Yellow eye discharge in infant
Eye - Pus or Discharge
Is this your child's symptom?
- Yellow or green discharge (pus) in the eye
- The eyelids are stuck (matted) together with pus after sleep
- After being wiped away, the pus comes back during the day
- Often caused by a bacterial eye infection
Causes of Eye with Pus
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis. This is a bacterial infection of the eye. The main symptom is eyelids stuck together with pus after sleep. Can be present in 1 or both eyes. A few viruses can cause pus in the eyes, but most don't.
- Viral Conjunctivitis. This is a viral infection of the eyes. Main symptom is pinkness of the white parts of the eyes. The eyes are also watery. Most often, there is no pus. Usually on both sides.
- Normal Discharge. A small amount of dried mucus only in the corner of the eye. It may not even be pus. A collection of mucus can be cream colored. Often due to an irritant that got in the eye from dirty hands.
Needs no treatment except wiping it away with warm water.
- Blocked Tear Duct. Present in 10% of newborns. Main symptom is a constant watery eye. Tears fill the eye and run down the face. This happens even when not crying. The eye is not red and the eyelid is not swollen. The wet eye may get secondary infections. This will cause the eyelids to become matted with pus.
- Foreign Object in Eye (Serious). Small particles such as sand, dirt or sawdust can be blown into the eyes. The grit often gets stuck under the upper eyelid. If not removed, the eye reacts by producing pus. The main clue is an eye infection that does not respond to antibiotic eyedrops. Older children complain of feeling something in the eye.
- Eyelid Cellulitis (Serious). This is a deep infection of the eyelid and tissues around it. The main symptom is a red, swollen, very tender eyelid. The eye can be swollen shut. Usually only on one side. This can be a problem caused by bacterial conjunctivitis.
 The eye infection spreads inward. More commonly this is caused by an ethmoid sinus infection. That type occurs without any pus in the eye.
The eye infection spreads inward. More commonly this is caused by an ethmoid sinus infection. That type occurs without any pus in the eye.
Symptoms of Bacterial Eye Infection
- Yellow or green discharge or pus in the eye
- Dried pus on the eyelids and eyelashes
- The eyelashes are more likely to be stuck together after sleep
- The whites of the eye may or may not be red or pink
- The eyelids are often puffy
When to Call for Eye - Pus or Discharge
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Eyelid is very red or very swollen
- Vision is blurred
- Eye pain or discomfort is more than mild
- Fever over 104° F (40° C)
- Fever in baby less than 12 weeks old. Caution: do NOT give your baby any fever medicine before being seen.
- Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- Pus in the eye, but none of the symptoms above.
 Reason: you may need antibiotic eyedrops to treat it.
Reason: you may need antibiotic eyedrops to treat it. - Using antibiotic eye drops more than 3 days and pus is still there
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
Care Advice for Pus In the Eye
- What You Should Know About Bacterial Eye Infections:
- Bacterial eye infections are common with colds.
- They respond to home treatment with antibiotic eye drops which need a prescription.
- They are not harmful to vision.
- Until you get some antibiotic eye drops, here is some advice that should help.
- Bacterial eye infections are common with colds.
- Remove Pus:
- Remove all the dried and liquid pus from the eyelids. Use warm water and wet cotton balls to do this.
- Do this whenever pus is seen on the eyelids.
- Also, remove the pus before the antibiotic eye drops are put in. Reason: they will not work if you don't.
- The pus can spread infection to others. So, dispose of it carefully.
- Wash your hands well after any contact with the pus.
- Antibiotic Eye Drops: How to Use
- For a cooperative child, gently pull down on the lower lid. Put 1 drop inside the lower lid. Then ask your child to close the eye for 2 minutes. Reason: so the medicine will get into the tissues.
- For a child who won't open his eye, have him lie down.
 Put 1 drop over the inner corner of the eye. If your child opens the eye or blinks, the eye drop will flow in. If he doesn't open the eye, the drop will slowly seep into the eye.
Put 1 drop over the inner corner of the eye. If your child opens the eye or blinks, the eye drop will flow in. If he doesn't open the eye, the drop will slowly seep into the eye.
- Contact Lenses:
- Children who wear contact lenses need to switch to glasses until the infection is gone.
