How to tell if your child needs speech therapy
Top Signs Your Child Needs Speech Therapy
Children accomplish a lot during the first 12-months of their lives. They should babble within the first 6-months, and by their first birthday, they should say their first word.
As a parent, it is only natural to worry if your child isn't saying as many as 20 words by the time they are 18-months old.
You must not forget that every child develops at their own pace, but it is crucial to consider their developmental milestones. You can refer to a standard speech and language development checklist to see how many boxes your child is ticking off.
Few parents still practice the "wait-and-see" approach. We recommend consulting with a speech-language pathologist (SLP) if your child is already showing signs of speech delay.
When Should You Consult A Speech Therapist For Your Child?Preschoolers often mispronounce words and have difficulty making complete sentences. It's entirely normal! When young children begin to learn a language, they experiment with different sounds, tongue, and lip movement to create new words and explore new ways of putting words together to make sentences.
It is often difficult to tell simple mispronunciations apart from speech problems in children.
Here are 17 common signs that your child requires speech therapy –
1. Your Child Isn’t BabblingYou should expect your child to begin babbling between the ages of 4-months to 6-months. If your 7-month old isn’t babbling yet, you need to check with your pediatrician for auditory deficits.
If reports suggest that your child has proper auditory functions, it may be time to meet with a speech-language pathologist (SLP) to determine the course of action.
Talking to a pediatric speech therapist can help you steer clear of the myths surrounding speech delay in children. A speech therapist can also tell you all about the exercises you can do at home to help your child’s speech and language development.
2. Your Child Has Been StutteringStuttering can develop by the time your child is around 2-years of age. Stuttering can resemble normal disfluency in children, but it is more frequent.
Stuttering can resemble normal disfluency in children, but it is more frequent.
They may repeat whole words, one syllable, or block altogether before saying a word. Toddlers typically show very few or no secondary behaviors of stuttering.
If your preschooler has been showing signs of stuttering for longer than a month, it’s wise to consult a speech therapist.
3. Your Child Doesn’t Engage In Group PlayA child who prefers being alone or playing parallelly in the presence of children their age may have autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Modern medical sciences have made early diagnosis of ASD possible to facilitate early intervention.
Children with ASD may experience speech and language delays, along with social communication disorders. Engaging in speech therapy early on can equip your child with the necessary skills to participate in social interactions and make friends at school.
4. Your Child’s Voice Is InconsistentMaybe you have noticed that your child's voice is unusually hoarse or shrill. Your child may also have a problem controlling the volume of their voice.
Your child may also have a problem controlling the volume of their voice.
Occasionally, every child may suffer from a sore throat and hoarse voice. It is common after cheering loudly at a ballgame or after too many ice Slurpees. So, if this continues for longer than a couple of weeks, you may need to consult a speech therapist.
Chronic dysphonia may require speech therapy to bring the vocal cords back to their proper working order.
5. Your Child Has Inconsistent SpeechVery young children often have incoherent speech. Sometimes, they make up new words to express themselves. These aren’t concerning as long as their mistakes are consistent.
Inconsistent speech may consist of the same word being spoken differently throughout their speech. For example, your child may want to say "bye," but they end up saying "tie," "pie," and "die."
These may be signs of childhood apraxia of speech (CAS). Early speech therapy may reduce the persistence of the signs and symptoms later in life.
By their first birthday, your child should be pointing at things and waving to people. Some children gesture less often than others. However, if your child doesn't gesture at all, you should talk to your pediatrician first.
The pediatrician may recommend speech-language pathologists (SLPs) or speech therapists who can explore the possible causes.
Sometimes, it is an early sign of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Speech therapy for autism can help a child develop speech and language skills significantly when started early.
7. Your Child Is Making Phonological MistakesIs your 3-year old still saying “fum” in place of “thumb”? Are they also saying “ba-wa-wa” instead of “ba-na-na”? Substituting words, omitting final consonants, and simplifying sound combinations are articulation or phonological errors.
It is imperative to consult a speech therapist in these cases. These may be signs that your child has weak articulatory muscles or they have trouble coordinating the movement of their speech muscles.
These may be signs that your child has weak articulatory muscles or they have trouble coordinating the movement of their speech muscles.
Regular articulatory exercises can increase the strength of a child's speech muscles. Speech therapy can improve a child's pragmatic language and social communication skills significantly.
8. Your Toddler Cannot Follow Simple InstructionsMany children have trouble understanding multi-step instructions. However, if your toddler doesn't respond to their name, struggles to follow simple directions like "the truck is behind you" or "look at the TV," then it may be concerning.
