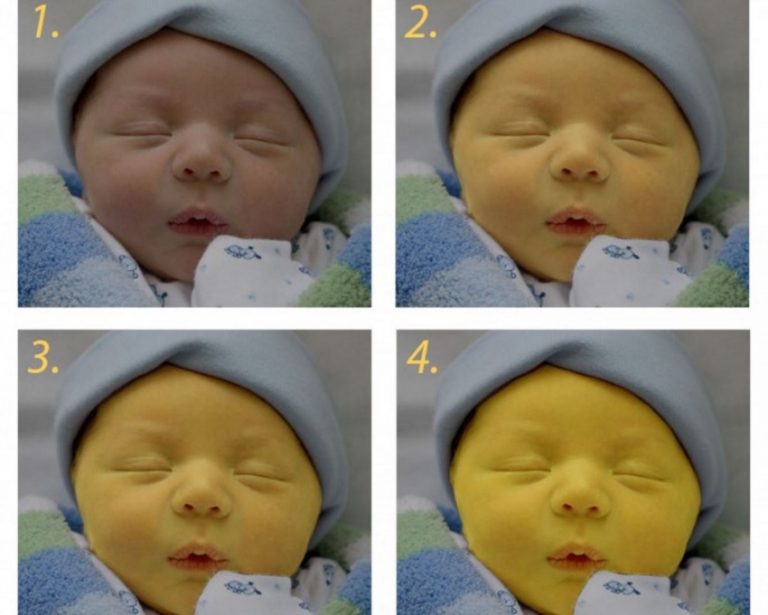
Is fish a lean meat
Top 13 Lean Protein Foods You Should Eat
By Jessica DiGiacinto and Marsha McCulloch, MS, RD — Medically reviewed by Peter Pace, MS, RDN, CSCS, CPT — Updated on March 3, 2022
Protein is an essential part of a balanced diet — but what if you’re looking for a high protein meal that’s also lower in fat and calories?
Fortunately, there are a variety of lean animal and plant sources of protein that can help you meet your quota.
The protein Reference Daily Intake (RDI) for an adult who eats 2,000 calories a day is 50 grams, although some people may benefit from eating more than that. Your individual calorie and protein needs are typically based on your age, weight, height, sex, and activity level (1).
Beyond protein’s essential roles in building and maintaining muscle and tissues in your body and helping regulate many body processes, protein also helps promotes satiety (fullness) and may aid in weight management (2, 3).
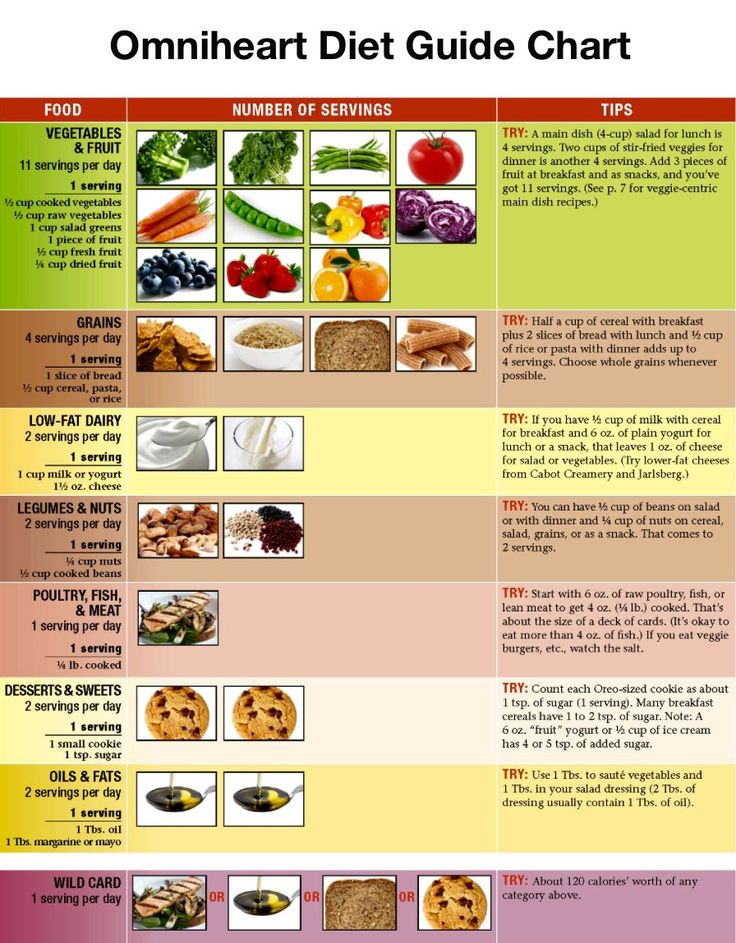
Here are 13 lean protein foods to consider.
1. White-fleshed fish
Most white-fleshed fish are quite lean and excellent protein sources, providing less than 3 grams of fat, 20–25 grams of protein, and 85–130 calories per 3.5-ounce (100-gram) plain, cooked serving (4, 5).
Examples of very lean white fish include cod, haddock, grouper, halibut, tilapia, and bass (6).
These white fish generally have only 10–25% as many omega-3 fatty acids as higher fat, higher calorie, darker-fleshed fish such as coho and sockeye salmon. Therefore, it’s a good idea to eat both types of fish (7, 8).
A convenient way to buy plain fish fillets is in the frozen food section of your supermarket. If you move the fillets from your freezer to the refrigerator first thing in the morning, they’ll be thawed and ready to cook for your evening meal.
