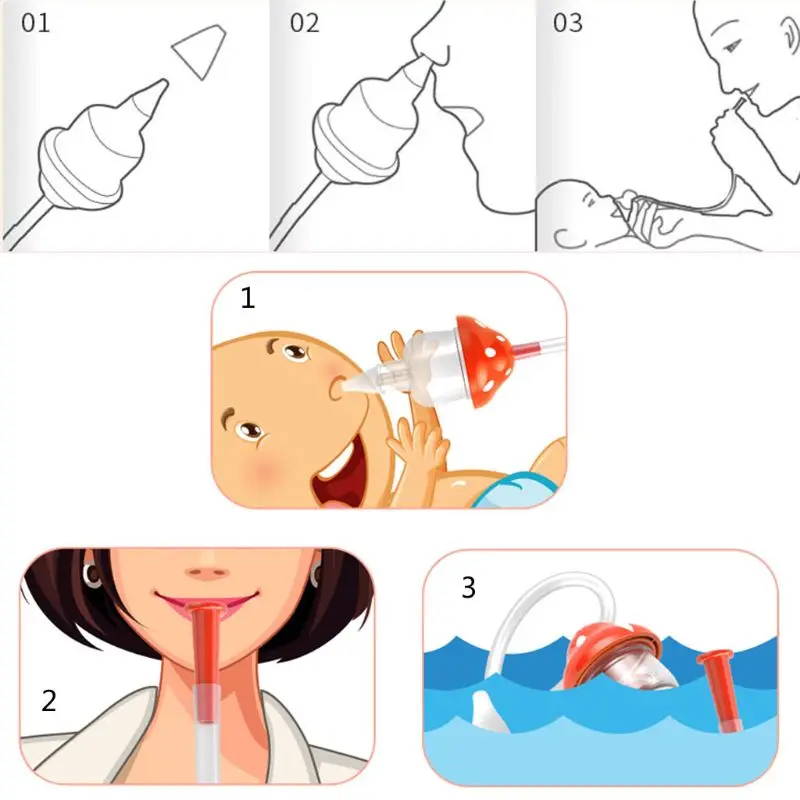
4 pound baby at 37 weeks
Small for Gestational Age | Cedars-Sinai
ABOUT CAUSES DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT NEXT STEPS
What does it mean to be small for gestational age?
Small for gestational age is a term used to describe babies who are smaller than usual for the number of weeks of pregnancy. These babies have birth weight below the 10th percentile. This means they are smaller than many other babies of the same gestational age. Many babies normally weigh more than 5 pounds, 13 ounces by the 37th week of pregnancy. Babies born weighing less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces are considered low birth weight.
What causes babies to be small for gestational age?
Some babies are small because their parents are small. But most babies who are small for gestational age have growth problems that happen during pregnancy. Many of these babies have a condition called intrauterine growth restriction. This happens when the unborn baby doesn’t get the nutrients and oxygen needed to grow and develop organs and tissues. This can begin at any time in pregnancy.
Growth restriction early in pregnancy (early onset) happens because of chromosome problems in the baby. It also happens because of disease in the mother,or severe problems with the placenta. Growth restriction is called late onset if it happens after week 32 of the pregnancy. It is usually related to other problems.
Who is at risk for being small for gestational age?
When the unborn baby doesn’t get enough oxygen or nutrients during pregnancy, the baby’s body and organs don't grow as much as they should. Some of the problems that cause babies to be small for gestational age limit how much blood flows through the placenta. This can cause the baby to get less oxygen than normal. This increases the baby’s risks during pregnancy and delivery, and later. Things that can cause babies to be small for gestational age are listed below.
Problems with the mother
- High blood pressure
- Chronic kidney disease
- Diabetes
- Heart disease or respiratory disease
- Malnutrition or anemia
- Infection
- Alcohol or drug use
- Cigarette smoking
- Weighing less than 100 pounds
Problems with the uterus and placenta
- Decreased blood flow in the uterus and placenta
- Placenta detaches from the uterus
- Placenta attaches low in the uterus
- Infection in the tissues around the baby
Problems with the developing baby
- Multiple pregnancy, such as twins or triplets
- Infection
- Birth defects
- Chromosome problems
What are the symptoms of small for gestational age babies?
Small for gestational age babies may look mature, but they are smaller than other babies of the same gestational age. They may be small all over, or they may be of normal length and size but have lower weight and body mass. These babies may be born:
These babies may be born:
- Premature. Before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- Full-term. Between 37 and 38 weeks (early term) through 41 weeks.
- Post-term. After 42 weeks of pregnancy.
Many small for gestational age babies have low birth weight. But not all are premature. They may not have the same problems as premature babies. Other babies, especially those with intrauterine growth restriction, may look thin and pale, and have loose, dry skin. The umbilical cord is often thin and dull-looking rather than shiny and fat.
