the placenta or membranes can remain in the womb. This is known as retained placenta. If untreated, a retained placenta can cause life-threatening bleeding.
Breastfeeding your baby as soon as possible after the birth can help your womb contract and push the placenta out.
Your midwife may also ask you to change your position (for example, by moving to a sitting or squatting position). In some cases, you may be given an injection of a medicine to help your womb contract.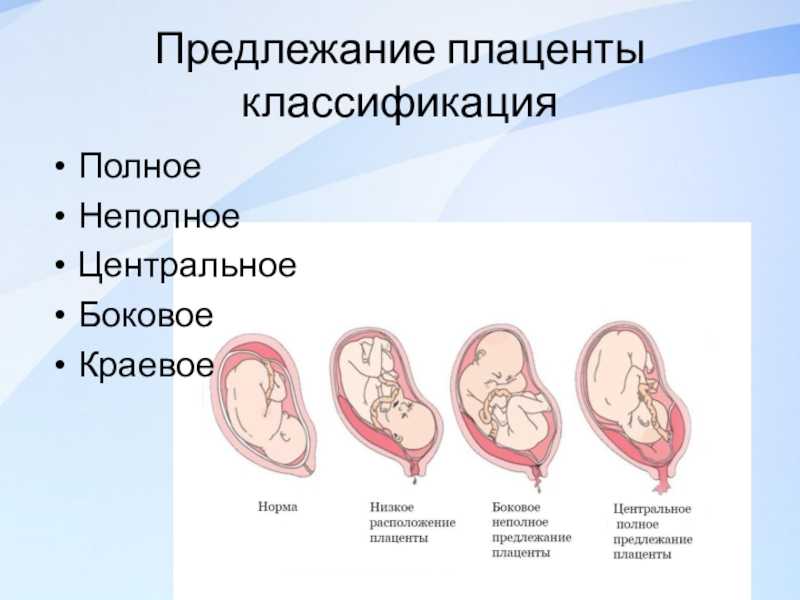
If these methods don't work, a doctor may need to remove the placenta by hand. This can be painful, so you'll be given an anaesthetic.
Placental abruption
Placental abruption is a serious condition in which the placenta starts to come away from the inside of the womb wall.
It can cause stomach pain, bleeding from the vagina and frequent contractions.
It can also affect the baby, increasing the risk of premature birth, growth problems and stillbirth.
It's not clear what causes placental abruption, but factors that increase the risk include injury to the abdominal area, smoking, cocaine use and high blood pressure.
If you're near your due date, the baby will need to be born straight away and a caesarean section may be recommended.
But if the baby's very premature and the abruption is minor, you may be kept in hospital for close observation.
Always speak to your midwife or GP if you're concerned about any aspect of your health when you're pregnant. You can also call NHS 111.
Further information
- Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy
- Antenatal care
Page last reviewed: 22 August 2022
Next review due: 22 August 2025
Placenta complications | Tommy's
What is the placenta?
The placenta is an organ that helps your baby grow and develop. It’s attached to the lining of the womb and is connected to your baby by the umbilical cord. The placenta passes oxygen, nutrients and antibodies from your blood supply to your baby. It also carries waste products from your baby to your blood supply, so your body can get rid of them.
The placenta develops in the first few weeks of pregnancy, wherever the fertilised egg embeds itself. This could be along the top, sides, front or back wall of the uterus.
This could be along the top, sides, front or back wall of the uterus.
What issues can affect the placenta?
Anterior placenta
An anterior placenta is when the placenta attaches to the front wall of the uterus. This is a normal place for the placenta to implant and develop and it is very unlikely to cause any complications.
Having an anterior placenta can make it a bit harder to feel your baby move because your baby is cushioned by the placenta lying at the front of your stomach.
Find out more about anterior placenta.
Chronic histiocytic intervillositis
Chronic histiocytic Intervillositis (CHI) is an extremely rare condition that may affect the placenta during pregnancy. In CHI, the mother’s immune system reacts abnormally to the pregnancy and causes damage to the placenta, increasing the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth.
Unfortunately, CHI has no symptoms and can only be diagnosed after pregnancy. Women with previous CHI will have extra treatment and care in any future pregnancies to help prevent any problems.
Find out more about chronic histiocytic intervillositis.
Fetal growth restriction
Fetal growth restriction (FGR) is a condition in which a baby's growth slows or stops during pregnancy. Most cases of FGR are caused by failure of the placenta but there are also other factors, including intrauterine infection and smoking in pregnancy.
FGR happens in around 3% pregnancies.
Find out more about fetal growth restriction.
Low-lying placenta (also known as placenta praevia)
A low-lying placenta (also known as placenta praevia) is when the placenta attaches lower down and may cover a part of or all of the cervix (the entrance to the womb).
This can cause bleeding in pregnancy or during your baby’s birth, so you may need to give birth in the hospital. If the placenta is near or covering the cervix you won’t be able to deliver vaginally and will need a caesarean section.
Find out more about low-lying placenta.
Placental abruption
Placental abruption is a serious condition in which the placenta starts to come away from the inside of the womb wall before the baby has delivered. This is an emergency because it means that the support system for the baby is failing.
This is an emergency because it means that the support system for the baby is failing.
Placental abruption is rare, complicating about 1% of pregnancies.
Find out more about placental abruption.
