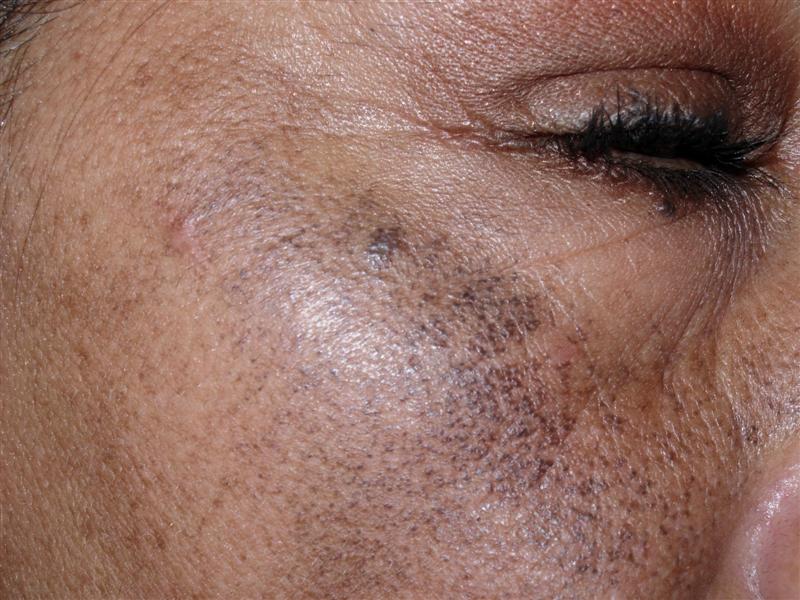
Melasma on neck during pregnancy
Melasma in Pregnancy: Treatment and Causes
Your body goes through tremendous changes during pregnancy.
Your belly gets larger and your blood volume increases as your baby grows. You may experience cramping, morning sickness, and all sorts of unfamiliar aches and pains. Your hair and skin may also go through a transformation for the better — or worse. (You’re beautiful all the same.)
If you’ve noticed dark patches of skin on your face, you may have melasma. Here’s more about this condition, why it crops up in pregnancy, and how you can treat it safely.
Melasma is a skin disorder where the melanocytes (color-producing cells) in your skin produce extra pigment for some reason. In pregnancy, it’s often referred to as chloasma, or the “mask of pregnancy.”
Chloasma is a cosmetic concern. It doesn’t affect your baby in any way or indicate any other pregnancy complications.
People with more pigment in their skin — for example, those of African, North African, Middle Eastern, Latin or Hispanic, Asian, Indian, or Mediterranean descent — are more likely to develop chloasma, as they naturally have more active melanin production.
Overall, between 50 and 70 percent of people will develop some form of melasma during pregnancy.
Related: Skin color needs to be factored in when discussing skin diseases
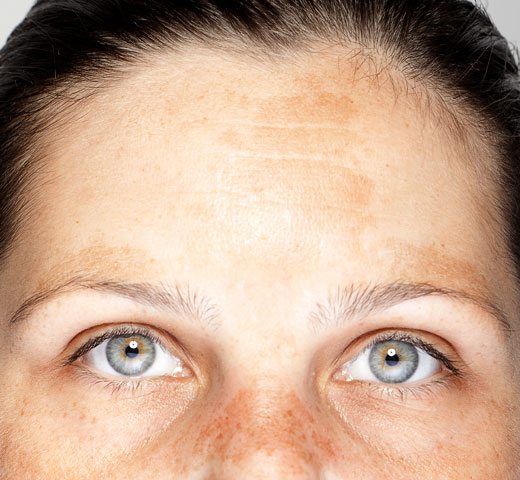
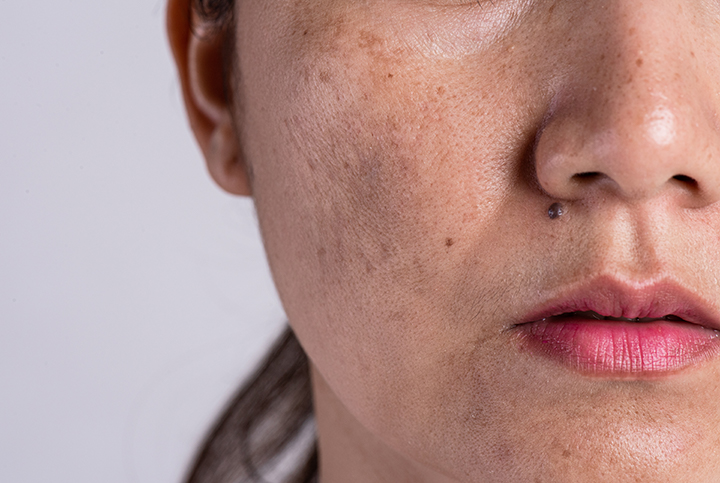
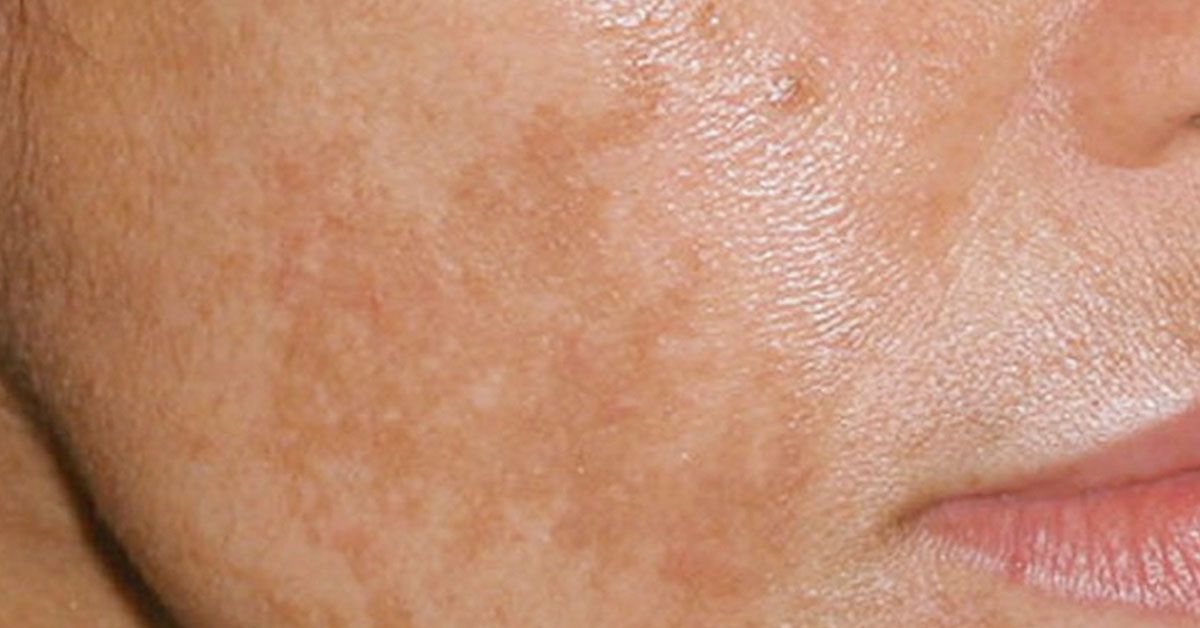
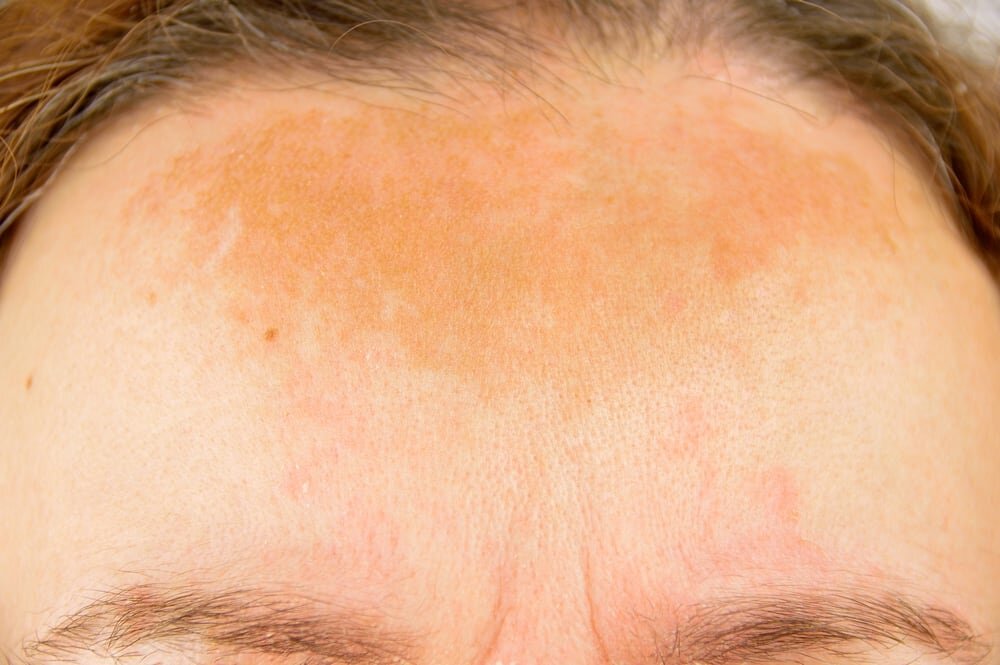
The primary symptom of chloasma is darkening of the skin on the face. You may notice dark patches or splotches on your forehead, cheeks, chin, or around your mouth. These areas may get darker the more you’re exposed to the sun or the further along you are in your pregnancy.