A toddler should be able to answer simple “what” and “where” questions. Just like the lack of gesturing or group play, the inability to follow simple directions may be a symptom of autism spectrum disorder.
Timely intervention with the help of a speech-language pathologist (SLP) can help a child overcome the challenges that come with ASD. Attending sessions can also help the parents learn more about speech exercises for children with autism they can do with their children at home to improve their speech-language skills.
Attending sessions can also help the parents learn more about speech exercises for children with autism they can do with their children at home to improve their speech-language skills.
By the time a child is 2-years-old, any stranger should understand their speech 50% of the time. By their 3rd birthday, their speech should be understandable at least 75% of the time.
In case your toddler’s speech isn’t clear enough, you can talk to a speech therapist.
Unintelligible speech can be a sign of several speech and language disorders. The speech therapist can help you get a proper diagnosis. A professional can also help them articulate their speech.
10. Your Child Has A Cleft PalateAround 1 in 1600 children are born with a cleft palate in the US. It is a common birth condition that can cause problems with feeding, drinking, and speaking.
If your child has a cleft lip with a cleft palate, you should speak with your pediatrician immediately. In several cases, surgery can correct a cleft palate and restore normal articulatory functions in a child.
An older child may require speech therapy to learn or re-learn ways to produce correct sounds while speaking.
11. Your Child Has Cerebral Palsy (CP)Children with cerebral palsy (CP) may have problems speaking if the palsy affects their mouth and speech muscles. With continuing speech therapy, many children not only learn how to talk almost clearly, but they can also learn how to chew and swallow safely.
Speech therapy for children with cerebral palsy (CP) aims to boost their independence by encouraging them to express themselves. Speech therapy for cerebral palsy may also teach your child alternative and augmentative communication (AAC) methods, such as using picture boards.
12. Your Infant Has Down Syndrome (DS)Down syndrome is a genetic condition in which an individual has extra chromosomal material (genes). It is characterized by distinct facial features and developmental delays. Many cases of Down syndrome co-occur with intellectual disability (ID).
It is characterized by distinct facial features and developmental delays. Many cases of Down syndrome co-occur with intellectual disability (ID).
Speech therapy for Down syndrome can help your child develop the necessary speech and language skills. It can also help with any eating, drinking, or swallowing difficulty that your child may face due to Down syndrome.
Speech therapy for Down syndrome can equip your child with alternative and augmentative communication methods like sign languages, picture boards, or electronic-synthesized speech. Speech therapists can teach your child how to speak clearly, and contribute to their communication skills, in general.
13. Your Child Isn’t Talking At SchoolYour child talks and shares their thoughts normally at home, but the moment they enter school or is at the playground, they don’t speak at all.
It is common for parents to receive complaints from teachers and caregivers about their children not speaking, if their child has selective mutism. It is a severe anxiety disorder that keeps children from speaking in social settings.
It is a severe anxiety disorder that keeps children from speaking in social settings.
Traditionally, it is not a speech-language disorder. However, the intervention of a behavioral therapist along with a speech therapist can help your kid overcome their anxiety.
14. My Child is a Late-TalkerPediatric speech and language therapy can help your child overcome any speech, language, and communication challenges they face. Delayed speech can be a sign of more than one speech and language disorder in children.
15. Your Child has a LispLisping is quite common among children. Some children outgrow lisping once they acquire language and conversation skills. However, if a 5-year old is still pronouncing /s/, and /z/ as /th/, it’s time to consult a speech therapist.
Almost all types of lisps can go away with proper diagnoses of the causes and speech therapy. Without proper treatment and therapy, lisping can persist during adolescence and adulthood. It can take a toll on a person’s self-esteem and confidence.
It can take a toll on a person’s self-esteem and confidence.
If your 6-year old is still struggling to read simple, monosyllabic words, it can be a serious issue. Same goes for similar-aged children who are having trouble writing. If your child is saying things like, “the words are moving around” or “the numbers won’t stay still”, you may be looking at a case of dyslexia. This condition can affect a child’s speech as well.
Reading and writing disorders can include dyslexia, dysgraphia, reading disorder, reading disability, specific reading disorder and specific reading comprehension deficit.
Speak to a speech language pathologist (SLP) or speech therapist in case your child has trouble reading, writing or understanding what they are reading. Typically, continued therapy can address these problems successfully. However, early intervention always helps more than delayed actions.