SummaryWhite-fleshed fish such as cod and halibut are excellent sources of hunger-satisfying protein with little fat and relatively few calories, but other types of fish, such as salmon, have higher amounts of healthy omega-3 fats.
2. Plain Greek yogurt
A 6-ounce (170-gram) serving of Greek yogurt packs 15–20 grams of protein, compared with only 9 grams in a serving of regular yogurt (9).
This is because of how Greek yogurt is made. It’s strained to remove the liquid whey, leaving a more concentrated product that has more protein and is thicker and creamier (9).
If you’re looking for the least calories and fat, opt for plain nonfat Greek yogurt, which has less than 2 grams of fat per 156-gram serving (10).
Low fat plain Greek yogurt, which has about 3 grams of fat and 125 calories per 6-ounce serving, is also a good choice. By opting for plain, you skip the unnecessary sweeteners and can add your own fruit (11).
SummaryPlain nonfat or low fat Greek yogurt contains about twice as much protein per serving as regular yogurt. It also contains much less sugar.
3. Beans, peas, and lentils
Dry beans, peas, and lentils, also called pulses, are a subgroup of legumes. They average 8 grams of protein per 1/2-cup (100-gram) cooked serving and are low in fat and high in fiber (12, 13).
They average 8 grams of protein per 1/2-cup (100-gram) cooked serving and are low in fat and high in fiber (12, 13).
The high fiber and protein content in pulses helps make them more filling. What’s more, the fiber may help lower your blood cholesterol if you eat pulses regularly (13).
In a review of 26 studies in 1,037 people, eating an average of 2/3 cup (130 grams) of cooked pulses daily for at least 3 weeks resulted in about a 7 mg/dL reduction in LDL (bad) cholesterol compared with control diets. That equaled an almost 5% reduction in LDL over time (14).
Notably, pulses are low in a few essential amino acids, the building blocks of protein in your body. However, by eating other plant protein sources over the course of a day, such as whole grains and nuts, you can fill in those gaps (13, 15, 16).
SummaryBeans, peas, and lentils are good sources of lean protein. They’re also high in fiber and may help lower your cholesterol if you eat them regularly.
4. Skinless white meat poultry
A 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving of cooked chicken or turkey breast has around 30 grams of protein (17, 18).
Skip dark meat cuts such as drumsticks and thighs to get the leanest meat. White meat includes the breasts, breast tenderloins (tenders), and wings.
If you’re looking to limit calories and fat, try to avoid the skin — 3.5 ounces (100 grams) of roasted chicken breast with skin has 200 calories and 8 grams of fat, while the same amount of skinless roasted chicken breast has around 161 calories and 3.5 grams of fat (17, 19).
You can remove the skin either before or after cooking — the fat savings are virtually the same either way. Typically, poultry cooked with the skin intact is moister (20).
SummaryWhite meat chicken and turkey, particularly the breasts, are rich in protein and low in fat if you remove the skin either before or after cooking.
5. Low fat cottage cheese
Low fat cottage cheese
Cottage cheese is a high protein, low fuss food.
A 1-cup (226-gram) serving of low fat (2% milk fat) cottage cheese has 163 calories, 2.5 grams of fat, and 28 grams of protein (21).
The newest trends in cottage cheese include single-serve containers, flavored options, and the addition of live and active probiotic cultures.
Besides protein, you get around 10–15% of the RDI for calcium in 1/2 cup of cottage cheese. Some food scientists have recently suggested that manufacturers add vitamin D, which aids calcium absorption, though this is not currently common practice (21, 22).
SummaryLow fat cottage cheese is an excellent source of protein and is becoming even more convenient with the increased availability of single-serving containers. It’s also a good source of calcium.
6. Tofu
Tofu is an especially viable protein option if you are trying to avoid animal foods. A 3-ounce (85-gram) serving of tofu has 71 calories, 3. 5 grams of fat, and 9 grams of protein, including sufficient amounts of all the essential amino acids (23).
5 grams of fat, and 9 grams of protein, including sufficient amounts of all the essential amino acids (23).
Tofu comes in different textures, which you can choose from based on how you plan to use it. For example, use firm or extra-firm tofu in place of meat that you’d bake, grill, or saute and soft or silken tofu in creamy soups or desserts.
If you’re not 100% sold on tofu, edamame and tempeh are two other whole food sources of soy that are high in protein and relatively low in calories and fat.
Note that about 95% of soybeans produced in the United States are genetically modified (GM). If you prefer to avoid GM foods, you can buy organic tofu — organic foods cannot be genetically modified (24, 25, 26).
SummaryTofu is a good source of plant protein that provides adequate amounts of all the essential amino acids and is very versatile in recipes.