Pain, itchiness, or soreness are not symptoms of melasma. If you experience these signs or develop severe irritation, you may be dealing with another condition. Bring up any additional symptoms you have with your doctor.
A dermatologist can accurately diagnose your condition using a Wood’s lamp, which helps show whether a skin condition is bacterial, fungal, or otherwise concerning.
Skin hyperpigmentation during pregnancy is very common. You may notice your nipples/areolas, armpits, or genitals become darker.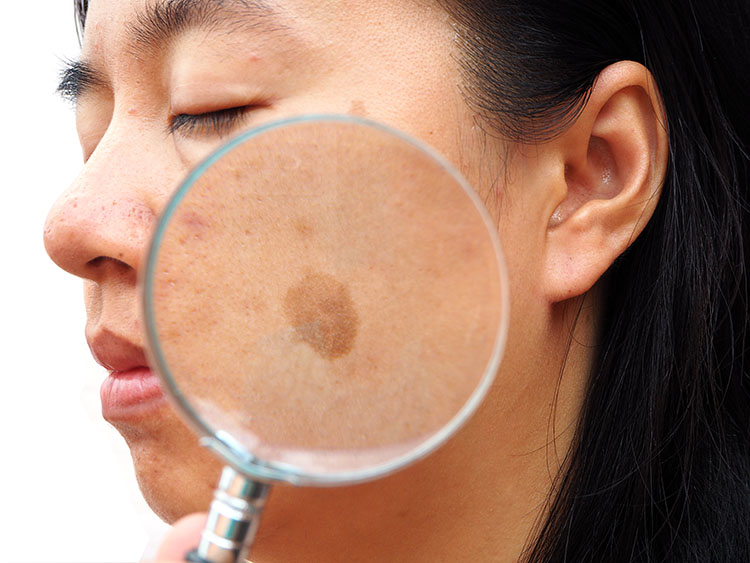 You may see a line (linea nigra) extending from the pubic area over the belly, or darkening of the skin all over the body.
You may see a line (linea nigra) extending from the pubic area over the belly, or darkening of the skin all over the body.
Changing hormones, particularly the excess of estrogen and progesterone, is the main cause of melasma during pregnancy. Beyond that, the dark patches on the face can be exacerbated by sun exposure, the use of certain skin care products or treatments, and even genetics.
Chloasma may also be worsened by hormonal imbalances that may have been present even before pregnancy.
Whatever the case, your melanocyte-stimulating hormones react to these triggers by making an excess of protective pigments (dark patches) on the skin called melanin.
Melasma may start at any point in your pregnancy, though it most commonly begins in the second or third trimester.
Again, there are a variety of factors at play when it comes to darkening pigment. Your skin color and type may make this condition more or less noticeable. How much you’re out in the sun or even the time of year when you’re pregnant may also affect when you first notice it.
The good news is that this hyperpigmentation likely won’t get worse after you deliver your child. That said, it may take time — possibly months — for it to completely fade without any targeted treatment.
Speak with your doctor about ways to treat your melasma during pregnancy. Your doctor may refer you to a dermatologist for more information.
Some experts don’t recommend treating melasma during pregnancy. One reason is that it may resolve on its own. And some treatment methods may not be safe or effective to use when pregnant.
The best course of treatment may actually be prevention, with the help of a few lifestyle changes.
Seek shade
Since the sun may trigger the development of more pigment, it’s a good idea to stay out of its rays, especially for long periods of time.
Yes, this also applies to tanning beds or any other environment where you would be exposed to UVA and UVB rays. Limit sunbathing and try relaxing under a tree or umbrella instead.
If you’re exercising, try avoiding peak sun hours in your area, generally the middle of the day. Head out early in the morning or later in the evening when the sun is low.
Wear sunscreen
This doesn’t mean you have to stay indoors when the sun is out, though. Wearing a good pregnancy-safe sunscreen with SPF 30+ is key.
Look for products that contain zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, or other physical blockers (mineral sunscreens) versus those that rely on chemical blockers. Physical blocking sunscreens tend to offer broader protection and may be less irritating to the skin.
Dress for success
Another option for sun cover is clothing with or without UV protection, such as SPF rash guards or sun protective clothing. Even if it’s hot outside, loose-fitting clothing can be comfortable and protect your skin.
What about the face? Wide brimmed hats are your best friend. And don’t forget a stylish pair of sunglasses — the bigger the better.
Use gentle skin care products
Face washes, lotions, and serums that irritate your skin may make melasma worse. Slather up with gentle products instead. Look on the label for words like “noncomedogenic,” “sensitive,” “fragrance-free,” or “dermatologist approved” if you get overwhelmed in the beauty aisle.
Slather up with gentle products instead. Look on the label for words like “noncomedogenic,” “sensitive,” “fragrance-free,” or “dermatologist approved” if you get overwhelmed in the beauty aisle.
The same goes for makeup you may use to conceal the dark areas. Look for noncomedogenic or hypoallergenic foundations, concealers, powders, and other products.
Related: Your guide to pregnancy-safe skin care
Try at-home masks and methods
You may be able to lighten your melasma using ingredients from your pantry. While there are no specific studies on these methods for chloasma, the following topical treatments may help:
- Lemon juice. Mix together a solution of half fresh lemon juice and half cucumber juice or water. The acid in the juice may help remove pigmentation in the top layer of the skin.
- Apple cider vinegar (ACV). Similar idea here. Mix a solution of half ACV and half water to use as a toner on dark areas.
- Milk of magnesia.
 After washing your face, apply milk of magnesia to dark areas using a cotton ball. Leave on the skin overnight and wash off in the morning.
After washing your face, apply milk of magnesia to dark areas using a cotton ball. Leave on the skin overnight and wash off in the morning. - Oatmeal and honey. Whip up a mask made with cooked oatmeal (let it cool down so it isn’t hot) and raw honey. Leave on the skin for 10 minutes before washing away. The mask helps to exfoliate your skin and the enzymes in the honey may lighten it a bit.
Eat well, rest, and try a few supplements
Since melasma may also be the result of hormonal imbalances, you may improve matters by giving yourself some much-needed TLC. Make sure you’re staying hydrated, eating a diet with plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables, and getting enough sleep each night.
Be sure that you’re rounding out your diet by consuming supplemental omega-3 fatty acids. And ask your doctor about any potential vitamin deficiencies. Some studies link melasma to deficiency in iron and possibly vitamin B12.
Be patient
After pregnancy, you may ask your dermatologist about other treatments if your melasma doesn’t fade on its own. Treatments include topical medications like:
Treatments include topical medications like:
- hydroquinone
- tretinoin
- corticosteroids
Your doctor may also recommend certain acids that lighten the skin, alone or in combination. There are also some procedures — including chemical peels, microdermabrasion, laser treatments, and other light therapies — that may work.