17. Your Child has a Limited Vocabulary
Your Child has a Limited VocabularyYour 18-month old should have a vocabulary of 50 words and they should learn around 10 to 20 new words per week. A 2-year old should begin to use two words together to form short “sentences”.
Children between the ages of 2 and 3 years should know spatial concepts such as “on,” “in,” “over,” and “under.” Take a look at this speech and language checklist to find out if your child’s speech and language skills are developing at par with their age.
If your child isn’t using or learning new words as expected according to their age, it’s time to speak to a speech-language pathologist (SLP) or speech therapist.
Speech therapy can help your child overcome developmental stuttering and articulation disorders.
While conditions like childhood apraxia of speech (CAS), dysarthria, Down syndrome, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), and Cerebral Palsy (CP) are not curable, speech therapy can help with the speech and language delay that these conditions may cause.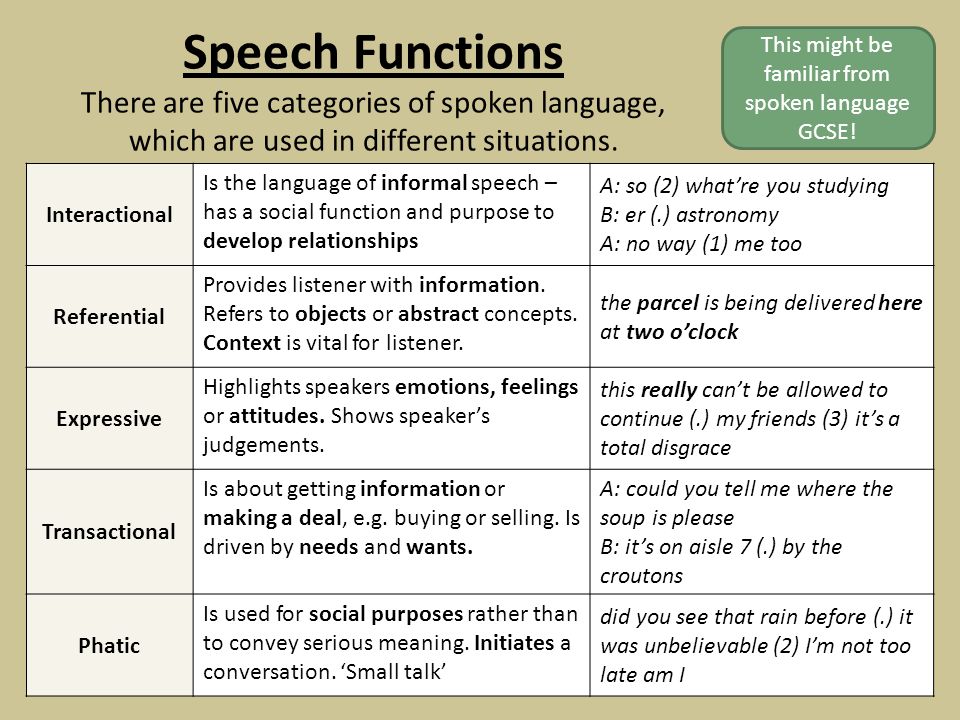
Do not wait if you think that your child needs professional attention. Speak to their pediatrician today if you don’t have recommendations for a speech therapist!
Stamurai has been used by more than 50,000 people from over 190 countries.
6 Signs Your Child Might Need Pediatric Speech Therapy
Are you worried that your child might have trouble communicating? Maybe he doesn’t use as many words as you feel he should at his age, or maybe other kids often don’t understand what she’s trying to say. If you’re noticing signs like these, your child might have a speech or language disorder.
Among U.S. children ages 3-17, 5 percent have a speech disorder that lasted for a week or longer and 3.3 percent have a language disorder that occurred for a week or more during the past year, according to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders.
Speech and language problems are different but often intersect, according to KidsHealth. Speech involves verbally expressing yourself and forming sounds and words, while language encompasses the broader process of understanding other people and being understood through verbal and non-verbal communication. A toddler with a speech issue might have difficulty making certain sounds and pronouncing words, while a child with a language problem could pronounce everything correctly but have trouble forming sentences to express ideas.
A toddler with a speech issue might have difficulty making certain sounds and pronouncing words, while a child with a language problem could pronounce everything correctly but have trouble forming sentences to express ideas.
It’s important for parents to educate themselves about both speech and language development and keep an eye out for signs of an issue, particularly during their child’s first few years. Here are some things to watch out for that could indicate your child is having trouble with speech and/or language acquisition.
1. Not babbling at age 4-7 months. A baby who seems strangely quiet and isn’t experimenting with sounds through babbling could be showing signs of a language disorder, according to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association.