How are small for gestational age babies diagnosed?
Babies with this problem are often diagnosed with intrauterine growth restriction before birth. During pregnancy, a baby’s size can be guessed in different ways. The height of the top of a mother’s uterus can be measured from the pubic bone. This measurement in centimeters usually links with the number of weeks of pregnancy after the 20th week. If the measurement is low for the number of weeks, then the baby may be smaller than expected.
Other tests used for diagnosis may include:
- Ultrasound to estimate the baby’s size
- Doppler flow to help check blood flow to the baby during pregnancy
- Mother’s weight gain to tell how a baby is growing during pregnancy
- Baby’s birth weight as compared with the gestational age once the baby is born. The healthcare provider may use a formula to figure out the baby’s body mass.
How are small for gestational age babies treated?
Treatment will depend on your child’s symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is.
Babies with this problem may be physically more mature than their small size would suggest. But they may be weak and less able to take large feedings or stay warm. Treatment may include:
- Temperature-controlled beds or incubators
- Tube feedings if the baby does not have a strong suck
- Blood tests to check for low blood sugar
- Watching oxygen levels
Babies who are also premature may have other needs.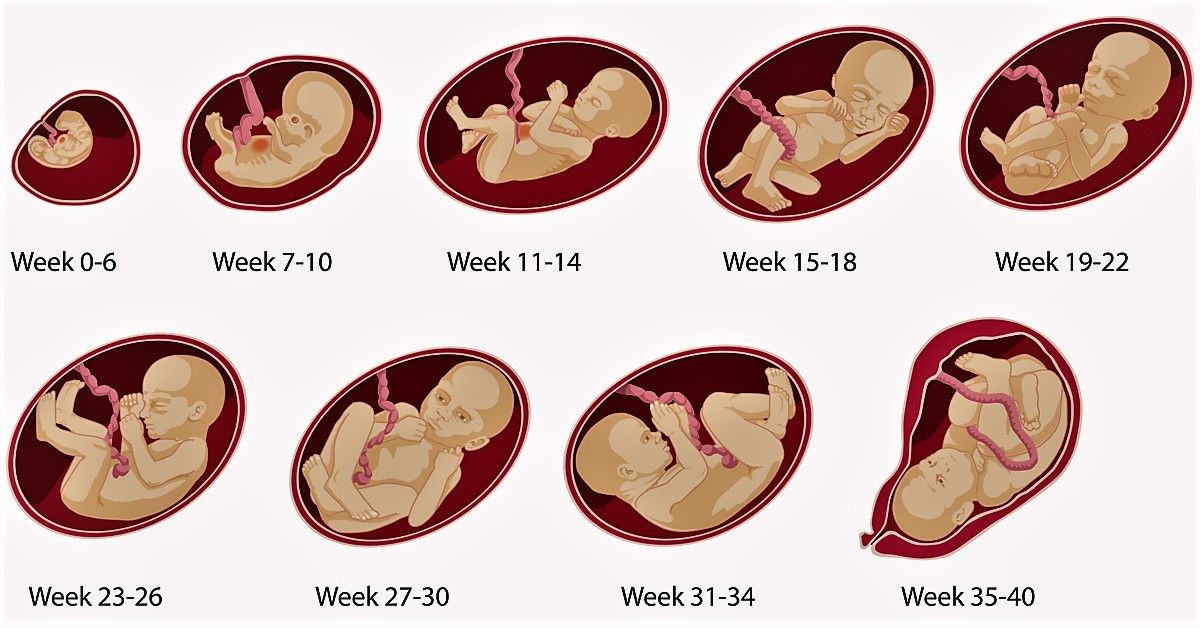 They may need oxygen and a breathing machine (ventilator).
They may need oxygen and a breathing machine (ventilator).
What are the complications of being small for gestational age?
Babies who are small for gestational age or who have intrauterine growth restriction may have problems at birth. These can include:
- Lower oxygen levels than normal
- Low Apgar scores
- Breathing in the first stools (meconium) passed in the womb. This can cause breathing problems.
- Low blood sugar
- Difficulty keeping a normal body temperature
- Too many red blood cells
Can small size for gestational age be prevented?
Prenatal care is important in all pregnancies. It is especially helpful to see any problems with the baby’s growth. For a healthy pregnancy, stop smoking if you smoke, and don't use drugs or alcohol while you are pregnant. Eating a healthy diet during pregnancy may also help.
Key points about small for gestational age babies
- Small for gestational age means a baby is smaller than expected for the number of weeks of pregnancy.

- Although some babies are small because their parents are small, most babies who are small for gestational age have growth problems that happen during pregnancy.
