How to take care of gestational diabetes
How to Treat Gestational Diabetes
Gestational Diabetes
Because gestational diabetes can hurt you and your baby, it is critical to start treatment quickly.
Treatment for gestational diabetes aims to keep blood glucose levels equal to those of pregnant women who don't have gestational diabetes. The treatment always includes special meal plans and scheduled physical activity, and it may also include daily blood glucose testing and insulin injections.
If you're testing your blood glucose, the American Diabetes Association suggests the following targets for women who develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy. More or less stringent glycemic goals may be appropriate for each individual.
- Before a meal (preprandial): 95 mg/dl or less
- One hour after a meal (postprandial): 140 mg/dl or less
- Two hours after a meal (postprandial): 120 mg/dl or less
If you’re diagnosed with gestational diabetes, you will need help from your doctor, nurse educator and other members of your health care team so that your treatment can change as needed. For you as the mother-to-be, proper treatment helps lower the risk of a cesarean section birth that very large babies may require.
Sticking with your treatment plan will give you a healthy pregnancy and birth, and may help your baby avoid poor health in the future.
Keeping worry in perspective
While gestational diabetes is a cause for concern, the good news is that you and your health care team—your doctor, obstetrician, nurse educator and dietitian—work together to lower your high blood glucose levels. And with this help, you can turn your concern into a healthy pregnancy for you and a healthy start for your baby.
Looking ahead
Gestational diabetes usually goes away after pregnancy. But once you've had gestational diabetes, your chances are two in three that it will return in future pregnancies. In a few women, however, pregnancy uncovers type 1 or type 2 diabetes. It is hard to tell whether these women have gestational diabetes or have just started showing their diabetes during pregnancy, but they will need to continue diabetes treatment after pregnancy.
Many women who have gestational diabetes go on to develop type 2 diabetes years later. There seems to be a link between the tendency to have gestational diabetes and type 2 diabetes since both involve insulin resistance. However, certain basic lifestyle changes may help prevent diabetes after gestational diabetes. Learn about prevention.
Lower your risk by losing weight
Are you more than 20% over your ideal body weight? Losing even a few pounds can help you avoid developing type 2 diabetes.
Making healthy food choicesFollow simple daily guidelines like eating a variety of foods including fresh fruits and vegetables, limiting fat intake to 30% or less of daily calories and watching your portion sizes. Healthy eating habits can go a long way in preventing diabetes and other health problems.
ExercisingRegular exercise allows your body to use glucose without extra insulin. This helps combat insulin resistance and is what makes exercise helpful to people with diabetes. However, it is important to check with your doctor before starting an exercise program.
However, it is important to check with your doctor before starting an exercise program.
More on losing weight
Gestational Diabetes and Pregnancy | CDC
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that is first seen in a pregnant woman who did not have diabetes before she was pregnant. Some women have more than one pregnancy affected by gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes usually shows up in the middle of pregnancy. Doctors most often test for it between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Often gestational diabetes can be managed through eating healthy foods and regular exercise. Sometimes a woman with gestational diabetes must also take insulin.
Learn more about Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support Services
Blood sugar that is not well controlled in a woman with gestational diabetes can lead to problems for the pregnant woman and the baby:
An Extra-Large Baby
Diabetes that is not well controlled causes the baby’s blood sugar to be high. The baby is “overfed” and grows extra-large. Besides causing discomfort to the woman during the last few months of pregnancy, an extra-large baby can lead to problems during delivery for both the mother and the baby. The mother might need a C-Section to deliver the baby. The baby can be born with nerve damage due to pressure on the shoulder during delivery.
The baby is “overfed” and grows extra-large. Besides causing discomfort to the woman during the last few months of pregnancy, an extra-large baby can lead to problems during delivery for both the mother and the baby. The mother might need a C-Section to deliver the baby. The baby can be born with nerve damage due to pressure on the shoulder during delivery.
C-Section (Cesarean Section)
A C-section is an operation to deliver the baby through the mother’s belly. A woman who has diabetes that is not well controlled has a higher chance of needing a C-section to deliver the baby. When the baby is delivered by a C-section, it takes longer for the woman to recover from childbirth.