2. Lack of gesturing. If your child doesn’t express herself by making gestures such as pointing and waving (or makes very few gestures) at the age of 7-12 months, that could be another indication of a possible language disorder, ASHA states.
3. Issues with verbal requests. Children between 12 and 24 months old should be able to comprehend simple spoken requests, according to KidsHealth. If your son or daughter doesn’t seem to understand your instructions, he or she could have a language development issue.
4. Not speaking in sentences. Between the ages of 1.5 to 2 years, kids should start putting words together to form sentences. If your toddler is struggling to make sentences, that might be a good reason to get her screened for a language disorder.
5. Trouble making certain sounds. Children with speech disorders might have issues producing p, b, m, h, and w sounds in words the majority of the time from 1 to 2 years old and/or trouble pronouncing k, g, f, t, d, and n from 2 to 3 years old, according to ASHA. Their speech might also just seem generally unclear and hard to understand when they are 2 to 3 years old.
If your child shows any of these signs or seems to have other speech and/or language issues, it’s best to seek help as soon as possible. At Little Steps, our pediatric speech therapists can help children of all ages with various speech and language disorders – including articulation, fluency, and language disorders, as well as general communication challenges. We provide the highest level of individualized pediatric speech therapy services to help our patients improve. If you’d like to learn more, contact us today by calling 847-707-6744 or emailing [email protected].
At Little Steps, our pediatric speech therapists can help children of all ages with various speech and language disorders – including articulation, fluency, and language disorders, as well as general communication challenges. We provide the highest level of individualized pediatric speech therapy services to help our patients improve. If you’d like to learn more, contact us today by calling 847-707-6744 or emailing [email protected].
How to understand that a child needs a speech therapist
First, parents wait for the child to speak, then they are touched by how funny he distorts the words, and then they begin to worry about the fact that the baby clearly incorrectly called “pike”. So when should you take your child to a speech therapist, and when can you relax? The psychologist, speech therapist and author of the series of books "Speech Therapy Practice" Elena Yanushko tells.
In almost every family with children, sooner or later the question arises: “Should we show our child to a speech therapist?”. Some parents put off a visit to a specialist until school time, others believe that certain speech problems will go away naturally. Still others turn to a speech therapist immediately after the child begins to form speech. Which of them is right? To answer this question, it is important to consider its background.
Some parents put off a visit to a specialist until school time, others believe that certain speech problems will go away naturally. Still others turn to a speech therapist immediately after the child begins to form speech. Which of them is right? To answer this question, it is important to consider its background.
How to understand if a child has speech therapy problems?
Different sounds appear in the child's speech in stages, depending on the degree of complexity of their pronunciation. The so-called sounds of early ontogenesis appear in the speech of a child at 1-2 years old - these are the sounds A, O, E, P, B, M. The sounds of middle ontogenesis appear in speech at 2-3 years old - these are the vowels I, Y, U, and consonants F, V, T, D, N, K, G, X, Y. When it comes to the correct pronunciation, they usually mean the sounds of late ontogenesis: at 3-5 years old, whistling sounds C, Z should appear in the child’s speech , C and hissing Sh, Zh, Sh, Ch, and at 5-6 years old - the most difficult sounds - L and R. It is important to consider these stages when assessing your child's speech. For example, you should not worry if a child does not have L or R sounds at 3-4 years old. You should wait until 5 years old and if the sound does not appear, you should contact a speech therapist.
It is important to consider these stages when assessing your child's speech. For example, you should not worry if a child does not have L or R sounds at 3-4 years old. You should wait until 5 years old and if the sound does not appear, you should contact a speech therapist.
Meeting with a speech therapist - before kindergarten or before school?
In order to start working on possible problems in time, it is worth taking a preschool child to a speech therapist at least twice - before entering kindergarten and before the first grade of school. The speech therapist's recommendations will either allow you to stop worrying about the child's speech, or start acting in time, for example, arrange a child in a kindergarten speech therapy group. The first time to visit a speech therapist is when the child is 2-3 years old, the second time - at the age of 5-6 years, so that there is time to correct problems if they are identified by a specialist.
When should I go to a speech therapist immediately?