Placenta accreta
Placenta accreta is when the placenta is attached and embedded too deeply into the wall of the uterus. This is a rare complication of pregnancy that makes it difficult to deliver the placenta after you give birth.
Find out more about placenta accreta.
Retained placenta
After your baby is born, your womb will carry on contracting and the placenta is delivered. This is called the third stage of labour.
Sometimes the placenta or part of the placenta or membranes can remain in the womb. This is known as retained placenta. It isn’t very common, but a retained placenta can cause complications if it isn’t treated.
Find out more about retained placenta.
Vasa praevia
In most pregnancies, blood vessels from the umbilical cord insert directly into the placenta.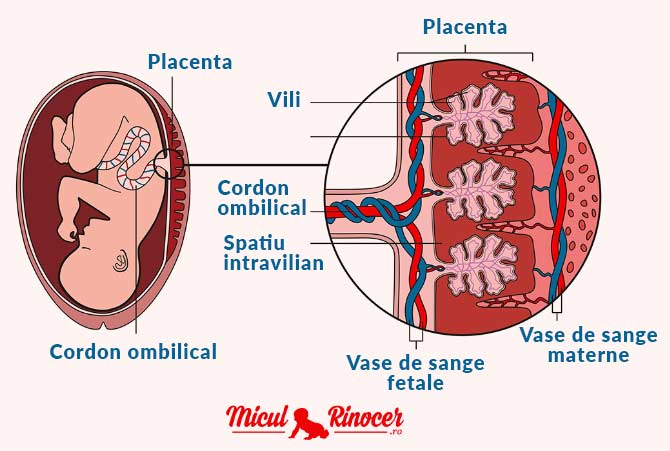 In vasa praevia, these vessels are not protected by the umbilical cord or the placenta tissue. Instead, they go across the entrance to the birth canal, beneath the baby.
In vasa praevia, these vessels are not protected by the umbilical cord or the placenta tissue. Instead, they go across the entrance to the birth canal, beneath the baby.
These blood vessels are very delicate. If they tear when you are in labour or when your waters break, this can cause blood loss.
Vasa praevia is rare, but it can be dangerous because the blood that is lost comes from your baby.
Find out more about vasa praevia.
Tommy's research
Tommy’s is the largest charity carrying out research into pregnancy loss and premature birth in the UK. We are funding various research projects that are focusing on the placenta and potential pregnancy complications. Find out more about our research.
Placental insufficiency - what is it and how to treat it
- Types and causes of placental insufficiency
- Diagnosis of placental insufficiency
- Treatment of placental insufficiency
Most women know that the placenta connects mother and baby during pregnancy and provides nutrients and oxygen to the baby.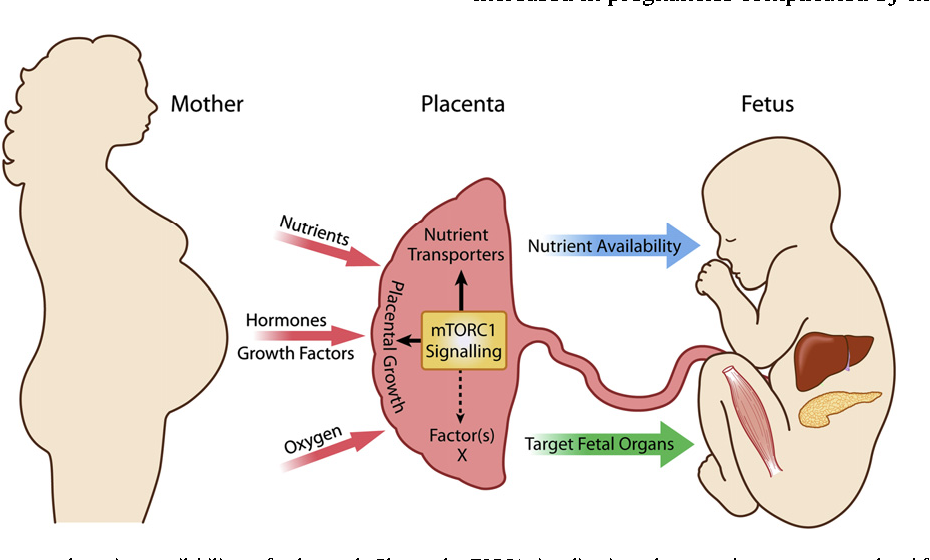
Are there situations when the placenta ceases to perform its function correctly and fully? Is it possible to somehow prevent this?
What is the function of the placenta
So, the placenta is an important organ that is formed only during pregnancy. The placenta is formed from the chorion - the embryonic membranes of the fetus. At the very beginning of pregnancy, chorionic villi - outgrowths of the membrane - evenly cover the entire surface of the fetal egg, starting from the second month of pregnancy, on one side of the fetal egg, the villi begin to lengthen, increase in size and form the placenta.
Inside the villi flows the blood of the baby, and outside they are bathed in the blood of the mother. Between the blood flow of mother and baby there is only one layer of cells, which plays the role of a barrier between the body of mother and child. Thanks to this membrane, the blood of the mother and fetus does not mix.
However, in recent years it has become known that fetal blood cells still penetrate the placental barrier into the mother's bloodstream, and thanks to this, it has become possible to conduct genetic analyzes and determine chromosomal abnormalities, Rh factor and fetal sex from the blood of a pregnant woman (non-invasive prenatal test) .