High Blood Pressure (Preeclampsia)
When a pregnant woman has high blood pressure, protein in her urine, and often swelling in fingers and toes that doesn’t go away, she might have preeclampsia. It is a serious problem that needs to be watched closely and managed by her doctor. High blood pressure can cause harm to both the woman and her unborn baby. It might lead to the baby being born early and also could cause seizures or a stroke (a blood clot or a bleed in the brain that can lead to brain damage) in the woman during labor and delivery. Women with diabetes have high blood pressure more often than women without diabetes.
It might lead to the baby being born early and also could cause seizures or a stroke (a blood clot or a bleed in the brain that can lead to brain damage) in the woman during labor and delivery. Women with diabetes have high blood pressure more often than women without diabetes.
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
People with diabetes who take insulin or other diabetes medications can develop blood sugar that is too low. Low blood sugar can be very serious, and even fatal, if not treated quickly. Seriously low blood sugar can be avoided if women watch their blood sugar closely and treat low blood sugar early.
If a woman’s diabetes was not well controlled during pregnancy, her baby can very quickly develop low blood sugar after birth. The baby’s blood sugar must be watched for several hours after delivery.
5 Tips for Women with Gestational Diabetes
- Eat Healthy Foods
Eat healthy foods from a meal plan made for a person with diabetes. A dietitian can help you create a healthy meal plan.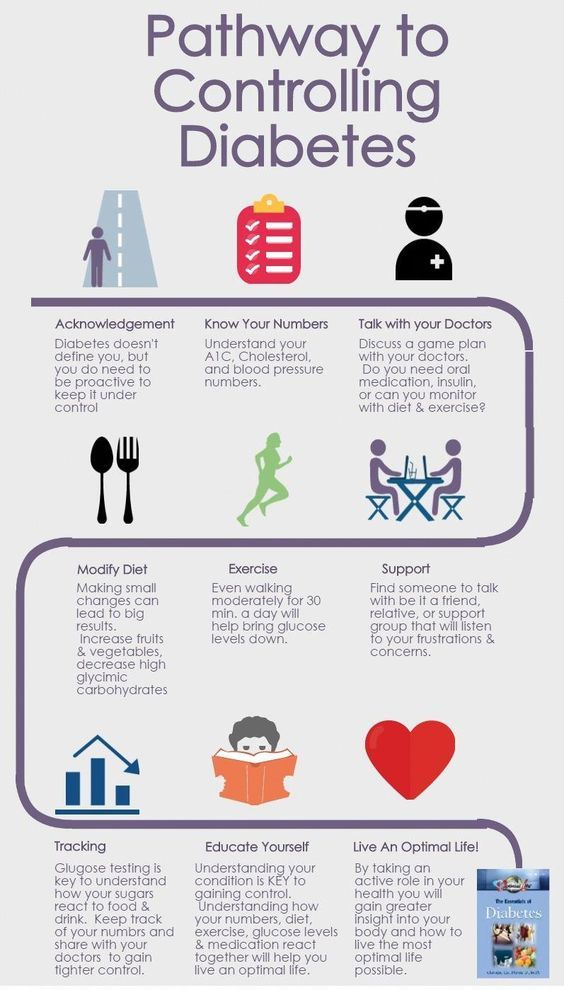 Learn more about diabetes meal planning.
Learn more about diabetes meal planning. - A dietitian can also help you learn how to control your blood sugar while you are pregnant. To find a registered dietician near you, please visit The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics website.
- Exercise Regularly
Exercise is another way to keep blood sugar under control. It helps to balance food intake. After checking with your doctor, you can exercise regularly during and after pregnancy. Get at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity at least five days a week. This could be brisk walking, swimming, or actively playing with children.Learn more about physical activity during pregnancy » - Monitor Blood Sugar Often
Because pregnancy causes the body’s need for energy to change, blood sugar levels can change very quickly. Check your blood sugar often, as directed by your doctor. - Take Insulin, If Needed
Sometimes a woman with gestational diabetes must take insulin. If insulin is ordered by your doctor, take it as directed in order to help keep blood sugar under control.
If insulin is ordered by your doctor, take it as directed in order to help keep blood sugar under control. - Get Tested for Diabetes after Pregnancy
Get tested for diabetes 6 to 12 weeks after your baby is born, and then every 1 to 3 years.For most women with gestational diabetes, the diabetes goes away soon after delivery. When it does not go away, the diabetes is called type 2 diabetes. Even if the diabetes does go away after the baby is born, half of all women who had gestational diabetes develop type 2 diabetes later. It’s important for a woman who has had gestational diabetes to continue to exercise and eat a healthy diet after pregnancy to prevent or delay getting type 2 diabetes. She should also remind her doctor to check her blood sugar every 1 to 3 years.