In some cases, it is important not to postpone a visit to a speech therapist - the sooner you start working on mistakes in speech, the easier it will be to correct them. For example, if a child uses non-physiological substitutions, he says “hapka” or “fapka” instead of “hat”, “uampa” instead of “lamp”, “tyasy” instead of “watch”, or “vuk” instead of “beetle”. It is worth making an appointment with a specialist if the child has a distorted pronunciation of some sounds - for example, "burr" Р (it does not vibrate the tip of the tongue, but the soft palate and "small tongue"), "lisping" C, Z (during the pronunciation of whistling sounds, the tongue sticks out between the incisors), “squishing” with an unpleasant shade of Sh, Zh, etc. Corrective classes with a speech therapist will help to avoid fixing the incorrect pronunciation of sounds in speech. Otherwise, it will not be easy to correct such a violation in a year or two.
For example, if a child uses non-physiological substitutions, he says “hapka” or “fapka” instead of “hat”, “uampa” instead of “lamp”, “tyasy” instead of “watch”, or “vuk” instead of “beetle”. It is worth making an appointment with a specialist if the child has a distorted pronunciation of some sounds - for example, "burr" Р (it does not vibrate the tip of the tongue, but the soft palate and "small tongue"), "lisping" C, Z (during the pronunciation of whistling sounds, the tongue sticks out between the incisors), “squishing” with an unpleasant shade of Sh, Zh, etc. Corrective classes with a speech therapist will help to avoid fixing the incorrect pronunciation of sounds in speech. Otherwise, it will not be easy to correct such a violation in a year or two.
What should be done for prevention?
You need to talk a lot with children and you need to do it right. Read books together, discuss what you read, talk on a variety of topics. For babies in a year or two, offer lightweight words for repetition: mom, dad, nanny, lala, etc. , gradually increasing the level of complexity. Learn together simple phrases that can be used in games and in everyday life, for example, “Mom, give me a drink!”, “Let's go for a walk, lala!”. Read poems and nursery rhymes, offer to finish the words at the end of the line and whole lines.
, gradually increasing the level of complexity. Learn together simple phrases that can be used in games and in everyday life, for example, “Mom, give me a drink!”, “Let's go for a walk, lala!”. Read poems and nursery rhymes, offer to finish the words at the end of the line and whole lines.
At preschool age, it is necessary to perform regular and high-quality articulation exercises in order to develop precise tongue movements. Particular attention should be paid to the development of phonemic hearing - this is one of the foundations of a child's future literacy. That is why it is so important for a child to hear correct, well-articulated speech.
It is important not to forget that all exercises should be offered to the child in a playful, exciting way. Various publications can help with this. For example, in the album "Speech Therapy Practice" there is an interactive format - as the child masters certain sounds, the child paints over the coloring pages in the album, thereby marking his progress. And the illustrations help children and parents learn and do the exercises.
And the illustrations help children and parents learn and do the exercises.
Illustration: olga boat / Shutterstock
You are in the Blogs section. The opinion of the author may not coincide with the position of the editors.
when you need it, how to find a specialist
Lada Trusevich
speech therapist
Author's profile
“I don't want to wear a coat! I went to needle in shawki!”
Such slurred speech can often be heard on the playground. Many parents, although they see the problem, do not know what to do with it, whether to worry or just wait until speech improves on its own.
I am a teacher with 30 years of experience. For the last nine years I have been practicing speech therapy and preparing children for school. I will tell you how to understand that a child needs the help of a speech therapist, where to look for the right specialist, and why it is also important for parents to get involved in the speech correction process.
What You Will Learn
- What Speech Pathologists Do
- When Parents Should Be Wary
- Where to Get Advice
- What a Conclusion Looks Like
- Where to Find a Specialist for Regular Practice
- How speech therapists work
- How long it takes to correct speech
- How parents can help a child
What speech therapists do
Speech therapy studies and eliminates speech disorders in children and adults. A speech therapist tries to understand the causes of speech problems and helps to eliminate them. Since speech begins to form from birth, most often a speech therapist works with preschoolers.
This is what he does:
- Conducts examination and detects speech disorders.
- Comprehensively works on the elimination of violations - correctly "puts" the sound, develops clear pronunciation skills, increases the child's vocabulary. Sometimes he works in a team with other specialists, for example, a neurologist or defectologist.
- Introduces correct speech into everyday life with the help of games, conversations, creative tasks and consolidates the result.
- Engaged in the prevention of speech disorders, including exercises for the development and strengthening of the speech apparatus, finger gymnastics, and educational games for the development of speech.
In short and simple, a speech therapist works to make speech correct and beautiful. This is important because:
- An increase in vocabulary and the ability to correctly express one's thoughts increase self-esteem.
- Competent speech allows you to take an active part in games, creative work, study.
- Reduces the risk of writing and reading disorders.
- When a person is understood by others, it facilitates communication.