- Reason: to prevent damage to the cornea.
- Disinfect the contacts before wearing them again.
- Discard them if they are disposable.
- Return to School:
- Your child can return to school when the pus is a small amount.
- Antibiotic eye drops should be used for 24 hours before going back.
- What to Expect:
- With treatment, the pus discharge should clear up in 3 days.
- The red eyes may last up to a week.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Eyelid gets red or swollen
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.

Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 11/30/2022
Last Revised: 01/13/2022
Copyright 2000-2022. Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Is it normal and how to treat it?
Eye discharge is common in newborns and typically occurs due to a blocked tear duct. However, parents and caregivers can often treat this at home.
Eye discharge is typically harmless and self-resolving. However, discharge that occurs alongside other symptoms in the eye area, such as swelling or tenderness, could indicate an infection or another eye problem. A parent or caregiver of a newborn with these symptoms will need to consult a doctor.
This article discusses how common eye discharge is and explains how to treat it at home. We also cover medical treatment, other causes, complications, and when to contact a doctor.
Eye discharge in newborns is common and rarely a cause for concern. A common cause of eye discharge is a blocked tear duct.
A common cause of eye discharge is a blocked tear duct.
According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, almost 20% of newborns have a blocked tear duct. This condition can occur because the end of the tear duct does not open properly when the baby is born.
Tears form in the lacrimal gland, which sits just above the eye. Tear fluid helps clean and lubricate the surface of the eye. When a person blinks, the eyelids sweep the tear fluid into these ducts, which drain it into the nose.
If something blocks a tear duct, fluid may no longer be able to drain away from the eye’s surface. Blockages can cause very watery eyes, and sticky discharge may form in the corners.
Learn more about blocked tear ducts.
Blocked tear ducts are a common cause of eye discharge in infants. However, other conditions and factors can also cause discharge.
Conjunctivitis
Eye discharge in newborns can also be a sign of conjunctivitis or pinkeye. Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, a thin membrane that protects the front of the eye.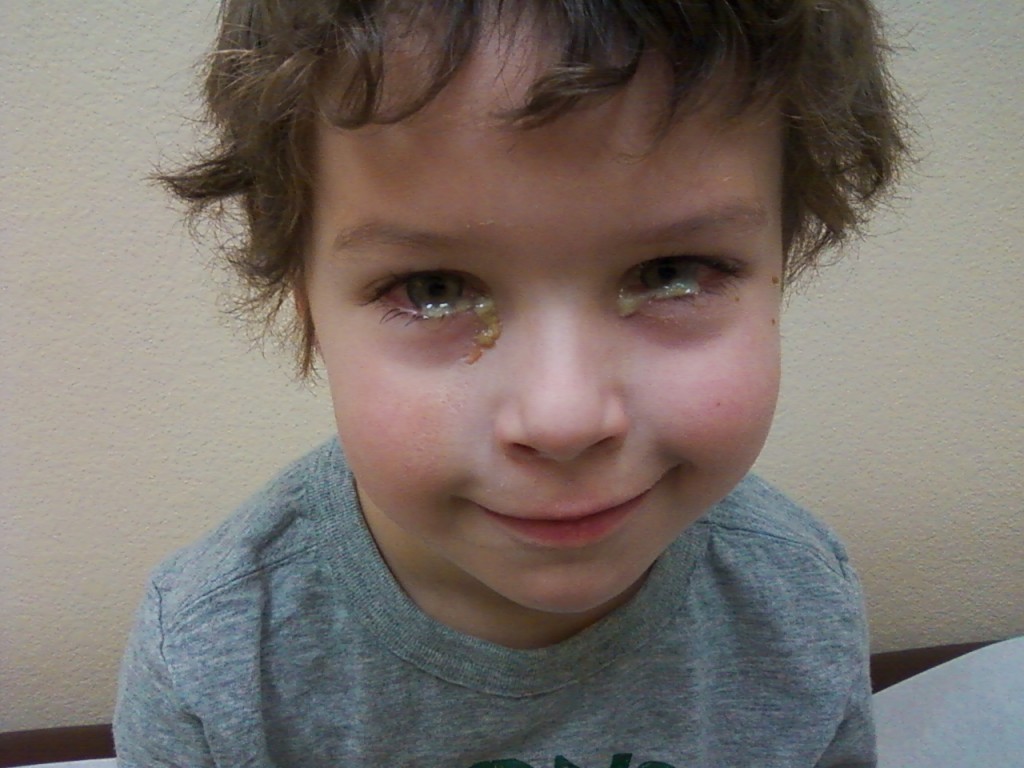 Unlike a blocked tear duct, conjunctivitis often causes the white part of the eye to appear red.