Women who had gestational diabetes or who develop prediabetes can also learn more about the National Diabetes Prevention Program (National DPP), CDC-recognized lifestyle change programs.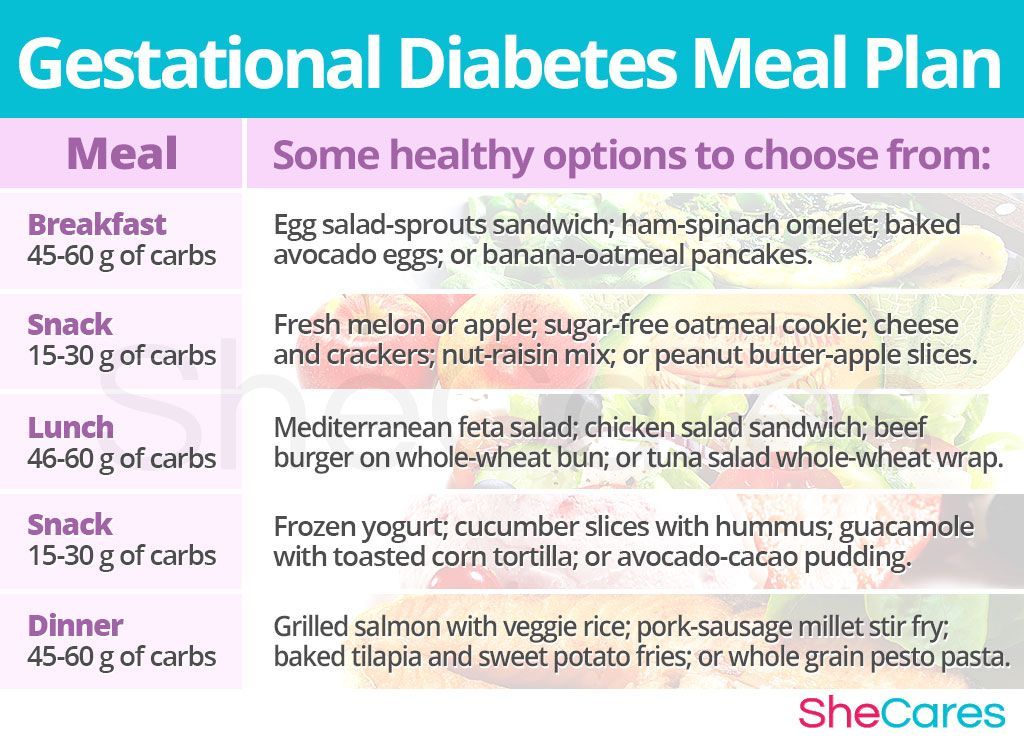 To find a CDC-recognized lifestyle change class near you, or join one of the online programs.
To find a CDC-recognized lifestyle change class near you, or join one of the online programs.
More Information
Gestational Diabetes and Pregnancy [PDF – 1 MB]
View, download, and print this brochure about gestational diabetes and pregnancy.
For more information on gestational diabetes, visit the American Diabetes Association’s website.
- Diabetes
- Before Pregnancy
- Healthy Pregnancy
- Birth Defects
- CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities
Gestational diabetes in pregnancy - treatment and diagnosis of diabetes in pregnant women in Moscow, Clinical Hospital on Yauza
Consult a gynecologist
Service in two languages: Russian, English.
Leave your phone number and we will call you back.
Contents
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Specialists of the Yauza Clinical Hospital diagnose and treat gestational diabetes and its complications. For a comfortable pregnancy and the safety of the expectant mother and baby, we exercise strict control over the blood sugar level of a pregnant woman, if necessary, prescribe a specially designed diet and medications.
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
- About 7% of pregnant women have manifestations of gestational diabetes. In 50% of cases, the disease is asymptomatic
- Gestational diabetes in pregnancy significantly increases the risk of pregnancy complications for both mother and fetus
- Perinatal mortality increases by 2-3% with a combination of diabetes mellitus and pregnancy
Pregnancy diabetes (gestational diabetes) is an increase in blood glucose that first occurs during pregnancy but is not high enough to warrant a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. These are hidden disorders of carbohydrate metabolism that threaten to develop into diabetes mellitus.