- Proper speech eliminates restrictions in choosing a profession.
/dysgraphia/
I spent 471,500 R over 12 years treating my son's speech and writing difficulties , hat - "sapka", fish - "iyba", cat - "that", stick - "soldering". But there are many other problems. For example, incorrect use of prepositions or agreement of words in a sentence: “red hat”, “the girl went to bed”. Or the replacement of syllables in words, their reduction, repeated pronunciation: stick - “papalka”, captain - “pikitan”, orange - “lupusin”.
But there are many other problems. For example, incorrect use of prepositions or agreement of words in a sentence: “red hat”, “the girl went to bed”. Or the replacement of syllables in words, their reduction, repeated pronunciation: stick - “papalka”, captain - “pikitan”, orange - “lupusin”.
Most often people come to the consultation with the following questions:
- The child is 2-3 years old, he does not speak at all, uses only babble words in his speech, cannot form a phrase, or his speech is illegible.
- A child of 4-5 years old, he uses only simple, short words, changes syllables in words, replaces, skips, distorts sounds, has a small vocabulary, cannot coherently tell about events.
Parents with babies under two years of age did not contact me. This is understandable: many believe that a speech delay of up to two years is the norm. Sometimes this is true: if the pregnancy and childbirth went well, the child is physically healthy and develops according to the schedule, understands the speech addressed to him, then most likely there is no reason for concern.
/pervoe-slovo/
How to help a child speak faster
If a mother had complications during pregnancy or childbirth, such as toxicosis, infectious diseases, asphyxia, then speech development is at risk. There are other signals that you need to respond to: for example, impaired reflexes of newborns, lack of cooing and babbling. If these signs are present, you need to contact a speech therapist, even if the baby is not yet two years old.
Next, I’ll tell you step by step what to do if parents notice any violations in the child’s speech and become worried.
What is the norm of speech development
In speech therapy there is the concept of "norm of speech development". In the table below, I described it by age stages. This information will help the mother analyze the child's speech and pay attention to speech defects in time, if any.
How children's speech should sound at different ages
| Age | The appearance of sounds | Vocabulary | Parts of speech | What the child can do | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-1 year | [a], [o], [y], [i] [p], [b], [m] | 20 words | Cry, coo, babble, first nouns | Performs simple requests | ||
| 2-3 years | [d], [n], [k], [g], [x] | 300 words | Nouns and verbs Can build a short sentence , for example "Mom, go!", ask a simple question and draw a conclusion | |||
| 3-4 years | [s], [s], [s], [s], [s], [ts]. Sounds differ in softness-hardness, deafness-voicedness Sounds differ in softness-hardness, deafness-voicedness | 800 words | Adds adjectives, pronouns and prepositions | Builds 3-4 word sentences | ||
| 4-5 years | [w], [w], [w], [w] | 20149 wordsAdverbs and numerals appear | Speaks in extended sentences, selects rhymes, composes poems and stories [p] | 5000 words | All parts of speech are present, the child uses them correctly | Can compose a story with a plot change. Owns intonation |
0—1 year
Appearance of sounds
[a], [o], [y], [u] [p], [b], [m]
Vocabulary
20 words
Parts of speech
Shouting, cooing, babbling, first nouns
What the child can do
Performs simple requests
2-3 years
Appearance of sounds
[d], [n], [k], [g], [x]
Vocabulary
300 words
Parts of speech
Nouns
What the child can do
Can build a short sentence, for example, “Mom, go!”, ask a simple question and draw a conclusion
3-4 years
Appearance of sounds
[s], [s], [s] , [s], [s], [c]. Sounds differ in softness-hardness, deafness-voicedness
Sounds differ in softness-hardness, deafness-voicedness
Vocabulary
800 words
Parts of speech
Adjectives, pronouns and prepositions added
What the child can do
Build sentences from 3-4 words
3 Appearance of sounds [w ], [w], [h], [u] Vocabulary 2000 words Parts of speech Adverbs and numerals appear What the child can do Speaks in extended sentences, selects rhymes and stories, composes 5—6 years Appearance of sounds The child pronounces all sounds normally, but [l], [l], [p], [p] may be absent Vocabulary 5000 words Parts of speech All parts of speech are present, the child uses them correctly What the child can do Can compose a story with a change in plot. Owns intonation Such norms are always averaged. Therefore, if during scheduled medical examinations, doctors did not reveal any deviations that could affect the development of the speech of a two-three-year-old child, but something is still bothering the mother, it is better to play it safe and make an appointment with a speech therapist. If the specialist did not find any problems, then the speech therapist should visit the second time when the child is 4-5 years old. A re-examination will allow you not to miss the violations that could have occurred after the first visit. Step 1 The choice of a specialist depends on the requests and capabilities of the parents. I advise you to choose according to the reviews of acquaintances and friends or look at the reviews on social networks. In extreme cases, you can always talk in person, form an opinion, and then decide whether you and your child will be comfortable working with this speech therapist. Here's how to get to your first consultation. Get