It can be frustrating to deal with changes to your skin during pregnancy. Fortunately, chloasma generally fades within a few months after giving birth.
There are various lifestyle changes you can try to prevent the condition from progressing during pregnancy. Otherwise, speak with your doctor about the options for treatment and the benefits and risks of each. You’ll be glowing again before you know it!
Melasma During Pregnancy: Causes, Prevention and Treatment
Categories
Written by Elizabeth Geddes-Bruce, MD, Board Certified Dermatologist on April 5, 2022 • No Comments
Melasma is a skin condition in which some skin cells become darker.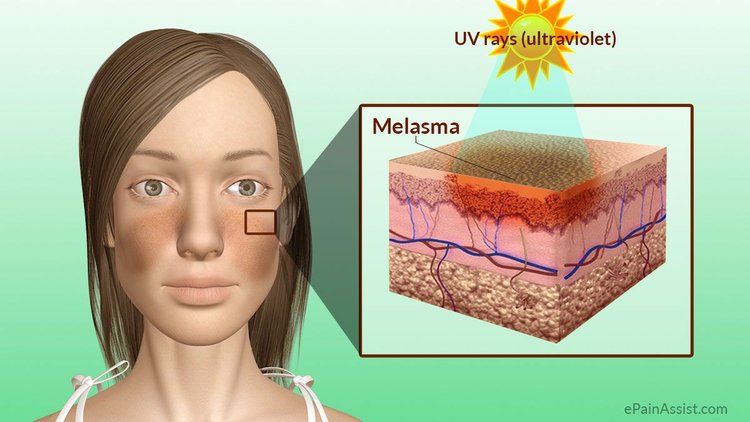 Commonly occurring during pregnancy, melasma is sometimes referred to as chloasma, or the ‘mask of pregnancy’ because dark patches on the face can resemble a mask. While not being harmful to the health of either mother or child, pregnancy melasma can be a source of embarrassment for some expecting mothers.
Commonly occurring during pregnancy, melasma is sometimes referred to as chloasma, or the ‘mask of pregnancy’ because dark patches on the face can resemble a mask. While not being harmful to the health of either mother or child, pregnancy melasma can be a source of embarrassment for some expecting mothers.
If you are currently expecting, or thinking about becoming pregnant, this post will cover everything you need to know about pregnancy-induced melasma, including ways to prevent occurrence and treatment options.
What is Pregnancy-Related Melasma?Melasma during pregnancy is a skin condition in which melanocytes, the skin cells that produce melanin, produce more pigment than usual. Melasma is only a pigmentary concern, and does not affect the health of the mother or baby.
Primary symptoms include darkening patches of skin on the face, especially around the forehead, cheekbones, nose and upper lip. Exposure to the sun can make melasma worse. In addition, melasma can make skin that is already darker even more so. Freckles or scars, and dark skin around nipples and genitals may become even darker than usual during pregnancy.
Freckles or scars, and dark skin around nipples and genitals may become even darker than usual during pregnancy.
If your hyperpigmentation is accompanied by consistent itching, irritation or discomfort, it’s important to note that these are not symptoms of melasma. See your dermatologist in that instance.
How Common is Melasma During Pregnancy?During pregnancy, the body goes through significant hormonal changes. This can be a trigger for melasma. This common condition occurs in 50-70% of pregnant women.
You’re also more likely to develop melasma during pregnancy if someone in your family has had it, if you have naturally dark skin, or if you spend a lot of time in the sun.
What Causes Melasma During Pregnancy?Melasma can occur at any point in a pregnancy, although it typically develops during the second or third trimester. It’s caused by hormonal changes that take place during pregnancy, which affect the skin’s pigment-producing melanocytes.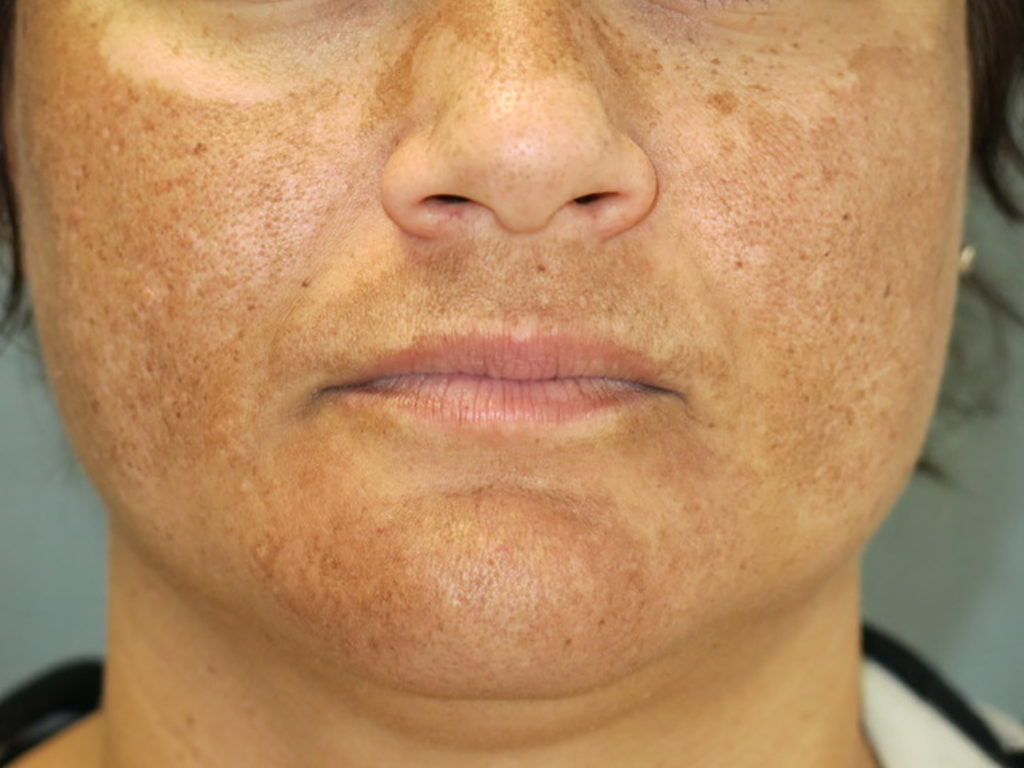 Melasma sometimes resolves itself one hormonal balance is restored. Sometimes, however, it persists.
Melasma sometimes resolves itself one hormonal balance is restored. Sometimes, however, it persists.
Does Pregnancy-Related Melasma Differ from Traditional Melasma?
Pregnancy is not the only cause of melasma. Non-pregnancy related hormonal changes like oral contraceptives may also cause skin hyperpigmentation. Melasma can even occur in men, although it’s far more common in women. The following are common melasma triggers:
- Pregnancy
- Non-pregnancy related hormonal imbalances
- Hormonal birth control
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Sun exposure
- Heat exposure
In addition to the above, genetics play a crucial role. If someone in your family has had melasma, you’re more vulnerable to the condition.
Can Melasma During Pregnancy Be Prevented?It’s impossible to prevent melasma with certainty, but there are ways to reduce your risk or minimize the appearance of your melasma.