These are hidden disorders of carbohydrate metabolism that threaten to develop into diabetes mellitus.
Norm of glucose (sugar) in the blood of a pregnant woman
During pregnancy, all women experience changes in insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance. This is fine. The difference between the norm and pathology in the degree of change.
Blood tests for diabetes during pregnancy - norm and pathology
- If the test of venous blood taken on an empty stomach shows a glucose level of more than 5.1 mmol / l, this is the norm for pregnant women.
- From 5.1 to 7.0 mmol/l - gestational diabetes.
- If 7.0 mmol / l or more - diabetes mellitus.
- Testing capillary blood (taken from a fingerstick) for the diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus is not recommended.
- If during an oral glucose tolerance test (when 75 g of glucose is taken orally during the study) after an hour the glucose level is more than 10.
 0 mmol/l, and after two hours the blood glucose level is in the range of 7.8-8.5 mmol/l - then for pregnant women this is a normal indicator.
0 mmol/l, and after two hours the blood glucose level is in the range of 7.8-8.5 mmol/l - then for pregnant women this is a normal indicator.
To better understand what gestational diabetes, or diabetes in pregnancy, is, you need to talk a little about hormonal changes in the body in pregnant women.
Causes of gestational diabetes
Hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy are associated with increased production of large amounts of steroid hormones. Some of them, such as cortisol and progesterone, have a significant effect on cell receptors, increasing their resistance to insulin.
This leads to an increase in blood glucose levels and requires a significant increase in insulin production by the pancreas. In cases where the compensatory capacity of the pancreas is not enough, sugar metabolism gets out of control and a condition called gestational diabetes or gestational diabetes develops.
This condition occurs quite often. Between 3 and 10% of pregnant women develop pathological insulin resistance leading to gestational diabetes.
Unlike diabetes mellitus diagnosed before pregnancy, pathological insulin resistance that occurs during pregnancy does not cause fetal malformations and in most cases does not require insulin treatment. But, nevertheless, uncompensated gestational diabetes can significantly complicate the course of pregnancy.
Specialists of the Yauza Clinical Hospital diagnose, treat and prevent diabetes in pregnant women and its complications, such as impaired fetal growth. The doctors of the Clinical Hospital on the Yauza strictly control the blood sugar level of a pregnant woman, if necessary, prescribe a specially designed diet. This ensures a comfortable pregnancy and the safety of the expectant mother and baby.
Pregnancy diabetes - consequences for the child
Large disproportionate fruit. The most important and frequent complication of gestational diabetes is fetal growth failure. Developing in conditions of increased blood glucose levels, which penetrate the fetoplacental barrier, the fetus is forced to compensate for the increased sugar level with its own insulin. Due to the fact that the structure of insulin and growth hormone are very similar, high levels of insulin stimulate the growth of the fetus. The problem is that a large fetus develops. In such a fetus, body proportions differ from those of normally developing newborns, in which the volume of the head is larger than the volume of the shoulder girdle. In fetuses with uncompensated gestational diabetes, the size of the shoulder girdle predominates, and the size of the abdomen increases. This leads to the fact that during childbirth after the fetus's head passes through the birth canal, the shoulders can get stuck (shoulder dystocia) and the child, along with the mother, can be severely injured or die.
Due to the fact that the structure of insulin and growth hormone are very similar, high levels of insulin stimulate the growth of the fetus. The problem is that a large fetus develops. In such a fetus, body proportions differ from those of normally developing newborns, in which the volume of the head is larger than the volume of the shoulder girdle. In fetuses with uncompensated gestational diabetes, the size of the shoulder girdle predominates, and the size of the abdomen increases. This leads to the fact that during childbirth after the fetus's head passes through the birth canal, the shoulders can get stuck (shoulder dystocia) and the child, along with the mother, can be severely injured or die.
Polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios. In addition, in gestational diabetes, the balance of the amount of amniotic fluid can be disturbed and either polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios develops. This is a serious risk factor for intrauterine fetal death or premature birth.