a referral from a pediatrician. This can be done at the polyclinic at the place of residence - free of charge. However, not every clinic has a speech therapist. And if there is, then it will not be possible to get to him quickly: usually everything is scheduled for several weeks in advance. Contact the center of psychological, pedagogical, medical and social assistance in your area. Here, the examination is carried out in a complex way - that is, the child is examined by several specialists at once. It's free, but there may be a queue. /free-logoped/ How I got my son free classes with a speech therapist in kindergarten Enroll in a private speech therapy center. It will be possible to get to a specialist quickly, you can choose a convenient time. But I recommend monitoring the cost of services: the spread is quite large. Often the amount depends not only on the qualifications of the specialist, but also on the pricing policy of the center's management. Visit a private speech therapist. The services of private speech therapists are quite expensive, but the choice of specialists is large. As an example, I will give my prices: the initial twenty-minute consultation costs 300 R, then - 700 R for 30 minutes. Step 2 How is the appointment. First, the speech therapist asks the parents about the development of the child - starting with how the pregnancy proceeded and ending with today. He tries to learn more about his health and what worries his parents. To set the child in a friendly way, he offers game exercises and tasks. Speech therapy examination includes the analysis of speech and non-verbal mental functions - thinking, memory, attention, gross and fine motor skills. The duration of the diagnosis depends on how quickly the speech therapist managed to find contact with the child, and on the severity of the speech disorder. For example, to study general motor skills, I ask a child to jump in place, first on two legs, then on the left, then on the right. I enter the data into a speech card. And so on for each of the functions. /list/pediatr-deti/ 11 important questions for pediatrician Sergei Butriy What questions does the specialist ask? At the first consultation, the speech therapist will ask a lot of questions - this is normal. For example, a speech therapist may be interested in the conditions of upbringing - so he will find out in what social environment the child grows up and how it affects his speech development. An example from my experience: the idea of correct speech was disturbed in a small patient, he made many mistakes. It turned out that the cause was a bilingual nanny who spoke Russian with an accent to the child. The speech therapist may also be interested in the child's diet: whether he eats solid food, how he chews it. In my practice, there was a case when the child ate in the main puree. As a result, very weak muscles of the mouth and tongue. This, in turn, led to a violation of the pronunciation of many sounds. I had to work with a child who developed dyslalia - the so-called impaired sound pronunciation in those who have normal hearing and a healthy articulatory apparatus. /baby-dont-cry/ 4 crises of child development from birth to school Therefore, I emphasize once again: a specialist can and should ask all these questions. The more openly the parents cooperate in the examination, the more accurately the problem can be identified. What will happen after the examination. After the diagnosis, a speech therapist can refer you to a neurologist or defectologist - this should not be frightened. Many types of speech disorders, such as dysarthria, alalia, aphasia, are associated with damage to the central nervous system. Their accurate diagnosis is possible only through the joint efforts of a speech therapist and, for example, a neurologist, otolaryngologist, psychotherapist, ophthalmologist. Speech therapy work is effective only when combined with special treatment that stimulates the maturation of the central nervous system. Dysarthria - impaired pronunciation of words due to damage to the nervous system Alalia - absence or underdevelopment of speech in children with normal hearing and primary intact intelligence Aphasia - a disorder in which the ability to use one's own speech and / or understand is partially or completely lost addressed speech The specialist also fills out a speech card - a notebook with information about the child, and then draws conclusions about the speech disorder and draws up a plan for corrective work. 👍 If the child has no problems with speech, then the speech therapist will give parents general recommendations: learn poetry, read books together, talk. ❗ If there is a problem, then the specialist draws up a plan for corrective work, taking into account the specifics of speech impairment. Sometimes it can be everyday conversations, listening to music, but the main form of corrective work of a speech therapist with children is classes. I'll tell you more about this. /guide/books-for-children/ How to choose the perfect book for your child Step 3 Often, parents start taking their child to the speech therapist who has been examined. Polyclinic at the place of residence. Classes will be free, which is a plus. Of the minuses - you may have to visit them at an inconvenient time. In addition, such classes are often limited in time, they may not be enough to completely eliminate the violation. Center for psychological, pedagogical, medical and social assistance in your area. Free classes are also held here, which are clearly limited in time. There is a queue. Private speech therapy center. You can choose a