Infant development growth
Your baby’s growth and development – first 12 months
Your baby’s growth and development – first 12 months | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of contentYour baby's growth and development - 1 month old
Your baby starts developing from the moment they are born. At 1 month, cuddling, sleeping and feeding are all that really matters to your baby.
Your baby's growth and development - 2 months old
At 2 months, your baby is growing fast and becoming more alert. They will also be making more sounds and getting better at moving their little bodies.
Your baby's growth and development - 3 months old
By 3 months, your baby will have formed a strong attachment to you. They will respond with lots of smiles, and you can really enjoy your baby as they ...
Your baby's growth and development - 4 months old
From 4 months, your baby should have more control over what they do. They should hear, touch and see better and will be starting to move around much m...
Your baby's growth and development - 5 months old
At 5 months, your baby is quickly growing and developing. They may soon be sitting up on their own, preparing for solid foods and learning new languag...
Your baby's growth and development - 6 months old
At age 6 months, your baby should be more coordinated, start to respond to particular words, and have a better sense of the world around them.
Your baby's growth and development - 7 months old
Your 7-month-old baby is growing fast and may even be sitting up on their own and eating solid foods. Learn more here about how your baby is developin...
Your baby's growth and development - 8 months old
At 8 months old, your baby will start to explore their little world. It might mean more running around for you, but it's a great time to watch them le...
Your baby's growth and development - 9 months old
Your 9-month-old will, by now, really be developing their personality. They will form stronger attachments with a few people, preferring some over oth...
Your baby's growth and development - 10 months old
A 10-month-old will be very active. As a parent, you’ll probably be chasing them around as they crawl, and be learning more about their developing per...
As a parent, you’ll probably be chasing them around as they crawl, and be learning more about their developing per...
Your baby's growth and development - 11 months old
At 11 months old, your baby is almost a toddler – you’ll probably be surprised at how quickly they can move around your home and how independent they ...
Your baby's growth and development - 12 months old
At 12 months, your baby is now a toddler. If they haven’t already, it won’t be long now before they take their first steps, develop a sense of humour,...
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.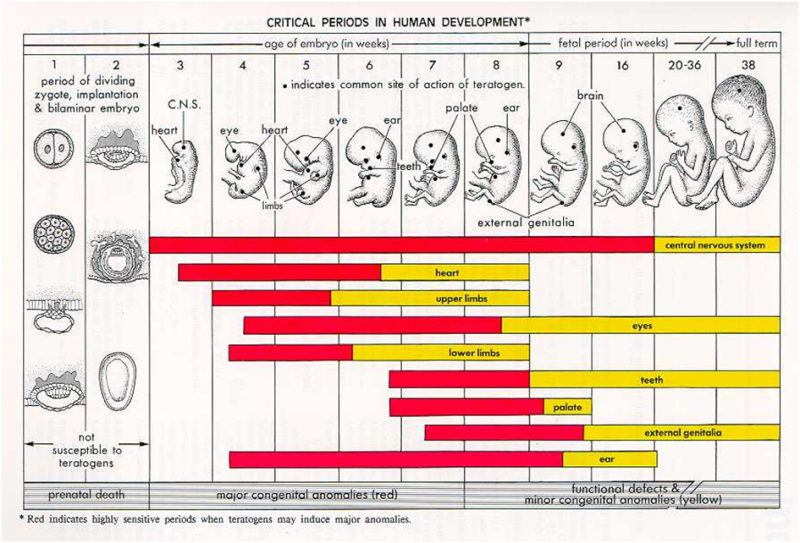
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Infants (0-1 years) | CDC
Developmental Milestones
Skills such as taking a first step, smiling for the first time, and waving “bye-bye” are called developmental milestones. Developmental milestones are things most children can do by a certain age. Children reach milestones in how they play, learn, speak, behave, and move (like crawling, walking, or jumping).
In the first year, babies learn to focus their vision, reach out, explore, and learn about the things that are around them.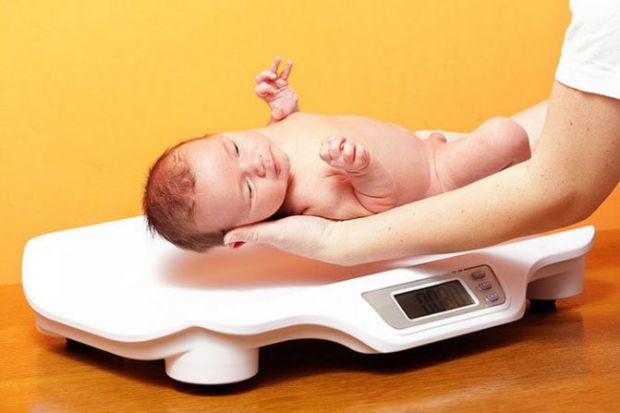 Cognitive, or brain development means the learning process of memory, language, thinking, and reasoning. Learning language is more than making sounds (“babble”), or saying “ma-ma” and “da-da”. Listening, understanding, and knowing the names of people and things are all a part of language development. During this stage, babies also are developing bonds of love and trust with their parents and others as part of social and emotional development. The way parents cuddle, hold, and play with their baby will set the basis for how they will interact with them and others.