Unlike a blocked tear duct, conjunctivitis often causes the white part of the eye to appear red.
Symptoms of conjunctivitis in newborns can include:
- drainage or discharge that develops between 5 and 12 days after birth
- puffy or tender eyelids, often with skin discoloration
- red, irritated eyes
Conjunctivitis in newborns can sometimes occur alongside a blocked tear duct. However, a pregnant person can also pass on a bacterial or viral infection to their baby when giving birth, leading to conjunctivitis.
Learn more about the symptoms of eye infections.
Chemical irritation
Chemical irritation can also cause conjunctivitis in newborns. Healthcare professionals often give antibacterial eye drops to newborns to prevent infections. These eye drops can sometimes cause irritation that can result in conjunctivitis symptoms.
Learn more about eye irritation.
If the eye discharge is due to a blocked tear duct, it will usually resolve without treatment within 4–6 months.
However, wind, cold weather, and strong sunlight can also worsen symptoms, so a parent or caregiver should aim to protect a newborn’s eyes from these elements.
Clearing discharge
A parent or caregiver can often treat a newborn with a blocked tear duct at home. Before touching the area close to the child’s eyes, it is essential to wash the hands with soap and warm water to prevent infections. A person should also take care to rinse the hands thoroughly after cleaning them to avoid getting soap in the baby’s eye.
To clear away discharge, dip a clean piece of gauze or soft cloth in some lukewarm water, then gently wipe the corner of the eye. If a blocked tear duct affects both eyes, always use a new area of the cloth or gauze to clean the other eye.
Tearduct massage
A doctor may also recommend gently massaging the blocked tear duct to help it open, and they will demonstrate how to do this safely.
To massage the tear duct:
- Lightly press the tip of the index finger against the inside bridge of the newborn’s nose, on the side of the blocked tear duct.

- Make 2 or 3 short downward strokes with the finger along the side of the nose. These should be gentle but firm.
- Perform the massage twice a day — once in the morning and once in the evening.
If the side of the newborn’s nose becomes red or swollen, stop the massage immediately and contact a doctor.
In newborns, blocked tear ducts tend to open up within several months of birth. However, medical intervention may be necessary in some cases.
Surgery
If the blockage has not gone away by the baby is 1 year of age, a doctor may recommend a medical treatment called a nasolacrimal duct probing.
This procedure involves inserting a small probe into the infant’s tear duct. By using probes that gradually increase in size, a doctor will be able to open up the tear duct. They will then use a saline solution to flush out any remaining debris.
Sometimes, the doctor may also insert a small tube, or stent, into the duct to keep it open.
Probing is usually successful in opening the tear duct.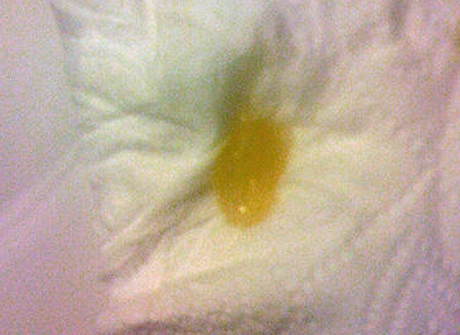 For children with a severe blockage, a doctor may recommend a more complicated surgical procedure called a dacryocystorhinostomy to clear out and open the tear duct.
For children with a severe blockage, a doctor may recommend a more complicated surgical procedure called a dacryocystorhinostomy to clear out and open the tear duct.
Antibiotics
If an infection is causing eye discharge, the newborn will need prompt medical attention. To treat cases of infectious discharge, a doctor may prescribe topical, oral, or intravenous antibiotics.