Underdevelopment of the lungs. In gestational diabetes, the lungs of the fetus mature later, as the production of surfactant (a special lubrication of the inner walls of the alveoli, where oxygen is exchanged in the lungs) is disrupted. Therefore, premature birth in gestational diabetes is especially dangerous.
Hypoglycemia and metabolic disorders in the fetus. Due to the constant increased production of its own insulin during pregnancy, immediately after birth, the child is in a state of hypoglycemia with electrolyte imbalance, which threatens his life.
All this dictates the need for the earliest possible detection of gestational diabetes in pregnant women, the level of sugar in the blood of a pregnant woman and to prevent the development of complications.
.
Diagnosis of diabetes in pregnant women at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
Signs of diabetes in pregnant women
Gestational diabetes in pregnancy is not usually associated with the classic symptoms of diabetes, such as thirst or excessive urination (polyuria).
Pregnancy tests for diabetes mellitus
First phase. At the first visit of a pregnant woman to a doctor at any time, she is tested for glucose levels in venous blood - fasting glucose, regardless of food intake, glycated hemoglobin. This is the first phase of research to detect diabetes mellitus or gestational diabetes in pregnant women. If diabetes mellitus is detected, the patient is referred for observation and treatment to an endocrinologist.
Second phase. For a period of 24-28 weeks, all patients who did not show identified disorders of carbohydrate metabolism at the first study are called for a glucose tolerance test (PGTT) to detect "hidden diabetes". This is done because the occurrence of gestational diabetes is associated with the development of insulin resistance under the influence of hormones produced by the placenta. Therefore, in the vast majority of cases, gestational diabetes develops in the second half of pregnancy after 24 weeks, when there is a peak in the production of placental hormones.
Glucose tolerance test
It is carried out to detect pathological insulin resistance, characteristic of latent diabetes in pregnant women. Pregnant women undergo a two-hour test, only in the laboratory.
During the 3 days leading up to the test, the woman should eat her usual diet, including carbohydrates (>150 g of carbohydrates per day), maintain her usual physical activity. The evening before testing, dinner should include 30-50 grams of carbohydrates.
On the day of the study, before the analysis, you should not smoke and take medications that can affect the level of glucose (vitamins, glucocorticoid hormones, iron preparations, which include carbohydrates, beta-agonists, beta-blockers). You can drink water.
Venous blood is taken on an empty stomach (after 8-14 hours of fasting, usually in the morning, before breakfast).
Then the patient takes a glucose solution (75 g).
And they take blood in an hour and two after the sugar load. Normally, the level of glucose in the blood after a sugar load should not exceed an hour later - 10 mmol / l, after 2 hours - 8.5 mmol / l.
Normally, the level of glucose in the blood after a sugar load should not exceed an hour later - 10 mmol / l, after 2 hours - 8.5 mmol / l.
If manifest diabetes mellitus is detected, the patient is referred to an endocrinologist, gestational diabetes mellitus is treated by an obstetrician-gynecologist or therapist.
Glucose tolerance test contraindications
- Strict bed rest for a pregnant woman (until doctor's approval).
- Pronounced toxicosis of pregnant women (with nausea and vomiting).
- Acute infectious or inflammatory disease.
- Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis.
- Dumping syndrome (syndrome of resected stomach).
Prenatal diabetes monitoring
Blood glucose monitoring, self-monitoring diary
When diagnosing gestational diabetes, it is necessary to establish strict control of sugar levels throughout the subsequent pregnancy and during childbirth. To do this, regularly examine the blood for sugar (glucose).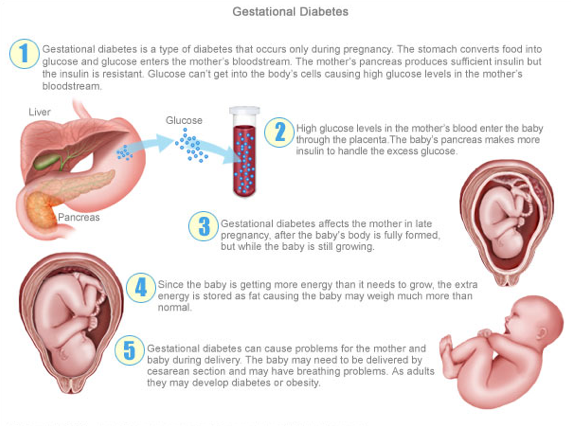 In addition, the patient conducts self-monitoring using a glucometer.