- Avoid Excess Sun Exposure
UV light exposure only makes hyperpigmentation worse by further darkening skin.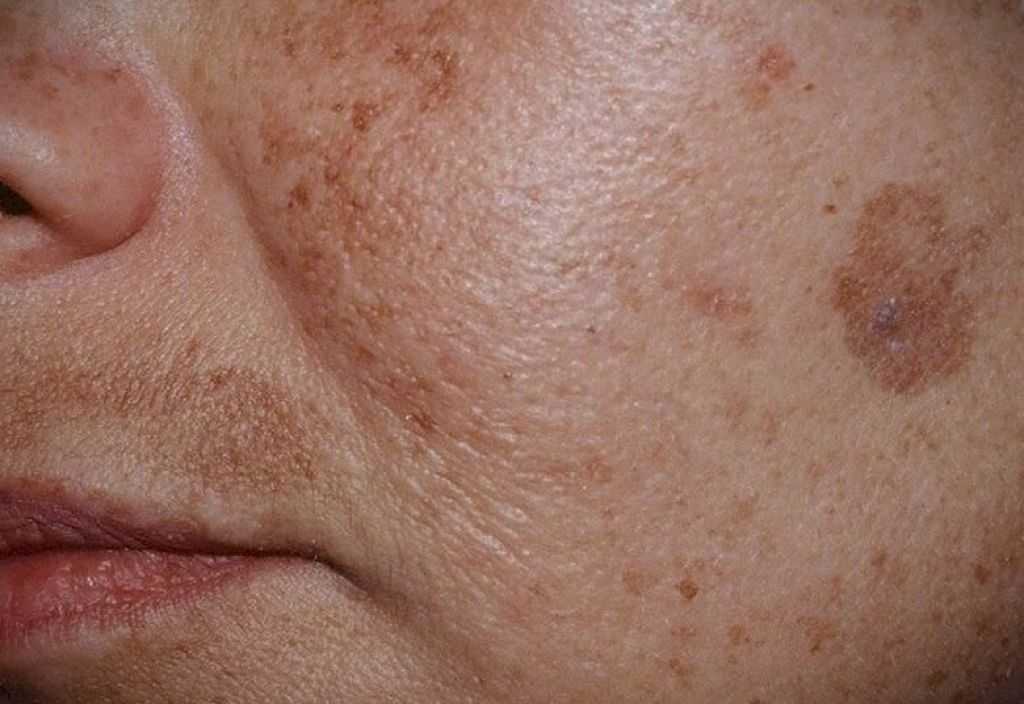 During your pregnancy, avoid spending too much time in the sun. Wear protective clothing and sunscreen as needed.
During your pregnancy, avoid spending too much time in the sun. Wear protective clothing and sunscreen as needed.
- Avoid Excess Heat
Heat can trigger melasma by causing the blood vessels in the skin to dilate and send signals to create pigmentation.
- Use Gentle Skin Care Products
Products that irritate the skin can make melasma worse. Swap out face washes, lotions or creams that contain fragrances or coloring. Look for products that say ‘fragrance-free,’ ‘for sensitive skin,’ or ‘non-comedogenic’ on the label.
- Use Make-Up Formulated for Sensitive Skin
If you’re using concealer or foundation to cover your melasma, choose products developed for sensitive skin. Make-up labeled as ‘non-comedogenic’ or ‘hypoallergenic’ is less likely to irritate skin and worsen melasma.
- Eat Well, Sleep Well and Hydrate
While pregnancy is a primary cause of melasma, eating a well-balanced diet and getting plenty of sleep can prevent hormonal imbalances or vitamin deficiencies that aren’t pregnancy-related. Eat a variety of healthy, whole foods, drink plenty of water and get sufficient rest.
Eat a variety of healthy, whole foods, drink plenty of water and get sufficient rest.
Some melasma treatments are safe to begin during pregnancy. See a board-certified dermatologist to figure out the best and safest option for your skin.
Will My Melasma Clear Away After Delivery?Melasma that arises during pregnancy may go away on its own, but it won’t happen overnight. It may take several months for your hormones to balance and skin pigmentation to fade. You may need to use different topicals or chemical peels to help get rid of stubborn pigment.
If Melasma Continues After Birth, What Treatments Are Available?Treatments for melasma include topical creams, chemical peels, as well as gentle skin resurfacing procedures. Your dermatologist may recommend one or more of the following:
- Topical Creams
Hydroquinone, corticosteroids, and tretinoin (Retin-A) are just a few of the many options used to treat melasma.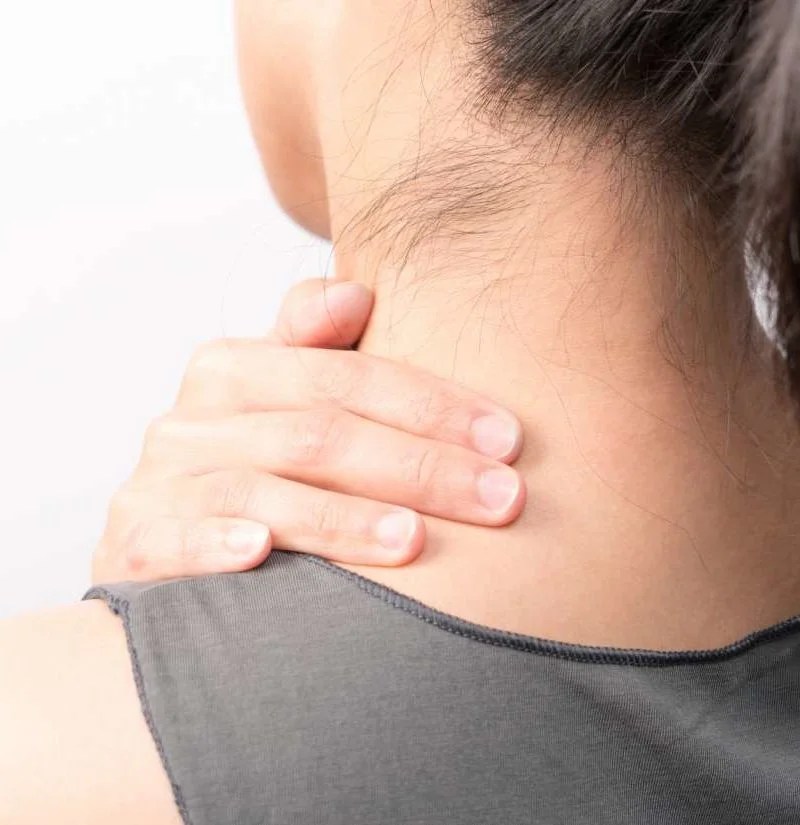
- Chemical Peels
Chemical peels address discoloration by exfoliating the top layers of skin, allowing newer and more evenly toned skin cells to rise to the surface.
- Laser Treatments
Not all laser therapies are ideal for treating discoloration. Fractional lasers are commonly used for treating melasma. If you have dark skin, seek a provider who is experienced in laser treatment for people of color.
About the Author
Elizabeth Geddes-Bruce, MD is a board certified dermatologist and dermatologic surgeon specializing in the practice of both cosmetic and medical dermatology. Dr. Geddes-Bruce is fellowship-trained in cosmetic dermatology and laser surgery. She served as Chief Resident at one of the nation’s top dermatology programs – The University of Texas at Houston and M.D. Anderson Cancer Center.
Elizabeth Geddes-Bruce, MD is a board certified dermatologist and dermatologic surgeon specializing in the practice of both cosmetic and medical dermatology.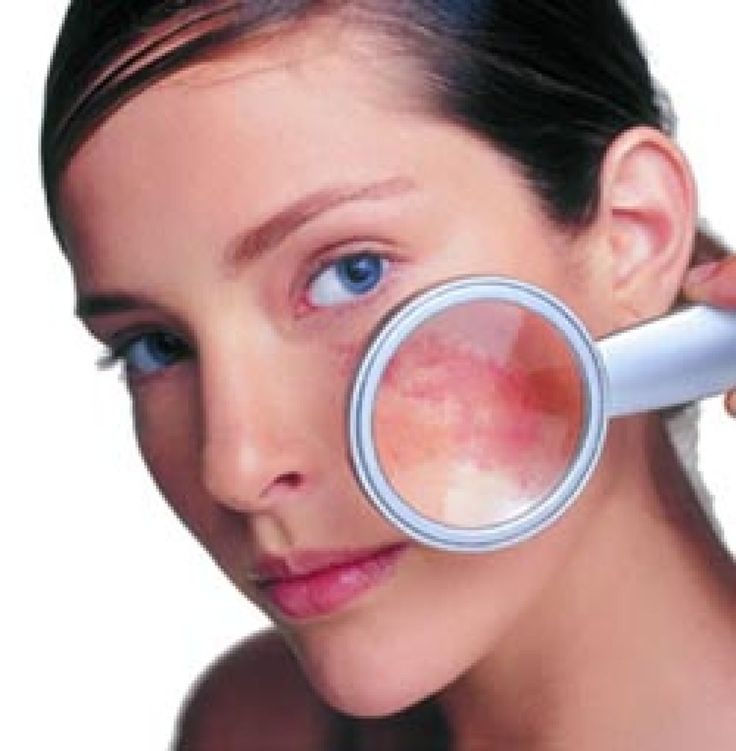 Dr. Geddes-Bruce is fellowship-trained in cosmetic dermatology and laser surgery. She served as Chief Resident at one of the nation’s top dermatology programs – The University of Texas at Houston and M.D. Anderson Cancer Center.