Blocked tear ducts can sometimes lead to an infection called dacryocystitis. Symptoms of this condition may include:
- excessive thick discharge from the eye
- redness in the corner of the eye
- a tender bump or swelling at the side of the nose
- fever
If a newborn has any of these symptoms, a parent or caregiver should consult a doctor.
Newborns with eye discharge or very watery eyes should speak with a pediatrician or an eye doctor specializing in children, called a pediatric ophthalmologist. These healthcare professionals can diagnose the cause of the discharge and check for signs of infection.
Parents or caregivers should seek medical attention if an infant’s eye discharge persists for more than 6 months.
Newborns with signs of an eye infection require immediate medical attention. Signs of an eye infection can include:
- sore or puffy eyes
- swollen eyelids
- yellow or green pus or discharge
- a bump or swelling on the inside corner of the eye
If a parent or caregiver notices any of these symptoms, they should contact a doctor immediately.
Eye discharge in newborns is common and often results from a blocked tear duct. The blockage will usually clear up by itself within 4 to 6 months.
However, newborns with eye redness, eye discharge, or excessive watering of the eyes should speak with a doctor to diagnose the cause and rule out an eye infection.
Parents and caregivers can treat a baby with a blocked tear duct at home by wiping away any discharge and gently massaging the area twice a day. A doctor can demonstrate how to do this.
Discoloration, swelling, or soreness in the eye can indicate an eye infection. Speak with a doctor immediately if an infant has these signs.
Conjunctivitis in a child. Medical articles on the site "MedMix plus"
Medical center "MedMix Plus", located in Penza at the addresses Ternovsky, 214 and st. New Caucasus, 8 offers a wide range of treatment for eye diseases for children, including childhood conjunctivitis.
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory eye disease characterized by inflammation of the conjunctiva.
The disease often occurs in children with non-compliance with the rules of hygiene and improper treatment, quickly passes from a diseased eye to a healthy one, from person to person. Not treating conjunctivitis is very dangerous for a child, because the advanced form of the disease threatens with serious inflammation of the cornea, which can even lead to loss of vision.
Symptoms of conjunctivitis in children:
- complaints of pain or feeling of sand in the eyes;
- eye redness, swelling;
- purulent discharge from the eye;
- eyelid gluing;
- fear of light;
- appearance of yellow crusts on the eyelids;
- foreign body sensation in the eye;
- the child becomes lethargic, often cries, is naughty;
- loss of appetite;
- fuzziness, blurring of images;
- Discomfort and burning in the eye.

The causes of conjunctivitis are varied, but most often associated with hypothermia, colds or allergic reactions.
Based on the causes of the disease, conjunctivitis can be:
- Bacterial - causative agents are gonococci, streptococci, etc.
- Viral - Herpes and adenovirus are the causative agents.
- Allergic - many pathogens - ranging from house dust and animal hair to certain foods.
Viral conjunctivitis in a child
Viral conjunctivitis is the most dangerous type of disease, so it is contagious, especially for babies. The virus is transmitted differently - by airborne droplets or by contact, by touching objects or a sick person. The disease is most common among children's groups, such as school, kindergarten, and often has the character of an epidemic.
Viral conjunctivitis can develop against the background of influenza, chickenpox, SARS and many other diseases.
The main signs of viral conjunctivitis:
- swelling, redness of the eyes, blood vessels become visible;
- lacrimation;
- fear of light;
- involuntary closing of the eyelids;
- the child complains of itching and pain in the eyes, feels a foreign body in the eye;
- children become capricious, cry, rub their eyes;
- vision may be impaired.
Most often, the disease affects one eye, and then passes to the second.
Bacterial conjunctivitis in a child
This type of disease is similar in its features to a viral one, but is accompanied by suppuration of the eyes in babies. Allocations are yellowish or whitish, opaque. As a result of suppuration, the child's eyelashes stick together, especially after sleep, and films or follicles form in front of the eyes. Dryness of the eye and the area around it can also be an indirect sign of infection.
Allergic conjunctivitis in a child
It is possible to avoid the occurrence of conjunctivitis, it is necessary to take only some preventive measures: This form of the disease is manifested by redness, swelling of the eyes, watery eyes, the symptoms do not go away for a long time. The severity of the symptoms depends on how much of the allergen has entered the body and how ready it is to show a protective reaction. It is important to determine which allergen caused the disease, and limit contact with it. Only an allergist can identify the allergen and cure such a condition, since against the background of the disease, serious manifestations of allergies can later develop.