Cognitive, or brain development means the learning process of memory, language, thinking, and reasoning. Learning language is more than making sounds (“babble”), or saying “ma-ma” and “da-da”. Listening, understanding, and knowing the names of people and things are all a part of language development. During this stage, babies also are developing bonds of love and trust with their parents and others as part of social and emotional development. The way parents cuddle, hold, and play with their baby will set the basis for how they will interact with them and others.
Positive Parenting Tips
Following are some things you, as a parent, can do to help your baby during this time:
- Talk to your baby. She will find your voice calming.
- Answer when your baby makes sounds by repeating the sounds and adding words. This will help him learn to use language.
- Read to your baby. This will help her develop and understand language and sounds.
- Sing to your baby and play music.
 This will help your baby develop a love for music and will help his brain development.
This will help your baby develop a love for music and will help his brain development. - Praise your baby and give her lots of loving attention.
- Spend time cuddling and holding your baby. This will help him feel cared for and secure.
- Play with your baby when she’s alert and relaxed. Watch your baby closely for signs of being tired or fussy so that she can take a break from playing.
- Distract your baby with toys and move him to safe areas when he starts moving and touching things that he shouldn’t touch.
- Take care of yourself physically, mentally, and emotionally. Parenting can be hard work! It is easier to enjoy your new baby and be a positive, loving parent when you are feeling good yourself.
Infants (0-1 year of age) pdf icon[PDF – 793K]
Child Safety First
When a baby becomes part of your family, it is time to make sure that your home is a safe place. Look around your home for things that could be dangerous to your baby. As a parent, it is your job to ensure that you create a safe home for your baby. It also is important that you take the necessary steps to make sure that you are mentally and emotionally ready for your new baby. Here are a few tips to keep your baby safe:
As a parent, it is your job to ensure that you create a safe home for your baby. It also is important that you take the necessary steps to make sure that you are mentally and emotionally ready for your new baby. Here are a few tips to keep your baby safe:
- Do not shake your baby―ever! Babies have very weak neck muscles that are not yet able to support their heads. If you shake your baby, you can damage his brain or even cause his death.
- Make sure you always put your baby to sleep on her back to prevent sudden infant death syndrome (commonly known as SIDS). Read more about new recommendations for safe sleep for infants here.
- Protect your baby and family from secondhand smoke. Do not allow anyone to smoke in your home.
- Place your baby in a rear-facing car seat in the back seat while he is riding in a car. This is recommended by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration pdf icon[1.15 MB / 1 page]external icon.
- Prevent your baby from choking by cutting her food into small bites.
 Also, don’t let her play with small toys and other things that might be easy for her to swallow.
Also, don’t let her play with small toys and other things that might be easy for her to swallow. - Don’t allow your baby to play with anything that might cover her face.
- Never carry hot liquids or foods near your baby or while holding him.
- Vaccines (shots) are important to protect your child’s health and safety. Because children can get serious diseases, it is important that your child get the right shots at the right time. Talk with your child’s doctor to make sure that your child is up-to-date on her vaccinations.
Healthy Bodies
- Breast milk meets all your baby’s needs for about the first 6 months of life. Between 6 and 12 months of age, your baby will learn about new tastes and textures with healthy solid food, but breast milk should still be an important source of nutrition.
- Feed your baby slowly and patiently, encourage your baby to try new tastes but without force, and watch closely to see if he’s still hungry.
- Breastfeeding is the natural way to feed your baby, but it can be challenging.
 If you need help, you can call the National Breastfeeding Helpline at 800-994-9662 or get help on-line at http://www.womenshealth.gov/breastfeedingexternal icon. You can also call your local WIC Program to see if you qualify for breastfeeding support by health professionals as well as peer counselors or use an online directory to find an International Board-Certified Lactation Consultantexternal icon in your community.
If you need help, you can call the National Breastfeeding Helpline at 800-994-9662 or get help on-line at http://www.womenshealth.gov/breastfeedingexternal icon. You can also call your local WIC Program to see if you qualify for breastfeeding support by health professionals as well as peer counselors or use an online directory to find an International Board-Certified Lactation Consultantexternal icon in your community. - Keep your baby active. She might not be able to run and play like the “big kids” just yet, but there’s lots she can do to keep her little arms and legs moving throughout the day. Getting down on the floor to move helps your baby become strong, learn, and explore.
- Try not to keep your baby in swings, strollers, bouncer seats, and exercise saucers for too long.
- Limit screen time. For children younger than 18 months of age, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that it’s best if babies do not use any screen media other than video chatting.
- Make sure your child gets the recommended amount of sleep each night: For infants 4-12 months, 12–16 hours per 24 hours (including naps)
For More Information
- Infants and toddlers
- Preschool
- Middle childhood
- Adolescence
CDC’s “Learn the Signs. Act Early.” Campaign
For more details on developmental milestones, warning signs of possible developmental delays, and information on how to help your child’s development, visit the “Learn the Signs. Act Early.” campaign website.
CDC’s Parent Information (Children 0―3 years)
This site has information to help you learn how to give your child a healthy start in life.
CDC’s Essentials for Parenting Toddlers and Preschoolers
Learn ways you can help build a safe, stable, and nurturing relationship with your child.
CDC’s Breastfeeding Information
This site has answers to frequently asked questions about breastfeeding.
CDC’s Information on Infant and Toddler Nutrition
Tips for Parents – Ideas to help children maintain a healthy weight.
CDC’s Protect the Ones You Love
CDC’s Injury Center has information on how you can protect your child from drowning and other common causes of injury.