In the placenta, there is a constant exchange of substances between mother and child. Oxygen and nutrients are supplied from the mother's blood to the fetus, carbon dioxide and metabolic products from the fetus back to the mother, to be removed from the body.
The placental barrier performs an immunological function, as it allows some protective antibodies - blood cells that fight infectious agents, in addition, it is impervious to certain harmful substances, viruses and bacteria. Unfortunately, the placental barrier is easily overcome by drugs, alcohol, nicotine, components of many drugs and some viruses.
An important function of the placenta is the production of hormones and biologically active substances. First of all, these are hormones that are important for successful pregnancy, for example, chorionic gonadotropin, placental lactogen, estrogens, etc.
Unfortunately, things don't always go well. Due to a variety of reasons, deviations in the development and functioning of the placenta may occur at different stages of pregnancy. These changes never go unnoticed for mom and baby, and often have dire consequences.
These changes never go unnoticed for mom and baby, and often have dire consequences.
If the placenta ceases to perform its functions to the fullest, the so-called placental insufficiency develops. In fact, it consists in the deterioration of blood circulation in the mother-placenta-fetus system.
Types and causes of placental insufficiency
Doctors distinguish between acute and chronic placental insufficiency:
Acute placental insufficiency
This is a condition that requires urgent medical attention. It is characterized by a rapid deterioration in placental blood flow. Acute placental insufficiency occurs mainly as a result of placental abruption or the death of certain areas of placental tissue, for example, during the formation of blood clots in the vessels. Abdominal trauma, antiphospholipid syndrome can serve as the cause of detachment.
Phospholipids are complex fats that are part of the membranes of all body cells. In some cases, the body's immune system produces a large number of antibodies to some of its own phospholipids and proteins that bind these lipids. They are called antiphospholipid antibodies and, when interacting with the cells of the body, cause cell damage and activation of the blood coagulation system, which leads to thrombosis.
They are called antiphospholipid antibodies and, when interacting with the cells of the body, cause cell damage and activation of the blood coagulation system, which leads to thrombosis.
Antiphospholipid syndrome is the most common cause of thrombotic complications in pregnancy, including placental abruption and acute placental insufficiency.
A severe course of gestosis, a formidable complication of the second half of pregnancy, manifested by edema, increased pressure and the appearance of protein in the urine, can also cause placental abruption.
Acute placental insufficiency develops when more than 2/3 of the placental surface is detached.
In case of acute placental insufficiency, it is necessary to perform a caesarean section as soon as possible to save the life of the baby and mother.
Chronic placental insufficiency
Chronic placental insufficiency is much more common in pregnant women. In this case, there is a violation of the formation and maturation of the placenta, the uteroplacental and fetal-placental blood flow decreases, gas exchange and metabolism in the placenta are limited, and the synthesis of placental hormones decreases. All these changes determine the insufficient supply of oxygen and nutrients to the baby, cause a delay in the growth and development of the fetus.
All these changes determine the insufficient supply of oxygen and nutrients to the baby, cause a delay in the growth and development of the fetus.
The most common causes of placental insufficiency are previous abortions, especially surgical abortion during the first pregnancy, smoking, while the number and strength of cigarettes smoked do not matter, since tobacco smoke, not nicotine, has a negative effect on the formation of defective placental vessels.
The risk group for the development of placental insufficiency also includes women with chronic diseases such as arterial hypertension, iron deficiency anemia, pyelonephritis, diabetes, thyroid disease.
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in placental insufficiency caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi. The reason for this can be both an acute infection suffered by the expectant mother during pregnancy, and the activation of a chronic infectious process in the body of a pregnant woman.
Of no small importance in the formation of chronic placental insufficiency is the pathology of the uterus: endometriosis, malformations of the uterus (saddle-shaped, bicornuate). Doctors also consider uterine fibroids to be a risk factor. Of course, a number of drugs have an adverse effect on the formation of the placenta and the development of the fetus. Currently, a list of drugs that are not approved for use during pregnancy has been defined.
Doctors also consider uterine fibroids to be a risk factor. Of course, a number of drugs have an adverse effect on the formation of the placenta and the development of the fetus. Currently, a list of drugs that are not approved for use during pregnancy has been defined.
Also of great importance in the development of placental insufficiency is thrombophilia - an increased tendency of the body to form blood clots - blood clots in the vessels.
In some cases, placental insufficiency may be due to the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, in particular in Down syndrome (the presence of an additional chromosome 21 in the fetus) or Edwards syndrome (an additional chromosome 18 in the fetus), placental dysfunction is diagnosed already in the early stages of pregnancy.
It should be noted that among the complications of pregnancy, most often leading to the development of chronic placental insufficiency, a significant factor is preeclampsia (or late preeclampsia) - a complication of the second half of pregnancy, manifested by edema, increased pressure and the appearance of protein in the urine.
Regardless of the factors contributing to the development of placental insufficiency, it is based on circulatory disorders in the uterine-placental complex, leading to disruption of all functions of the placenta. Consequently, the symptoms of chronic placental insufficiency will be due to a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus.