7. Lean beef
Lean cuts of beef are those with less than 10 grams of total fat and no more than 4.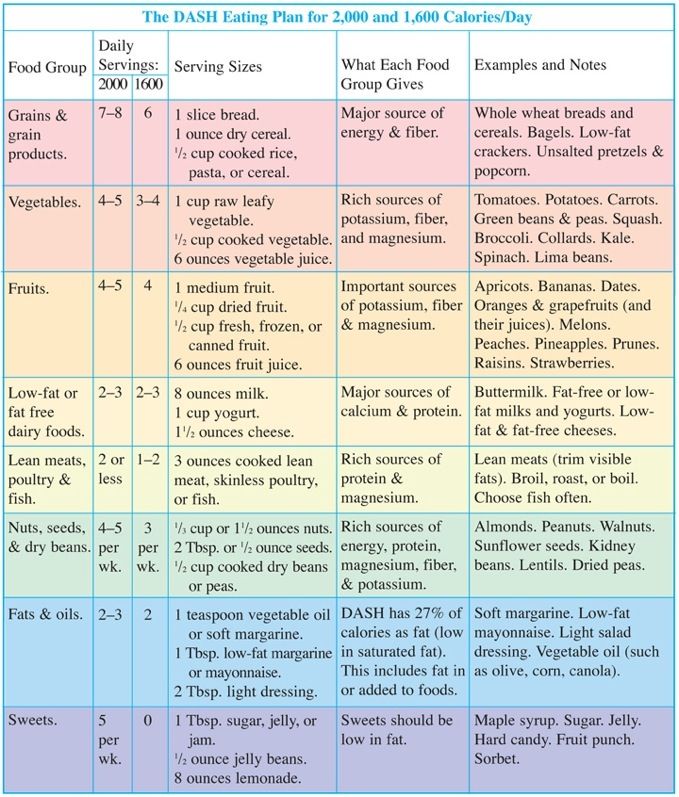 5 grams of saturated fat per 3.5-ounce (100-gram) cooked serving (27).
5 grams of saturated fat per 3.5-ounce (100-gram) cooked serving (27).
If you’re buying fresh beef that doesn’t have a nutrition label, certain words, such as “loin” and “round,” tell you the meat is lean. For example, sirloin and tenderloin steaks, eye of round roast, and round steak are all lean (28).
When it comes to ground beef, opt for something that’s at least 90% lean. A 4-ounce (113-gram) cooked hamburger patty made with 95% ground beef has 155 calories, 5.6 grams of total fat (including 2.4 grams of saturated fat), and 24 grams of protein (28, 29).
What’s more, a serving of lean beef is an excellent source of several B vitamins, zinc, and selenium (29).
SummaryLean beef is generally signaled by the word “loin” or “round.” If buying ground beef, try to find something that’s at least 90% lean. Lean beef is an excellent source of protein and also packs B vitamins, zinc, and selenium.
8. Powdered peanut butter
The natural oil in peanut butter is heart-healthy but can pack a lot of calories. Just 2 tablespoons (32 grams) of regular peanut butter have about 200 calories and 16 grams of fat, along with 7 grams of protein (30).
Just 2 tablespoons (32 grams) of regular peanut butter have about 200 calories and 16 grams of fat, along with 7 grams of protein (30).
A lower calorie option is unsweetened powdered peanut butter. Most of its fat is pressed out during processing. A 2-tablespoon serving has just 45 calories and 1 gram of fat but 4 grams of protein (31).
To use the powder like peanut butter, mix it with a little water at a time until it reaches a similar consistency to regular peanut butter. Keep in mind that it won’t be quite as creamy.
Reconstituted powdered peanut butter works especially well for dipping apples, bananas, or even dark chocolate. Alternatively, you can mix the dry powder into smoothies, shakes, oatmeal, or pancake or muffin batter to add a punch of flavor and protein.
SummaryPowdered peanut butter is a convenient protein source that has just a fraction of the calories and fat of regular peanut butter.
9. Low fat milk
Whether you drink it, cook with it, or add it to cereal, low fat milk is an easy way to get protein.
A 1-cup serving of low fat milk with 1% milk fat has 8 grams of protein, 2 grams of fat, and 105 calories. In comparison, a serving of whole milk with 3.25% milk fat has the same amount of protein but 146 calories and about 8 grams of fat (32, 33).
Clearly, opting for low fat milk will save you calories and fat. However, some recent studies suggest that drinking whole milk may not increase heart disease risk, as was once thought, and may even help with weight management (34, 35).
However, more studies need to be done in both areas before any conclusions can be made. If you aren’t sure which dairy milk option is best for you, especially if you’re already living with high cholesterol or heart disease, talk it over with a doctor or a registered dietitian.
SummaryLow fat milk is a good source of protein and can save you a significant amount of fat and calories compared with whole milk, especially if you consume it often.
10. Pork loin
Pork loin
A handful of pork cuts meet the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s definition of “lean,” which means less than 10 grams of fat and no more than 4.5 grams of saturated fat per 3.5-ounce (100-gram) cooked serving (27).
The keywords that indicate lean pork are “loin” and “chop.” Therefore, lean cuts include pork tenderloin, pork (loin) chops, and pork top loin or sirloin roasts (28).
Pork tenderloin, the leanest cut, has 123 calories, 23 grams of protein, and about 2 grams of fat per 4-ounce (113-gram) cooked serving (36).
Before cooking pork, trim off any fat around the edges. You can use low fat cooking methods, such as grilling or broiling, if you’re looking to cut back on fat and calories.
Like lean beef, lean pork is an excellent source of several B vitamins and selenium and a good source of zinc (36).
SummaryYou can find lean pork by looking for the word “loin” or “chop.” Even so, be sure to cut off excess fat on the meat if you’re trying to limit fat and calories.
Pork is also rich in B vitamins, selenium, and zinc.
11. Frozen shrimp
If you’re looking for a lot of protein for fewer calories, frozen unbreaded shrimp are a convenient option. A 3-ounce (85-gram) serving has 110 calories, 22 grams of protein, and 2 grams of fat (37).
Though the same serving also has 150 mg of cholesterol, scientists have found that consuming cholesterol as part of a nutritious diet generally has little impact on the heart health of people who are not currently living with heart disease or high cholesterol (38).
However, the high amount of sodium often added to shrimp during processing may be of concern for some people. Most of this sodium comes from additives, including sodium tripolyphosphate, which helps retain moisture, and the preservative sodium bisulfite (39).