CDC’s Information on Vaccinations
View the immunization schedule for infants and children and find out if your child’s vaccinations are up to date.
My Plate – Infantsexternal icon
The U.S. Department of Agriculture provides information on health and nutrition for 2 through 5 years of age.
My Plate – Toddlersexternal icon
The U.S. Department of Agriculture provides information on health and nutrition for toddlers
HealthyChildren.orgexternal icon
AAP’s Healthy Children website provides information on feeding, nutrition, and fitness for all developmental stages from infancy to young adulthood.
Just in Time Parentingexternal icon (JITP)
Quality, research-based information to families at the time it can be most useful.
Healthy Kids Healthy Futureexternal icon
You will find information on physical activity for young children and on ways to keep them moving.
National Highway Traffic Safety Administrationexternal icon (NHTSA)
NHTSA has information on safety recalls and safety tips for children riding in motor vehicles, walking, biking, playing outside, waiting at school bus stops, and more.
National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.external icon (NICHD)
Visit NICHD to learn how to reduce the risk of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) and about safe sleep environments.
World Health Organization information on infant nutritionexternal icon
This site has information to promote proper feeding for infants and young children.
CDC’s “Learn the Signs. Act Early.” Campaign
For more details on developmental milestones, warning signs of possible developmental delays, and information on how to help your child’s development, visit the “Learn the Signs. Act Early.” campaign website.
Act Early.” campaign website.
CDC’s Parent Information (Children 4−11 years)
This site has information to help you guide your child in leading a healthier life.
CDC’s Essentials for Parenting Toddlers and Preschoolers
Learn ways you can help build a safe, stable, and nurturing relationship with your child.
CDC’s Healthy Weight Information.
Tips for parents – Ideas to help children maintain a healthy weight.
CDC’s Youth Physical Activity Guidelines
This site has information on how to help children be active and play.
My Plate- Preschoolersexternal icon
The U.S. Department of Agriculture provides information on health and nutrition for preschoolers.
HealthyChildren.orgexternal icon
AAP’s Healthy Children website provides information on feeding, nutrition, and fitness for all developmental stages from infancy to young adulthood.
Just in Time Parentingexternal icon (JITP)
Quality, research-based information to families at the time it can be most useful.
Healthy Kids Healthy Futureexternal icon
You will find information on physical activity for young children and on ways to keep them moving.
National Highway Traffic Safety Administrationexternal icon (NHTSA)
NHTSA has information on safety recalls and safety tips for children riding in motor vehicles, walking, biking, playing outside, waiting at school bus stops, and more.
CDC’s Parent Information (Children 4 — 11 years)
This site has information to help you guide your child in leading a healthier life.
CDC’s Healthy Weight Information.
Tips for parents – Ideas to help children maintain a healthy weight.
CDC’s Youth Physical Activity Basics
This site has information on how to help children be active and play.
CDC’s Kids Quest
Kids Quest is a CDC website designed for students in fourth, fifth, and sixth grades, to get them to think about people with disabilities and some of the issues related to daily activities, health, and accessibility.
CDC’s BAM! Body and Mind
CDC’s BAM! Body and Mind is a website designed for kids 9 through 13 years of age to give them the information they need to make healthy lifestyle choices. The site focuses on topics that kids told us are important to them—such as stress and physical fitness—using kid-friendly lingo, games, quizzes, and other interactive features.
My Plate – Kidsexternal icon.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture provides information on health and nutrition for children over 5 years of age.
HealthyChildren.orgexternal icon
AAP’s Healthy Children website provides information on feeding, nutrition, and fitness for all developmental stages from infancy to young adulthood. Visit this website to learn more about emotional problemsexternal icon, learning disabilitiesexternal icon and other health and development concerns.
Just in Time Parentingexternal icon (JITP)
Quality, research-based information to families at the time it can be most useful.
Let’s Move-Kidsexternal icon
Five simple steps for parents towards creating a healthy environment at home.
National Highway Traffic Safety Administrationexternal icon (NHTSA)
NHTSA has information on safety recalls and safety tips for children riding in motor vehicles, walking, biking, playing outside, waiting at school bus stops, and more.
StopBullying.govexternal icon
StopBullying.gov provides information from various government agencies on how children, parents, educators and others in the community can prevent or stop bullying.
SAMHSA’s KnowBullying appexternal icon
A free app for parents to help prevent bullying, created by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Agency (SAMHSA).
Teens Healthexternal icon
Visit this site for information on healthy eating and exerciseexternal icon for children and teenagers, safety tips for your child at homeexternal icon when you can’t be there, and other important health and safety topics.
CDC’s Adolescent and School Mental Health
Learn how connection is key to good adolescent mental health.
CDC’s Parent Information (Teens 12— 19)
This site has information to help you learn how to guide your teen to be safe and become a healthy and productive adult.
CDC’s Healthy Weight Information.
Tips for parents – Ideas to help children maintain a healthy weight.
CDC’s Youth Physical Activity Guidelines
This site has information on how to help children be active and play.
CDC’s Pregnancy Prevention for Teens.
Tips and information especially for teens and designed with input from teens.
CDC’s BAM! Body and Mind
CDC’s BAM! Body and Mind is a website designed for kids 9 through 13 years of age, to give them the information they need to make healthy lifestyle choices. The site focuses on topics that kids told us are important to them—such as stress and physical fitness—using kid-friendly lingo, games, quizzes, and other interactive features.