This is, first of all, intrauterine fetal growth retardation - a lag in the size of the fetus and a slowdown in its growth. Often there is a change in the motor activity of the fetus. At first there may be some increase in movements, and then a decrease. Violation of the protective function of the placenta leads to intrauterine infection of the fetus under the action of pathogenic (pathogenic) microorganisms penetrating the placenta. The fetus, the development of which occurs in conditions of placental insufficiency, is much more at risk of trauma during childbirth, they have a violation of adaptation to extrauterine life, increased morbidity in the first year of life.
According to the time of occurrence, doctors divide placental insufficiency into early and late.
Early (or primary) placental insufficiency
Develops before 16 weeks of gestation. It occurs already at the stage of placenta formation and is associated with diseases of a pregnant woman that are present before pregnancy, for example, with uterine pathology, chronic arterial hypertension, and endocrinological diseases. In this case, the formation of defective vessels in the placenta occurs.
Late (or secondary) placental insufficiency
Occurs after 16 weeks of pregnancy and is most often associated with diseases that have already occurred during pregnancy. Most often, these are iron deficiency anemia (that is, a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin and iron in the blood), gestational diabetes mellitus (that is, a violation of the absorption of glucose by the body that occurred during pregnancy), past viral and bacterial infections.
It is important to subdivide placental insufficiency into compensated and decompensated forms.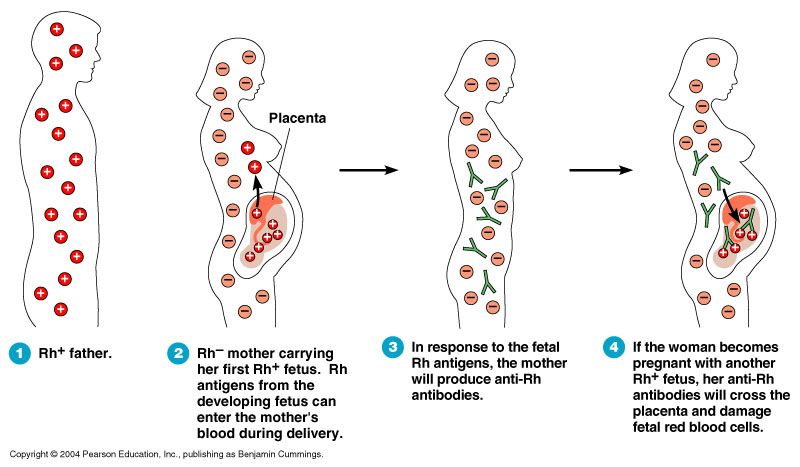
Compensated placental insufficiency
It develops, for example, with the threat of abortion and mild forms of late preeclampsia, if these complications are successfully amenable to medical correction.
Decompensated placental insufficiency
Causes the development of fetal growth retardation, chronic intrauterine hypoxia, up to fetal death.
Learn more about services:
- Ultrasound for pregnant women
- Ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy
- Ultrasound of vessels during pregnancy
- Consultation with a gynecologist
Diagnosis of placental insufficiency
It is almost impossible to treat an already developed placental insufficiency, so doctors actively seek to identify pregnant women who are at risk of developing placental dysfunction. If placental insufficiency is detected in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy, there is no effective treatment, unfortunately. Therefore, all methods of identifying in the early stages of pregnancy those women whose formation of the placenta has been disturbed are being very actively used.
Therefore, all methods of identifying in the early stages of pregnancy those women whose formation of the placenta has been disturbed are being very actively used.
First of all, when registering for pregnancy, the most significant risk factors are identified - smoking, abortions, aggravated heredity (low birth weight, tendency to thrombosis), the presence of chronic diseases of the heart, blood vessels, diabetes mellitus.
Preventive measures against the development of placental insufficiency are especially relevant and necessary until 16-17 weeks of pregnancy, when the formation of placental structures occurs.
Significant assistance in assessing the risk of developing placental insufficiency is provided by prenatal screening, which is carried out at 11-14 weeks of pregnancy. It is carried out to detect Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome and other chromosomal diseases in the fetus. Currently, the most relevant is to conduct a comprehensive early screening of a pregnant woman to predict the risk of developing placental insufficiency, preeclampsia and intrauterine growth retardation. Since this type of diagnostics is one of the most modern and advanced, unfortunately, it is not yet included in the list of services provided in the antenatal clinic within the framework of compulsory medical insurance, but is available to everyone in prenatal diagnostic centers.
Since this type of diagnostics is one of the most modern and advanced, unfortunately, it is not yet included in the list of services provided in the antenatal clinic within the framework of compulsory medical insurance, but is available to everyone in prenatal diagnostic centers.
Determination of proteins produced by the placenta
First of all, the PAPP-A protein is determined, it is also a marker of chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus. A decrease in the concentration of PAPP-A in the blood at 11-14 weeks of gestation occurs in pregnant women who have a high risk of placental insufficiency and fetal growth retardation.
The second placental hormone that helps in assessing the risk of placental insufficiency is PIGF (placental growth factor). Its concentration in the blood decreases long before the first manifestations of placental insufficiency. Its definition is not as widely used as PAPP-A, but many laboratories have already included this protein in 1st trimester prenatal screening. It is extremely important when screening the 1st trimester to measure blood flow in the vessels of the uterus. It has been unambiguously proven that the narrowing of the vessels of the uterus, determined during the study, indicates the inferiority of the formation of the placenta, which will worsen with increasing gestational age and lead to a decrease in the nutrition of the baby and the supply of oxygen, that is, to the development of placental insufficiency and fetal growth retardation. With normal sizes of uterine vessels at 11-14 weeks of gestation, the risk of severe placental insufficiency is negligible.