If salt is a concern for you, look for frozen shrimp that contain only naturally occurring sodium.
SummaryUnbreaded frozen shrimp are a convenient, low fat, high protein food.
Read nutrition labels when shopping to avoid products with high sodium content.
12. Egg whites
You can eat whole eggs (cholesterol and all) as part of a heart-healthy diet, but if you’re looking for something a little lighter, you can use just the whites (40, 41, 42).
One egg white contains less than 0.5 grams of fat but 3.5 grams of protein, which is about half of the protein in a whole egg (43, 44, 45).
You may want to try an egg white omelet or egg white muffins made with baby spinach and chives or diced peppers and onions. Alternatively, you can scramble egg whites with veggies to make a filling or topping for wraps, tostadas, or toast.
You can also buy powdered egg whites and egg white protein powders with minimal or no additives. These products are pasteurized, so you don’t have to cook them to ensure food safety (46).
You can mix powdered egg whites with water and use them like fresh egg whites. You can also add powdered egg whites to smoothies, shakes, or homemade protein bars.
SummaryHalf the protein in eggs comes from the whites, but the whites contain only trace amounts of fat and less than a quarter of the calories of whole eggs.
13. Bison
Whether you call it bison or buffalo, it’s a nutritious, lean protein source that may have an edge over conventionally raised beef.
First, bison is leaner than beef. When scientists compared sirloin steak and chuck roast from grain-fed cattle (beef) to bison, the beef had more than twice as much fat as the bison meat (47).
Additionally, bison is more likely to be grass-fed rather than raised in a feedlot like cattle, which are primarily fed grains.
That gives bison a healthier fat profile, including 3–4 times more anti-inflammatory omega-3 fats, particularly alpha-linolenic acid. Preliminary research suggests that consuming bison may yield health benefits (47).
In a 2013 study, when healthy men ate 12 ounces of beef or bison (sirloin steak and chuck roast) 6 times weekly for 7 weeks, their levels of C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation, increased by 72% on the beef-rich diet but only slightly on the bison-rich diet (47).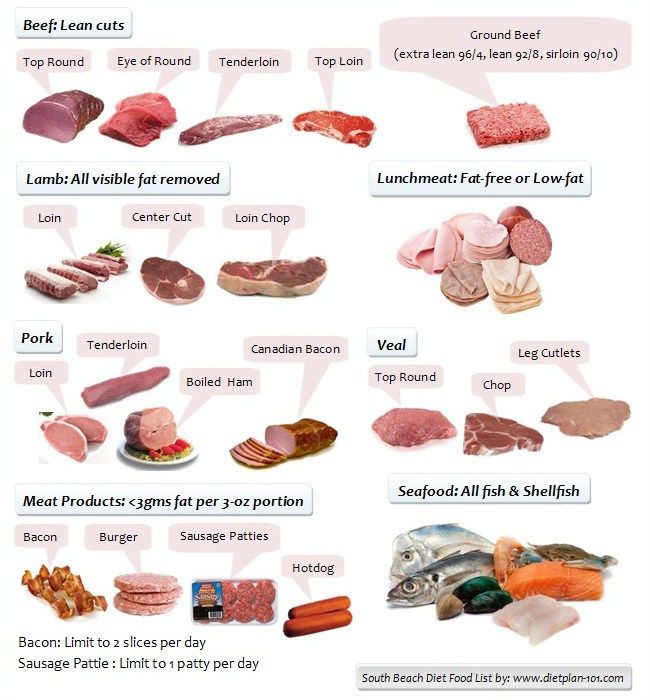
Like most other foods, red meat should be consumed in moderate amounts. But if you enjoy red meat and want to keep your health in check, bison may be a good option.
SummaryBison is leaner than beef and has a healthier, less inflammatory fat profile.
The bottom line
A balanced, nutritious diet will always include some fats along with protein and fiber. But if you’re specifically looking to limit your fat and calorie intake for dietary reasons, lean animal and plant protein sources are plentiful.
White-fleshed fish and skinless white meat poultry are among the leanest animal proteins. However, you can also find lean red meat by looking for the words “loin” and “round.”
Many dairy products, such as low fat cottage cheese, yogurt (especially Greek yogurt), and low fat milk, are also low in fat and are good sources of protein.
Plant proteins such as beans, tofu, and powdered peanut butter offer ample amounts of protein as well.
Because everyone’s health histories and nutritional needs are different, it’s important to consult a doctor or registered dietitian before making big changes to your diet.
Just one thing
Try this today: If you’re looking for more plant-powered protein ideas, don’t forget quinoa, which has around 8 grams of protein and only 2.5 grams of fat in 1 cooked cup (48)!
Lean meat, fish, poultry and meat alternatives
Lean meat, fish, poultry and meat alternatives | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content2-minute read
Listen
The protein food group offers the most variety when it comes to preparing and eating healthy foods. It includes lean meat, fish, chicken and vegetarian protein sources – such as eggs, beans (legumes), tofu and nuts.
These foods give your child iron, zinc, vitamin B12, omega-3 fatty acids and protein for growth, and brain, nerve and muscle development.
Lean meat, poultry and fish
Lean meat, poultry and fish provide protein and a variety of minerals and vitamins. There is also a lot to choose from and can be prepared in many different ways.
- lean meat — beef, lamb, pork, veal, kangaroo and lean sausages
- poultry — chicken, turkey and duck
- fish and seafood — fish, prawns, crabs, mussels, scallops
Alternatives to meat
A variety of foods that provide the same amounts of protein as meat and seafood. These include:
- eggs
- legumes — beans, lentils, chickpeas and tofu
- nuts — almonds, peanuts, hazelnuts and walnuts
- seeds — pumpkin, sesame and sunflower seeds
Legumes, nuts and seeds also have dietary fibre, so it’s a good idea to choose a variety of foods from this group.