CDC’s Information on Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender Youth Health
Learn about the physical and mental health of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender youth
American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatryexternal icon
The American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry has many fact sheets for parents on child and adolescent health and development.
My Plate – Teenexternal icon
The U.S. Department of Agriculture provides information on health and nutrition for teens.
HealthyChildren.orgexternal icon
AAP’s Healthy Children website provides information on feeding, nutrition, and fitness for all developmental stages from infancy to young adulthood.
Just in Time Parentingexternal icon (JITP)
Quality, research-based information to families at the time it can be most useful.
National Highway Traffic Safety Administrationexternal icon (NHTSA)
NHTSA has information on safety recalls and safety tips for children riding in motor vehicles, walking, biking, playing outside, waiting at school bus stops, and more.
National Institute of Mental Healthexternal icon
The National Institute of Mental Health has information on mental disorders affecting children and adolescents, including anxiety and depression.
StopBullying.govexternal icon
StopBullying.gov provides information from various government agencies on how children, parents, educators, and others in the community can prevent or stop bullying.
SAMHSA’s KnowBullying appexternal icon
A free app for parents to help prevent bullying, created by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Agency (SAMHSA).
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA)external icon
SAMHSA works to improve the quality and availability of substance abuse prevention, alcohol and drug addiction treatment, and mental health services.
Teens Healthexternal icon
Visit this site for information on healthy eating and exercise for children and teenagers.
Norms of height and weight of children and adolescents
The physical development of a child as a combination of various indicators (length, weight, shape, strength, etc.) characterizing his growth and development is due to a complex of hereditary and social factors. To study the physical development of children and adolescents, a unified method for measuring the human body and its parts has been developed. All anthropometric indicators can be divided into two groups: basic (body length, body weight, chest and head circumference) and additional (other anthropometric indicators, for example, leg length, head height, etc. ). Analysis of the main anthropometric indicators at the time of the examination makes it possible to assess the physical condition of the child, in dynamics - the pace of physical development. At the same time, the features of the physique, the state of the musculoskeletal system, the degree of puberty, etc. are taken into account. Physical development is analyzed by comparing individual or group indicators with average data (standards) characteristic of the corresponding age and gender of the child.
). Analysis of the main anthropometric indicators at the time of the examination makes it possible to assess the physical condition of the child, in dynamics - the pace of physical development. At the same time, the features of the physique, the state of the musculoskeletal system, the degree of puberty, etc. are taken into account. Physical development is analyzed by comparing individual or group indicators with average data (standards) characteristic of the corresponding age and gender of the child.
The value of indicators of a child's physical development can be explained by a number of arguments. For many chronic diseases of childhood, there are no specific symptoms related to the early stage of the development of the disease, therefore, a violation of physical development is one of the first signs of trouble and serves as an indication for an in-depth examination of the child. Violations of the physical development of children and adolescents may be the result of malnutrition, lack of necessary care, improper or harsh treatment of the child, etc.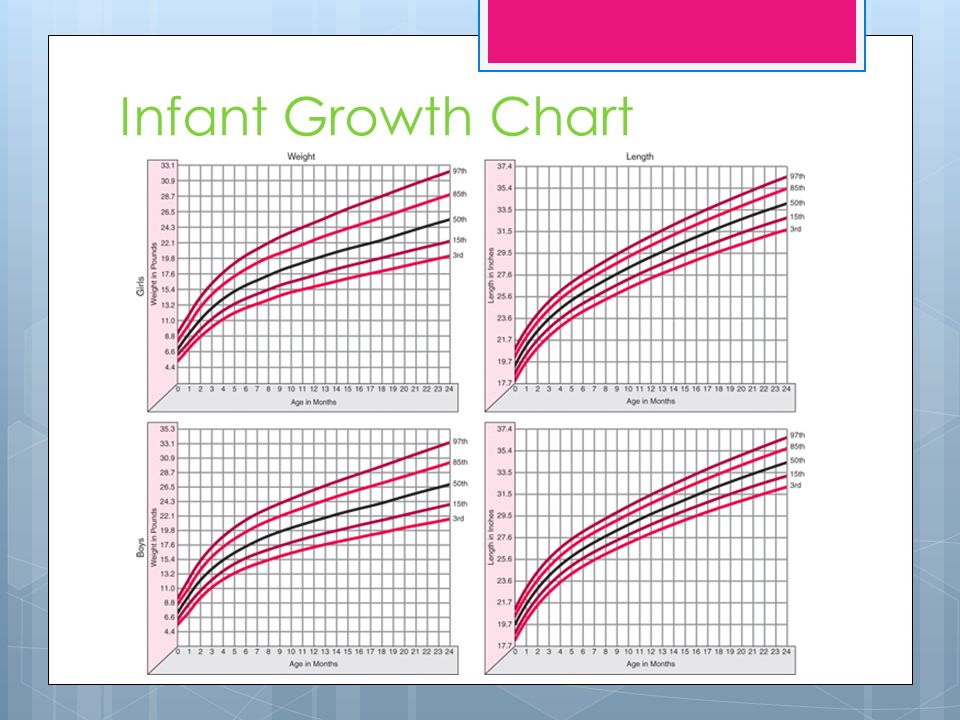 Violations of physical development can cause constitutional features, congenital or hereditary pathology of the developmental apparatus. Such children have imperfect mechanisms of adaptation and anti-infective protection, for example, a lack of body weight in a child may be accompanied by a higher frequency of minor developmental anomalies. Any deviations of anthropometric parameters from the norm at the birth of a child can become one of the reasons for the decrease in immunological resistance, increasing the likelihood of a disease in the first year of life by half, and the probability of death by 4 times. All factors characterizing the growth and development of the child's body can be divided into genetic and environmental factors. The influence of heredity affects the growth of the child after 2 years of life.