It is extremely important when screening the 1st trimester to measure blood flow in the vessels of the uterus. It has been unambiguously proven that the narrowing of the vessels of the uterus, determined during the study, indicates the inferiority of the formation of the placenta, which will worsen with increasing gestational age and lead to a decrease in the nutrition of the baby and the supply of oxygen, that is, to the development of placental insufficiency and fetal growth retardation. With normal sizes of uterine vessels at 11-14 weeks of gestation, the risk of severe placental insufficiency is negligible.
The next mandatory screening ultrasound is at 20-21 weeks of gestation. In this case, measurements of the fetus must be carried out in order to assess whether there is a lag in growth. After all, with oxygen starvation, the growth rate of the fetus slows down and its size begins to lag behind the norm for each period of pregnancy. In addition, the doctor must evaluate the condition and maturity of the placenta. During ultrasound, dopplerometry of the uterine vessels is also performed to detect early changes that precede the clinical manifestations of placental insufficiency.
During ultrasound, dopplerometry of the uterine vessels is also performed to detect early changes that precede the clinical manifestations of placental insufficiency.
In patients belonging to the high-risk group, in addition to ultrasound and dopplerometry, daily monitoring of blood pressure fluctuations is also carried out, the amount of protein in the urine sample collected per day is determined, and the indicators of the blood coagulation system are evaluated.
The third ultrasound is performed for all expectant mothers at 30-34 weeks of pregnancy. The doctor measures the circumference of the head and abdomen of the crumbs, the length of the bones of his arms and legs, and calculates the estimated weight of the fetus. These measurements allow the doctor to make sure that the baby is developing normally. The structure of the placenta is also important, the presence of signs of aging in it, as a result of which it usually ceases to fully supply the baby with blood, which means that it ceases to have enough oxygen and nutrients and the development of the child is disturbed.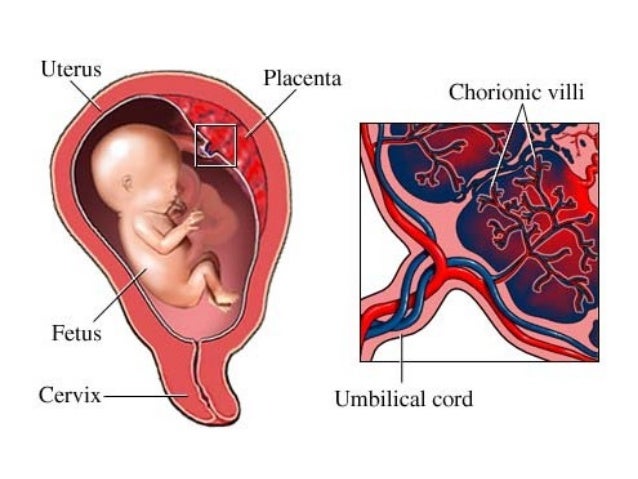 During ultrasound, the amount and type of amniotic fluid is assessed, which can also change with intrauterine fetal suffering.
During ultrasound, the amount and type of amniotic fluid is assessed, which can also change with intrauterine fetal suffering.
Doppler
Doppler of the placental and umbilical cord vessels (method of studying blood flow velocities in these vessels) also allows you to assess the well-being of the baby. The doctor examines the blood flow in the arteries of the uterus, umbilical cord, heart and brain of the child. This study allows you to determine whether the placenta is working well, whether there are signs of a lack of oxygen in the baby, or the development of preeclampsia in the mother. With a decrease in the speed of blood flow in any vessel, one can speak of fetal malnutrition of varying severity.
A well-timed examination makes it possible to identify the initial stages of blood supply deficiency. In such cases, treatment can prevent formidable complications, such as hypoxia and intrauterine growth retardation of the baby. Dopperometry is carried out at 20-21 weeks and at 30-32 weeks of pregnancy, if there are changes, control is carried out at least every two weeks.
Cardiotocography
This is an important method for assessing the condition of the fetus. CTG is performed at a gestational age of 33 weeks or more, since only at this stage of the intrauterine development of the baby is a complete regulation of the activity of the cardiovascular system of the fetus established by the centers of the spinal cord and brain. Recording of fetal heartbeats is carried out for 20-40 minutes, and if necessary, the study can be extended up to 1.5 hours.