- When the unborn baby does not get enough oxygen or nutrients during pregnancy, he or she does not grow as much as normal.
- The condition is often suspected before birth.
- Prenatal care is important in all pregnancies. It is especially helpful to see any growth problems of the developing baby.
Next steps
Tips to help you get the most from a visit to your child’s healthcare provider:
- Know the reason for the visit and what you want to happen.
- Before your visit, write down questions you want answered.
- At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis, and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. Also write down any new instructions your provider gives you for your child.
- Know why a new medicine or treatment is prescribed and how it will help your child.
 Also know what the side effects are.
Also know what the side effects are. - Ask if your child’s condition can be treated in other ways.
- Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
- Know what to expect if your child does not take the medicine or have the test or procedure.
- If your child has a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for that visit.
- Know how you can contact your child’s provider after office hours. This is important if your child becomes ill and you have questions or need advice.
Fetal Chart from Baby My Baby
Free info for you and your baby! Text BABY to 511411
Search
Search for:
(crown to rump measurements)
| Gestational Age | Length (inches) | Weight (oz/lb) | Length (cm) | Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 weeks | 0.63 | 0.04 oz | 1.6 | 1 |
| 9 weeks | .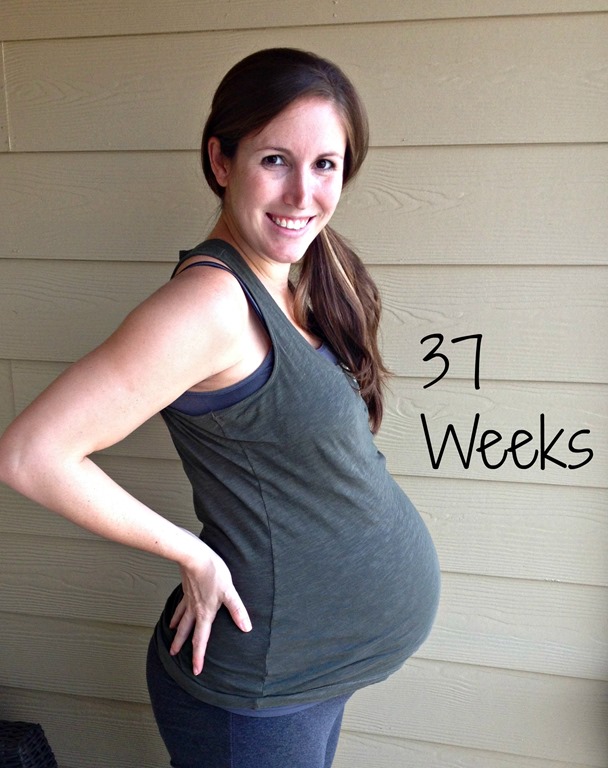 9 9 | 0.07 oz | 2.3 | 2 |
| 10 weeks | 1.22 | 0.14 oz | 3.1 | 4 |
| 11 weeks | 1.61 | 0.25 oz | 4.1 | 7 |
| 12 weeks | 2.13 | 0.49 oz | 5.4 | 14 |
| 13 weeks | 2.19 | 0.81 oz | 7.4 | 23 |
| 14 weeks | 3.42 | 1.52 oz | 8.7 | 43 |
| 15 weeks | 3.98 | 2.47 oz | 10.1 | 70 |
| 16 weeks | 4.57 | 3.53 oz | 11.6 | 100 |
| 17 weeks | 5.12 | 4.94 oz | 13 | 140 |
| 18 weeks | 5.59 | 6.70 oz | 14.2 | 190 |
| 19 weeks | 6.02 | 8.47 oz | 15.3 | 240 |
| 20 weeks | 6.46 | 10.58 oz | 16.4 | 300 |
| 21 weeks | 10. 51 51 | 12.70 oz | 26.7 | 360 |
| 22 weeks | 10.94 | 15.17 oz | 27.8 | 430 |
| 23 weeks | 11.38 | 1.10 lb | 28.9 | 501 |
| 24 weeks | 11.81 | 1.32 lb | 30 | 600 |
| 25 weeks | 13.62 | 1.46 lb | 34.6 | 660 |
| 26 weeks | 14.02 | 1.68 lb | 35.6 | 760 |
| 27 weeks | 14.41 | 1.93 lb | 36.6 | 875 |
| 28 weeks | 14.80 | 2.22 lb | 37.6 | 1005 |
| 29 weeks | 15.2 | 2.54 lb | 38.6 | 1153 |
| 30 weeks | 15.71 | 2.91 lb | 39.9 | 1319 |
| 31 weeks | 16.18 | 3.31 lb | 41.1 | 1502 |
| 32 weeks | 16.19 | 3.75 lb | 42.4 | 1702 |
| 33 weeks | 17. 20 20 | 4.23 lb | 43.7 | 1918 |
| 34 weeks | 17.72 | 4.73 lb | 45 | 2146 |
| 35 weeks | 18.19 | 5.25 lb | 46.2 | 2383 |
| 36 weeks | 18.66 | 5.78 lb | 47.4 | 2622 |
| 37 weeks | 19.13 | 6.30 lb | 48.6 | 2859 |
| 38 weeks | 19.61 | 6.80 lb | 49.8 | 3083 |
| 39 weeks | 19.96 | 7.25 lb | 50.7 | 3288 |
| 40 weeks | 20.16 | 7.63 lb | 51.2 | 3462 |
| 41 weeks | 20.35 | 7.93 lb | 51.7 | 3597 |
| 42 weeks | 20.28 | 8.12 lb | 51.5 | 3685 |
| 43 weeks | 20.20 | 8.19 lb | 51.3 | 3717 |
English
37-40 weeks of pregnancy
37th week of pregnancy for a baby
At 37 weeks of gestation, the baby is approximately 48 cm tall and weighs 2,600 g. facial features, pronounced cartilage tissue. The accumulation of subcutaneous fat at this stage of pregnancy makes the outline of the body softer and more rounded. The skin of the child is gradually smoothed out, it is no longer as pink as in the previous weeks of intrauterine development, the integument gradually brightens. The body of the baby is still abundantly covered with grease, but the amount of fluff is noticeably reduced, fluff hair remains only on the shoulders and back, in some babies they disappear almost completely.