Dr. Geddes-Bruce is fellowship-trained in cosmetic dermatology and laser surgery. She served as Chief Resident at one of the nation’s top dermatology programs – The University of Texas at Houston and M.D. Anderson Cancer Center.
Leave a Reply
Subscribe
Sign Up For Our Newsletter
Learn about special offers, current clinical research studies, and more.
(Typically only 2 messages sent per month.)
Search Blog
Search for:
Book Online
Choose one option below
Select LocationAlamo HeightsCedar ParkDomain NorthsideDowntown AustinDripping SpringsFar WestLakewayLamar CentralMarble FallsNorth AustinOnion CreekRiver OaksRound RockSouth AustinSouthwest ParkwayTelehealth (Texas Only)University ParkWestlakeWest UniversitySelect ProviderAdam Smithee, MDAli Shahbaz, MDAlison Moseley, MDAmy Bekanich, MDAndrea Medina, LAAvery StevensBernice Martinez, LACameron Craven, MD, FACSCameron Erickson, MDChandler Fore, RN BSNChanel Flores, LACheryl Kosarek, MDChrista Tomc, DOChuma Chike-Obi, MDCorina Cardenas, LADaniel Friedmann, MDDavid Smith, PA-CDevan WrightDonna Hart, MDElizabeth Geddes-Bruce, MDEmily White, LAEmily Wood, MDFareesa Sandoval, MDFrida CastanedaGregory Nikolaidis, MDHeidi Prather, MDHolly Singletary, MDHubert Chodkiewicz, MDJamie Cantu, LAJennifer Gordon, MDJessica “Nikki” Dietert, MDJohnny Zhao, MDJonathan Bielfield, DOJonathan Nathan, MDJulie Jackson, MDKara Roth, LAKatie Fowler, PA-CKellie Reed, MDKelly Wala, RN BSNKellyanne CrevistonKevin Flynn, MDKristen Gabbard, FNP-CKristi Cardona, LAKristin Kutac, PA-CKristy Hamilton, MD, FACSKylie Fuller, LALaura Buford, MDLaura Speck, MDLauren Rimoin, MDLeilani Townsend, DOLela Lankerani, DOLeslie Robbins, MPAS, PA-CLeti HernandezLindsey Hunter-Ellul, MD, FAADLindsey Richards, MDLisa Rhodes, MDMacey Delcambre, MDMalini Fowler, MDMelinda Conroy, DOMia BaroniMichael Coverman, MDMichelle Sivolob, RNMinas Constantinides, MD, FACSMorgan Covington, M.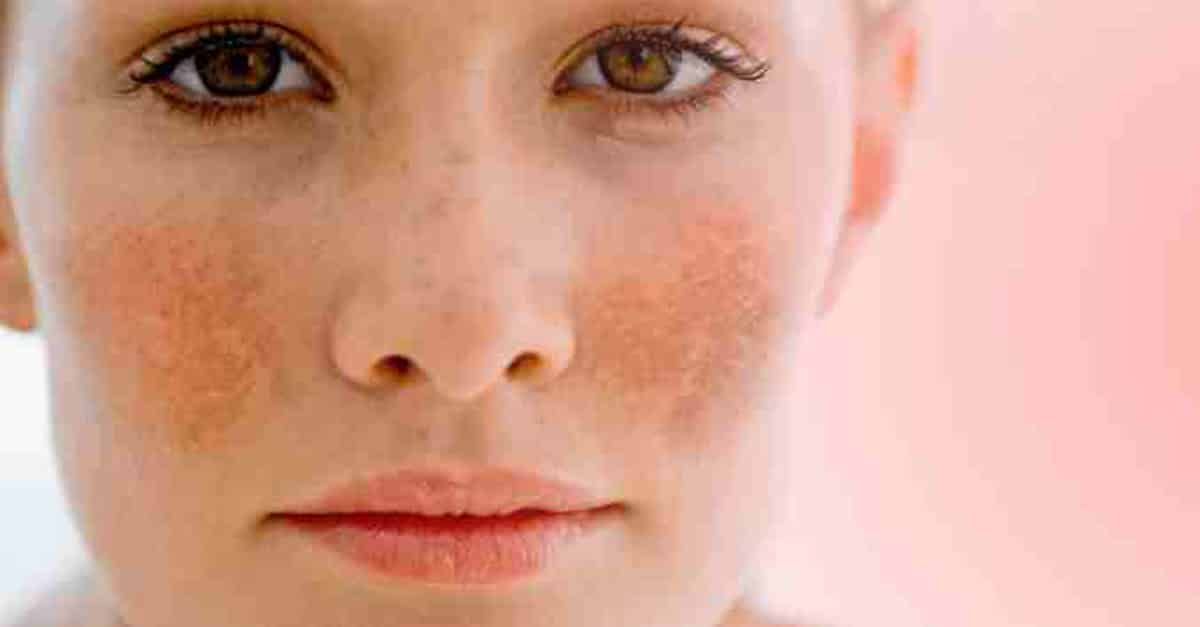 DNeil Farnsworth, MDNicole Deaver, LANicole Hill, FNPPeggy Chern, MDQuynh-Giao Sartor, MDRamya Kollipara, MDSally Matika, PA-CSara Bode, FNP-CSarah Grimmer, RN BSNTatiana Sousa, MDTaylor BiniTimothy McGee, MD, FACS
DNeil Farnsworth, MDNicole Deaver, LANicole Hill, FNPPeggy Chern, MDQuynh-Giao Sartor, MDRamya Kollipara, MDSally Matika, PA-CSara Bode, FNP-CSarah Grimmer, RN BSNTatiana Sousa, MDTaylor BiniTimothy McGee, MD, FACS
Select First Available Appointment
Testimonials
I just want to say thanks to the whole staff at Westlake Dermatology for treating me with such kindness and for doing such an excellent job in taking care of my problem.
– Loren J.
SCHEDULE AN APPOINTMENT
Testimonials
Cannot think of a single thing which would make my visit more enjoyable – every detail is taken care of and done so very professionally – it seems that all employees involved in any type of patient contact are genuinely concerned, very patient oriented and, friendly!! In short, they are always quite courteous and professional.
– Bill G.
Testimonials
Every staff member I spoke with was warm, friendly, and extremely accommodating. From start to finish, I felt valued and well taken care of…I wish all of my medical experiences were this pleasant! Thank you!
– Jennifer B.
melasma, chloasma, lentigo, melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is the appearance of darker spots or stripes on the skin. Melanosis of the skin, as increased pigmentation is also called, develops imperceptibly and, as a rule, does not cause physical discomfort, pain, or itching. Emerging skin defects are located on different parts of the body, the face is uneven. They can be of different shapes and different shades.
In most cases, the pathology is benign and does not pose a direct threat to health. And the main problem of the disease is aesthetic unattractiveness. Excessive pigmentation on the face and body is often perceived as a cosmetic defect.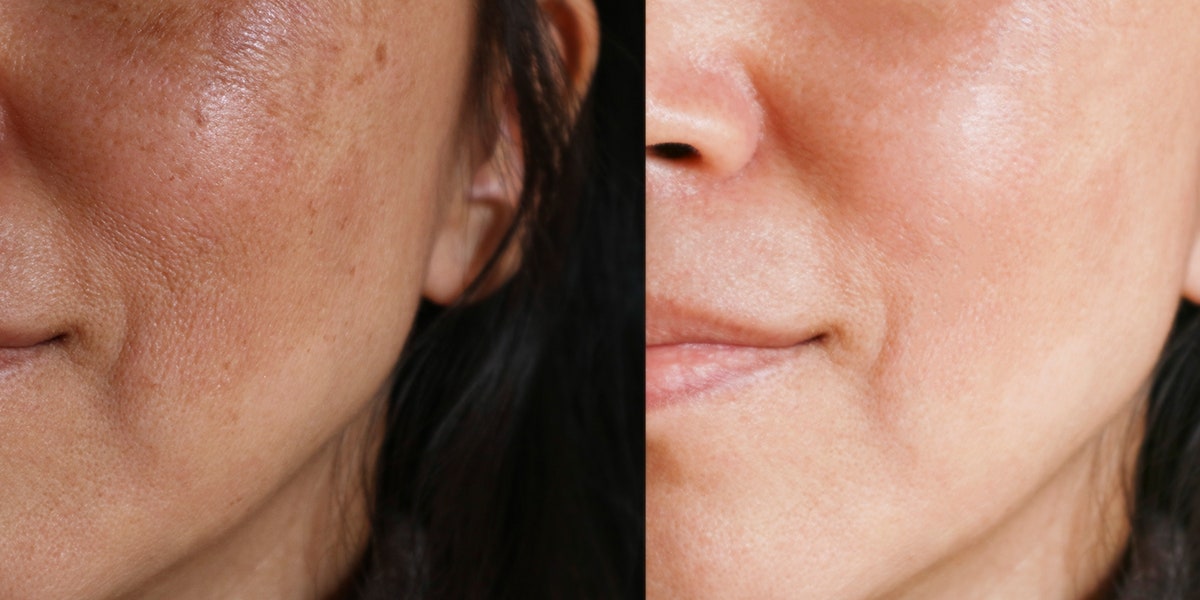 Spots attract the attention of others, become the cause of ridicule. A person experiences psychological discomfort, fear of communication. Social activity decreases, isolation develops. However, this is not the only reason to start pathology treatment.