In addition, the patient conducts self-monitoring using a glucometer.
It is recommended that a pregnant woman keep a diary of observations in which to record:
- blood glucose level (normal <5.1 mmol/l),
- the presence of ketone bodies in the urine, which is determined by test strips sold in a pharmacy (normally, ketone bodies are absent),
- blood pressure readings (normal <130|80 mmHg),
- fetal movements,
- body weight,
- diet.
Expert ultrasound
Conducting an expert ultrasound examination reveals signs of intrauterine suffering of the fetus (diabetic fetopathy), polyhydramnios. Most often, this is a sign of chronically elevated blood glucose levels, penetrating into the blood of the fetus. This requires urgent correction of the diet and normalization of the level of glycemia (blood sugar). If necessary, insulin therapy.
Make an appointment
Treatment of gestational diabetes
Diet for gestational diabetes
In most cases, it is sufficient to follow a special diet recommended by a nutritionist based on the body mass index of the pregnant woman and her taste preferences. The effectiveness of diet therapy is determined by the maintenance of normal blood glucose levels. Diet in pregnancy diabetes recommends:
The effectiveness of diet therapy is determined by the maintenance of normal blood glucose levels. Diet in pregnancy diabetes recommends:
- Avoid simple carbohydrates - sweets, pastries, white bread, honey, sugar, jam, sweet drinks and fruits, ice cream.
- Limit complex carbohydrates - cereals (semolina, rice - exclude), potatoes, corn, legumes, durum wheat pasta. Distribute their intake evenly over several meals throughout the day to eliminate starvation (causes the formation of ketone bodies).
- Eat enough protein - meat, fish, seafood, poultry, mushrooms, eggs, hard cheese, dairy and sour-milk products of medium fat content (3-5%).
- It is necessary to enrich the diet with fiber and vitamins - greens, vegetables (except for boiled carrots and beets), sweet and sour berries (excluding grapes).
- Correctly choose fats, do not exceed their amount recommended by the doctor - vegetable oils (add to ready-made meals), nuts, seeds. Animal fats (butter, sausages) - limit.

- When cooking, boil, stew, steam and bake dishes. Don't fry. Do not deep fry.
A detailed menu for a pregnant woman with gestational diabetes will be compiled by a doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of each particular woman.
It is not worth using table No. 9 in its pure form for pregnant women with diabetes mellitus due to a significant restriction of its calorie content.
In detail, what you can eat with diabetes in pregnant women will be told by the doctor at an in-person consultation.
Pharmacotherapy
In cases where the diet fails to achieve the desired control of the level of glycemia in the blood, there are signs of a negative effect on the fetus - they resort to prescribing drugs - insulin. In case of diabetes in pregnant women, antidiabetic drugs in tablets should not be used. Insulin therapy is prescribed by an endocrinologist. Pregnant women with diabetes who are on insulin therapy are jointly managed by an endocrinologist, an internist and an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Physical activity
Patients are recommended regular physical activity - walking in the fresh air (at least 150 minutes per week), swimming.
Prenatal diabetes - childbirth
With a compensated course of gestational diabetes, normal development of the fetus and the condition of the woman, childbirth is carried out in time in a natural way. The question of early delivery, caesarean section may arise if there are relevant indications from the mother or fetus.
Specialists of the Yauza Clinical Hospital have included mandatory fetal development screenings and tests to diagnose sugar metabolism disorders in the pregnancy monitoring program. Recommendations are given on a special diet for women with manifestations of gestational diabetes. If necessary, strict glycemic control is carried out throughout pregnancy, ensuring its successful completion and the birth of a healthy child.
Make an appointment
Cost of services
Prices for services you can see in the price list or check by phone listed on the site.
Attention! Website prices may vary.
Please check the current cost with the administrators by phone.
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT. WE WORK WITHOUT DAYS OFF
Service in two languages: Russian, English.
Leave your phone number and we will call you back.
Advantages of the clinic
More diabetes during pregnancy
Causes
Classification
Symptoms
Complications
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prognosis and prevention
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman experiences high blood glucose levels for the first time during pregnancy. This condition can develop both with natural conception and with the use of IVF technology.