Tips for serving protein
- Legumes can be added to pasta and stir-fry dishes.

- Lean meats and poultry can be used in soups, stews, stir-fries, bakes and pasta dishes.
- Eggs can be used for breakfast, lunch and dinner - scrambled, fried, boiled, poached, in a quiche or an omelette.
- Nuts make a great snack or can be used in salads, main courses or breakfast cereal
How much protein should my child be eating?
- 2 to 3-year olds should have 1 serve a day
- 4 to 8-year olds should have 1 ½ serves day
A serve is 65g cooked red meat (not more than 455g per week), 80g poultry, 100g fish, 2 eggs, 1 cup legumes, 170g tofu, 30g nuts or seeds or pastes (peanut butter, tahini).
To put in practical terms, a serve of meat or chicken is about the size of a deck of cards.
Five food groups
Read more about the other 4 of the 5 food groups:
- Vegetables and legumes/beans
- Fruit
- Grains and cereals
- Milk, cheese, yoghurt and dairy alternatives
Sources:
Eat For Health (Australian Dietary Guidelines), Eat for Health (The five food groups), Women's and Children's Health Network (A guide to vegetarian diets in children), Eat for Health (Lean meat and poultry, fish, eggs, tofu, nuts and seeds and legumes/beans), Eat for Health (Recommended number serves children, adolescents and toddlers)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: January 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Vegetables and legumes/beans
- Fruit
- Milk, cheese and yoghurt
- Grains and cereal
- Five food groups
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
9 types of low-fat fish / Which is ideal for a diet - an article from the "Food and weight" section on Food.ru
The benefits of fish
If you want to lose weight or a diet is recommended for you for medical reasons, lean fish should become an integral part of the diet. Regular use of this product improves metabolism, enriches the body with vitamins A and D, minerals such as iodine, phosphorus and fluorine.
Fish are generally divided into three groups according to their fat content:
-
lean species (less than 4% fat) - tilapia, cod, pollock, bream, pike, zander;
-
medium-fat (from 4 to 8% fat) - pink salmon, tuna, carp, trout, catfish, sea bass, horse mackerel;
-
fatty (more than 8% fat) - herring, mackerel, eel, sturgeon, halibut.
Diet recipes use low-fat varieties: they are high in protein and low in calories. In addition, this is a fairly satisfying product, you will not feel hungry for a long time.
Advice
For weight loss, nutritionists advise replacing 2-3 meat meals per week with fish from the list below: this way you can reduce the calorie content of the diet without compromising health.
1. Pollack
This lean fish is perfect for a diet. It has practically no contraindications, except for allergies and individual intolerance.
Just like oily fish, pollock contains essential acids Omega-3 and Omega-6, but it contains significantly fewer calories.
This lean fish can be prepared in many different ways, but the simple rule is the better. Pollock can be steamed, baked in the oven or stewed in a slow cooker with the addition of vegetables and spices.
2. Cod
Nutritious and low-calorie meals can be prepared with cod. Due to the high content of easily digestible protein, this variety of marine fish can serve as an excellent substitute for meat.
Important
In a low-calorie diet, it is not recommended to use cod liver because of its high calorie content (almost 600 kcal per 100 g of product) and a large amount of fat.
Cod fish is often found in the lists of ingredients in European cuisine. Appetizing soups are cooked from it, baked, stewed, steamed or fried. And in order to have fewer calories and fat in the dish, it is better to fry cod in a grill pan without adding oil or on a barbecue grill.
3. Haddock
Another type of cod fish, haddock, is very similar to cod. It is less popular and cheaper. However, in terms of taste and benefits, haddock is in no way inferior to cod.
However, in terms of taste and benefits, haddock is in no way inferior to cod.
This lean fish is best suited for pan frying or grilling. If you want the dish to be low-calorie, cook the fish in the oven. Use a special roasting sleeve to keep the product juicy.
4. Hake
Hake is called one of the most useful types of cod fish. It is quite tasty and low fat. This fish is characterized by a small number of bones, so it is easy to cook and cut it.
Low-fat hake broth is recommended during cold and flu season. It is believed that it helps to improve health or recover faster after illness. This is facilitated by a large number of minerals and vitamins in the composition of the fish.
5. Flounder
Sea flounder also belongs to lean fish species. It has a delicate, neutral taste that goes well with various sauces and spices. Almost any diet includes dishes from this fish.
Tip
This type of fish should be cooked quickly: no more than 8 minutes on the grill or 15 minutes in the oven. So the maximum amount of useful substances will be preserved in the fish fillet.
So the maximum amount of useful substances will be preserved in the fish fillet.
Baking or grilling is the best cooking method. But it is not recommended to cook this low-fat type of fish: after heat treatment in water, its meat will become tough and tasteless.
6. Tilapia
Tilapia is an inexpensive and delicious source of protein. This fish is popular all over the world. In taste and appearance, it is often confused with another low-fat variety - pangasius. In many recipes, they are interchangeable.
Interesting fact
Low-fat varieties of fish are often used for fasting days, during which only this product is allowed. However, you can eat in this way for no more than 1-3 days, so as not to harm your health.
Often on the Internet you can find an opinion that heavy metals are found in the fillet of this fish. However, the risk can be avoided by purchasing wild tilapia rather than farm-raised tilapia.