Spots attract the attention of others, become the cause of ridicule. A person experiences psychological discomfort, fear of communication. Social activity decreases, isolation develops. However, this is not the only reason to start pathology treatment.
The disease melanosis under adverse factors can lead to the development of malignant melanoma - an aggressive skin cancer. And the sudden appearance of excessive skin pigmentation can be a direct indicator of a serious disease of internal organs or body systems.
What is hyperpigmentation?
The cause of hyperpigmentation is a malfunction of the cells that produce the pigment melanin. When there is too much of it in certain areas of the skin, dark stripes and spots appear on the body, face. In this case, the color of abnormal manifestations can vary from light beige to black. This is the nature of melanosis. It remains to understand the reasons that cause such an anomaly.
Hyperpigmentation of the skin: causes
As already noted, the cause of the disease lies in the accumulation of melanin in certain areas of the skin.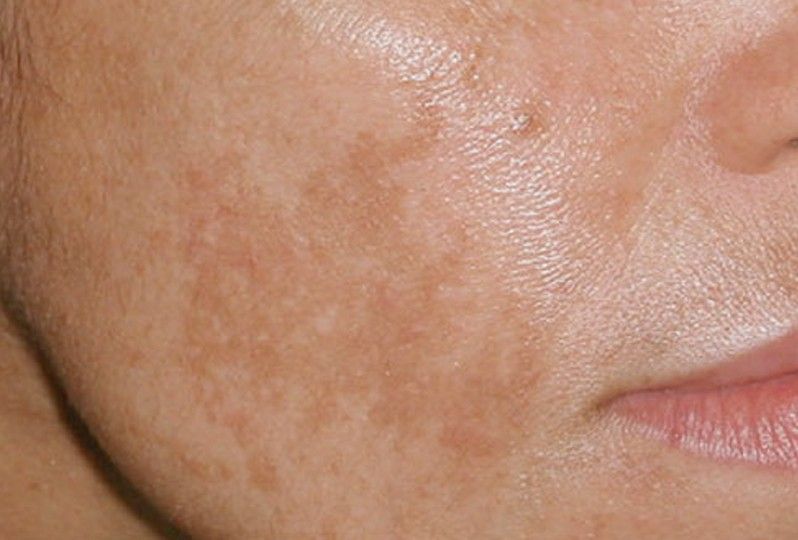
- Most often, pigment production is the body's response to excessive solar radiation. Melanocyte cells produce pigment to protect the skin from destruction. Melanin is a powerful antioxidant. It neutralizes solar radiation. With excessive sun exposure, melanocytes work in an enhanced mode, produce more pigment than usual. This is how melanin hyperpigmentation is formed.
- Hormonal failure can provoke the production of an increased amount of melanin. Hormonal fluctuations often cause the development of such types of hyperpigmentation as melasma and age-related hyperpigmentation. So female hormones provoke the release of melanin during pregnancy. In women, pigmented circles appear around the eyes. Many dermatologists observe the appearance of age spots on the face and body of older women during the onset of menopause. Pathology is called senile hyperpigmentation.
- The appearance of spots on the skin can be a symptom of a number of diseases. For example, pigmentation is caused by autoimmune diseases.
 Provoke the development of pathology failures in the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine system, beriberi.
Provoke the development of pathology failures in the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine system, beriberi. - Another reason for the increased production of melanin is the use of a number of drugs, the side effect of which is an increase in photosensitivity.
- Often, moles and spots appear on the skin at the site of acne. In this case, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation of the skin develops. A prime example of this is post-acne (darkening of the skin after acne). In place of acne, not only scarring of the skin occurs, but hyperpigmentation develops. In children, dark spots may also appear at the site of abrasions on the legs.
- The hereditary factor also has a place to be on the list of causes for the development of hyperpigmentation. For example, freckles in children. The child at the gene level receives a predisposition to excessive production and uneven accumulation of melanin on the cheeks, nose, under the eyes, on the back, on the arms.
- It should be mentioned that stress can also cause metabolic disorders.
 This can lead to excess melanin production.
This can lead to excess melanin production.
No matter what the reason for the appearance of age spots and streaks on the skin. To exclude serious diseases, including oncology, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist.
We invite everyone to be examined at the specialized medical center for diagnosing moles "Lazersvit". The use of modern diagnostic methods makes it possible to identify even the initial mutations of the skin and prevent oncology.
Hyperpigmentation: types
Hyperpigmentation is classified according to various criteria. The disease is hereditary and acquired. Hereditary pathology is what a person is born with, even if the visual manifestation of excessive skin pigmentation did not appear immediately.
For example , the same freckles are hereditary hyperpigmentation. They are clearly manifested by the age of three years of a baby's life. In spring and summer, the spots appear more strongly, but in winter they are visible, they do not disappear completely.
Acquired pigmentation is more common. As already mentioned, it can be a protective reaction of the body to aggressive external factors. Or it could be a symptom of a serious internal illness.
Types of secondary hyperpigmentation
1. Chloasma is an increased pigmentation, manifested by irregularly shaped spots, but with clear boundaries. The size of manifestations, as a rule, exceeds 1 cm in diameter. Pigmentation has a light brown or brown color, a shade of strong coffee. Chloasma appears on the face and body. The disease is often diagnosed in women during pregnancy. They have hyperpigmentation of this kind appears on the abdomen. Education with low oncological risk. Its treatment is recommended for cosmetic purposes.
2. Lentigo is an increased pigmentation of the skin, which is manifested by the appearance of rounded brown spots with clear boundaries. Neoplasms of this type are benign, but can significantly complicate life due to a decrease in the attractiveness of appearance.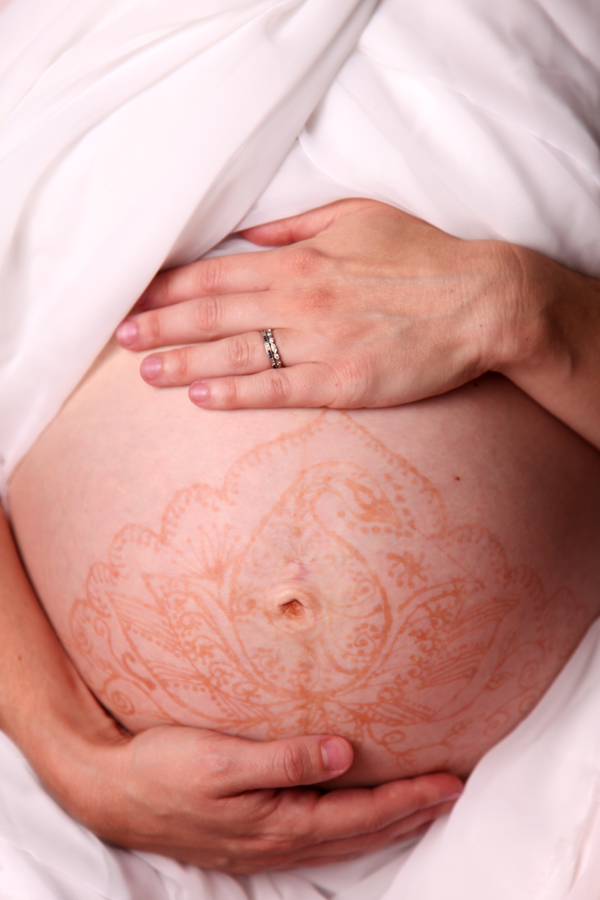 Treatment of lentigo on the face is a popular service for which people turn to our center. It doesn’t matter if it is a congenital form of pathology, acquired solar lentigo or hyperpigmentation caused by age-related changes.