The severity of the symptoms depends on how much of the allergen has entered the body and how ready it is to show a protective reaction. It is important to determine which allergen caused the disease, and limit contact with it. Only an allergist can identify the allergen and cure such a condition, since against the background of the disease, serious manifestations of allergies can later develop.
- follow the rules of personal hygiene of the child;
- monitor the cleanliness of bed linen, toys;
- ventilate the room;
- use air purifiers and humidifiers;
- keep food clean;
- include fortified and healthy foods in the diet;
- to walk in the fresh air;
- avoid contact with sick people.
Clinical diagnosis and treatment of conjunctivitis "MedMix Plus"
How to quickly cure and how to treat conjunctivitis in a child is determined only by an ophthalmologist at the medical center "MedMix Plus".
Children's ophthalmologist of the first category Elizarova T.V.
Treatment of conjunctivitis is prescribed by a specialist only after he determines the cause and type of the disease. Strictly follow the doctor's instructions, use only clean gauze pads, do not reuse a cotton pad, check the expiration dates of medicines, use pipettes for instilling medicines with a rounded tip.
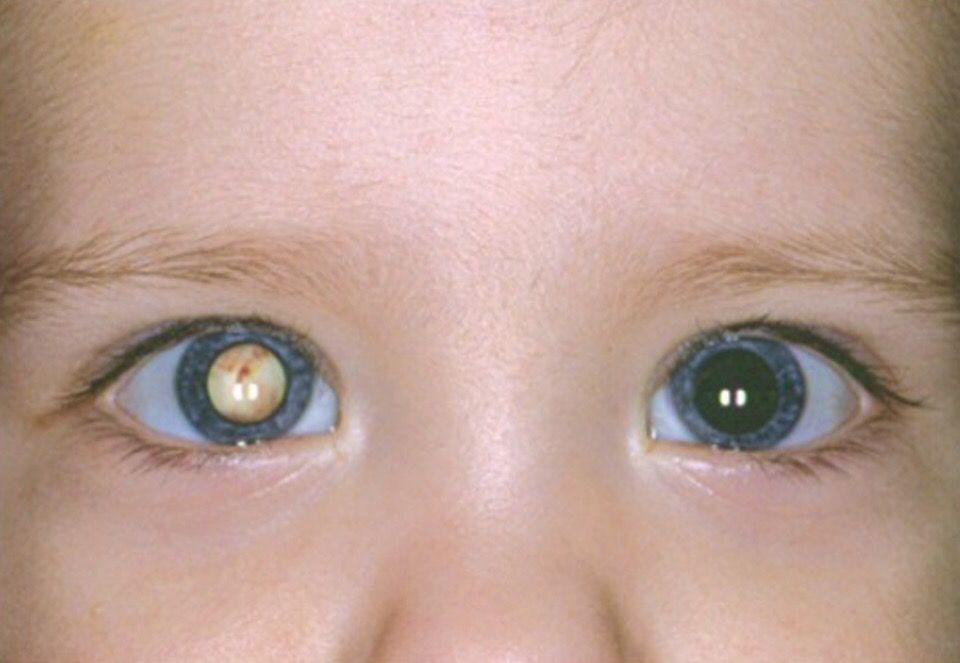
It is necessary to know that in young children (under 3 years old) symptoms similar to those of conjunctivitis, namely, redness and inflammation of the eye, may be associated with foreign bodies or the development of an allergic reaction. However, similar symptoms also indicate more serious causes - increased intraocular and intracranial pressure.
Do not try to treat this disease on your own, in order to avoid serious health problems for your baby, seek quick, professional and affordable help from pediatric ophthalmologists at the MedMix Plus clinic.
You can make an appointment with a pediatric ophthalmologist by phone:
+7 (8412)204-003, +7 (8412)204-007 - st. New Caucasus, 8 (city district - CENTER)
New Caucasus, 8 (city district - CENTER)
+7 (8412)206-003, +7 (8412)205-003 - st. Ternovskogo, 214 (district of the city - TERNOVKA)
Why is there mucus in the eyes. How to treat eye discharge in a child.