7. Perch
Dietary products include perch fillet, both sea and river perch. However, river perch has much less fat and calories than sea perch. But sea bass is often called one of the most delicious varieties of fish.
However, river perch has much less fat and calories than sea perch. But sea bass is often called one of the most delicious varieties of fish.
This fish is versatile: it can be prepared in almost any way, in all cases the dish will turn out delicious.
Gourmet perch dishes are found, for example, in Italian and Finnish cuisines.
8. Pike
You can diversify the menu during the diet with pike meat. It is also useful because it contains special acids that promote the breakdown of fats. On a diet, in addition to pike, it is recommended to eat vegetables, eggs, dairy products and fruits.
Regular consumption of low-fat pike meat also helps to strengthen the immune system: it is rich in natural antiseptics. This fish is considered hypoallergenic.
9. Pike perch
Pike perch occupies a special place among freshwater river fish: it is rightfully considered one of the most delicious and healthy species. Pike perch is also valued for a small amount of bones in the meat and hypoallergenicity: this fish can be given to children.
Nutritionists recommend including lean zander meat in the menu not only for those who want to lose weight, but also for people recovering from operations or injuries: it contains many minerals that help strengthen bones and muscles.
What can be done?
In addition to lean fish, include seafood such as shrimp, squid or mussels, which can be used to prepare many delicious dishes. They, like fish, contain little fat, are rich in protein and useful substances.
Find out more about dietary dishes at Food.ru:
-
Top 10 dietary salads. Recipes and advice on proper nutrition
-
Diet breakfasts. Selection of recipes and recommendations
-
4 recipes for dietary desserts. How to replace the usual products for baking
Low-fat varieties of fish: a list of dietary fish, table
Fish varieties with a low percentage of fat are suitable for preparing dietary dishes, as indicated by nutritionists. Eating such fish, a person does not risk gaining extra pounds. Fish meat contains up to 17 percent of the protein and amino acids that the human body needs every day. In addition, seafood is rich in vitamins and minerals.
Eating such fish, a person does not risk gaining extra pounds. Fish meat contains up to 17 percent of the protein and amino acids that the human body needs every day. In addition, seafood is rich in vitamins and minerals.
Content
- 1 category of fat content
- 2 Frequency of fish
- 3 varieties with an average fat content
- 4 varieties with the least fat content
- 5 Fish calorie content
- 6 trout and seeds: what is 9000 9000 9000 7,000 7,000 7,000 7,0009 7,0009 7,0009 7,0009 7,0009 7,0009 7 Proper preparation of fish for a diet
- 8 Easy lean fish recipes
- 8.1 Cod steak with potatoes
- 8.2 Tilapia patties
- 8.3 Vietnamese halibut
- 9 Some useful tips
Fat content categories
subdivide seafood into 3 categories, depending on the fat content:
- .
- The second category includes varieties with a fat content of up to 8.
 5 percent.
5 percent. - The third category are varieties of fish that contain more than 8.5 percent fat.
An important point! The fat content of fish is not constant and fluctuates depending on the season. The fattest fish before the breeding process.
Fish meat, regardless of variety, can contain 14 to 27 percent protein and 0.3 to 36 percent fat. As a rule, there are special tables that indicate the percentage of fat, depending on the type of fish, from which it is permissible to prepare diet meals.
Fatty fish
There are varieties of fish that are not suitable for dietary nutrition. These include fish such as:
- Mackerel and catfish.
- Sprat and stellate sturgeon.
- Fatty herring and eel.
- Sturgeon and halibut.
- Saury.
These fish species have a rather high fat content (more than 8.5 percent), and their energy value is from 270 to 350 kcal per 100 grams of product.
Despite such a high percentage of fat, these fish species are considered the most useful for humans, because their meat contains more iodine and fatty acids. The presence of such components allows a person to deal with a number of ailments associated with the cardiovascular system, as well as with metabolic processes in the body.
Unfortunately, they are not suitable for diet food.
Varieties with an average fat content
Such varieties are characterized by an average level of fat and include:
- Catfish and horse mackerel.
- Carp and silverfish.
- Carp and red-eye.
- Salak and anchovies.
- Low-fat pink salmon and herring.
- Pike perch and smelt.
- Ide and bream.
- Salmon and sea bass.
- Tuna.
The energy value of these types of fish is at the level of 126 to 145 kcal per 100 grams of the finished product.
These types of fish are suitable for preparing dietary dishes, but they should only be consumed with the permission of a specialist.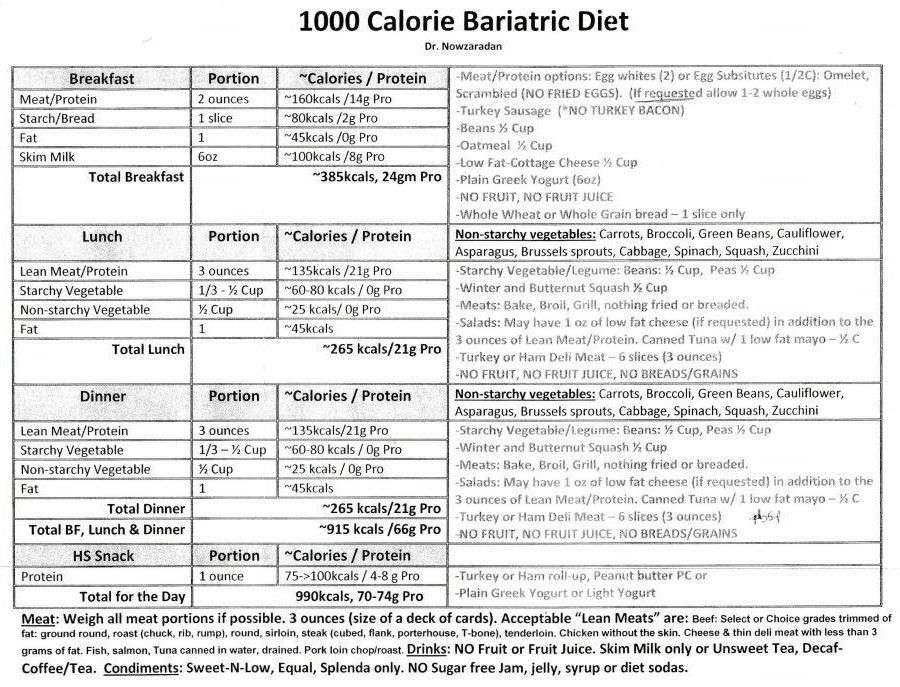 These varieties of seafood are high in protein, so they are suitable for sports nutrition. To preserve the usefulness of seafood, it is better to cook dishes from these types of fish by stewing, salting, smoking, and also steaming.