Violations of physical development can cause constitutional features, congenital or hereditary pathology of the developmental apparatus. Such children have imperfect mechanisms of adaptation and anti-infective protection, for example, a lack of body weight in a child may be accompanied by a higher frequency of minor developmental anomalies. Any deviations of anthropometric parameters from the norm at the birth of a child can become one of the reasons for the decrease in immunological resistance, increasing the likelihood of a disease in the first year of life by half, and the probability of death by 4 times. All factors characterizing the growth and development of the child's body can be divided into genetic and environmental factors. The influence of heredity affects the growth of the child after 2 years of life.
Hereditary factors mainly determine the rate and possible limit of a child's growth under optimal environmental conditions.
The influence of environmental factors on the growth rate of the child's body can be traced very clearly.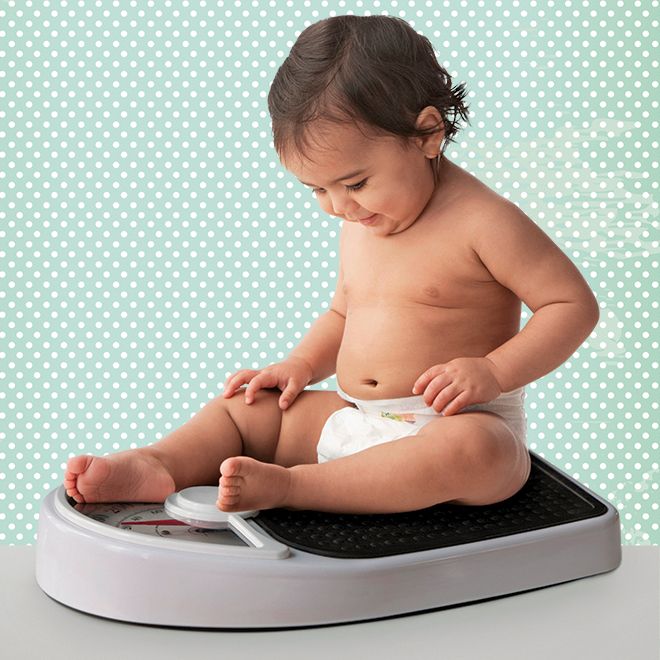 Among these factors, nutrition and vitamin sufficiency, motor mode and emotional stress, acute and chronic diseases, the influence of climatic and geographical conditions, etc. are distinguished. At the same time, environmental factors can slow down or accelerate growth processes, but in general the growth trend is quite stable, it obeys the conservation law growth. A variety of adverse influences that disrupt the individual growth rate of a child can subsequently be neutralized by the phenomenon of "catch-up or compensatory growth." What happens to the physical development of your baby from the moment of birth to its full maturity? We observe the growth and development of a child in the first year of life: How can we understand if he is healthy, is everything okay with him? Remember: the health of a child is judged primarily by its weight, height and head circumference. On average, a newborn's body weight is 3.0-3.5 kg, body length 50 cm, head circumference 35 cm. But do not expect your baby to necessarily meet this standard.
Among these factors, nutrition and vitamin sufficiency, motor mode and emotional stress, acute and chronic diseases, the influence of climatic and geographical conditions, etc. are distinguished. At the same time, environmental factors can slow down or accelerate growth processes, but in general the growth trend is quite stable, it obeys the conservation law growth. A variety of adverse influences that disrupt the individual growth rate of a child can subsequently be neutralized by the phenomenon of "catch-up or compensatory growth." What happens to the physical development of your baby from the moment of birth to its full maturity? We observe the growth and development of a child in the first year of life: How can we understand if he is healthy, is everything okay with him? Remember: the health of a child is judged primarily by its weight, height and head circumference. On average, a newborn's body weight is 3.0-3.5 kg, body length 50 cm, head circumference 35 cm. But do not expect your baby to necessarily meet this standard.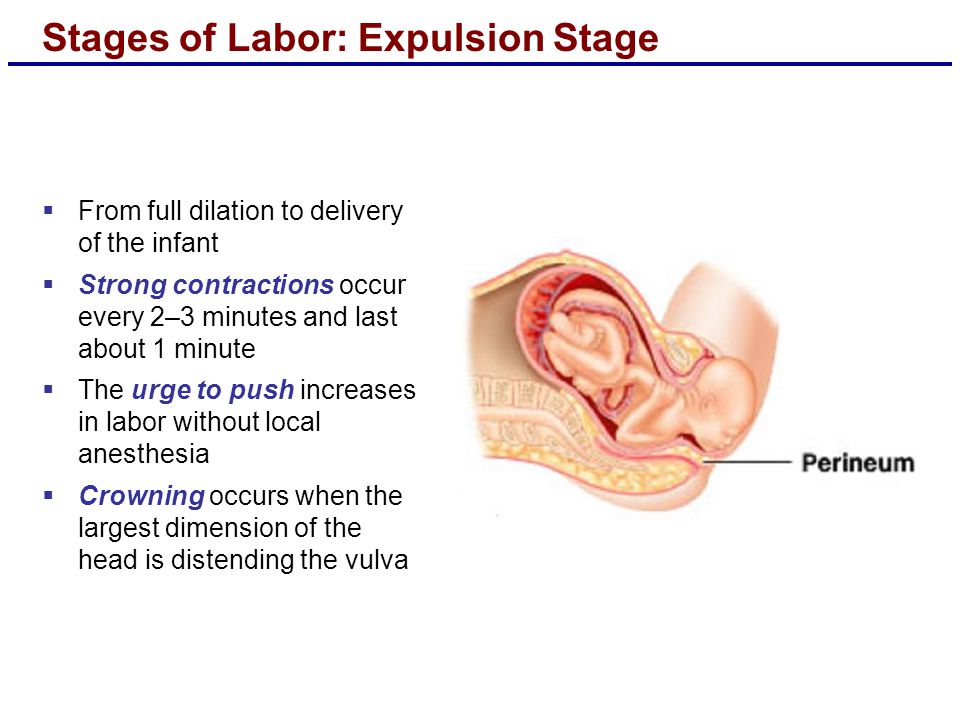 Children are considered normal if their indicators are within the following limits: body weight 2.5-4.5 kg, length 45-55 cm, head circumference 33-37 cm. Immediately after birth, babies lose some weight, and then regain it and start adding. Further weight gain as well as height and head circumference are important indicators of your child's condition. By the end of the 1st year of life, body length increases by 47% in relation to body length at birth.