Treatment of lentigo on the face is a popular service for which people turn to our center. It doesn’t matter if it is a congenital form of pathology, acquired solar lentigo or hyperpigmentation caused by age-related changes.
3. Melanosis (melasma) develops due to hormonal failures, endocrine disorders. With melanosis, excess pigment is deposited on the skin of the eyelids, in the area of the eyebrows, on the skin of the forehead, in the area of \u200b\u200bthe ears. Less often, melanosis of the conjunctiva of the eyeball is diagnosed.
4. Melasma is an increased pigmentation of the skin caused by excessive sun exposure. Most often, dark spots appear on areas exposed to the sun - on the face, neck, hands. Less often, the accumulation of melanin in this type of hyperpigmentation is observed on the legs and back. Get rid of melasma on the face and neck most often in terms of increasing aesthetic appeal.
5. Post-traumatic hyperpigmentation appears on any part of the skin as a result of a protracted inflammatory process, frequent trauma to the same area. In this case, the pigment accumulates in the epidermal and dermal tissues.
In this case, the pigment accumulates in the epidermal and dermal tissues.
There is another parameter by which dermatologists must classify hyperpigmentation. It is about the depth of the pigment. According to this characteristic, it happens:
- Epidermal (simple) hyperpigmentation, for example, superficial chloasma.
- Dermal hyperpigmentation characterized by deep pigmentation, such as dermal melasma.
- A mixed form of excessive skin pigmentation in which melanin is concentrated in both dermal and epidermal tissues.
Diagnosis and a clear classification of hyperpigmentation is extremely important, as it allows you to choose the best method aimed at getting rid of color spots.
How to treat hyperpigmentation?
Removal of age spots today is carried out in several ways:
- Chemical peeling involves the use of aggressive acid solutions that lead to the removal of superficial skin layers. In fact, a chemical burn of the skin is performed, due to which part of it exfoliated, making room for evenly pigmented skin.
 The procedure is traumatic, dangerous and requires a long rehabilitation period. In addition, this method is only suitable for superficial hyperpigmentation. If melanin has accumulated in deep tissues, chemical peeling will not help.
The procedure is traumatic, dangerous and requires a long rehabilitation period. In addition, this method is only suitable for superficial hyperpigmentation. If melanin has accumulated in deep tissues, chemical peeling will not help. - Phototherapy is a popular method, the essence of which is the exposure of pigmented skin to light waves without ultraviolet rays. Due to this effect, melanin is destroyed, skin color is evened out.
- Sclerotherapy is a method of treating age spots by introducing drugs into the bloodstream that destroy melanin. This method has shown high efficiency in the treatment of wine stains (vascular pathologies that cause red spots on the skin). However, for the treatment of excessive pigmentation, it is not the most effective.
- Laser therapy has the same effect as phototherapy, but more pronounced, productive. The procedure involves “burning out” of pigmented areas of the skin with a high-energy beam. The dermatologist sets the intensity and depth of the laser pulse, so neighboring healthy tissues are not adversely affected.
 The procedure can be performed both on the surface layer of the skin and on the dermis. The procedure is carried out without blood, painlessly and without negative consequences for the skin. The positive effect is noticeable even after one session. In some cases, several procedures are performed to completely remove a deep pigment spot.
The procedure can be performed both on the surface layer of the skin and on the dermis. The procedure is carried out without blood, painlessly and without negative consequences for the skin. The positive effect is noticeable even after one session. In some cases, several procedures are performed to completely remove a deep pigment spot.
Professionally performed dermatological procedures allow you to completely or partially remove age spots. The optimal method is chosen by the doctor based on the history and individual characteristics of a particular patient. The laser method for the treatment of hyperpigmentation remains recommended, as it provides for a gentle effect and high results.
It is strongly not recommended to use folk remedies and remove age spots in dubious ways at home. This can lead to serious complications - skin burns, damage to the integrity of the skin, the addition of a secondary infection.
Contact the specialized clinic "Lazersvit" if you have age spots. We will not only carry out a diagnosis to eliminate the risk of rebirth, but also conduct an effective treatment to overcome hyperpigmentation.
We will not only carry out a diagnosis to eliminate the risk of rebirth, but also conduct an effective treatment to overcome hyperpigmentation.
The laser method used in our clinic has a minimum of contraindications and can be used at any age (including infancy). We will be happy to answer any questions on the topic "Hyperpigmentation" at an in-person consultation. You can make an appointment with a doctor by phone at a convenient time for you.
Age spots that disfigure appearance are no longer a sentence. In a few procedures, they will disappear without a trace!
Skin hyperpigmentation: causes, treatment
Hyperpigmentation is the darkening of certain areas of the face and body as a result of the deposition of a large amount of pigment in the cells of the epidermis. This phenomenon can be both diffuse (occupying rather large areas of the skin) and focal.
Contents
- 1 Types of hyperpigmentation
- 2 Causes of hyperpigmentation
- 3 Methods for combating hyperpigmentation
Types of hyperpigmentation
In everyday life, hyperpigmentation is an accumulation of freckles.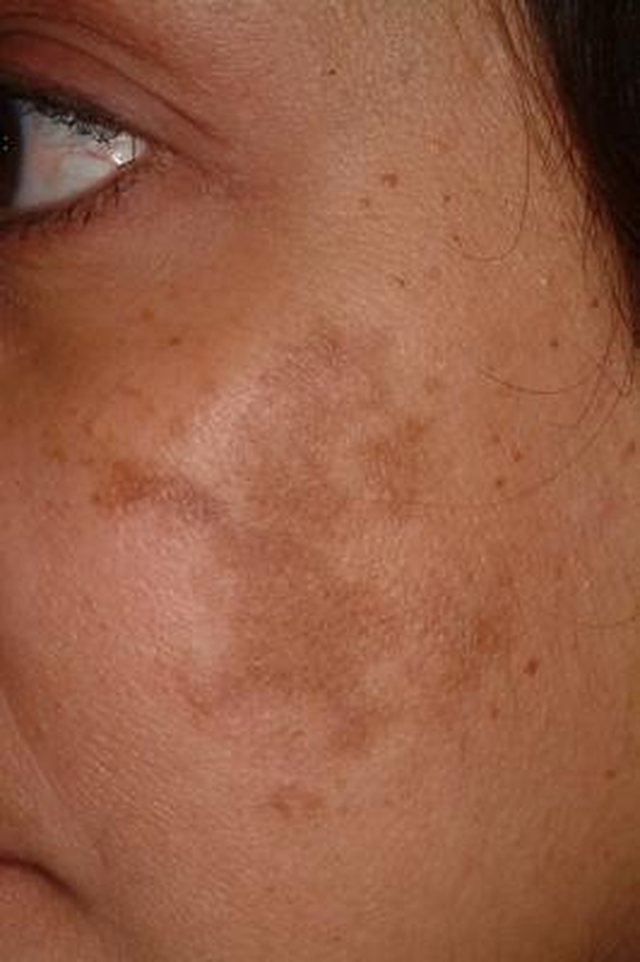 However, this is just one of the types of this skin defect. Depending on the causes, severity and nature of pigmentation, several more of its varieties can be distinguished.
However, this is just one of the types of this skin defect. Depending on the causes, severity and nature of pigmentation, several more of its varieties can be distinguished.
- Melasma - brown symmetrical spots localized on the neck, shoulders, sometimes face
- Chloasma - irregularly shaped dark brown patches most commonly found on the face
- Secondary hyperpigmentation - dark or light brown spots resulting from past skin diseases: neurodermatitis, eczema, etc.