The device registers and records the baby's heart rate. The obstetrician-gynecologist evaluates the heartbeat recording curve, episodes of slowing down and a sharp increase in the fetal heart rate, and based on these data, makes a conclusion about how comfortable the baby feels in the mother's stomach. For example, with a decrease in the concentration of oxygen in the blood of the fetus, its supply to the cells of the nervous system also decreases, which in turn affects the heart rate. In the normal course of pregnancy, CTG is performed after 33 weeks 1 time in 10-14 days, sometimes more often.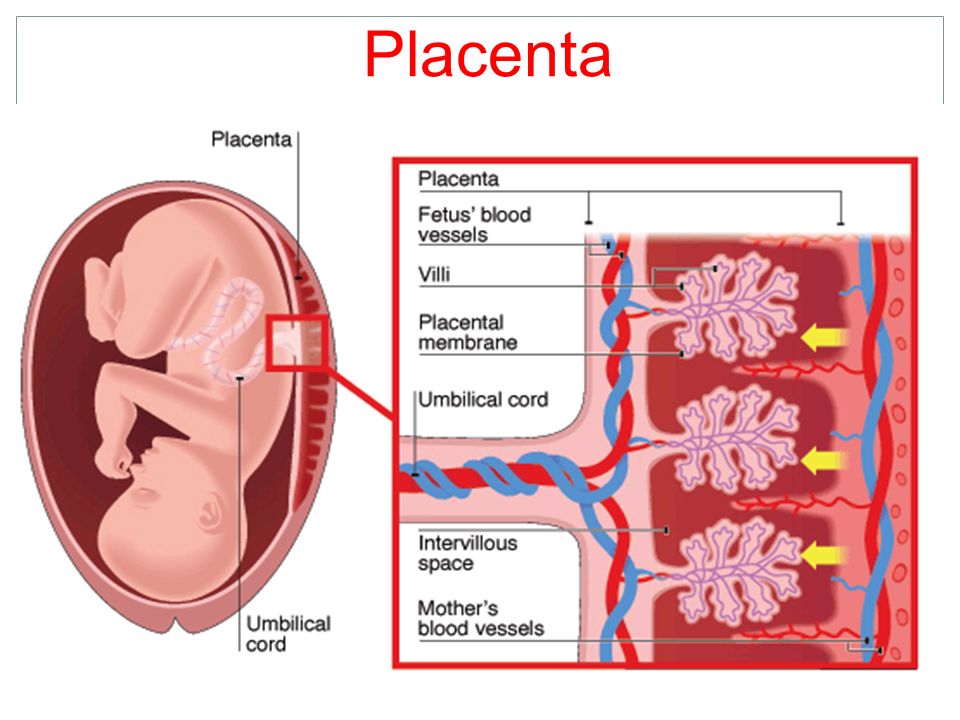 Some clinics currently offer the service of continuous CTG monitoring, which becomes relevant in the presence of signs of placental insufficiency. A pregnant woman is given a monitor that records changes in the baby's heart activity and these data are transmitted via the Internet to the attending physician.
Some clinics currently offer the service of continuous CTG monitoring, which becomes relevant in the presence of signs of placental insufficiency. A pregnant woman is given a monitor that records changes in the baby's heart activity and these data are transmitted via the Internet to the attending physician.
Treatment of placental insufficiency
There are currently no specific treatments for placental insufficiency because there are no drugs that selectively improve uteroplacental blood flow. That is why all measures to combat placental insufficiency are aimed at prevention. If the patient is at high risk for the development of placental insufficiency, from early pregnancy she is prescribed drugs whose effectiveness is well proven and which prevent the early development of severe placental dysfunction.
If during the additional methods of assessing the condition of the fetus, initial disturbances in the supply of oxygen to the baby are detected, drug treatment is carried out aimed at increasing the flow of blood and oxygen through the placenta and mandatory control examinations against the background of ongoing therapy.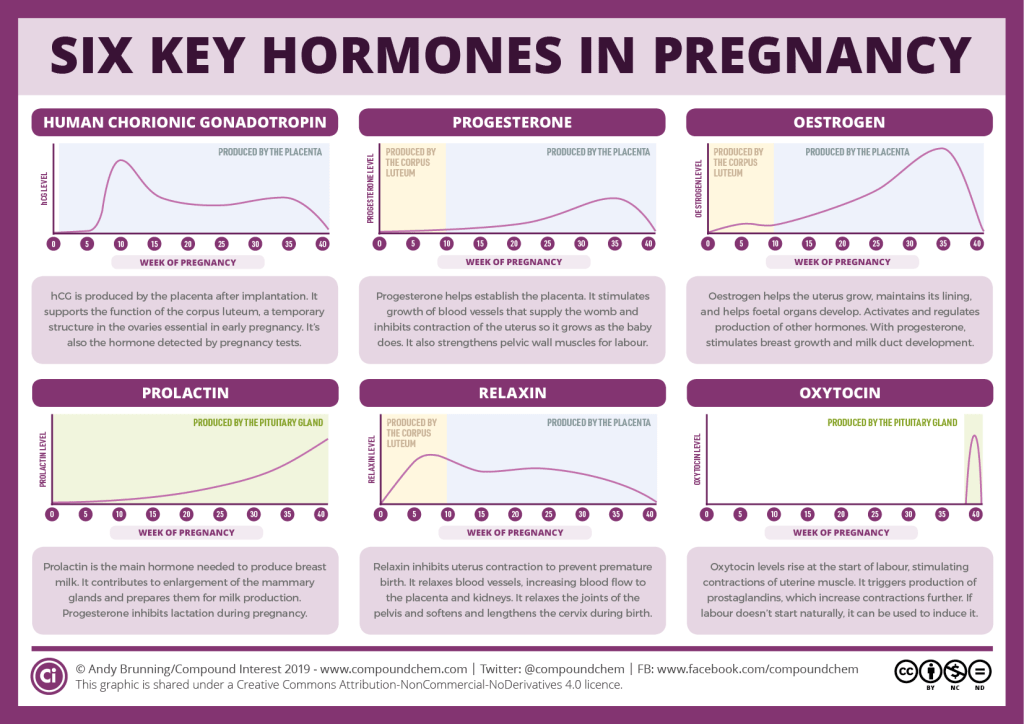 If the changes are serious and the baby experiences a pronounced deficiency of oxygen and nutrients, his condition suffers, then in such cases an emergency delivery is performed.