From All About Vision
Eye discharge is a combination of mucus, fat, skin cells, and other particles that accumulate in the corners of the eyes during sleep." They may be wet and sticky or dried out, depending on how much fluid is present. managed to evaporate.0003
Mucous secretions have a protective function, flushing waste products and potentially dangerous particles from the tear film and the anterior surface of the eye.
Throughout the day, the eyes secrete mucus, but the ever-present tear film bathes your eyes with every blink, removing the secretions before they have time to harden.
When you sleep and do not blink, the discharge accumulates and dries up in the corners of the eyes, and sometimes along the lash line. accompanied by blurry vision, sensitivity to light or eye pain may indicate a serious eye infection or eye disease.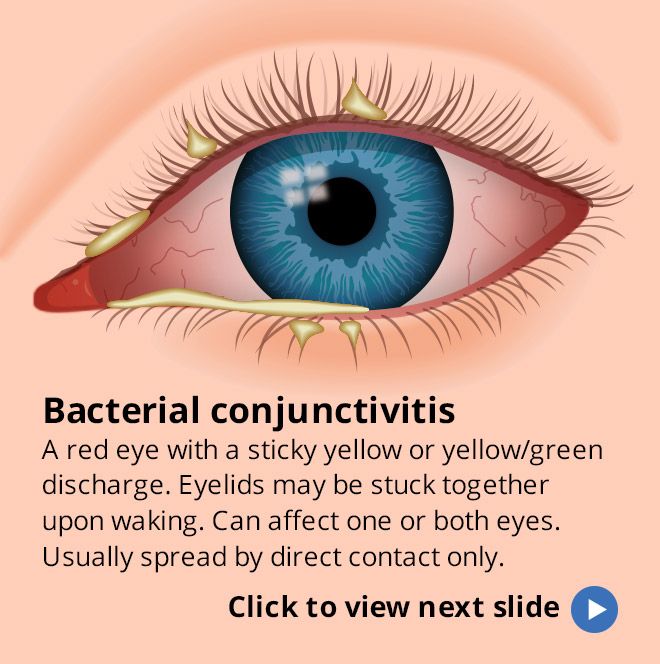 Therefore, you should immediately contact an optometrist.
Therefore, you should immediately contact an optometrist.
FIND AN OCULIST OR OPTICS SHOP NEAR YOU : Whether you need an eye exam or are ready to buy eyeglasses or contact lenses, our locator will help you find a safe place nearby.
Where does eye discharge come from?
The discharge from the eyes consists mainly of a watery mucous secretion (mucin) produced by the conjunctiva and the secretion of the meibomian glands, an oily substance that helps to moisten the eyes between blinks.
Those impurities that are not washed away by tears accumulate in the inner corners of the eye and along the lash line. ""
Causes of discharge from the eyes the consistency, color, or amount of discharge, this may indicate an infection or eye disease.
Common eye conditions with abnormal eye discharge include:
Conjunctivitis. Discharge from the eyes is a common symptom Conjunctivitis Inflammation of the thin membrane that lines the "alkaline" of the eye (the sclera) and the inner surface of the eyelids.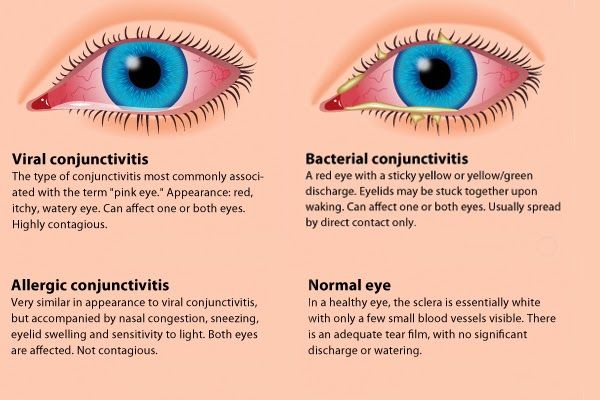
In addition to itching, stinging, eye irritation and redness , conjunctivitis is usually accompanied by white, yellow or green mucus that may form a crust along the eyelash line during sleep. In some cases, the crust formed on the eyelid can be so dense that it does not allow you to open your eyes.