Children are considered normal if their indicators are within the following limits: body weight 2.5-4.5 kg, length 45-55 cm, head circumference 33-37 cm. Immediately after birth, babies lose some weight, and then regain it and start adding. Further weight gain as well as height and head circumference are important indicators of your child's condition. By the end of the 1st year of life, body length increases by 47% in relation to body length at birth.
Weight gain of a child in the first year of life: by 4-5 months, body weight doubles, by the 1st year it increases 3 times. The head circumference of a child in the first 6 months of life increases by approximately 1 cm per month, but if the father of the child is large and the mother is small, the growth rate of the head circumference may be above the norm, and in the opposite ratio - below the norm. The circumference of the chest of newborns is less than the circumference of the head, these dimensions are equalized only by the age of one. In the first month of life, the child must be weighed daily. Thus, you monitor the development of lactation and fix the daily weight gain. Body weight is the most sensitive indicator of a child's health: whether he fell ill, whether his appetite worsened, whether his sleep was disturbed, whether you made any errors in care - all this will immediately be reflected in grams. A sign of nutritional adequacy is normotrophy - the correspondence of body weight due to a given body length of a child. If the weight of the baby has decreased by more than 10%, this is already a sign of malnutrition (malnutrition). Equally alarming is excess weight - parotrophy (excess nutrition). But the increase in the growth of the child is a more stable indicator, and its violations often indicate the presence of the disease.
In the first month of life, the child must be weighed daily. Thus, you monitor the development of lactation and fix the daily weight gain. Body weight is the most sensitive indicator of a child's health: whether he fell ill, whether his appetite worsened, whether his sleep was disturbed, whether you made any errors in care - all this will immediately be reflected in grams. A sign of nutritional adequacy is normotrophy - the correspondence of body weight due to a given body length of a child. If the weight of the baby has decreased by more than 10%, this is already a sign of malnutrition (malnutrition). Equally alarming is excess weight - parotrophy (excess nutrition). But the increase in the growth of the child is a more stable indicator, and its violations often indicate the presence of the disease.
Assess the rate of development of your child in the first year of life, prescribe additional examinations in case of violations of the rate of weight gain, body length, head and chest circumference, correct nutrition, if necessary, a pediatrician will be able to, therefore the cooperation of parents is so important with a doctor from the very first year of a baby's life.
It must be remembered that during the first month the pediatrician examines the child weekly, then, if the development of the baby corresponds to normal indicators, monthly. Assessment of the physical development of a child from one to 10 years. After your baby is one year old, he begins to grow by leaps and bounds. In the second year of life, he adds about 2.5-4.0 kg, and growth increases by 10-15 cm. At the age of 3 to 5 years, the baby adds 2 kg and 3 kg per year.