If the changes are serious and the baby experiences a pronounced deficiency of oxygen and nutrients, his condition suffers, then in such cases an emergency delivery is performed.
Premature placental abruption: what a future mother needs to know and how not to miss its signs | Blog
First, let's talk about what is the placenta?
The placenta is the embryonic organ that connects the body of mother and child. Its uniqueness lies in the fact that it is the only "disposable" organ. The placenta begins to develop from the 2nd week of pregnancy, forms up to 15-16 weeks and reaches full functional maturity by 36 weeks. And after the birth of the fetus (in the third stage of childbirth), it separates and leaves the mother's body, starting the process of lactation at the endocrinological level.
The placenta performs important functions such as gas exchange, nutrient exchange between mother and child, provides immunological protection and works as an endocrine gland, producing hormones necessary for the development of the fetus and the normal course of pregnancy. Every minute, about 500 ml of blood enters the placenta, but at the same time it is a kind of barrier that does not allow the blood of the mother and child to mix, and also prevents many toxic substances from entering the bloodstream of the baby.
Every minute, about 500 ml of blood enters the placenta, but at the same time it is a kind of barrier that does not allow the blood of the mother and child to mix, and also prevents many toxic substances from entering the bloodstream of the baby.
In this article we will talk about placental abruption.
This condition is quite rare (up to 1.5% of all pregnancies), but causes such threatening complications as massive bleeding and hemorrhagic shock, fetal distress, which in some cases can cause death. Normally, the detachment of the placenta from the inner wall of the uterus occurs only after the birth of the fetus. If this happens before the onset of labor, as well as in the first or second stage of labor, this is the premature detachment of a normally located placenta. This condition is a very dangerous pathology that requires immediate diagnosis and decision of further medical tactics in the near future.
Causes of premature placental abruption
Unfortunately, the only cause of premature placental abruption has not been established to date. There are many theories, but in general, the occurrence of this condition is associated with many provoking factors.
There are many theories, but in general, the occurrence of this condition is associated with many provoking factors.
Major risk factors include:
- arterial hypertension,
- diabetes mellitus
- pregnant woman over 40 years old
- multiple pregnancy
- polyhydramnios
- postterm pregnancy and large fetus
- previous uterine surgery
- blood coagulation disorder,
- autoimmune diseases
- kidney disease
- bad habits such as smoking and drug use
- inflammatory diseases of the uterus and placenta, anomalies in the development of the uterus.
Causes that can provoke placental abruption: physical trauma of a pregnant woman (accident, fall, blow to the stomach), disruption of the contractile activity of the uterus, stress, gross obstetric manipulations.
Types of placental abruption
There are the following types of placental abruption: partial and complete.
Partial detachment, in turn, can be central and marginal.
Why is this classification so important? And because both the clinical picture and medical tactics depend on the place and volume of the detachment. Partial detachment can be progressive or non-progressive.
Non-progressive detachment has a significantly better prognosis for a pregnant woman, because in this case, conservative treatment is possible with preservation of pregnancy.
Symptoms of placental abruption:
Here is a triad of main symptoms that may be a sign of placental abruption:
- abdominal pain, feeling of increased uterine tone;
- spotting from the genital tract;
- violation of the fetal heartbeat, which indicates fetal distress.
Also, a woman can feel the baby's reaction to a decrease in the amount of oxygen supplied to him due to placental abruption - he begins to move more actively, reacting to hypoxia.
These symptoms do not always appear at the same time! For example, with marginal abruption of the placenta, blood flows into the vagina, which means that the woman sees signs of bleeding.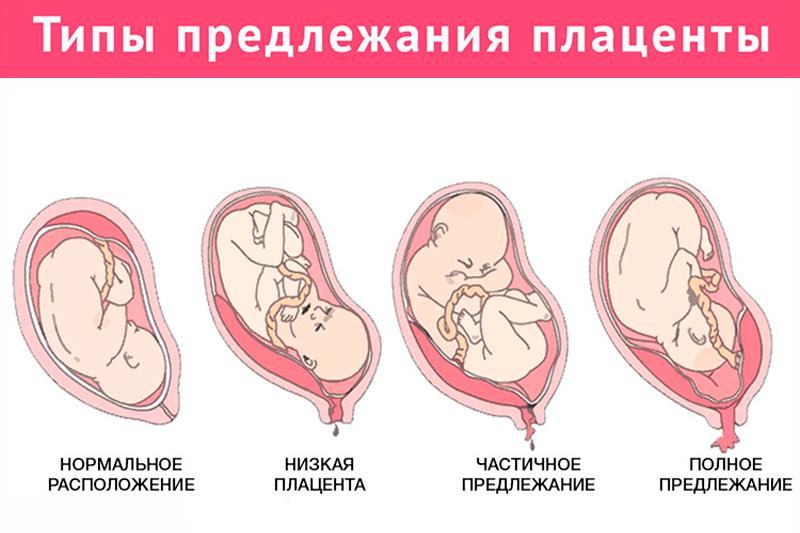 With central detachment, a retroplacental hematoma is formed. Bleeding is internal, which means that a pregnant woman may not notice its signs. The appearance of an accelerated heartbeat in a woman, a decrease in blood pressure, nausea, dizziness, and severe weakness may indicate internal bleeding.