Gestational diabetes does not go away on its own after delivery. Subsequently, a woman may develop an insulin-dependent or non-insulin-dependent form of the disease. Sometimes it is possible to achieve stabilization of the condition after delivery. However, elevated blood sugar levels during pregnancy are always an alarming indicator, and in the future, a woman should receive full supervision from an endocrinologist.
However, elevated blood sugar levels during pregnancy are always an alarming indicator, and in the future, a woman should receive full supervision from an endocrinologist.
Causes and triggers
The causes of gestational diabetes are currently unclear, but it is believed that a factor such as genetic predisposition plays a big role here.
The following can also provoke the disease:
- the woman is overweight before pregnancy;
- large weight gain during pregnancy;
- unhealthy diet and love for fast food or food that is rich in fats or carbohydrates;
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements before pregnancy;
- late birth after 35 years or early birth before 18 years;
- the presence of relatives with obesity or diabetes;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- large fruit;
- the appearance of glucose in the urine;
- smoking during pregnancy;
- addiction to alcoholic beverages while carrying a child.

14% of all pregnancies are accompanied by this condition. On average, the number of children of such mothers is up to 18 million a year. All of them are at risk for obesity and diabetes at any age.
Classification
Gestational diabetes during pregnancy does not have a specific classification that would be unique to this disease. This species belongs to the varieties of SD and is included in its specific type.
After delivery, the symptoms may disappear completely, but often high blood sugar develops into a form of diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is typical for children, adolescents and young adults. It is associated with the presence in the body of autoantibodies that destroy the cells that produce insulin, which leads to a complete deficiency of this hormone.
Type 2 diabetes is more commonly found in adults. It is based on the lack of insulin in the body, as certain cells are disrupted. However, the synthesis of insulin is not disturbed, and the symptoms of the disease are not as pronounced as in the first type.
However, the synthesis of insulin is not disturbed, and the symptoms of the disease are not as pronounced as in the first type.
MODY diabetes is a genetic disease that occurs in people under 25 years of age and has symptoms of type 2 diabetes.
Manifest diabetes mellitus - a condition in which an increased concentration of sugar in the blood occurred before pregnancy, but for some reason was not diagnosed. As a result, it can lead to diabetes of any of two types.
Symptoms
Symptoms of gestational diabetes mellitus occur in a pregnant woman already in the first trimester, but often they go unnoticed, as they resemble toxicosis in their manifestations. Therefore, it is very important, starting with the first positive pregnancy test and registration, to monitor blood glucose levels. Such analyzes should be done strictly on an empty stomach.
At the appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, a woman usually complains of severe and persistent dry mouth, the need to drink more than 2 liters of water per day, and profuse urination. Appetite is either increased or decreased. There are constant weakness, lethargy, skin itching, sleep disturbance. Another important symptom is sudden weight loss, which has nothing to do with a change in diet.
Appetite is either increased or decreased. There are constant weakness, lethargy, skin itching, sleep disturbance. Another important symptom is sudden weight loss, which has nothing to do with a change in diet.
Gestational diabetes in pregnant women can manifest itself in the form of persistent pustular rashes on the skin, the appearance of pimples and blackheads, boils and other pyodermas. If a woman had carbohydrate metabolism disorders even before pregnancy and she knew that she had high blood sugar, there would be complaints about a violation or a noticeable deterioration in vision, deterioration in the sensitivity of the skin of the legs, and permanent swelling.
Sometimes there are no signs of gestational diabetes at all, and then only analysis helps to detect elevated sugar levels. Also, reasons to suspect diseases will be polyhydramnios, too much fetal weight that does not correspond to the gestational age, and malformations.
Complications
What can be dangerous gestational diabetes for a pregnant woman and child? Even during pregnancy, a woman may begin to show symptoms of preeclampsia and eclampsia, which is a direct threat to the life of the mother and fetus.
In the long term, a woman may develop one of two types of diabetes, obesity. In 10% of these pregnant women, diabetes develops in the first 6-12 months after childbirth, in the rest in the next 5-10 years. If during pregnancy insulin injections were prescribed for gestational diabetes, then the risk of diabetes in the future is 100%.
Babies born with GDM to their mothers may have fetal diabetic syndrome. Their weight exceeds the norm, they have an increased risk of distress syndrome, and they are also likely to develop hypoglycemia, which is an emergency condition and requires immediate medical attention. At a later age, the risk of developing obesity and diabetes is 100%.