Causes of hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is caused by the deposition of melanin pigment under the skin. Depending on its amount, the skin can take on various shades - from flesh to dark brown. This process plays a protective role for the body: melanin is able to absorb ultraviolet rays, protecting the skin from excessive solar activity. That is why in the warm season, pigmentation intensifies. If the process of melanin synthesis is normal, then, as a rule, there are no special problems with the appearance of the skin.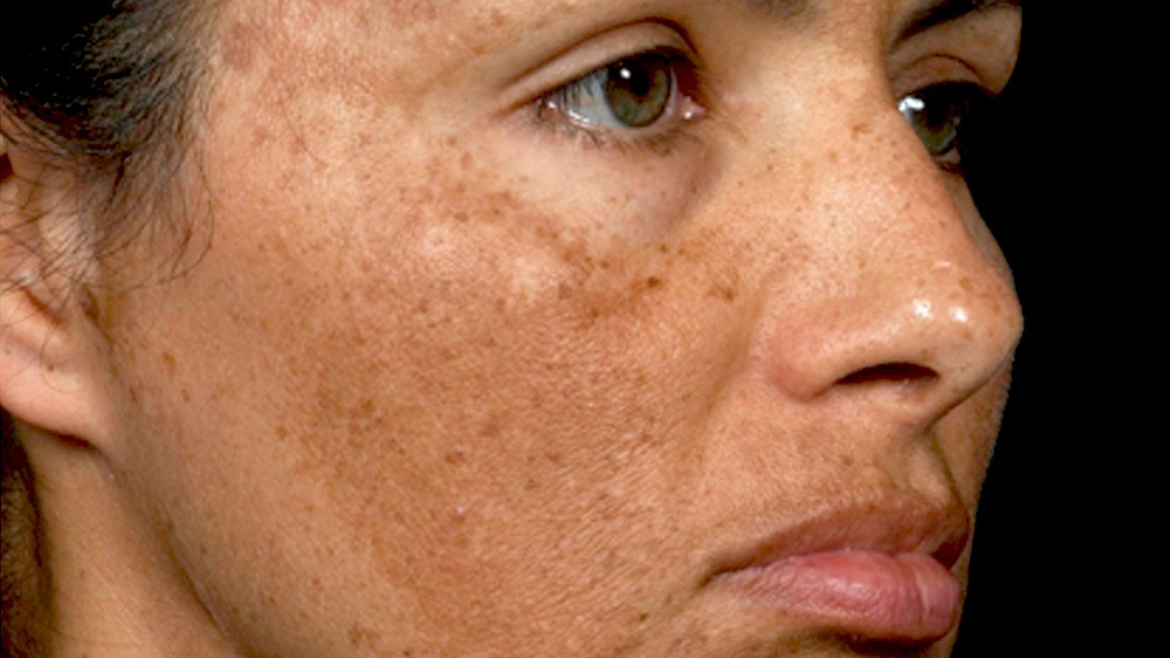 In case of violation of some functions of the body, hyperpigmentation appears. It can increase during periods of hormonal imbalance (pregnancy, menopause), with violations of metabolic processes in the body, hormonal failure, and also with certain diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Some drugs, such as antibiotics, can also provoke hyperpigmentation. An important role in this process is played by heredity and skin type: the lighter it is, the more prone to hyperpigmentation. Long-term exposure to the sun without the use of protective creams can also cause excessive freckles.
In case of violation of some functions of the body, hyperpigmentation appears. It can increase during periods of hormonal imbalance (pregnancy, menopause), with violations of metabolic processes in the body, hormonal failure, and also with certain diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Some drugs, such as antibiotics, can also provoke hyperpigmentation. An important role in this process is played by heredity and skin type: the lighter it is, the more prone to hyperpigmentation. Long-term exposure to the sun without the use of protective creams can also cause excessive freckles.
Methods of combating hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation does not pose a danger to human health, but it is a cosmetic defect that spoils the lives of many women and causes serious psychological discomfort. Home remedies (peelings, scrubs and other cosmetics) may not only not bring the desired result, but also aggravate the defect. It makes no sense to experiment on your own - after all, today there are many effective professional remedies for combating skin hyperpigmentation.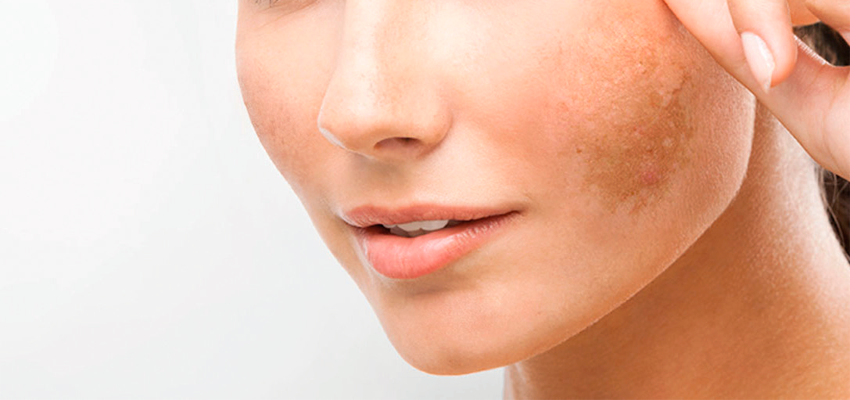 The clinic uses the following treatment methods.
The clinic uses the following treatment methods.
- Phototherapy is one of the safest and most effective treatments for hyperpigmentation. The skin is treated with special light waves with the exception of ultraviolet rays. Depending on the nature of pigmentation, the cosmetologist selects the optimal length and power of the light wave, which contributes to the destruction of melanin. As a result, skin color is evened out. Skin whitening is possible immediately after the first procedure. With severe hyperpigmentation, several sessions may be required: an average of 4 to 6. A year later, the course of procedures can be repeated to consolidate the result. It is not recommended to carry out procedures in the summer.
- Chemical peels. The effectiveness of chemical peels in the fight against hyperpigmentation is due to the body's response to microdamages in the skin. Peeling activates regenerative processes in skin cells, as a result of which metabolic processes are accelerated.
 This allows you to eliminate shallow skin pigmentation, and at the same time renew the upper layer of the epidermis, restore a healthy complexion, enhance the effect of nourishing and moisturizing cosmetics. The clinic uses glycolic and yellow peels, as well as Kojicol Gel to combat hyperpigmentation. This effective remedy for restoring the appearance of the skin has a beneficial effect not only on its color, but also on the overall tone.
This allows you to eliminate shallow skin pigmentation, and at the same time renew the upper layer of the epidermis, restore a healthy complexion, enhance the effect of nourishing and moisturizing cosmetics. The clinic uses glycolic and yellow peels, as well as Kojicol Gel to combat hyperpigmentation. This effective remedy for restoring the appearance of the skin has a beneficial effect not only on its color, but also on the overall tone. - Mesotherapy with whitening cocktails. The method allows you to deliver active substances directly to the cells of the epidermis, affecting pigment spots from the inside. Performed by experienced cosmetologists with the help of the finest needles, the injection procedure is effective, safe and painless.
- Beauty care. For the care of pigmented skin, specialists use special products of professional cosmetic premium brands Germaine De Capuccini (Spain) and Ericson Laboratoire (France).
 Comprehensive skin care includes cleansing, nourishing and moisturizing. All products contain whitening ingredients that reduce the appearance of pigmentation on the skin of the face and prevent its further spread.
Comprehensive skin care includes cleansing, nourishing and moisturizing. All products contain whitening ingredients that reduce the appearance of pigmentation on the skin of the face and prevent its further spread. - Microfractional therapy. The procedure consists in the treatment of pigmented areas of the skin with a special device equipped with microneedles. Penetrating into the skin to a depth of 0.25-2 mm, they cause microdamages. This process promotes the release of growth factors in skin cells, their regeneration. And this, in turn, leads to the disappearance of pigmentation, skin rejuvenation and an increase in its tone.
- Cosmetics for home skin care. For home care of pigmented skin, cosmetologists individually select cosmetic products for patients that contain whitening components and block melanogenesis.
- Sun protection products. Hyperpigmentation is a recurring problem, so the use of sunscreen all year round is a must for such skin.