With central detachment, a retroplacental hematoma is formed. Bleeding is internal, which means that a pregnant woman may not notice its signs. The appearance of an accelerated heartbeat in a woman, a decrease in blood pressure, nausea, dizziness, and severe weakness may indicate internal bleeding.
However, with central placental abruption, blood accumulates in front of the placenta and begins to “press” on nearby tissues. As a result, a pronounced pain syndrome occurs.
It must be emphasized that if at least one of the symptoms appears, it is necessary to immediately inform the doctor about it! This condition can be very dangerous for you and your baby, so it is important to diagnose it in a timely manner.
Diagnosis of placental abruption
Diagnosis of placental abruption is based not only on clinical symptoms and gynecological examination. Ultrasound diagnostics is the main method that allows you to accurately assess the location and area of the exfoliated area of the placenta and see the presence or absence of a hematoma.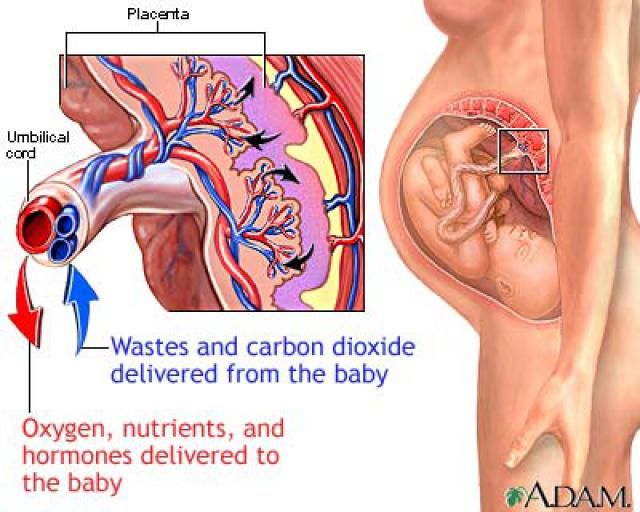 Also, ultrasound can distinguish premature detachment from placenta previa (its abnormal location, in which it overlaps the internal pharynx of the cervix). This condition can have similar symptoms, as it is often accompanied by bleeding. The condition of the fetus and the degree of its hypoxia will be determined using cardiotocography, and Dopplerography, in turn, assesses violations of the uteroplacental circulation. Based on these examination results, the obstetrician-gynecologist, and more often a council of doctors, decides on the type of further medical tactics.
Also, ultrasound can distinguish premature detachment from placenta previa (its abnormal location, in which it overlaps the internal pharynx of the cervix). This condition can have similar symptoms, as it is often accompanied by bleeding. The condition of the fetus and the degree of its hypoxia will be determined using cardiotocography, and Dopplerography, in turn, assesses violations of the uteroplacental circulation. Based on these examination results, the obstetrician-gynecologist, and more often a council of doctors, decides on the type of further medical tactics.
Treatment of placental abruption
Treatment of placental abruption always requires hospitalization of the pregnant woman in the maternity hospital for constant monitoring of her condition. In cases of non-progressive mild placental abruption with a stable state of the mother and fetus, conservative tactics with drug therapy and preservation of pregnancy are possible. Progressive detachment, as well as severe detachment, certainly requires an emergency caesarean section.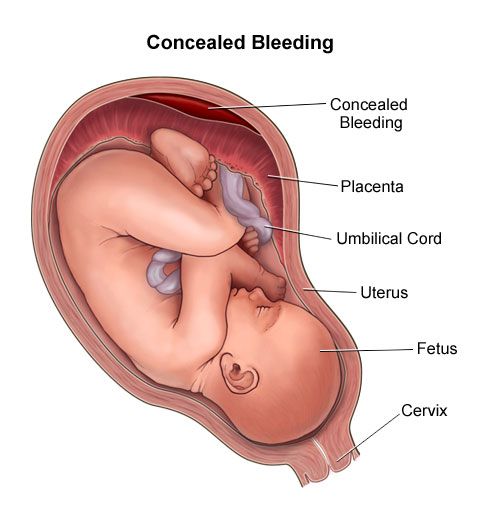
In case of complete detachment of the placenta, with the rapid progression of this condition, massive bleeding occurs, which threatens the life of both the pregnant woman and the child. In such a situation, surgeons always prioritize the life of a woman and do everything necessary to save her. Some cases may, unfortunately, require even such radical surgical tactics as removal of the uterus. However, at the current level of development of medicine, more and more technologies are emerging that, with timely assistance, can save not only the life of the mother and child, but also the reproductive functions of a woman. In particular, our obstetrician-gynecologists and anesthesiologists use up-to-date international medical protocols to ensure the safest possible delivery. Appropriate algorithms have also been developed for surgical interventions with a high risk of bleeding. Thanks to the latest technologies in vascular surgery with X-ray and ultrasound control, massive bleeding can be quickly and safely stopped.