facial features, pronounced cartilage tissue. The accumulation of subcutaneous fat at this stage of pregnancy makes the outline of the body softer and more rounded. The skin of the child is gradually smoothed out, it is no longer as pink as in the previous weeks of intrauterine development, the integument gradually brightens. The body of the baby is still abundantly covered with grease, but the amount of fluff is noticeably reduced, fluff hair remains only on the shoulders and back, in some babies they disappear almost completely.
Fat accumulation continues this week. It reaches a maximum of 15% of the total body weight of the child. It is difficult to overestimate the importance of adipose tissue for newborns, it is it that protects the child from overheating or hypothermia, since the baby's thermoregulation system after childbirth is still not sufficiently formed and continues to develop in the first months of a small person's life.
At this time, not only the volume of subcutaneous fat increases, but muscles and skeleton also develop intensively. The child constantly moves arms and legs. These unique workouts help increase muscle mass. Also, the baby makes rhythmic respiratory movements that strengthen the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm, and prepare the respiratory organs for childbirth.
The child constantly moves arms and legs. These unique workouts help increase muscle mass. Also, the baby makes rhythmic respiratory movements that strengthen the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm, and prepare the respiratory organs for childbirth.
Pregnant woman at 37 weeks
As the due date approaches, pregnant women begin to notice the appearance of their precursors, that is, certain signs, changes that occur under the influence of hormones. The body of a woman is preparing to give birth to a child, progesterone gives way to the dominant role of the birth hormone estrogen, the state of health of a pregnant woman changes.
From the 37th week, expectant mothers can observe the following changes:
- slight weight loss;
- abdominal shrinkage;
- the appearance of training or "false" contractions and the increase in their intensity;
- discharge of mucus from the cervix.
The nature of the stool changes, it becomes looser, aching pains in the lower back of varying intensity may appear, the fundus of the uterus descends. A woman notes some signs on her own, others are observed by a gynecologist during a routine examination.
A woman notes some signs on her own, others are observed by a gynecologist during a routine examination.
Harbingers do not appear in all women. Some expectant mothers notice only some of the above symptoms, while others observe signs of an impending birth not two or three weeks before their date, but just a few hours. Both the appearance of precursors at the 37th week and their absence are a variant of the norm and depend on the individual characteristics of the woman's body.
This week the woman's body is intensified preparation for the birth of a child. If the fetus is located correctly, head down, it gradually descends, goes to the lower part of the uterus, presses to the body and bends the limbs, intuitively taking the most comfortable position for passing the birth canal. The consequence of the movement of the fetus is the omission of the bottom of the uterus. The abdomen drops, the pressure on the diaphragm significantly decreases, the pregnant woman can breathe easily, the shortness of breath that haunted her in previous weeks disappears. The pressure on the stomach also decreases, heartburn disappears, a feeling of heaviness after eating and other unpleasant sensations. Moving the baby can put pressure on the bowels and bladder. A pregnant woman at this time often experiences the urge to urinate, may suffer from frequent loose stools. The reason for frequent bowel movements is not only the mechanical effect of the uterus on it, but also an increase in the content of estrogens in the body, hormones that contribute to the excretion of fluid. At the 37th week, the expectant mother can empty her intestines up to 3-4 times a day and at the same time observe a significant liquefaction of feces.