Diagnosis
Elevated sugar in gestational diabetes can be detected during a blood test. It is performed only for blood taken from a vein. Before donating blood, do not eat for at least 10 hours. If DM is suspected in the middle of the term, an OGTT test with a load is performed.
A urine sample collected in the morning may be required to confirm the diagnosis. Diagnosis of gestational diabetes includes fetal ultrasound to detect severe manifestations of diabetic fetopathy.
Treatment
Diet for gestational diabetes is the mainstay of treatment for this dangerous condition. Women are given advice on proper nutrition. Any pastries, honey, all dairy with sugar in the composition, fast food, white bread and any muffins, carbonated sweet drinks, store juices, natural homemade juices of fresh pomace, all sweet fruits and vegetables must be excluded from the diet.
The menu for gestational diabetes should be made up of vegetables, soy products, healthy herbs, natural sour-milk and dairy products of home origin, buckwheat. The rest of the dishes should be consumed only in strict accordance with the amounts of food eaten.
Since gestational diabetes is not a disease, there is no specific treatment for it.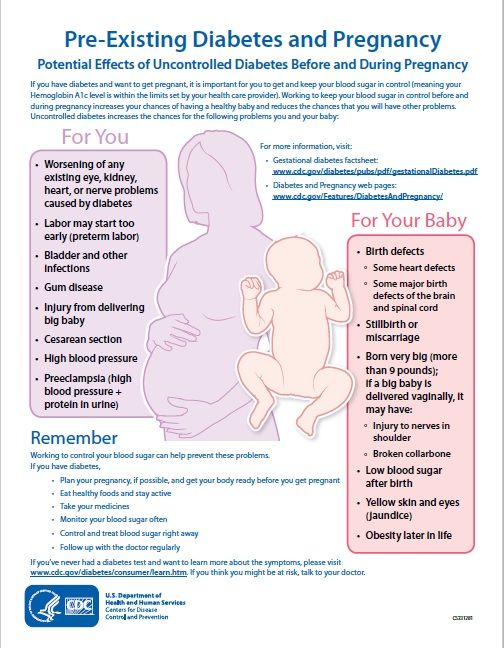 A pregnant woman is advised to follow proper nutrition, walk more in the fresh air, attend special fitness courses for pregnant women, take vitamin and mineral complexes on the recommendation of a doctor.
A pregnant woman is advised to follow proper nutrition, walk more in the fresh air, attend special fitness courses for pregnant women, take vitamin and mineral complexes on the recommendation of a doctor.
If all the above steps fail and blood sugar levels do not return to normal within 2-3 weeks, then clinical guidelines for gestational diabetes recommend using insulin therapy. But if a woman follows all the doctor's recommendations and at the same time eats right, does not violate diets and lifestyle, then the likelihood of prescribing insulin is reduced to zero.
Prognosis and prevention
Caesarean section in the presence of GDM is done only according to strict indications and in the event of complications. In all other cases, doctors recommend natural childbirth.
If during pregnancy all prescriptions and recommendations of the doctor are followed and a strict diet is followed, then in the future this will have a positive effect on both the condition of the mother and the newborn child. The risk of developing obesity or diabetes in the future will be reduced to a minimum.
The risk of developing obesity or diabetes in the future will be reduced to a minimum.
The author of the article:
Abakumova Maria Evgenievna
endocrinologist
work experience 12 years
reviews leave feedback
Clinic
m. Street 1905 Goda
Reviews
Services
- Title
- Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with an endocrinologist2300 905 years. Red Gates. AvtozavodskayaPharmacy. Glades. Sukharevskaya. st. Academician Yangelam. Frunzenskaya Zelenograd
Godulyan Aleksey Viktorovich
chief physician of "Polyclinika.ru" at Krasnye Vorota, endocrinologist, KMN
reviews
Clinic
m. Red Gate
Abdrazyakova Rosa Rafkhatovna
endocrinologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Polyanka
Polyanka
Avramenko Marina Vladimirovna
endocrinologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Frunzenskaya
Gagloeva Victoria Valerievna
endocrinologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Frunzenskaya
Dobrica Veronika Alekseevna
endocrinologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. st. Academician Yangel
Zabotin Mikhail Valerievich
endocrinologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
Zelenograd
Zatona Natalia Viktorovna
endocrinologist, diabetologist, podologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m.