These varieties of seafood are high in protein, so they are suitable for sports nutrition. To preserve the usefulness of seafood, it is better to cook dishes from these types of fish by stewing, salting, smoking, and also steaming.
Least fat varieties
Fish species with the least amount of fat.
These varieties include:
- Cod and navaga.
- Haddock and Lemonema.
- Saithe and pollock.
- Vobla and perch.
- Pike and pangasius.
- Pike perch and crucian carp.
- Omul and tilapia.
- Burbot and mullet.
- Flounder and white-eye.
- Lamprey and grayling.
- Wet and roach.
- Whitefish and roach.
This list may also include crustaceans and molluscs.
The energy value of the meat of these fish species does not exceed 100 kcal per 100 grams of the product.
By eating non-fatty fish varieties, as well as varieties with an average fat content, it is possible to get rid of extra pounds, as well as getting rid of a number of diseases. Experts recommend teaching children to seafood, preparing dishes from non-fat varieties.
Experts recommend teaching children to seafood, preparing dishes from non-fat varieties.
Important to know! Carp belong to non-fat varieties of fish and are the only representatives of the cyprinid family, which have such a low percentage of fat. The remaining representatives of this family are characterized by an average level of fat content.
Calorie content table
| Fish | calories | Squirrels | Carbohydrates||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sea bass (balychok) | 199.00 | 26.40 | 10.40 | 0.00 | ||||
| 225.00 | 20.30 | 16.00 | 0.00 | |||||
| 150.00 | 23.40 | 6.40 | 0.00 | |||||
| Mackerel cold smoked | 94.00 | 17.10 | 2.80 | 0.00 | 159.00 | 32. 00 00 | 3.40 | 0.00 |
Information about fish of different varieties. What is the best fish to eat on a diet?
Watch this video on YouTube
Trout and salmon: which fish is fatter
Many people for some reason believe that trout and salmon have a low percentage of fat, attributing them to dietary seafood. Actually this is a delusion. If we compare these types of fish in terms of energy value, then these breeds do not belong to low-fat varieties of fish. For example, the energy value of trout meat is about 147 kcal with a fat content of 7 percent, and the energy value of salmon is 219kcal at 15 percent fat. Therefore, both trout and salmon do not belong to dietary seafood, although trout is less fatty and belongs to fish species with an average fat content.
Proper preparation of fish for a diet
For people who decide to go on a diet, the best option is to eat fish dishes.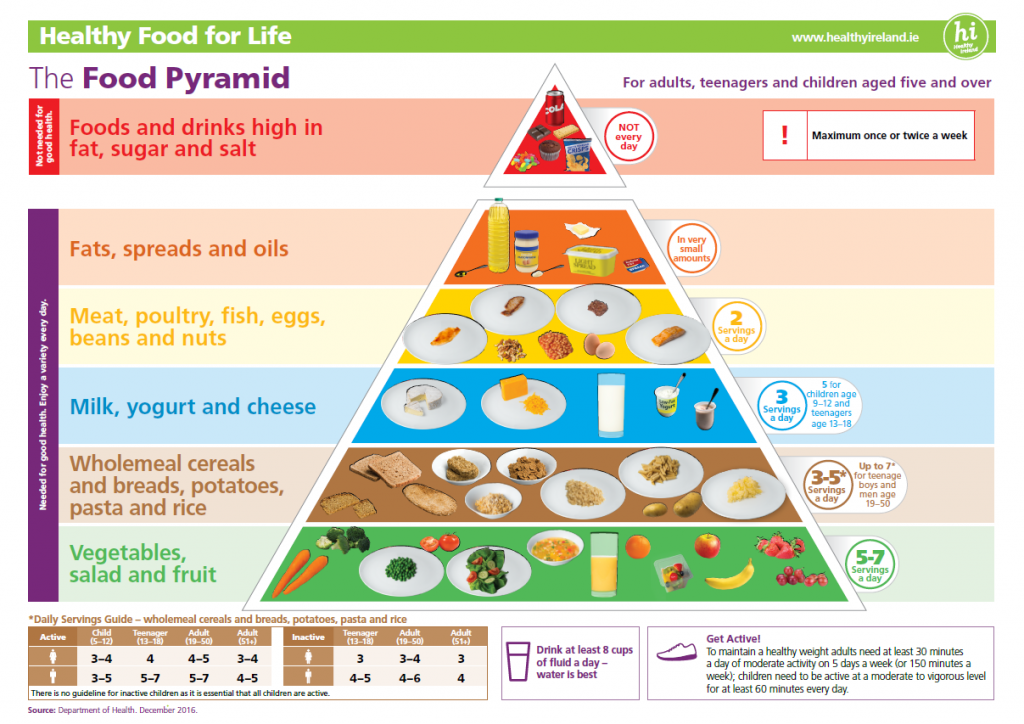 Such dishes help to endure such a difficult period for the body much easier. Due to the fact that the dishes are low in calories, weight loss is stimulated, in addition, they perfectly satisfy the appetite.