The pressure on the stomach also decreases, heartburn disappears, a feeling of heaviness after eating and other unpleasant sensations. Moving the baby can put pressure on the bowels and bladder. A pregnant woman at this time often experiences the urge to urinate, may suffer from frequent loose stools. The reason for frequent bowel movements is not only the mechanical effect of the uterus on it, but also an increase in the content of estrogens in the body, hormones that contribute to the excretion of fluid. At the 37th week, the expectant mother can empty her intestines up to 3-4 times a day and at the same time observe a significant liquefaction of feces.
38th week of pregnancy: the development of the future baby
At the 38th week, the fetus is fully formed, so childbirth at this time is no longer dangerous for both the mother and the baby. The weight of the fetus is about 3 kg, but this indicator can vary significantly for different babies, the weight depends on the individual characteristics of the mother and child, the structural features of the body and other factors. The body length of a newborn is approximately 50 cm.
The body length of a newborn is approximately 50 cm.
All organs and systems at 38 weeks of age are characterized by physiological and morphological maturity, they are fully ready for work. At this time, the child prepares for childbirth, makes respiratory movements and prepares the intercostal muscles for breathing. The tissues of the lungs are bathed in amniotic fluid, which helps maintain the right level of surfactant that coats the baby's lungs from the inside. All elements of the respiratory system are ready for use. With the first breath after birth, the alveoli begin to transfer oxygen from the air to the blood, gas exchange occurs, the respiratory and circulatory systems begin to work intensively.
Pregnant woman
The body of a pregnant woman continues to actively prepare for the birth of a baby, the estrogen content rapidly increases, and the progesterone level decreases significantly. A change in the hormonal background contributes to the softening of the tissues of the birth canal and cervix. Throughout pregnancy, the lumen of the cervical canal is closed by a plug of thick mucus, which protects the baby from infection, and the uterine cavity protects against the penetration of microorganisms dangerous to health. In the last weeks of pregnancy, the consistency of the mucus changes, it becomes more liquid and begins to gradually flow out. In some women, mucus leaves gradually, while in other women in labor at the same time. The discharge resembles colorless egg white in its consistency and appearance. Sometimes the mucus is colored pinkish, brown or yellow. The discharge of the cork is painless, a woman may experience a slight feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen. More abundant vaginal discharge than during the entire pregnancy can signal the passage of the cork.
Throughout pregnancy, the lumen of the cervical canal is closed by a plug of thick mucus, which protects the baby from infection, and the uterine cavity protects against the penetration of microorganisms dangerous to health. In the last weeks of pregnancy, the consistency of the mucus changes, it becomes more liquid and begins to gradually flow out. In some women, mucus leaves gradually, while in other women in labor at the same time. The discharge resembles colorless egg white in its consistency and appearance. Sometimes the mucus is colored pinkish, brown or yellow. The discharge of the cork is painless, a woman may experience a slight feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen. More abundant vaginal discharge than during the entire pregnancy can signal the passage of the cork.
A woman should carefully monitor the color and volume of discharge, since too much colorless discharge may indicate not only the cork has come off, but also be one of the symptoms of amniotic fluid leakage. Indicator pads and amnio tests or test strips will help determine the cause of the discharge. Pads are sold in many pharmacies and can be easily used at home. If amniotic fluid leakage is confirmed, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Indicator pads and amnio tests or test strips will help determine the cause of the discharge. Pads are sold in many pharmacies and can be easily used at home. If amniotic fluid leakage is confirmed, you should immediately consult a doctor.
After the mucus plug has passed, you should stop visiting the pool and swimming in open water, as the risk of infection of the child increases significantly. It is also necessary to exclude sexual contact.
39th week of pregnancy: what happens to the fetus?