There are three types of conjunctivitis:
Viral conjunctivitis
Viral conjunctivitis is highly contagious and is caused by the common cold or herpes simplex virus. Eye discharge from viral conjunctivitis is usually clear and watery, and may include white or yellowish mucus.
Bacterial conjunctivitis
Bacterial conjunctivitis, as the name suggests, is caused by a bacterial infection. If not promptly treated, it can pose a threat to vision. Eye discharge from bacterial conjunctivitis is usually thicker and purulent (like pus) than from viral conjunctivitis and is usually yellow, green, or even gray in color. In the morning after sleep, patients often cannot open their eyelids, which are completely stuck together with secretions.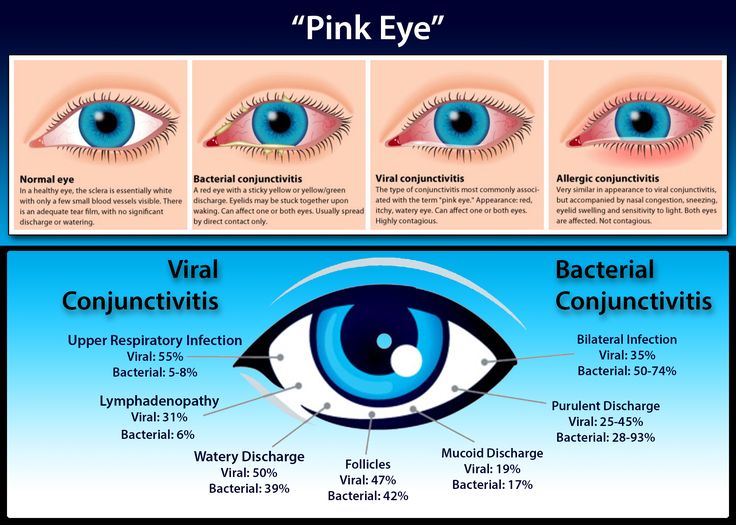
Allergic conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis is triggered by allergens - pollen, dander, dust and other common irritants that cause eye allergies . It can also be caused by an allergic reaction to chemical pollutants, cosmetics, contact lens solutions, and eye drops. In allergic conjunctivitis, the discharge from the eyes is usually watery. Allergic conjunctivitis is not contagious and always affects both eyes.
Other eye infections
In addition to conjunctivitis, there are many eye infections that cause abnormal eye discharge. For example:
-
Herpes ocularis (recurrent viral eye infection)
-
Fungal keratitis (a rare but serious inflammation of the cornea)
-
while wearing contact lenses).
The discharge from an eye infection varies considerably - it can be clear and watery or thick, green and sticky, so you should see an eye doctor as soon as possible for diagnosis and treatment.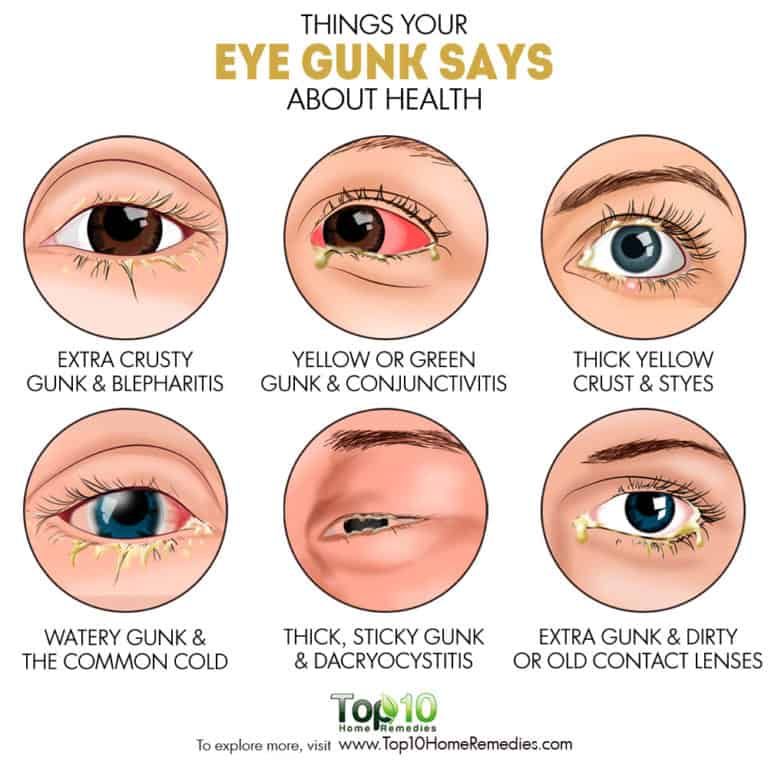
Blepharitis
A chronic disease of the eyelids, blepharitis, is either an inflammation of the eyelash hair follicles or an abnormal secretion of the meibomian glands at the inner edge of the eyelids.