Such dishes help to endure such a difficult period for the body much easier. Due to the fact that the dishes are low in calories, weight loss is stimulated, in addition, they perfectly satisfy the appetite.
The most important thing is to prepare meals in such a way that they retain as many healthy ingredients as possible. Therefore, experts advise eating boiled, stewed or baked dishes.
Diet food does not include fried, smoked, salted or dried seafood. You should also not get carried away with canned fish.
Seafood can be used to make a wide variety of tasty, low-calorie dishes. Therefore, soups, cutlets, meatballs can be prepared from fish, but only for a couple, as well as casseroles and soufflés.
Interesting to know! Low-fat varieties of fish will help not only to solve the problem of being overweight, but also help to cope with some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Due to the low calorie content, the food is easily absorbed and digested without burdening the stomach.

Daily consumption of fish dishes allows you to regularly replenish the human body with all the necessary useful components, having a beneficial effect on the functioning of all internal organs. This allows you to reduce weight, strengthen the immune system, optimize the functioning of the central nervous system, prevent aging of the body, rejuvenate the skin, etc.
Simple recipes from low-fat varieties of fish
Cooking diet meals will never be a superfluous task, especially if the goal is to lose weight or recover from a serious illness.
Cod steak with potatoes
This recipe makes 4 servings.
To prepare the dish you will need:
- 700 grams of cod fillet.
- 10 medium potatoes.
- One small onion.
- One small lemon.
- Plain yogurt in the amount of 3 dessert spoons.
- Approximately 50 g rye flour.
- Olive oil in the amount of 3 dessert spoons.
- Small horseradish root.
In addition, you will also need dill, parsley and lettuce in a small bunch, as well as some spices.
In addition to cod, other fish, such as pollock or saffron cod, are also suitable for cooking.
The cooking process is as follows:
- First, peel the potatoes and rinse them in cold water. After that, the potatoes are cut into circles, up to 1 centimeter thick and boiled.
- Onions are also peeled, washed with cold water and cut into either half rings or rings.
- Half a lemon is also cut into slices.
- The fish fillet is deboned and cut into portions. After that, they are rolled on all sides in flour, but before that they are sprinkled with various spices. Finally, the fish pieces are fried in olive oil until golden brown.
- Horseradish must be washed and peeled, removed from the skin, and then minced on a grater.
- To prepare the sauce, you will have to mix yogurt with lemon juice, as well as with grated horseradish and herbs.
 All ingredients must be mixed thoroughly.
All ingredients must be mixed thoroughly.
Before serving the dish, it is decorated with chopped herbs, lettuce, and lemon slices.
Cod is a low-fat fish and dishes prepared from it are great for dietary nutrition, since its calorie content is only 235 kcal.
Tilapia patties
Set of products for preparing 5 portions. What you need:
- 700 grams of tilapia meat.
- One bulb.
- One chicken egg.
- Boiled round rice - about 100 grams.
- Vegetable oil - 3 tbsp. spoons.
- Dill - not a big bunch.
Various spices and seasonings can be used.
Cooking technology
- Fish meat is deboned and minced by any means available.
- Onions are peeled, washed and chopped until smooth.
- Add an egg to minced meat, onion and boiled rice.
- Then the greens are taken and chopped, after which they are added to the minced meat along with spices and seasonings.
 After that, all ingredients are thoroughly mixed.
After that, all ingredients are thoroughly mixed. - Finally, minced meat with spices and other ingredients is formed into patties.
To prepare cutlets, take a greased baking sheet and place cutlets on it. After that, the baking sheet is placed in the oven, with a temperature of about 150 degrees. After 20 minutes, the dish will be covered with a golden crust, which means that it can be served at the table. The dish is in perfect harmony with both boiled potatoes and fresh vegetables.
Vietnamese halibut
To make 4 servings, you need the following ingredients:
- Halibut fillet - about 600 grams.
- 2 tomatoes.
- 2 bell peppers.
- 2 garlic cloves.
- One lemon or one lime.
- Fish sauce - 40 ml.
- Ginger minced - 15 grams.
- Sugar - 10 grams.
- Mint - three sprigs.
Various spices and seasonings will not interfere either.
How to cook the dish correctly:
- The fillet is washed and cut into portions.

- Lemon juice is taken and mixed with sesame oil, fish sauce and spices. After that, fillet pieces are poured with the prepared mixture and left in this form for a while.
- Tomatoes are peeled and diced.
- Garlic and peppers are peeled and minced as finely as possible. After that, they are added to tomatoes and ginger.
- The mint is washed and finely chopped.
- Lemon or lime sliced, but washed before cutting.
- A mixture of vegetables is laid out on prepared pieces of fish meat and poured over with marinade.
- After that, each piece of fish is taken and wrapped in foil, then they are laid out on a baking sheet.
- The oven is heated to 150 degrees and a baking sheet with fish pieces is placed in it for about half an hour.
After this time, each piece is removed from the foil and placed on plates. Before serving, the dish is garnished with mint and slices of lime or lemon.
Note! The energy value of the dish is about 192 kcal, so it can be considered dietary.