At 39 weeks, the baby weighs 3100-3500 g and is 50-52 cm tall. Height and weight are very relative and can vary significantly. The baby is rapidly preparing for the most important test of his life - birth, which requires endurance and considerable effort. During this period of pregnancy, the size and weight of the child's adrenal glands, that is, the glands of the endocrine system, which are responsible for the reaction of the human body to stress factors, increase. It is the hormones adrenaline and norepinephrine produced by the adrenal glands that help the child quickly adapt to new temperature conditions, tactile, sound and light impulses.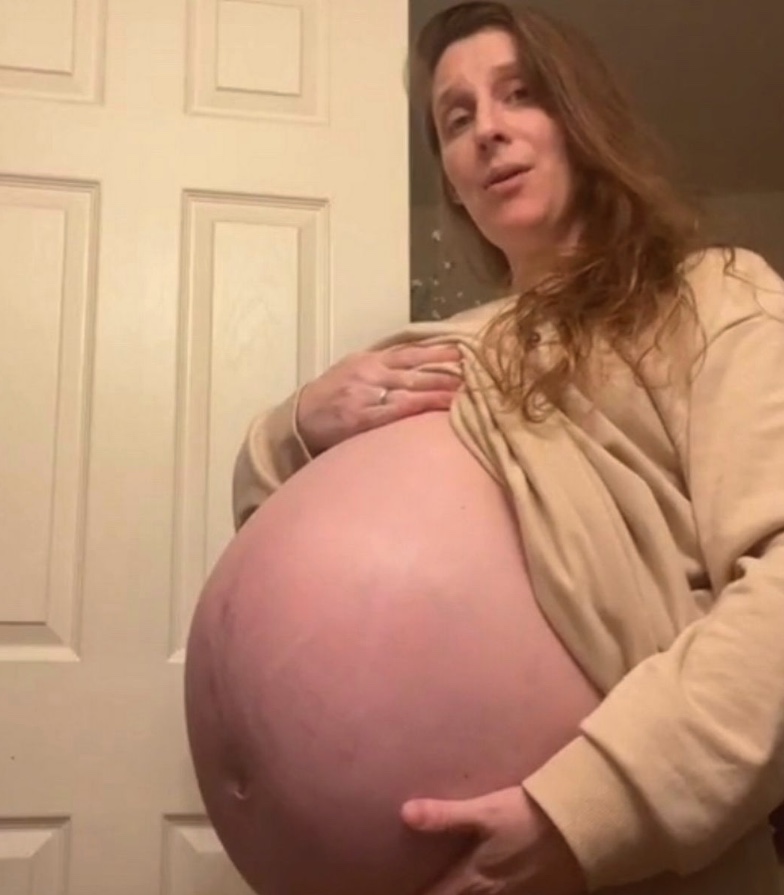
All the senses of the baby are developed at 39 weeks. Within a few moments after birth, the baby can focus his eyes, he reacts to bright light and moving objects, many scientists claim that newborns distinguish colors, see the faces of parents and doctors. The hearing of the baby in the last weeks of fetal life is also fully developed; after birth, he reacts to loud sounds and noise. A newborn baby is able to determine the main shades of taste, recognize sour, bitter, sweet and salty.
In the womb, the baby is in an aquatic environment that minimizes contact. Immediately after birth, the baby experiences many tactile sensations, unlike intrauterine life, he feels the touch of his mother's hands and diapers, towels, dressings and other materials. Babies especially like the touch of skin to skin, so in a modern maternity hospital, newborns must be laid out on their mother's stomach even before cutting the umbilical cord. The child adapts to the new environment more easily, feels protected. Laying out a child has not only a psychological aspect, since it contributes to the colonization of microorganisms from the mother's skin to the skin and mucous membranes of the baby, and increases its immunity.
Laying out a child has not only a psychological aspect, since it contributes to the colonization of microorganisms from the mother's skin to the skin and mucous membranes of the baby, and increases its immunity.
Pregnant woman
In the last weeks of pregnancy, the expectant mother strives to prepare her apartment or house as much as possible for the arrival of a new family member. Scientists call this sign of impending birth the nesting syndrome. Many women observe signs of the syndrome from the thirtieth week of pregnancy, however, nesting reaches its maximum point at the 39-40th week. Pregnant women tend to do general cleaning and repairs, re-paste the wallpaper and purchase a lot of new things that, in their opinion, are simply necessary in the house. After giving birth, many purchases are puzzling. The reason for this behavior is an increase in the level of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the body. These hormones are produced by the adrenal glands, they are necessary not only for the woman, but also for the baby to prepare for the upcoming birth.
40th week of pregnancy: how does the baby develop?
40 weeks - term pregnancy. The weight of a child who was born at such a period ranges from 2,600 g to 4,400 g, and his body length is 48-53 cm. These indicators are very arbitrary, since miniature babies weighing 2,600 g and real heroes are born at 40 weeks, whose body weight approaches 5,000 g. The length of the newborns can also vary from 45 to 55 cm.
Most women give birth exactly at 40 weeks. At this time, the baby is completely ready for birth, it meets all the parameters of a full-term baby. Before childbirth, the child closely presses the arms and legs to the body, bends the head as much as possible and presses against the exit from the uterus. This position allows you to make it possible to pass the birth canal with the narrowest part of the skull. In the course of labor, with each contraction, the child gradually moves down, he does not move in a straight line, but makes helical-translational movements, as if screwing into the mother's birth canal. During the progress of the newborn, the complete descent of his head, the cervix fully opens. This is followed by attempts, that is, contractions of the uterus, which advance the child through the birth canal. Gradually, the head of the baby is shown, and after it - his torso. Childbirth is a complex mechanism that is aimed not only at the safe passage of the birth canal by the child, protecting him from accidental injuries due to increased pressure, but also at preventing ruptures of the woman's soft tissues.