The head circumference of a child from 51 cm at the age of 5 increases to 53-54 cm at the age of 12. At 5-8 years old, the first traction occurs. But not all children grow in the same way - depending on a variety of factors, such as genetic ones. Children of undersized parents are usually smaller than their peers, but their puberty processes still occur on time. Faster growth than that of peers, with normal body proportions, is characteristic of children of tall parents. In some babies, the growth rate slows down from the second year of life, but after 2-3 years it accelerates again to normal.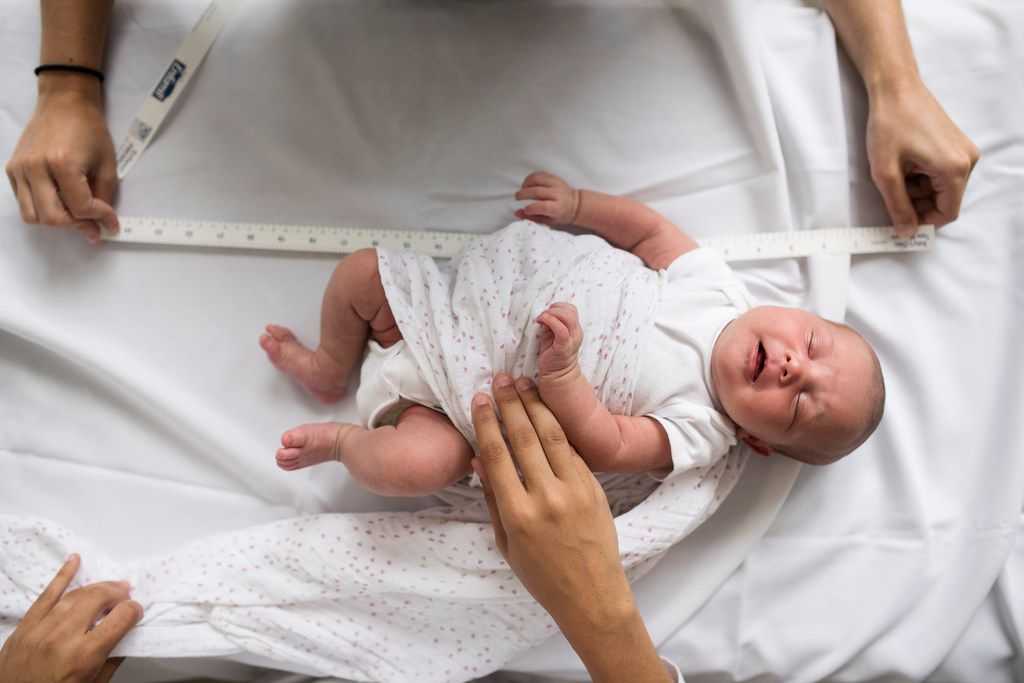 They have both growth and the onset of puberty delayed by a period during which growth was retarded, but final growth is in line with genetic potential. You must understand: the growth rate of the child should not correspond to any exact parameters, the criteria for “normality” are not at all rigid, but nevertheless, deviations in the growth rate of the child can also be pathological: for example, grossly out of proportion to age or accompanied by a violation of proportions body. Such cases require expert advice. It is also necessary to control body weight. As mentioned above, the lack and excess of body weight requires close monitoring of pediatricians, endocrinologists. In children with reduced body weight, there is a decrease in the immunological reactivity of the body, which leads to frequent colds. And excess everything is a risk factor for acquiring obesity in the future and all the serious diseases associated with it: atherosclerosis, heart disease, colon cancer, etc.
They have both growth and the onset of puberty delayed by a period during which growth was retarded, but final growth is in line with genetic potential. You must understand: the growth rate of the child should not correspond to any exact parameters, the criteria for “normality” are not at all rigid, but nevertheless, deviations in the growth rate of the child can also be pathological: for example, grossly out of proportion to age or accompanied by a violation of proportions body. Such cases require expert advice. It is also necessary to control body weight. As mentioned above, the lack and excess of body weight requires close monitoring of pediatricians, endocrinologists. In children with reduced body weight, there is a decrease in the immunological reactivity of the body, which leads to frequent colds. And excess everything is a risk factor for acquiring obesity in the future and all the serious diseases associated with it: atherosclerosis, heart disease, colon cancer, etc.
- Increase in the recommended amount of food;
- Quenching a child's thirst with milk, sugary drinks or formula;
- Excessive (more than 50-100 ml per day) consumption of sweet fruit juices and nectars;
- Use of excess high-calorie foods - fat, sweets, baked cottage cheese;
- Calming the child with food;
- Familial overeating that distorts the child's development of a real sense of need for food;
- Force-feeding, inculcating the habit of eating everything on the plate.

Your pediatrician and endocrinologist will be able to establish the correct diet, give recommendations on the daily diet. Please remember that in the second year of life, the pediatrician examines the child once a quarter, from the third year of life once every six months, in the fourth year and then once a year. Your child is between 10 and 15 years old. A uniform increase in the growth of preschoolers is replaced by its sharp acceleration in adolescence. At 10-13 years old (for girls) and at 12-15 years old (for boys) there is a second traction and at the same time an increase in body weight. The maximum growth rate in girls usually occurs at 12 years of age. The increase in height at this age is approximately 8 cm per year. The maximum increase in body weight in girls usually occurs later at 13 years of age. In boys, the maximum growth rate usually occurs at 14-15 years of age and is approximately 10 cm per year. The maximum increase in the body of a boy usually occurs with a maximum increase in height. The probable final height depends on the height of the parents. It can be calculated using the following formula: Boy's height = 1/2 x (father's height + mother's height) + 6.5 cm Girl's height = 1/2 x (father's height + mother's height) - 6.5 cm. Possible error must be taken into account - the final height can be 8.5 cm more or less.
The probable final height depends on the height of the parents. It can be calculated using the following formula: Boy's height = 1/2 x (father's height + mother's height) + 6.5 cm Girl's height = 1/2 x (father's height + mother's height) - 6.5 cm. Possible error must be taken into account - the final height can be 8.5 cm more or less.
Boys themselves and their parents are often concerned about the delay in growth acceleration, while girls, on the contrary, are worried about excessively rapid growth. However, you need to worry only if the child's growth parameters differ significantly from the parameters indicated in special tables and graphs. In such a situation, it is necessary to contact an endocrinologist.