Meibomian gland dysfunction
Also called MGD, this sebaceous gland disorder in the eyelid can cause foamy discharge from the eyes, clumping of the eyelids, yellow or green pus, and irritation and pain.
Barley
Barley is a blockage of the meibomian gland at the base of the eyelid, usually caused by an infected eyelash follicle. Also called hordeolum, it resembles a pimple at the edge of the eyelid and is usually accompanied by redness, swelling of the eyelids, and tenderness at the site of the lesion. Yellow pus, sticking of the eyelids, and discomfort when blinking may also occur.
SEE. ALSO: How to Get Rid of Styes
The tear duct system provides moisture and protection to the eyes.
Dry eye
Insufficient tear production or dysfunction of the meibomian glands can lead to dry eye syndrome , a frequently chronic condition in which the surface of the eye is not properly lubricated, becoming irritated and inflamed. Symptoms include reddened, bloodshot eyes, a burning sensation, blurred vision, and a foreign body sensation in the eye. "" Sometimes dry eyes can also cause very heavy watering.
Contact lenses
When wearing contact lenses, there may be more discharge from the eyes than usual. This can be due to a variety of reasons, including eye infection from contact lens wear, contact lens discomfort resulting in dry and irritated eyes, and contact lens wearers rubbing their eyes more frequently. If you notice more discharge due to contact lenses, remove your lenses and see an optometrist to rule out a potentially serious eye disease.
Eye injury
A foreign body in the eye (such as dirt, particles, or a chemical) or eye injury may cause watery discharge as a natural defense reaction. If you notice pus or blood in your eye (subconjunctival hemorrhage) after injury to eye , contact your optometrist immediately for treatment. All eye injuries should be treated as an emergency.
If you notice pus or blood in your eye (subconjunctival hemorrhage) after injury to eye , contact your optometrist immediately for treatment. All eye injuries should be treated as an emergency.
Corneal ulcer
A corneal ulcer is a vision-threatening abscess-like infection of the cornea, usually caused by trauma to the eye or an advanced eye infection. If left untreated, corneal ulcers can lead to permanent vision loss. Corneal ulcers are characterized by pain, redness, swelling of the eyelids, and thick discharge from the eyes. The discharge of pus can be so strong that it causes clouding of the cornea and blurred vision.
Dacryocystitis
When the lacrimal duct is blocked, inflammation and infection of the lacrimal sac in the drainage system of the lacrimal apparatus can occur, resulting in a painful and swollen bump under the inner eyelid. In addition to pain and redness, common symptoms of dacryocystitis include watery eyes, sticky discharge from the eyes, and blurry vision.
Eye discharge treatment
A small amount of eye discharge is harmless, but if you notice changes in color, frequency, consistency and quantity, contact your optometrist.
If mucus in the eyes is due to an eye infection, the optometrist may prescribe antibiotics or antiviral eye drops and ointments. If an eye allergy is causing watery eyes and irritation, over-the-counter antihistamine eye drops and decongestants may help relieve symptoms.
Warm compresses help soothe itching and general discomfort, and remove discharge from the eyes.
For sticky eyelids, soak a kitchen towel in warm water and place it over your eyes for a few minutes, then gently wipe the discharge."
Home Checklist from them:
Do not touch your eyes to avoid getting or spreading an eye infection.0003
Wash your hands frequently, especially if you have contagious conjunctivitis.
If you experience bleeding while wearing contact lenses, remove your lenses and see your optometrist.