During the progress of the newborn, the complete descent of his head, the cervix fully opens. This is followed by attempts, that is, contractions of the uterus, which advance the child through the birth canal. Gradually, the head of the baby is shown, and after it - his torso. Childbirth is a complex mechanism that is aimed not only at the safe passage of the birth canal by the child, protecting him from accidental injuries due to increased pressure, but also at preventing ruptures of the woman's soft tissues.
Pregnant woman
The long wait for meeting her unborn child is coming to an end, and the 40th week of pregnancy is the last for most women. Every day, the anxiety of the expectant mother increases, a long wait affects the mood and well-being. Women strive to have a baby as soon as possible so that pregnancy and painful contractions are a thing of the past. Every pregnant woman dreams of meeting a baby, wants to hug him to her chest and stroke the delicate head.
Many women, especially primiparas, are afraid that labor will begin unnoticed, but such cases are extremely rare. A woman feels the onset of childbirth, feels regular contractions, which are repeated at regular intervals and gradually increase, the time interval between them is reduced.
A woman feels the onset of childbirth, feels regular contractions, which are repeated at regular intervals and gradually increase, the time interval between them is reduced.
Labor may be preceded by prenatal rupture of amniotic fluid, which occurs in a certain percentage of women in labor. After the waters break, contractions may be quite weak or completely absent. Regardless of the intensity of contractions, the outpouring of water is one of the signs of the onset of labor and requires immediate contact with specialists, hospitalization of a woman in a maternity hospital or hospital, since when the water breaks, the integrity of the bladder is violated and the risk of penetration of microorganisms dangerous to the health of the child increases into the uterine cavity. It is important that after the water breaks, the baby is born in a maximum of 10-12 hours.
A pregnant woman should properly tune in to childbirth, concentrate on the desired result and believe in her own strength, fulfill the task assigned to her by nature.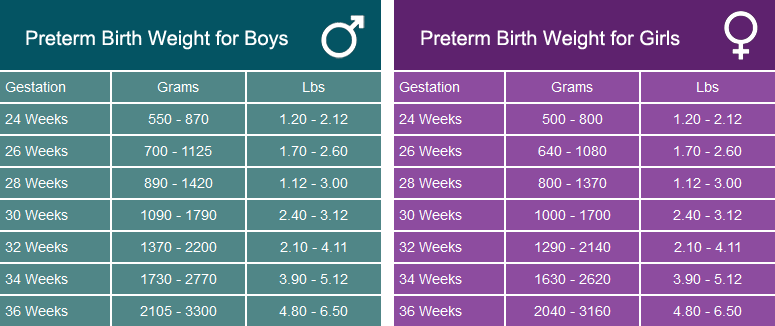 The right psychological attitude and theoretical knowledge will help a woman become a mother, successfully go through all the stages of childbirth and press the long-awaited child to her heart.
The right psychological attitude and theoretical knowledge will help a woman become a mother, successfully go through all the stages of childbirth and press the long-awaited child to her heart.
what happens to the baby and mother, fetus, discharge, movements, stomach
Table of contents
- Mom
- General condition
- Physical activity
- Belly at 37 weeks pregnant
- Weight gain
- Precursors of labor in primiparous and multiparous
- What tests should be done at week 37
- False contractions
- How to take care of yourself
- child
- Fetus 37 weeks pregnant
- Child development
- Child sizes
- Baby weight at 37 weeks pregnant
- Movement at 37 weeks of pregnancy
MAMA
General condition
The 37th obstetric week of pregnancy began, which is approximately 35 weeks from the expected date of conception. If you count from the first day of your last period, which is the most common method of determining your gestational age, you'll be in your tenth month.
If you count from the first day of your last period, which is the most common method of determining your gestational age, you'll be in your tenth month.
There are only a few weeks left before the birth, and maybe a few days. Therefore, it is not surprising that all your thoughts are now connected with the expectation of this event.
Preparing for childbirth with an experienced obstetrician-gynecologist
Physical activity
It is becoming more and more difficult to maintain motor activity: shortness of breath and increased fatigue, heaviness in the legs and a change in gait make themselves felt. And yet, it is critically important for mom and baby to be in the fresh air. Try to walk at least 20-30 minutes a day. Better in the evenings: this will improve the quality of sleep. It is useful to perform breathing exercises and a small set of exercises or yoga under the guidance of a trainer who specializes in working with pregnant women. Breathing exercises in standing, sitting "Turkish" and in the knee-hand or elbow position will improve blood flow and prevent diastasis of the abdominal muscles.