Remember - there are methods that can influence these processes. One of the most important features of the physical development of children and adolescents is the uneven change in growth rate. In children, the distal segments of the body grow at a faster rate and in a shorter time than the upper and proximal segments. So, for example, during the period of postnatal stretching, the child's foot increases more significantly than the lower leg, and the lower leg - more than the thigh. Against this background, the increase in neck length or head height will be minimal. In certain periods, this feature of the child's growth leads to a certain disproportion, some clumsiness in movements and gait. And only during puberty, the growth rate of the trunk will be much greater than the rate of stretching of the lower limbs. Thus, the physical development of children and adolescents should be constantly in the field of view of pediatricians and healthcare organizers. Physical development subtly reflects the health of the generation, the well-being of the environment, and makes it possible to predict the longevity and resilience of the population.
So, for example, during the period of postnatal stretching, the child's foot increases more significantly than the lower leg, and the lower leg - more than the thigh. Against this background, the increase in neck length or head height will be minimal. In certain periods, this feature of the child's growth leads to a certain disproportion, some clumsiness in movements and gait. And only during puberty, the growth rate of the trunk will be much greater than the rate of stretching of the lower limbs. Thus, the physical development of children and adolescents should be constantly in the field of view of pediatricians and healthcare organizers. Physical development subtly reflects the health of the generation, the well-being of the environment, and makes it possible to predict the longevity and resilience of the population.
Author of the material: pediatrician of the clinic on Nikulinskaya Ilyina ID
Growth and development of the child - "Zhardem"
Growth and development are two interrelated and interdependent sides of the same process.
The process of growth and development of each child is characterized by a number of patterns that need to be known and taken into account in the practice of education and training.
Early age is the period of the most intensive development of all organs and systems of the child's body, the formation of a variety of skills and behavior of the baby. In children under three years old, the activity of the sense organs, visual and auditory perceptions is rapidly improving. Already at 5-7 months, the child can distinguish the main colors and musical sounds. From 11-12 months, the baby begins to walk independently. His active vocabulary by the end of the first year of life consists of 6-10 words, and by 3 it increases to 1200-1500 words. At 3 years old, children dress with a little help from an adult, draw, sculpt, and build simple buildings from building material. Already in the first years of a child’s life, it is important to lay the foundation for health , protect against illness, overwork and at the same time cultivate endurance. Physical education gives a positive result provided that the organization of nutrition and regimen are correct, used for hardening under natural factors, massage, gymnastics, various outdoor games. At the same time, it is important not only to correctly organize the process of education, carry it out comprehensively, but also control how harmoniously and at the required pace the child develops j. For this, an analysis is carried out, comparison
Physical education gives a positive result provided that the organization of nutrition and regimen are correct, used for hardening under natural factors, massage, gymnastics, various outdoor games. At the same time, it is important not only to correctly organize the process of education, carry it out comprehensively, but also control how harmoniously and at the required pace the child develops j. For this, an analysis is carried out, comparison
in order to assess the child’s ability to meet the requirements of the education program in a preschool institution, indicators of physical and mental development. Such an analysis is carried out in the first year every month, in the second group of early age once every 3 months, and in the third year once every six months. Compare similar indicators, for example, height and body weight, whether they correspond to age, whether they are in harmony with each other. Conducting anthropometric data of our children, we can say that children are quite consistent with their age in all respects. Growth,
Growth,
body length is one of the most important indicators of a child's physical development. That is why at the birth of a child, not only its weight is fixed, but also its height. Subsequently, with the development of the child, according to the change, first of all his growth, it will be possible to judge how he develops. It is growth that will then determine the level of his physical development, while body weight will speak about the harmony or not the harmony of the development of the child.
Factors affecting growth
Genetic factors: determine the limits of the biological growth potential of the child, as well as the growth rate. They are very closely related to environmental factors that affect growth. is quite large, but under favorable external conditions - good nutrition, the absence of diseases that negatively affect growth, a favorable social and emotional background in the family, you can count on a significantly greater growth in a child compared to his parents. It has also been established that a favorable The impact on the growth of the child, despite his disappointing genetics, is provided by special physical exercises, with which you can stimulate the growth zones of the long bones and the spine, increasing the growth rate.
It has also been established that a favorable The impact on the growth of the child, despite his disappointing genetics, is provided by special physical exercises, with which you can stimulate the growth zones of the long bones and the spine, increasing the growth rate.
Environmental factors: These include: Harmful effects during fetal development or after childbirth that interfere with growth and development. They may be chemical, physical, immunological or result from infection. Nutritional factors affecting growth (complete proteins, salts, trace elements, vitamins, etc.) may be closely related to socioeconomic factors. Social and emotional factors that may alter growth potential include the child's position in the family, the nature of his relationship with his parents, his upbringing, and the individual interests and needs of the parents.
Thus, the growth and development of a child are the result of a complex combined influence of many factors, both genetic and environmental, on him.
Growth rates
The importance of assessing the growth of a child makes it very relevant the question of what growth figures are normal for a child at a particular age, as well as what figures allow us to suspect certain developmental abnormalities.
The development of a child can be most clearly and simply assessed by various anthropometric indicators, which is widely used in pediatrics. There are 4 main stages in human development: intrauterine development, childhood, adulthood and aging. During these periods, the body grows and develops. Weight increases and the surface of the body, tissues, organs and organ systems develop, their functions and mechanisms of regulation improve.
Features of human development.
The main features of human development are the development of speech, thinking and motor activity, closely related to labor activity. For the development of these functions, a period of 2 to 4 years is very important.