convenient time to visit and study as much as you need. Typically, classes last from 30 to 60 minutes, their cost varies from 700 to 3000 RUR. Speech therapy garden. Classes in the garden are held regularly. In parallel, work is underway with other specialists: a psychologist, a neurologist, a defectologist. /list/atypical-kindergarten/ English with a native speaker and early career guidance: 10 kindergartens in Moscow with an atypical program Municipal kindergarten with a speech therapy group or speech center. Here, classes are also held free of charge and regularly. But speech therapists in general developmental kindergartens have a large workload, so the number of places is usually limited. And if the child needs the help of other specialists, they will most likely have to be sought in other institutions. Private speech therapist. The services of private speech therapists are quite expensive - from 1000 R. But the choice of specialists is large, and you can discuss the format of classes, for example, ask a specialist to conduct them at your home. Classes can be conducted both individually with a speech therapist, and as part of a group. The first option is more expensive, but more effective, since all attention and time is given to one child. If you decide to save money and study in a group, then you need to pay attention to the fact that all children have the same type of speech disorders. Usually there are 10-12 people in a group. It is worth considering that, despite similar problems, the success of some children in the group will be higher. But since the classes are joint, the speech therapist will not be able to devote more time to lagging behind children, so it will not be possible to force events. The content of the classes depends on the tasks set and on the stage of speech correction. Here is what a speech therapist usually does: To make it more interesting for the child to study, the specialist uses various aids - from puzzles to rpg games. /list/kids-dev-apps/ 14 educational apps for kids It is almost impossible to determine the time it will take to solve a problem. This is very individual and depends on many factors: The same, at first glance, violation in two children will be eliminated at different times. For example, last year I studied with two preschoolers. They were both five years old, and they both did not pronounce the sound [r]. /list/pediatrics-2/ “Most often, a child does not need medicines”: 10 important questions to pediatrician Fedor Katasonov Speech correction is work, and sometimes not very pleasant. As a rule, a speech therapist devotes a lot of time to strengthening the muscles of the speech apparatus, pronouncing a large number of words with practicing various sounds. This is monotonous work, it is difficult and sometimes boring for children to do it. Therefore, they can be capricious and refuse to study. It is important for a parent to help the child, to be consistent and persistent, because the best assistant in speech therapy work is discipline. For example, with a child of four and a half years old, who had complex speech disorders, we practiced the production of the sound [w] and the stable fixation of the delivered sound [s] in words. I recommended that parents do articulation exercises daily with exercises aimed specifically at the sound [w]. And also - speech games using words with the sound [s]: "One-many", "Fourth extra" and others. Lost time only reinforces incorrect speech development. This is confirmed by statistics: about 60% of Russian schoolchildren come to the first grade with speech disorders, to which problems with writing and reading are added after. Therefore, the sooner parents start correcting mistakes in speech, the easier and faster it will be possible to achieve results.

 But I am familiar with speech therapists who charge 1500-2500 R per hour.
But I am familiar with speech therapists who charge 1500-2500 R per hour.
Speech disorders are often associated with causes that, at first glance, do not relate to speech itself: with the psychophysical development of the child, family and concomitant diseases, social and living conditions.
With the help of questions, we managed to find out the reason: the baby almost did not hear the correct speech, since the parents had serious hearing problems.
The task of a speech therapist is to achieve a long and smooth exhalation
The type of speech map depends on the age - 2-3 years, 4-7 years, as well as on violations - for children with stuttering, with general underdevelopment of speech, and so on. But they all represent a survey plan. At the end, the speech therapist issues a conclusion to the parents.
But it is not necessary to do this, the choice is up to the parents. This is where they also work with children who have speech problems.
It's free. But it is difficult to get into the speech therapy garden, there are not enough places for everyone. Therefore, usually only children with serious speech therapy problems are taken there.
How the classes go
How long does it take to achieve a result
The first boy managed to correct the sound pronunciation in eight sessions of 30 minutes, and the second - in nine months. It was a matter of the speech apparatus: the first boy had it normal, while the second had a shortened hyoid ligament.
How parents can help a child
You will have to work hard together with the child: you must follow all the recommendations and homework given by the speech therapist. These can be daily articulation exercises, tasks for working out the desired sound in words, phrases, sentences, tracking sound in colloquial speech.