Breathing exercises in standing, sitting "Turkish" and in the knee-hand or elbow position will improve blood flow and prevent diastasis of the abdominal muscles.
Belly at 37 weeks pregnant
At 37 weeks, some women feel the drooping of the abdomen. Before, he propped up the diaphragm and squeezed the stomach and lungs so hard that my mother was tormented by heartburn and shortness of breath. Now the baby's head has sunk lower into the mother's pelvis, and sometimes this is noticeable not only to the woman herself, but even to her relatives. Breathing becomes easier, heartburn and belching go away, or at least become less painful, but now you need to go to the toilet more often, because the baby's head is pressing on the pelvic area. A slight increase in temperature at 37 weeks of gestation (up to 37-37.5 0 ) may be a physiological phenomenon associated with an increase in the volume of circulating blood and other fluids. However, this should be reported to your doctor at your next visit.
Weight gain
Usually, by the 37th week of pregnancy, the expectant mother gains a total of 12-12.5 kg. However, at this stage, there may be no weekly increase and even a slight weight loss. This is due to the fact that excess fluid leaves the body, and swelling decreases. Weight loss at week 37 should not be abrupt (within 1-1.2 kg).
Harbingers of childbirth in primiparous and multiparous
Another harbinger of childbirth may be the discharge of the mucous plug. The substance that covered the cervical canal throughout pregnancy has a jelly-like consistency, light or pink in color, sometimes even streaked with blood. If you notice this kind of discharge during pregnancy at 37 weeks, this is the norm. In itself, the discharge of the mucous plug is not a signal of the onset of labor, so there is no need to urgently go to the hospital, it is enough to inform the doctor about this at the next examination. In women who are expecting their first child, such harbingers of childbirth as prolapse of the abdomen, weight loss, cork discharge, as a rule, are more pronounced than in multiparous ones. Each pregnancy is individual, between the precursors and childbirth in one case it can take several weeks, and in the other - a couple of hours.
Each pregnancy is individual, between the precursors and childbirth in one case it can take several weeks, and in the other - a couple of hours.
What tests should be done at week 37
At this time, the expectant mother visits her doctor every week. Usually, the examination is accompanied by CTG (cardiotocography) to assess the fetal heart function. The same procedure is performed in the first stage of labor (during contractions), which allows the doctor to monitor the baby's condition in real time. It is very important to tell the obstetrician-gynecologist about your health in as much detail as possible. Then, if necessary, he will be able to prescribe additional tests or studies.
False contractions
At this time, many mothers are faced with such a phenomenon as false contractions. Drawing pains in the lower abdomen, reminiscent of the sensations during menstruation, are irregular and pass by themselves - this is the difference between training contractions and the true onset of labor. If your stomach is pulling at the 37th week of pregnancy, arm yourself with a stopwatch: they begin to measure the contraction from the onset of pain, note its duration and time until the next contraction. If the contractions are felt regularly, and each time they become stronger, longer and with a shorter interval of time, this is no longer a “training”, but the beginning of childbirth.
If your stomach is pulling at the 37th week of pregnancy, arm yourself with a stopwatch: they begin to measure the contraction from the onset of pain, note its duration and time until the next contraction. If the contractions are felt regularly, and each time they become stronger, longer and with a shorter interval of time, this is no longer a “training”, but the beginning of childbirth.
How to take care of yourself
To stop the discomfort from false contractions, try massage or self-massage (if there is no one to help you at this moment) and breathing techniques. It is believed that the tension of the facial muscles contributes to the aggravation of pain, so it is better to relax the mouth, forehead, eyes, although this is not easy during contractions. A warm bath or shower also improves well-being, swaying movements in the knee-elbow position (“on all fours”). You can choose the natural pain relief techniques that are right for you by using training contractions as a “birthing rehearsal”.
BABY
Development of the child's organs
Childbirth can begin at any time, because the fetus has already formed by the 37th week of pregnancy, now it is gaining weight and saving up strength for the birth. The baby's bones remain soft enough to allow safe passage through the birth canal. The digestive system is already slowly working: the baby can swallow amniotic fluid, and the so-called meconium (original feces) accumulates in his intestines. The child's vision and hearing are already well developed, and facial expressions and gestures become more diverse: the baby frowns, grimace, touches his face, back of the head and the inside of the uterus. At such moments, on the surface of the abdomen, you can see the distinct outlines of the palm.
Height and weight of the child
The baby reaches a height of 48-50 centimeters, the weight of the child at 37 weeks of gestation approaches 3 kilograms. However, now individual factors are already very noticeable: the baby can be slim, medium or large build.